Optical Force Effects of Rayleigh Particles by Cylindrical Vector Beams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
2.1. Calculation of Cylindrical Vector Beam with Arbitrary Polarization Distribution
2.2. Theory of Optical Force on a Rayleigh Particle
3. Results and Discussion
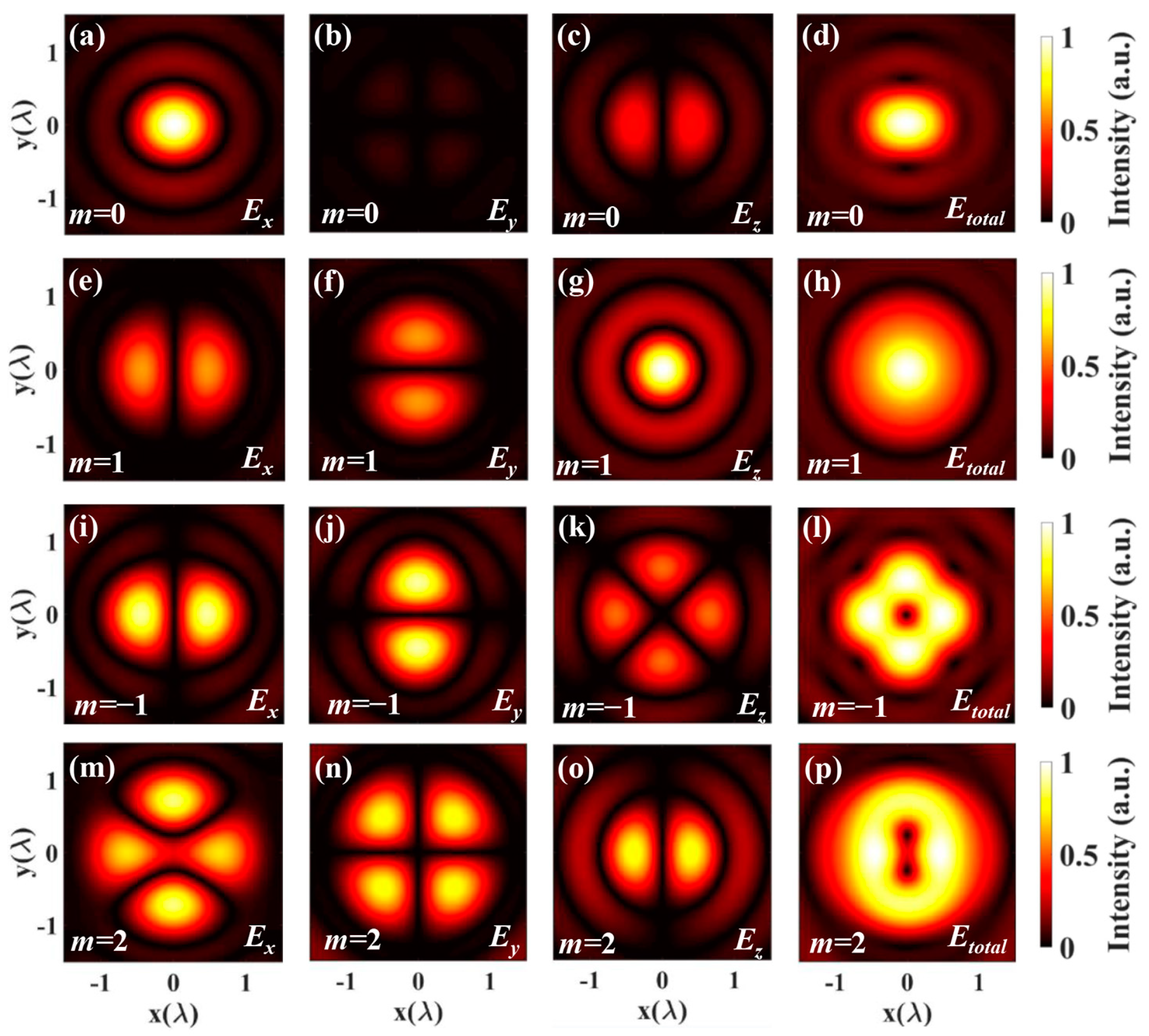
3.1. Electric and Magnetic Fields of High-Order Vector Beams
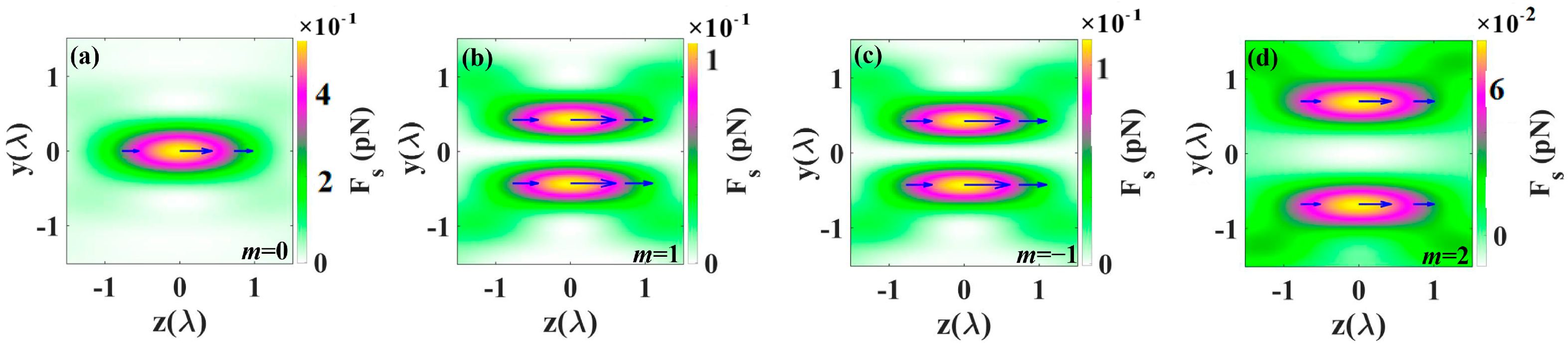
3.2. Optical Forces on Rayleigh Particle in Tight Focusing of CV Beams
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, Q. Cylindrical vector beams: From mathematical concepts to applications. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2009, 1, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Haus, J.W.; Zhan, Q. Propagation of vector vortex beams through a turbulent atmosphere. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 17829–17836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, H. A new type of vector fields with hybrid states of polarization. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10786–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Wang, H. Polarization interferometric prism: A versatile tool for generation of vector fields, measurement of topological charges, and implementation of a spin–orbit controlled-Not gate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 011105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Polarization singularities: Progress, fundamental physics, and prospects. APL Photonics 2021, 6, 040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, X. Near-perfect fidelity polarization-encoded multilayer optical data storage based on aligned gold nanorods. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2021, 4, 210002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhan, Q. Vectorial optical field generator for the creation of arbitrarily complex fields. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 20692–20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Ni, W.; Guo, C.; Wang, H. Generation of arbitrary vector beams with a spatial light modulator and a common path interferometric arrangement. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 3549–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, G.; Zhan, Q. Trapping of resonant metallic nanoparticles with engineered vectorial optical field. Nanophotonics 2014, 3, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, H. Optical orbital angular momentum from the curl of polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 253602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, A. Focusing properties of cylindrical vector vortex beams. Opt. Commun. 2018, 414, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnatovsky, C.; Shvedov, V.; Krolikowski, W.; Rode, A. Revealing local field structure of focused ultrashort pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 123901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yan, S.; Yao, B.; Lei, M.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Dan, D. Intrinsic optical torque of cylindrical vector beams on Rayleigh absorptive spherical particles. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Gu, B.; Rui, G.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhan, Q. Optical forces of focused femtosecond laser pulses on nonlinear optical Rayleigh particles. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmuskero, A.; Johansson, P.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H.; Tong, L.; Kall, M. Laser trapping of colloidal metal nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3453–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Ding, W.; Nieto-Vesperinas, M.; Ding, X.; Rahman, M.; Zhang, T.; Lim, C.; Qiu, C.W. Optical manipulation from the microscale to the nanoscale: Fundamentals, advances and prospects. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, D.G. A revolution in optical manipulation. Nature 2003, 424, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkin, A.; Dziedzic, J.M.; Bjorkholm, J.E.; Chu, S. Observation of a single-beam gradient force optical trap for dielectric particles. Opt. Lett. 1986, 11, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Ren, Z.; Kong, L.; Tu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Theoretical analysis based on mirror symmetry for tightly focused vector optical fields. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 23416–23432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliokh, K.Y.; Rodríguez-Fortuño, F.J.; Nori, F.; Zayats, A.V. Spin–orbit interactions of light. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Min, C.; Yuan, X. Detecting cylindrical vector beams with an on-chip plasmonic spin-Hall metalens. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 10758–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, M.; Li, X. Spin-orbit Hall effect in the tight focusing of a radially polarized vortex beam. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 39419–39427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xie, Z.; Ye, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Fan, D. Cylindrical vector beam multiplexer/demultiplexer using off-axis polarization control. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, G.; Huttunen, M.J.; Makitalo, J.; Kontio, J.M.; Simonen, J.; Kauranen, M. Second-harmonic generation imaging of metal nano-objects with cylindrical vector beams. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q. Trapping metallic Rayleigh particles with radial polarization. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 3377–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yan, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yao, B. Transverse spinning of particles in highly focused vector vortex beams. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 053802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekshaev, A.Y.; Angelsky, O.V.; Hanson, S.G.; Zenkova, C.Y. Scattering of inhomogeneous circularly polarized optical field and mechanical manifestation of the internal energy flows. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 023847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelsky, O.V.; Bekshaev, A.Y.; Maksimyak, P.P.; Maksimyak, A.P.; Mokhun, I.I.; Hanson, S.G.; Zenkova, C.Y.; Tyurin, A.V. Circular motion of particles suspended in a Gaussian beam with circular polarization validates the spin part of the internal energy flow. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 11351–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, T.G.; Kuebler, S.M. Vector diffraction analysis of high numerical aperture focused beams modified by two- and three-zone annular multi-phase plates. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canales, V.F.; Oti, J.E.; Cagigal, M.P. Three-dimensional control of the focal light intensity distribution by analytically designed phase masks. Opt. Commun. 2005, 247, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, G.; Wang, X.; Gu, B.; Zhan, Q.; Cui, Y. Manipulation metallic nanoparticle at resonant wavelength using engineered azimuthally polarized optical field. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 7212–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ng, J.; Lin, Z.; Chan, C.T. Optical pulling force. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.; Wolf, E. Electromagnetic diffraction in optical systems II. Structure of the image field in an aplanatic system. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. A 1959, 253, 358–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnatovsky, C.; Shvedov, V.G.; Shostka, N.; Rode, A.V.; Krolikowski, W. Polarization-dependent ablation of silicon using tightly focused femtosecond laser vortex pulses. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youngworth, K.; Brown, T. Focusing of High Numerical Aperture Cylindrical-Vector Beams. Opt. Express 2000, 7, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.P. Radiation Forces and Momenta in Dielectric Media. Phys. Rev. A 1973, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Vesperinas, M.; Xu, X. Reactive helicity and reactive power in nanoscale optics: Evanescent waves. Kerker conditions. Optical theorems and reactive dichroism. Phys. Rev. Res. 2021, 3, 043080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yan, S.; Yao, B.; Liang, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, P. Optical trapping force and torque on spheroidal Rayleigh particles with arbitrary spatial orientations. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2016, 33, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yan, S.; Yao, B.; Lei, M.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Dan, D. Trapping of Rayleigh spheroidal particles by highly focused radially polarized beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2015, 32, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo, S.; Marques, M.I.; Laroche, M.; Saenz, J.J. Scattering forces from the curl of the spin angular momentum of a light field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 113602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Min, C.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Sheng, Y.; Zayats, A.V.; Yuan, X. Nonlinearity-Induced Multiplexed Optical Trapping and Manipulation with Femtosecond Vector Beams. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5538–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marago, O.M.; Jones, P.H.; Gucciardi, P.G.; Volpe, G.; Ferrari, A.C. Optical trapping and manipulation of nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.M.; Bulanov, S.; Weber, S.; Korn, G. Analysis on the longitudinal field strength formed by tightly-focused radially-polarized femtosecond petawatt laser pulse. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 33091–33107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Chen, Z.; Pu, J. Radiation forces on a Rayleigh particle by highly focused partially coherent and radially polarized vortex beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2013, 30, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical Constants of the Noble Metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Preez-Wilkinson, N.; Stilgoe, A.B.; Alzaidi, T.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H.; Nieminen, T.A. Forces due to pulsed beams in optical tweezers: Linear effects. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 7190–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qiu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, L. Multiple trapping using a focused hybrid vector beam. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 094202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Panmai, M.; Peng, Y.; Lan, S. Optical pulling and pushing forces exerted on silicon nanospheres with strong coherent interaction between electric and magnetic resonances. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 12357–12371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberal, I.; Ederra, I.; Gonzalo, R.; Ziolkowski, R.W. Near-field electromagnetic trapping through curl-spin forces. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 063807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, L.; Shi, Q. Optical Force Effects of Rayleigh Particles by Cylindrical Vector Beams. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080691
Zhao Y, Zhou L, Jiang X, Zhu L, Shi Q. Optical Force Effects of Rayleigh Particles by Cylindrical Vector Beams. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(8):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080691
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yuting, Liqiang Zhou, Xiaotong Jiang, Linwei Zhu, and Qiang Shi. 2024. "Optical Force Effects of Rayleigh Particles by Cylindrical Vector Beams" Nanomaterials 14, no. 8: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080691
APA StyleZhao, Y., Zhou, L., Jiang, X., Zhu, L., & Shi, Q. (2024). Optical Force Effects of Rayleigh Particles by Cylindrical Vector Beams. Nanomaterials, 14(8), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080691




