Meso-Macroporous Hydroxyapatite Powders Synthesized in Polyvinyl Alcohol or Polyvinylpyrrolidone Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
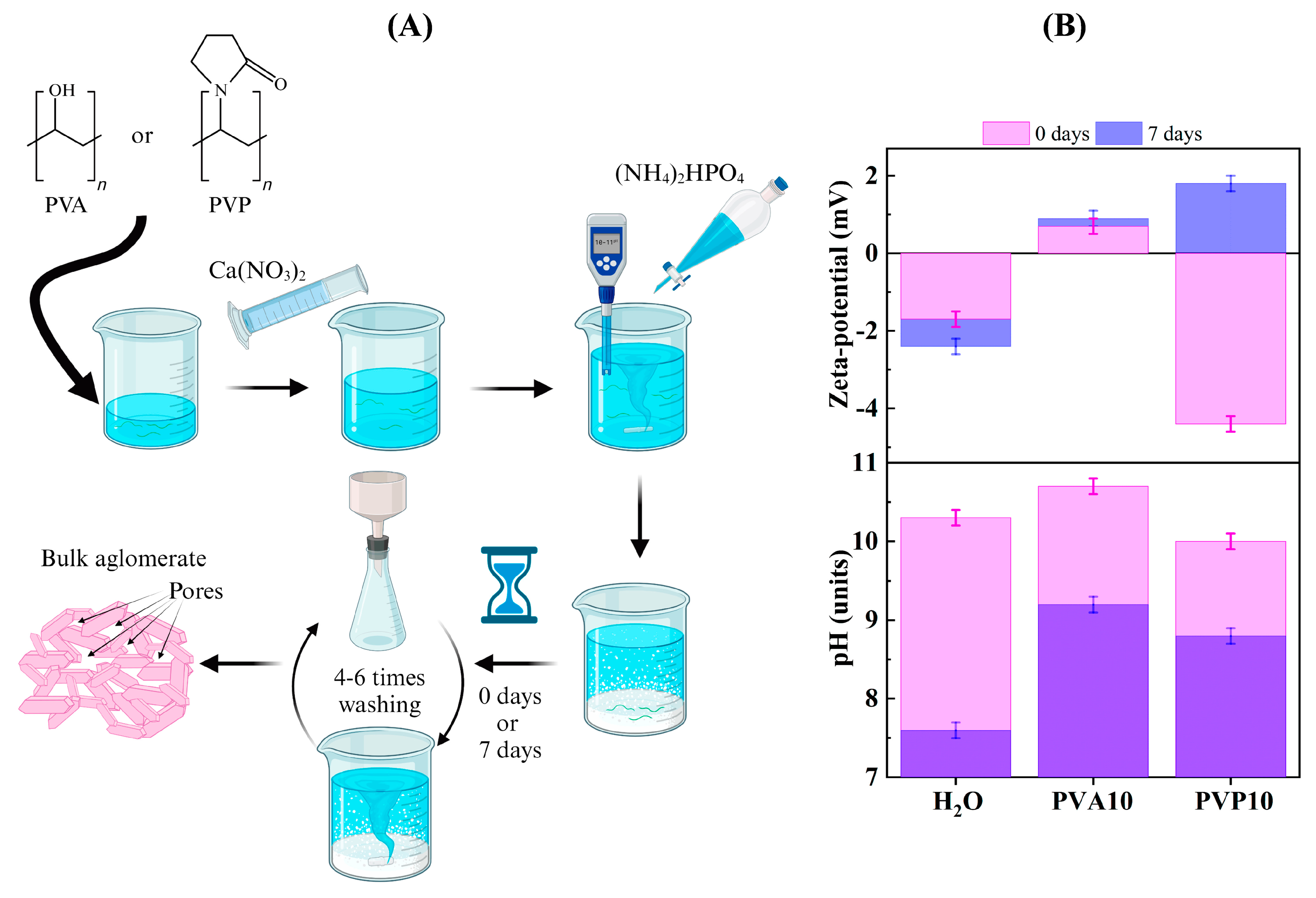
2.1. Powder Synthesis
2.2. Materials’ Characterization
2.2.1. Suspension Characterization
2.2.2. Powders’ Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Suspension Properties
3.2. Chemical Composition of Powders
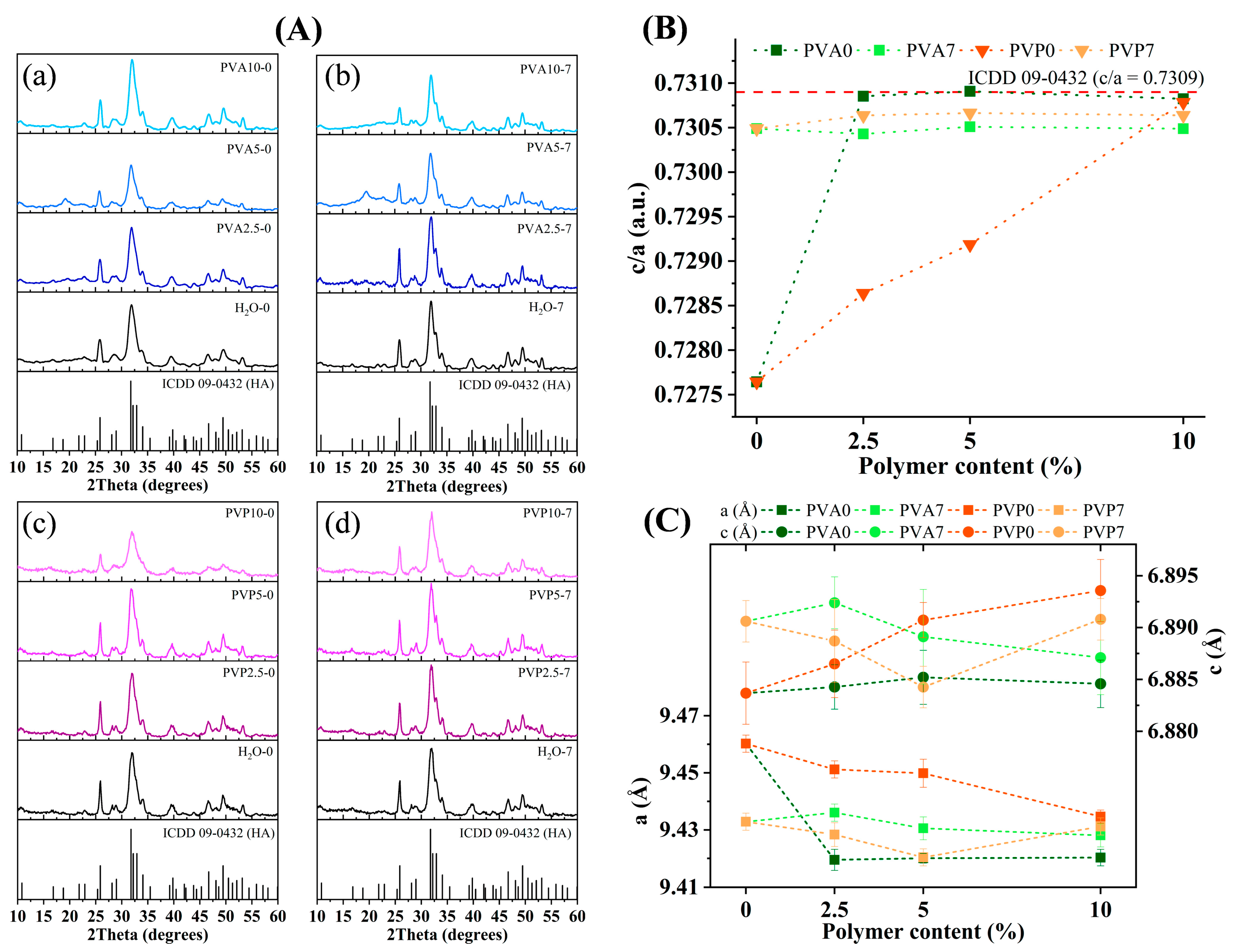
3.3. XRD Analysis
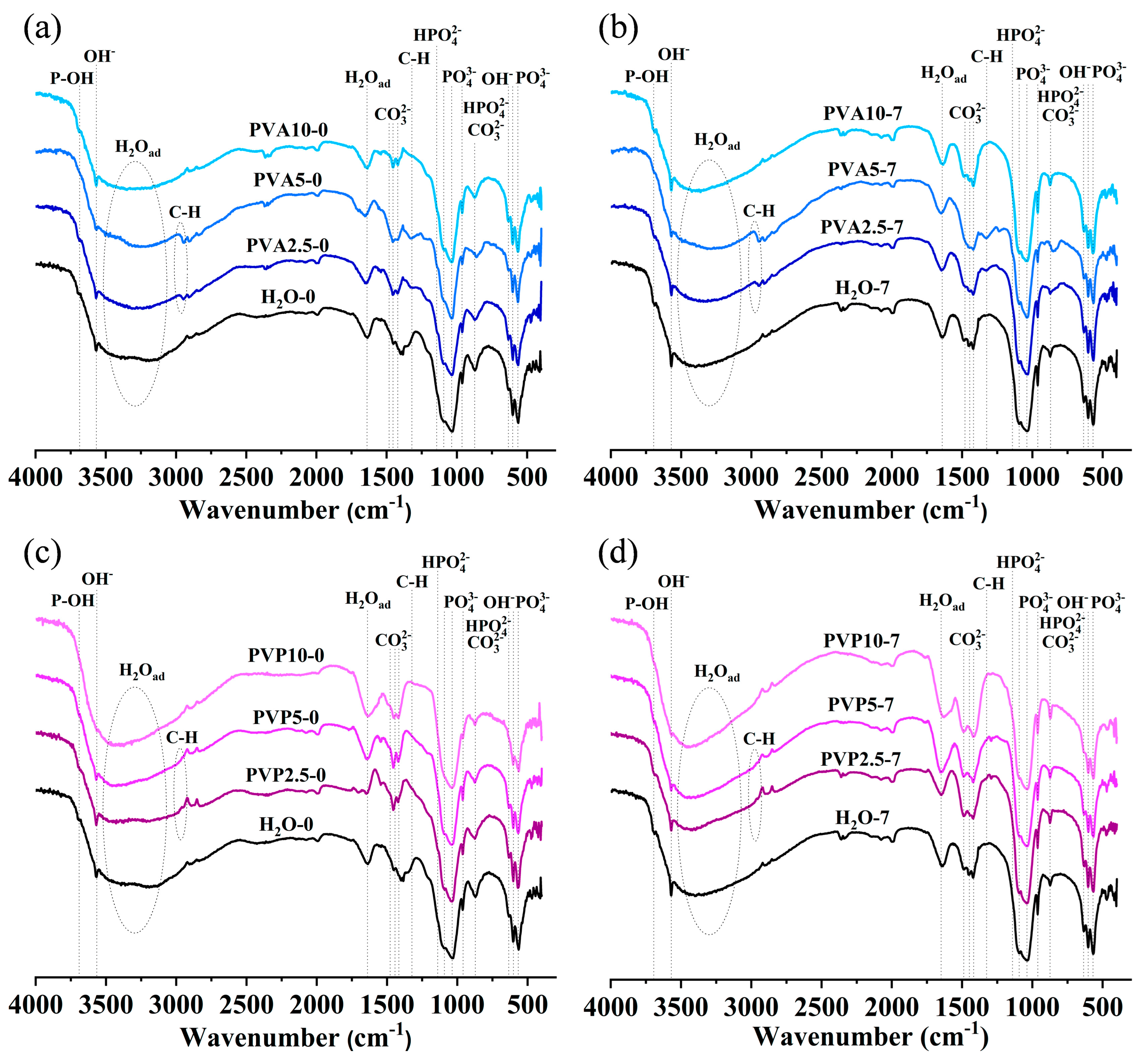
3.4. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.5. EPR Spectroscopy
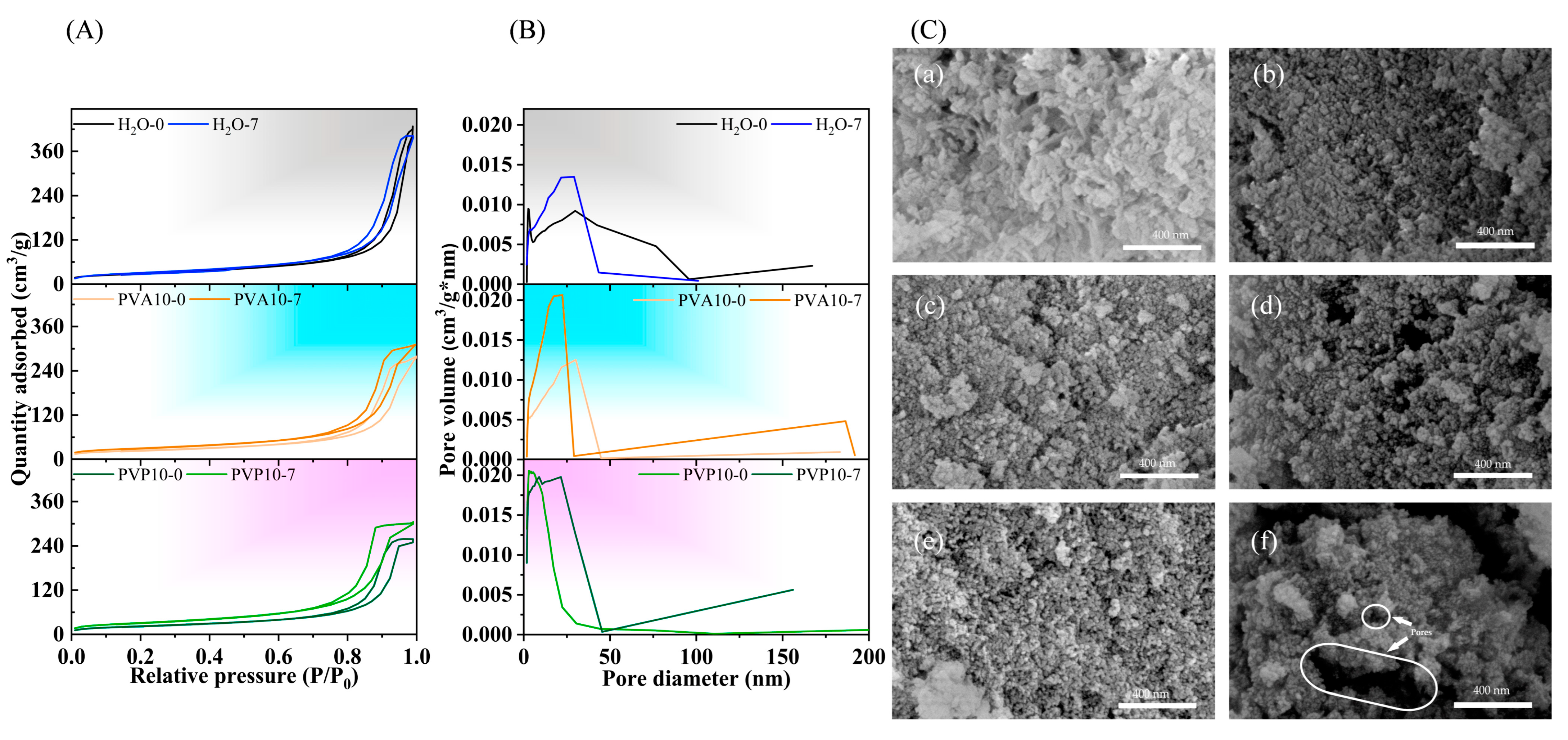
3.6. Textural Properties of the Powders According to Measures of Nitrogen Adsorption
3.7. SEM Investigation
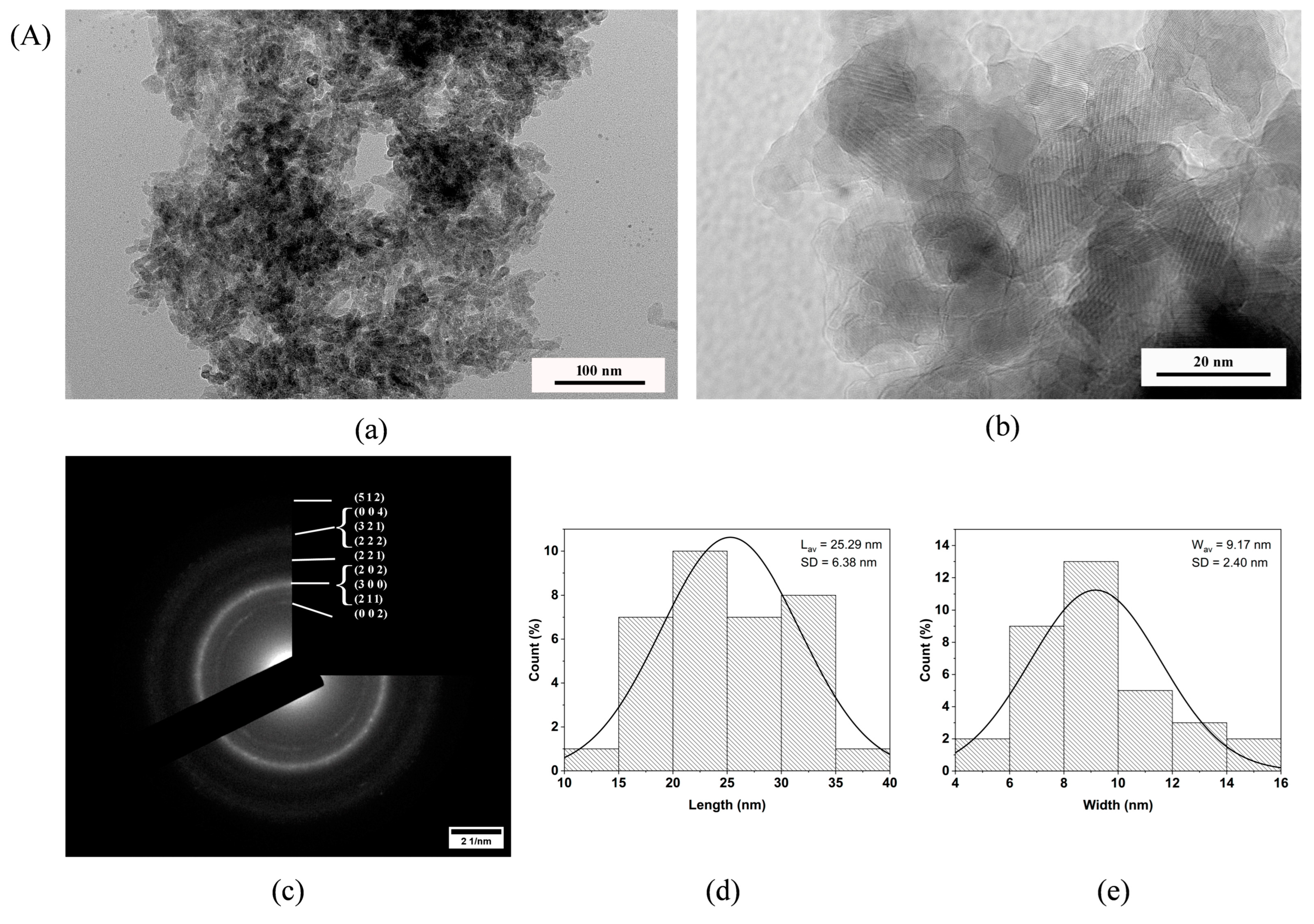
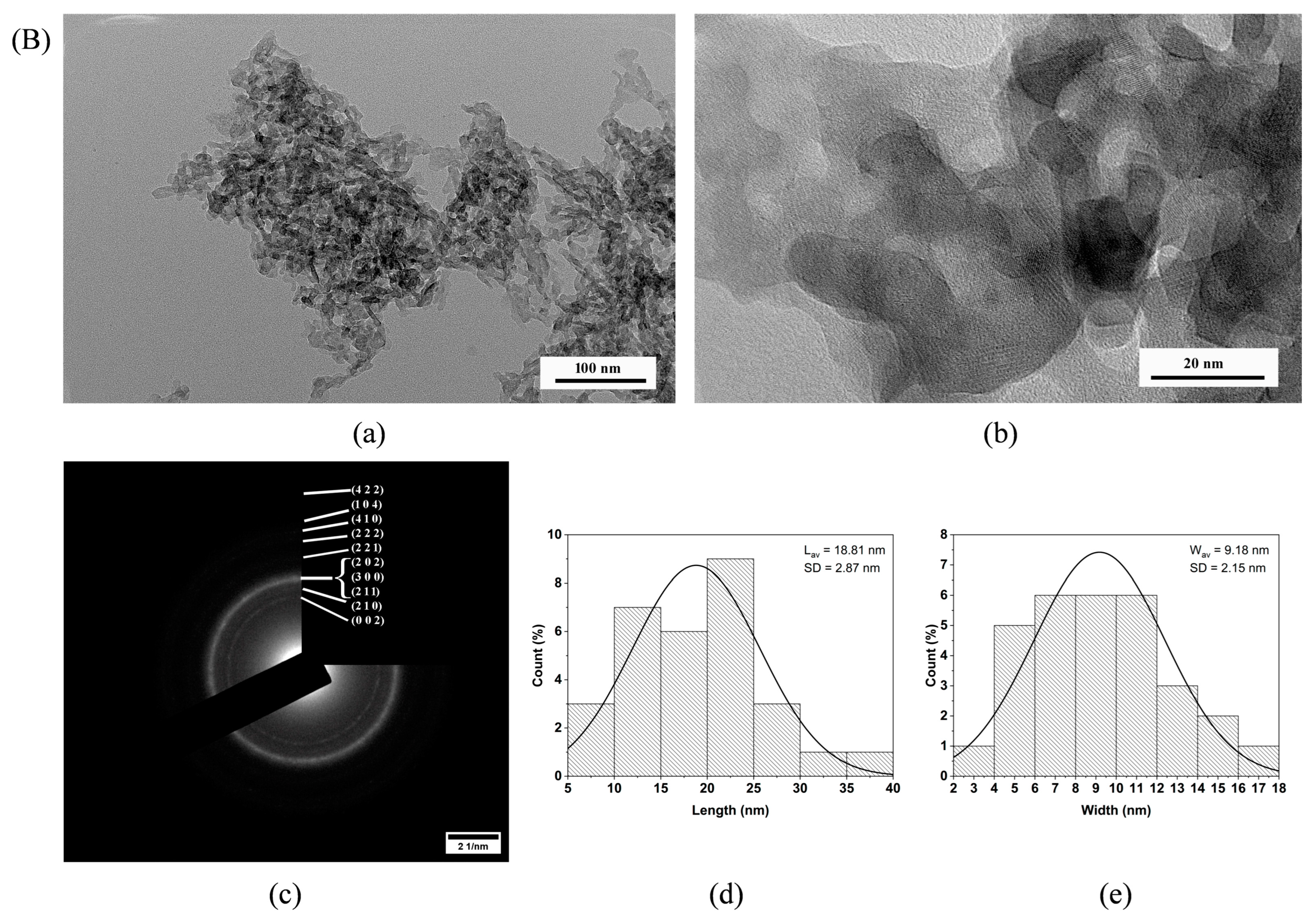
3.8. TEM Investigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radulescu, D.-E.; Neacsu, I.A.; Grumezescu, A.-M.; Andronescu, E. Novel Trends into the Development of Natural Hydroxyapatite-Based Polymeric Composites for Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszta, M.J.; Cheng, X.; Jee, S.S.; Kumar, R.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kaufman, M.J.; Douglas, E.P.; Gower, L.B. Bone structure and formation: A new perspective. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2007, 58, 77–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasuney, S. Green Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Controlled Morphologies and Surface Properties Toward Biomedical Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater 2020, 30, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, I.S.; Kolen’ko, Y.V.; Lebedev, O.I.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Gupta, H.S.; Guitián, F.; Yoshimura, M. An Effective Morphology Control of Hydroxyapatite Crystals via Hydrothermal Synthesis. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Onuma, K. Growth of Hydroxyapatite Crystals. In Crystal Growth Technology; Byrappa, K., Ohachi, T., Michaeli, W., Warlimont, H., Weber, E., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 525–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Eika, Y.; Ikada, Y. In situ hydroxyapatite crystallization for the formation of hydroxyapatite/polymer composites. J. Mater Sci. 1997, 32, 5533–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.S.; Karunakaran, G.; Girija, E.K.; Kolesnikov, E.; Van Minh, N.; Gorshenkov, M.V.; Kuznetsov, D. Size and morphology-controlled synthesis of mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanocrystals by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Ceram Int. 2018, 44, 11257–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenaghawon, A.N.; Anyalewechi, C.L.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Kusuma, H.S. Hydroxyapatite-based adsorbents: Applications in sequestering heavy metals and dyes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, I.L.; Chen, J.; Gedara, S.M.K.; Han, Y.; Wickramaratne, M.N. Applications of Nano Hydroxyapatite as Adsorbents: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yook, H.; Hwang, J.; Yeo, W.; Bang, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Han, J.W. Design Strategies for Hydroxyapatite-Based Materials to Enhance Their Catalytic Performance and Applicability. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2204938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, A.; Sodenaga, R.; Gangarajula, Y.; Taketoshi, A.; Murayama, T.; Honma, T.; Sakaguchi, N.; Shimada, T.; Takagi, S.; Haruta, M.; et al. Enhancement effect of strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) on the catalytic activity of substituted-hydroxyapatite supported Au clusters. J. Catal 2022, 410, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, X. Recent progress of rare earth doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: Luminescence properties, synthesis and biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2022, 148, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oni, O.P.; Hu, Y.; Tang, S.; Yan, H.; Zeng, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Yang, C.; Ran, J. Syntheses and applications of mesoporous hydroxyapatite: A review. Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7, 9–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, G.; Palmieri, M.C.; Montalbano, G.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Biomimetic and mesoporous nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue application: A short review. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safi, S.; Karimzadeh, F.; Labbaf, S. Mesoporous and hollow hydroxyapatite nanostructured particles as a drug delivery vehicle for the local release of ibuprofen. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, E.; Akshata, C.R. Dextrose, maltose and starch guide crystallization of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite: A comparative study for bone tissue engineering application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, N.T.; Quan, V.M.; Boonrungsiman, S.; Sukyai, P. Effectiveness of bio-dispersant in homogenizing hydroxyapatite for proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 611, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidsavar, M.; Khakbaz, M.; Mir Mohammad Sadeghi, G.; Moradi, M. Porous nanocomposite scaffolds prepared from gelatin and hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering: Direct mixing and biomimetic. J. Text. Polym. 2023, 11, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galotta, A.; Rubenis, K.; Locs, J.; Sglavo, V.M. Dissolution-precipitation synthesis and cold sintering of mussel shells-derived hydroxyapatite and hydroxyapatite/chitosan composites for bone tissue engineering. Open Ceram. 2023, 15, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Mondal, S.; Ray, S.; Singh, Y.P.; Maji, K. Hydroxyapatite-collagen nanoparticles reinforced polyanhydride based injectable paste for bone substitution: Effect of dopant addition in vitro. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2021, 32, 1312–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. A Mild and Efficient Biomimetic Synthesis of Rodlike Hydroxyapatite Particles with a High Aspect Ratio Using Polyvinylpyrrolidone As Capping Agent. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursamar, S.A.; Rabiee, M.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A.; Tahriri, M.; Karimi, M.; Azami, M. Influence of the value of the pH on the preparation of nano hydroxyapatite polyvinyl alcohol composites. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2009, 10, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Koczkur, K.M.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Polavarapu, L.; Skrabalak, S.E. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in nanoparticle synthesis. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 17883–17905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, R.; Tabassum, S.; Gilani, M.A.; Ahmed, E.; Sharif, A.; Manzoor, F.; Shah, A.T.; Asif, A.; Sharif, F.; Iqbal, F.; et al. In situ synthesis of mesoporous polyvinyl alcohol/hydroxyapatite composites for better biomedical coating adhesion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Gafurov, M.R.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Fomin, A.S.; Antonova, O.S.; Khairutdinova, D.R.; Pyataev, A.V.; Makshakova, O.N.; Konovalov, A.A.; Leonov, A.V.; et al. Mesoporous iron(Iii)-doped hydroxyapatite nanopowders obtained via iron oxalate. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gol’dberg, M.A.; Smirnov, V.V.; Ievlev, V.M.; Barinov, S.M.; Kutsev, S.V.; Shibaeva, T.V.; Shvorneva, L.I. Influence of ripening time on the properties of hydroxyapatite-calcium carbonate powders. Inorg. Mater. 2012, 48, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.Q.; João, C.F.C.; Silva, J.C.; Borges, J.P. Electrospun hydroxyapatite fibers from a simple sol–gel system. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanael, A.J.; Seo, Y.H.; Oh, T.H. PVP assisted synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanorods with tunable aspect ratio and bioactivity. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 621785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridi-Majidi, R.; Nezafati, N.; Pazouki, M.; Hesaraki, S. The effect of synthesis parameters on morphology and diameter of electrospun hydroxyapatite nanofibers. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 53, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 10779-78; Spirt polivinilovyy. Tekhnicheskie usloviya (Polyvinyl alcohol. Specifications). USSR State Committee for Standards: Moscow, Russia, 1987.
- Klinger, M. More features, more tools, more CrysTBox. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017, 50, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, Q.A.; Baloch, M.K.; Schwarz, S.; Petzold, G. Impact of Various Parameters Over the Adsorption of Polyvinylpyrrolidone onto Kaolin. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, L.; Oktar, F.N.; Stan, G.E.; Popescu-Pelin, G.; Serban, N.; Luculescu, C.; Mihailescu, I.N. Novel doped hydroxyapatite thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewumi-Musa, R.T.; Bello, M.O.; Abdus-Salam, N.; Olabode, S.O. Preparation and Characterization of Hydroxyapatite by Chemical Treatment. Fudma J. Sci. 2023, 7, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriakose, T.A.; Kalkura, S.N.; Palanichamy, M.; Arivuoli, D.; Dierks, K.; Bocelli, G.; Betzel, C. Synthesis of stoichiometric nano crystalline hydroxyapatite by ethanol-based sol–gel technique at low temperature. J. Cryst. Growth. 2004, 263, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Orthophosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fleet, M.E.; Liu, X.; King, P.L. Accommodation of the carbonate ion in apatite: An FTIR and X-ray structure study of crystals synthesized at 2–4 GPa. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.M.; Elliott, J.C.; Dowker, S.E.P.; Smith, R.I. Rietveld structure refinement of precipitated carbonate apatite using neutron diffraction data. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, A.; Cacciotti, I.; Lombardi, M.; Montanaro, L.; Gusmano, G. Thermal stability and sintering behaviour of hydroxyapatite nanopowders. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 88, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouet, C. Apatite Formation: Why It May Not Work as Planned, and How to Conclusively Identify Apatite Compounds. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 490946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosanov, I.Y.; Matvienko, A.A. Study of PVA thermal destruction by means of IR and Raman spectroscopy. Phys. Solid State 2010, 52, 2203–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murzakhanov, F.F.; Grishin, P.O.; Goldberg, M.A.; Yavkin, B.V.; Mamin, G.V.; Orlinskii, S.B.; Fedotov, A.Y.; Petrakova, N.V.; Antuzevics, A.; Gafurov, M.R.; et al. Radiation-induced stable radicals in calcium phosphates: Results of multifrequency epr, ednmr, eseem, and endor studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, F.J.; Cychosz, K.A.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Micro/Mesoporous Materials by Physisorption: Concepts and Case Studies. Acc. Mater. Surf. Res. 2018, 3, 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaría, E.; Maestro, A.; Porras, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; González, C. Preparation of structured meso–macroporous silica materials: Influence of composition variables on material characteristics. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamieniak, J.; Doyle, A.M.; Kelly, P.J.; Banks, C.E. Novel synthesis of mesoporous hydroxyapatite using carbon nanorods as a hard-template. Ceram Int. 2017, 43, 5412–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.-H.; Ling, Y.P.; Pung, S.-Y.; Yeoh, F.-Y. Mesoporous hydroxyapatite derived from surfactant-templating system for p-Cresol adsorption: Physicochemical properties, formation process and adsorption performance. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, N.; Imae, T. Fabrication and Characterization of Dendrimer-Functionalized Mesoporous Hydroxyapatite. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14018–14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, N.F.; Othman, R.; Yeoh, F.Y. The Effect of Surfactant Extraction Method on Pore Characteristics of Mesoporous Carbonated Hydroxyapatite. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 858, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Dai, H.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous hydroxyapatite powder by microemulsion technique. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 3158–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, R.O.; Bulut, N.; Kaygili, O. Hydroxyapatite biomaterials: A comprehensive review of their properties, structures, medical applications, and fabrication methods. J. Chem. Rev. 2024, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Gao, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J. Environmental pH-controlled loading and release of protein on mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-J.; Chen, J.-H.; Fan, T.-T.; Zhou, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-J. Effect of nanoparticle hydroxyapatite on the immobilization of Cu and Zn in polluted soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R. Physicochemical characterization of hydroxyapatite and its application towards removal of nitrate from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjubaashini, N.; Radha, G.; Balakumar, S. A comprehensive review on functionalized Hydroxyapatite nanostructures based gas sensors for environmental pollutant monitoring. J. Mater. NanoSci. 2022, 9, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadipour, N.; Paul, S.; Katryniok, B.; Dumeignil, F. Calcium hydroxyapatite: A highly stable and selective solid catalyst for glycerol polymerization. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Akopyan, A.V.; Gafurov, M.R.; Makshakova, O.N.; Donskaya, N.O.; Fomin, A.S.; Polikarpova, P.P.; Anisimov, A.V.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Leonov, A.V.; et al. Iron-Doped Mesoporous Powders of Hydroxyapatite as Molybdenum-Impregnated Catalysts for Deep Oxidative Desulfurization of Model Fuel: Synthesis and Experimental and Theoretical Studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 11604–11619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Ling, E.G.Y.; Gwie, C.G.; White, T.J.; Borgna, A. Structure and Surface Reactivity of WO42–, SO42–, PO43– Modified Ca-Hydroxyapatite Catalysts and Their Activity in Ethanol Conversion. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 18736–18745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amedlous, A.; Amadine, O.; Essamlali, Y.; Maati, H.; Semlal, N.; Zahouily, M. Copper Loaded Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles as eco-friendly Fenton-like catalyst to Effectively Remove Organic Dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yuan, X.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Impact of pore structure on hydroxyapatite supported nickel catalysts (Ni/HAP) for dry reforming of methane. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 202, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Mori, K.; Mizugaki, T.; Ebitani, K.; Kaneda, K. Creation of a Monomeric Ru Species on the Surface of Hydroxyapatite as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 7144–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-Y.; Su, B.-L. Insights into hierarchically meso–macroporous structured materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, A.; Abid, Z.; Said, B.; Didi, Y.; Szymanska, K.; Jarzębski, A.; Tancret, F.; Hamaizi, H.; Bengueddach, A.; Di Renzo, F.; et al. Synthesis and textural characterization of mesoporous and meso-/macroporous silica monoliths obtained by spinodal decomposition. Inorganics 2016, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenshin, A.S.; Seredin, P.V.; Agapov, B.L.; Minakov, D.A.; Kashkarov, V.M. Preparation and degradation of the optical properties of nano-, meso-, and macroporous silicon. Mater. Sci. Semicond Process. 2015, 30, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Arandiyan, H.; Scott, J.; Bagheri, A.; Dai, H.; Amal, R. Recent advances in ordered meso/macroporous metal oxides for heterogeneous catalysis: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2017, 5, 8825–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.Z.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Azioune, A.; Pireaux, J.J.; Su, B.L. Tailoring the porous hierarchy of titanium phosphates. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3886–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.Z.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Su, B.L. Thermally stable macroporous zirconium phosphates with supermicroporous walls: A self-formation phenomenon of hierarchy. Chem. Commun. 2004, 2730–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, A.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Colilla, M.; de Laorden, C.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Preparation of 3-D scaffolds in the SiO2–P2O5 system with tailored hierarchical meso-macroporosity. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balas, F.; Arcos, D.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Textural properties of SiO2 · CaO · P2O5 glasses prepared by the sol-gel method. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.A.; Antonova, O.S.; Donskaya, N.O.; Fomin, A.S.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Gafurov, M.R.; Konovalov, A.A.; Kotyakov, A.A.; Leonov, A.V.; Smirnov, S.V.; et al. Effects of various ripening media on the mesoporous structure and morphology of hydroxyapatite powders. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.P.; Abdul-Wahab, M.F.; Jaafar, J.; Chan, G.F.; Rashid, N.A.A. Effect of pH and biological media on polyvinylpyrrolidone-capped silver nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1756, 080002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, S.; Sreenivasan, K. Synthesis and Characterization of a Cytotoxic Cationic Polyvinylpyrrolidone–Curcumin Conjugate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Houwen, J.A.M.; Cressey, G.; Cressey, B.A.; Valsami-Jones, E. The effect of organic ligands on the crystallinity of calcium phosphate. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 249, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, W.; Gibson, I.R. Novel synthesis and characterization of an AB-type carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gol’dberg, M.A.; Smirnov, V.V.; Kutsev, S.V.; Shibaeva, T.V.; Shvorneva, L.I.; Sergeeva, N.S.; Sviridova, I.K.; Barinov, S.M. Hydroxyapatite-calcium carbonate ceramic composite materials. Inorg. Mater. 2010, 46, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, C.C.; Ismail, H.; Noor, A.F.M. Effect of Synthesis Technique and Carbonate Content on the Crystallinity and Morphology of Carbonated Hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunks, W.J.; Ozin, G.A. Single-Source Precursors For Synthesizing Bifunctional Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhilal, O.; Winarsih, S.; Hidayat, S.; Sumiarsa, D.; Risdiana, R. High Sulfur Content of Mesoporous Activated Carbon Composite Derived from Water Hyacinth. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanakumar, E.S.; John, J.C.; Raja, T.; Gopinath, C.S. Functional and Disordered Meso-Macroporous γ-Al2−xMxO3±y (M = Cu and/or Ce). J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 2682–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckel, D.; Kübel, C.; Hormann, K.; Höltzel, A.; Smarsly, B.M.; Tallarek, U. Morphological Analysis of Disordered Macroporous–Mesoporous Solids Based on Physical Reconstruction by Nanoscale Tomography. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9022–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Medium | Concentration, % | Ripening Time, Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O-0 | H2O * | - | 0 |
| H2O-7 | H2O * | - | 7 |
| PVA2.5-0 | PVA | 2.5 | 0 |
| PVA2.5-7 | PVA | 2.5 | 7 |
| PVA5-0 | PVA | 5 | 0 |
| PVA5-7 | PVA | 5 | 7 |
| PVA10-0 | PVA | 10 | 0 |
| PVA10-7 | PVA | 10 | 7 |
| PVP2.5-0 | PVP | 2.5 | 0 |
| PVP2.5-7 | PVP | 2.5 | 7 |
| PVP5-0 | PVP | 5 | 0 |
| PVP5-7 | PVP | 5 | 7 |
| PVP10-0 | PVP | 10 | 0 |
| PVP10-7 | PVP | 10 | 7 |
| Mother Liquor | Concentration, % | Viscosity, mPa·s |
|---|---|---|
| H2O | - | 1.0 |
| PVA | 10 | 1.5 |
| PVP | 10 | 2.5 |
| Sample | pH Values | Agglomerate Size, μm * | Zeta potential, mV ** | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Days | 7 Days | 0 Days | 7 Days | 0 Days | 7 Days | |
| H2O | 10.3 ± 0.02 | 7.5 ± 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.04 | −1.7 | −2.4 |
| PVA10 | 10.7 ± 0.03 | 9.2 ± 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.10 | +0.7 | +0.9 |
| PVP10 | 10.0 ± 0.02 | 8.8 ± 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.06 | −4.4 | +1.8 |
| Sample | CCa1 *, mmol/L | CP1 *, mmol/L | CCa2 **, mmol/L | CP2 **, mmol/L | Ca/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O-0 | 31.00 | 0.01 (1) | 316.00 | 207.99 | 1.52 |
| H2O-7 | 0.56 | 0.01 (5) | 346.44 | 207.98 | 1.67 |
| PVA10-0 | 12.43 | 0.01 (8) | 334.57 | 207.98 | 1.61 |
| PVA10-7 | 0.64 | 0.17 (6) | 346.36 | 207.82 | 1.67 |
| PVP10-0 | 9.72 | 0.08 (6) | 337.28 | 207.91 | 1.62 |
| PVP10-7 | 1.07 | 0.27 (7) | 345.93 | 207.72 | 1.67 |
| Sample | Ca Concentration * | P Concentration * | Ca/P Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | wt.% | ||
| H2O-0 | 36.2 | 18.6 | 1.51 |
| H2O-7 | 36.8 | 17.7 | 1.61 |
| PVA10-0 | 36.3 | 17.7 | 1.59 |
| PVA10-7 | 37.9 | 17.2 | 1.71 |
| PVP10-0 | 36.5 | 17.8 | 1.59 |
| PVP10-7 | 38.4 | 16.3 | 1.83 |
| Sample | H2O-0/ H2O-7 | PVA2.5-0/ PVA2.5-7 | PVA5-0/ PVA5-7 | PVA10-0/ PVA10-7 | PVP2.5-0/ PVP2.5-7 | PVP5-0/ PVP5-7 | PVP10-0/ PVP10-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D, nm | 11 (2) | 12 (2) | 11 (9) | 11 (7) | 13 (0) | 13 (4) | 7 (0) |
| 12 (8) | 14 (4) | 12 (5) | 14 (4) | 15 (1) | 14 (1) | 12 (7) |
| Sample | SSA, m2/g | DSSA, nm | Total Pore Volume, cm3/g | Pore Size, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O-0 | 101.3 | 20 | 0.66 | 23 |
| H2O-7 | 112.2 | 18 | 0.62 | 19 |
| PVA2.5-0 | 86.9 | 23 | 0.42 | 18 |
| PVA2.5-7 | 107.9 | 19 | 0.48 | 16 |
| PVA5-0 | 73.7 | 27 | 0.27 | 12 |
| PVA5-7 | 82.5 | 24 | 0.29 | 12 |
| PVA10-0 | 81.4 | 25 | 0.40 | 16 |
| PVA10-7 | 113.4 | 18 | 0.47 | 13 |
| PVP2.5-0 | 88.5 | 23 | 0.37 | 15 |
| PVP2.5-7 | 139.3 | 14 | 0.52 | 12 |
| PVP5-0 | 94.8 | 21 | 0.42 | 16 |
| PVP5-7 | 139.1 | 14 | 0.51 | 12 |
| PVP10-0 | 158.0 | 13 | 0.37 | 8 |
| PVP10-7 | 195.8 | 10 | 0.71 | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonova, O.S.; Goldberg, M.A.; Fomin, A.S.; Kucheryaev, K.A.; Konovalov, A.A.; Sadovnikova, M.A.; Murzakhanov, F.F.; Sitnikov, A.I.; Leonov, A.V.; Andreeva, N.A.; et al. Meso-Macroporous Hydroxyapatite Powders Synthesized in Polyvinyl Alcohol or Polyvinylpyrrolidone Media. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161338
Antonova OS, Goldberg MA, Fomin AS, Kucheryaev KA, Konovalov AA, Sadovnikova MA, Murzakhanov FF, Sitnikov AI, Leonov AV, Andreeva NA, et al. Meso-Macroporous Hydroxyapatite Powders Synthesized in Polyvinyl Alcohol or Polyvinylpyrrolidone Media. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(16):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161338
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonova, Olga S., Margarita A. Goldberg, Alexander S. Fomin, Kirill A. Kucheryaev, Anatoliy A. Konovalov, Margarita A. Sadovnikova, Fadis F. Murzakhanov, Aleksey I. Sitnikov, Alexander V. Leonov, Nadezhda A. Andreeva, and et al. 2024. "Meso-Macroporous Hydroxyapatite Powders Synthesized in Polyvinyl Alcohol or Polyvinylpyrrolidone Media" Nanomaterials 14, no. 16: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161338
APA StyleAntonova, O. S., Goldberg, M. A., Fomin, A. S., Kucheryaev, K. A., Konovalov, A. A., Sadovnikova, M. A., Murzakhanov, F. F., Sitnikov, A. I., Leonov, A. V., Andreeva, N. A., Khayrutdinova, D. R., Gafurov, M. R., Barinov, S. M., & Komlev, V. S. (2024). Meso-Macroporous Hydroxyapatite Powders Synthesized in Polyvinyl Alcohol or Polyvinylpyrrolidone Media. Nanomaterials, 14(16), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161338








