Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of N, S Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Fe(III) and Hydroquinone in Water and Cell Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
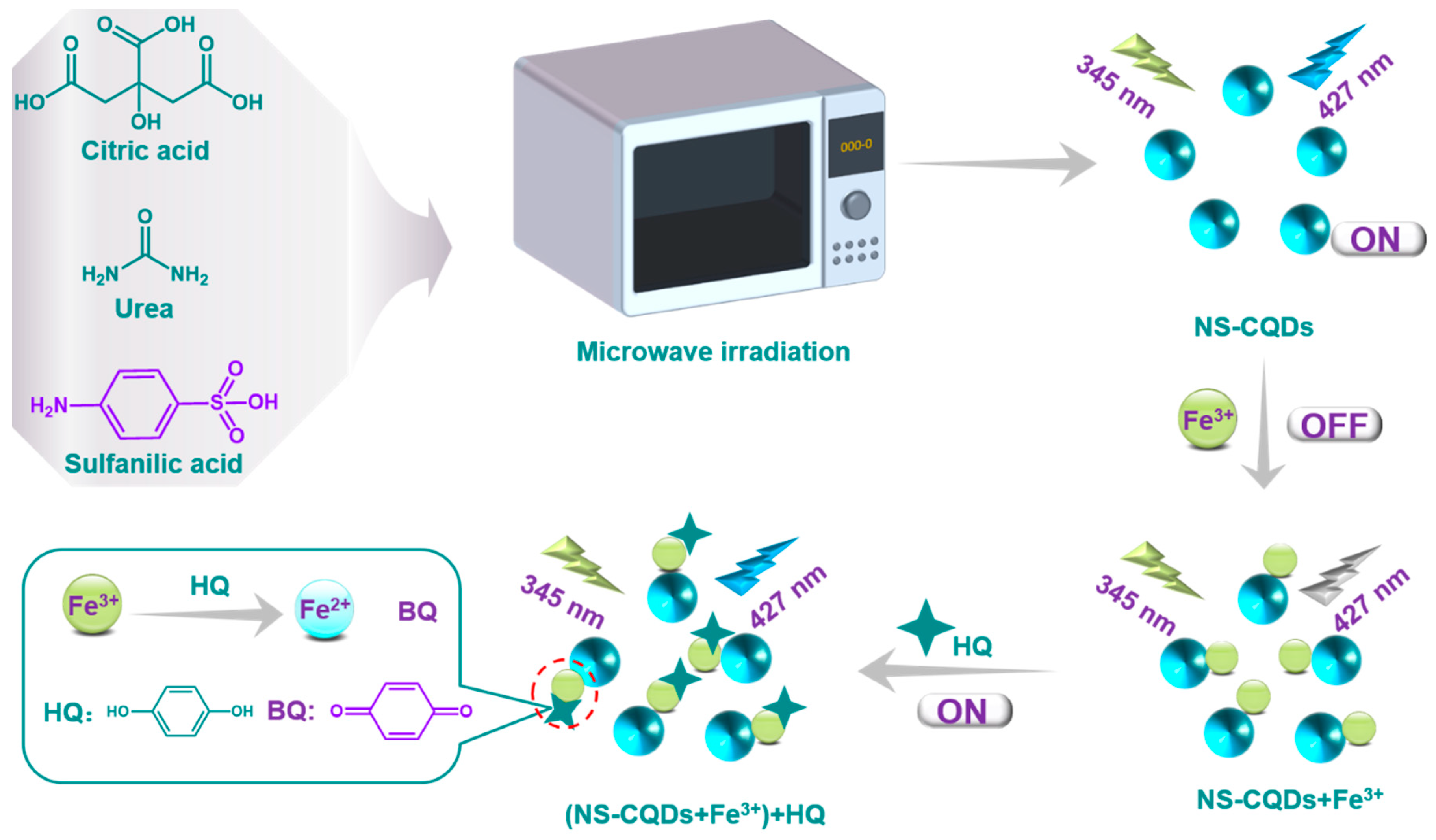
2.2. Preparation of N and S Co-Dopped Carbon Quantum Dots (NS-GQDs)
2.3. Fluorescence Measurements
2.4. Detection of Fe3+ and HQ in Actual Water Samples
2.5. Cytotoxicity and Imaging Studies
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
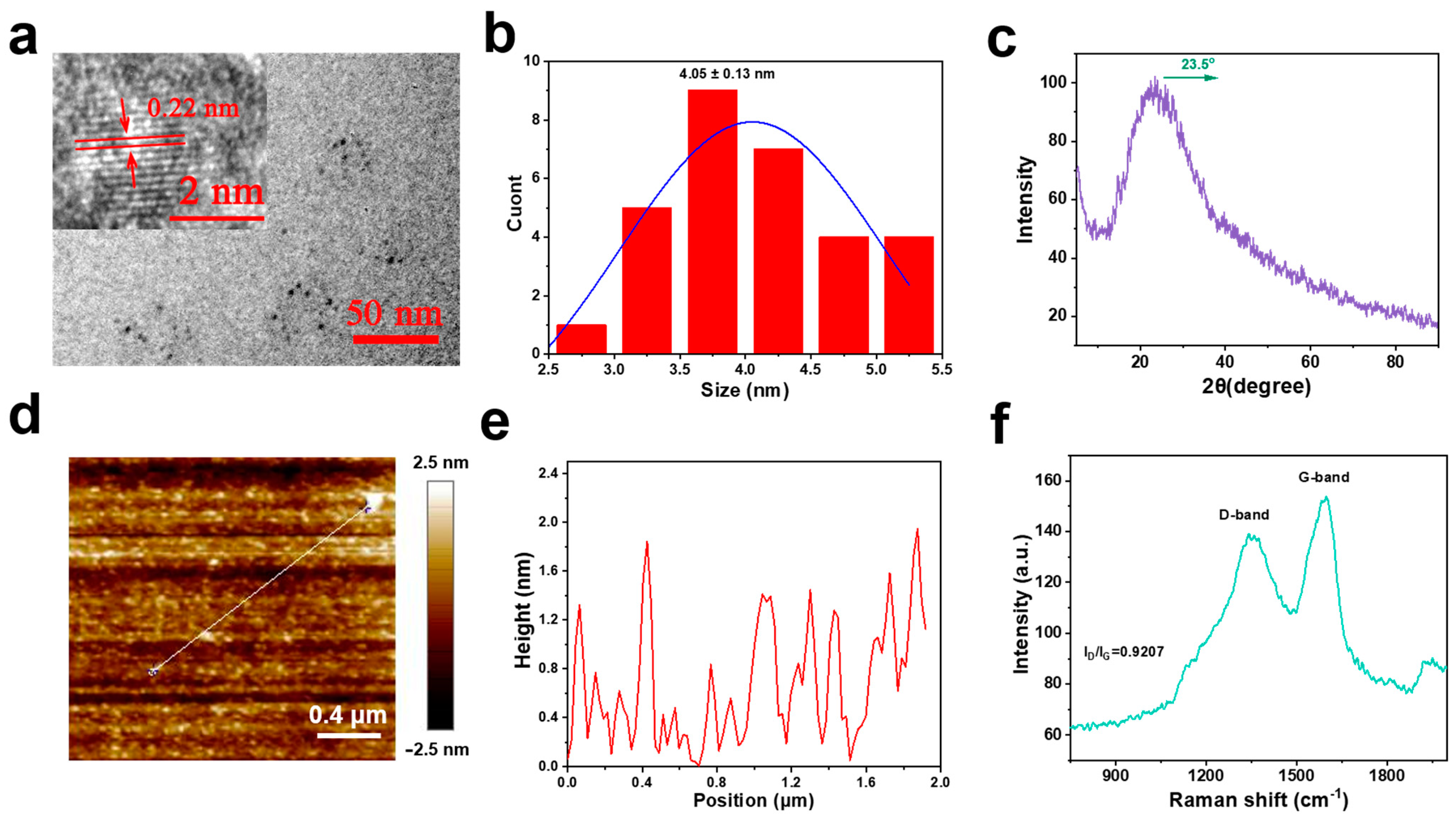
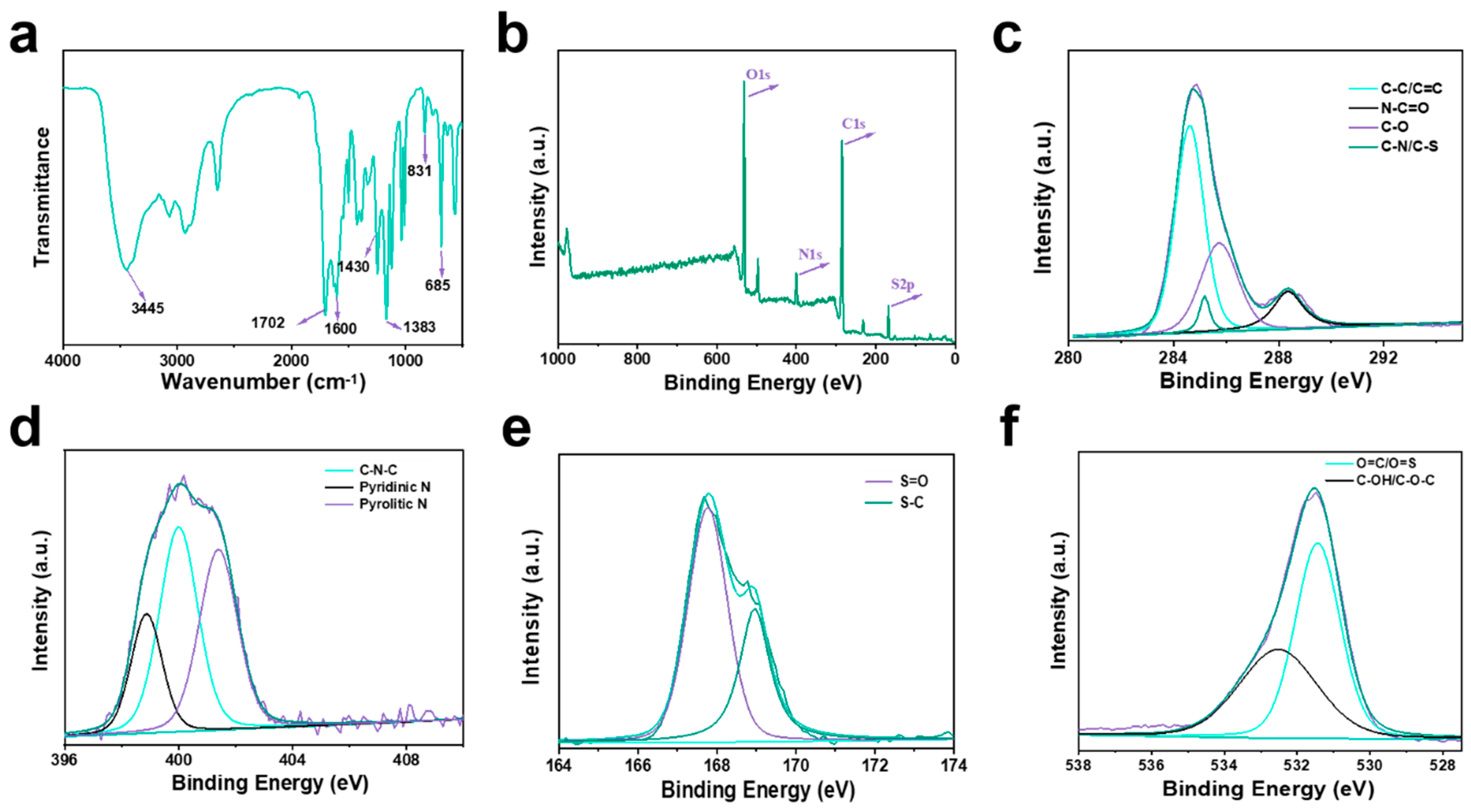
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of NS-CQDs
3.2. Photoluminescence Study of NS-CQDs
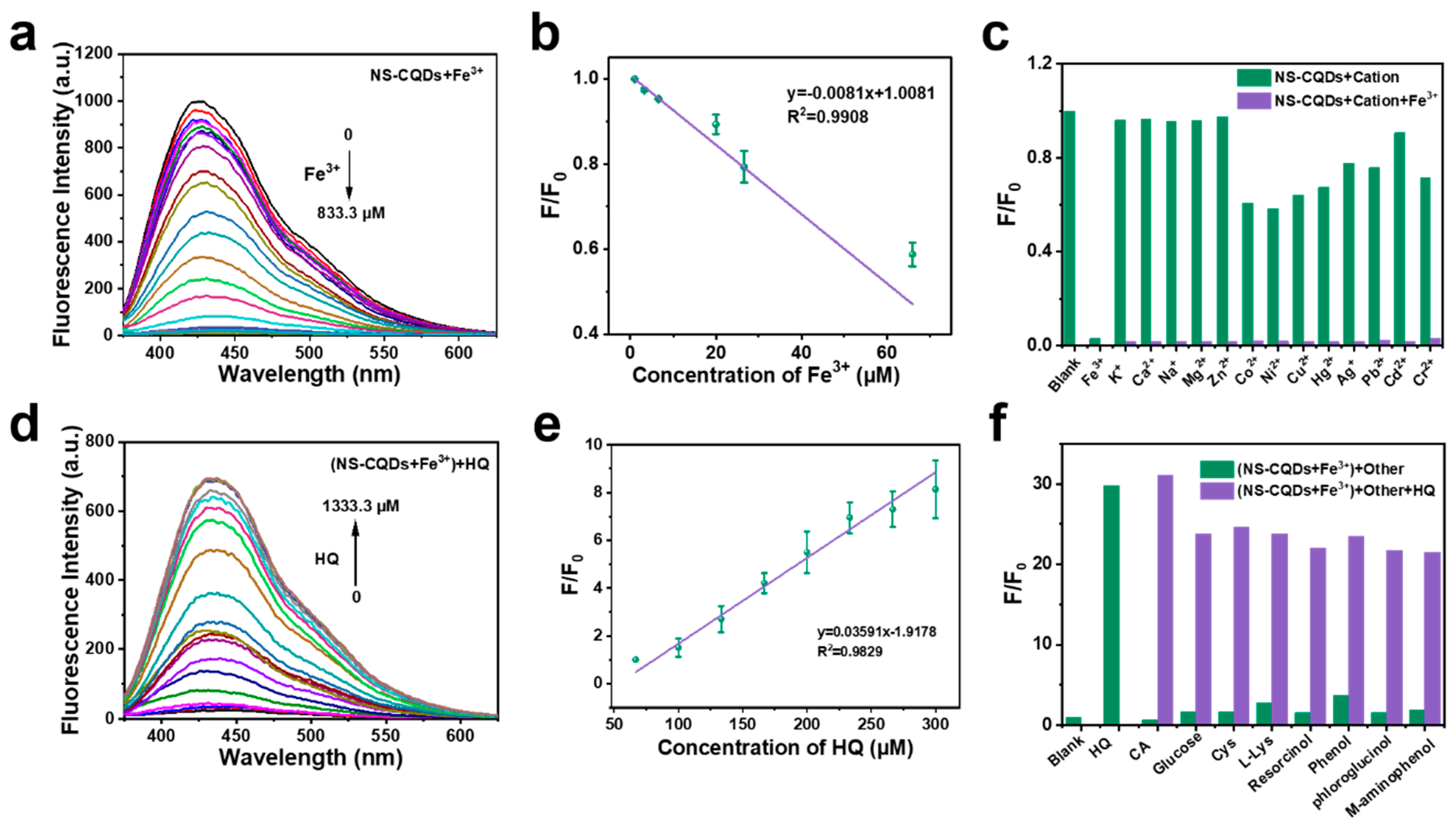
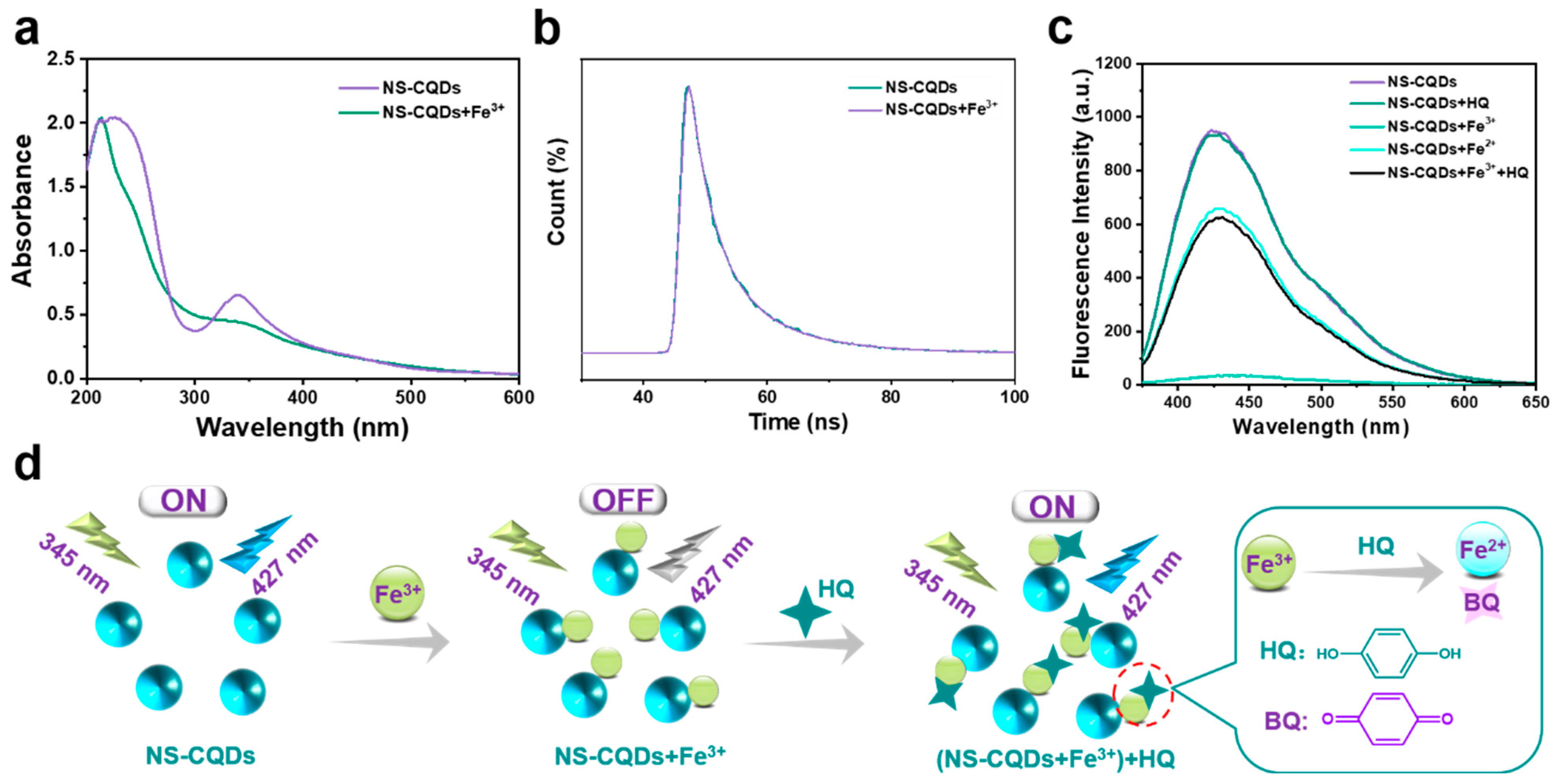
3.3. NS-CQDs Sensor for Detection of Fe3+ and HQ
3.4. Mechanism of Fluorescence “On-Off-On” Detection for Fe3+ and HQ
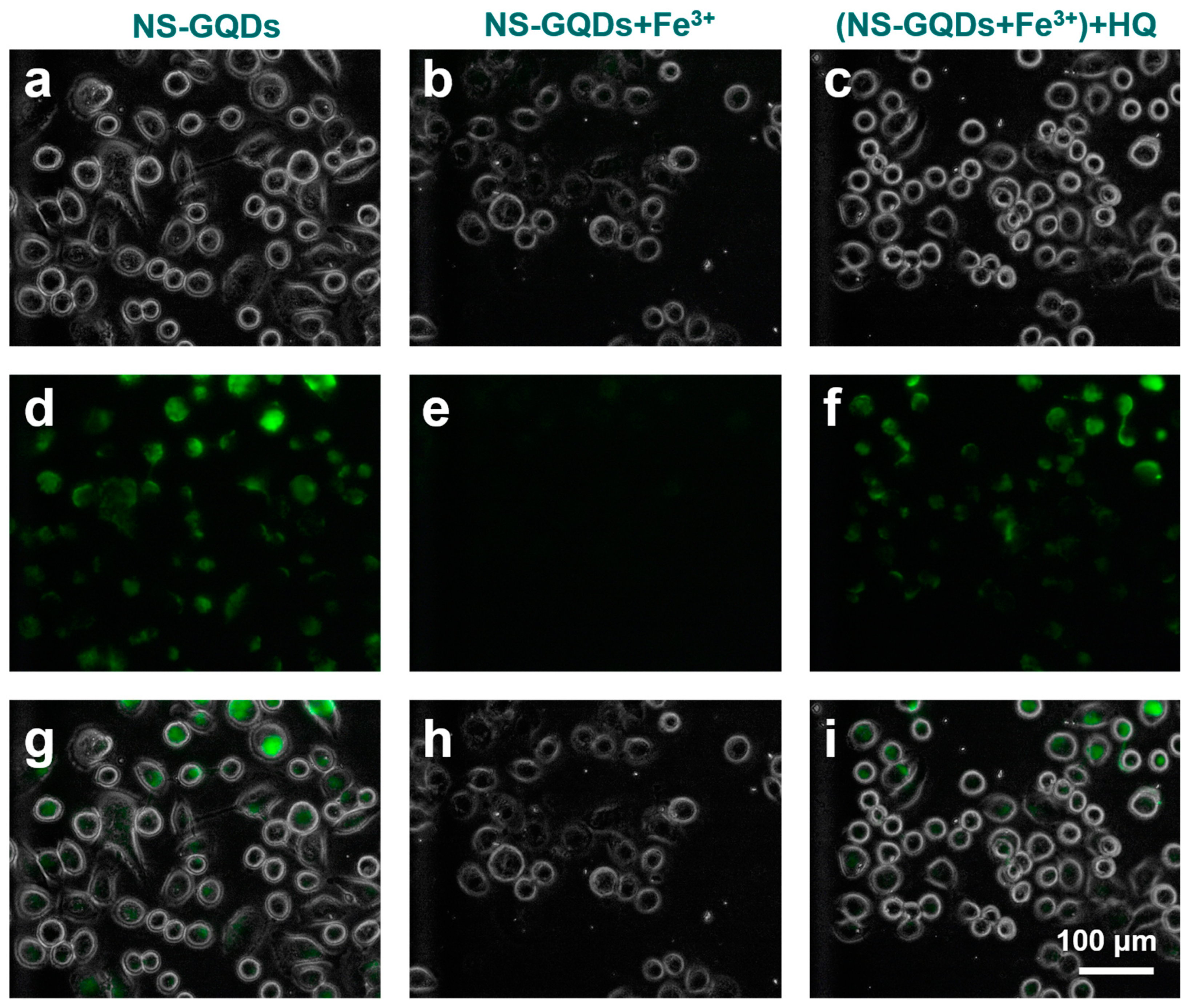
3.5. Fluorescence Imaging of NS-CQDs in Living Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Shi, Q.; Song, N.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; James, T.D. Current trends in the detection and removal of heavy metal ions using functional materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 5827–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Luo, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Sparks, D.L.; Yamauchi, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. the challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gladyshev, V.N. Comparative genomics of trace elements: Emerging dynamic view of trace element utilization and function. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4828–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomova, K.; Makova, M.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Essential metals in health and disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G. Relevance, Essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardhan, K.H.; Kumar, P.S.; Panda, R.C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liquids 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Inno. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Shafeeq, A.; Siddiq, U.; Bashir, F.; Ahmad, T.; Athar, M.; Butt, M.T.; Ullah, S.; Mukhtar, A.; Hussien, M.; et al. A mechanistic approach for toxicity and risk assessment of heavy metals, hydroquinone and microorganisms in cosmetic creams. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, R.M.; Ríos, J.L.; Máñez, S. Antioxidant activity of natural hydroquinones. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyers, T.; Westerhof, W. Toxicology and health risks of hydroquinone in skin lightening formulations. J. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 20, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, J. The Safety of Hydroquinone: A dermatologist’s response to the 2006 federal register. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 854–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Afkhami, A.; Saber-Tehrani, M.; Khoshsafar, H. Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of schiff base/silica/magnetite as a preconcentration phase for the trace determination of heavy metal ions in water, food and biological samples using atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 97, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Pumpanen, J.; Keinänen, M.; Laudon, H.; Ojala, A.; Palviainen, M.; Kiirikki, M.; Neitola, K.; Berninger, F. Assessment of a portable UV–Vis spectrophotometer’s performance for stream water doc and fe content monitoring in remote areas. Talanta 2021, 224, 121919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, M.; He, Q.; Zhao, M.; Cui, H. Photoenhanced oxidase-peroxidase-like NiCo2O4@MnO2 nanozymes for colorimetric detection of hydroquinone. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 5651–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, J.E.; Bard, A.J. Toward the digital electrochemical recognition of cobalt, iridium, nickel, and iron ion collisions by catalytic amplification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8446–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjith, K.S.; Ezhil Vilian, A.T.; Ghoreishian, S.M.; Umapathi, R.; Hwang, S.-K.; Oh, C.W.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Hybridized 1D–2D MnMoO4–MXene nanocomposites as high-performing electrochemical sensing platform for the sensitive detection of dihydroxybenzene isomers in wastewater samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khand, N.H.; Solangi, A.R.; Shaikh, H.; Shah, Z.-H.; Bhagat, S.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; López-Maldonado, E.A. Novel electrochemical ZnO/MnO2/rGO nanocomposite-based catalyst for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and pyrocatechol. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xu, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. Rapid methods for detecting acrylamide in thermally processed foods: A review. Food Control 2015, 56, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, L.-C.; Wang, S.; Sillanpää, M.; Sun, H. Design and engineering heterojunctions for the photoelectrochemical monitoring of environmental pollutants: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 248, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Li, H.; Yan, X.; Lin, Y.; Lu, G. Biosensors based on fluorescence carbon nanomaterials for detection of pesticides. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fan, M.; Liu, Q.; Su, Z.; Li, X.; Pan, Q.; Hu, X. Two Highly water-stable imidazole-based Ln-MOFs for sensing Fe3+, Cr2O72–/CrO42– in a water environment. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Niu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, T. Highly sensitive and fast responsive “turn-on” fluorescent sensor for selectively sensing Fe3+ and Hg2+ in aqueous media based on an oligothiophene derivative and its application in real water samples. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 2017, 244, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Hou, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X. Facile synthesis of MoS2 quantum dots as fluorescent probes for sensing of hydroquinone and bioimaging. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3307–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yang, M.; Duan, Y. Chemistry, biology, and medicine of fluorescent nanomaterials and related systems: New insights into biosensing, bioimaging, genomics, diagnostics, and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6130–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, U.A.; Ng, L.Y.; Ng, C.Y.; Mahmoudi, E. A review of carbon quantum dots and their applications in wastewater treatment. Adv. Colloid Interface 2020, 278, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.; Fei, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. A review on sustainable synthetic approaches toward photoluminescent quantum dots. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Lee, N.Y. Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots and their environmental applications. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Jiang, S.; Park, S.-J.; Meng, L.-Y. A Review: Recent advances in preparations and applications of heteroatom-doped carbon quantum dots. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 6915–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huo, D.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Bian, M.; Ma, Y.; Hou, C. N, P-Doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for carbendazim detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 274, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Q.-S.; Guo, W.-Q.; Wang, H.-Z.; Liu, B.-H.; Ren, N.-Q. Carbon quantum dots-based semiconductor preparation methods, applications and mechanisms in environmental contamination. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2556–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, C.; Tian, Z.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Z. Facilely synthesized n-doped carbon quantum dots with high fluorescent yield for sensing Fe3+. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, R. Facile synthesis of doped CxNy QDs as photoluminescent matrix for direct detection of hydroquinone. Spectrochim. Part A 2021, 246, 119019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, S.; Kalimuthu, R.; Kanagaraj, T.; Kulandaivelu, R.; Nagappan, R.; Pragasan, L.A.; Ponnusamy, V.K. Microwave-Assisted green synthesis of multi-functional carbon quantum dots as efficient fluorescence sensor for ultra-trace level monitoring of ammonia in environmental water. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Bu, L.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G.; Huang, J. One-Step microwave-assisted preparation of oxygen-rich multifunctional carbon quantum dots and their application for Cu2+-Curcumin detection. Talanta 2019, 205, 120117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shabasy, R.M.; Farouk Elsadek, M.; Mohamed Ahmed, B.; Fawzy Farahat, M.; Mosleh, K.N.; Taher, M.M. Recent developments in carbon quantum dots: Properties, fabrication techniques, and bio-applications. Processes 2021, 9, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Ahmed, H.E.; Soylak, M. Exploring the potential of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) as an advanced nanomaterial for effective sensing and extraction of toxic pollutants. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2024, 180, 117939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.A.; Candela, C.H.; Gallego, J.; Marin, J.; Patiño, L.E.; Ospina, N.; Patiño, E.; Molano, M.; Villamil, F.; Bernal, K.M.; et al. Easy and rapid synthesis of carbon quantum dots from mortiño (vaccinium meridionale swartz) extract for use as green tracers in the oil and gas industry: Lab-to-field trial development in colombia. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 11359–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laysandra, L.; Getachew, G.; Chang, J.-R.; Chang, J.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-C. “Grafting from” enabled stretchable and highly fluorescent carbon quantum dot–polyisoprene elastomers. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Farid, M.A.; Lease, J.; Yoshito, A. Lignocellulosic biomass-derived carbon quantum dots (CQDs): A novel approach utilizing organosolv lignin from Moso bamboo waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Ba, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, H. One-Step synthesis of carbon quantum dot-carbon nanotube composites on waste eggshell-derived catalysts for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Qin, W. Graphene oxide functionalization with aminocoumarin nanosheet fluorescent dye: Preparation, electrochemistry, spectroscopy and imaging in the living cells. Dyes Pigments 2015, 113, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, P. Tuning the functional groups of carbon quantum dots in thin film nanocomposite membranes for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wan, X.; Su, Y.; Zeng, X.; Tang, J. Acidophilic S-doped carbon quantum dots derived from cellulose fibers and their fluorescence sensing performance for metal ions in an extremely strong acid environment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12841–12849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Weng, B.; Wang, B.; Li, C. Facile synthesis of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots and application for Fe(III) ions detection and cell imaging. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 2016, 223, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, D.; Liu, Q.; Wu, C.; Gu, S. Sustainable synthesis of bright green fluorescent carbon quantum dots from lignin for highly sensitive detection of Fe3+ ions. Appl. Surface Sci. 2021, 565, 150526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Gong, X.; Nan, M.; Liu, Y.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Comparative study for n and s doped carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization and applications for Fe3+ probe and cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 898, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots with strong blue luminescence. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13817–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Deng, C.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Seidi, F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Han, J.; et al. Smart paper-based materials incorporating nitrogen and boron co-doped mxene quantum dots for rapid adsorption and sensitive detection of Cr2O72−. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 679, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, W.; Świergosz, T.; Bednarz, S.; Walas, K.; Bashmakova, N.V.; Bogdał, D. Luminescence phenomena of carbon dots derived from citric acid and urea-a molecular insight. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13889–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckmeier, C.J.; Schneider, J.; Xiong, Y.; Häusler, J.; Kasák, P.; Schnick, W.; Rogach, A.L. Aggregated molecular fluorophores in the ammonothermal synthesis of carbon dots. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 10352–10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowska, J.D.; Murphy, A.; Mellor, C.; Fernandes, D.; Gibbons, E.N.; Krysmann, M.J.; Kelarakis, A.; Burgaz, E.; Moore, J.; Yeates, S.G. A rich gallery of carbon dots based photoluminescent suspensions and powders derived by citric acid/urea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, Q.; Tao, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.-Z. Fluorometric determination of hydroquinone by using blue emitting N/S/P-codoped carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.-W.; Bao, Y.-W.; Wang, H.-Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Bacteria-derived fluorescent carbon dots for microbial live/dead differentiation. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2150–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, G. Facile and highly effective synthesis of controllable lattice sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots via hydrothermal treatment of durian. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelarakis, A. From highly graphitic to amorphous carbon dots: A critical review. MRS Energy Sustain. 2014, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Yu, Z.; Liang, F.; Liu, Y.; Seidi, F.; Yong, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Xiao, H. Surface nano-engineering of cellulosic textiles for superior biocidal performance and effective bacterial detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Han, J.; Gong, W.; Li, D.; Yao, Z. A Ratiometric fluorescent probe for the determination of quinolone antibiotics in milk based on N and S co-doped carbon quantum dots. Food Control 2025, 167, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zou, T.; Wang, Z.; Xing, X.; Peng, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. The fluorescent quenching mechanism of n and s co-doped graphene quantum dots with Fe3+ and Hg2+ ions and their application as a novel fluorescent sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Torabi, S.-F.; Lake, R.J.; Hong, S.; Yu, Z.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Nelson, K.; Guo, W.; Pawel, G.T.; et al. Simultaneous Fe2+/Fe3+ imaging shows Fe3+ over Fe2+ enrichment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse brain. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.G.; King, A.; De Moliner, F.; Vendrell, M.; Da Silva Júnior, E.N. quinone-based fluorophores for imaging biological processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, R.; Liu, S.; Patil, A.; Gong, H.; Yi, J.; Sheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. A Machine—Fabricated 3D honeycomb-structured flame-retardant triboelectric fabric for fire escape and rescue. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, M.N.; Tomskaya, A.E.; Kapitonov, A.N.; Smagulova, S.A.; Alekseev, A.A. Investigation of luminescence quantum yields of carbon dots synthesized from ethylene glycol, citric acid and berries. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1124, 081002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Zhai, Y.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J. A rapid microwave synthesis of green-emissive carbon dots with solid-state fluorescence and pH-sensitive properties. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cui, Y.; Song, L.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z. Microwave assisted one-pot synthesis of graphene quantum dots as highly sensitive fluorescent probes for detection of iron ions and pH value. Talanta 2016, 150, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angamuthu, R.; Rajendran, R.; Vairamuthu, R. Quick Microwave Assisted Synthesis and In Vitro Imaging Application of Oxygen Doped Fluorescent Carbon Dots. J. Fluoresc. 2018, 28, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaraki, R.; Sadeghinejad, N. Microwave assisted synthesis of doped carbon dots and their application as green and simple turn off–on fluorescent sensor for mercury (II) and iodide in environmental samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaisare, M.L.; Talib, A.; Khan, M.S.; Pandey, S.; Wu, H.-F. Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots via microwave carbonization of citric acid in presence of tetraoctylammonium ion, and their application to cellular bioimaging. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Shi, H.; Ji, W.; Guo, X.; Yuan, W.; Hu, Q. One-step microwave synthesis of carbon dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of copper ions in aqueous solution. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3097–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shao, F.-Q.; Zou, S.-Y.; Yang, Q.-J.; Huang, H.; Feng, J.-J.; Wang, A.-J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of N,P-doped carbon dots for fluorescent cell imaging. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Bao, R.; Kong, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Yi, J. Room-temperature synthesis of carbon polymer dots from biomass for advanced sensing and fluorescent applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krushna, B.R.R.; Sharma, S.C.; Srinivasan, A.R.; Sahu, S.; Ponnazhagan, K.; George, A.; Rathla, K.S.G.; Manjula, M.V.; Shivakumar, V.; Devaraja, S.; et al. Carbon dots as a distinctive platform fabricated through a sustainable approach for versatile applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 703, 135135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, H.S.; Selvaraj, H.; Ilangovan, A.; Almutairi, B.O.; Sheit, M.K.; Sathishkumar, K. Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of carbon dots from biomass: Fe(III) ion sensing and in-situ methylene blue reduction catalytic activity. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, L.J.; Omer, K.M. Converting Plastic Waste into Functional Carbon Nanodots for the Selective Detection of Iron and Mercury Ions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamishehkar, H.; Ghasemzadeh, B.; Naseri, A.; Salehi, R.; Rasoulzadeh, F. Carbon dots preparation as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of Fe(III) ions in biological systems. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 150, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butwong, N.; Heng, S.; Kunawong, T.; Kunthadong, P.; Mukdasai, S.; Uppachai, P. Carbon dots preparation as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of Fe(III) ions in biological systems. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2024, 19, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W.; Huang, H.; Li, Y. Selective sensing of catechol based on a fluorescent nanozyme with catechol oxidase activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 302, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Dai, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Carbon dots based fluorescent sensor for sensitive determination of hydroquinone. Talanta 2015, 144, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Deng, C.; Ma, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, H. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of N, S Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Fe(III) and Hydroquinone in Water and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14221827
Yu Z, Deng C, Ma W, Liu Y, Liu C, Zhang T, Xiao H. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of N, S Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Fe(III) and Hydroquinone in Water and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(22):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14221827
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhaochuan, Chao Deng, Wenhui Ma, Yuqian Liu, Chao Liu, Tingwei Zhang, and Huining Xiao. 2024. "Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of N, S Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Fe(III) and Hydroquinone in Water and Cell Imaging" Nanomaterials 14, no. 22: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14221827
APA StyleYu, Z., Deng, C., Ma, W., Liu, Y., Liu, C., Zhang, T., & Xiao, H. (2024). Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of N, S Co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Fe(III) and Hydroquinone in Water and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials, 14(22), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14221827





