Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Magneto-Mechanical Actuation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
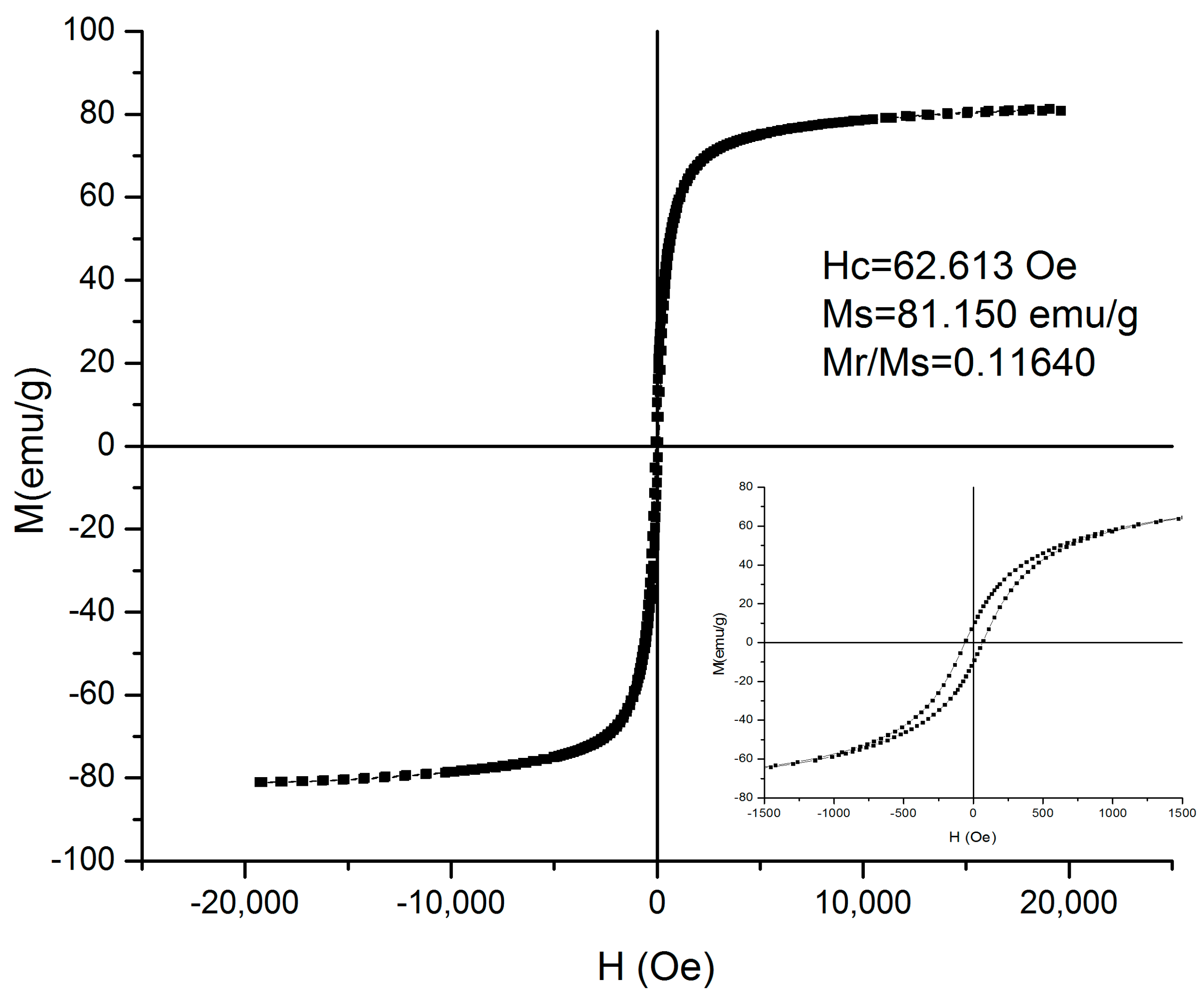
3.1. Preparation of Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles
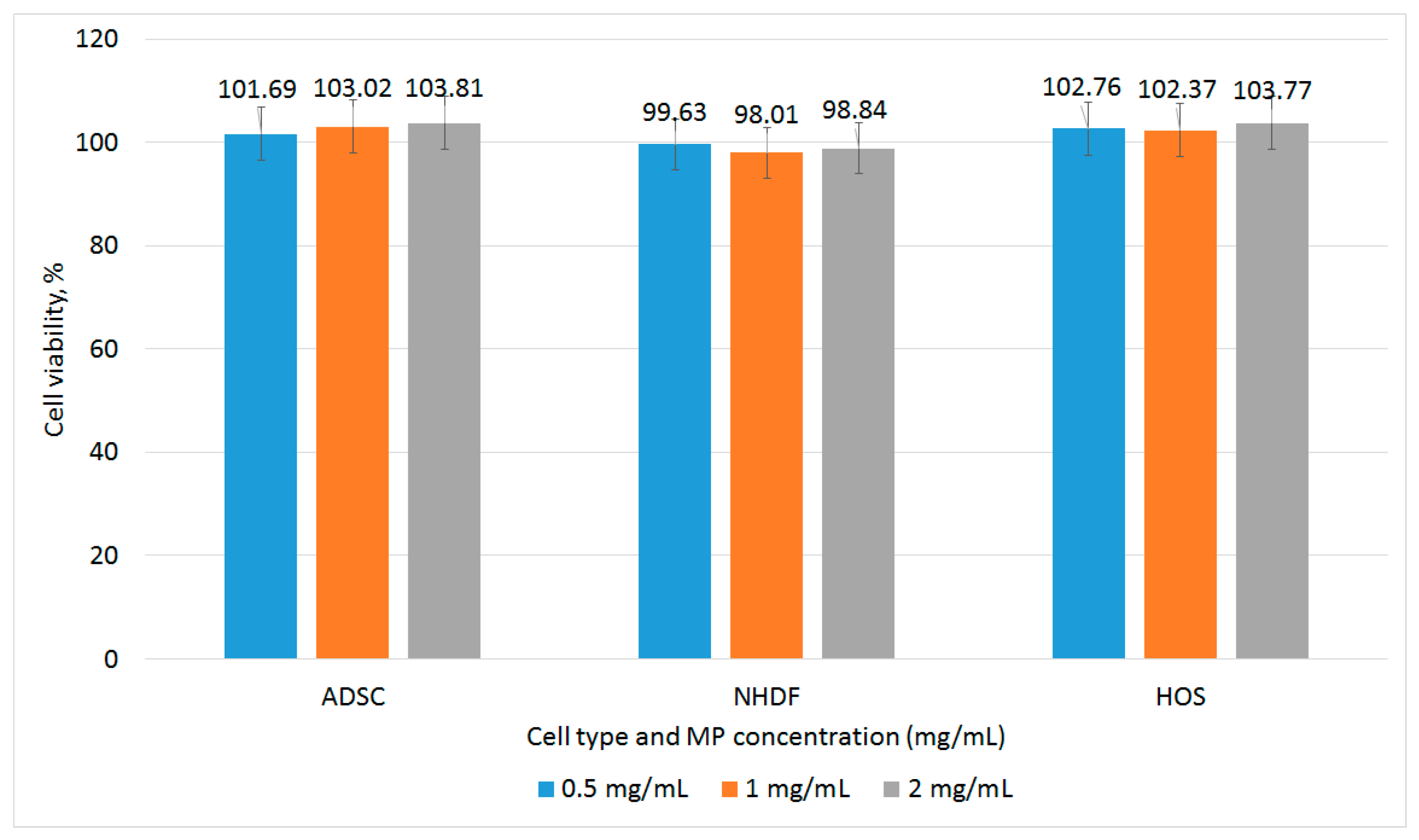
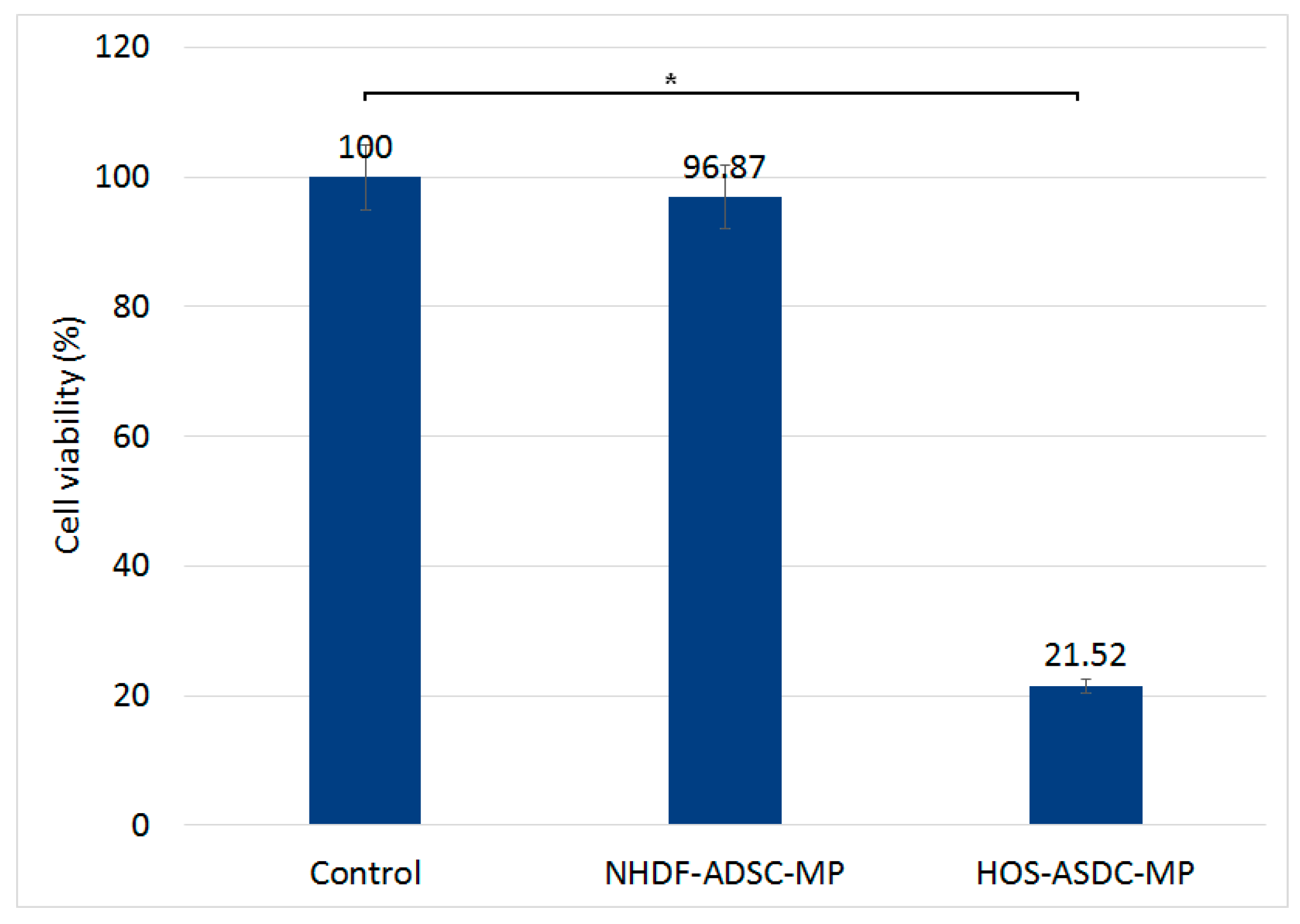
3.2. Biocompatibility of Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles
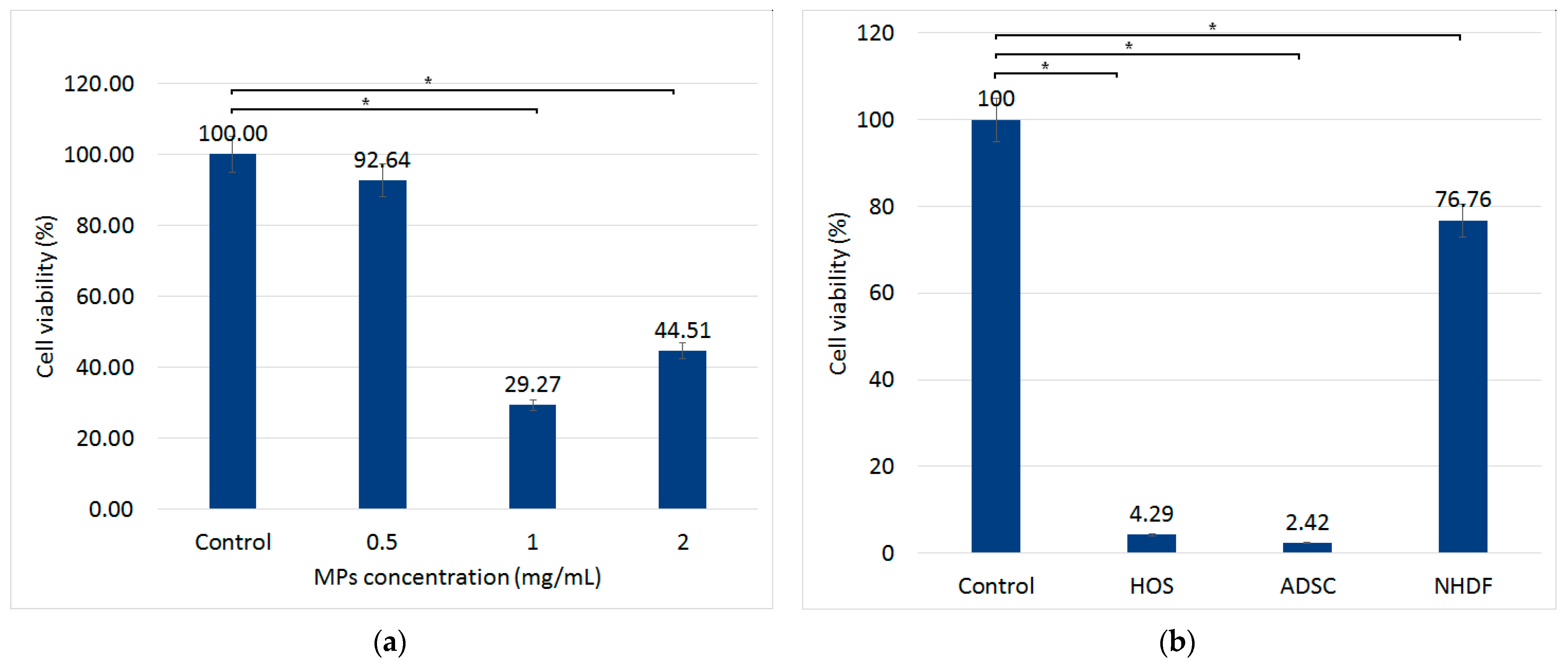
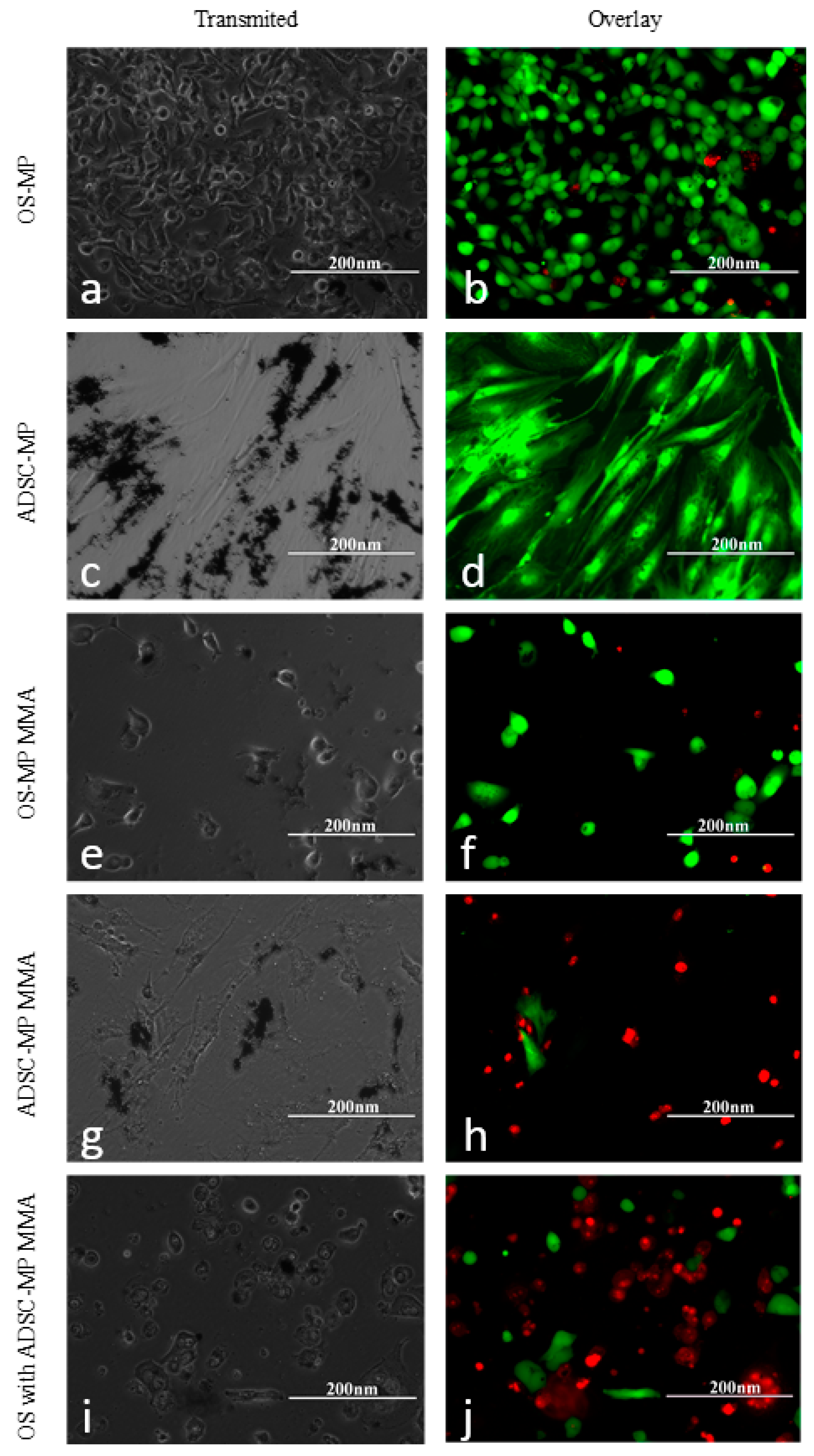
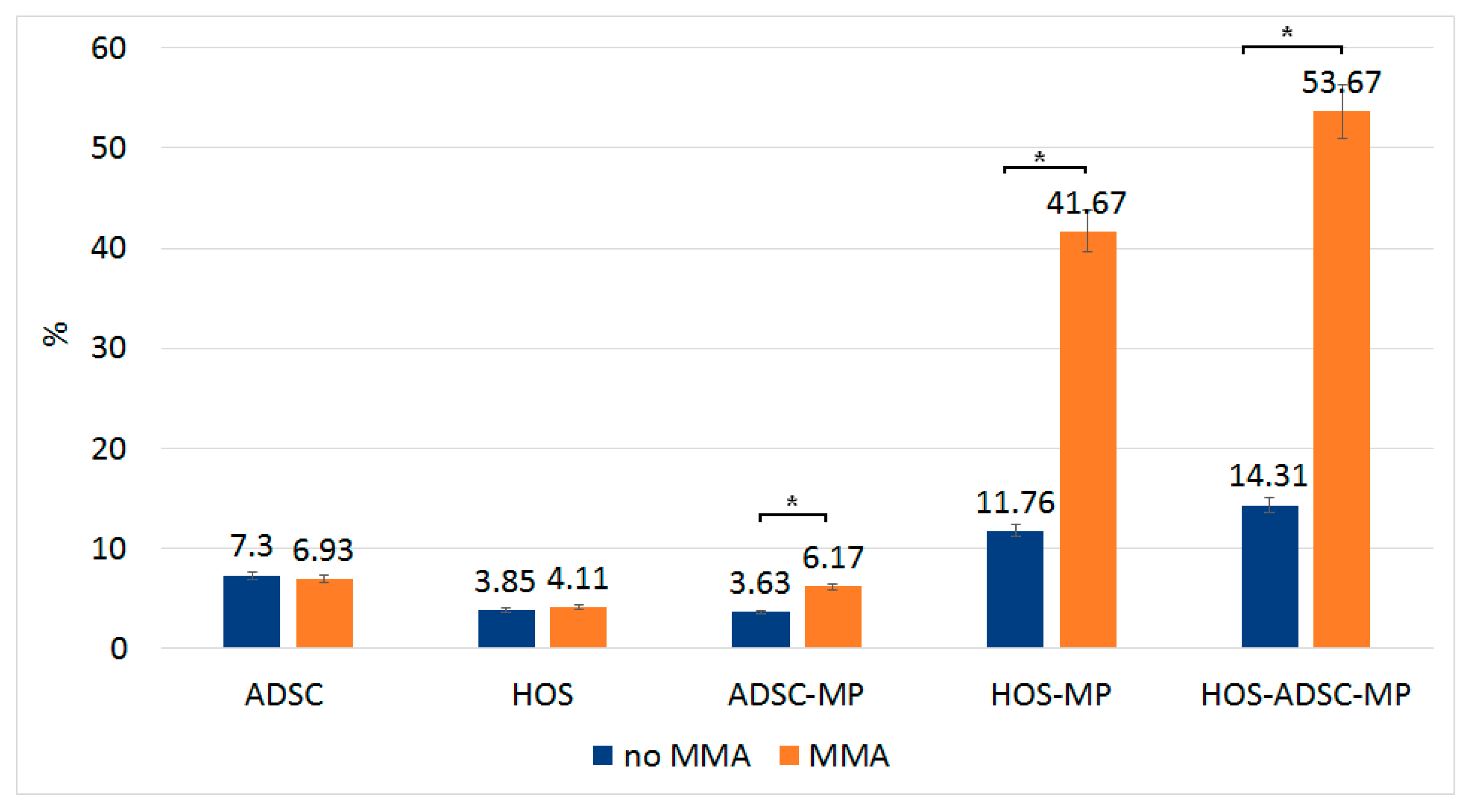
3.3. The Effect of Magneto-Mechanical Actuation on HOS, ADSCs, and NHDF
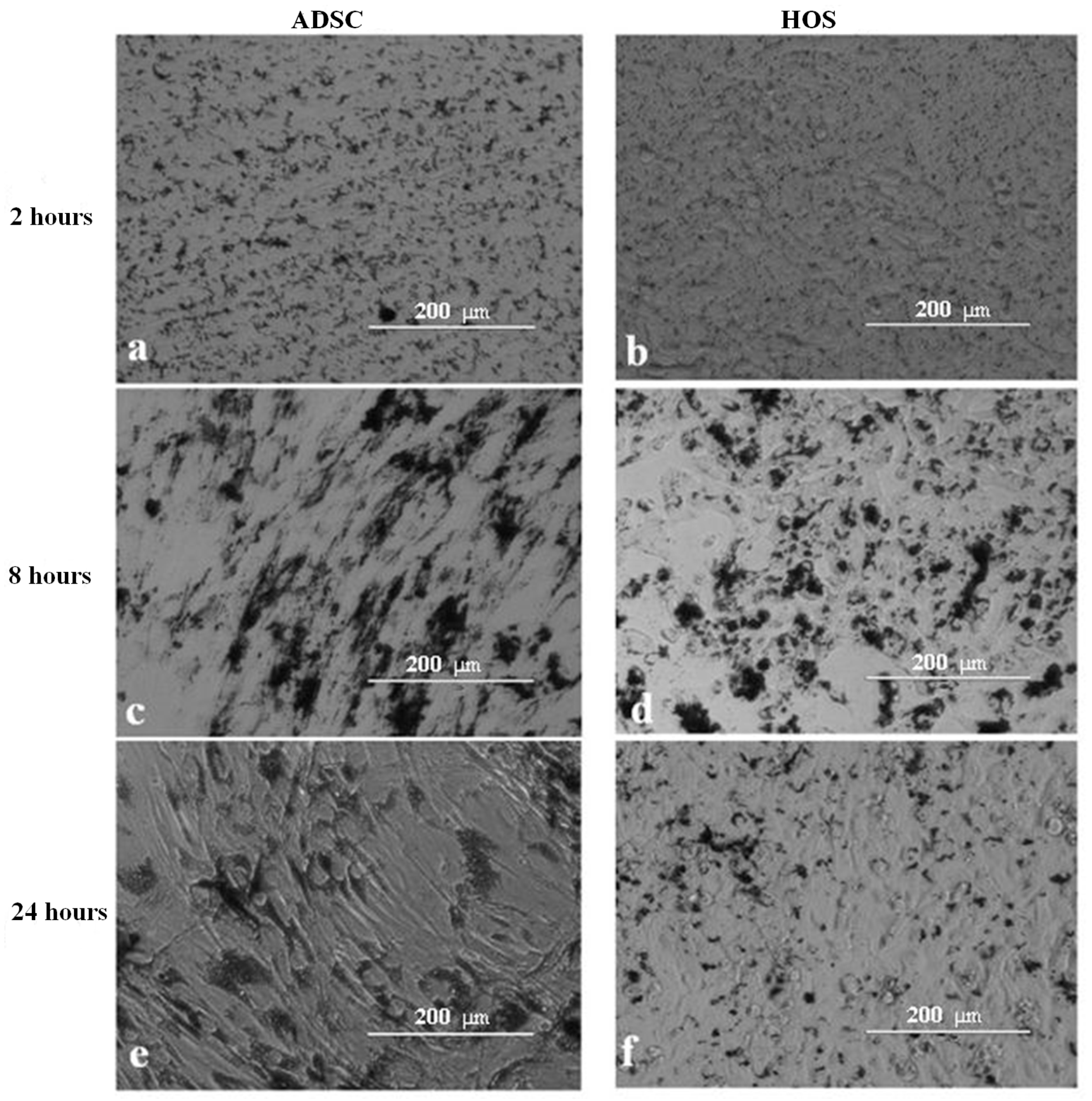
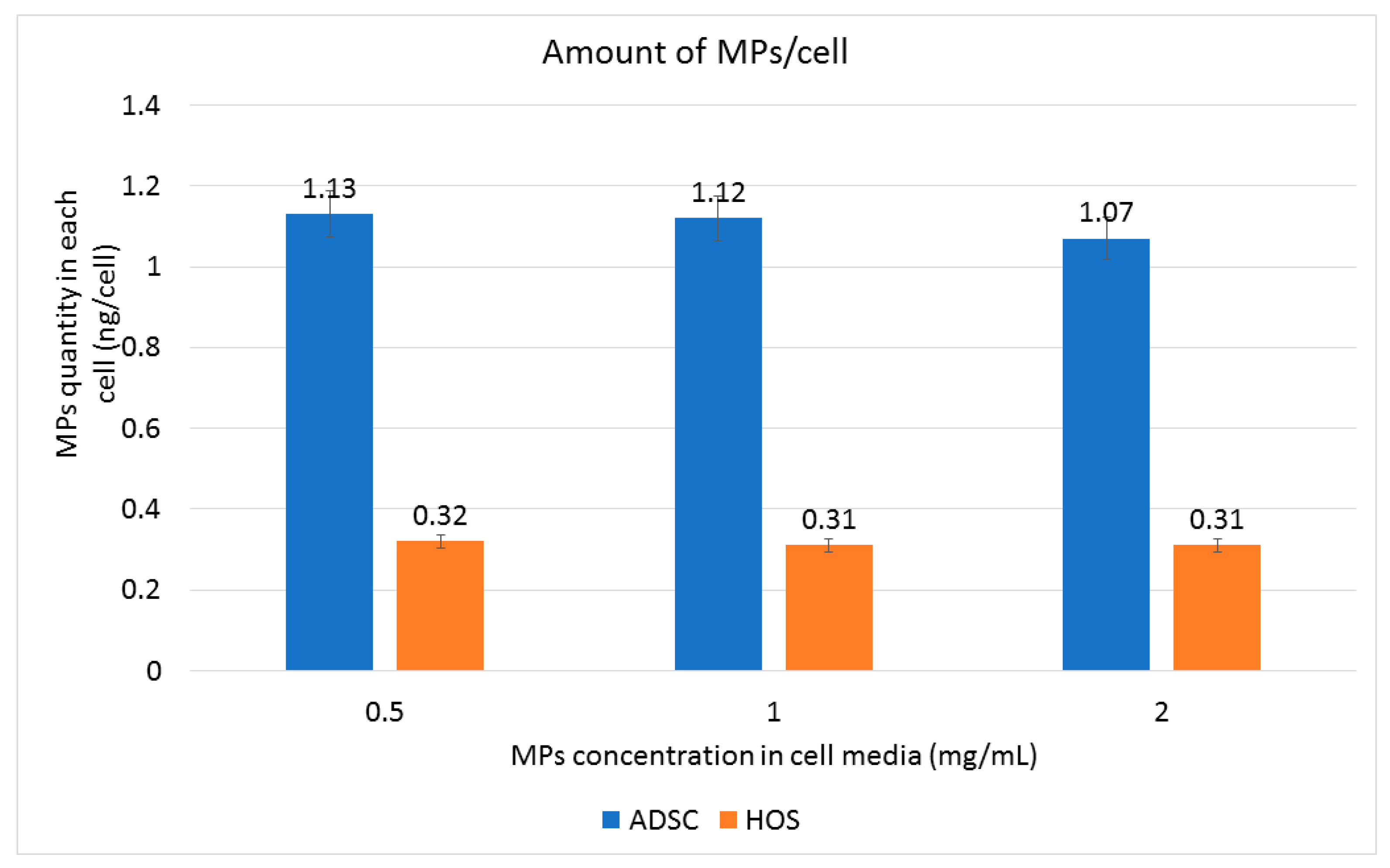
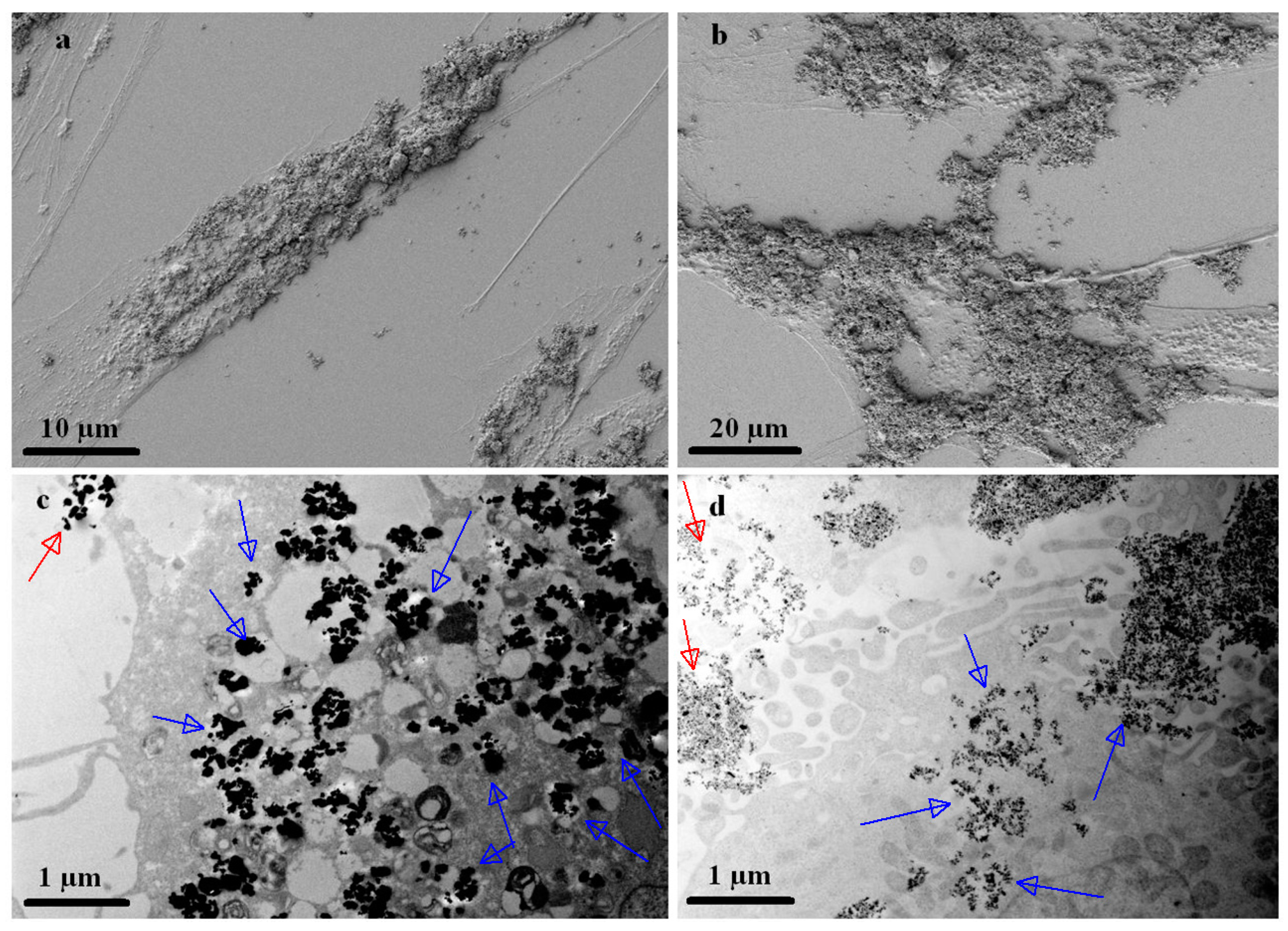
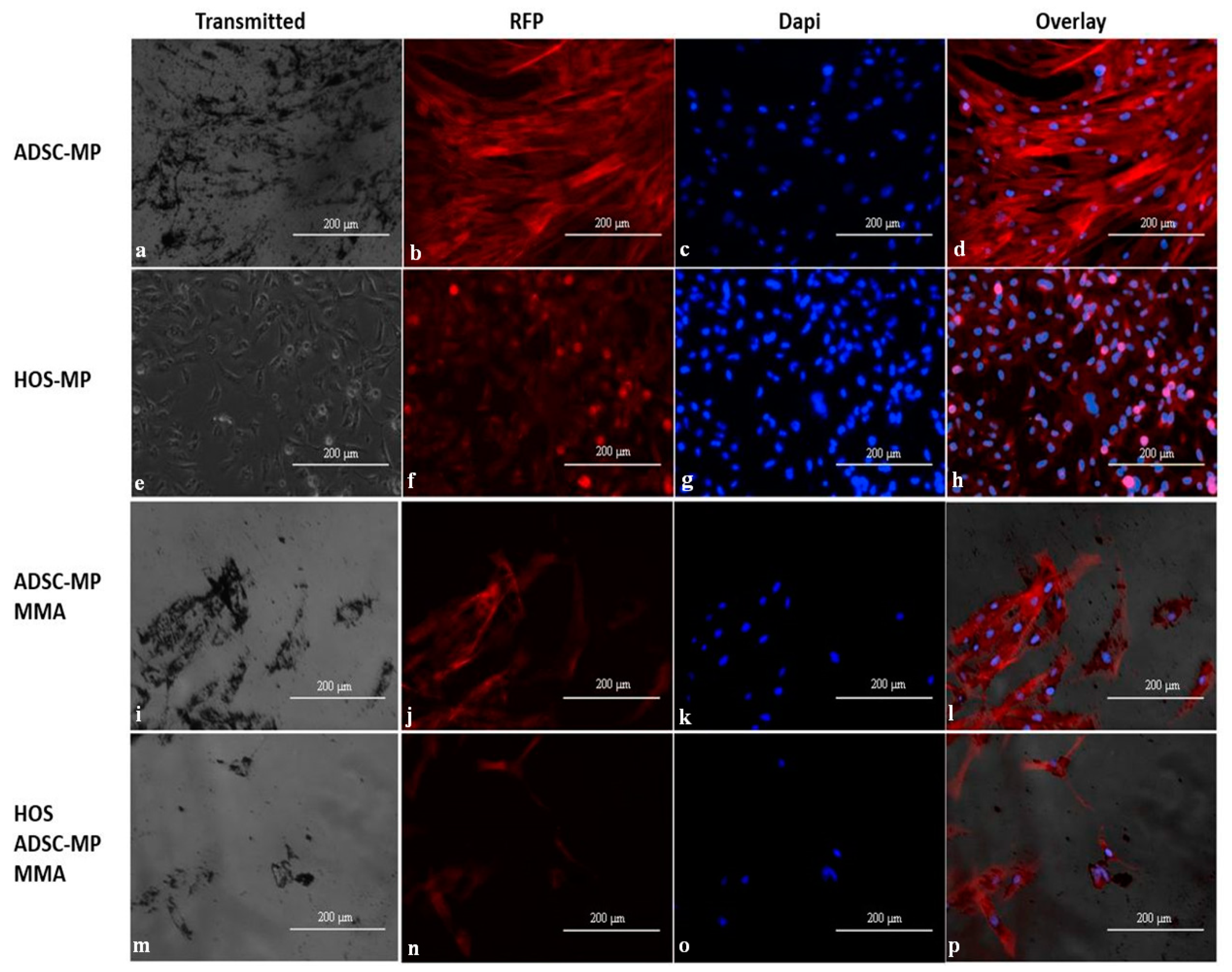
3.4. Internalization of Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles by HOS and ADSCs
3.5. ADSC Motility for Targeting HOS Cells In Vitro
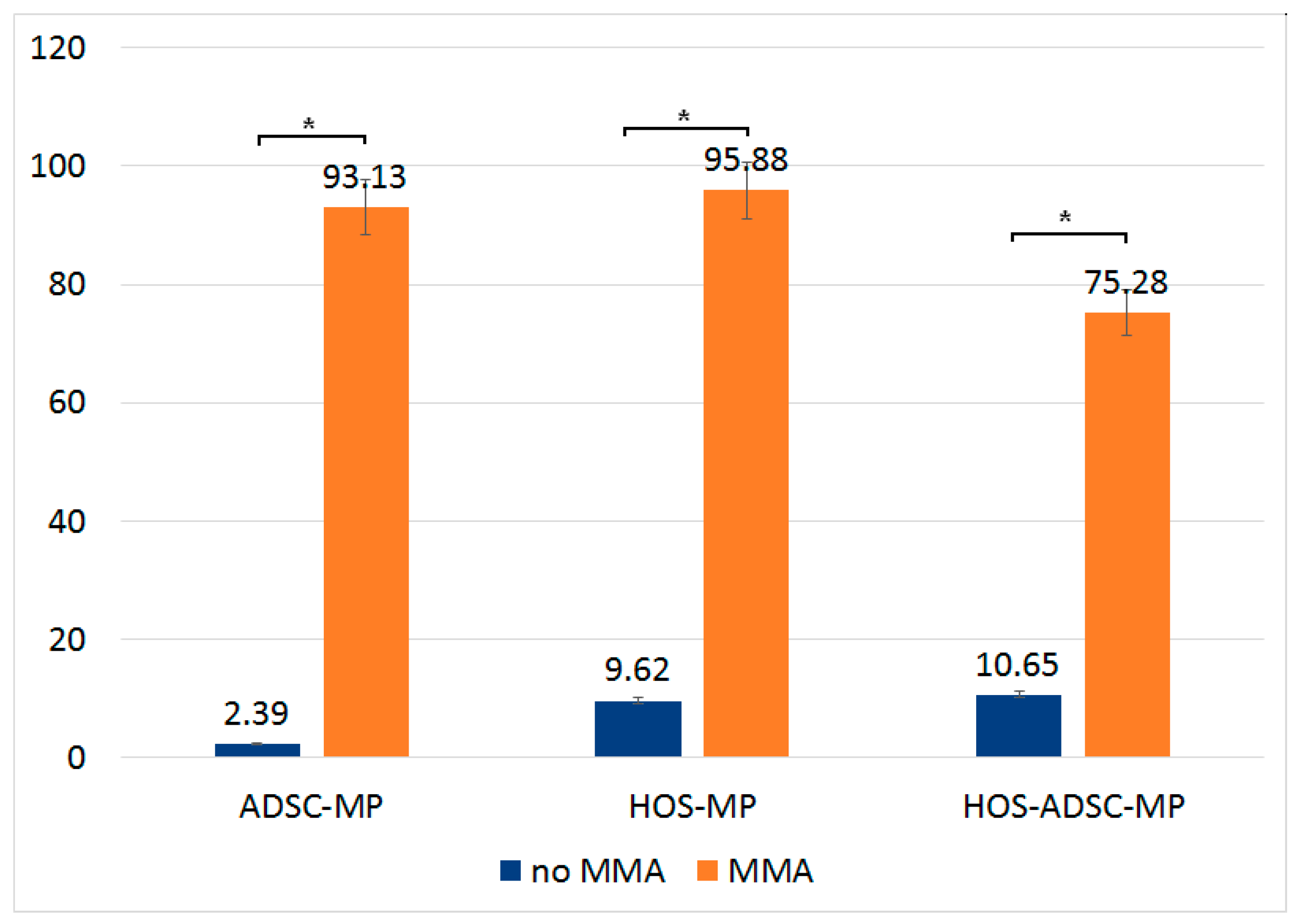
3.6. Effect of Magneto-Mechanical Actuation of Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles Transported by ADSCs on the Viability of HOS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, L.H.; Arias, J.L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic nanoparticles: Design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Pérez-Andrés, E.; Thevenot, J.; Sandre, O.; Berra, E.; Lecommandoux, S. Magnetic field triggered drug release from polymersomes for cancer therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Müller, R.; Eberbeck, D.; Hilger, I.; Zeisberger, M. Magnetic nanoparticles adapted for specific biomedical applications. Biomed. Tech. 2015, 60, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafrouni, L.; Savadogo, O. Recent progress on magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. Prog. Biomater. 2016, 5, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; McBain, S.; Dobson, J.; El Haj, A.J. Selective activation of mechanosensitive ion channels using magnetic particles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannix, R.J.; Kumar, S.; Cassiola, F.; Montoya-Zavala, M.; Feinstein, E.; Prentiss, M.; Ingber, D.E. Nanomagnetic actuation of receptor-mediated signal transduction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Shi, H. Morphological effect of oscillating magnetic nanoparticles in killing tumor cells. Nanoscale Res. 2014, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Radu, E.; Țibu, M.; Stoian, G.; Ababei, G.; Lăbușcă, L.; Herea, D.-D.; Lupu, N. Fe-Cr-Nb-B ferromagnetic particles with shape anisotropy for cancer cell destruction by magneto-mechanical actuation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Ulasov, I.V.; Bader, S.D.; Rajh, T.; Lesniak, M.S.; Novosad, V. Biofunctionalized magnetic-vortex microdiscs for targeted cancer-cell destruction. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leulmi, S.; Chauchet, X.; Morcrette, M.; Ortiz, G.; Joisten, H.; Sabon, P.; Livache, T.; Hou, Y.; Carrière, M.; Lequien, S.; et al. Triggering the apoptosis of targeted human renal cancer cells by the vibration of anisotropic magnetic particles attached to the cell membrane. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15904–15914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.O.; Kapadia, V.; Pierstorff, E.; Ho, D.; Chen, Y. Induction of cell death by magnetic actuation of nickel nanowires internalized by fibroblasts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15085–15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Yang, E.H. Internationalization of gold and nickel nanowires by living cells. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kralj, S.; Makovec, D. Magnetic Assembly of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Clusters into Nanochains and Nanobundles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Lupu, N.; Lostun, M.; Ababei, G.; Grigoraş, M.; Dănceanu, C. Low TC Fe-Cr-Nb-B glassy submicron powders for hyperthermia applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17B520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, J.W.V.; de Medeiros Fernandes, T.A.A.; Fernandes, J.V., Jr.; de Azevedo, J.C.V.; Lanza, D.C.F.; Bezerra, C.M.; Andrade, V.S.; de Araújo, J.M.G.; Fernandes, J.V. Biology and pathogenesis of human osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 2020, 19, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Spaeth, E.; Klopp, A.; Dembinski, J.; Andreeff, M.; Marini, F. Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: Defining the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, B. Human skin dermis-derived fibroblasts are a kind of functional mesenchymal stromal cells: Judgements from surface markers, biological characteristics, to therapeutic efficacy. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minuti, A.E.; Stoian, G.; Herea, D.-D.; Radu, E.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H. Fe-Cr-Nb-B ferrofluid for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.M.L. Tetrazolium (MTT) assay for cellular viability and activity. Methods Mol. Biol. 1998, 79, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Sari, G.; Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E. Guidelines for cell viability assays. Food Front. 2020, 1, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.R.; Hansen, B.T.; Nair, V.; Hoyt, F.H.; Dorward, D.W. Scanning Electron Microscopy. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2012, 2B.2.1–2B.2.47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrand, A.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Dai, L.; Hussain, S.M. Preparation of cells for assessing ultrastructural localization of nanoparticles with transmission electron microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, H.; Masuzawa, K.; Minachi, Y.; Iida, K. Preparation of Oxide Magnetic Material. U.S. Patent 5,951,937, 27 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Herea, D.D.; Lăbușcă, L.; Radu, E.; Chiriac, H.; Grigoraș, M.; Dragoș Pânzaru, O.; Lupu, N. Human adipose-derived stem cells loaded with drug-coated magnetic nanoparticles for in-vitro tumor cells targeting. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 94, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Liu, D.D.; Thakor, A.S. Mesenchymal stromal cell homing: Mechanisms and strategies for improvement. iScience 2019, 15, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, E.; Sato, T.; Kimori, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Haga, K.; Kato, H.; Tabeta, K.; Nanba, D.; Izumi, K. Noninvasive measurement of cell/colony motion using image analysis methods to evaluate the proliferative capacity of oral keratinocytes as a tool for quality control in regenerative medicine. J. Tissue Eng. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Choi, K.Y.; Liu, D.; Choi, J.-S.; Shin, T.-H.; Cheon, J.; Niu, G.; et al. Design considerations of iron-based nanoclusters for noninvasive tracking of mesenchymal stem cell homing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4403–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIVE/DEADTM Viability/Cytotoxicity Kit, for Mammalian Cells. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/L3224 (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Guggenheim, E.J.; Rappoport, J.Z.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms for cellular uptake of nanosized clinical MRI contrast agents. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 504–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunov, O.; Uzhytchak, M.; Smolková, B.; Lunova, M.; Jirsa, M.; Dempsey, N.M.; Dias, A.L.; Bonfim, M.; Hof, M.; Jurkiewicz, P.; et al. Remote actuation of apoptosis in liver cancer cells via magneto-mechanical modulation of iron oxide nanoparticles. Cancers 2019, 11, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiriac, H.; Minuti, A.E.; Stavila, C.; Herea, D.-D.; Labusca, L.; Ababei, G.; Stoian, G.; Lupu, N. Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Magneto-Mechanical Actuation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222941
Chiriac H, Minuti AE, Stavila C, Herea D-D, Labusca L, Ababei G, Stoian G, Lupu N. Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Magneto-Mechanical Actuation. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(22):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222941
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiriac, Horia, Anca Emanuela Minuti, Cristina Stavila, Dumitru-Daniel Herea, Luminita Labusca, Gabriel Ababei, George Stoian, and Nicoleta Lupu. 2023. "Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Magneto-Mechanical Actuation" Nanomaterials 13, no. 22: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222941
APA StyleChiriac, H., Minuti, A. E., Stavila, C., Herea, D.-D., Labusca, L., Ababei, G., Stoian, G., & Lupu, N. (2023). Fe-Cr-Nb-B Magnetic Particles and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Cells Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Magneto-Mechanical Actuation. Nanomaterials, 13(22), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222941







