Single Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Migration Tracking into Glioblastoma Using Photoconvertible Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Materials for Synthesis
2.1.2. Materials for In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
2.2. Synthesis of Photoconvertible Vesicles
2.3. Characterization of Photoconvertible Vesicles
2.4. Photoconversion and Imaging of Vesicles Using a Confocal Microscope
2.5. Cell Experiments
2.5.1. Isolation of mMSCs
2.5.2. Cultivation of mMSCs and EPNT-5 Cells
2.5.3. Viability Investigation on mMSCs (MTT Test)
2.5.4. Influence of Vesicle Amount on Internalization Efficiency and mMSC Proliferation
2.5.5. Influence of Vesicles on mMSC Movement (Scratch Test)
2.5.6. mMSC Tracking into the EPNT-5 2D and 3D Colonies
2.6. Animal Experiments
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyelectrolyte Fluorescent Vesicles
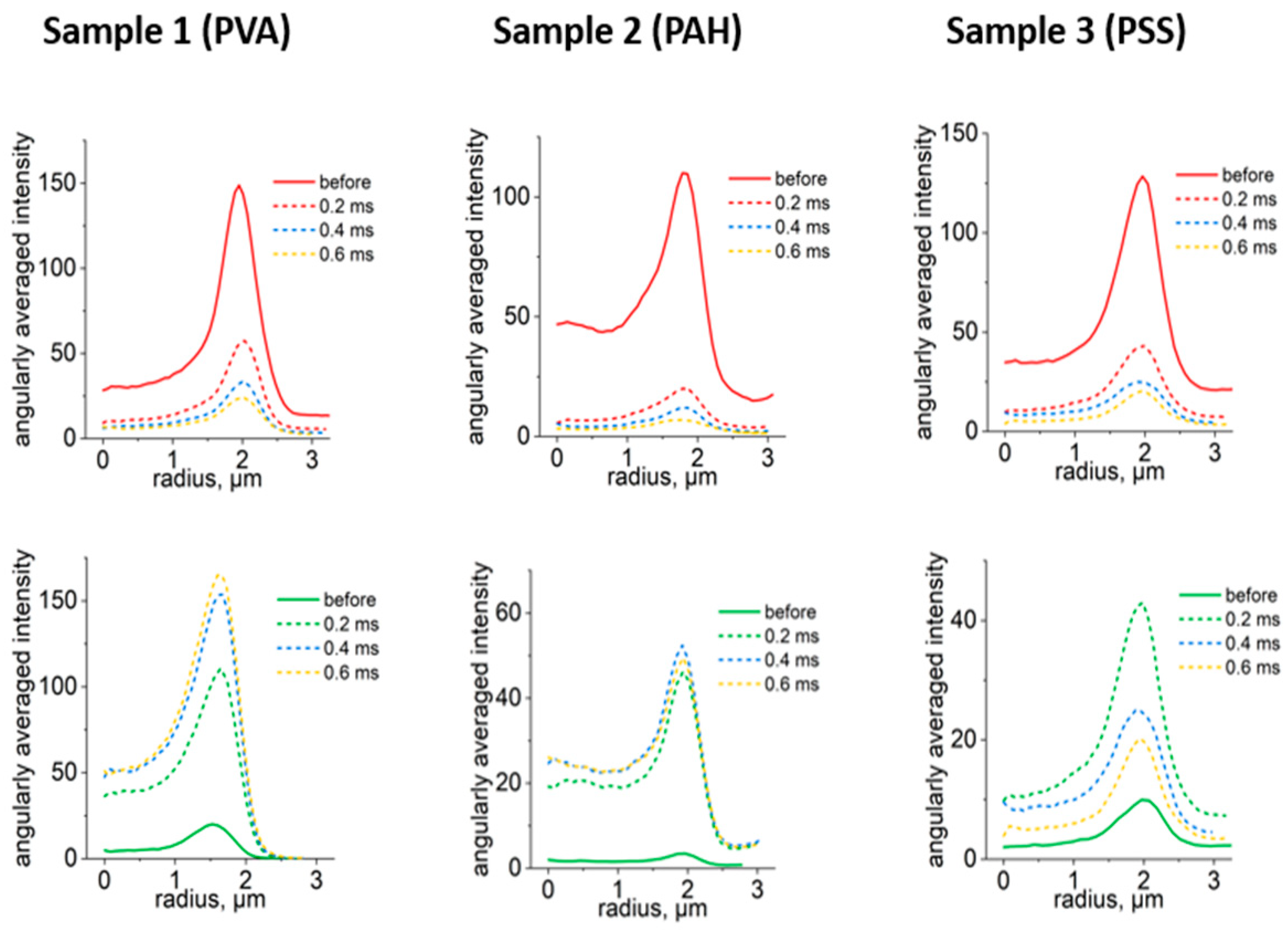
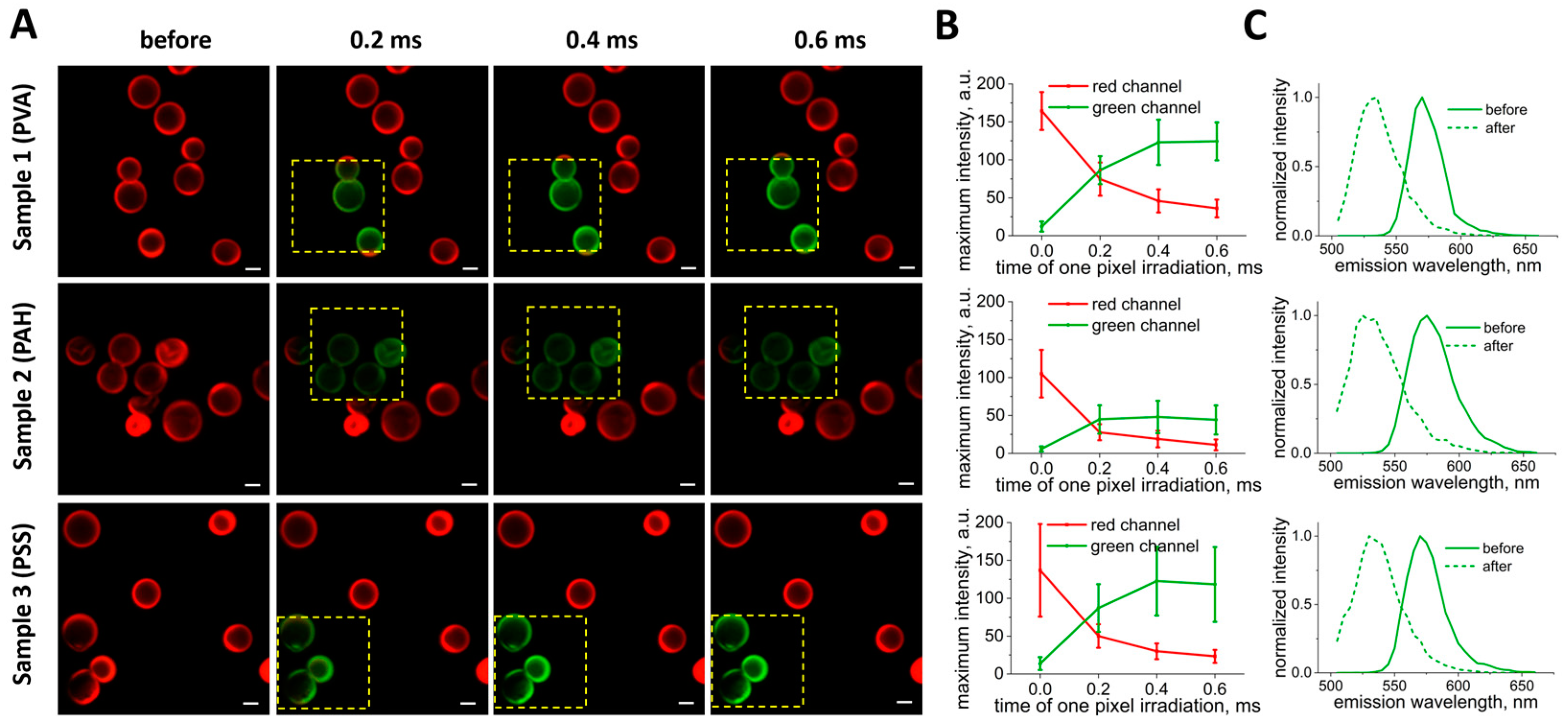
3.2. Selection of Optimal Photoconversion Parameters Using Confocal Microscope
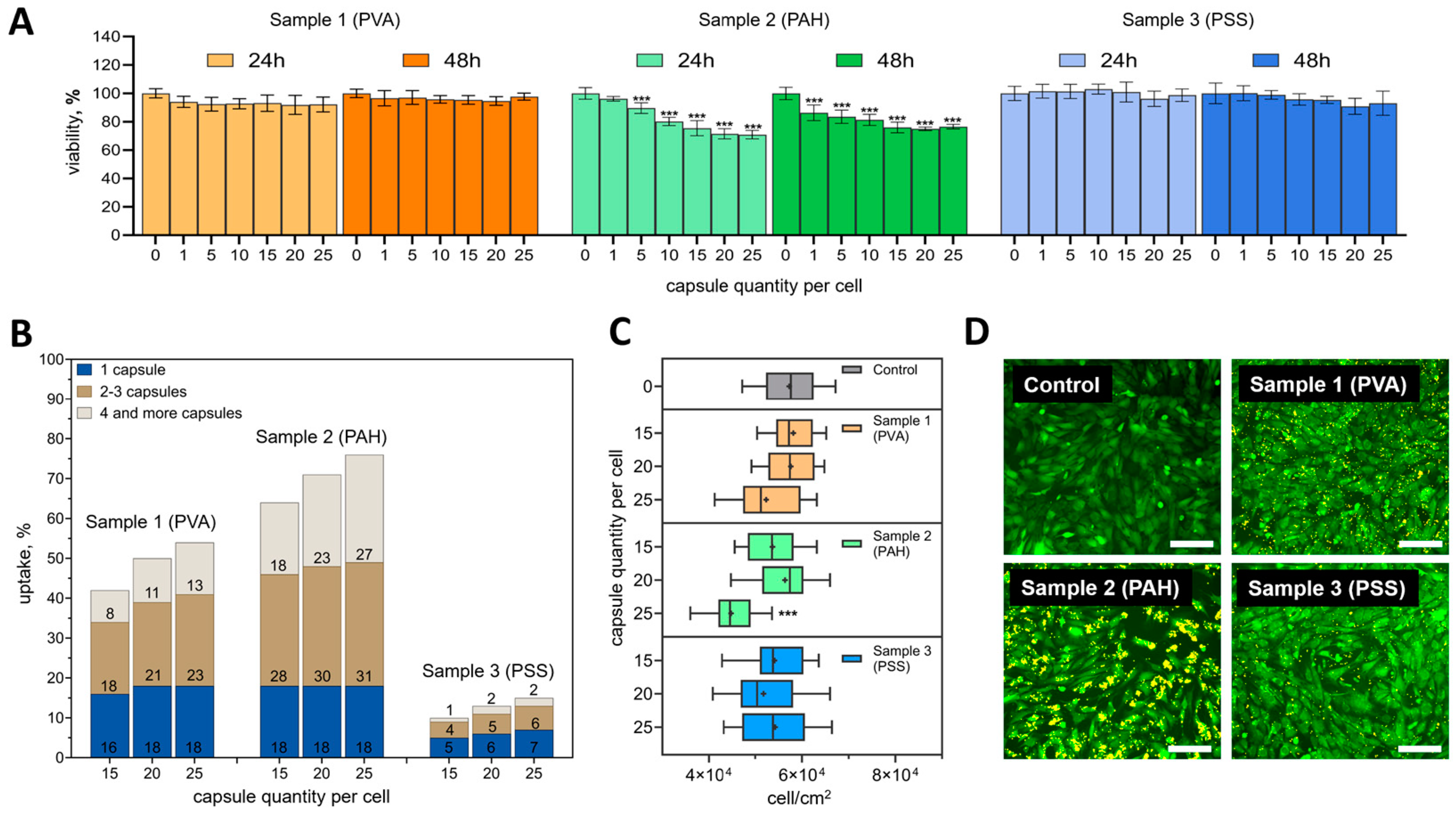
3.3. Selection of the Optimal Ratio of Capsules per Cell for Effective and Safe Labeling of mMSCs
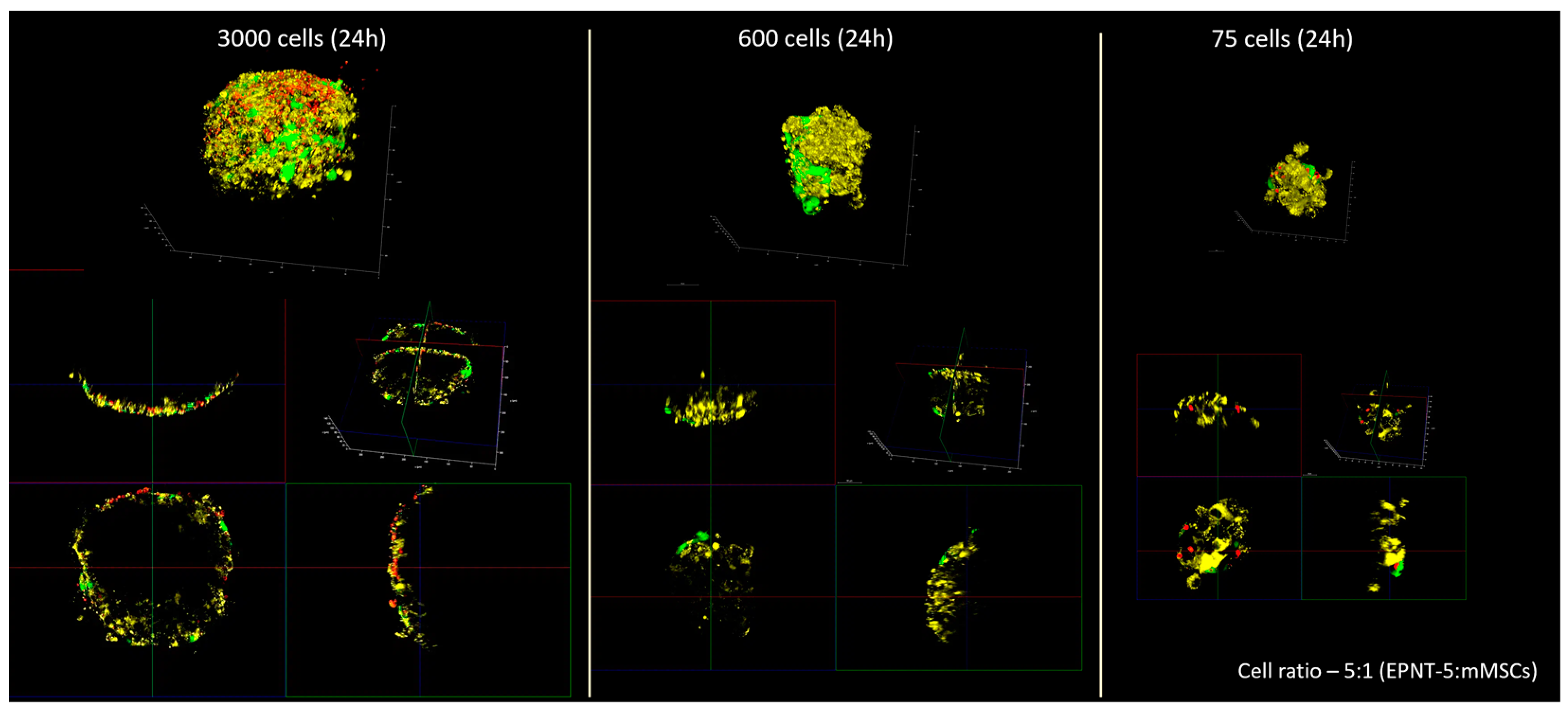
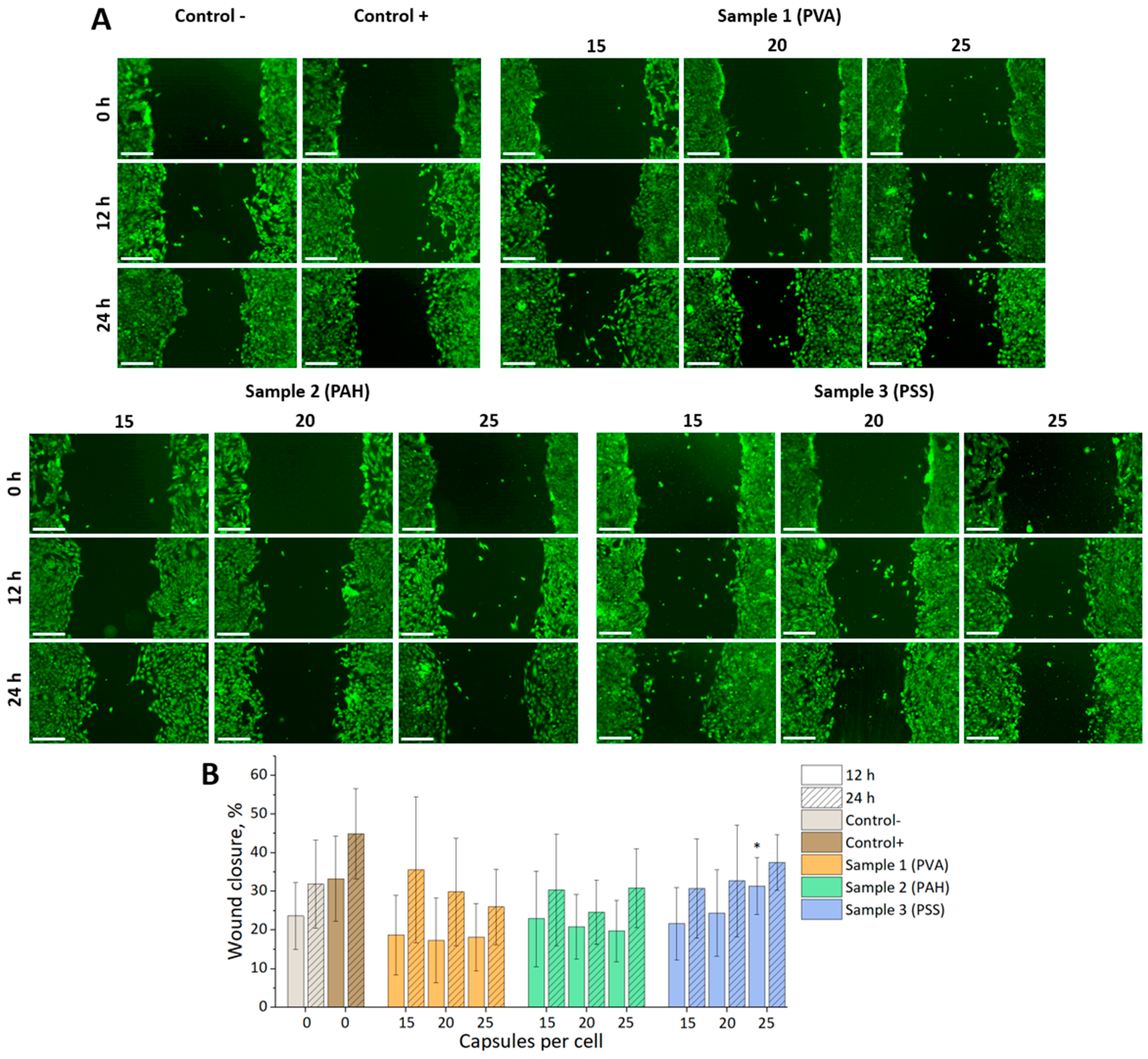
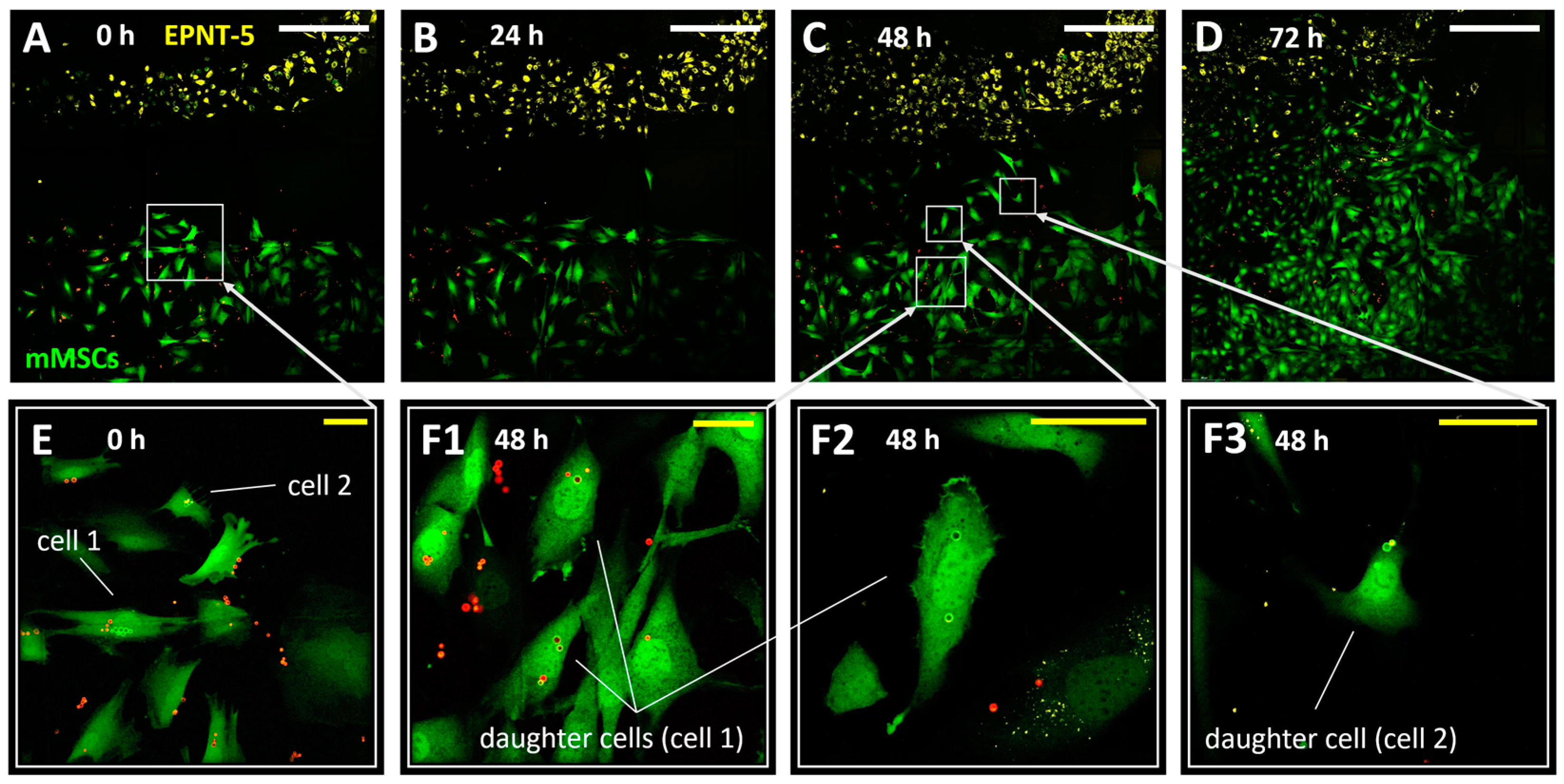
3.4. Tracking the Migration of Individual mMSCs Labeled Using Photoconverted Vesicles in 2D and 3D EPNT-5 Glioblastoma Cell Colonies
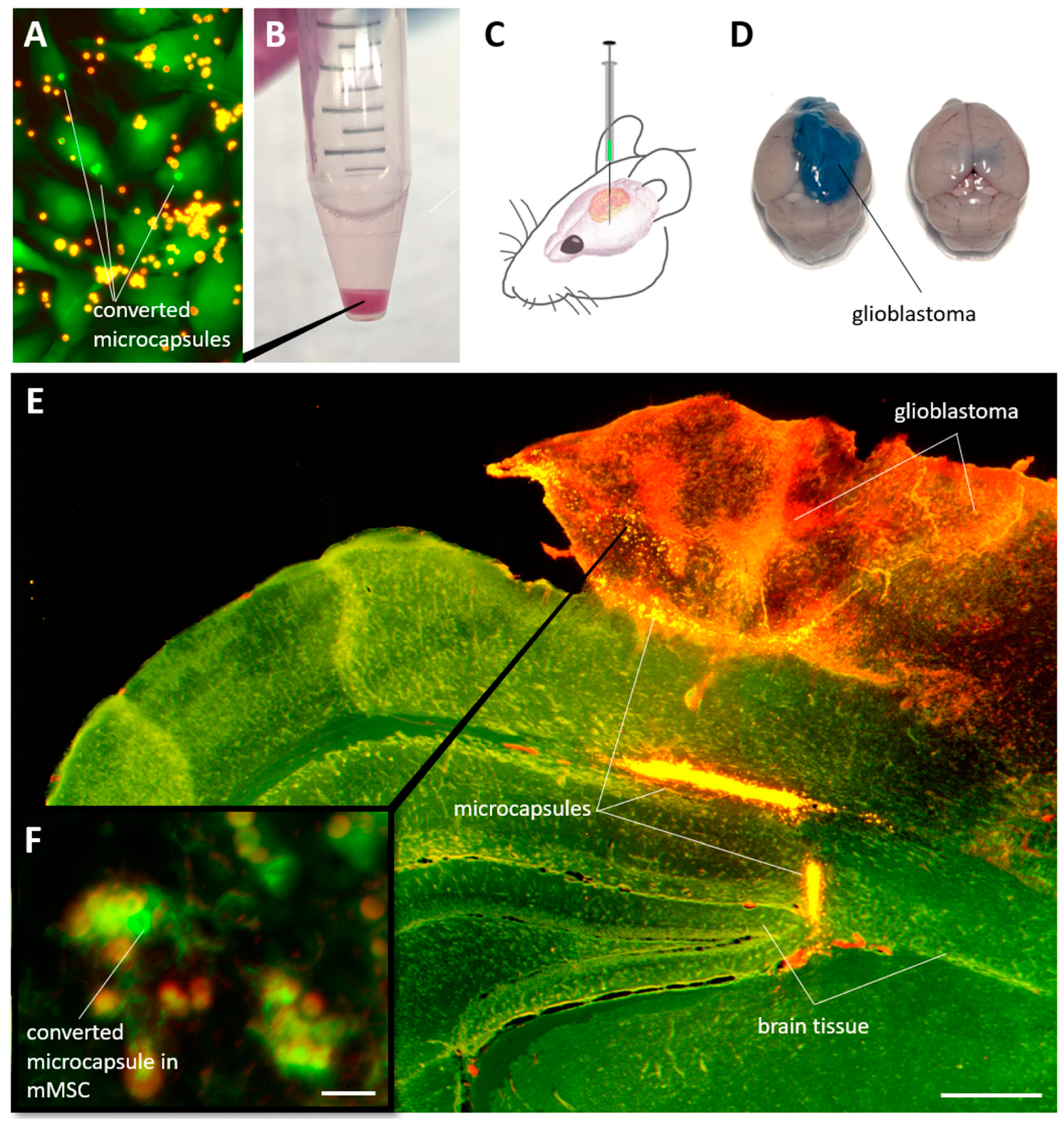
3.5. Detection of Individual mMSCs Labeled Using Photoconverted Nanocomposite Vesicles in Mouse Brain with Glioblastoma
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Rendra, E.; Scaccia, E.; Bieback, K. Recent Advances in Understanding Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. F1000Research 2020, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, W. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Occurrence, Development, and Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, A.; Ghaemi, B.; Bulte, J.W.M.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A. Tumor-Tropic Trojan Horses: Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Cellular Nanotheranostics. Theranostics 2024, 14, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, A.; Drela, K.; Rozycka, J.; Janowski, M.; Lukomska, B. Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells as an Anti-Cancer Trojan Horse. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1513–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Wang, X.; Kraatz, H.-B.; Ahmadi, S.; Gao, J.; Lv, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y. A Trojan Horse Biomimetic Delivery Strategy Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells for PDT/PTT Therapy against Lung Melanoma Metastasis. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimov, A.R.; Timin, A.S.; Bichaykina, V.R.; Peltek, O.O.; Karpov, T.E.; Dubavik, A.; Nominé, A.; Ghanbaja, J.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Zyuzin, M.V. Biomimetic Drug Delivery Platforms Based on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impregnated with Light-Responsive Submicron Sized Carriers. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimov, A.R.; Timin, A.S.; Petrova, A.V.; Epifanovskaya, O.S.; Shakirova, A.I.; Lepik, K.V.; Gorshkov, A.; Il’inskaja, E.V.; Vasin, A.V.; Afanasyev, B.V.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Engineering: Microcapsules-Assisted Gene Transfection and Magnetic Cell Separation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, A.D.; Kurniawati, I.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Wong, T.-T.; Lin, Y.-L.; Sung, S.-Y. Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Targeted Delivery to the Brain: Potential and Challenges of the Extracellular Vesicle-Based Approach for Brain Tumor Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, L.; Hou, J.; Ye, F.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Han, Z.; et al. The Distinct Roles of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Initial and Progressive Stage of Hepatocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, B.; Rogujski, P.; Janowski, M.; Lukomska, B.; Andrzejewska, A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Glioblastoma Therapy and Progression: How One Cell Does It All. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tario, J.D., Jr.; Humphrey, K.; Bantly, A.D.; Muirhead, K.A.; Moore, J.S.; Wallace, P.K. Optimized Staining and Proliferation Modeling Methods for Cell Division Monitoring Using Cell Tracking Dyes. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 70, e4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaiyya, M.; Kulkarni, M.B.; Pattnaik, P.K.; Goel, S. Internet of Things-enabled Photomultiplier Tube- and Smartphone-based Electrochemiluminescence Platform to Detect Choline and Dopamine Using 3D-printed Closed Bipolar Electrodes. Luminescence 2022, 37, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.; Muhamadali, H.; Goodacre, R. Monitoring Phenotype Heterogeneity at the Single-Cell Level within Bacillus Populations Producing Poly-3-Hydroxybutyrate by Label-Free Super-Resolution Infrared Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 17733–17740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, V.; Moeyaert, B.; David, C.C.; Mizuno, H.; Lelimousin, M.; Dedecker, P.; Ando, R.; Miyawaki, A.; Michiels, J.; Engelborghs, Y.; et al. Rational Design of Photoconvertible and Biphotochromic Fluorescent Proteins for Advanced Microscopy Applications. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osseiran, S.; Austin, L.A.; Cannon, T.M.; Yan, C.; Langenau, D.M.; Evans, C.L. Longitudinal Monitoring of Cancer Cell Subpopulations in Monolayers, 3D Spheroids, and Xenografts Using the Photoconvertible Dye DiR. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, A.L.; Fujisaki, J.; Wu, J.; Runnels, J.M.; Turcotte, R.; Celso, C.L.; Scadden, D.T.; Strom, T.B.; Lin, C.P. Tracking Single Cells in Live Animals Using a Photoconvertible Near-Infrared Cell Membrane Label. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, K.; Tsujii, H.; Omura, T. Cell Tracking Using a Photoconvertible Fluorescent Protein. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomura, M.; Ikebuchi, R.; Moriya, T.; Kusumoto, Y. Tracking the Fate and Migration of Cells in Live Animals with Cell-Cycle Indicators and Photoconvertible Proteins. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 355, 109127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caires, H.R.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Oliveira, C.M.; Gomes, D.; Mateus, D.D.; Oliveira, C.; Barrias, C.C.; Barbosa, M.A.; Almeida, C.R. Finding and Tracing Human MSC in 3D Microenvironments with the Photoconvertible Protein Dendra2. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennacchietti, F.; Alvelid, J.; Morales, R.A.; Damenti, M.; Ollech, D.; Oliinyk, O.S.; Shcherbakova, D.M.; Villablanca, E.J.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Testa, I. Blue-Shift Photoconversion of near-Infrared Fluorescent Proteins for Labeling and Tracking in Living Cells and Organisms. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburg, S.; Hodson, N.W.; Hill, P.I.; Richardson, S.M.; Hoyland, J.A. Bi-Directional Exchange of Membrane Components Occurs during Co-Culture of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Nucleus Pulposus Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-S.; Xin, Z.-C.; Dai, J.; Lue, T.F. Commonly Used Mesenchymal Stem Cell Markers and Tracking Labels: Limitations and Challenges. Histol. Histopathol. 2013, 28, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomura, M.; Yoshida, N.; Tanaka, J.; Karasawa, S.; Miwa, Y.; Miyawaki, A.; Kanagawa, O. Monitoring Cellular Movement in Vivo with Photoconvertible Fluorescence Protein “Kaede” Transgenic Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10871–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemet, I.; Ropelewski, P.; Imanishi, Y. Applications of Phototransformable Fluorescent Proteins for Tracking the Dynamics of Cellular Components. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 1787–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, W.N.; Novoselova, M.V.; Bratashov, D.N.; Khlebtsov, B.N.; Gorin, D.A.; Galanzha, E.I.; Zharov, V.P. Photoswitchable Spasers with a Plasmonic Core and Photoswitchable Fluorescent Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Huang, H.; Pudavar, H.E.; Cui, Y.; Prasad, P.N. Intraparticle Energy Transfer and Fluorescence Photoconversion in Nanoparticles: An Optical Highlighter Nanoprobe for Two-Photon Bioimaging. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5650–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, P.A.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Abramova, A.M.; Prikhozhdenko, E.S.; Verkhovskii, R.A.; Lengert, E.V.; Sapelkin, A.V.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Fluorescent Convertible Capsule Coding Systems for Individual Cell Labeling and Tracking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19701–19709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demina, P.A.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Abramova, A.M.; Saveleva, M.S.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Goryacheva, I.Y. Fluorescent Polymer Markers Photoconvertible with a 532 Nm Laser for Individual Cell Labeling. J. Biophotonics 2023, 16, e202200379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demina, P.A.; Grishin, O.V.; Malakhov, S.N.; Timaeva, O.I.; Kulikova, E.S.; Pylaev, T.E.; Saveleva, M.S.; Goryacheva, I.Y. Effect of Photoconversion Conditions on the Spectral and Cytotoxic Properties of Photoconvertible Fluorescent Polymer Markers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 13078–13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyreva, Z.V.; Demina, P.A.; Sapach, A.Y.; Terentyeva, D.A.; Gusliakova, O.I.; Abramova, A.M.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Trushina, D.B.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Sindeeva, O.A. Multiple Dyes Applications for Fluorescent Convertible Polymer Capsules as Macrophages Tracking Labels. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindeeva, O.A.; Demina, P.A.; Kozyreva, Z.V.; Muslimov, A.R.; Gusliakova, O.I.; Laushkina, V.O.; Mordovina, E.A.; Tsyupka, D.; Epifanovskaya, O.S.; Sapach, A.Y.; et al. Labeling and Tracking of Individual Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Using Photoconvertible Fluorescent Microcapsules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinchuk, T.M.; Ivantsov, K.M.; Alekseenko, L.L.; Kozhukharova, I.V.; Zaichik, A.M.; Petrov, N.S.; Mikhailov, V.M.; Popov, B.V. Characterizations of the Murine Mesenchymal Cell Line Expressing GFP. Cell Tissue Biol. 2009, 3, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, B.I.; Cruz, N.D.; Lujan, O.R.; Propper, C.R.; Kellar, R.S. In Vitro Scratch Assay to Demonstrate Effects of Arsenic on Skin Cell Migration. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 144, e58838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, D.A.; Portnov, S.A.; Inozemtseva, O.A.; Luklinska, Z.; Yashchenok, A.M.; Pavlov, A.M.; Skirtach, A.G.; Möhwald, H.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Magnetic/Gold Nanoparticle Functionalized Biocompatible Microcapsules with Sensitivity to Laser Irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, B. PH-Controlled Drug Loading and Release from Biodegradable Microcapsules. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2008, 4, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klelemen, H.; Hancu, G.; Kacsó, E.; Papp, L.-A. Photosensitivity Reactions Induced by Photochemical Degradation of Drugs. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Javier, A.; Kreft, O.; Piera Alberola, A.; Kirchner, C.; Zebli, B.; Susha, A.S.; Horn, E.; Kempter, S.; Skirtach, A.G.; Rogach, A.L.; et al. Combined Atomic Force Microscopy and Optical Microscopy Measurements as a Method to Investigate Particle Uptake by Cells. Small 2006, 2, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merhi, M.; Dombu, C.Y.; Brient, A.; Chang, J.; Platel, A.; Le Curieux, F.; Marzin, D.; Nesslany, F.; Betbeder, D. Study of Serum Interaction with a Cationic Nanoparticle: Implications for in Vitro Endocytosis, Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Lee, J.S.; Xiao, W.; Gonik, A.M.; Agarwal, R.G.; Lam, K.S. The Effect of Surface Charge on in Vivo Biodistribution of PEG-Oligocholic Acid Based Micellar Nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Gao, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Zheng, A. Size, Shape, Charge and “Stealthy” Surface: Carrier Properties Affect the Drug Circulation Time in Vivo. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, S.L.; Sajja, K.C.; Jang, C.; Behringer, R.R. Generation and Characterization of IUBC-KikGR Photoconvertible Transgenic Mice for Live Time-lapse Imaging during Development. genesis 2011, 49, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reihani, S.N.S.; Oddershede, L.B. Confocal Microscopy of Thick Specimens. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 030513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S.J.J.; Choi, M.; Bhayana, B.; Zhang, X.; Ran, C.; Yun, S.-H. Two-Photon Excited Photoconversion of Cyanine-Based Dyes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matikonda, S.S.; Helmerich, D.A.; Meub, M.; Beliu, G.; Kollmannsberger, P.; Greer, A.; Sauer, M.; Schnermann, M.J. Defining the Basis of Cyanine Phototruncation Enables a New Approach to Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröhl, J.; Schellenberg, M.; Dreher, K.; Maier-Hein, L. Deep Learning for Biomedical Photoacoustic Imaging: A Review. Photoacoustics 2021, 22, 100241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusliakova, O.I.; Prikhozhdenko, E.S.; Plastun, V.O.; Mayorova, O.A.; Shushunova, N.A.; Abdurashitov, A.S.; Kulikov, O.A.; Abakumov, M.A.; Gorin, D.A.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; et al. Renal Artery Catheterization for Microcapsules’ Targeted Delivery to the Mouse Kidney. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theparambil, S.M.; Kopach, O.; Braga, A.; Nizari, S.; Hosford, P.S.; Sagi-Kiss, V.; Hadjihambi, A.; Konstantinou, C.; Esteras, N.; Gutierrez Del Arroyo, A.; et al. Adenosine Signalling to Astrocytes Coordinates Brain Metabolism and Function. Nature 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, K.; Gong, Y.; Choi, Y.; Deng, N.; Yang, K.; Bai, S.; Cabrera, L.; Keller, E.; McCauley, L.; Cho, K.R.; et al. Human Ovarian Carcinoma–Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulate Cancer Stem Cells and Tumorigenesis via Altered BMP Production. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3206–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ginestier, C.; Ou, S.J.; Clouthier, S.G.; Patel, S.H.; Monville, F.; Korkaya, H.; Heath, A.; Dutcher, J.; Kleer, C.G.; et al. Breast Cancer Stem Cells Are Regulated by Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Cytokine Networks. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, K.; Zheng, P.; Liang, X.; Liu, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Maintain the Stemness of Colon Cancer Stem Cells via Interleukin-8/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Ok Lee, S.; Liang, L.; Huang, C.-K.; Li, L.; Wen, S.; Chang, C. Infiltrating Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Population and Metastatic Ability via Secreting Cytokines to Suppress Androgen Receptor Signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.-L.; De Vito, C.; Provero, P.; Stehle, J.-C.; Baumer, K.; Cironi, L.; Janiszewska, M.; Petricevic, T.; Suvà, D.; et al. EWS-FLI-1 Modulates MiRNA145 and SOX2 Expression to Initiate Mesenchymal Stem Cell Reprogramming toward Ewing Sarcoma Cancer Stem Cells. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, N.S.; Zhang, C.; Hwang, Y.; Varghese, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation and Roles in Regenerative Medicine. WIREs Syst. Biol. Med. 2009, 1, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley-Novatny, A.; Arumugasaamy, N.; Kimicata, M.; Baker, H.; Mikos, A.G.; Fisher, J.P. Concurrent Multi-Lineage Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Spatial Presentation of Growth Factors. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 055035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickert, S.; Schröter-Bobsin, U.; Groß, A.-F.; Hempel, U.; Wojciechowski, C.; Rentsch, C.; Corbeil, D.; Günther, K.P. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation during Long-Term Ex Vivo Cultivation Is Not Age Dependent. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2011, 29, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallis, P.; Michalopoulos, E.; Chatzistamatiou, T.; Giokas, C.S. Interplay between Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Immune System: Clinical Applications in Immune-Related Diseases. Explor. Immunol. 2021, 1, 112–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarugaser, R.; Hanoun, L.; Keating, A.; Stanford, W.L.; Davies, J.E. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Self-Renew and Differentiate According to a Deterministic Hierarchy. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Liu, G.; Halim, A.; Ju, Y.; Luo, Q.; Song, G. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells 2019, 8, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Tunger, A.; Wobus, M.; von Bonin, M.; Towers, R.; Bornhäuser, M.; Dazzi, F.; Wehner, R.; Schmitz, M. Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: An Update. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 637725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.K.; Shih, H.-H.; Parveen, F.; Lenzen, D.; Ito, E.; Chan, T.-F.; Ke, L.-Y. Identifying the Therapeutic Significance of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, G.; Cofano, F.; Salvati, L.F.; Monticelli, M.; Zeppa, P.; Di Perna, G.; Melcarne, A.; Altieri, R.; La Rocca, G.; Sabatino, G.; et al. Fluorescence-Guided Surgery for High-Grade Gliomas: State of the Art and New Perspectives. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 153303382110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.S.; Salinas, R.; Lee, J.Y.K. Indocyanine-Green for Fluorescence-Guided Surgery of Brain Tumors: Evidence, Techniques, and Practical Experience. Front. Surg. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppa, P.; De Marco, R.; Monticelli, M.; Massara, A.; Bianconi, A.; Di Perna, G.; Greco Crasto, S.; Cofano, F.; Melcarne, A.; Lanotte, M.M.; et al. Fluorescence-Guided Surgery in Glioblastoma: 5-ALA, SF or Both? Differences between Fluorescent Dyes in 99 Consecutive Cases. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
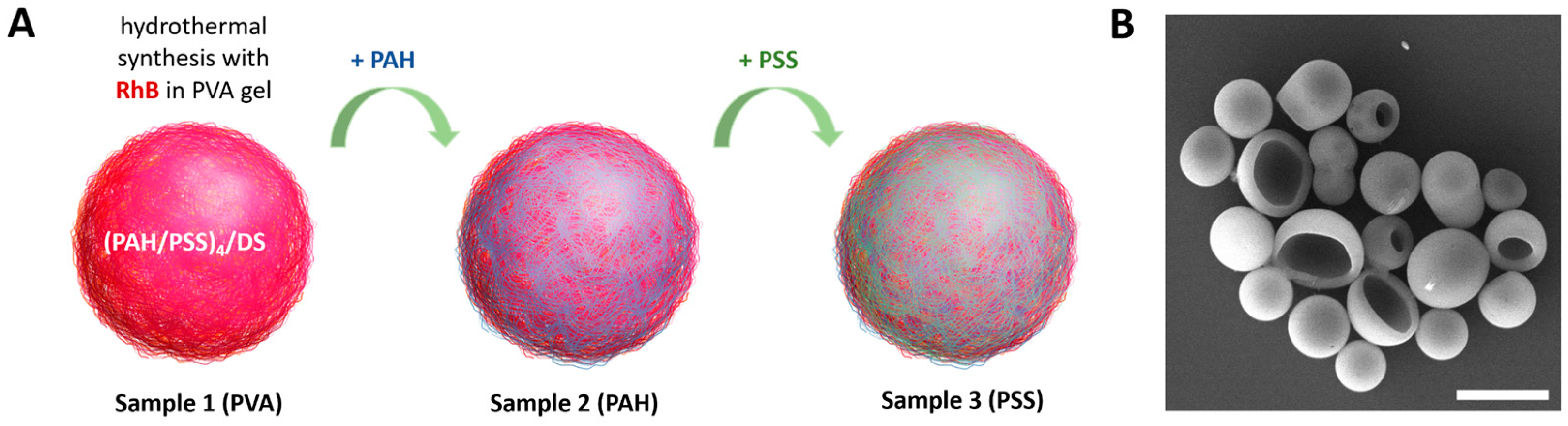

| Type of Vesicles | Size, µm | ζ-Potential, mV |
|---|---|---|
| Thermally treated (PAH/PSS)4/DS in PVA gel with RhB (Sample 1 (PVA)) | 3.3 ± 0.6 | −17.5 ± 1.2 |
| Thermally treated (PAH/PSS)4/DS in PVA gel with RhB, covered with PAH (Sample 2 (PAH)) | 3.4 ± 0.7 | −7.6 ± 0.6 |
| Thermally treated (PAH/PSS)4/DS in PVA gel with RhB, covered with PAH/PSS (Sample 3 (PSS)) | 3.3 ± 0.8 | −18.6 ± 2.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sindeeva, O.A.; Demina, P.A.; Kozyreva, Z.V.; Terentyeva, D.A.; Gusliakova, O.I.; Muslimov, A.R.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Single Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Migration Tracking into Glioblastoma Using Photoconvertible Vesicles. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141215
Sindeeva OA, Demina PA, Kozyreva ZV, Terentyeva DA, Gusliakova OI, Muslimov AR, Sukhorukov GB. Single Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Migration Tracking into Glioblastoma Using Photoconvertible Vesicles. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(14):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141215
Chicago/Turabian StyleSindeeva, Olga A., Polina A. Demina, Zhanna V. Kozyreva, Daria A. Terentyeva, Olga I. Gusliakova, Albert R. Muslimov, and Gleb B. Sukhorukov. 2024. "Single Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Migration Tracking into Glioblastoma Using Photoconvertible Vesicles" Nanomaterials 14, no. 14: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141215
APA StyleSindeeva, O. A., Demina, P. A., Kozyreva, Z. V., Terentyeva, D. A., Gusliakova, O. I., Muslimov, A. R., & Sukhorukov, G. B. (2024). Single Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Migration Tracking into Glioblastoma Using Photoconvertible Vesicles. Nanomaterials, 14(14), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14141215








