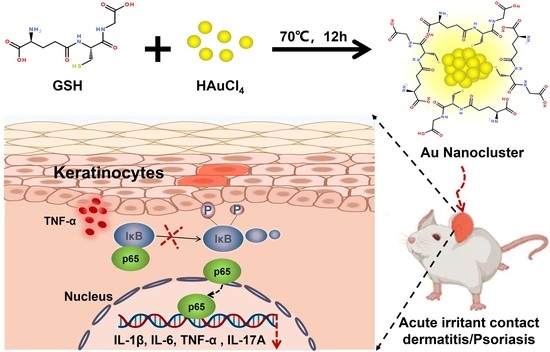
Peptide-Protected Gold Nanoclusters Efficiently Ameliorate Acute Contact Dermatitis and Psoriasis via Repressing the TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-17A Axis in Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
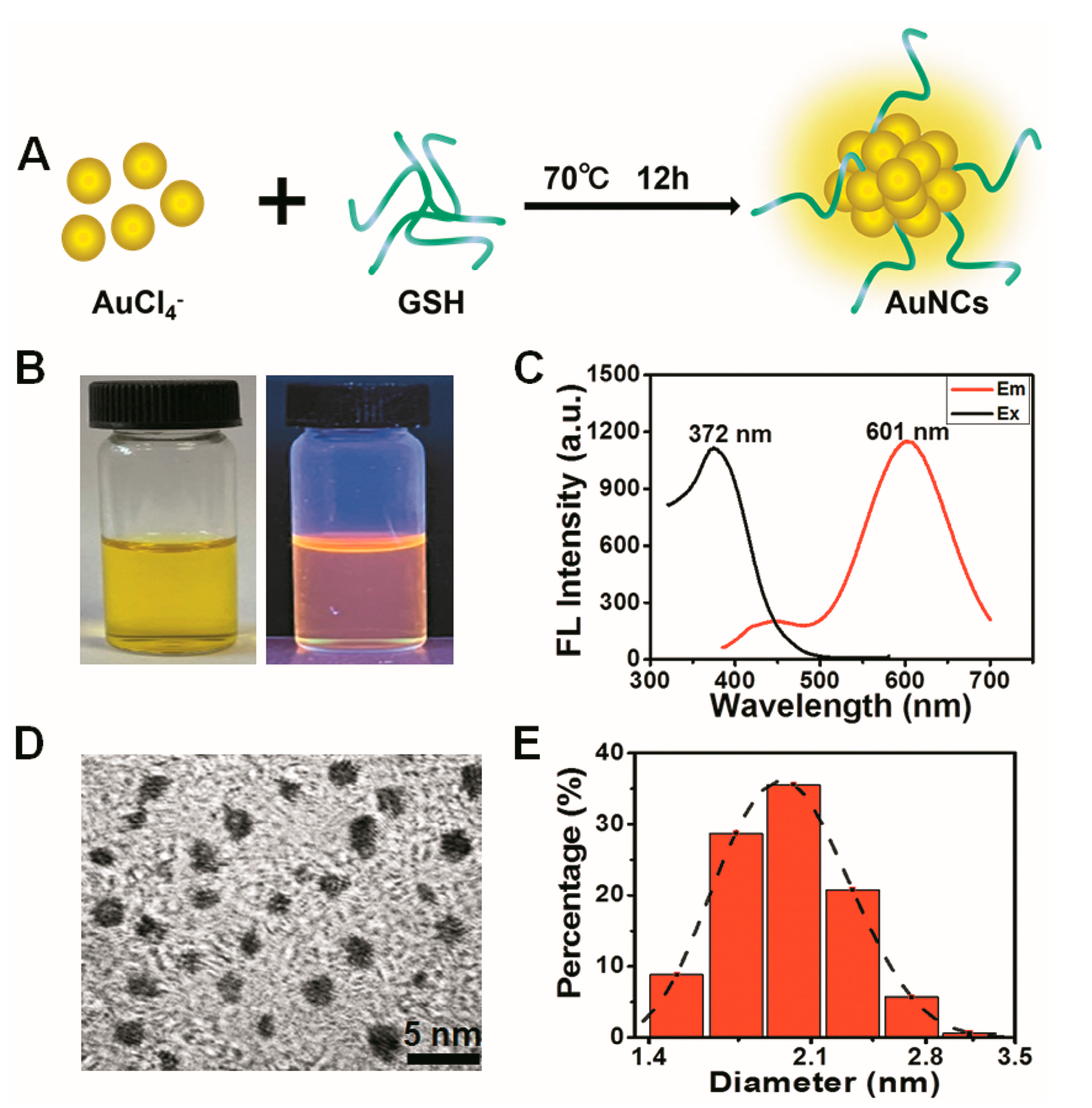
2.2. Synthesis of GSH-Protected AuNCs
2.3. Characterization of the Au Nanoclusters
2.4. Experiments In Vitro
2.4.1. Culture and Treatment of Cells
2.4.2. Cell Viability Assay with Cell Counting Kit-8
2.4.3. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
2.4.4. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.5. Experiments In Vivo
2.5.1. Animals
2.5.2. TPA-Induced Ear Inflammation in the Mice
2.5.3. OXA-Induced Psoriasis-like Mouse Model
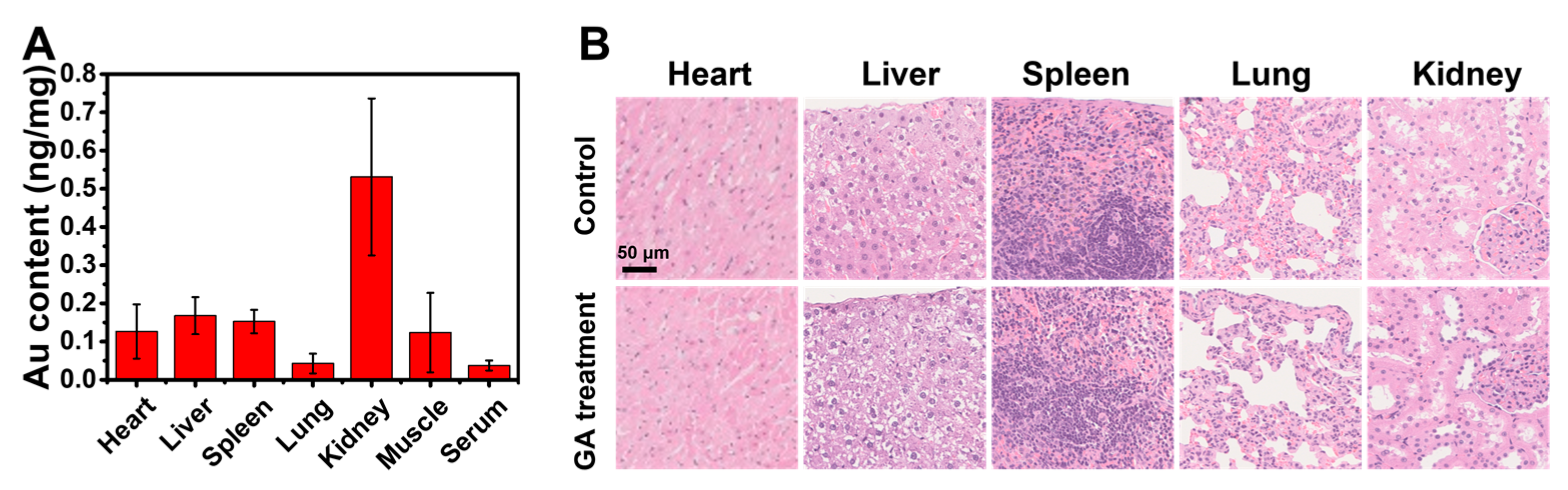
2.5.4. In Vivo Distribution
2.5.5. Histopathological Examination
2.5.6. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.5.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of GSH-Protected Gold Nanoclusters
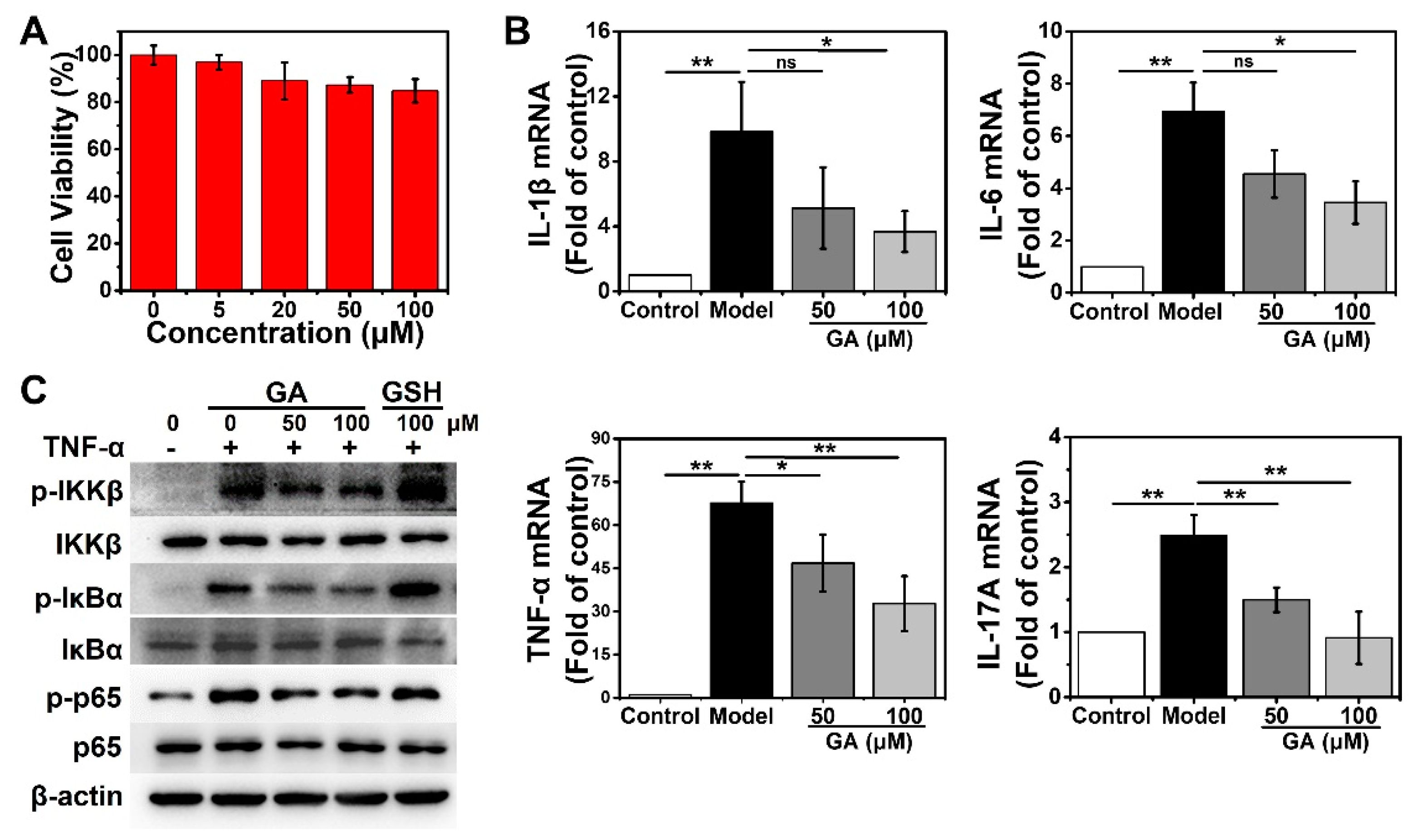
3.2. GA Suppress the TNF-α-Stimulated NF-κB Pathway and the Subsequent Upregulation of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Human Keratinocytes
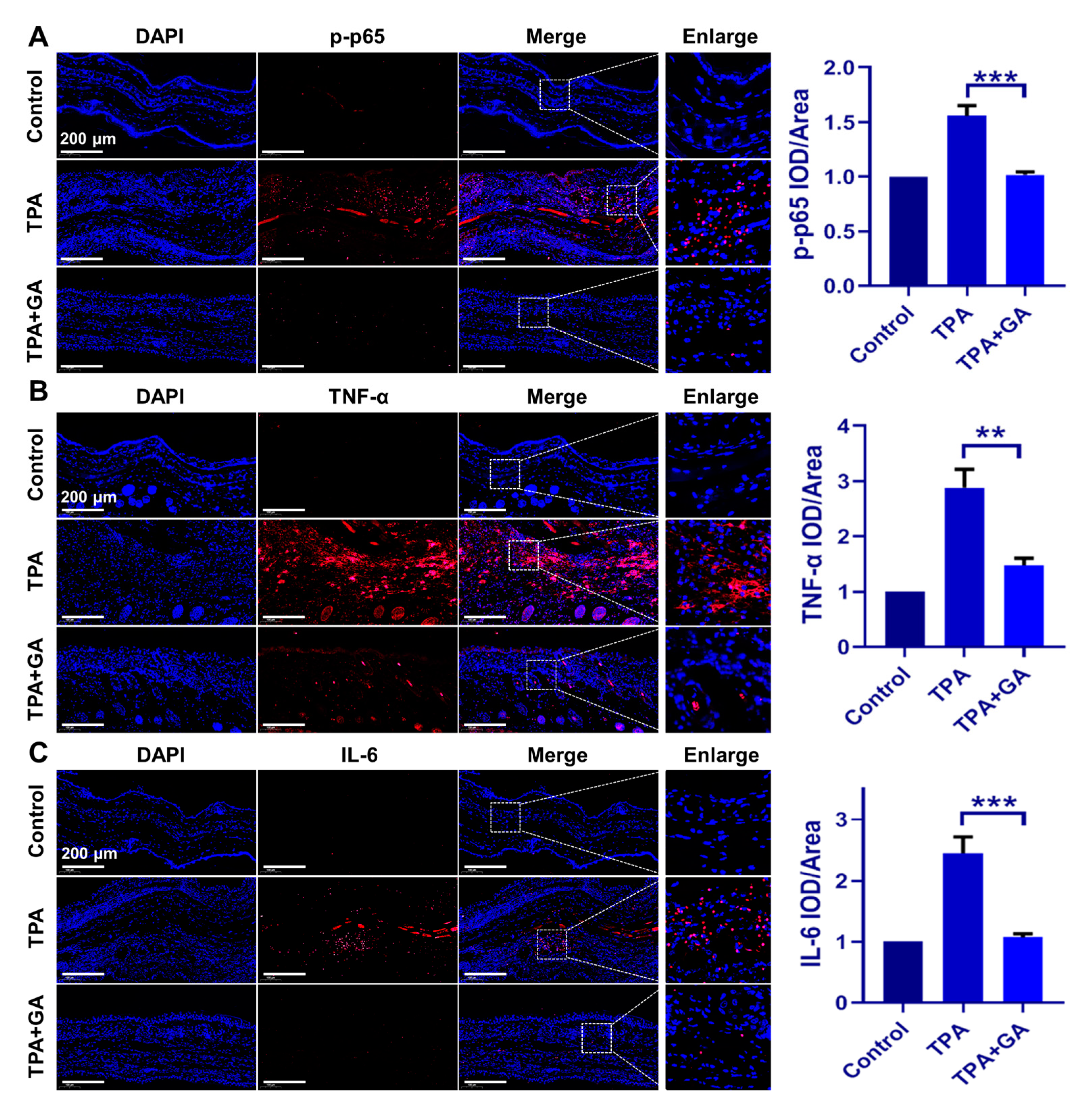
3.3. GA Ameliorate 12-O-Tetradecanoyl Phorbol-13-Acetate (TPA)-Induced Acute Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD) In Vivo
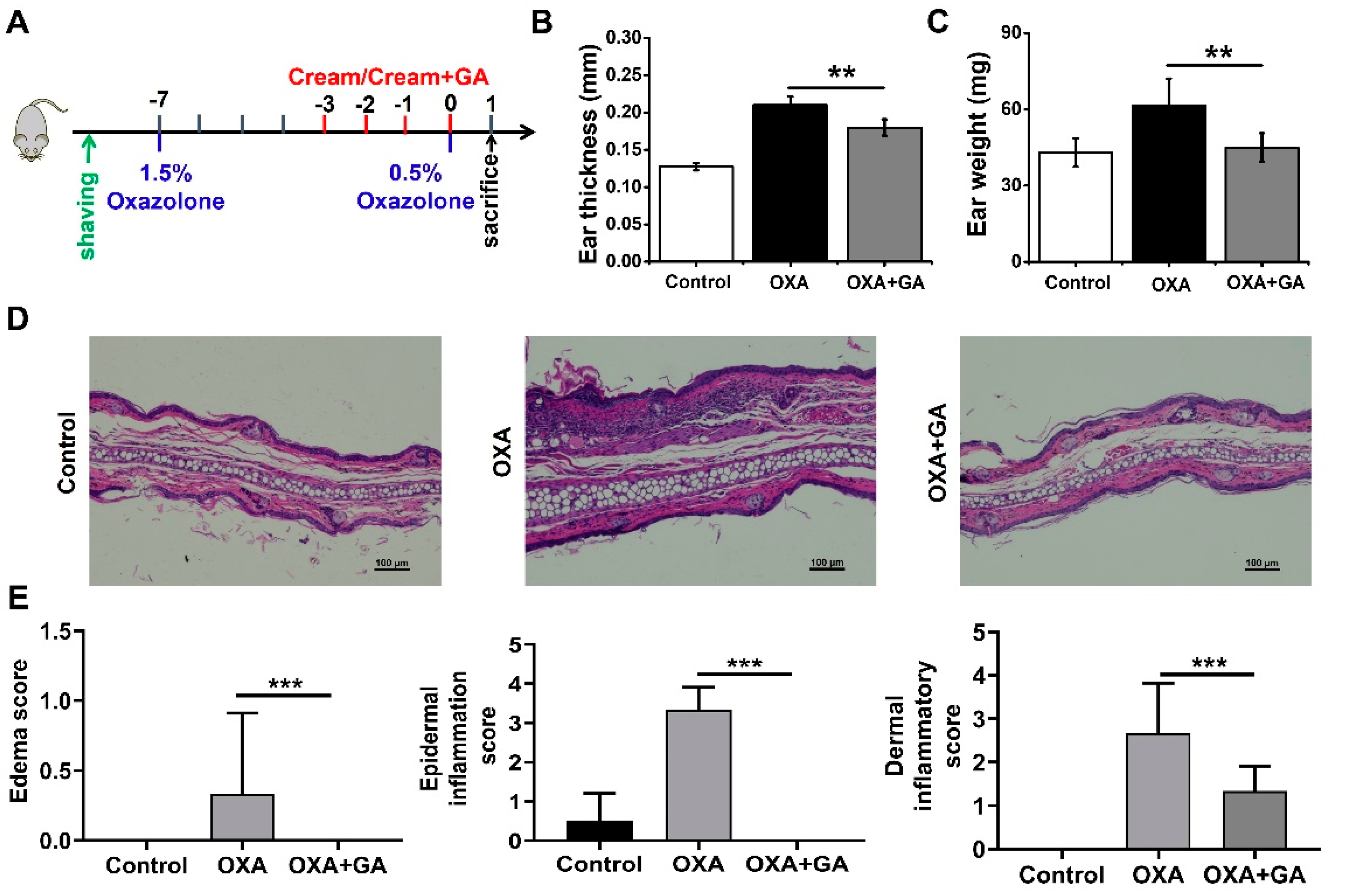
3.4. GA Attenuate Skin Inflammation and Keratinocyte Abnormality in Oxazolone (OXA)-Induced Psoriasis-Like Mice
3.5. GA Ameliorate Skin Inflammation via Repressing the TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-17A Axis in ICD and Psoriasis-Like Mice
3.6. The Topical Cutaneous Administration of GA Possesses High Biosafety
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Significance of Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, J.D.; Zeichner, J.; Alexis, A.; Cohen, D.; Berson, D. Understanding the Epidermal Barrier in Healthy and Compromised Skin: Clinically Relevant Information for the Dermatology Practitioner: Proceedings of an Expert Panel Roundtable Meeting. J. Clin. Aesthet Dermatol. 2016, 9 (Suppl. S1), S2–S8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, M.; Zang, X.; Liu, Q.; Du, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, Z.; Xiang, Z. Luteolin attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice via suppression of inflammation response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I. Gold therapy and its indications in dermatology. A review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 16, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.E.; Papandrea, R.A. Treatment of psoriasis with topical auranofin. Med. J. Aust. 1993, 158, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, K.F.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Leyden, J.J.; Guzzo, C.; Krueger, G.G.; Griffiths, T.W.; Griffiths, C.E. Topical auranofin ointment for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 33, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisler, R. Chrysotherapy: A synoptic review. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfourier, A.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Luciani, N.; Carn, F.; Gazeau, F. Gold-based therapy: From past to present. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22639–22648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.G.; Jr Helm, K.F.; Krueger, G.G.; Griffiths, C.E.; Guzzo, C.A.; Leyden, J.J. Contact dermatitis from topical auranofin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1995, 32 Pt 1, 813–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, R.; Gao, F.; Gao, L.; Gao, X. Peptide protected gold clusters: Chemical synthesis and biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 12095–12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zheng, K.; Xie, J. Engineering ultrasmall water-soluble gold and silver nanoclusters for biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5143–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, N.; Zheng, K.; Xie, J. Bio-NCs--the marriage of ultrasmall metal nanoclusters with biomolecules. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13328–13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Jin, X.; Zhang, S.; Xing, D. RGD peptide-modified fluorescent gold nanoclusters as highly efficient tumor-targeted radiotherapy sensitizers. Biomaterials 2017, 144, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Chen, R.; He, M.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, T. Gold nanoclusters for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Biomaterials 2019, 194, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Yao, Q.; Yuan, X.; Xie, J. Gold nanocluster with AIE: A novel photodynamic antibacterial and deodorant molecule. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lu, C.; Gao, L.; Cao, K.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Yuan, Q. Gold Cluster Capped with a BCL-2 Antagonistic Peptide Exerts Synergistic Antitumor Activity in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 21108–21118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Hou, K.; Hou, K.; Du, Z.; Gao, X.; et al. Gold clusters prevent breast cancer bone metastasis by suppressing tumor-induced osteoclastogenesis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4042–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Gao, F.; Yao, Y.; Cai, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Hou, K.; Gao, L.; Ren, X.; Gao, X. Gold Clusters Prevent Inflammation-Induced Bone Erosion through Inhibiting the Activation of NF-kappaB Pathway. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hou, K.; Yao, Y.; Du, Z.; Lu, C.; Yuan, Q.; Gao, X. Gold Clusters Attenuate Inflammation in Rat Mesangial Cells via Inhibiting the Activation of NF-kappaB Pathway. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, J.; Tran, J.; Chen, X.; Bacacao, B.; Bekale, L.A.; Santa Maria, P.L. Antimicrobial Gold Nanoclusters Eradicate Escherichia coli Biofilms and Are Nontoxic by Oral Administration. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 5275–5286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X. Small Molecule-Capped Gold Nanoclusters for Curing Skin Infections. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35306–35314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Yamamoto, O.; Honda, T. Pathophysiology of psoriasis: A review. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.M.; Bae, S.; Koo, J.E.; Kim, E.S.; Bae, O.N.; Lee, J.Y. Suppression of skin inflammation in keratinocytes and acute/chronic disease models by caffeic acid phenethyl ester. Arch Dermatol Res. 2015, 307, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, P.D.; Jakschitz, T.; Gstir, R.; Stuppner, S.; Perkams, S.; Kruus, M.; Trockenbacher, A.; Griesbeck, C.; Bonn, G.K.; Huber, L.A.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Extract from Soil Algae Chromochloris zofingiensis Targeting TNFR/NF-kappaB Signaling at Different Levels. Cells 2022, 11, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Fukunaga, A.; Ono, R.; Nishigori, C.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin ameliorates cutaneous inflammation by regulating the epithelial production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: The diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedberg, I.M.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Komine, M.; Blumenberg, M. Keratins and the keratinocyte activation cycle. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Xue, F.; Quan, C.; Qu, M.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Fleming, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.-g.; Weichselbaum, R.; et al. A Critical Role of the IL-1beta-IL-1R Signaling Pathway in Skin Inflammation and Psoriasis Pathogenesis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Q. Khasianine ameliorates psoriasis-like skin inflammation and represses TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB axis mediated transactivation of IL-17A and IL-33 in keratinocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 292, 115124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. The Interplay Between Keratinocytes and Immune Cells in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Wei, J.; Lu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhong, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Dai, Z.; Han, L. Genistein suppresses psoriasis-related inflammation through a STAT3-NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism in keratinocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 69, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.P.; Duffin, K.C.; Helms, C.; Ding, J.; Stuart, P.; Goldgar, D.; Gudjonsson, J.; Li, Y.; Tejasvi, T.; Feng, B.-J.; et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Bowcock, A.M.; Krueger, J.G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 2007, 445, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Au, S.C.; Kim, N.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Lizzul, P.F. NF-kappaB: An essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Mao, J.; Cai, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; et al. An Autocrine Circuit of IL-33 in Keratinocytes Is Involved in the Progression of Psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 596–606.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebholz, B.; Haase, I.; Eckelt, B.; Paxian, S.; Flaig, M.J.; Ghoreschi, K.; Nedospasov, S.A.; Mailhammer, R.; Debey-Pascher, S.; Schultze, J.L.; et al. Crosstalk between keratinocytes and adaptive immune cells in an IkappaBalpha protein-mediated inflammatory disease of the skin. Immunity 2007, 27, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, F.; Hashizume, E.; Chan, G.P.; Kamimura, A. Skin-whitening and skin-condition-improving effects of topical oxidized glutathione: A double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial in healthy women. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilokthornsakul, W.; Dhippayom, T.; Dilokthornsakul, P. The clinical effect of glutathione on skin color and other related skin conditions: A systematic review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Wu, D.; Shen, X.; Liu, P.X.; Fan, F.Y.; Fan, S.J. In vivo renal clearance, biodistribution, toxicity of gold nanoclusters. Biomaterials. 2012, 33, 4628–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Yuan, Q.; Cai, P.; Gao, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Yao, Y.; Chai, Z.; Gao, X. Au Clusters Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis with Uniquely Reversing Cartilage/Bone Destruction. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Sun, M.; Ye, L.; Yang, B.; Hu, L.; Man, M.Q. Topical Applications of a Novel Emollient Inhibit Inflammation in Murine Models of Acute Contact Dermatitis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5594646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.N.; Khan, I.; Dey, D.K.; Cho, K.-H.; Hwang, B.S.; Bae, K.B.; Kang, S.C.; Park, J.G. Decursinol angelate ameliorates 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate (TPA) -induced NF-kappaB activation on mice ears by inhibiting exaggerated inflammatory cell infiltration, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brembilla, N.C.; Senra, L.; Boehncke, W.H. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Psoriasis: IL-17A and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Meng, C.; Li, Y.; Xia, D.; Lu, C.; Lai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, K.; Gao, X.; Yuan, Q. Peptide-Protected Gold Nanoclusters Efficiently Ameliorate Acute Contact Dermatitis and Psoriasis via Repressing the TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-17A Axis in Keratinocytes. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040662
Liu Y, Meng C, Li Y, Xia D, Lu C, Lai J, Zhang Y, Cao K, Gao X, Yuan Q. Peptide-Protected Gold Nanoclusters Efficiently Ameliorate Acute Contact Dermatitis and Psoriasis via Repressing the TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-17A Axis in Keratinocytes. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(4):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040662
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu, Cong Meng, Yanggege Li, Dongfang Xia, Cao Lu, Jing Lai, Yulu Zhang, Kai Cao, Xueyun Gao, and Qing Yuan. 2023. "Peptide-Protected Gold Nanoclusters Efficiently Ameliorate Acute Contact Dermatitis and Psoriasis via Repressing the TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-17A Axis in Keratinocytes" Nanomaterials 13, no. 4: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040662
APA StyleLiu, Y., Meng, C., Li, Y., Xia, D., Lu, C., Lai, J., Zhang, Y., Cao, K., Gao, X., & Yuan, Q. (2023). Peptide-Protected Gold Nanoclusters Efficiently Ameliorate Acute Contact Dermatitis and Psoriasis via Repressing the TNF-α/NF-κB/IL-17A Axis in Keratinocytes. Nanomaterials, 13(4), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040662