Facile Synthesis of Ce-MOF for the Removal of Phosphate, Fluoride, and Arsenic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Synthesis of Cerium Terephthalic Acid Complex
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
2.3. Characterizations and Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD) of Ce-MOF
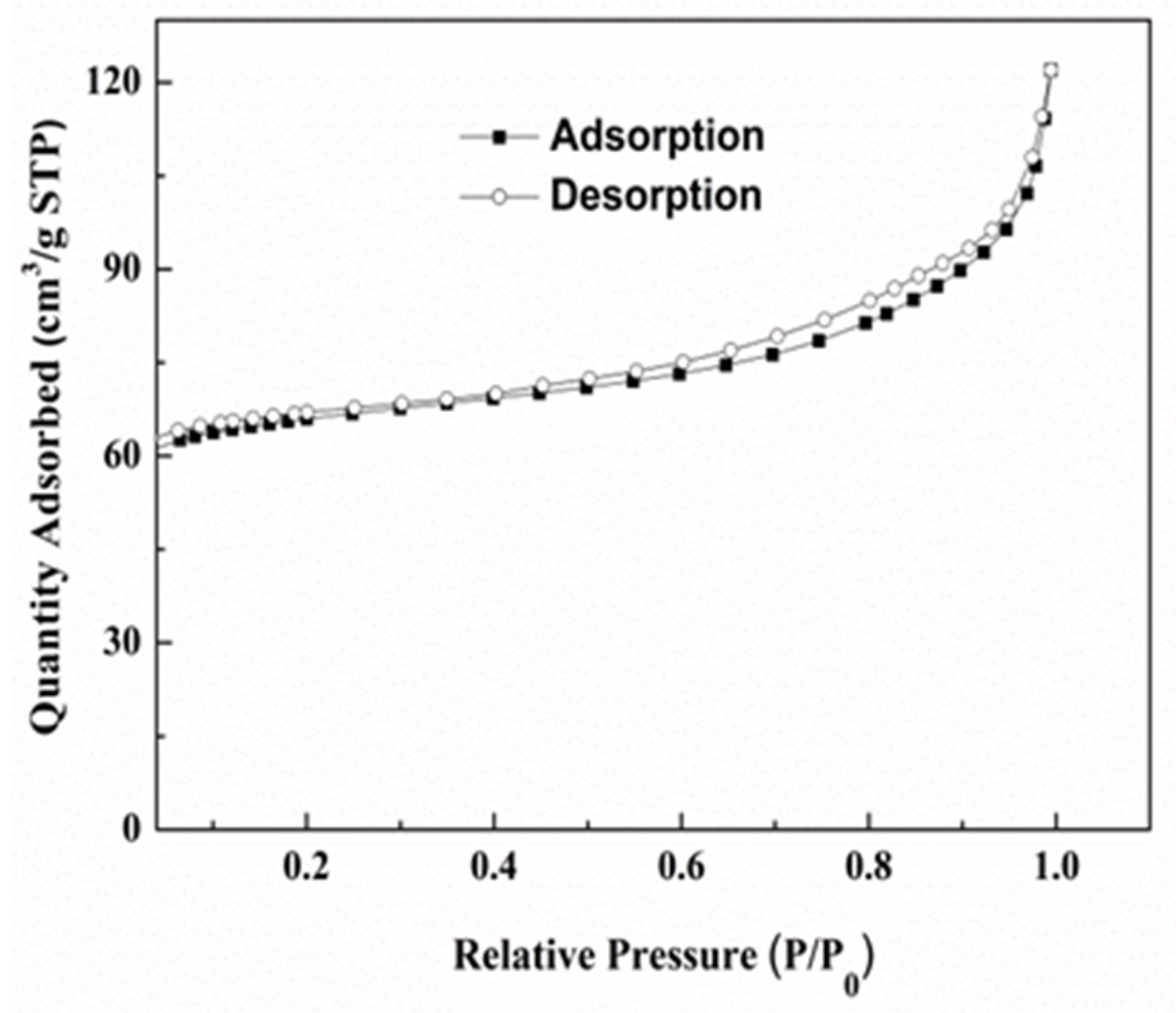
3.2. Nitrogen Adsorption–Desorption Isotherms of Ce-MOF
3.3. SEM Analysis
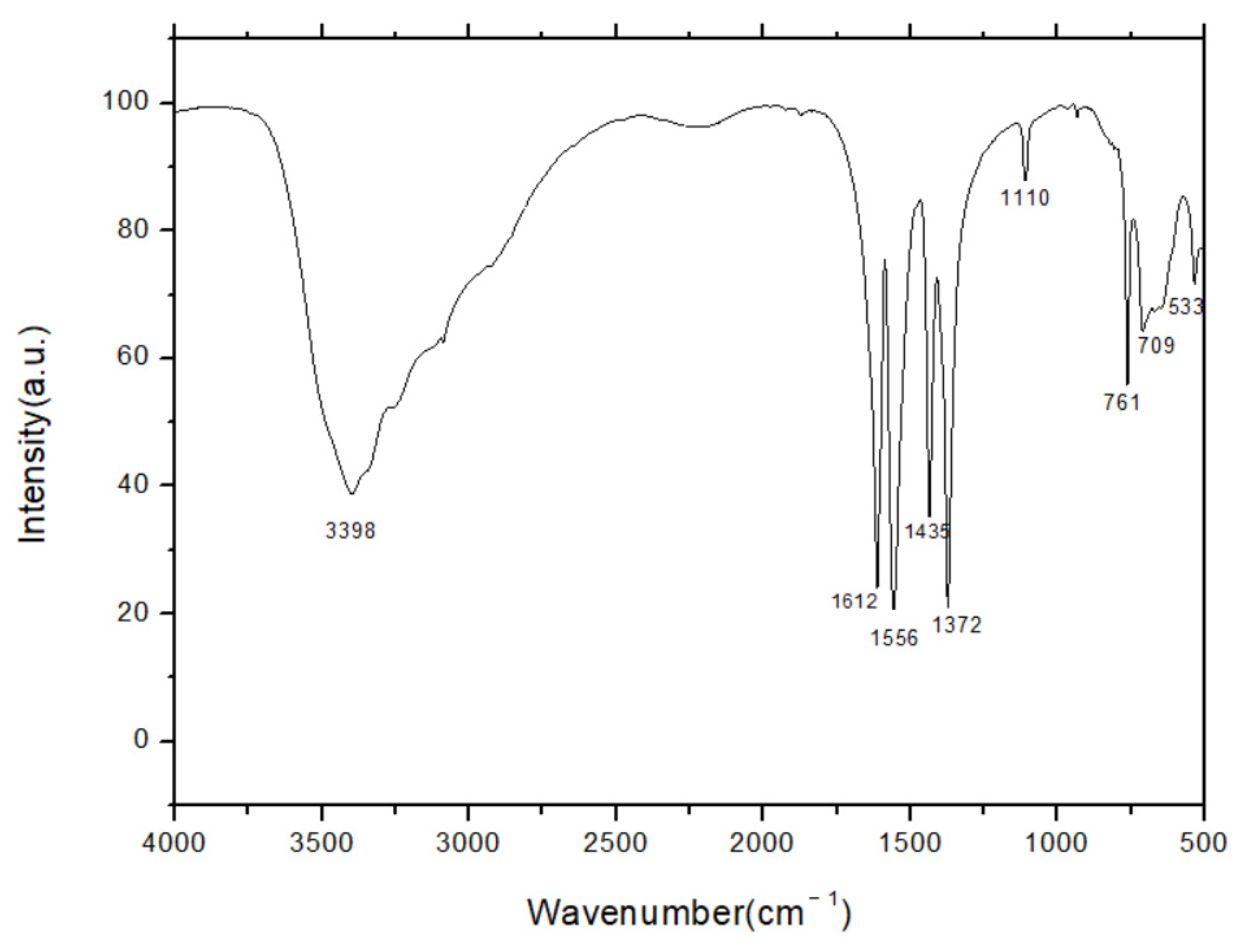
3.4. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.5. Effect of Operating Parameters on Phosphate Removal
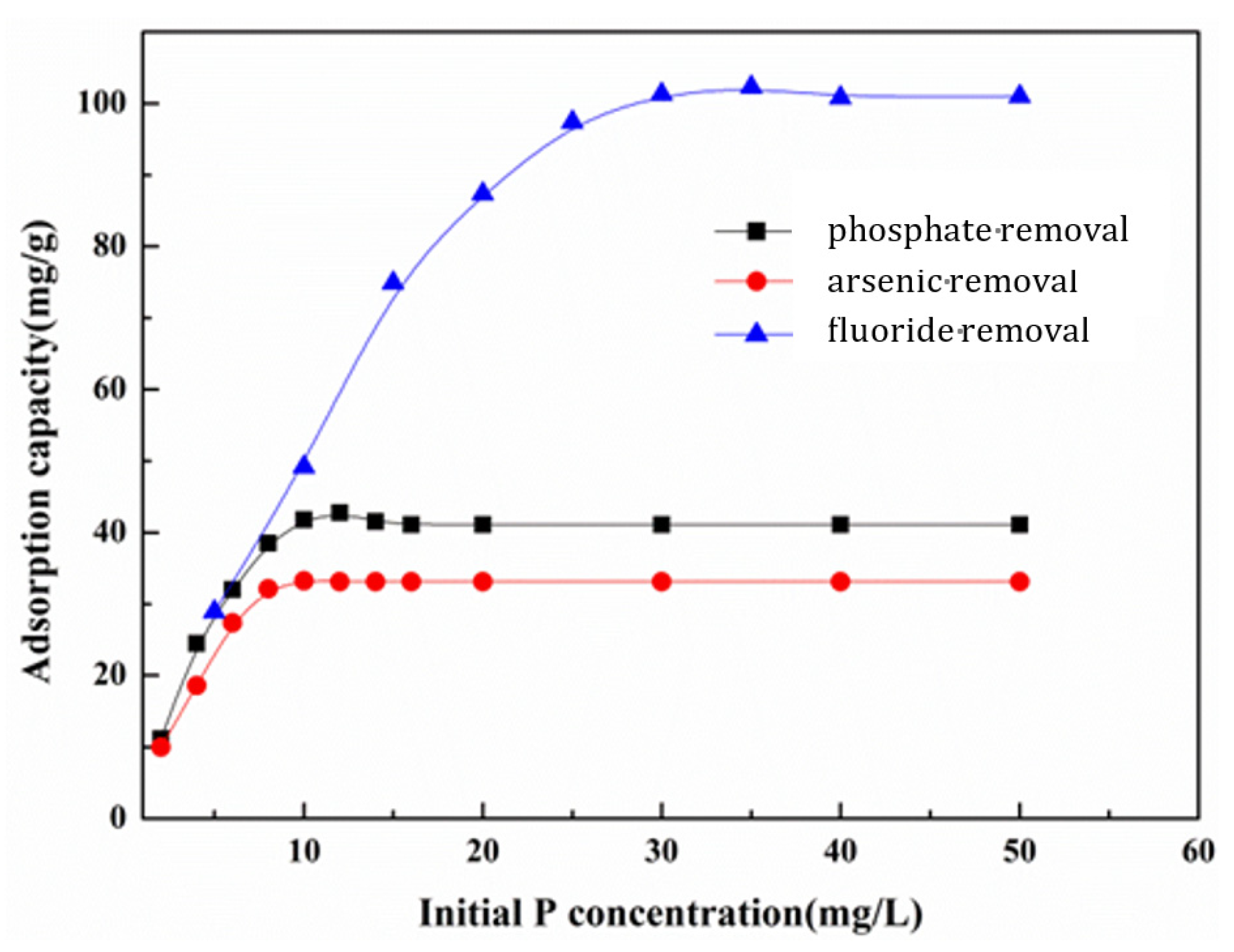
3.5.1. Effect of Initial Anion Concentration
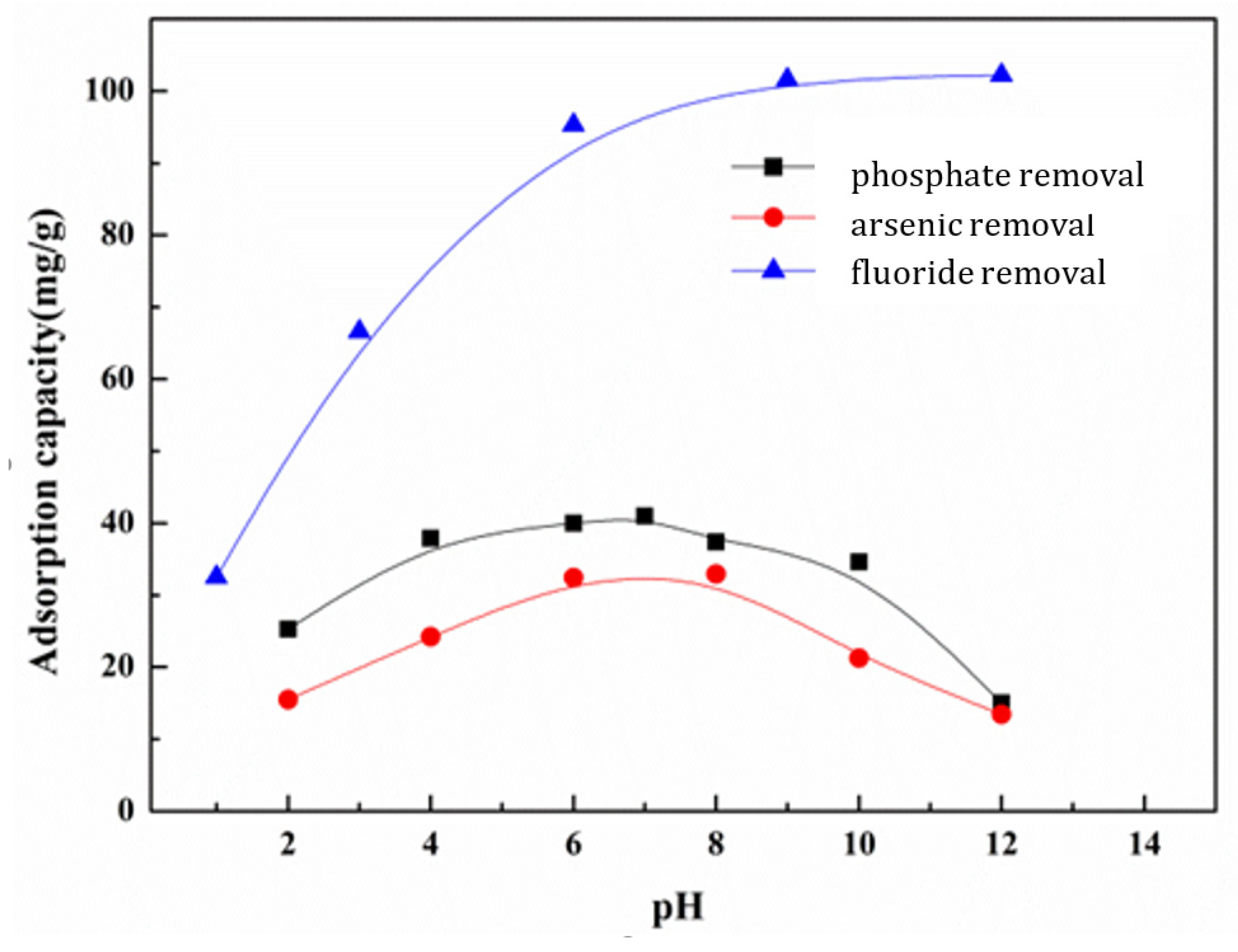
3.5.2. Effect of pH
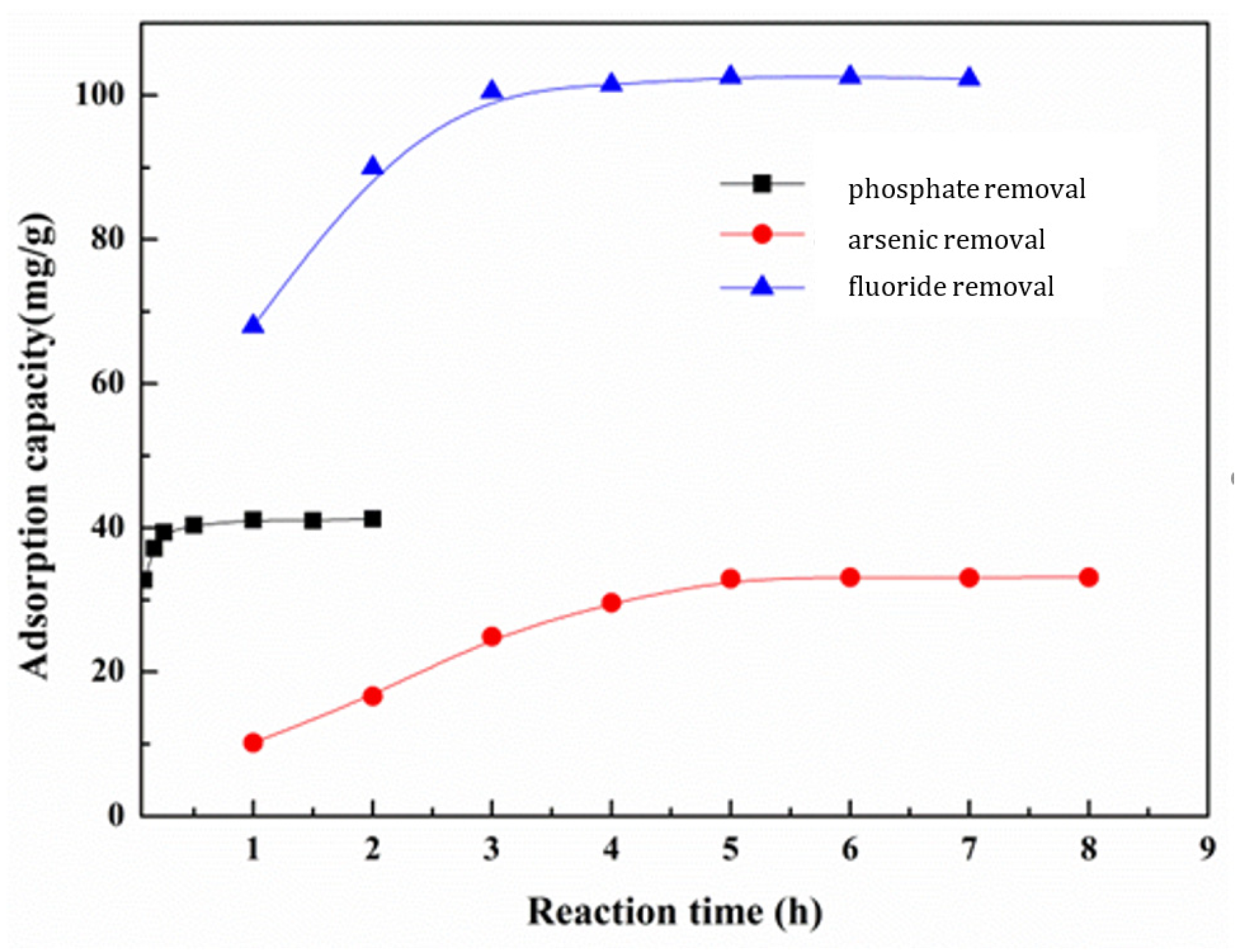
3.5.3. Effect of Reaction Time
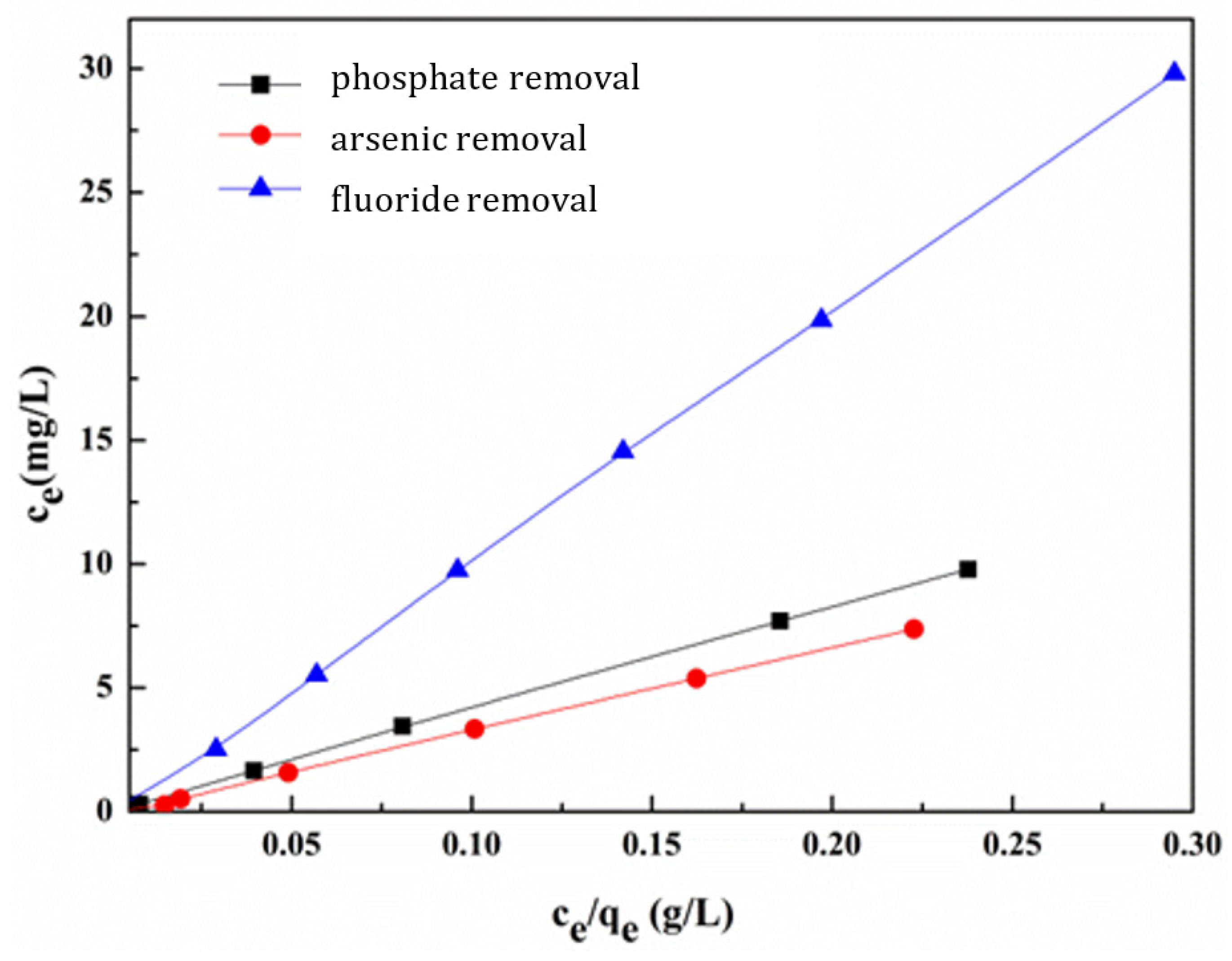
3.5.4. Adsorption Isotherm
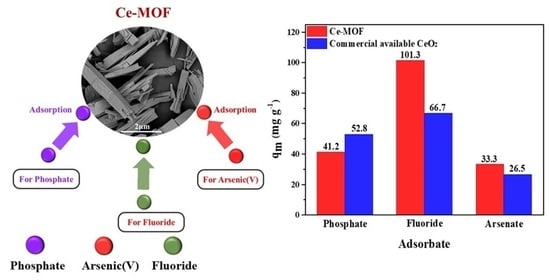
3.6. Comparison of Anion Removal Performance of Different Adsorbents
3.7. Adsorption Recyclability of Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samanta, P.; Chandra, P.; Dutta, S.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. Chemically stable ionic viologen-organic network: An efficient scavenger of toxic oxo-anions from water. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7874–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhu, C. Phosphorus removal from aqueous solutions containing low concentration of phosphate using pyrite calcinate sorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Li, H.; Lv, L. Engineering Case of High Phosphorus Organic Printing and Dyeing Wastewater Treatment. Technol. Water. Treat. 2019, 8, 133–135, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, Y. 200 million people around the world have excessive levels of arsenic in their drinking water. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 11, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, I.; Du, X.; Huang, S.; Wen, W. Effect of pyrite on enhancement of zero-valent iron corrosion for arsenic removal in water: A mechanistic study. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Fu, D.; Wang, X.; Bao, Q.; Yu, T.; Naddeo, V.; Tian, H.; Cao, C.; Zhao, Y. A bifunctional α-FeOOH@ GCA nanocomposite for enhanced adsorption of arsenic and photo Fenton-like catalytic conversion of As (III). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintor, A.M.; Vilar, V.J.; Botelho, C.M.; Boaventura, R.A. Oil and grease removal from wastewaters: Sorption treatment as an alternative to state-of-the-art technologies. A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Sha, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S. The preparation of black titanium oxide nanoarray via coking fluorinated wastewater and application on coking wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, M.; Coreño, O.; Nava, J.L. Removal of hydrated silica, fluoride and arsenic from groundwater by electrocoagulation using a continuous reactor with a twelve-cell stack. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water. Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, S.; Kamran, M.A.; Sultana, J.; Farooqi, A. Occurrence and methods to remove arsenic and fluoride contamination in water. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 125–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Song, Z.; Khan, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Qiu, W. Enhanced As (III) removal from aqueous solution by Fe-Mn-La-impregnated biochar composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez-Jimenez, L.H.; Arcibar-Orozco, J.A.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R. Overview of As (V) adsorption on Zr-functionalized activated carbon for aqueous streams remediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 212, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Hao, S.; Lu, X. Exfoliated Mg–Al–Fe layered double hydroxides/polyether sulfone mixed matrix membranes for adsorption of phosphate and fluoride from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, S.; Taghavi, M.; Khaksefidi, R.; Ahmadi, S. Adsorption of arsenic (V) from aqueous solution using modified saxaul ash: Isotherm and thermodynamic study. Appl. Water. Sci. 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.A.; Viswanathan, N. A facile synthesis of magnetic particles sprayed gelatin embedded hydrotalcite composite for effective phosphate sorption. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, H.L.; Molla, N.J.; Cherukumilli, K.; Boden, K.S.; Gadgil, A.J. Addressing technical barriers for reliable, safe removal of fluoride from drinking water using minimally processed bauxite ores. Dev. Eng. 2018, 3, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Development and characterization of yttrium-ferric binary composite for treatment of highly concentrated arsenate wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Koduru, J.R.; Chang, Y.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, J.K. Facile synthesis of flowered mesoporous graphene oxide-lanthanum fluoride nanocomposite for adsorptive removal of arsenic. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 279, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Peng, L.; Wu, X.; Zeng, Q. Synthesis of calcined La-doped layered double hydroxides and application on simultaneously removal of arsenate and fluoride. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 275, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, M.S.; Seo, J.; Lee, C. La-modified ZSM-5 zeolite beads for enhancement in removal and recovery of phosphate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 279, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Nallathamby, K.; Mitchell, D.R. Electrochemical characterization of an aqueous lithium rechargeable battery: The effect of CeO2 additions to the MnO2 cathode. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 479, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Mitchell, D.R.; Carter, M.L.; Appadoo, D.; Nallathamby, K. Microstructural and spectroscopic investigations into the effect of CeO2 additions on the performance of a MnO2 aqueous rechargeable battery. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3244–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, L. Ce (III) nanocomposites by partial thermal decomposition of Ce-MOF for effective phosphate adsorption in a wide pH range. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barpaga, D.; Nguyen, V.T.; Medasani, B.K.; Chatterjee, S.; McGrail, B.P.; Motkuri, R.K.; Dang, L.X. Insight into fluorocarbon adsorption in metal-organic frameworks via experiments and molecular simulations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Liao, C. Advances of metal-organic frameworks in adsorption and separation applications. Acta Chim. Sin. 2017, 75, 841–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Awasthi, G.P.; Kim, H.J. Novel insight into the adsorption of Cr (VI) and Pb (II) ions by MOF derived Co-Al layered double hydroxide@ hematite nanorods on 3D porous carbon nanofiber network. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Yu, C. MOF-on-MOF hybrids: Synthesis and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Du, M.; Yin, K.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Gao, Y.; Pang, H. Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Water Treatment: A Review. Small 2022, 18, 2105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcaro, P.; Normandin, F.; Takahashi, M.; Scopece, P.; Amenitsch, H.; Costacurta, S.; Buso, D. Dynamic Control of MOF-5 Crystal Positioning Using a Magnetic Field. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3901–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Cheng, C.; Shao, Z.; Wang, H. Strategies to fabricate metal–organic framework (MOF)-based luminescent sensing platforms. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 10743–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Lee, J.E.; Jang, I.T.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Jegal, J.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution with metal-organic frameworks, porous chromium-benzenedicarboxylates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Xu, J.; Bu, X. Recent advances about metal–organic frameworks in the removal of pollutants from wastewater. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 378, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Bendre, A.; Mariappan, E.; Altalhi, T.; Kigga, M.; Ching, Y.C.; Kigga, M.; Kurkuri, M. Recent trends in the application of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of toxic dyes and their removal mechanism—A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00378B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Guo, P.; Tan, H.; Zhang, S. Studies on the removal of phosphate in water through adsorption using a novel Zn-MOF and its derived materials. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, C.; Xia, W.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, W.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Z. Recent advances in metal–organic framework-based materials for removal of fluoride in water: Performance, mechanism, and potential practical application. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, A.; Liao, C. Preparation of Fe–Co based MOF-74 and its effective adsorption of arsenic from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Naddeo, V.; Zhao, Y. Tuning the structure of cerium-based metal-organic frameworks for efficient removal of arsenic species: The role of organic ligands. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, G.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. High-performance lanthanum-based metal–organic framework with ligand tuning of the microstructures for removal of fluoride from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, X.; Shi, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, X.; Pang, H. Recent Progress in 2D Metal-Organic Framework-Related Materials. Small 2023, 2305548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, S.; Tang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, S. Highly efficient capture of phosphate from water via cerium-doped metal-organic frameworks. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhou, T.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Pang, H. Metal–Organic Frameworks and Their Composites for Environmental Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2204141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Tang, L. Metal organic framework g-C3N4/MIL-53 (Fe) heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activity for Cr (VI) reduction under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Bai, X.; Liang, M.; Ma, J. Recent progress on metal-organic framework-derived porous carbon and its composite for pollutant adsorption from liquid phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Nanostructured iron (III)-copper (II) binary oxide: A novel adsorbent for enhanced arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Water. Res. 2013, 47, 4022–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Han, R. Preparation of novel magnetic microspheres with the La and Ce-bimetal oxide shell for excellent adsorption of fluoride and phosphate from solution. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 64, 3641–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Chi, R.A. Selective removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by MIL-101 (Fe)/bagasse composite prepared through bagasse size control. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Deng, S.; Peng, F.; Luo, T. A new adsorbent of a Ce ion-implanted metal–organic framework (MIL-96) with high-efficiency Ce utilization for removing fluoride from water. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 1996–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, C.; Yan, X. Metal-organic framework-801 for efficient removal of fluoride from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, C. The stability and defluoridation performance of MOFs in fluoride solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 185, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Yu, X.; Jia, Y.; Peng, F.; Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X. Iron and 1, 3, 5-benzenetricarboxylic metal–organic coordination polymers prepared by solvothermal method and their application in efficient As (V) removal from aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8601–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Sui, K.; Yin, N. Facile synthesis of metal-organic framework MOF-808 for arsenic removal. Mater. Lett. 2015, 160, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.A.; Le, G.H.; Dao, C.D.; Dang, L.Q.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Lee, G.D. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption using novel MIL-53 (Fe) as a highly efficient adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5261–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Adsorbents | Removal Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphate Removal (%) | Fluoride Removal (%) | Arsenic Removal (%) | |
| Calcium salt | 79 | 90 | 44 |
| Alum | 69 | 68 | 12 |
| Hydrotalcite | 76 | 72 | 24 |
| Commercial CeO2 | 25 | 40 | 1 |
| Ce-MOF | 98 | 96 | 88 |
| Adsorbents | Phosphate Removal (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| First adsorption | 98 | - |
| Second adsorption | 95 | 89 |
| Third adsorption | 91 | 74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Mao, D.; Qu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, J. Facile Synthesis of Ce-MOF for the Removal of Phosphate, Fluoride, and Arsenic. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233048
Zhang L, Mao D, Qu Y, Chen X, Zhang J, Huang M, Wang J. Facile Synthesis of Ce-MOF for the Removal of Phosphate, Fluoride, and Arsenic. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(23):3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lili, Decheng Mao, Yining Qu, Xiaohong Chen, Jindi Zhang, Mengyang Huang, and Jiaqiang Wang. 2023. "Facile Synthesis of Ce-MOF for the Removal of Phosphate, Fluoride, and Arsenic" Nanomaterials 13, no. 23: 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233048
APA StyleZhang, L., Mao, D., Qu, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, J., Huang, M., & Wang, J. (2023). Facile Synthesis of Ce-MOF for the Removal of Phosphate, Fluoride, and Arsenic. Nanomaterials, 13(23), 3048. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13233048