A Novel Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles via Recycling of Titanium Slag by Pyrite Reduction Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Thermodynamic Modelling
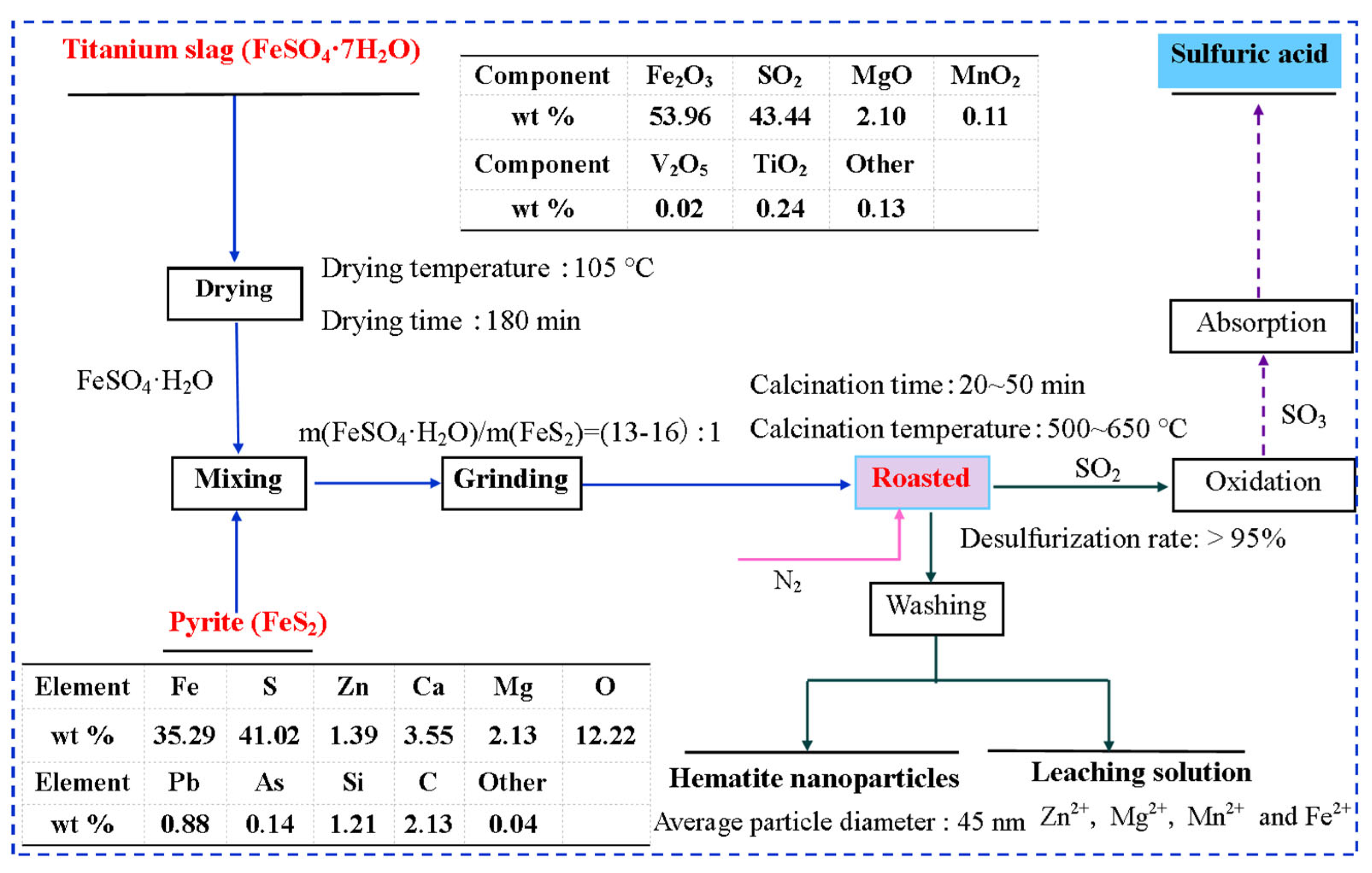
2.3. Fabrication of HNPs
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermodynamic Analysis
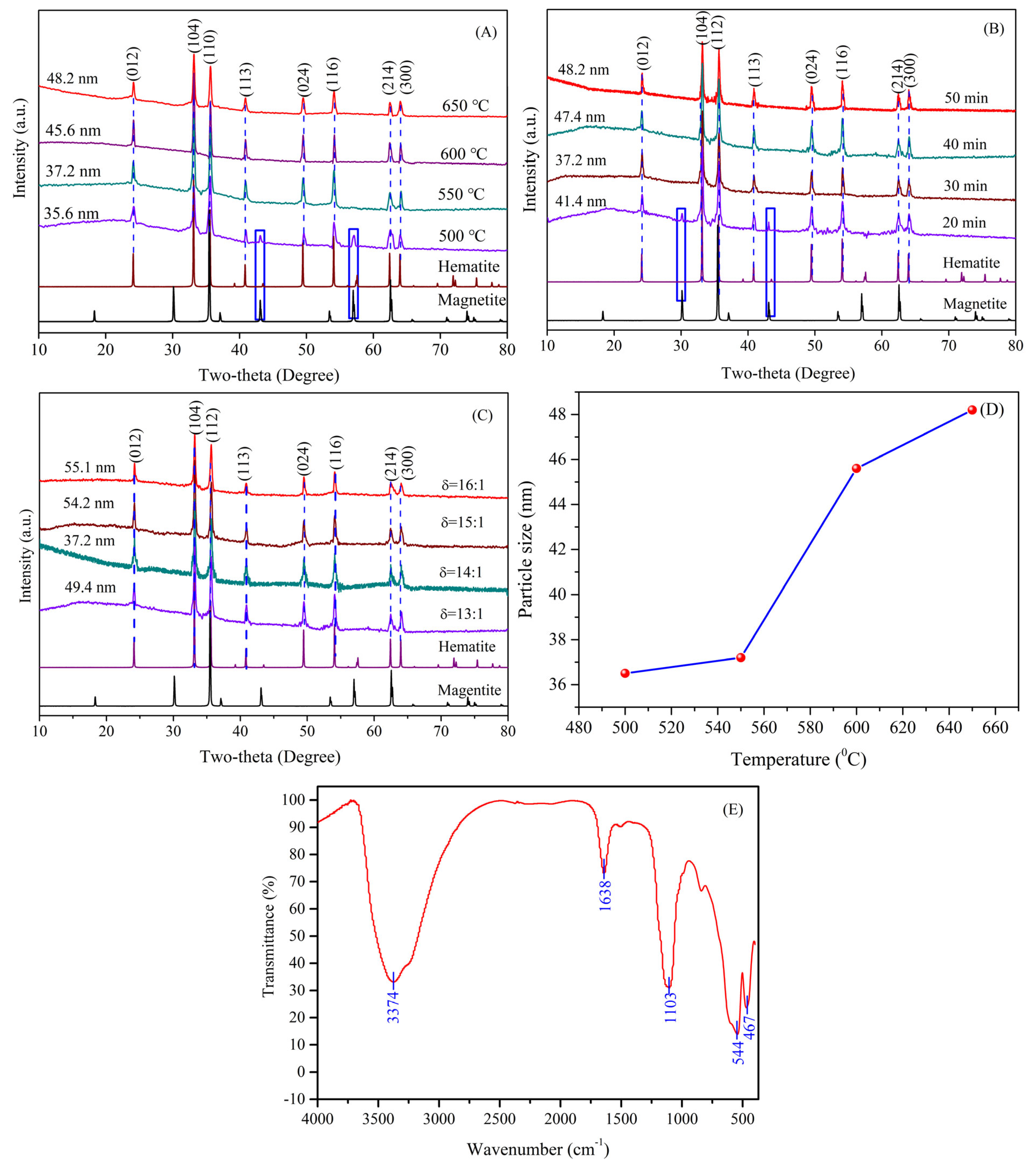
3.2. Reaction Process Analysis
3.3. Effect of Synthesis Conditions
3.4. Surface Property
3.5. Micrograph and Element Composites
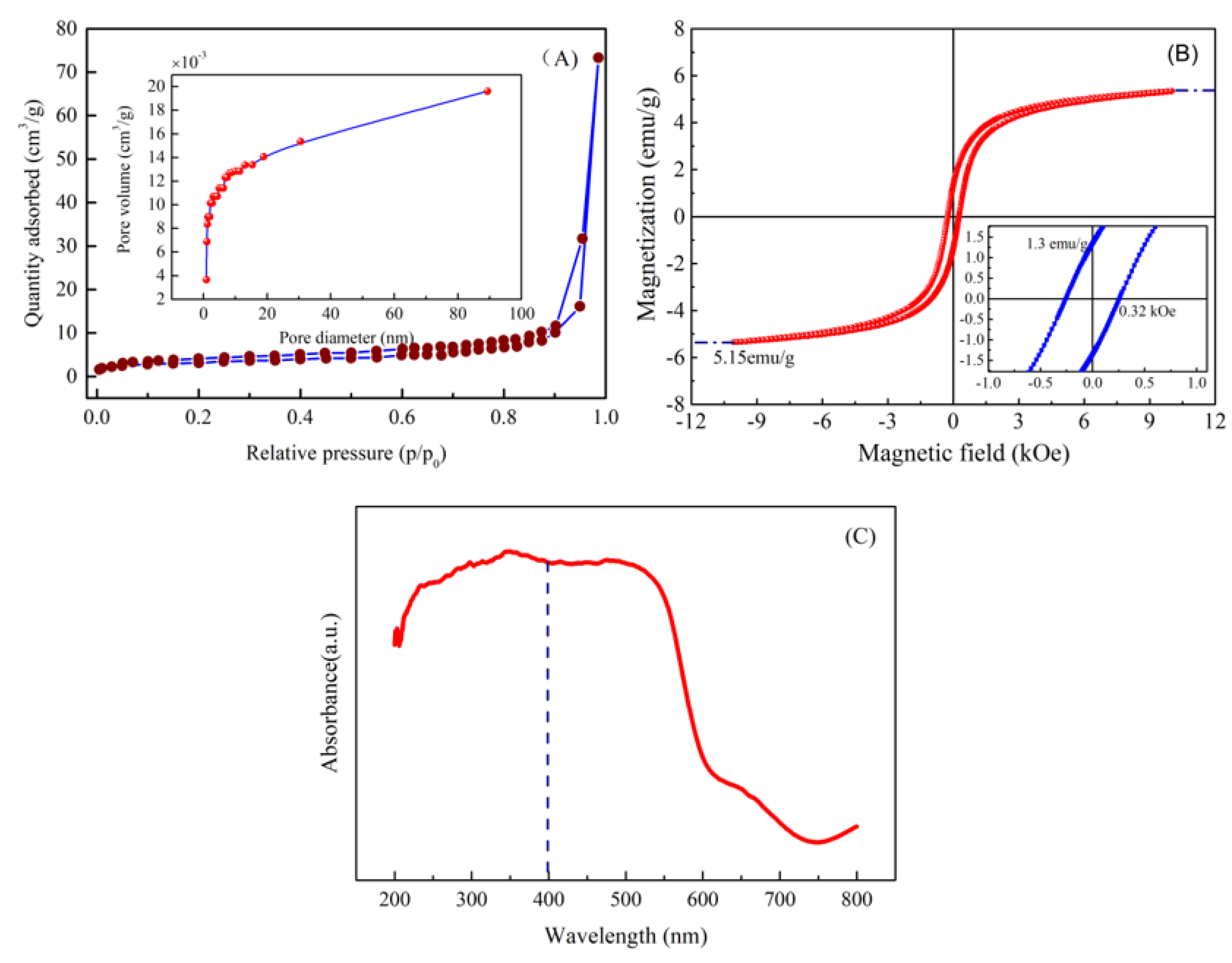
3.6. Surface Area and Pore Diameter
3.7. Magnetism and Absorbance of Material
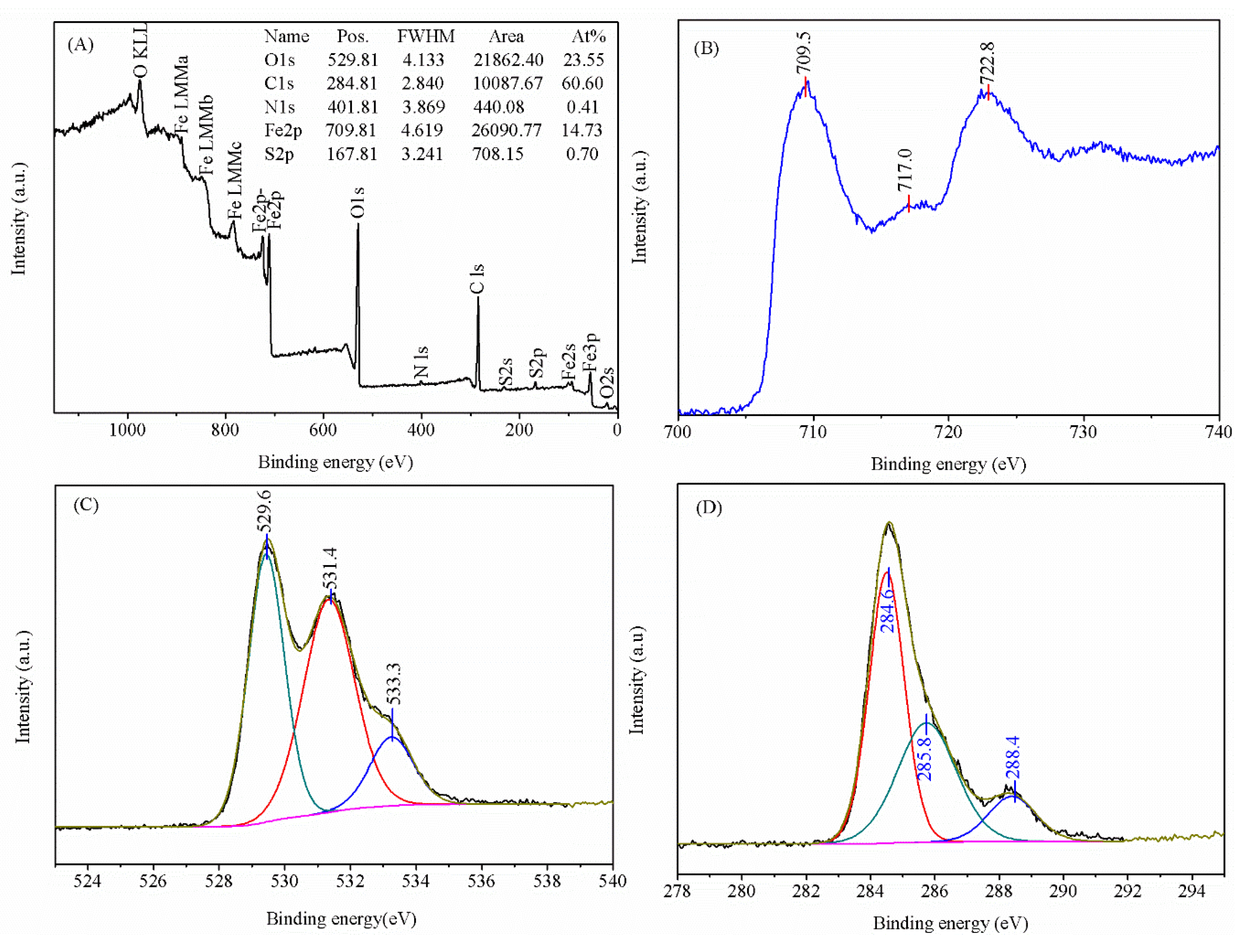
3.8. XPS Analysis and Chemical State
3.9. Recovery of Metal Ions in Washing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sukidpaneenid, S.; Chawengkijwanich, C.; Pokhum, C.; Isobe, T.; Opaprakasit, P.; Sreearunothai, P. Multi-function adsorbent-photocatalyst MXene-TiO2 composites for removal of enrofloxacin antibiotic from water. J. Environ. Sci.-China 2023, 124, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghani, S.M.; Ghazali, M.J.; Muchtar, A.; Daud, A.R. Mechanical properties of plasma sprayed nanostructured TiO2 coatings on mild steel. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 7049–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wu, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, X. Low temperature synthesis and characterization of rutile TiO2-coated mica-titania pigments. Dye. Pigment. 2012, 95, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, R.P.; de Oliveira, D.M.; Da Silva, L.D.M.; Giménez, J.; Esplugas, S.; Oliveira, S.C.; Dantas, R.F.; Sans, C.; Machulek, A. Evaluation of the main active species involved in the TiO2 photocatalytic degradation of ametryn herbicide and its by-products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C. A novel preparation of high purity TiO2 from industrial low concentration TiOSO4 solution via short sulfate process. Mat. Sci. Semicon Proc. 2022, 137, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Jin, H. Report on China Titanium Industry Progress in 2023. Titan. Ind. Prog. 2024, 41, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Ren, C.; Tang, J.; Gao, L.; Omran, M.; Guo, C. The effect of mechanical activation duration on the structure and physical properties of titanium slag. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Ma, G.; Chen, Q. Preparation of Iron Phosphate Battery Materials from Industrial Ferrous Sulfate Waste by Liquid Phase Method. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2023, 234, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhou, K.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. Recovery of iron from titanium white waste for the preparation of LiFePO4 battery. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanari, N.; Filippova, I.; Diot, F.; Mochón, J.; Ruiz-Bustinza, I.; Allain, E.; Yvon, J. Utilization of a waste from titanium oxide industry for the synthesis of sodium ferrate by gas–solid reactions. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 575, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lei, Z.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q. Synthesizing slow-release fertilizers via mechanochemical processing for potentially recycling the waste ferrous sulfate from titanium dioxide production. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufus, A.; Sreeju, N.; Vilas, V.; Philip, D. Biosynthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanostructures: Size effects on applications in thermal conductivity, catalysis, and antibacterial activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Yurddaskal, M.; Dikici, T.; Sarıoğlu, C. Fabrication and characterization of novel iodine doped hollow and mesoporous hematite (Fe2O3) particles derived from sol-gel method and their photocatalytic performances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 345, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, N.; Ma, R. Advanced hematite nanomaterials for newly emerging applications. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 2776–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Qin, M.; Jia, B.; Gu, Y.; Chen, P.; Volinsky, A.A.; Qu, X. One pot solution combustion synthesis of highly mesoporous hematite for photocatalysis. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Shan, C.; Liang, J.; Tong, M. Efficient adsorption of Selenium(IV) from water by hematite modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjad, A.; Hussain, S.; Jaffari, G.H.; Hanif, S.; Qureshi, M.N.; Zia, M. Fabrication of Hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles under different spectral lights transforms physio chemical, biological, and nanozymatic properties. Nano Trends 2023, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.Q.; Gao, D.; Sun, Y.X. Uniform hematite α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Morphology, size-controlled hydrothermal synthesis and formation mechanism. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaashani, R.; Radiman, S.; Tabet, N.; Daud, A. Rapid synthesis and optical properties of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanostructures using a simple thermal decomposition method. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 550, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utari; Maulidina, H.; Arilasita, R.; Widiyandari, H.; Su, H.; Purnama, B. Citric acid concentration tune of structural and magnetic properties in hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized by sol−gel method. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 10, 36101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Peng, J.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, S. Preparation of microsized hematite powder from ferrous sulfate via microwave calcination. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2017, 24, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un Nisa, M.; Gouadria, S.; Houda, S.; Jabbour, K.; Manzoor, S.; Aman, S.; Najam-Ul-Haq, M.; Naeem Ashiq, M. Coral like gadolinium doped hematite nanostructure as stable and robust electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution water splitting. Fuel 2023, 338, 127313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Preethi, J.B.; Bora, D.K. The anthocyanin coated hematite (α-Fe2O3) photoanode shows highest photoelectrochemical current density among a library of light-harvesting pigments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 438, 114554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, R.; Saghatforoush, L.A.; Sanati, S. Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanodiscs and Mn3O4 nanoparticles with 1,10-phenanthroline. Superlattices Microstruct. 2012, 52, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darezereshki, E.; Bakhtiari, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Behrad Vakylabad, A.; Ranjbar, M. Direct thermal decomposition synthesis and characterization of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. Mat. Sci. Semicon Proc. 2012, 15, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Li, P.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y. Bacteria-assisted preparation of nano α-Fe2O3 red pigment powders from waste ferrous sulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.; Bhuyan, B.; Purkayastha, D.D.; Dhar, S.S. Facile synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles and their catalytic activity in oxidation of benzyl alcohols with periodic acid. Catal. Commun. 2015, 69, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Patnaik, Y.; Brijesh, P.; Prabhu, D.; Quadras, M.; Pai, S.; Narasimhan, M.K.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Selvaraj, R. Superparamagnetic hematite spheroids synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadic, M.; Panjan, M.; Tadic, B.V.; Kralj, S.; Lazovic, J. Magnetic properties of mesoporous hematite/alumina nanocomposite and evaluation for biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 10004–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, P.; Rao, M.; Murugesan, G.; Narasimhan, M.K.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Vinayagam, R.; Lan Chi, N.T.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Selvaraj, R. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of the green-synthesized hematite nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Mani, R.J.; Parvathiraja, C.; Sheik, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Islam, M.A.; Lai, W.C. Photocatalytic Dye Degradation and Bio-Insights of Honey-Produced α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Water 2022, 14, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmad, B.; Leonard, K.; Shariful Islam, M.; Kurawaki, J.; Muruganandham, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Kuroda, Y. Green synthesis of mesoporous hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, S.J.; Parasuraman, K.; Anburaj, D.B.; Jothibas, M.; Arunkumar, B. The impacts of Mn ion incorporation on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of hematite NPs. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, E.; Muñoz-Meneses, R.A.; Marín, L.; Mora, M.; Tabares, J.A.; Manotas-Albor, M.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Diosa, J.E.; Mosquera-Vargas, E. Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of submicron hematite (α-Fe2O3) particles synthesized from industrial steel waste. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 288, 116170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.X.; Ma, S.Y.; Tie, Z.Z.; Jiang, X.H.; Li, W.Q.; Luo, J.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, T.T. Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse porous cube, cake and spheroid-like α-Fe2O3 particles and their high gas-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, D.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Meng, Y.; Lv, B. Crystal facet-dependent reduction behavior of α-Fe2O3 in hydrogen atmosphere. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 638, 158056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Meng, D.; Qin, X.; Diao, G. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Hematite Nanoparticles and Their Electrochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16276–16285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.D.; Pathan, H.M.; Min, S.; Jung, K.; Joo, O.S. FT-IR, XPS and PEC characterization of spray deposited hematite thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiphaneendra, B.; Saxena, T.; Singh, S.A.; Madras, G.; Srivastava, C. Synergistic effect of co-existence of hematite (α-Fe2O3) and magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles on graphene sheet for dye adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Minakshi, M.; Ralph, D.E.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Guo, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of cubic α-Fe2O3 microparticles using glycine: Surface characterization, reaction mechanism and electrochemical activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 9821–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Zeng, M. Separation of Co and Mn from acetic acid leaching solution of spent lithium-ion battery by Cyanex272. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.Y.; Chi, Y.; Ma, X.L. Adsorption of Zn2+ in wastewater by vinylamine modified weathered coal. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 266, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadian, M.; Gilani, H.G. Adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ by engineered biochar: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption properties. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2023, 42, e14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshadlou, S.; Mobasherpour, I.; Majidian, H.; Salahi, E.; Shirani, B.F.; Mei, C.T.; Ebrahimi, M. Adsorption system for Mg2+ removal from aqueous solutions using bentonite/gamma-alumina nanocomposite. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2020, 568, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadari, S.; Rahimi, M.; Zinadini, S. Novel antibacterial and antifouling PES nanofiltration membrane incorporated with green synthesized nickel-bentonite nanoparticles for heavy metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolainen, S.; Wesselborg, T.; Kaukinen, A.; Sainio, T. Removal of iron, aluminium, manganese and copper from leach solutions of lithium-ion battery waste using ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 202, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, G.; Deng, Y.; Yang, X. A Novel Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles via Recycling of Titanium Slag by Pyrite Reduction Technology. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161330
Ren G, Deng Y, Yang X. A Novel Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles via Recycling of Titanium Slag by Pyrite Reduction Technology. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(16):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161330
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Genkuan, Yinwen Deng, and Xiushan Yang. 2024. "A Novel Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles via Recycling of Titanium Slag by Pyrite Reduction Technology" Nanomaterials 14, no. 16: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161330
APA StyleRen, G., Deng, Y., & Yang, X. (2024). A Novel Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles via Recycling of Titanium Slag by Pyrite Reduction Technology. Nanomaterials, 14(16), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14161330





