Pain-Free Alpha-Synuclein Detection by Low-Cost Hierarchical Nanowire Based Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrode Fabrication
- Au NP electrodeposition
- 2.
- GA electro-polymerization
- 3.
- Functionalization with EDC-NHS
- 4.
- Anti-α-synuclein and BSA immobilization
- 5.
- α-synuclein recognition and anchoring
2.3. Clinical Sample Preparation and Testing
2.4. Apparatus and Instrumentations
3. Results and Discussion
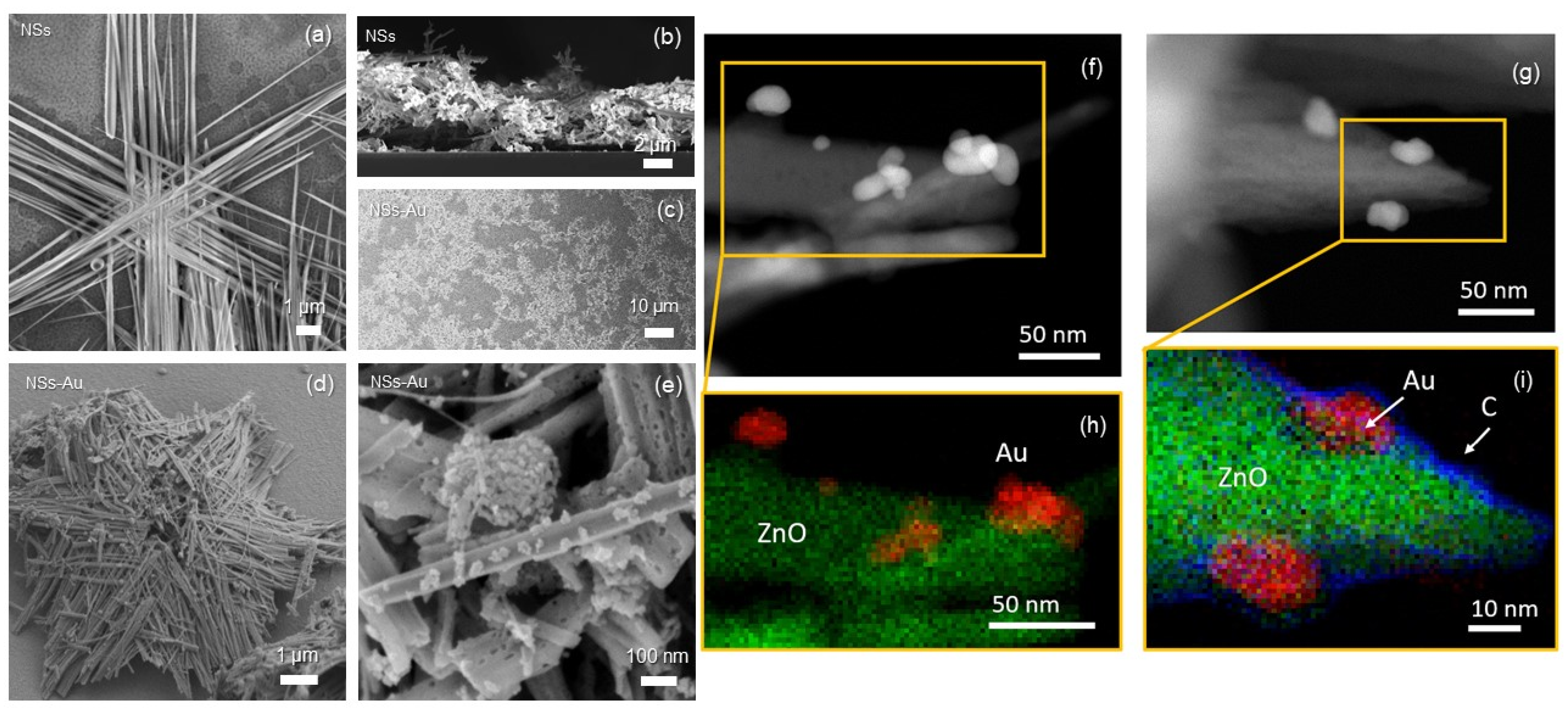
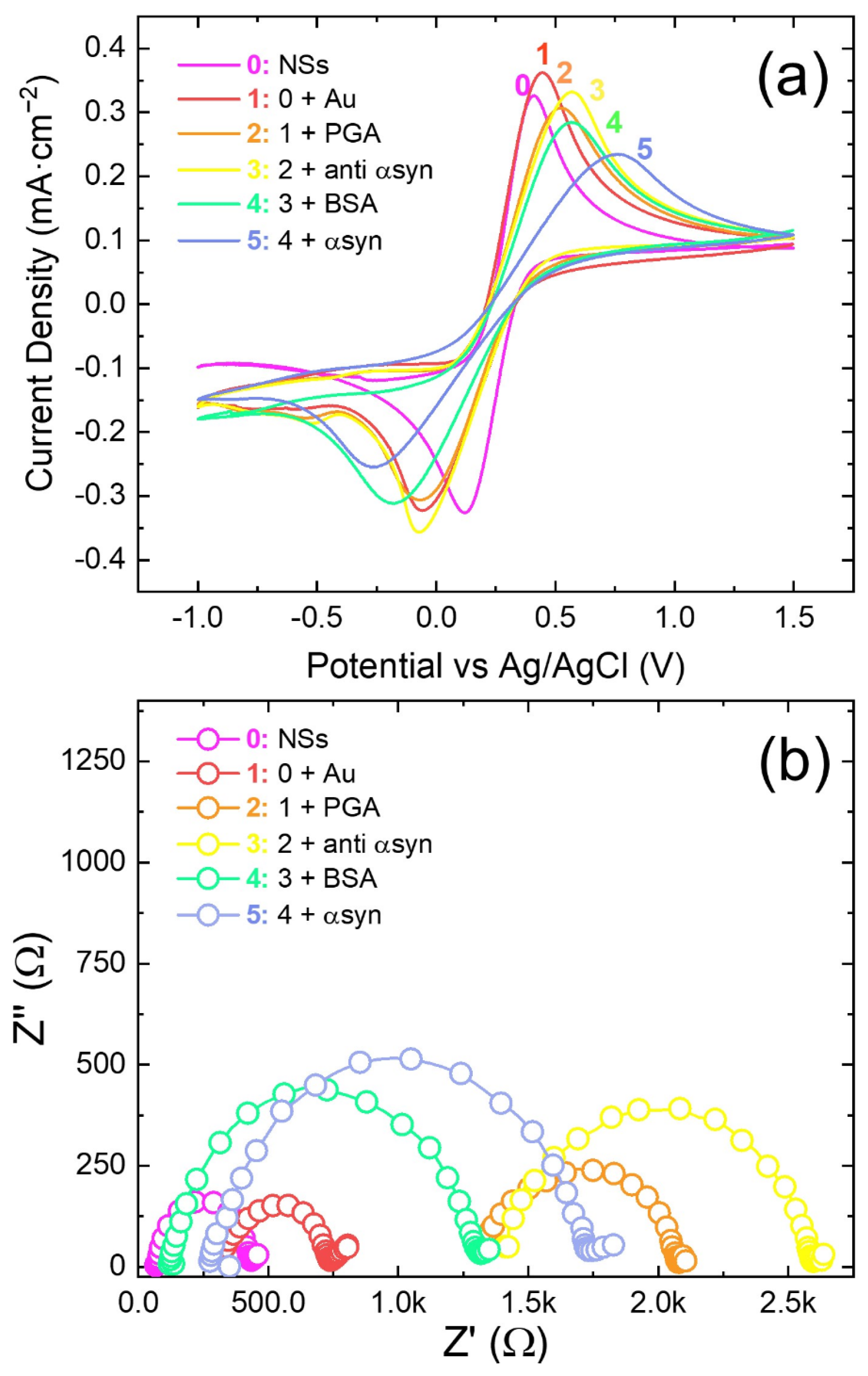
3.1. Structural and Electrochemical Characterization
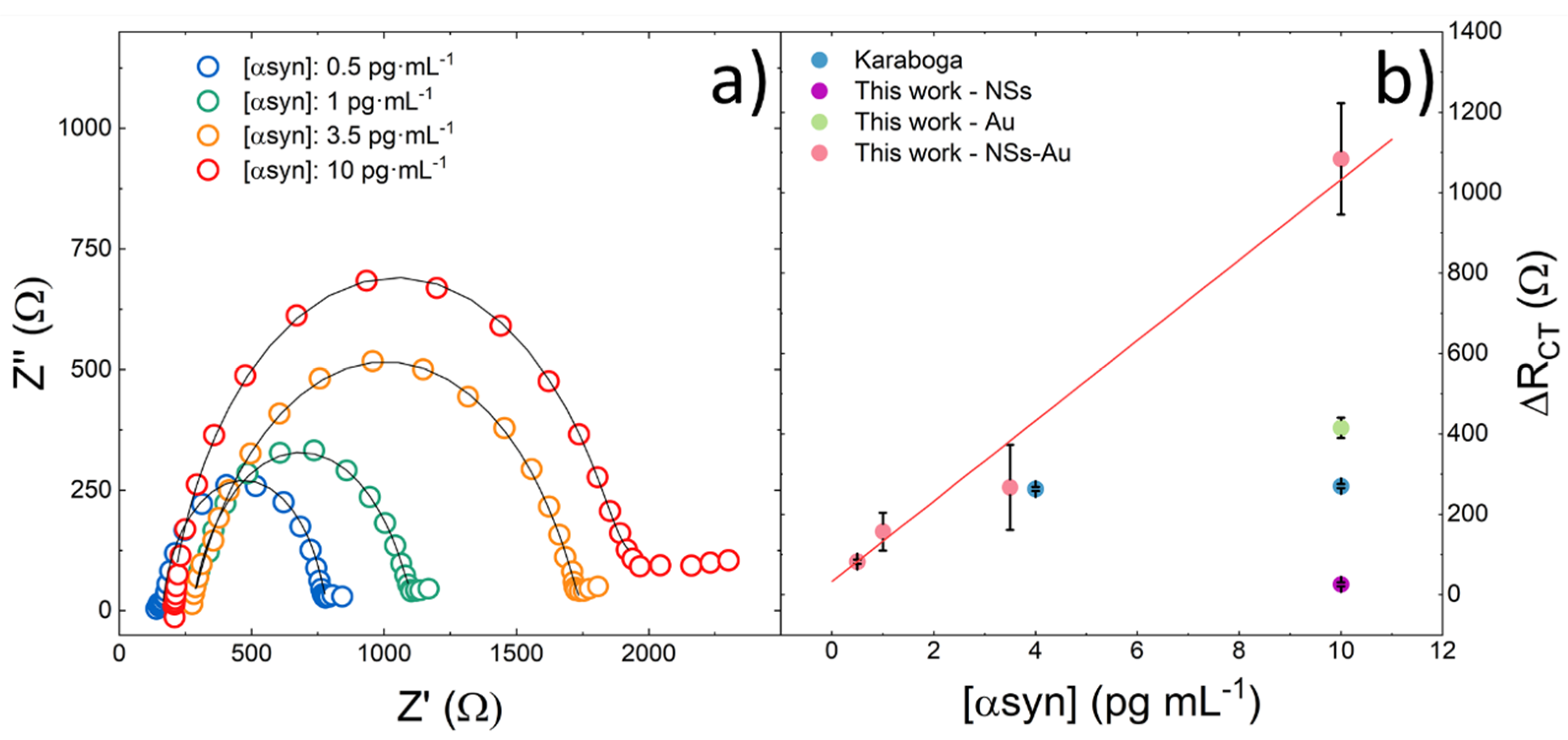
3.2. α-Synuclein Determination: Sensitivity, Reproducibility and Stability of the Biosensor
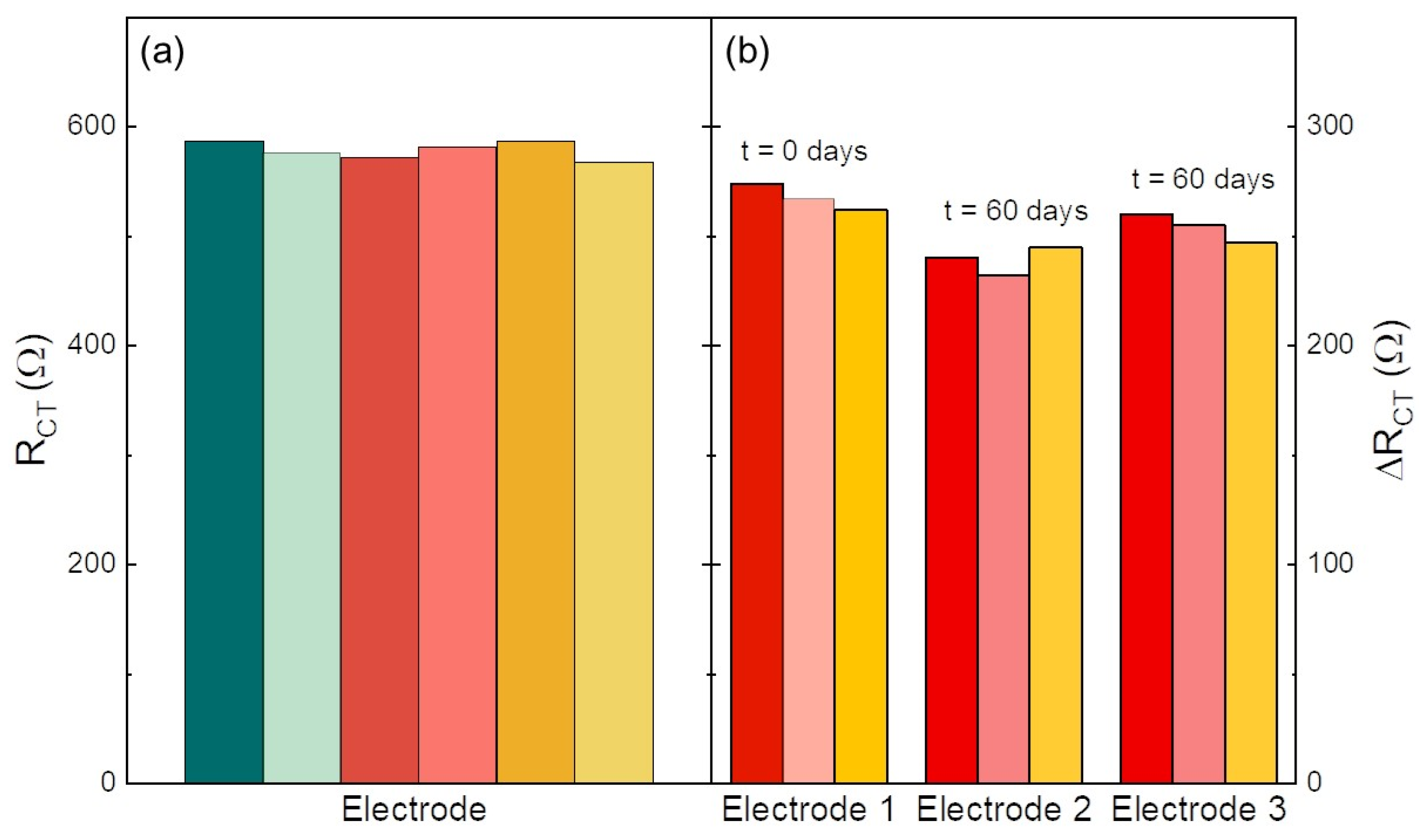
3.3. Reproducibility and Stability Test
3.4. Clinical Samples Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, L.; Cookson, M.R.; Petrucelli, L.; La Spada, A.R. Converging pathways in neurodegeneration, from genetics to mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 63–75.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurd, M.D.; Martorell, P.; Delavande, A.; Mullen, K.J.; Langa, K.M. Monetary Costs of Dementia in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalenchuk, M.; Gentleman, S.M.; Marzi, S.J. Linking environmental risk factors with epigenetic mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Grosso, G.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Lanza, G.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Caruso, G.; Castellano, S. Mediterranean diet, mental health, cognitive status, quality of life, and successful aging in southern Italian older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 175, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Iba, M.; Kim, C.; Masliah, E. Immunotherapies for Aging-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases—Emerging Perspectives and New Targets. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.P.; Hardy, J.; Fischbeck, K.H. Toxic proteins in neurodegenerative disease. Science 2002, 296, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Benito, M.; Granado, N.; García-Sanz, P.; Michel, A.; Dumoulin, M.; Moratalla, R. Modeling Parkinson’s Disease with the Alpha-Synuclein Protein. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-W.; Yang, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-C.; Chang, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-R. Plasma and Plasma Alpha-Synuclein as a Biomarker of Diagnosis in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 10, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnetti, L.; Gaetani, L.; Eusebi, P.; Paciotti, S.; Hansson, O.; El-Agnaf, O.; Mollenhauer, B.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P. CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, N.K.U.; Stransky, E.; Meyer, M.; Gaertner, S.; Shing, M.; Schnaidt, M.; Celej, M.S.; Jovin, T.M.; Leyhe, T.; Laske, C.; et al. Alpha-synuclein levels in blood plasma decline with healthy aging. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menne, F.; Schipke, C.G. Diagnose it yourself: Will there be a home test kit for Alzheimer’s disease? Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2021, 11, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Qian, K. Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors: Mechanism, Preparation, and Application in Biomedicine. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2021, 1, 2000104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey Roslyn, S.; McConnell, E.M.; Chan, D.; Holahan Matthew, R.; DeRosa Maria, C.; Prakash, R. Non-invasive Monitoring of α-Synuclein in Saliva for Parkinson’s Disease Using Organic Electrolyte-Gated FET Aptasensor. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xia, N.; Zhao, L.; Liu, K.; Hou, W.; Liu, L. Aptasensors for the selective detection of alpha-synuclein oligomer by colorimetry, surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 245, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaboǧa, M.N.S.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of alpha-synuclein measured using a poly-glutamic acid-modified gold nanoparticle-doped disposable neuro-biosensor system. Analyst 2019, 144, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, D.; Gu, Y.; Song, S.; Nguyen, E.P.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, Q.; Pan, H.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Guo, Z. Ultrasensitive detection of alpha-synuclein oligomer using a PolyD-glucosamine/gold nanoparticle/carbon-based nanomaterials modified electrochemical immunosensor in human plasma. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Fan, H.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Feng, S.; Anbu, P.; et al. Gold-nanourchin seeded single-walled carbon nanotube on voltammetry sensor for diagnosing neurogenerative Parkinson’s disease. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1094, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byakodi, M.; Shrikrishna, N.S.; Sharma, R.; Bhansali, S.; Mishra, Y.; Kaushik, A.; Gandhi, S. Emerging 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D nanostructures for efficient point-of-care biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 12, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, N.; Kim, D.H. Metal oxide modified ZnO nanomaterials for biosensor applications. Nano Converg. 2018, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandurra, A.; Bruno, E.; Condorelli, G.G.; Grimaldi, M.G.; Mirabella, S. Microscopic model for pH sensing mechanism in zinc-based nanowalls. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Kyle, C.; Luo, H.; Zhang, D.-W.; Das, A.; Briscoe, J.; Dunn, S.; Titirici, M.; Krause, S. Ammonia Gas Sensor Response of a Vertical Zinc Oxide Nanorod-Gold Junction Diode at Room Temperature. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.S.; Singh, S.; Batool, M.; Fahmy, H.M.; Seku, K.; Shalan, A.E.; Senentxu, L.-M.; Zafar, M.N. A review on 2D-ZnO nanostructure based biosensors: From materials to devices. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 320–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Casas, B.; Galdámez-Martínez, A.; Gutiérrez-Flores, J.; Baca Ibañez, A.; Panda, P.K.; Santana, G.; de la Vega, H.A.; Suar, M.; Gutiérrez Rodelo, C.; Kaushik, A.; et al. Bio-acceptable 0D and 1D ZnO nanostructures for cancer diagnostics and treatment. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 533–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doǧan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morko̧, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.K.; Chakravadhanula, V.S.K.; Hrkac, V.; Jebril, S.; Agarwal, D.C.; Mohapatra, S.; Avasthi, D.K.; Kienle, L.; Adelung, R. Crystal growth behaviour in Au-ZnO nanocomposite under different annealing environments and photoswitchability. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 064308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, V.; Basu, A.; Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, A.; Mishra, Y.K.; Basu, A.K. Smart nanomaterials to support quantum-sensing electronics. Mater. Today Electron. 2023, 6, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbakan, B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A sensitive and disposable indium tin oxide based electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of MAGE-1. Talanta 2017, 169, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mari, G.M.; Mineo, G.; Franzò, G.; Mirabella, S.; Bruno, E.; Strano, V. Low-Cost, High-Yield ZnO Nanostars Synthesis for Pseudocapacitor Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldous, L.; Silvester, D.S.; Villagrán, C.; Pitner, W.R.; Compton Richard, G.; Lagunas, M.C.; Hardacre, C. Electrochemical studies of gold and chloride in ionic liquids. New J. Chem. 2006, 11, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkhof, S.; Sinz, A. Chances and pitfalls of chemical cross-linking with amine-reactive N-hydroxysuccinimide esters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 392, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E.J.F.; Wain, A.J. The Butler-Volmer equation in electrochemical theory: Origins, value, and practical application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 872, 114145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


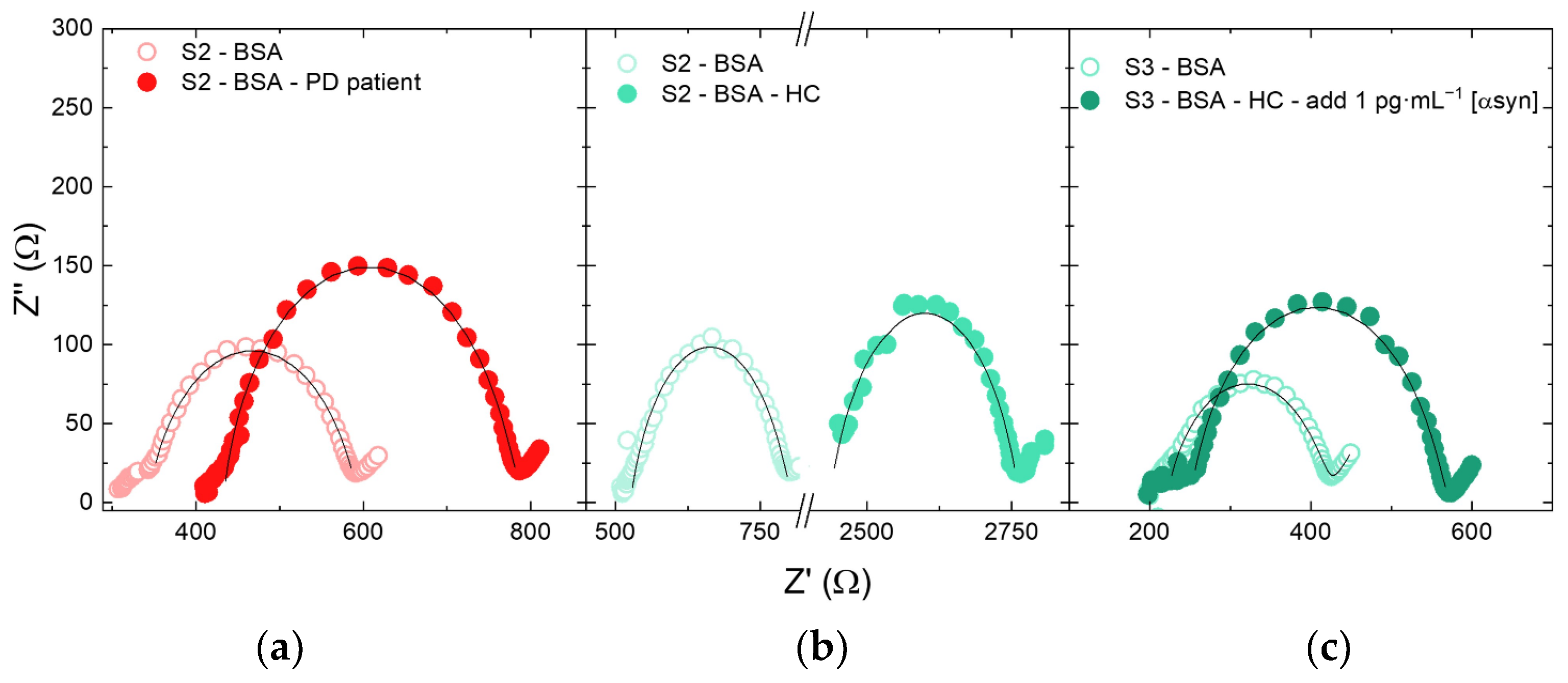
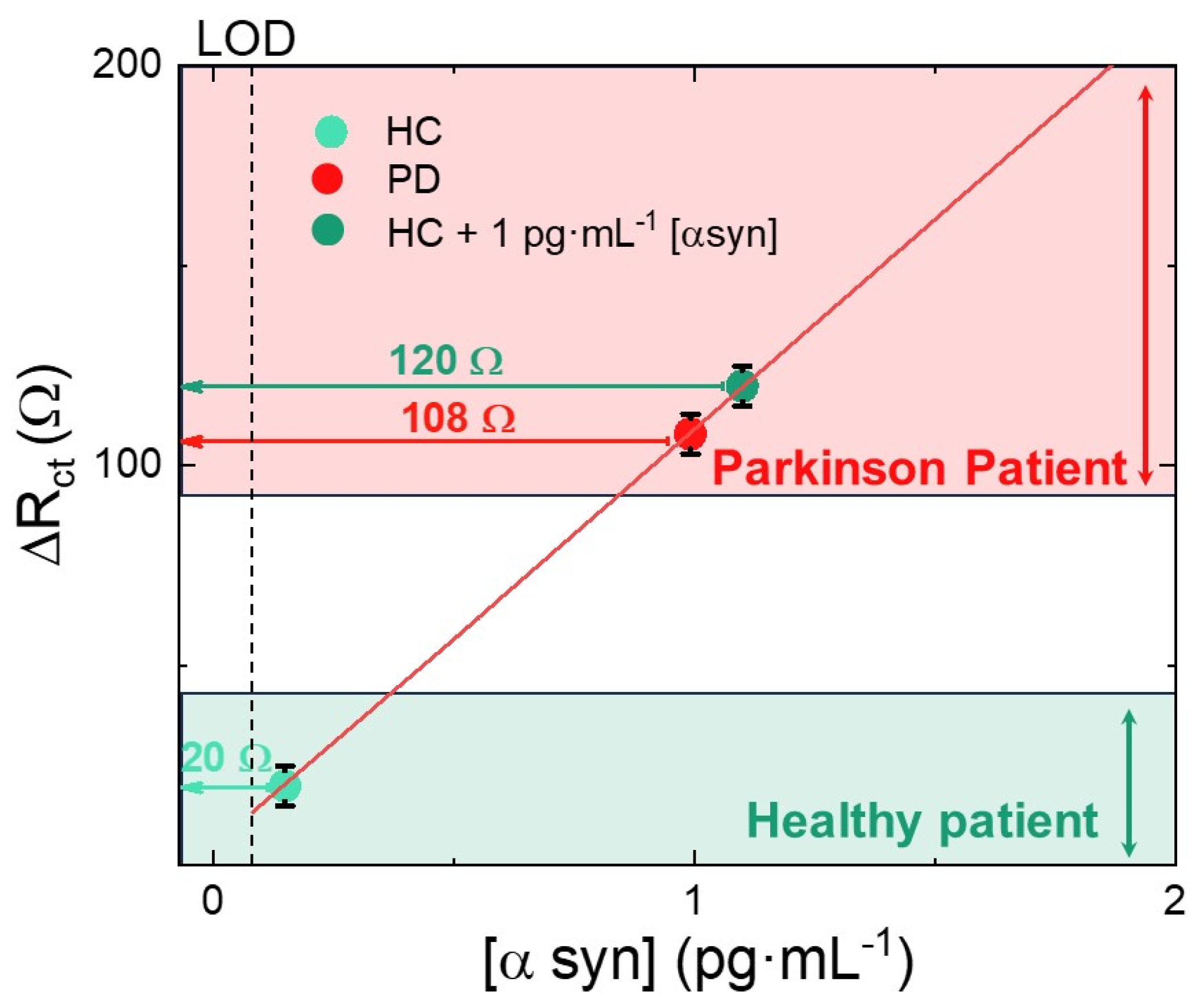
| α-Synuclein Concentration pg·mL−1 | RΩ Ω | Rct Ω | ΔRct Ω | Cdl µF | Zw Ω·s−0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (BSA step) | 411.7 | 546 | - | 10.1 | 27.2 |
| 0.5 | 163 | 628.9 | 82.9 | 10.5 | 25.5 |
| (BSA step) | 170 | 655 | - | 9 | 14.5 |
| 1 | 276 | 812 | 157 | 11 | 44 |
| (BSA step) | 110 | 1194 | - | 3.8 | 47 |
| 3.5 | 273 | 1461 | 267 | 3.4 | 19 |
| (BSA step) | 399 | 605 | - | 12.3 | 21 |
| 10 | 192 | 1691 | 1086 | 3.2 | 25 |
| Active Material | Detection Method | Sample | Detection Range pg·mL−1 | Limit of Detection pg·mL−1 | Testing with Real Human Samples from PD and HC Patients | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Electrolyte-Gated FET Aptasensor | Electrolyte-gated field-effect transistor | DI water solution of α-synuclein; diluted saliva | 10−4–104 | 10−5 | No | [15] |
| Au NPs | EIS | Plasma (addition method) | 7·103–70·103 | 14 | No | [16] |
| Au NPs | EIS | CSF | 4–2000 | 0.135 | No | [17] |
| MWCNTs/Au NPs | SWV | HC Plasma (addition method) | 0.7–700 | 0.4 | No | [18] |
| Au-nanourchin coniugated SWCN | IDE sensor, voltammetry | Solution of α-synuclein | 0.14–14 | 0.14 | No | [19] |
| ZnO NSs + Au NPs | EIS | PD and HC plasma, direct and addition method | 0.5–10 | 0.08 | Yes | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Mari, G.M.; Scuderi, M.; Lanza, G.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Salemi, M.; Caraci, F.; Bruno, E.; Strano, V.; Mirabella, S.; Scandurra, A. Pain-Free Alpha-Synuclein Detection by Low-Cost Hierarchical Nanowire Based Electrode. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14020170
Di Mari GM, Scuderi M, Lanza G, Salluzzo MG, Salemi M, Caraci F, Bruno E, Strano V, Mirabella S, Scandurra A. Pain-Free Alpha-Synuclein Detection by Low-Cost Hierarchical Nanowire Based Electrode. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(2):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14020170
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Mari, Gisella M., Mario Scuderi, Giuseppe Lanza, Maria Grazia Salluzzo, Michele Salemi, Filippo Caraci, Elena Bruno, Vincenzina Strano, Salvo Mirabella, and Antonino Scandurra. 2024. "Pain-Free Alpha-Synuclein Detection by Low-Cost Hierarchical Nanowire Based Electrode" Nanomaterials 14, no. 2: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14020170
APA StyleDi Mari, G. M., Scuderi, M., Lanza, G., Salluzzo, M. G., Salemi, M., Caraci, F., Bruno, E., Strano, V., Mirabella, S., & Scandurra, A. (2024). Pain-Free Alpha-Synuclein Detection by Low-Cost Hierarchical Nanowire Based Electrode. Nanomaterials, 14(2), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14020170