Composition Regulation of Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films through Post-Annealing under Alkali Element Atmospheres
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
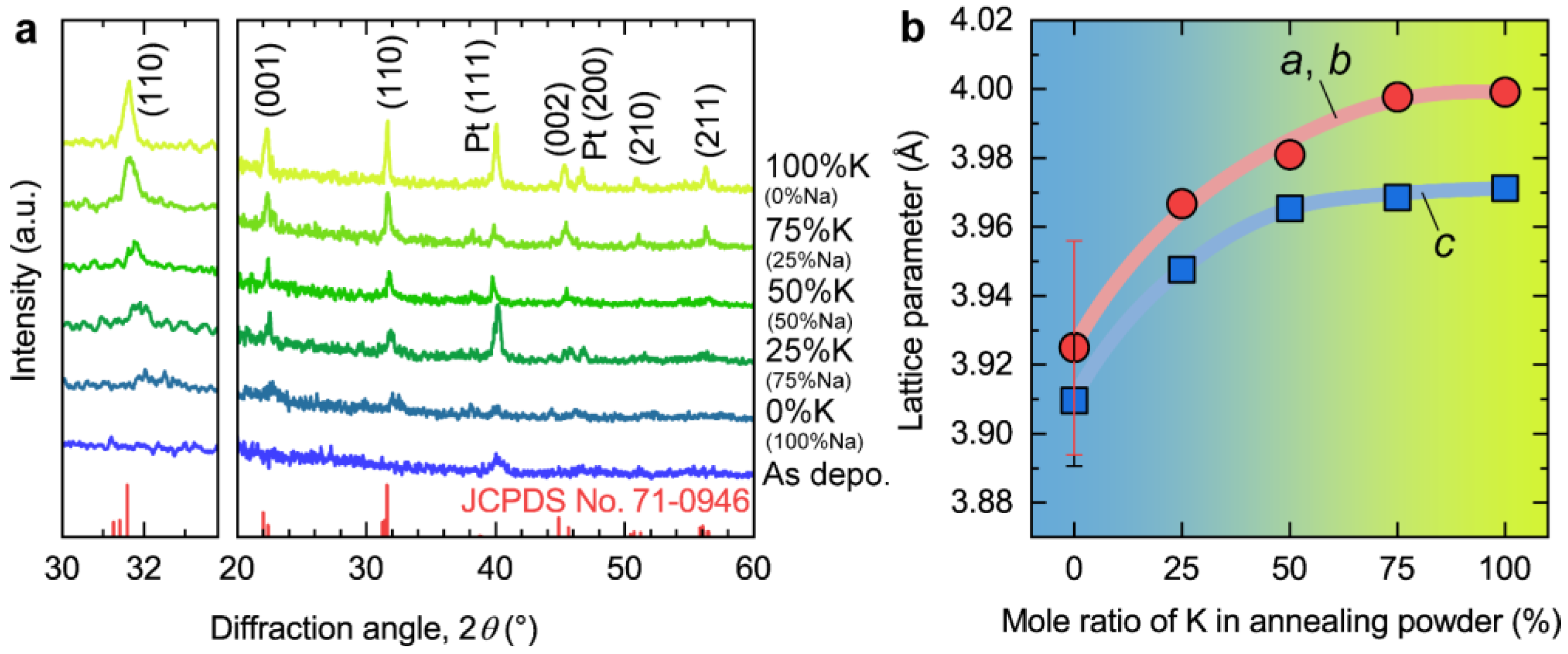
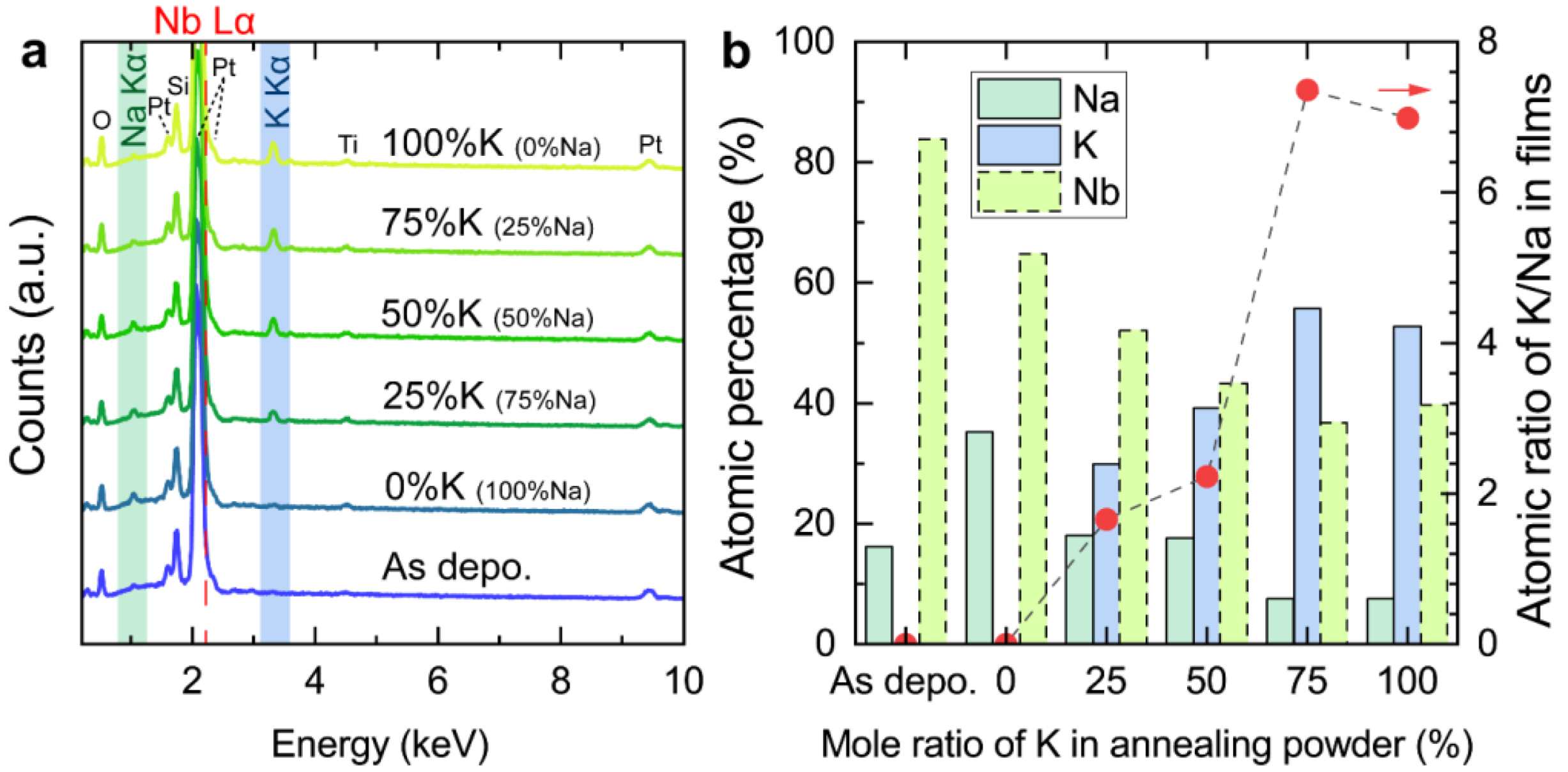
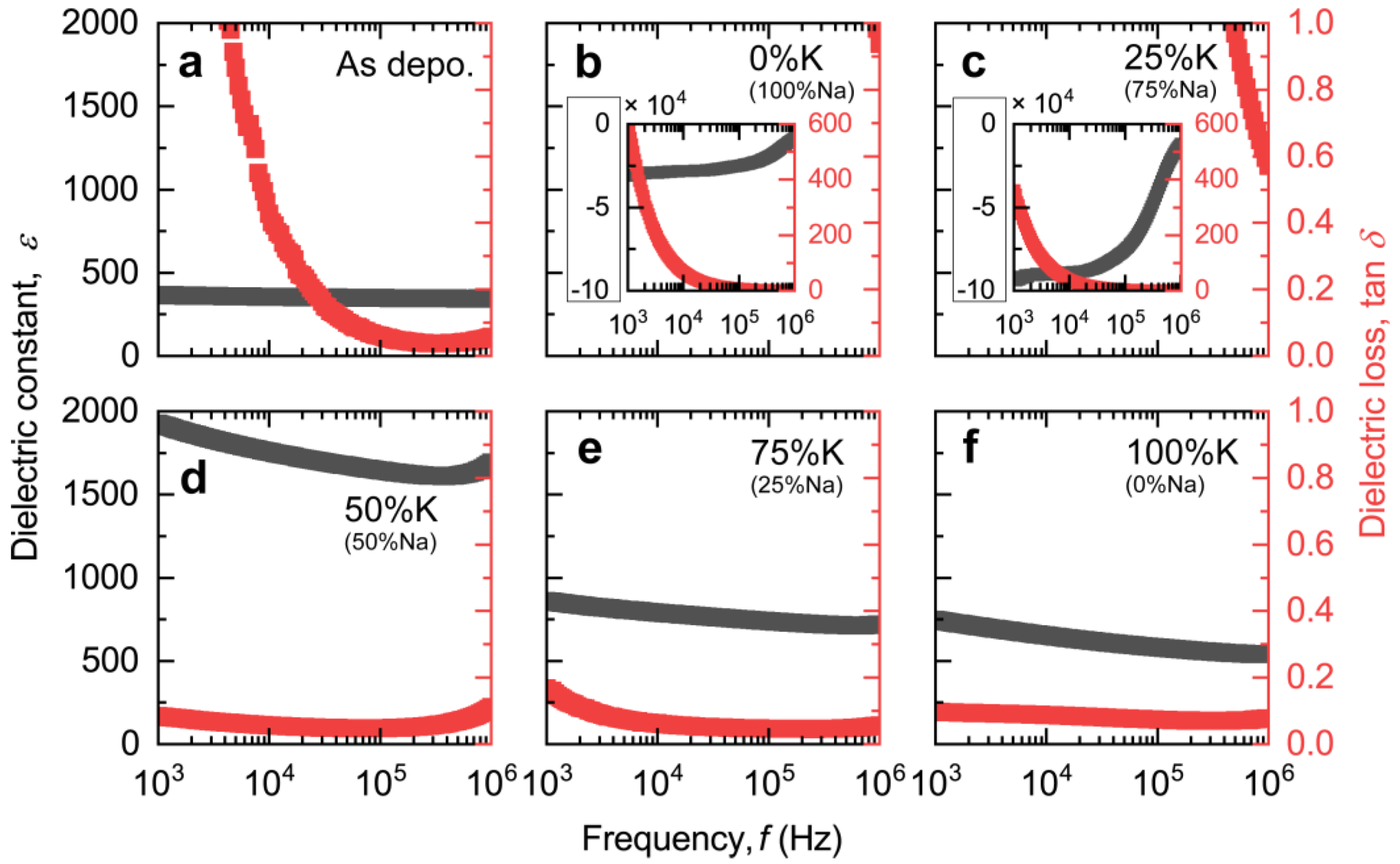
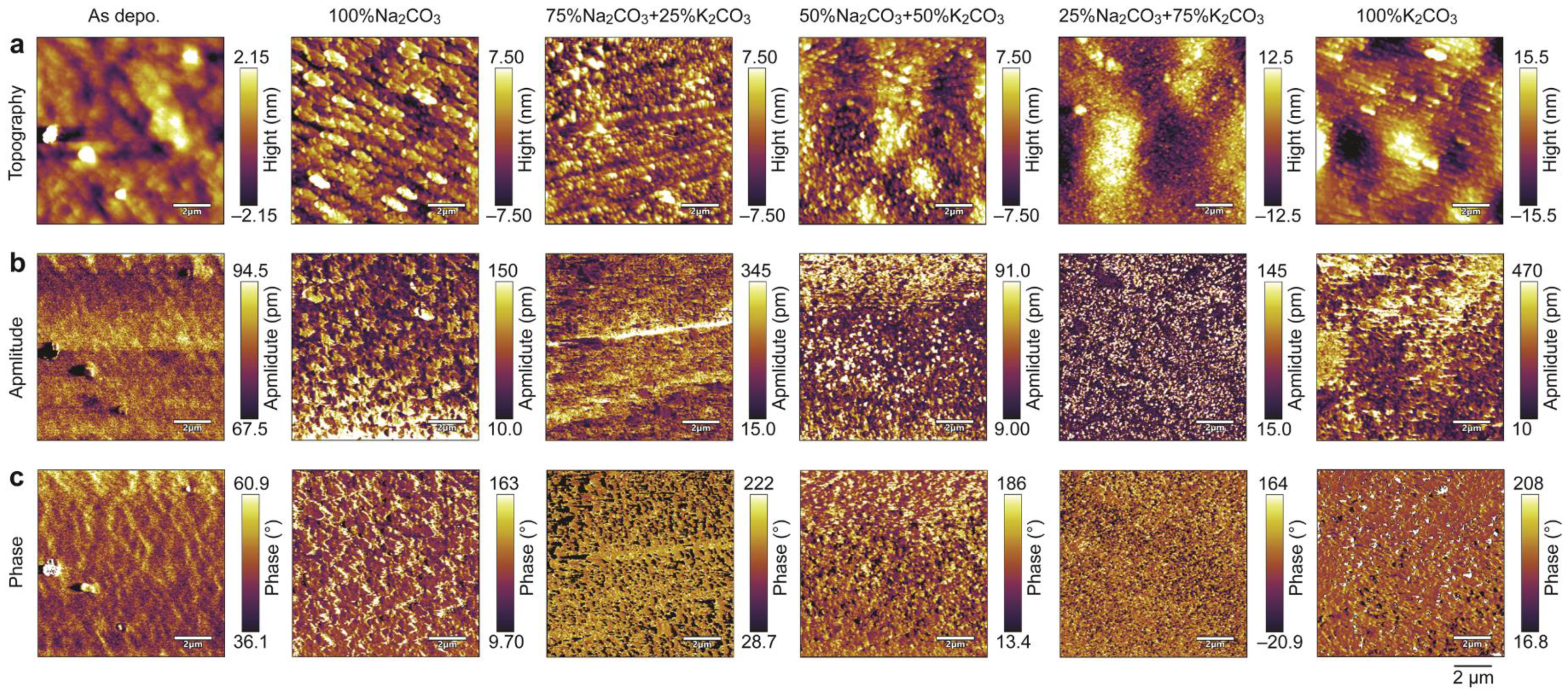
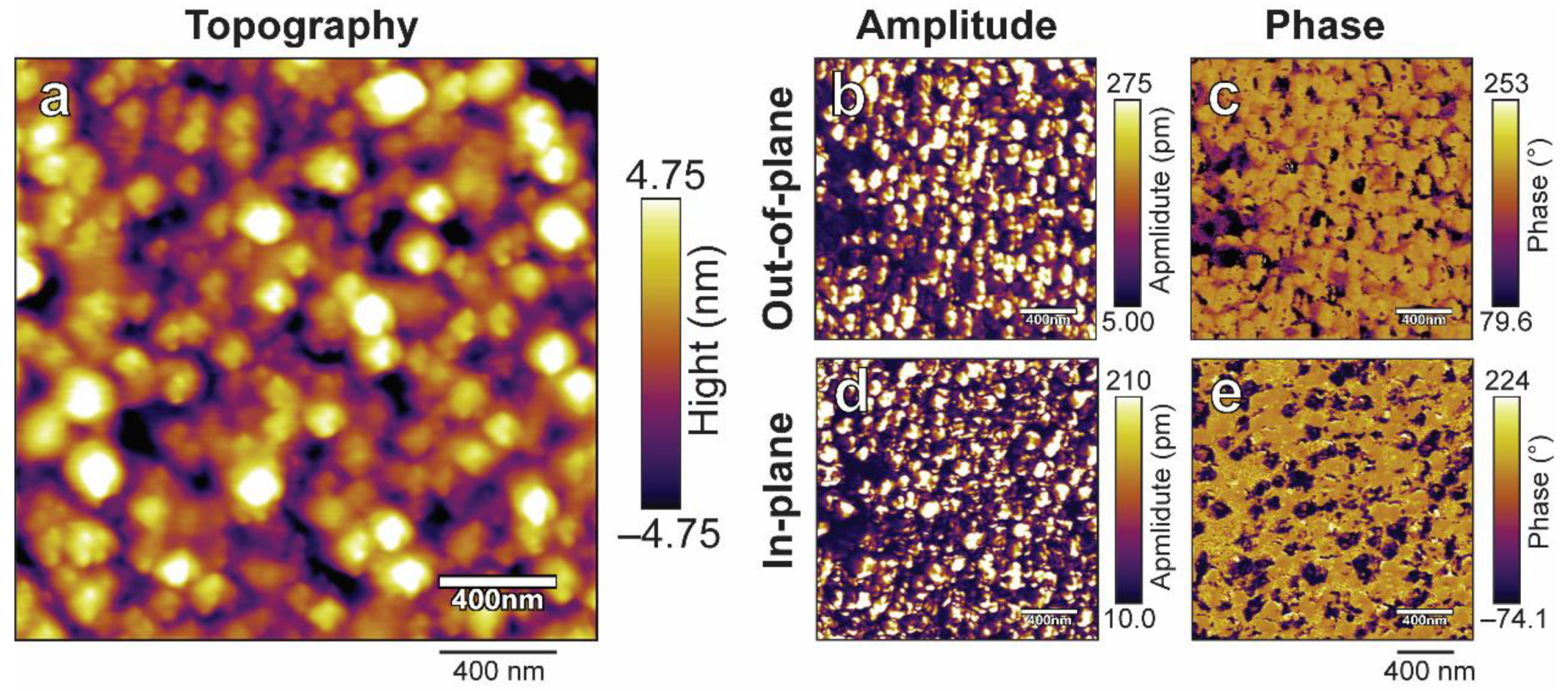
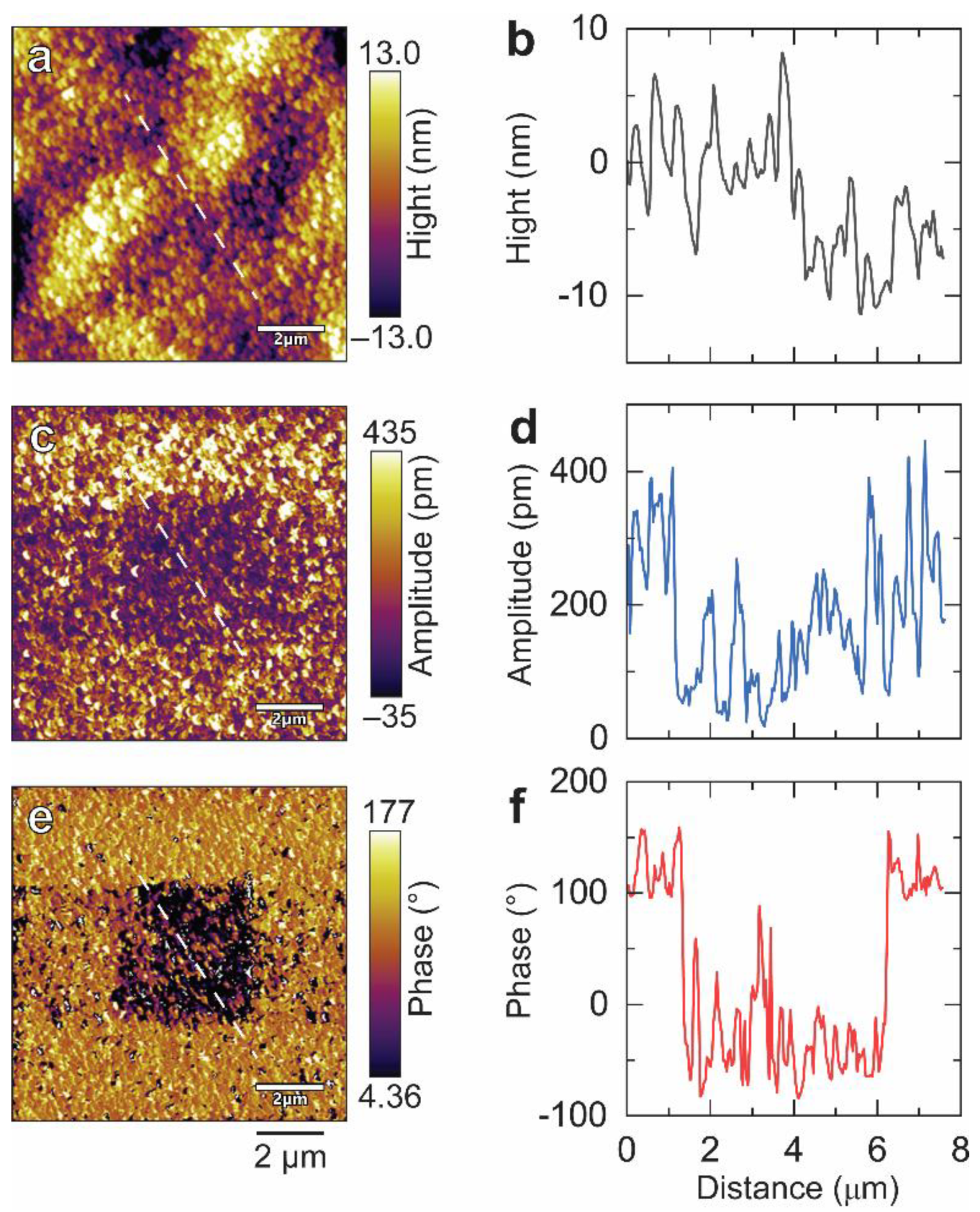
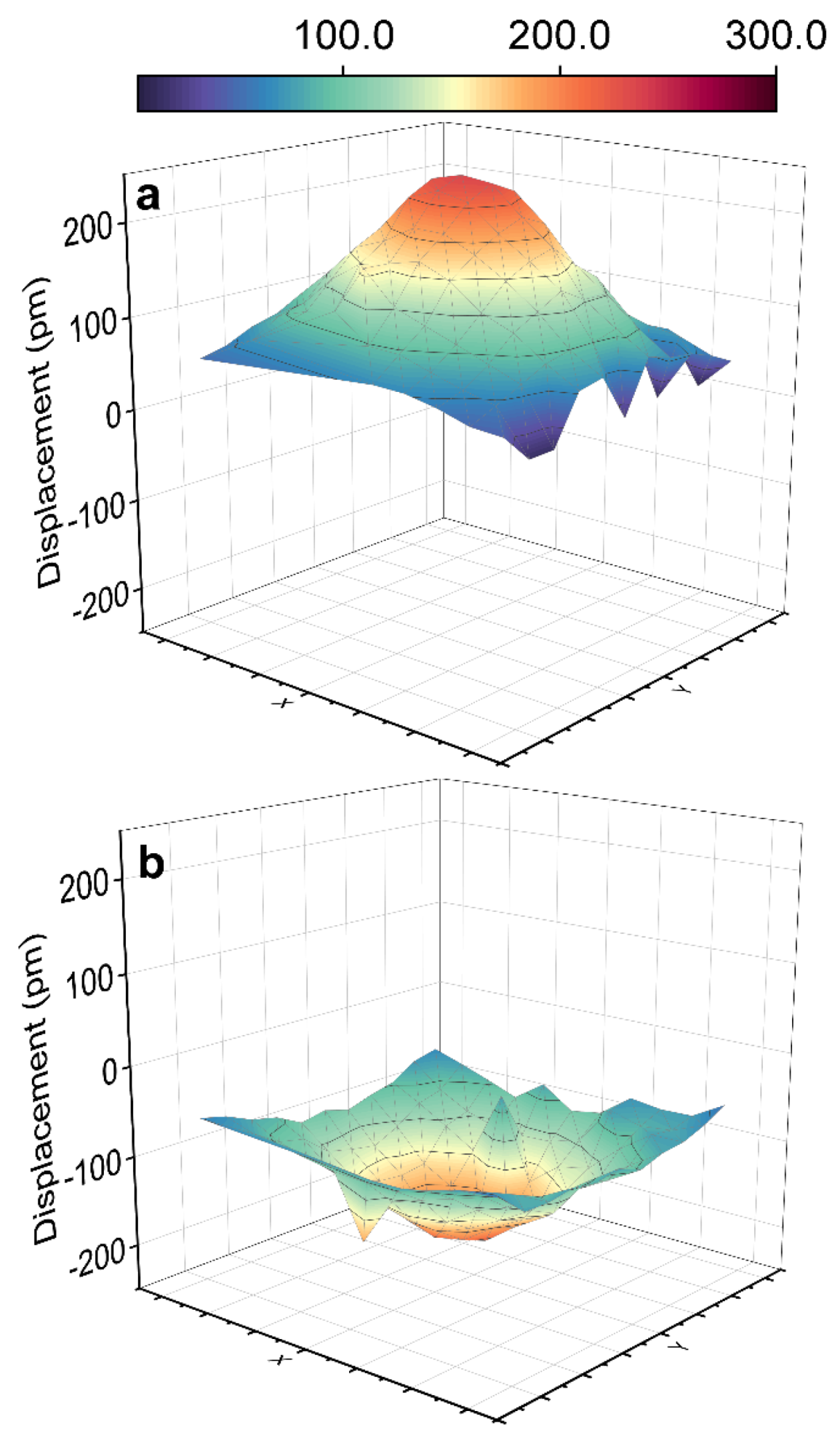
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagata, H.; Takenaka, T. Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics of (Bi1/2Na1/2) TiO3–KNbO3–1/2 (Bi2O3·Sc2O3) System. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, T.R.; Zhang, S.J. Lead-free piezoelectric ceramics: Alternatives for PZT? J. Electroceram. 2007, 19, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Wang, K.; Zhu, F.Y.; Cheng, L.Q.; Yao, F.Z. (K,Na)NbO3-Based Lead-Free Piezoceramics: Fundamental Aspects, Processing Technologies, and Remaining Challenges. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 3677–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Takao, H.; Tani, T.; Nonoyama, T.; Takatori, K.; Homma, T.; Nagaya, T.; Nakamura, M. Lead-Free Piezoceramics. Nature 2004, 432, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokay, O.; Yazıcı, M. A Review of Potassium Sodium Niobate and Bismuth Sodium Titanate based Lead Free Piezoceramics. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, F.; Meng, D.; Zheng, T.; Wu, J. Grain Boundary Diffusion Hardening in Potassium Sodium Niobate-Based Ceramics with Full Gradient Composition and High Piezoelectricity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.-F. Review of Chemical Modification on Potassium Sodium Niobate Lead-free Piezoelectrics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 4284–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wu, J.; Xing, J.; Zhu, J. Potassium Sodium Niobate-Based Lead-Free High-Frequency Ultrasonic Transducers for Multifunctional Acoustic Tweezers. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2022, 14, 30979–30990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, A.; Kasashima, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Okimura, Y. Application of (K,Na)NbO3-based Lead-free Piezoelectric Ceramics to Ultrasonic Sensors. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 128, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.B.W.; Li, C.; Lu, J.T.; Xu, Z.; Yao, F.Z.; Nan, H.; Wang, D. Multi-Length Engineering of (K,Na)NbO3 Films for Lead-Free Piezoelectric Acoustic Sensors with High Sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2312699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S.; Teli, A.; Deonikar, V.; Patil, D.; Shin, J.C. Hydrothermally Prepared Nano Bricks of Potassium Sodium Niobate for Enhancing Thermal and Electrical Properties of Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride). Mater. Lett. 2023, 338, 134040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, D.Y.; Lee, G.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.-J.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.-K.; Park, K.-I. High-temperature Workable Flexible Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Comprising Thermally Stable (K,Na)NbO3-based Ceramic and Polyimide Composites. Compos. Part B 2022, 234, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralt, P. Recent Progress in Materials Issues for Piezoelectric MEMS. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.L.; Pulskamp, J.S.; Sanchez, L.M.; Potrepka, D.M.; Proie, R.M.; Ivanov, T.G.; Rudy, R.Q.; Nothwang, W.D.; Bedair, S.S.; Meyer, C.D. PZT-based Piezoelectric MEMS Technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 1777–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.C.; Forsberg, F.; Lapisa, M.; Bleiker, S.J.; Stemme, G.; Roxhed, N.; Niklaus, F. Integrating MEMS and ICS. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2015, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jin, F.; Li, T.; Xu, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, K.; Chen, F. Influence of Growth Oxygen Pressure on the Electrical Properties and Phase Transformation of the Epitaxial (K,Na)NbO3-based Lead-free Ferroelectric Films. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 194101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Oka, F.; Ohishi, A.; Mishima, T.; Kanno, I. Piezoelectric Properties of (K,Na)NbO3 Films Seposited by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Appl. Phys. Express 2008, 1, 011501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, J.; Li, J.F. Potassium-Sodium-Niobate-Based Thin Films: Lead Free for Micro-Piezoelectrics. Ann. Phys. 2019, 531, 1800525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, J.; Kungl, H.; Schierholz, R.; Wagner, S.; Eichel, R.-A.; Hoffmann, M.J. Microstructure of Sodium-Potassium Niobate Ceramics Sintered under High Alkaline Vapor Pressure Atmosphere. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 4213–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaldo, C.; Gill, D.; Eason, R.; Mendiola, J.; Chandler, P. Growth of KNbO3 Thin films on MgO by Pulsed Laser Deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 65, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Helmersson, U.; Olafsson, S.; Rudner, S.; Wernlund, L.-D.; Gevorgian, S. Growth and Field Dependent Dielectric Properties of Epitaxial Na0.5K0.5NbO3 Thin Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, I.W.; Kim, J.S.; Ahn, C.W.; Park, B.H. Ferroelectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Na0.52K0.48NbO3 Thin Films Prepared by Radio Frequency Mgnetron Sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 092902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shang, X.; Chang, G.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; He, Y. Pulsed Laser Deposition of Single-Phase Lead-Free NKLNST Thin Films with K-and Na-Excess Targets. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 567, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Ghe, P.; Wolff, N.; Rubab, A.; Kienle, L.; Quandt, E. Tailoring Growth Modes by Excess Alkali Addition in Magnetron Sputtered Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ahn, C.W.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, I.W.; Lee, J.S.; Jin, B.M. The Ferroelectric Properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3 Thin Films Fabricated by RF-magnetron Sputtering. Ferroelectrics 2006, 335, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, I.W.; Jin, B.M. The Effect of the Substrate Temperatures on (Na,K)NbO3 Ferroelectric Thin Films Fabricated by RF Magnetron Sputtering. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2010, 56, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Seong, T.-G.; Seo, I.-T.; Jang, M.-S.; Nahm, S.; Kang, J.-Y.; Yoon, S.-J. Effects of Annealing Atmosphere on the Structural and Electrical Properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3 Thin Films Grown by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nili, H.; Kandjani, A.E.; Du Plessis, J.; Bansal, V.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M. Alkali Ratio Control for Lead-free Piezoelectric Thin Films Utilizing Elemental Diffusivities in RF Plasma. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 7222–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennery, V.J.; Hang, K.W. Thermal and X-ray Diffraction Studies of the NaNbO3–KNbO3 System. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 4749–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Suenaga, K.; Watanabe, K.; Horikiri, F.; Nomoto, A.; Mishima, T. Improvement of Piezoelectric Properties of (K,Na)NbO3 Films Deposited by Sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 041503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, R.; Vilarinho, R.; Moreira, J.A.; Zorro, F.; Ferreira, P.; Ivanov, M.; Tkach, A.; Costa, M.E.; Vilarinho, P.M. Stress Induced Effects on Piezoelectric Polycrystalline Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 7758–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojisavljević, K.; Vrabelj, T.; Ursic, H.; Malic, B. Effects of Strontium Doping on Microstructure and Functional Properties of Solution-Derived Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2020, 14, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Li, Y.; Krill Iii, C.; Chen, L. Effect of Grain Orientation and Grain Size on Ferroelectric Domain Switching and Evolution: Phase Field Simulations. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Han, K.-S.; Chun, M.-P.; Nam, J.-H.; Kim, B.-I. Effect of Domain Size on the Coercive Field of Orthorhombic (Li,K,Na)NbO3 Ceramics. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2010, 57, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, L.; Cox, G. Charging Artefacts in Atomic Force Microscopy. Micron 1994, 25, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, D.; Braga, P.C. Recognizing and Avoiding Artifacts in AFM Imaging. At. Force Microsc. Biomed. Methods Appl. 2004, 242, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Ong, K.P.; Yang, T.; Yang, P.; Das, P.K.; Chi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, C.; Wong, W.K.A. Giant Piezoelectricity in Oxide Thin Films with Nanopillar Structure. Science 2020, 369, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, M.; Wu, H.; Ong, K.P.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Yang, P.; Zang, W.; Liew, W.H.; Diao, C.; Xi, S. Origin of Giant Electric-Field-induced Strain in Faulted Alkali Niobate Films. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zarkadoula, E.; Crespillo, M.L.; Weber, W.J.; Rathod, V.; Zinkle, S.J.; Ramuhalli, P. Laser Doppler Vibrometry for Piezoelectric Coefficient (d33) Measurements in Irradiated Aluminum Nitride. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2022, 347, 113886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-Y.; Li, J.-F. Enhancement of Piezoelectric Constant d33 in BaTiO3 Ceramics Due to Nano-domain Structure. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yako, K.; Kakemoto, H.; Tsurumi, T.; Wada, S. Domain Size Dependence of d33 Piezoelectric Properties for Barium Titanate Single Crystals with Engineered Domain Configurations. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 120, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Kwon, S.J.; Yeom, N.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.H.; Chun, M.P.; Nam, J.H.; Paik, J.H.; Kim, B.I.; Cho, J.H. Effects of the Domain Size on Local d33 in Tetragonal (Na0.53K0.45Li0.02)(Nb0.8Ta0.2)O3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlt, G. The Role of Domain Walls on the Dielectric, Elastic and Piezoelectric Properties of Ferroelectric Ceramics. Ferroelectrics 1987, 76, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Tao, C.; Fan, W.; Shen, B.; Ju, M.; Dou, Z.; Wu, C.; Yao, F.-Z.; Gong, W.; Wang, K. Composition Regulation of Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films through Post-Annealing under Alkali Element Atmospheres. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030288
Chen B, Tao C, Fan W, Shen B, Ju M, Dou Z, Wu C, Yao F-Z, Gong W, Wang K. Composition Regulation of Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films through Post-Annealing under Alkali Element Atmospheres. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(3):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030288
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Binjie, Chuanyang Tao, Wenying Fan, Binglin Shen, Min Ju, Zhongshang Dou, Chaofeng Wu, Fang-Zhou Yao, Wen Gong, and Ke Wang. 2024. "Composition Regulation of Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films through Post-Annealing under Alkali Element Atmospheres" Nanomaterials 14, no. 3: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030288
APA StyleChen, B., Tao, C., Fan, W., Shen, B., Ju, M., Dou, Z., Wu, C., Yao, F.-Z., Gong, W., & Wang, K. (2024). Composition Regulation of Potassium Sodium Niobate Thin Films through Post-Annealing under Alkali Element Atmospheres. Nanomaterials, 14(3), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030288





