Enhanced Power Generation by Piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO Nanocomposite Thin Film
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
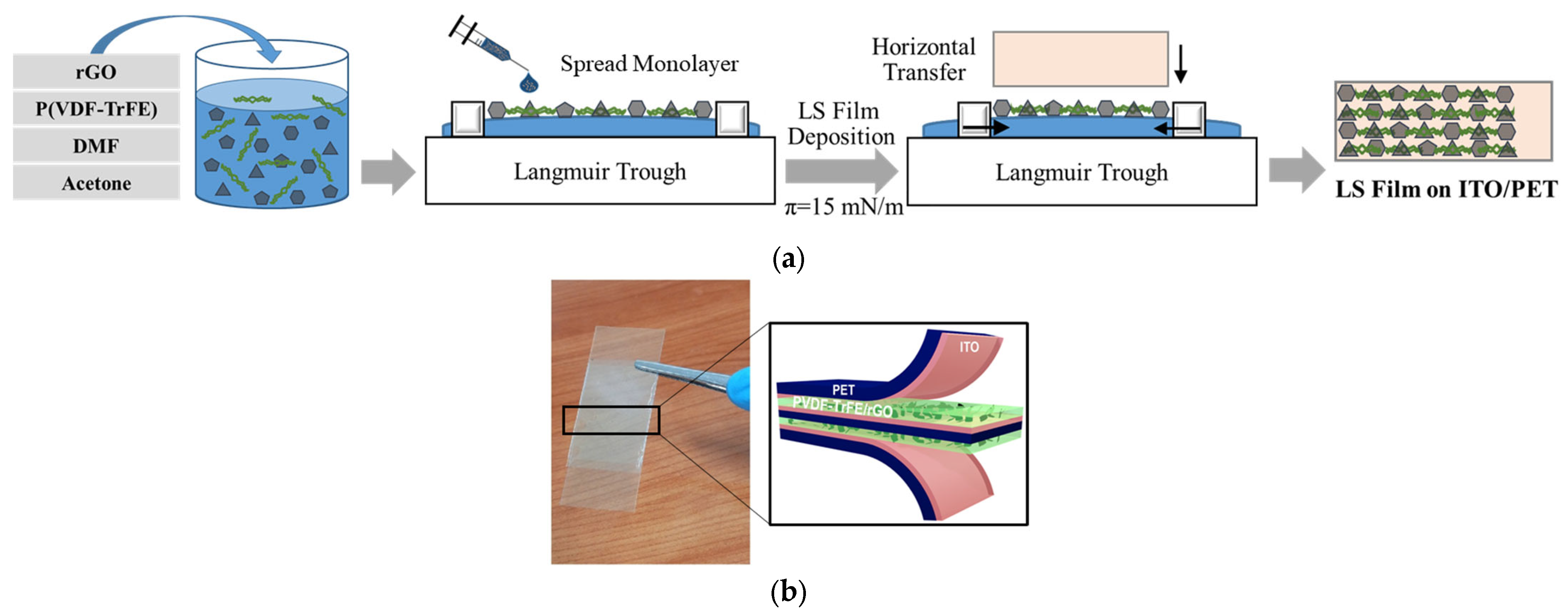
2.2. Preparation of P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO Solution and LS Thin Film
2.3. Fabrication of PENG Device
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Nanocomposite Monolayer
3.2. Morphology Analysis by SEM
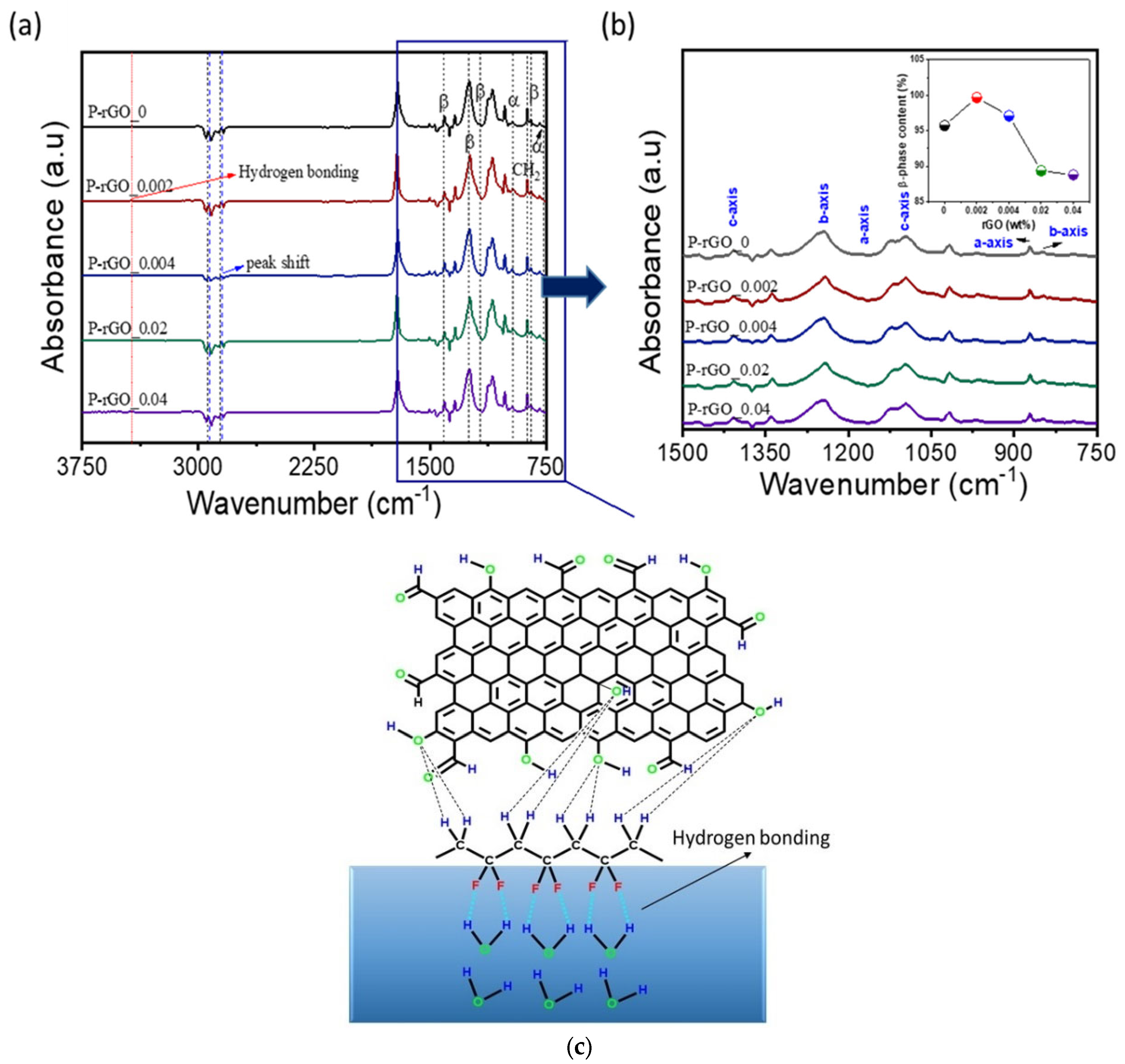
3.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.4. XRD Analysis
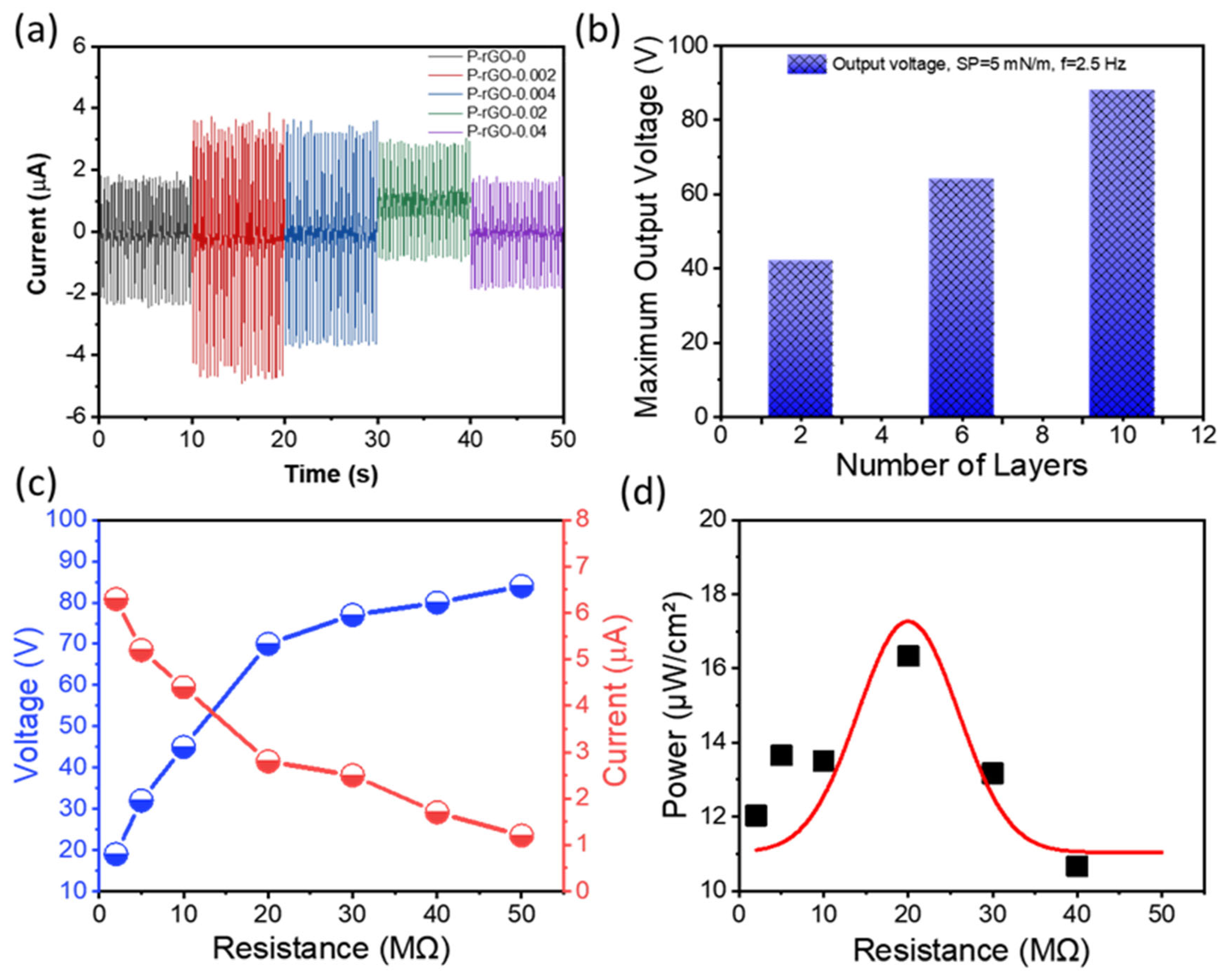
3.5. Piezoelectric Modulus and Dielectric Properties
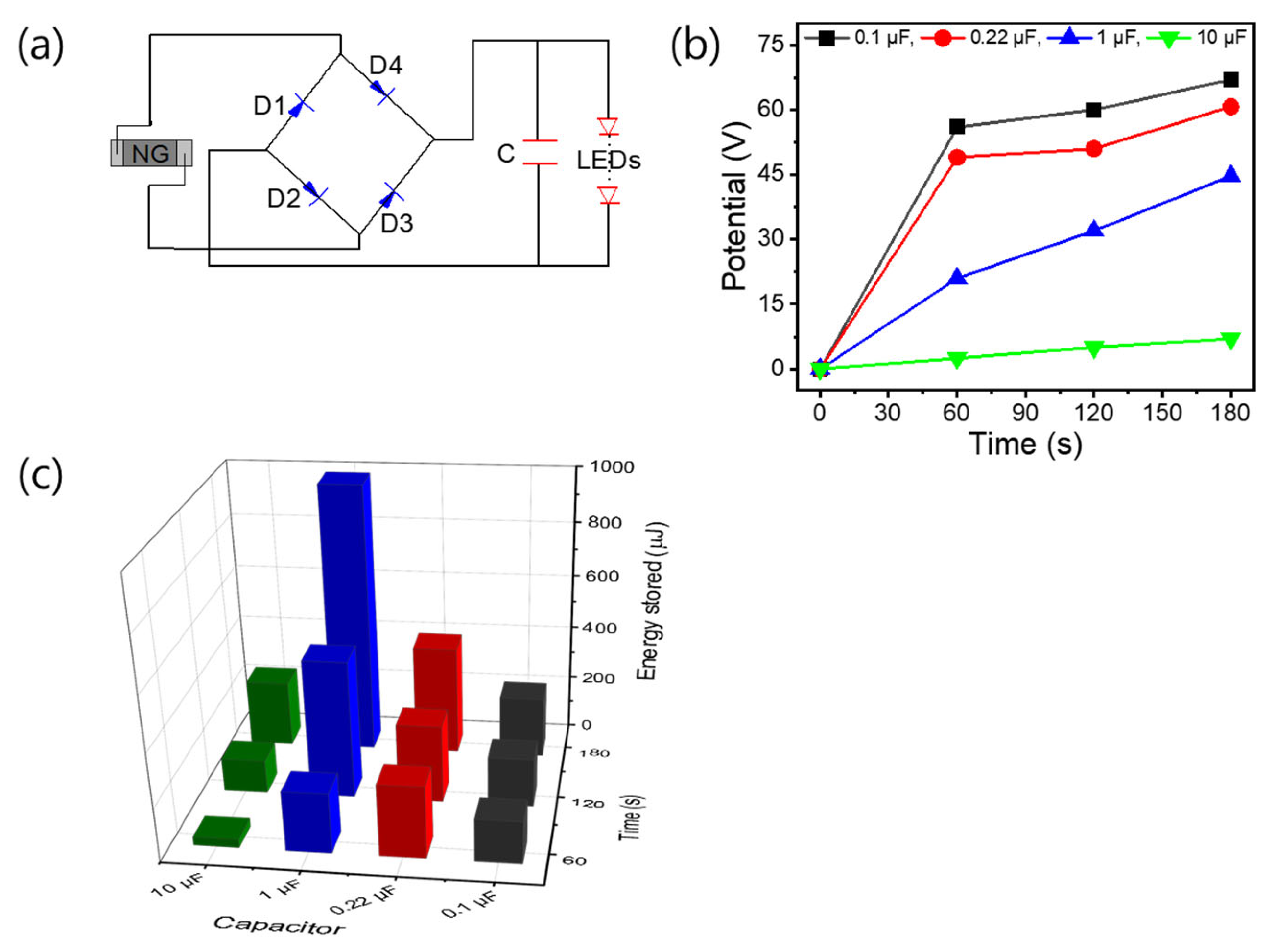
3.6. Energy Harvesting
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, L.; Todaro, M.T.; Guido, F.; Mastronardi, V.; Desmaele, D.; Qualtieri, A.; Giannini, C.; Sibillano, T.; De Vittorio, M. Flexible Piezoelectric Energy-Harvesting Exploiting Biocompatible AlN Thin Films Grown onto Spin-Coated Polyimide Layers. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 5203–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Takahashi, Y. Factors governing ferroelectric switching characteristics of thin VDF/TrFE copolymer films. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2006, 13, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P. Emerging artificial intelligence in piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Q. Preparation and Property Enhancement of Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride)(PVDF)/Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) Composite Piezoelectric Films. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 6426–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, U.; Habibur, R.M.; Sheeraz, M.; Kim, H.C. Realization of self-poled, high performance, flexible piezoelectric energy harvester by employing PDMS-rGO as sandwich layer between P (VDF-TrFE)-PMN-PT composite sheets. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 150, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.J.; Choi, C.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Spinks, G.M.; Lima, M.D.; Baughman, R.H.; Kim, S.J. Flexible, stretchable and weavable piezoelectric fiber. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yuan, W.; Hu, N.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Qiu, J.; Ying, J.; Li, Y. Improved piezoelectricity of PVDF-HFP/carbon black composite films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 135302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Closson, A.B.; Hao, N.; Oglesby, M.; Escobar, G.P.; Fu, S.; Han, X.; Wen, C.; et al. Tunable Buckled Beams with Mesoporous PVDF-TrFE/SWCNT Composite Film for Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33516–33522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Mondal, S.; Das, P.; Bhawal, P.; Das, T.K.; Ghosh, S.; Remanan, S.; Das, N.C. An Insight Into the Physico-Mechanical Signatures of Silylated Graphene Oxide in Poly(ethylene methyl acrylate) Copolymeric Thermoplastic Matrix. Macromol. Res. 2019, 27, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remanan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Das, T.K.; Das, N.C. Nano to microblend formation in poly (ethylene-co-methyl acrylate)/poly (vinylidene fluoride) blend and investigation of its anomalies in rheological properties. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 23, 100487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilla, T.; Bhadra, S.; Yao, D.; Kim, N.H.; Bose, S.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene based polymer composites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1350–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shao, Z.-G.; Hao, Q.; Zhao, H. Intrinsic carrier mobility of a single-layer graphene covalently bonded with single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 233701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Shen, B.; Lv, F.; Chu, P.K. Fabrication and dielectric properties of oriented polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposites incorporated with graphene nanosheets. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibur, R.M.; Yaqoob, U.; Muhammad, S.; Uddin, A.S.M.I.; Kim, H.C. The effect of RGO on dielectric and energy harvesting properties of P(VDF-TrFE) matrix by optimizing electroactive β phase without traditional polling process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 215, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, V.; Jain, Y.; Kumari, M.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Sachdev, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Oxide (GO) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) for Gas Sensing Application. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 376, 1700006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Pu, H.; Chen, J. Graphene oxide and its reduction: Modeling and experimental progress. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2643–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Yousefi, A. Analysis method: FTIR studies of β-phase crystal formation in stretched PVDF films. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Park, J.B.; Kim, B.-S.; Lee, J.; Hong, W.-K.; Park, I.-K.; Jang, J.E.; Sohn, J.I.; Cha, S.; Kim, J.M. Enhanced energy harvesting based on surface morphology engineering of P (VDF-TrFE) film. Nano Energy 2015, 16, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, N.; Garg, A.; Gupta, R.K. Engineered thiol anchored Au-BaTiO3/PVDF polymer nanocomposite as efficient dielectric for electronic applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 158–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-I. Solvent-controlled crystalline beta-phase formation in electrospun P(VDF-TrFE) fibers for enhanced piezoelectric energy harvesting. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 71109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, N.; Czerw, R.; Xing, S.; Iyer, P.; Carroll, D.L. Properties of polyvinylidene difluoride− carbon nanotube blends. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, L.; Hu, N.; Qiu, J.; Chang, C.; Atobe, S.; Fukunaga, H.; Watanabe, T.; Liu, Y.; Ning, H. Evaluation of piezoelectric property of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)–poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7250–7255. [Google Scholar]
- Karan, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Khatua, B.B. Self-powered flexible Fe-doped RGO/PVDF nanocomposite: An excellent material for a piezoelectric energy harvester. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10655–10666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karan, S.K.; Bera, R.; Paria, S.; Das, A.K.; Maiti, S.; Maitra, A.; Khatua, B.B. An approach to design highly durable piezoelectric nanogenerator based on self-poled PVDF/AlO-rGO flexible nanocomposite with high power density and energy conversion efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1601016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yao, K.; Tay, F.E.H.; Liow, C.L. Ferroelectric poly (vinylidene fluoride) thin films on Si substrate with the β phase promoted by hydrated magnesium nitrate. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Caseli, L.; Ariga, K. The past and the future of Langmuir and Langmuir–Blodgett films. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6459–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Yao, K.; Tay, F.E.H.; Kumar, A.; Zeng, K. Self-polarized ferroelectric PVDF homopolymer ultra-thin films derived from Langmuir–Blodgett deposition. Polymer 2012, 53, 1404–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Van Breemen, A.J.; Shen, J.; Gao, Q.; Ivan, M.G.; Reimann, K.; Meinders, E.R.; Gelinck, G.H. Multilevel information storage in ferroelectric polymer memories. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Bae, I.; Shin, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Huh, J.; Park, S.-M.; Kim, H.-C.; Park, C. Nonvolatile polymer memory with nanoconfinement of ferroelectric crystals. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavanasi, V.; Kumar, V.; Parida, K.; Wang, J.; Lee, P.S. Enhanced Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Performance of Flexible PVDF-TrFE Bilayer Films with Graphene Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, M.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kang, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, N.; Cheng, B.; Yang, G. Performance enhancements in poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based piezoelectric nanogenerators for efficient energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 662–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Park, J.-S.; Choi, J.-S.; Kang, D.-Y. π-A isotherms and electrical properties of polyamic acid alkylamine salts (PAAS) Langmuir-Blodgett films. Thin Solid Film. 1996, 284, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.; Pei, J. Influence of PZT piezoelectric ceramics on the structure and electric properties of piezoelectric lead zirconate titanate/poly (vinylidene fluoride) composites. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X. A critical analysis of the a, b and c phases in poly (vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tashiro, K.; Itoh, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Tadokoro, H. Polarized Raman spectra and LO-TO splitting of poly (vinylidene fluoride) crystal form I. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Fabrication, characterization, properties and theoretical analysis of ceramic/ PVDF composite flexible films with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 2, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamankar, N.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A.A.; Rashidi, A.; Golestanifard, F. An experimental model for predicting the piezo and dielectric constant of PVDF-PZT nanocomposite fibers with 0–3 and 1–3 connectivity. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 23567–23581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Rault, F.; Lewandowski, M.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Salaün, F. Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement. Polymers 2021, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, N.; Yoda, S.; Sakai, W. Infrared spectra and ferro-electricity of ultra-thin films of vinylidene fluoride and trifluoroethylene copolymer. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, X.; Shen, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Kim, J.-K. Exceptional dielectric properties of chlorine-doped graphene oxide/poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. Carbon 2015, 89, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ding, Z.; Fei, L.; Xiang, Y. Wearable piezoelectric nanogenerators based on reduced graphene oxide and in situ polarization-enhanced PVDF-TrFE films. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 6401–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.H.; Yaqoob, U.; Kim, H.C. The effects of conductive nano fillers alignment on the dielectric properties of copolymer matrix. Adv. Manuf. Polym. Compos. Sci. 2019, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, R.; Gupta, S.; Fatma, B.; Prateek; Gupta, R.K.; Garg, A. Milli-watt power harvesting from dual triboelectric and piezoelectric effects of multifunctional green and robust reduced graphene oxide/P (VDF-TrFE) composite flexible films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38177–38189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Lv, C.; Jing, Y.; Chen, F.; Fu, Q. Fabrication of electrospun PVDF nanofibers with higher content of polar β phase and smaller diameter by adding a small amount of dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium chloride. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 35, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongun, M.Z.; Oguzlar, S.; Doluel, E.C.; Kartal, U.; Yurddaskal, M. Enhancement of piezoelectric energy-harvesting capacity of electrospun β-PVDF nanogenerators by adding GO and rGO. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 1960–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Paralı, L.; Şan, O. Fabrication and vibrational energy harvesting characterization of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator (PEN) based on PVDF/PZT. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Jiang, P.; Huang, X. Role of reduced graphene oxide in dielectric enhancement of ferroelectric polymers composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Lu, X.; Chao, D.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. Graphene-based composite materials with high dielectric permittivity via an in situ reduction method. Phys. Status Solidi A 2011, 208, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharme, S.; Reece, T.J.; Othon, C.M.; Rannow, R.K. Ferroelectric polymer Langmuir-Blodgett films for nonvolatile memory applications. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2005, 5, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maria Joseph Raj, N.P.; Alluri, N.R.; Khandelwal, G.; Kim, S.-J. Lead-free piezoelectric nanogenerator using lightweight composite films for harnessing biomechanical energy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 161, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jing, M.; Liu, Y.; Ning, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, L.; Hu, N.; Liu, L. Power generation by PVDF-TrFE/graphene nanocomposite films. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 164, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | P-rGO-0 | P-rGO-0.002 | P-rGO-0.004 | P-rGO-0.02 | P-rGO-0.04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (cm2) at π = 5 mN/m | 79.6 | 86.8 | 92.6 | 99.1 | 106.9 |
| A (cm2) at π = 15 mN/m | 69.7 | 82.8 | 87.5 | 92.9 | 102.4 |
| Absorption Peak (cm−1) | Vibrational Modes | Phase | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 761 | bCH2 | α | [35] |
| 846 | 𝜈σ CF2 + 𝜈σCC | β | [36,37] |
| 880 | rCH2 − 𝜈aCF2 − rCF2 | β | [36,37] |
| 1095 | 𝜈aCC + wCH2 − wCF2 | β | [36,38] |
| 1177 | 𝜈aCF2 − rCF2 | β | [36,37] |
| 1408 | wCH2 − 𝜈aCC | β | [36,37] |
| Sample | Percentage Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|
| P-rGO-0 | 35 |
| P-rGO-0.002 | 56 |
| P-rGO-0.004 | 36 |
| P-rGO-0.02 | 29 |
| P-rGO-0.04 | 25 |
| Sample | β-Phase (%) | Crystallinity (%) | d33 (pC/N) | Dielectric Constant (ε) | Dielectric Loss (tan δ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-rGO-0 | 95 | 35 | 55.8 | 17 | 2.4 |
| P-rGO-0.002 | 98 | 56 | 98 | 21 | 1.1 |
| P-rGO-0.004 | 96 | 36 | 69.4 | 20 | 1.6 |
| P-rGO-0.02 | 89 | 29 | 39.6 | 07 | 2.9 |
| P-rGO-0.04 | 87 | 25 | 39.6 | 05 | 3.2 |
| PENG | Coating Method | Form | Size (cm2) | Peak-Peak VOC (V) | Year | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Filler Content (wt%) | ||||||
| P(VDF-TrFE)/Gr | 0.15 | solution casting | film | 0.1 × 0.3 | 12.43 | 2019 | [52] |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO | 0.5 | spin coating | film | 2.5 × 2.5 | 89.7 | 2019 | [44] |
| PVDF/rGO | 0.8 | electrospinning | nanofiber | 4 × 5 | 4.38 | 2020 | [46] |
| PVDF/GO | 0.4 | electrospinning | nanofiber | 4 × 5 | 1.15 | 2020 | [46] |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO | 0.1 | drop casting | sheet | 3 × 2 | 2.40 | 2018 | [43] |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO | 0.1 | scrap coating | film | 4 × 5 | 8.32 | 2019 | [42] |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/GO | - | drop casting | film | - | 4.30 | 2015 | [31] |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO | 0.002 | LS depsition | LS film | 8 × 2.5 | 88 | 2023 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaseen, H.M.A.; Park, S. Enhanced Power Generation by Piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO Nanocomposite Thin Film. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050860
Yaseen HMA, Park S. Enhanced Power Generation by Piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO Nanocomposite Thin Film. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(5):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050860
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaseen, Hafiz Muhammad Abid, and Sangkwon Park. 2023. "Enhanced Power Generation by Piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO Nanocomposite Thin Film" Nanomaterials 13, no. 5: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050860
APA StyleYaseen, H. M. A., & Park, S. (2023). Enhanced Power Generation by Piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO Nanocomposite Thin Film. Nanomaterials, 13(5), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050860





