Nanostructured N, S, and P-Doped Elaeagnus Angustifolia Gum-Derived Porous Carbon with Electrodeposited Silver for Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
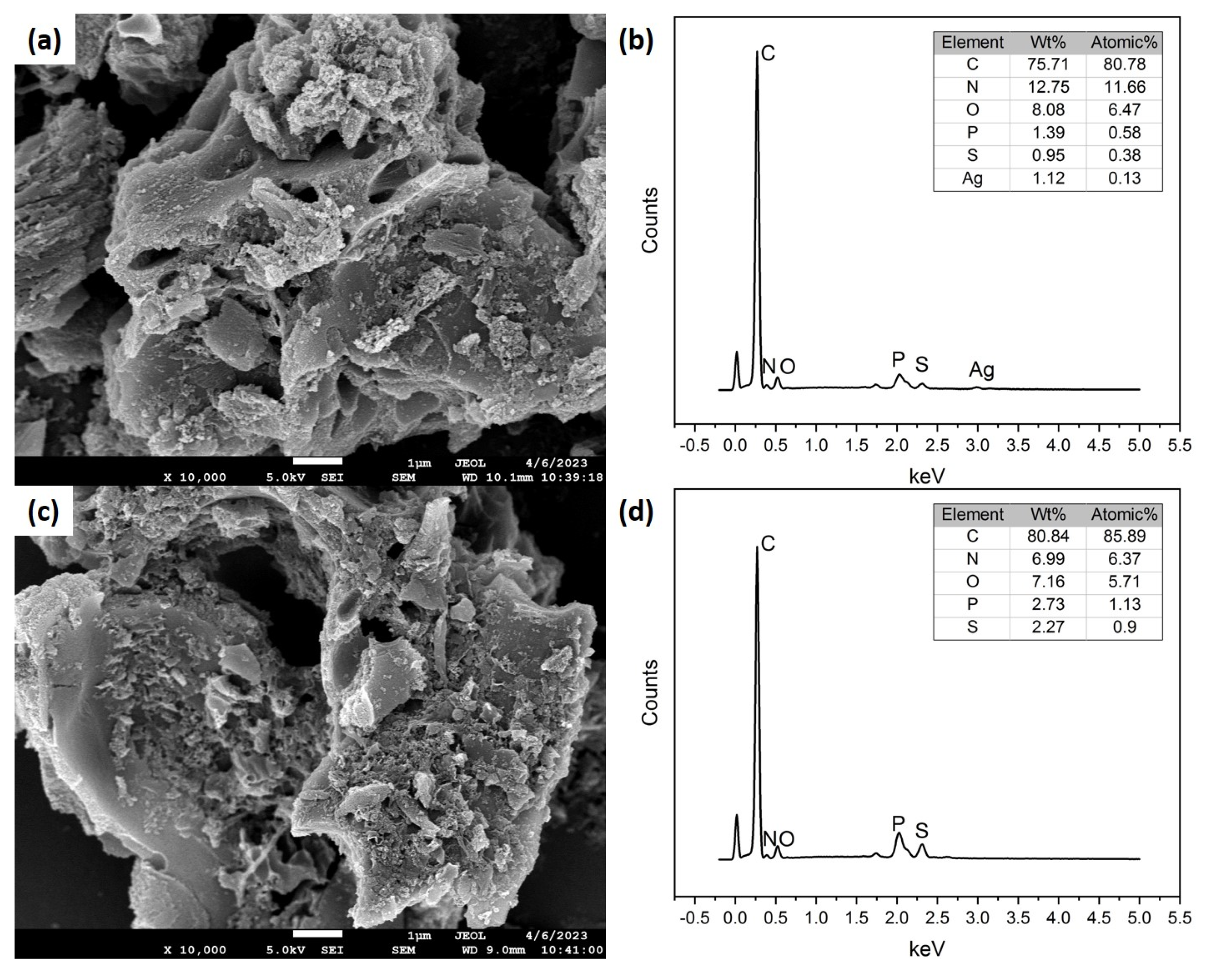
3.1. Material Characterization
Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-ray Characterization
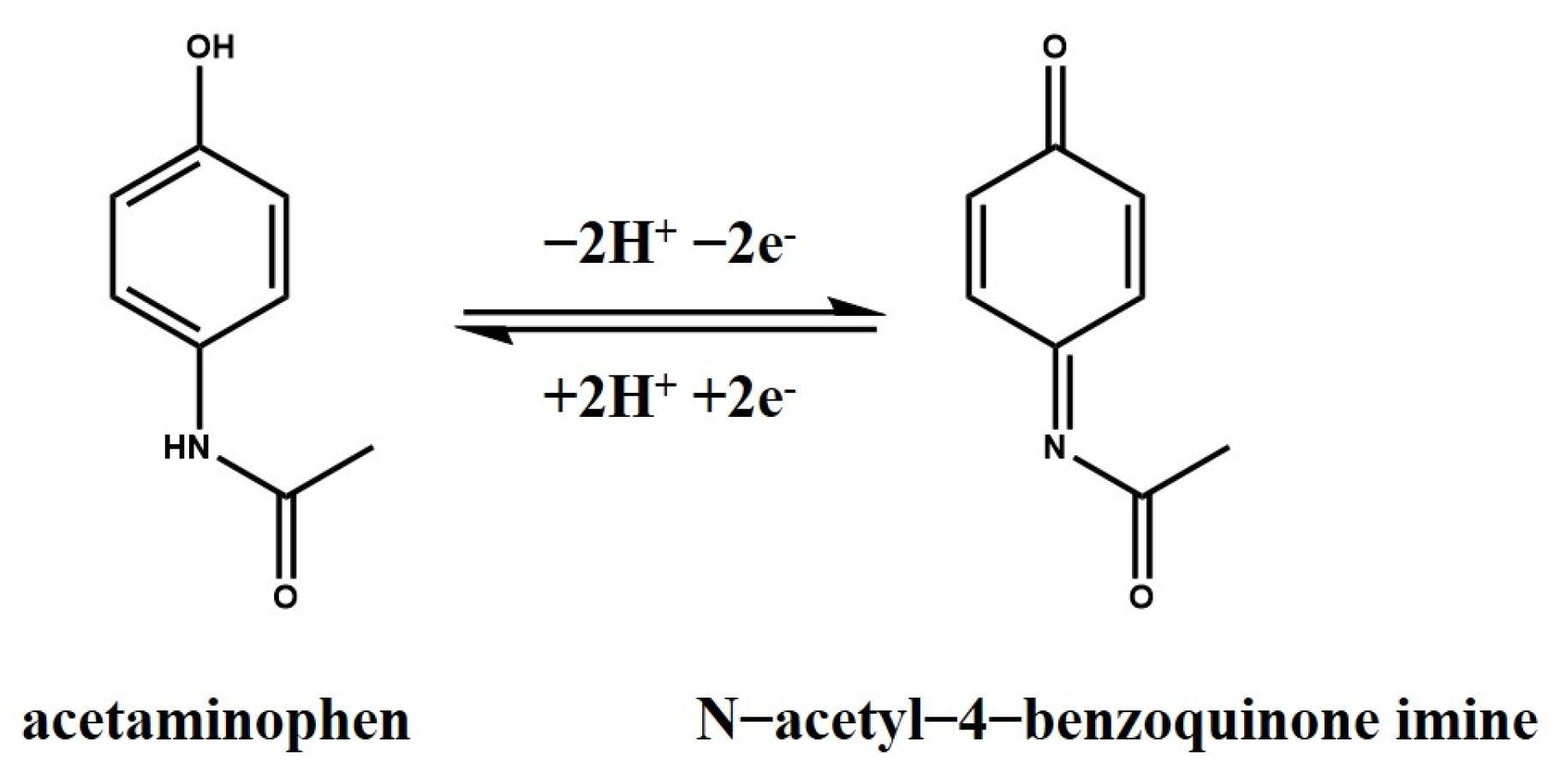
3.2. Electrochemical Sensing Performance
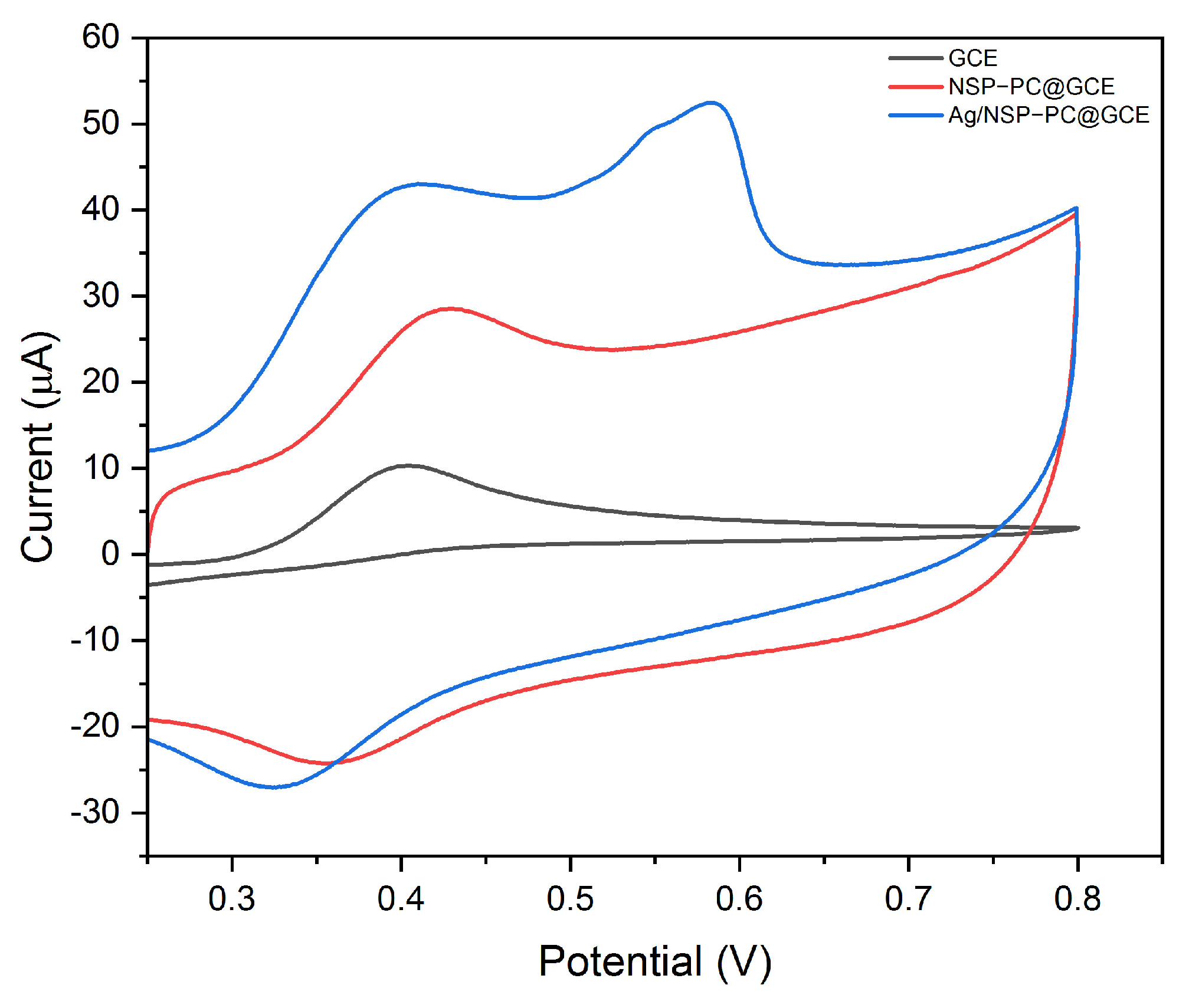
3.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
3.2.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.2.3. APAP Concentration Dependence
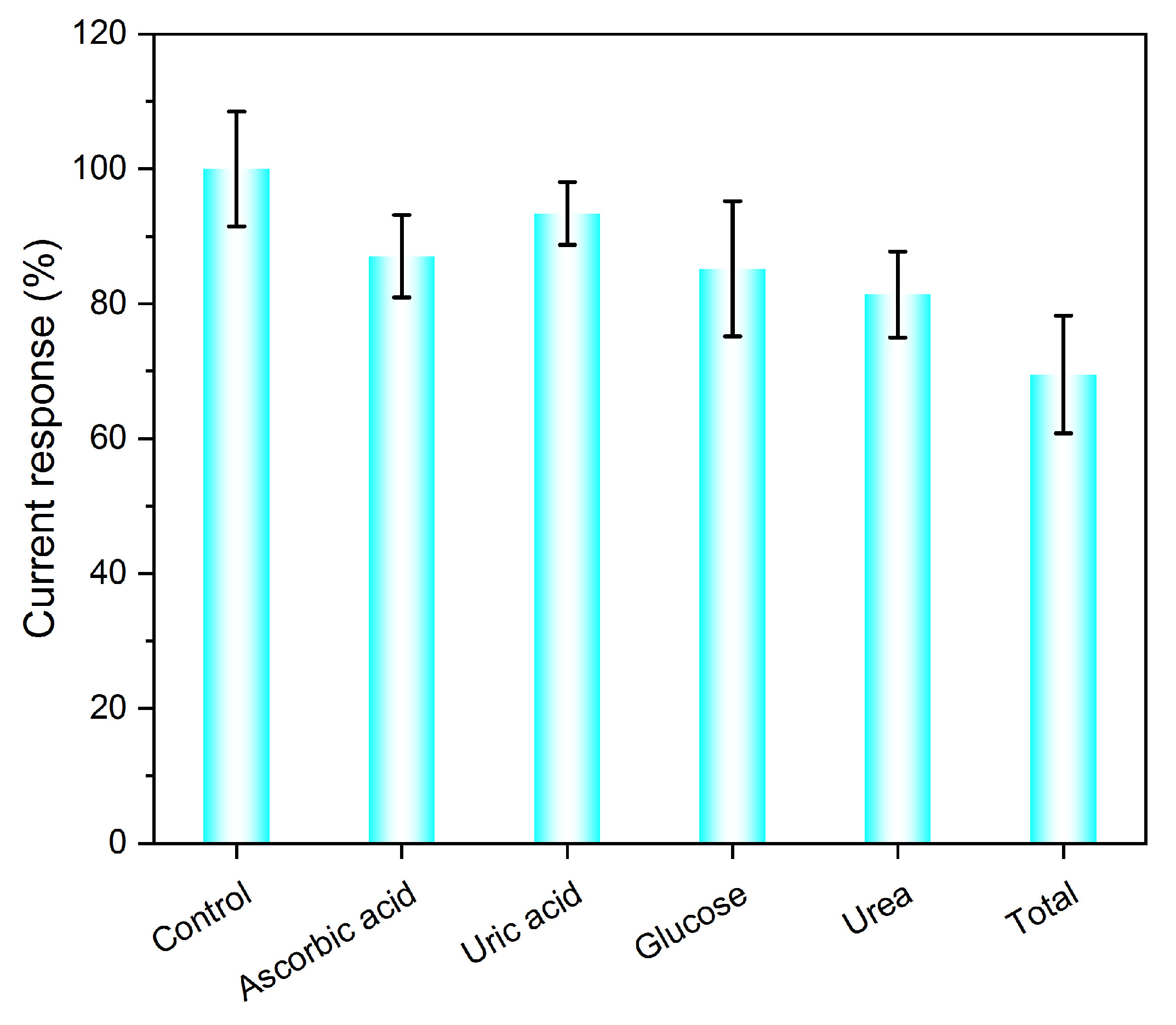
3.2.4. Anti-Interference
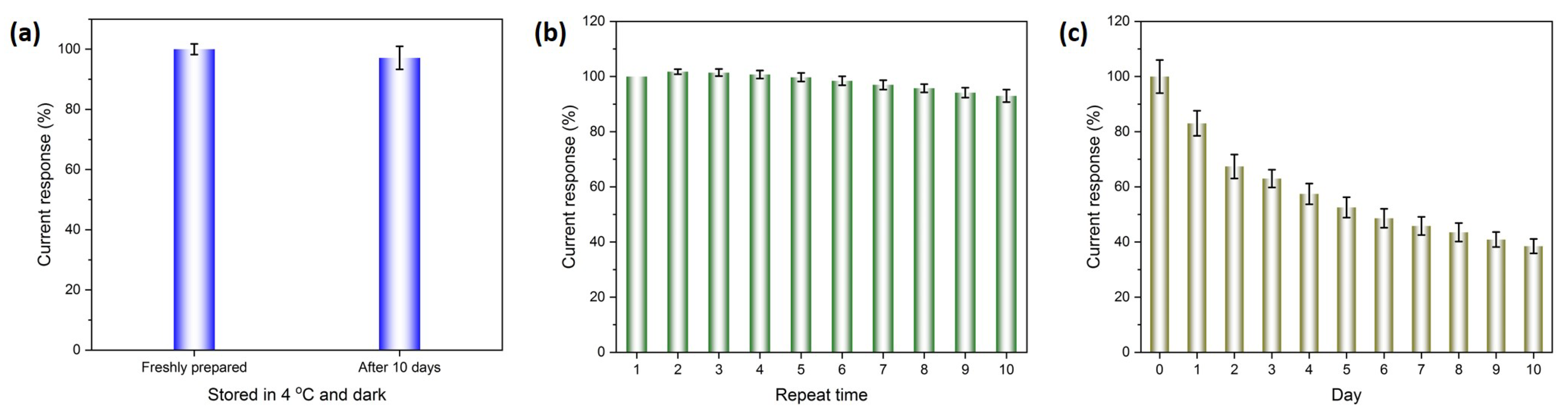
3.2.5. Stability and Repeatability, Real Sample Measurement, and Comparison with Other Works
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Ueno, H.; Esch, M.B. Body-in-a-Cube: A microphysiological system for multi-tissue co-culture with near-physiological amounts of blood surrogate. Microphysiol. Syst. 2020, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.M.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.; Hooch Antink, W.; Kim, D.; Piao, Y. Novel two-step activation of biomass-derived carbon for highly sensitive electrochemical determination of acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.U.; Qin, Y.; Catalano, M.; Wang, L.; Kim, M.J.; Howlader, M.M.R.; Hu, N.-X.; Deen, M.J. Tailoring MWCNTs and β-Cyclodextrin for Sensitive Detection of Acetaminophen and Estrogen. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 21411–21427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smarr, M.M.; Grantz, K.L.; Sundaram, R.; Maisog, J.M.; Honda, M.; Kannan, K.; Buck Louis, G.M. Urinary paracetamol and time-to-pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labib, M.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Electrochemical Methods for the Analysis of Clinically Relevant Biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9001–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Kung, C.-W.; Wei, H.-Y.; Boopathi, K.M.; Chu, C.-W.; Ho, K.-C. A high performance electrochemical sensor for acetaminophen based on a rGO–PEDOT nanotube composite modified electrode. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7229–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmandoust, M.; Li, G.; Erk, N. Biomass-Derived Carbon Materials as an Emerging Platform for Advanced Electrochemical Sensors: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 62, 4628–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shen, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Xia, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Biomass-Derived Carbon Materials: Controllable Preparation and Versatile Applications. Small 2021, 17, 2008079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Ma, C.; Bai, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, M. Biomass derived worm-like nitrogen-doped-carbon framework for trace determination of toxic heavy metal lead (II). Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Xu, F.; Chen, S.; Jia, J.; Tan, H.; Hou, H.; Song, Y. Electrochemical Sensing and Biosensing Platform Based on Biomass-Derived Macroporous Carbon Materials. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Koventhan, C.; Chen, S.-M. Copper-palladium alloy nanoparticles immobilized over porous carbon for voltammetric determination of dimetridazole. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 931, 167474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, H.; Wei, K.; Shi, C.; Sun, M.; Duan, R.; Wang, X.; et al. DFT-assisted design inspired by loofah-derived biomass carbon decorated CoFe-CoFe2O4 conjugated molecular imprinting strategy for hazardous thiamphenicol analysis in spiked food. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 374, 132852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malode, S.J.; Shanbhag, M.M.; Kumari, R.; Dkhar, D.S.; Chandra, P.; Shetti, N.P. Biomass-derived carbon nanomaterials for sensor applications. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 222, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Amin, H.M.A. Silver nanoparticles modified electrodes for electroanalysis: An updated review and a perspective. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, H.; Liang, H.; Qiang, W.; Xu, D. Disposable Electrochemical Aptasensor Array by Using In Situ DNA Hybridization Inducing Silver Nanoparticles Aggregate for Signal Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chandra, P.; Shim, Y.-B. Ultrasensitive and Selective Electrochemical Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Based on a Hydrazine–Au Nanoparticle–Aptamer Bioconjugate. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Yang, D.; Wei, P.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J. One-Step Electrodeposition of Silver Nanostructures on 2D/3D Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-67: Comparison and Application in Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41960–41968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, C.; Wang, F.; Jing, N.; Jiang, G. Co/Co3O4 Nanoparticles Coupled with Hollow Nanoporous Carbon Polyhedrons for the Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18582–18592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanthappa, M.; Duraisamy, V.; Arumugam, P.; Senthil Kumar, S.M. Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, Uric Acid, and Acetaminophen on N, P-Doped Hollow Mesoporous Carbon Nanospheres. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 18417–18426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, B.G.; Khairy, M.; Rashwan, F.A.; Banks, C.E. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Acetaminophen and Isoniazid (Hepatotoxicity-Related Drugs) Utilizing Bismuth Oxide Nanorod Modified Screen-Printed Electrochemical Sensing Platforms. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2170–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mamat, X.; Aisa, H.A. Determination of aflatoxin B1 by biomass derived porous carbon modified electrode with molecularly imprinted polymer. Electroanalysis 2023, e202200371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalikun, N.; Mamat, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, P.; Hu, G. N, S, P-Triple Doped Porous Carbon as an Improved Electrochemical Sensor for Metronidazole Determination. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B1131–B1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yayalikun, N.; Mamat, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, P.; Xin, X.; Hu, G. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Chloramphenicol Based on Biomass Derived Porous Carbon. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2020, 12, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandke, M.V.; Han, S.-H.; Pathan, H.M. Growth of silver dendritic nanostructuresvia electrochemical route. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, A.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, Q. Ultrasensitive Immunoassay of Proteins Based on Gold Label/Silver Staining, Galvanic Replacement Reaction Enlargement, and In Situ Microliter-Droplet Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, O.S.; Zamborini, F.P. Size-Dependent Electrochemical Oxidation of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kulyk, B.; Pereira, S.O.; Fernandes, A.J.S.; Fortunato, E.; Costa, F.M.; Santos, N.F. Laser-induced graphene from paper for non-enzymatic uric acid electrochemical sensing in urine. Carbon 2022, 197, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shachar, R.; Chen, Y.; Luo, S.; Hartman, C.; Reed, M.; Nijhout, H.F. The biochemistry of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and rescue: A mathematical model. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2012, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food & Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/dont-double-acetaminophen (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Bhat, S.A.; Rather, M.A.; Pandit, S.A.; Ingole, P.P.; Bhat, M.A. Sensitive electrochemical sensing of acetaminophen and hydroquinone over single-pot synthesized stabilizer free Ag/Ag-oxide-graphene nanocomposites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 783, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipekci, H.H.; Ozcan, M.; Turkyilmaz, B.G.; Uzunoglu, A. Ni/NiO/Ni–B/graphene heterostructure-modified electrodes and their electrochemical activities towards acetaminophen. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Lu, W.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, L.; Cao, X.; Jia, J.; Wu, H. Ni2P Nanosheets: A High Catalytic Activity Platform for Electrochemical Detection of Acetaminophen. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Sharma, S.; Singh, R.; Sharma, K.; Majhi, S.; Guin, D.; Tripathi, C.S.P. Barium Titanate Nanocubes as a Dual Electrochemical Sensor for Detection of Dopamine and Acetaminophen. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 067512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, C.; Sha, J.; Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Li, M.; Jiao, T. Ferrocene-reduced graphene oxide-polyoxometalates based ternary nanocomposites as electrochemical detection for acetaminophen. Talanta 2021, 235, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Dong, J.; Wen, B.; Wen, X.; Li, J. Facile Synthesis of Hollow Fe3O4-rGO Nanocomposites for the Electrochemical Detection of Acetaminophen. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Species | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine 1 | APAP | 200 | 211 ± 27 | 106 ± 14 |
| Urine 2 | APAP | 200 | 201 ± 35 | 101 ± 18 |
| Urine 3 | APAP | 400 | 392 ± 40 | 98 ± 10 |
| Urine 4 | APAP | 300 | 261 ± 39 | 87 ± 13 |
| Electrode Material | Sensing Range (μM) | Limit of Detection (μM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnCl2-KOH activated kelp carbon | 0.01–20 | 0.004 | [2] |
| hollow nanoporous carbon polyhedrons embedded with Co/Co3O4 nanoparticles | 0.025−50 | 0.0083 | [18] |
| N, P-doped hollow mesoporous carbon nanospheres | 5–1200 | 0.02 | [19] |
| Bismuth oxide nanostructures | 0.5–1250 | 0.03 | [20] |
| Ag/Ag-oxide-graphene | 9.9–64.9 | 0.022 | [31] |
| Ni/NiO/Ni–B/graphene heterostructure | 10–2500 | 14 | [32] |
| Ni2P nanosheets | 0.5–4500 | 0.107 | [33] |
| Barium titanate nanocubes | 10–100 | 0.23 | [34] |
| Ferrocene-reduced graphene oxide-polyoxometalates nanocomposites | 1–1000 | 0.013 | [35] |
| Hollow Fe3O4-rGO nanocomposites | 0.5–500 | 0.11 | [36] |
| Ag/NSP–PC | 0.061–500 | 0.033 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamat, X.; Aisa, H.A.; Chen, L. Nanostructured N, S, and P-Doped Elaeagnus Angustifolia Gum-Derived Porous Carbon with Electrodeposited Silver for Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13091571
Mamat X, Aisa HA, Chen L. Nanostructured N, S, and P-Doped Elaeagnus Angustifolia Gum-Derived Porous Carbon with Electrodeposited Silver for Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(9):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13091571
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamat, Xamxikamar, Haji Akber Aisa, and Longyi Chen. 2023. "Nanostructured N, S, and P-Doped Elaeagnus Angustifolia Gum-Derived Porous Carbon with Electrodeposited Silver for Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen" Nanomaterials 13, no. 9: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13091571
APA StyleMamat, X., Aisa, H. A., & Chen, L. (2023). Nanostructured N, S, and P-Doped Elaeagnus Angustifolia Gum-Derived Porous Carbon with Electrodeposited Silver for Enhanced Electrochemical Sensing of Acetaminophen. Nanomaterials, 13(9), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13091571






