Unsupervised Learning for the Automatic Counting of Grains in Nanocrystals and Image Segmentation at the Atomic Resolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
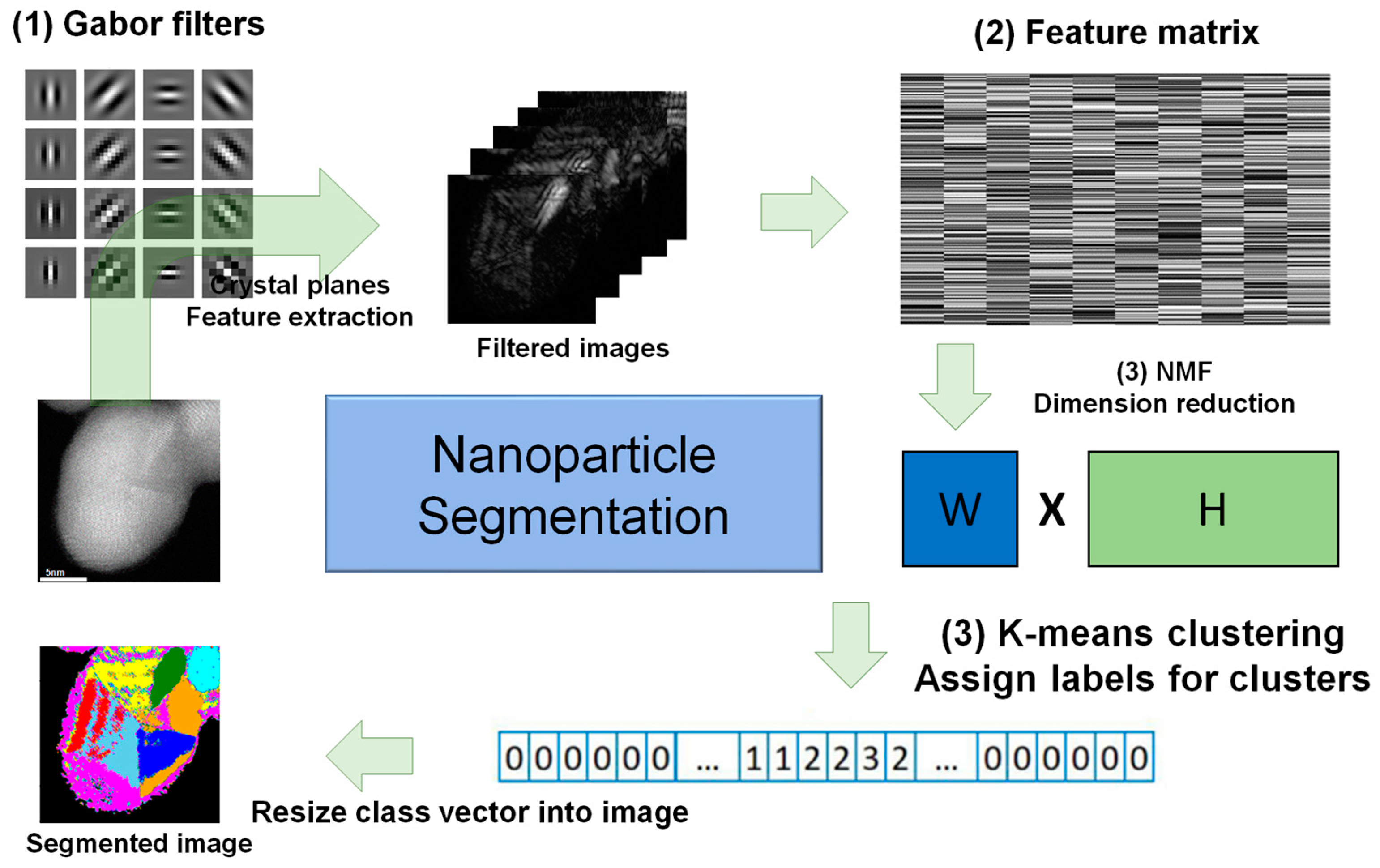
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Gabor Filter
2.2. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
2.3. K-Means Clustering
2.4. Synthesis of Au Nanoparticles
2.5. Synthesis of PtNi Intermetallic Nanoparticles
2.6. Synthesis of PtCo Intermetallic Nanoparticles
2.7. STEM Characterization and Simulation of Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
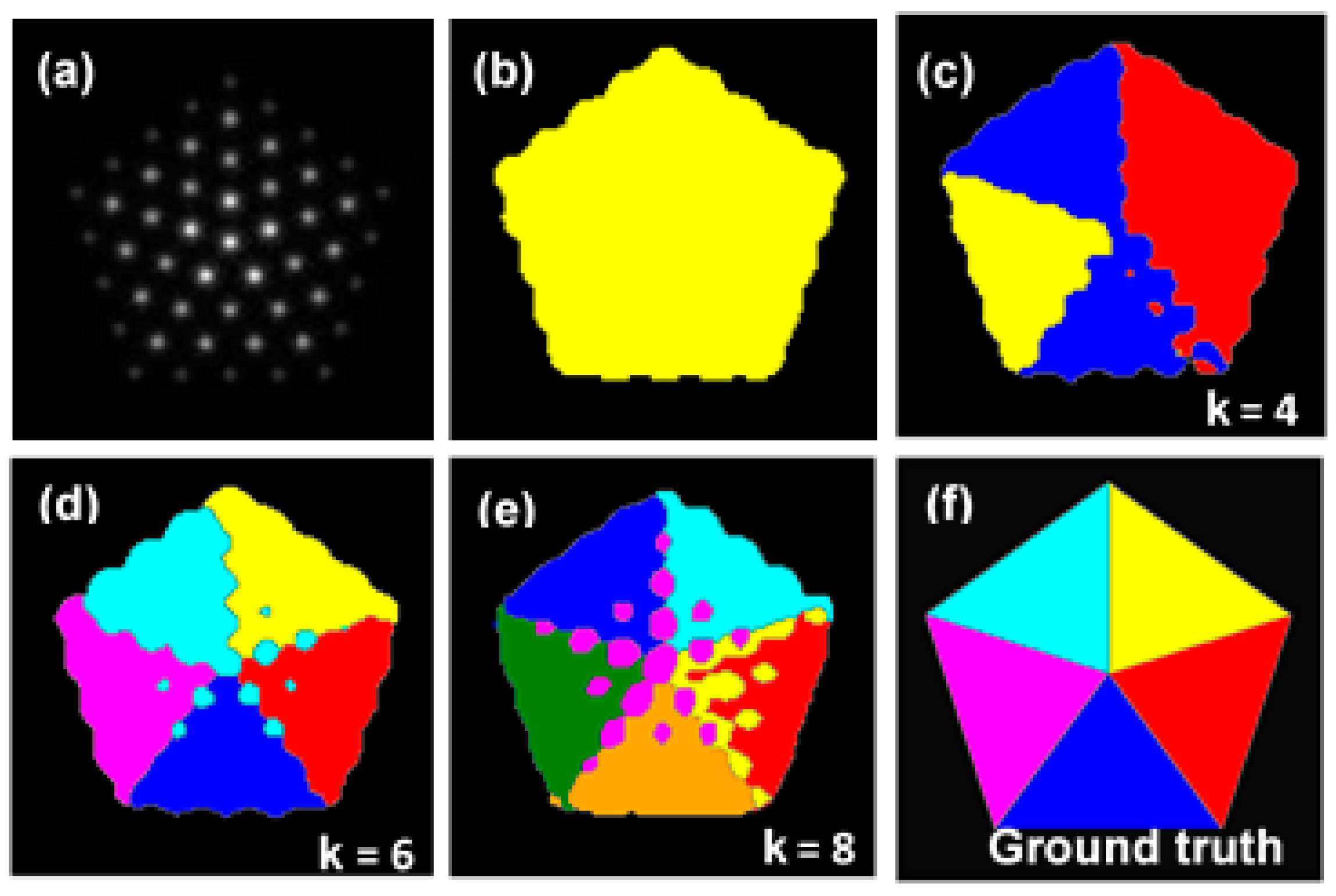
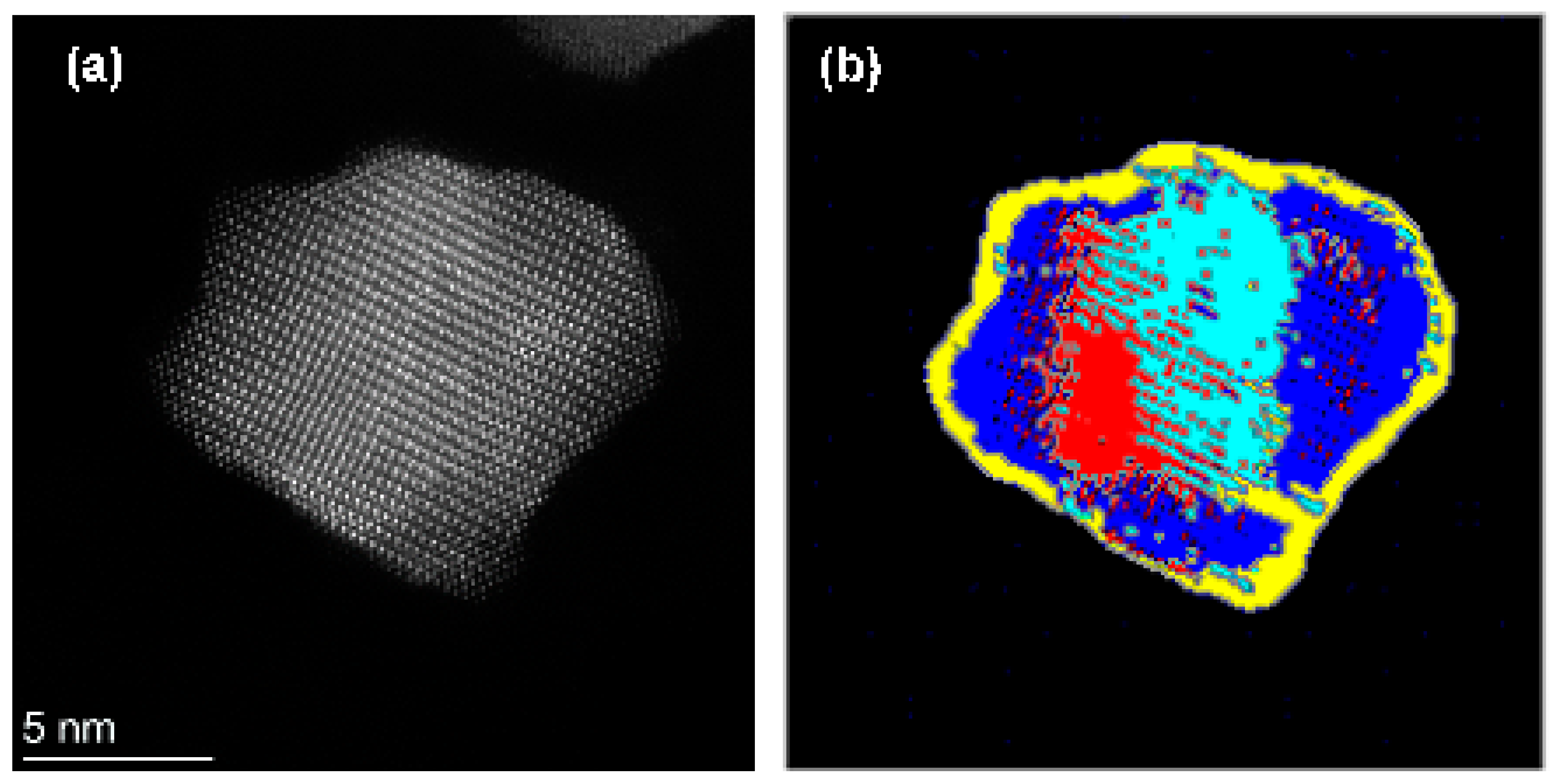
3.1. Segmentation of Polycrystalline Nanoparticles
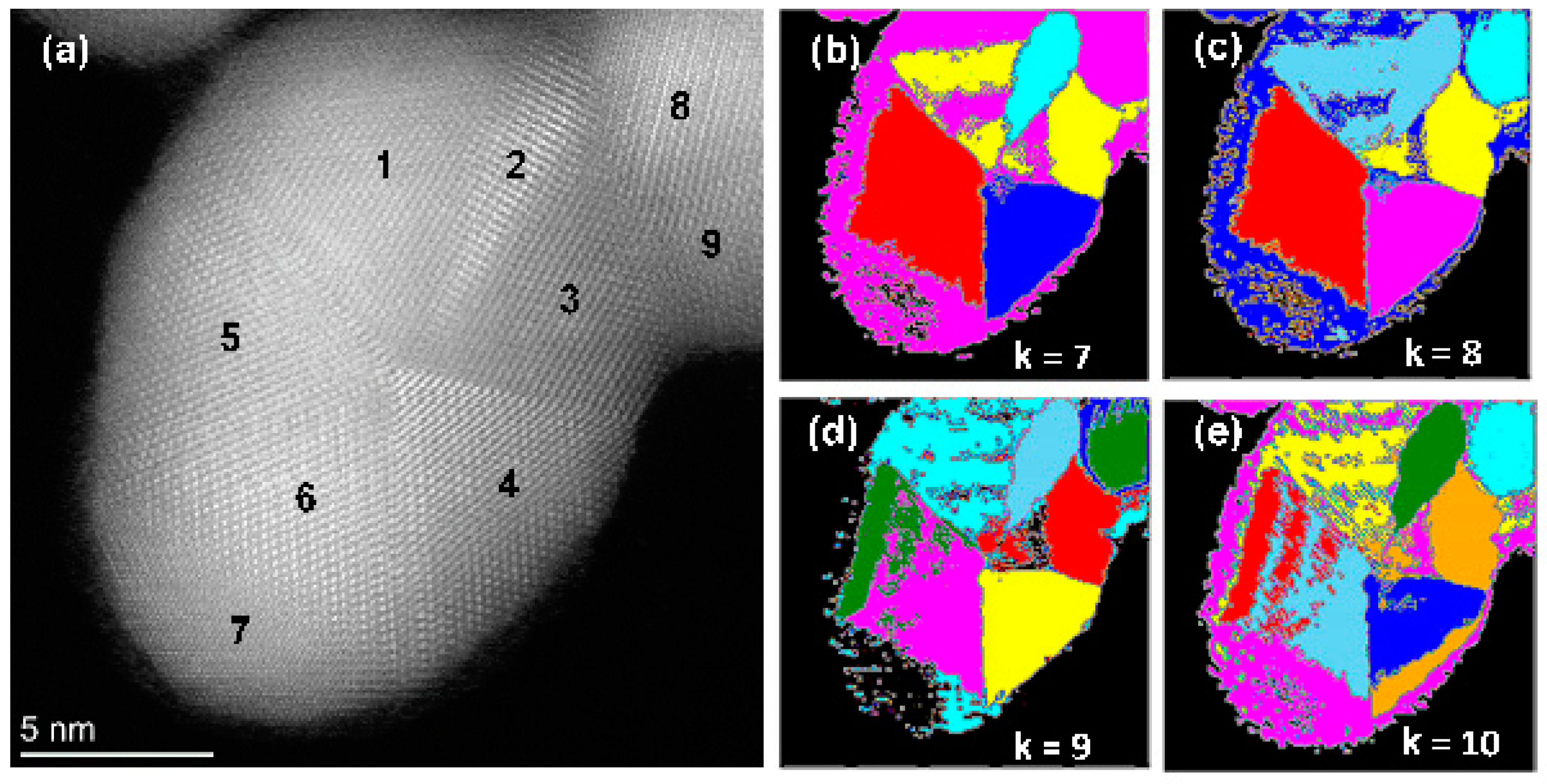
3.2. Potential of the Methodology: Capturing Unknown Features
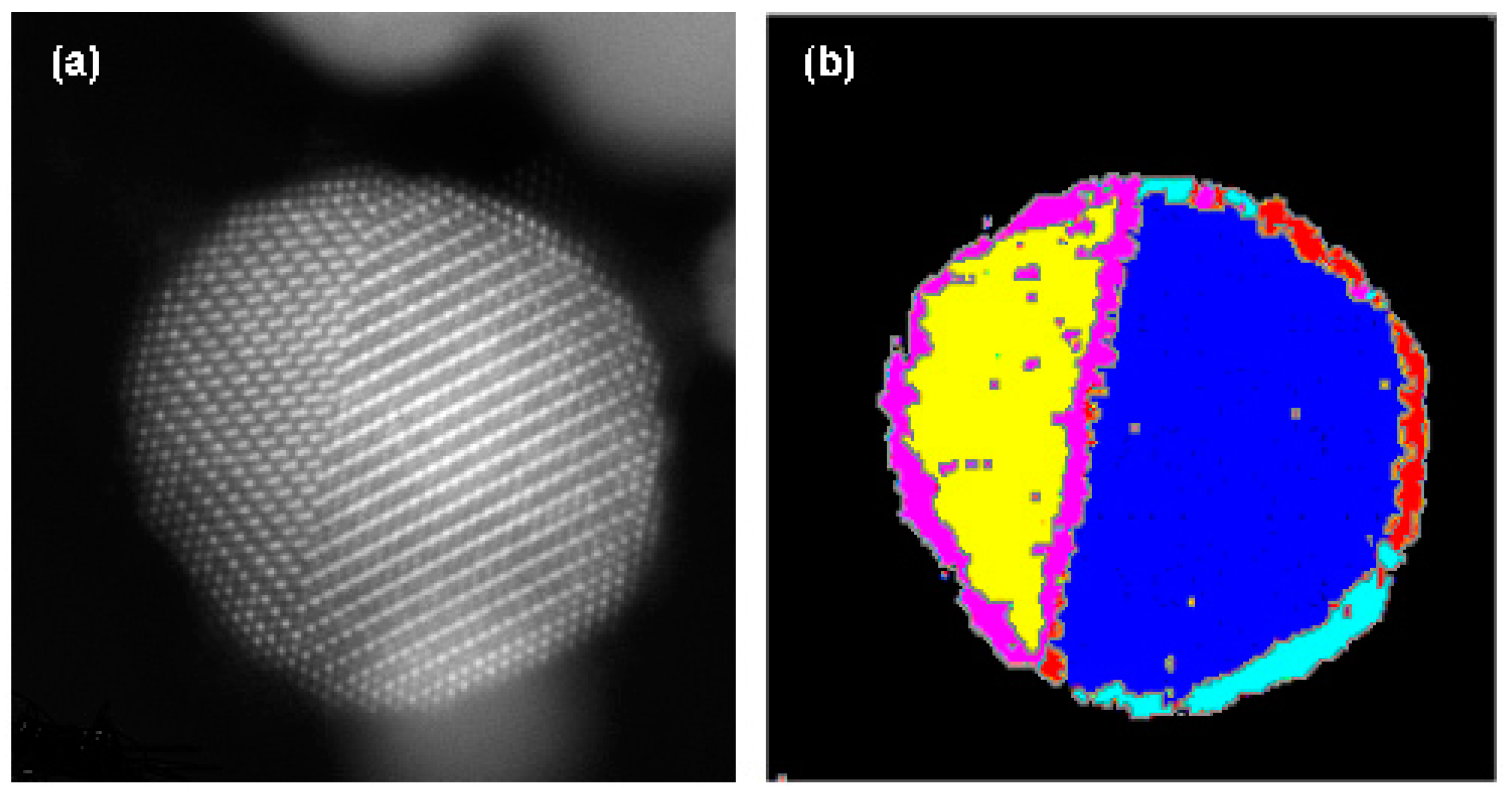
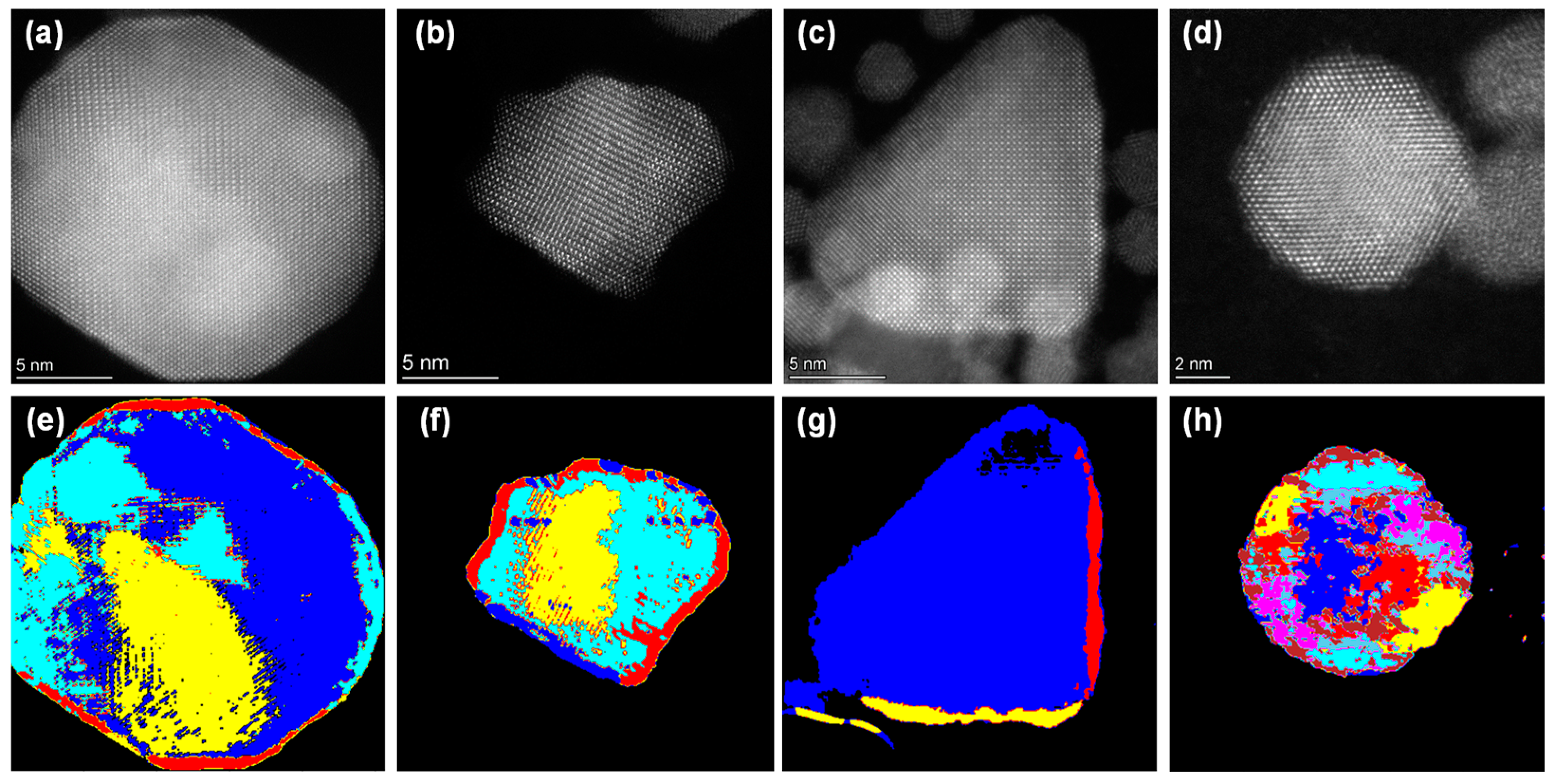
3.3. Automated Segmentation of Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.; Yu, J.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, J. Grain size effects in polycrystalline gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tai, X.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Yu, J. Analytical transmission electron microscopy for emerging advanced materials. Matter 2021, 4, 2309–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.-U.; Lee, M.-J. Influence of defects and nanoscale strain on the photovoltaic properties of CdS/CdSe nanocomposite co-sensitized ZnO nanowire solar cells. Electro. Acta 2016, 220, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.-D.; Maligal-Ganesh, R.V.; Wang, L.-L.; Johnson, D.D.; Kramer, M.J.; Huang, W.-Y.; Zhou, L. Toward phase and catalysis control: Tracking the formation of intermetallic nanoparticles at atomic scale. Chem 2019, 5, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Baaziz, W.; et al. Reversible loss of core-shell structure for Ni-Au bimetallic nanoparticles during CO2 hydrogenation. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, R.; Du, K.; Cheng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Ye, H. Undulating slip in Laves phase and implications for deformation in brittle materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 165505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Hong, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J. Free-standing two-dimensional gold membranes produced by extreme mechanical thinning. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17091–17099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, X.R.; Casillas, G.S.; Yamini, A.; Gazder, A.A. Multiphase identification in Ni-PbTe contacts by EBSD and aberration-corrected STEM. Mater. Des. 2020, 185, 108252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, D.J.; Yu, K.; Rasouli, S.; Polarinakis, J.; Bovik, A.C.; Ferreira, P.J. Automatic segmentation of inorganic nanoparticles in BF TGEM micrographs. Ultramicroscopy 2018, 194, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Field, K.G.; Morgan, D. Automated defect analysis in electron microscopic images. Npj Comput. Mater. 2018, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, A.B.; Gurses, A. Automatic detection, localization and segmentation of nano-particles with deep learning in microscopy images. Micron 2019, 120, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytwu, K.; Groschner, C.; Scott, M.C. Understanding the influence of receptive field and network complexity in neural network-guided TEM image analysis. Microsc. Microanal. 2022, 28, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschner, C.K.; Choi, C.; Scott, M.C. Machine learning pipeline for segmentation and defect identification from high-resolution transmission electron microscopy data. Microsc. Microanal. 2021, 27, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Cautaerts, N.; Dehm, G.; Liebscher, C.H. Automated acrystal orientation mapping by precession electron diffraction-assisted four-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy using a scintillator-based CMOS detector. Microsc. Microanal. 2021, 27, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, B.; Cole, J.M. Bayesian particle instance segmentation for electron microscopy image quantification. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chen, A.; Motta, A.; Wang, X. Automated analysis of grain morphology in TEM images using convolutional neural network with CHAC algorithm. J. Nuc. Mater. 2024, 588, 154813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena-González, G.; Hernández-Robles, A.; Mayoral, Á.; Martinez, L.; Huttel, Y.; Galindo, P.L.; Ponce, A. Unsupervised learning for the segmentation of small crystalline particles at the atomic level. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2023, 58, 2200211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, E. Special issue on developments of electron holography for material science. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 380201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McCartney, M.R.; Smith, D.J. Electron holography: Phase imaging with nanometer resolution. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2007, 37, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertog, M.I.D.; Schmid, H.; Cooper, D.; Rouviere, J.L.; Björk, M.T.; Riel, H.; Rivallin, P.; Karg, S.; Riess, W. Mapping active dopants in single silicon nanowires using off-axis electron holography. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béché, A.; Rouvière, J.L.; Barnes, J.P.; Cooper, D. Dark field electron holography for strain measurement. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hÿtch, M.J.; Snoeck, E.; Kilaas, R. Quantitative measurement of displacement and strain fields from HREM micrographs. Ultramicroscopy 1998, 74, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles: Optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pach, A.; Szot, A.; Fitzner, K.; Luty-Blocho, M. Opportunities and challenges in the synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles via the chemical route in microreactor systems. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.-J.; Wang, C.; Yan, Q.-Q.; Yin, P.; Tong, L.; Liang, H.-W. Phase diagrams guide synthesis of highly ordered intermetallic electrocatalysts: Separating alloying and ordering stages. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, J. Probe: A software for high-resolution STEM image simulation. Ultramicroscopy 2018, 193, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Scott, M.C.; Ophus, C.; Xu, R.; Pryor, A.; Wu, L.; Sun, F.; Theis, W.; Zhou, J.; et al. Deciphering chemical order/disorder and material properties at the single-atom level. Nature 2017, 542, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, C.; Yang, Y. Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Lee, Y.; Hong, Y.; Lee, K.; Baik, H. Three-dimensional reconstruction of Y-IrNi rhombic dodecahedron nanoframe by STEM/EDS tomography. Appl. Microsc. 2023, 53, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, C.; Lee, T.; Ryu, S.; Yang, Y. Direct observation of three-dimensional atomic structure of twinned metallic nanoparticles and their catalytic properties. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, G.; Moniri, S.; Ophus, C.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, C.; et al. Atomic-scale identification of active sites of oxygen reduction nanocatalysts. Nat. Catal. 2024, 7, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohn, W.; Kim, T.; Moon, C.W.; Shin, D.; Park, Y.; Jin, H.; Baik, H. Unsupervised Learning for the Automatic Counting of Grains in Nanocrystals and Image Segmentation at the Atomic Resolution. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201614
Sohn W, Kim T, Moon CW, Shin D, Park Y, Jin H, Baik H. Unsupervised Learning for the Automatic Counting of Grains in Nanocrystals and Image Segmentation at the Atomic Resolution. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(20):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201614
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohn, Woonbae, Taekyung Kim, Cheon Woo Moon, Dongbin Shin, Yeji Park, Haneul Jin, and Hionsuck Baik. 2024. "Unsupervised Learning for the Automatic Counting of Grains in Nanocrystals and Image Segmentation at the Atomic Resolution" Nanomaterials 14, no. 20: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201614
APA StyleSohn, W., Kim, T., Moon, C. W., Shin, D., Park, Y., Jin, H., & Baik, H. (2024). Unsupervised Learning for the Automatic Counting of Grains in Nanocrystals and Image Segmentation at the Atomic Resolution. Nanomaterials, 14(20), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14201614





