Hydrogel Extinguishants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Evolution of Hydrogel Applied for Fire Extinguishing and Prevention

3. Types of Hydrogel Extinguishants
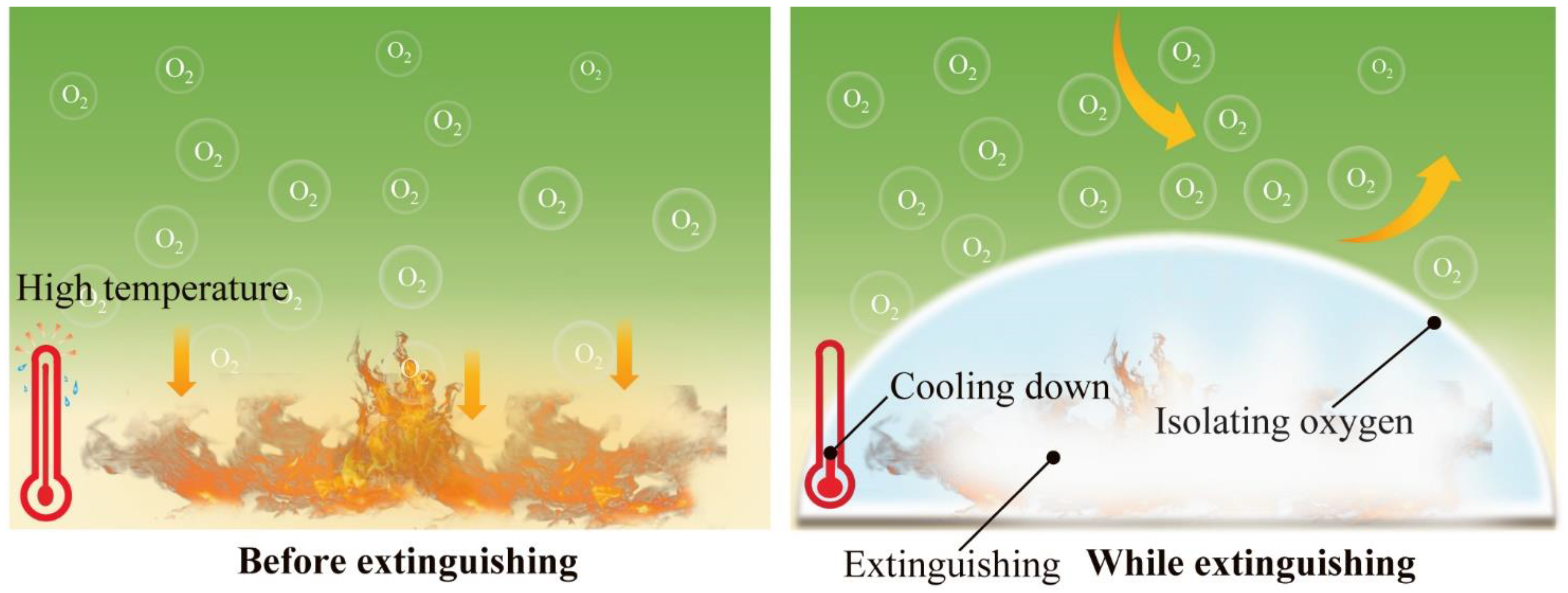
3.1. The Characterizes of Different Hydrogel Extinguishants
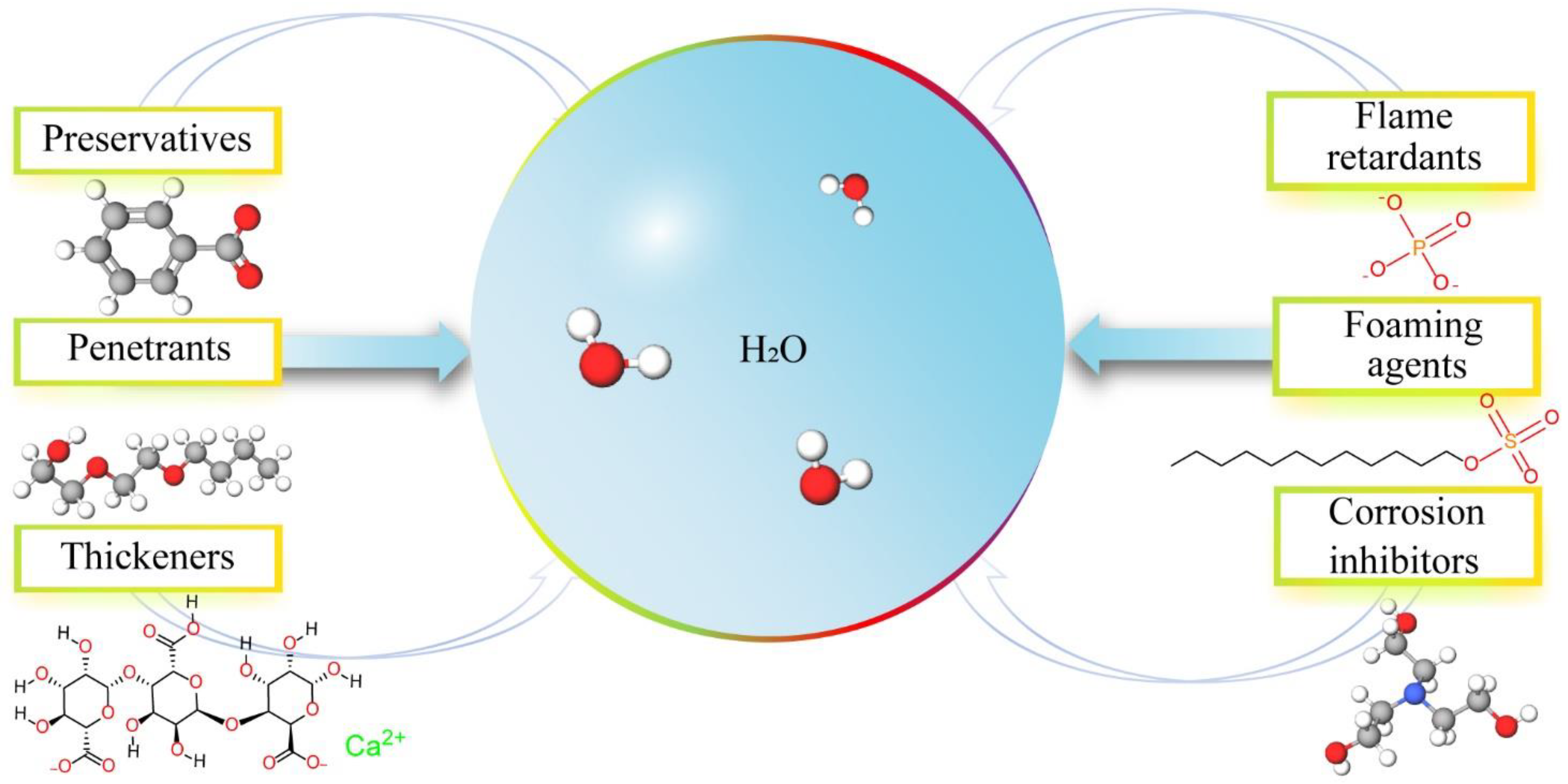
3.2. Critical Raw Materials
3.3. Preparation Strategies
3.4. Evaluation System of Hydrogel Extinguishants
3.4.1. Water-Based Extinguishants
3.4.2. Hydrogel Extinguishants
4. Commercial Aspects of Hydrogel Extinguishants
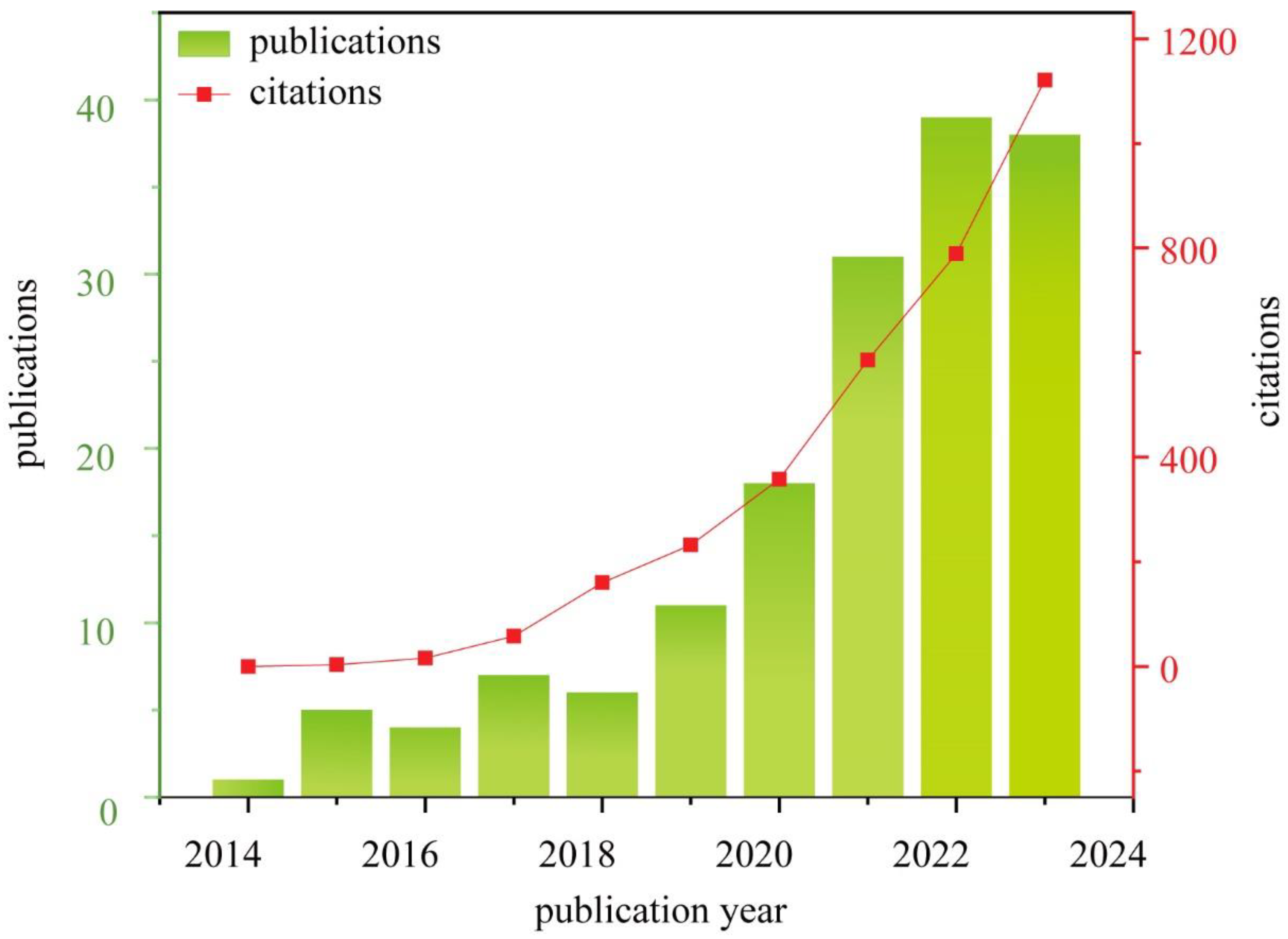
4.1. Commercialization Situation of Hydrogel Extinguishants
4.2. The Future Development Trend of Commercial Hydrogel Extinguishants
- (1)
- Expanding the use of hydrogel extinguishants. Hydrogel extinguishants have the advantages of wide sources of materials and low cost due to the water being the main component of hydrogel, which provides natural, convenient conditions for production. The scope of its use can be expanded by improving the formula and process to carve out a larger market.
- (2)
- Promoting advanced auxiliary equipment. To better apply hydrogel extinguishants, equipment technology needs to be improved to maximize its efficiency and reduce limitations in terms of storage, transportation, and equipment functionality. For example, an automatic premix device for extinguishants before spraying can be designed to improve the extinguishing performance of water in water supply networks or fixed tanks, thereby expanding the synthesis and application of hydrogel extinguishants. In addition, the research on the atomization mechanism can be further deepened, and new atomization nozzles can be innovatively developed to improve the spraying effect.
- (3)
- Promoting multidisciplinary integration. To better study hydrogel extinguishants, it is necessary to promote multidisciplinary integration. Biological science can be used to find microorganisms with specific properties suitable for hydrogel extinguishants to reduce the pressure on environmental protection.
- (4)
- Promoting the development of standardization. To lead the development direction of hydrogel extinguishants, it is necessary to establish and improve the design specifications and environmental performance evaluation system for hydrogel extinguishants in China.
5. Hydrogel for Fire Prevention
5.1. Fire Prevention Fabric
5.2. Fire Warning Systems
6. Conclusions: Challenges and Prospects of Hydrogel Extinguishants
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scholten, R.C.; Jandt, R.; Miller, E.A.; Rogers, B.M.; Veraverbeke, S. Overwintering Fires in Boreal Forests. Nature 2021, 593, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.A. Risk of Spontaneous and Anthropogenic Fires in Waste Management Chain and Hazards of Secondary Fires. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.M.; Pacheco, J.L.; Fendorf, S. Metal Toxin Threat in Wildland Fires Determined by Geology and Fire Severity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasslop, G.; Hantson, S.; Harrison, S.P.; Bachelet, D.; Burton, C.; Forkel, M.; Forrest, M.; Li, F.; Melton, J.R.; Yue, C.; et al. Global Ecosystems and Fire: Multi-Model Assessment of Fire-Induced Tree-Cover and Carbon Storage Reduction. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 5027–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjold, T.; Souprayen, C.; Dorofeev, S. Fires and Explosions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 64, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tan, W.; Liu, L. “Relay-Mode” Promoting Permeation of Water-Based Fire extinguishing Agent in Granular Materials Porous Media Stacks. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 47, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.W.; Pan, W.J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.R.; Ouyang, L. ming Inhibition of Coal Spontaneous Combustion by an Environment-Friendly, Water-Based Fire extinguishing Agent. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 144, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Shang, Z.; Intelligent, J.J.; Bai, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Study on Fire extinguishing Effect of Water-Based Fixed Fire Extinguishing System in Full-Scale Bus Cabin. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Fire Science and Fire Protection Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhalichko, B.; Lavrenyuk, H.; Mykhalichko, O. New Water-Based Fire Extinguishant: Elaboration, Bench-Scale Tests, and Flame Extinguishment Efficiency Determination by Cupric Chloride Aqueous Solutions. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 105, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Jiang, J.C.; Huang, A.C. Experimental Study on Extinguishing Oil Fire by Water Mist with Polymer Composite Additives. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 4811–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Wang, J.L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhang, A. Formulation and Performance of Aqueous Film-Forming Foam Fire extinguishing Agent Composed of a Short-Chain Perfluorinated Heterocyclic Surfactant as the Key Component. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 6763–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Unuma, K.; Uemura, K. Two Fatal Cases Due to Inadvertent Discharge of Carbon Dioxide Fire Suppressant: Intoxication or Asphyxiation? J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2022, 90, 102390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Jiao, J.; Wu, J.; Lang, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Cui, P.; Shang, Z.; Mu, X.; Mu, S.; et al. Environmentally Friendly Fluorine-Free Fire extinguishing Agent Based on the Synergistic Effect of Silicone, Hydrocarbon Surfactants and Foam Stabilizers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 694, 134216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etz, B.D.; Mifkovic, M.; Vyas, S.; Shukla, M.K. High-Temperature Decomposition Chemistry of Trimethylsiloxane Surfactants, a Potential Fluorine–Free Replacement for Fire Suppression. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Qi, L.; Wu, J.; Lang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cui, P.; Shang, Z.; Mu, X.; Mu, S.; et al. Synthesis of Carboxyl Modified Polyether Polysiloxane Surfactant for the Biodegradable Foam Fire extinguishing Agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Yin, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Deng, Y.; Lu, S. Preliminary Ecotoxicity Hazard Evaluation of DOPO-HQ as a Potential Alternative to Halogenated Flame Retardants. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Zeng, J.; Zou, Q.; Zheng, L.; Pan, R. Fluorine-Free Foaming Extinguishing Agent: Design Route, Fire Extinguishing Performance, Foam Stability Mechanism. Arabian J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Z. In Depth Study on the Fire extinguishing Mechanism of Octafluoro-2-Butene as a New Promising Halon Substitute. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2022, 122, e26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.L.; Tang, K. A Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel for Suppressing Oil Fire. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 785, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hai, Y.; Zhong, X.; Xiao, S.; Jiang, S. Influence of Phytic Acid on Flame Retardancy and Adhesion Performance Enhancement of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogel Coating to Wood Substrate. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, H. Development of a Novel Bentonite–Acrylamide Superabsorbent Hydrogel for Extinguishing Gangue Fire Hazard. Powder Technol. 2018, 323, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, K.; Liu, C.; Yu, R.; Huang, A.; Wu, C.; Yang, Y. 3D Printed All-Natural Hydrogels: Flame-Retardant Materials Toward Attaining Green Sustainability. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2306360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaninia, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Yan, N. Self-Healing, Flame-Retardant, and Antimicrobial Chitosan-Based Dynamic Covalent Hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Gholami, F.; Tomas, M.; Movahedifar, E.; Yazdi, M.K.; Saeb, M.R. Hydrogel and Aerogel-Based Flame-Retardant Polymeric Materials: A Review. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2024, 30, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G. Organohydrogel Based on Cellulose-Stabilized Emulsion for Electromagnetic Shielding, Flame Retardant, and Strain Sensing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastalska-Popławska, J.; Wójcik, Ł.; Izak, P. Applications of Hydrogels with Fire Retardant Properties—A Review. J. Solgel. Sci. Technol. 2023, 105, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; He, H.; Ma, S.; Yao, J. Flame-Retardant PNIPAAm/Sodium Alginate/Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogels Used for Fire-Fighting Application: Preparation and Characteristic Evaluations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, B.; Frankl, S.; Becher, D.; Menz, F.; Baier, T.; Bauer, M.; Böse, O.; Hölzle, M. Naturally Derived Thermal Barrier Based on Fiber-Reinforced Hydrogel for the Prevention of Thermal Runaway Propagation in High-Energetic Lithium-Ion Battery Packs. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koparipek-Arslan, N.; Kaynak-Uraz, E.; Senses, E. Dynamically Bonded Cellulose Nanocrystal Hydrogels: Structure, Rheology and Fire Prevention Performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 334, 122013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; He, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.; Tang, H.; Hu, X.; Xue, D.; Wang, W.; Qi, G. Preparation of a Self-Adhesive Hydrogel and Research on Its Flame-Retardant Properties. Fuel 2022, 324, 124691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.F.; Zheng, W.J.; Zou, W.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, H.; Yan, J.; Gao, Y. Water-Retaining, Tough and Self-Healing Hydrogels and Their Uses as Fire-Resistant Materials. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 5151–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, L.; Meng, D.; Wu, J. From Hydrogel to Aerogel: A Green Fabrication of Multifunctional Polyimide Absorbents. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 89, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiri, K.; Omidian, H.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Doroudiani, S. Superabsorbent Hydrogel Composites and Nanocomposites: A Review. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Yang, X.; Qi, G.; Tu, Y. Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Thermochromic Hydrogel with Efficient Passive Radiative Cooling and Adjustable Visible Light Transmittance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2024, 271, 112871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Suryawanshi, A.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Thermal Insulating and Fire-Retarding Behavior of Treated Cotton Fabrics with a Novel High Water-Retaining Hydrogel Used in Thermal Protective Clothing. Cellulose 2021, 28, 2581–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Lu, B.; Zhao, X. Hydrogel Bioelectronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1642–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Xue, Z.; He, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Hydrogel Use in Burn Therapy, Thermal Management, Wastewater Treatment and Fire Fighting: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 3273–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhao, D.L.; Guo, J. Mechanism and Property of Extinguishing Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogels. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, ICICTA, Changsha, China, 25–26 October 2014; pp. 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, W.; Shao, Z. Novel Authigenic Gas Foaming Hydrogels for Preventing Coal Spontaneous Combustion. E-Polym 2015, 15, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Huang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Gui, C.X.; Yu, Z.Z. Highly Compressible Anisotropic Graphene Aerogels Fabricated by Directional Freezing for Efficient Absorption of Organic Liquids. Carbon 2016, 100, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Lu, B.; Gao, J.; Jin, X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Qu, L. Reconstruction of Inherent Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals for Large-Scale Fabrication of Structure-Intact Graphene Aerogel Bulk toward Practical Applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11407–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, G.; Jin, X.; Lu, B.; Zhang, P.; Lin, T.; Qu, L. Superplastic Air-Dryable Graphene Hydrogels for Wet-Press Assembly of Ultrastrong Superelastic Aerogels with Infinite Macroscale. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.L.; Yang, N.; Apostolopoulou-Kalkavoura, V.; Qin, B.; Ma, Z.Y.; Xing, W.Y.; Qiao, C.; Bergström, L.; Antonietti, M.; Yu, S.H. Fire-Retardant and Thermally Insulating Phenolic-Silica Aerogels. Angew. Chem. —Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4538–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, L.Y.; Jing, L.; Li, K.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.Y. Carbon Nanotube-Integrated Conductive Hydrogels as Multifunctional Robotic Skin. Carbon 2020, 161, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, G.; Huang, B. Self-Protecting Aqueous Lithium-Ion Batteries. Small 2022, 18, 2203035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S. Highly Water Retention, Flexible and Self-Extinguished Temperature Sensors Based on Double Network Hydrogel for Early Fire Warning. Compos. B Eng. 2023, 260, 110753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Ji, S.; Jiang, Y.; Su, J.; Xia, H.; Li, H.; Tian, C.; Wong, Y.J.; Feng, X.; Chen, X. Mitigating the Overheat of Stretchable Electronic Devices Via High-Enthalpy Thermal Dissipation of Hydrogel Encapsulation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Bae, J.S.; Hong, J.C.; Kim, J.G.; Park, J.; Park, J.H.; Shin, J.S.; Choi, Y.C. Hybrid Fuel Preparation Combining Glycerol-Derived Hydrogel and Coal and Its Characterization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 16206–16210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Gong, L.; Du, Z.; Duan, H. A Novel Environmental-Friendly Gel Dry-Water Extinguishant Containing Additives with Efficient Combustion Suppression Efficiency. Fire Technol. 2020, 56, 2365–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Chai, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W. Experimental Study on the Effect of Release Pressure on the Extinguishing Efficiency of Dry Water. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 101177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianwei, Z.; Xiangchen, L.; Guofeng, W.; Hao, L.; Lei, X.; Qiaohan, Y.; Qiang, L.; Cunwei, Z. Sustained Effect of Dry Water in a Thermal Environment after Fire extinguishing: Fuel Surface Coating Methods. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Ding, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Yu, R.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P. Study on the Inhibition Performance of Double Network Physicochemical Nanocomposite Gel Inhibitor on Coal Spontaneous Combustion. Fuel 2023, 350, 128697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, W.; Dong, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.X.; Cao, X. Preparation and Characteristic Study of the Hydrogel of Coal Spontaneous Combustion Environmental Protection. Fuel 2024, 360, 130505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Feng, Y.; He, Z.; Qi, G.; Ren, W.; Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Research and Development of a Sodium Alginate/Calcium Ion Gel Based on in Situ Cross-Linked Double-Network for Controlling Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. Fuel 2022, 322, 124260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xue, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Shao, Z.; Cheng, W.; Dong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xin, L.; Lu, W. Novel Sodium Silicate/Polymer Composite Gels for the Prevention of Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Tian, F.; Xu, C.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, W. Synthesis and Performance Characteristics of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Fire Prevention and Extinguishing Gel Based on Phytoextraction-Medical Stone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, X.; Wu, Z. Mining Polyethylene Glycol-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel Materials: Preparation and Flame Retardant Properties. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5947–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Hu, X.; Dong, H.; Cheng, W.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y. Examination of Characteristics of Anti-Oxidation Compound Inhibitor for Preventing the Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. Fuel 2022, 310, 122160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Dou, G.; Wang, Y.; Xin, H.; Ma, L.; Wang, D. A Superabsorbent Hydrogel–Ascorbic Acid Composite Inhibitor for the Suppression of Coal Oxidation. Fuel 2017, 190, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Jian, H.; Zhong, X. Preparation and Characterization of a Lignin Based Hydrogel Inhibitor on Coal Spontaneous Combustion. Fuel 2022, 308, 122074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Jing, B.; Qu, Y. Synthesis and Characteristics of Fire extinguishing Gel with High Water Absorption for Coal Mines. Process. Saf. Environ. 2019, 125, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Dou, G. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan Grafting Hydrogel for Mine-Fire Fighting. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lv, X.; Liu, N.; Qi, G.; Huang, Q. Spontaneous Coal Combustion Prevention Mechanisms of Thermosensitive Composite Hydrogel: An Experimental Study. Fuel 2023, 331, 125796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, S.; Meng, Q.; Tian, F.; Sun, L. Synthesis and Performance of a New Temperature-Sensitive and Super-Absorbent Fire Prevention Hydrogel Based on Ultrasonic Method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Hu, X.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Y. An Intelligent Gel Designed to Control the Spontaneous Combustion of Coal: Fire Prevention and Extinguishing Properties. Fuel 2017, 210, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Huang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wei, G. Experimental Study on Thermosensitive Hydrogel Used to Extinguish Class a Fire. Polymers 2021, 13, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shu, C.M.; Deng, J. Comparison of the Inhibition Mechanisms of Five Types of Inhibitors on Spontaneous Coal Combustion. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 1158–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H. Experimental Study of Thermal Stability and Spread Characteristics of Gel-Protein Foam for Liquid Tank Fires. Energy 2024, 294, 130792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Hu, X.; Cheng, W.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, L. Fire Prevention and Control Using Gel-Stabilization Foam to Inhibit Spontaneous Combustion of Coal: Characteristics and Engineering Applications. Fuel 2020, 264, 116903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R. Preparation and Characterization of Fire extinguishing Efficiency of Novel Gel-Protein Foam for Liquid Pool Fires. Energy 2023, 263, 130792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Tian, F.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, T. Preparation of New Gel Foam and Evaluation of Its Fire extinguishing Performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 629, 127443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Han, C.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Dai, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C. Preparation of the Environmentally Friendly and High Stable Gel Foam Based on Biomass Xanthan Gum for Inhibiting Coal Spontaneous Combustion. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2214693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Qin, B.; Xu, Y.; Hao, M.; Shao, X.; Zhuo, H. Experimental Investigation of the Drainage Characteristic and Stability Mechanism of Gel-Stabilized Foam Used to Extinguish Coal Fire. Fuel 2022, 313, 122685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, A.; Yuan, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y. Renewable Biomass Gel Reinforced Core-Shell Dry Water Material as Novel Fire extinguishing Agent. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2019, 59, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Wang, C.; Yan, C.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Lignin-Based Hydrogel Reinforced Dry Water as Inhibitor for Coal Spontaneous Combustion. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z.; Xu, F.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. New-Type Gel Dry-Water Extinguishants and Its Effectiveness. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 166, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Peng, K.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Yao, W. Construction of Physically Crosslinked Chitosan/Sodium Alginate/Calcium Ion Double-Network Hydrogel and Its Application to Heavy Metal Ions Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, R.; Mu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Ran, R. Strong Tough Conductive Hydrogels via the Synergy of Ion-Induced Cross-Linking and Salting-Out. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yuk, H.; Hu, F.; Wu, J.; Tian, F.; Roh, H.; Shen, Z.; Gu, G.; Xu, J.; Lu, B.; et al. 3D Printable High-Performance Conducting Polymer Hydrogel for All-Hydrogel Bioelectronic Interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.; Lu, B.; Gu, G. 3D-Printed PEDOT:PSS for Soft Robotics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 604–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, P.; Hu, F.; Rong, Y.; Lu, B.; Gu, G. High-Stretchability, Ultralow-Hysteresis Conducting Polymer Hydrogel Strain Sensors for Soft Machines. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 202203650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. 3D Printing of Highly Conductive and Strongly Adhesive PEDOT:PSS Hydrogel-Based Bioelectronic Interface for Accurate Electromyography Monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Yu, J.; Quan, Z.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, D.; et al. A Reusable, Healable, and Biocompatible PEDOT:PSS Hydrogel-Based Electrical Bioadhesive Interface for High-Resolution Electromyography Monitoring and Time–Frequency Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Qiu, R.; Liu, W. Photocurable 3D Printing of High Toughness and Self-Healing Hydrogels for Customized Wearable Flexible Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, G.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; An, C.; Ding, J. Research on the Fire extinguishing Effectiveness of a New Nano-Scale Aerogel Fire extinguishing Agent. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 37, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shi, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Wettability of HPMC/PEG/CS Thermosensitive Porous Hydrogels. Gels 2023, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Ruan, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, G.; Ma, Y.; Dai, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Insight to Hydrophobic SiO2 Encapsulated SiO2 Gel: Preparation and Application in Fire extinguishing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Du, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X. Dry Water: Toward an Ideal Extinguishant for Lithium-Ion Battery Fire. J. Energy Storage 2024, 80, 110204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, T.; Yuan, S.; Chang, C.; Wang, K.; Song, Z.; Qian, X. Patent-Based Technological Developments and Surfactants Application of Lithium-Ion Batteries Fire extinguishing Agent. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 88, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Chen, P.; Hou, M.; Li, Q.; Su, G.; Meng, J.; Shi, B.; Deng, J. Modification of Freezing Point for Hydrogel Extinguishant and Its Effect on Comprehensive Properties in Simulated Forest Fire Rescue. Sustainability 2022, 14, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, R.; Liu, S.; Patil, A.; Gong, H.; Yi, J.; Sheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. A Machine-Fabricated 3D Honeycomb-Structured Flame-Retardant Triboelectric Fabric for Fire Escape and Rescue. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, P.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; An, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.Z. A Dimensional Stable Hydrogel-Born Foam with Enhanced Mechanical and Thermal Insulation and Fire-Retarding Properties via Fast Microwave Foaming. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Huan, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, C. Low-Cost, Superhydrophobic, Flame-Retardant Sunflower Straw-Based Xerogel as Thermal Insulation Materials for Energy-Efficient Buildings. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 38, e00748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kang, G.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Qiu, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Li, B.; Li, F.; et al. Hybrid Nanoparticles Based on Novel Schiff Base for Durable Flame Retardant and Antibacterial Properties. Compos. B Eng. 2022, 238, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingtipi, K.; Choudhury, B.J.; Moholkar, V.S. Kaolin-Embedded Cellulose Hydrogel with Tunable Properties as a Green Fire Retardant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.T.; Wang, X.; Acuña, P.; Zhu, P.; Wagenknecht, U.; Heinrich, G.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.Y. Effect of Phosphorus-Containing Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Coating on the Flammability of Cotton Fabrics: Synthesis, Characterization and Flammability. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, X.; Jin, B.; Chen, G.; Lo, S. Arbitrarily and Repeatedly Programmable Multi-Layer Soft Actuators via “Stress-Caching”. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 139054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lai, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhu, Y. A High-Thermopower Ionic Hydrogel for Intelligent Fire Protection. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2022, 10, 21368–21378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Novel Flame-Retardant Composite Material Based on Calcium Alginate/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphite Hydrogel: Thermal Kinetics, Combustion Behavior and Thermal Insulation Performance. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8751–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Qin, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Qu, X.; et al. A Wearable Self-Powered Fire Warning e-Textile Enabled by Aramid Nanofibers/MXene/Silver Nanowires Aerogel Fiber for Fire Protection Used in Firefighting Clothing. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Feng, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, F.F.; Yu, Y. Smart Fire Alarm Systems for Rapid Early Fire Warning: Advances and Challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Z.; Ye, X.; He, W.; Qu, L.; Tian, M. A Smart Self-Powered Rope for Water/Fire Rescue. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 202210111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Wan, R.; Cao, J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Design of Highly Conductive, Intrinsically Stretchable, and 3D Printable PEDOT:PSS Hydrogels via PSS-Chain Engineering for Bioelectronics. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5936–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wan, R.; Tian, F.; Cao, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Lin, T.; et al. 3D Printing of Robust High-Performance Conducting Polymer Hydrogel-Based Electrical Bioadhesive Interface for Soft Bioelectronics. Small 2024, 20, 2308778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xu, X.; Yang, R.; Ma, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J.; Lu, B. Design of Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene): Polystyrene Sulfonate-Polyacrylamide Dual Network Hydrogel for Long-Term Stable, Highly Efficient Solar Steam Generation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, W.; Cao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Yuan, S.; et al. Full-Spectrum-Responsive Ti4O7-PVA Nanocomposite Hydrogel with Ultrahigh Evaporation Rate for Efficient Solar Steam Generation. Desalination 2024, 577, 117400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Xu, X.; Ma, H.; Hou, J.; Xu, Q.; Yang, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Robust PEDOT:PSS-Based Hydrogel for Highly Efficient Interfacial Solar Water Purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, X.; Ma, H.; Zheng, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Qu, K.; Yang, R.; et al. Low-Cost Fabrication of High-Performance Fluorinated Polythiophene-Based Vis-NIR Electrochromic Devices toward Deformable Display and Camouflage. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 9923–9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. Low Hysteresis and Fatigue-Resistant Polyvinyl Alcohol/Activated Charcoal Hydrogel Strain Sensor for Long-Term Stable Plant Growth Monitoring. Polymers 2022, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Xue, Y.; Duan, Q.; Liang, X.; Lin, T.; Wu, Z.; Tan, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, W.; et al. Fatigue-Resistant Conducting Polymer Hydrogels as Strain Sensor for Underwater Robotics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Types of Hydrogel Extinguishants | Foam Type | Dry Water Type | Thermosensitive Type | Common Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The key components | Surfactants | SiO2 | N-isopropylacrylamide | Natural polymers |
| Characteristics | Suitable for oil fire | Physical and chemical dual inhibition | Smart stive-responsive | High adhesion |
| Forms | Foam | Powder | Solution | Sol |
| Gelling Agents | Crosslinking Agents | Initiators | Crosslinking Ways | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC, PEG | MBA | KPS | Free-radical copolymerization | [63] |
| Xylan, CMC, NIPAM, AMPS | MBA | APS | Free-radical copolymerization | [64] |
| AMPS, pretreated straw | MBA | KPS | Free-radical copolymerization | [65] |
| MC, PAAS | MgCl2 | - | Ionic crosslinking | [66] |
| NIPAM, SA | MgCl2 | - | Ionic crosslinking | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Yao, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, K.; Liu, X. Hydrogel Extinguishants. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131128
Li G, Wang Q, Liu G, Yao M, Wang Y, Li Y, Lin K, Liu X. Hydrogel Extinguishants. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(13):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131128
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guineng, Qiaobo Wang, Guiqun Liu, Mutian Yao, Yue Wang, Yeying Li, Kaiwen Lin, and Ximei Liu. 2024. "Hydrogel Extinguishants" Nanomaterials 14, no. 13: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131128
APA StyleLi, G., Wang, Q., Liu, G., Yao, M., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Lin, K., & Liu, X. (2024). Hydrogel Extinguishants. Nanomaterials, 14(13), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14131128






