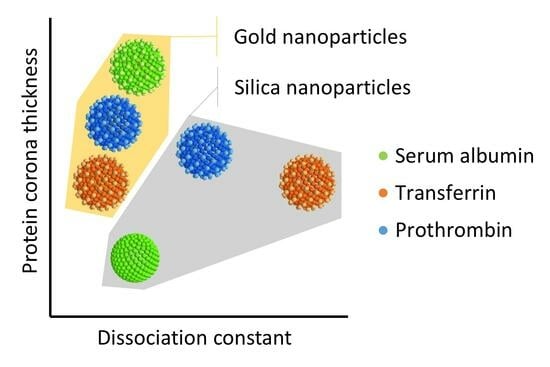
Multivariate Analysis of Protein–Nanoparticle Binding Data Reveals a Selective Effect of Nanoparticle Material on the Formation of Soft Corona
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ke, P.C.; Lin, S.; Parak, W.J.; Davis, T.P.; Caruso, F. A Decade of the Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11773–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle Interaction with Plasma Proteins as It Relates to Particle Biodistribution, Biocompatibility and Therapeutic Efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkey, C.D.; Olsen, J.B.; Guo, H.; Emili, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry Determine Serum Protein Adsorption and Macrophage Uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Kuharev, J.; Musyanovych, A.; Fetz, V.; Hecht, R.; Schlenk, F.; Fischer, D.; Kiouptsi, K.; Reinhardt, C.; et al. Rapid Formation of Plasma Protein Corona Critically Affects Nanoparticle Pathophysiology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M. Antibody Orientation Determines Corona Mistargeting Capability. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, S.; Alnasser, F.; Polo, E.; Garry, D.; Lo Giudice, M.C.; Hristov, D.R.; Rocks, L.; Salvati, A.; Yan, Y.; Dawson, K.A. Identification of Receptor Binding to the Biomolecular Corona of Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalinardo, M.; Bertacchini, J.; Bergamini, L.; Magarò, M.S.; Ortolani, L.; Sanson, A.; Palumbo, C.; Cavallini, M.; Gentili, D. Surface Properties Modulate Protein Corona Formation and Determine Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 14119–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalinardo, M.; Caicci, F.; Cavallini, M.; Gentili, D. Protein Corona Mediated Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast. Small 2018, 14, 1801219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, S.; Ghosh, S.; McDougall, D.R.; Whitten, A.E.; Mata, J.P.; Köper, I.; McGillivray, D.J. Structure of Soft and Hard Protein Corona around Polystyrene Nanoplastics—Particle Size and Protein Types. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjappa, V.; Thomas, J.K.; Marimuthu, A.; Muthusamy, B.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Sharma, R.; Ahmad Khan, A.; Balakrishnan, L.; Sahasrabuddhe, N.A.; Kumar, S.; et al. Plasma Proteome Database as a Resource for Proteomics Research: 2014 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D959–D965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Algar, W.R.; Berti, L.; Gemmill, K.B.; Casey, B.J.; Oh, E.; Stewart, M.H.; Medintz, I.L. Functionalizing Nanoparticles with Biological Molecules: Developing Chemistries that Facilitate Nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1904–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Rosfa, S.; Wlodarski, A.; Kuharev, J.; Rekik, A.; Knauer, S.K.; Bantz, C.; Nawroth, T.; Bier, C.; et al. Nanoparticle Size Is a Critical Physicochemical Determinant of the Human Blood Plasma Corona: A Comprehensive Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7155–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Åberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, S.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Pitek, A.S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J. Reversible versus Irreversible Binding of Transferrin to Polystyrene Nanoparticles: Soft and Hard Corona. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2532–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Álvarez, R.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hard and Soft Protein Corona of Nanomaterials: Analysis and Relevance. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baimanov, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Cong, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Qiao, R.; et al. In Situ Analysis of Nanoparticle Soft Corona and Dynamic Evolution. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheibani, S.; Basu, K.; Farnudi, A.; Ashkarran, A.; Ichikawa, M.; Presley, J.F.; Bui, K.H.; Ejtehadi, M.R.; Vali, H.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanoscale Characterization of the Biomolecular Corona by Cryo-Electron Microscopy, Cryo-Electron Tomography, and Image Simulation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Beigi, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Zeuthen, C.M.; Eskandari, H.; Scavenius, C.; Juul-Madsen, K.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Enghild, J.J.; Sutherland, D.S. Mapping and Identification of Soft Corona Proteins at Nanoparticles and Their Impact on Cellular Association. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Simon, J.; Mailänder, V.; Morsbach, S.; Landfester, K. Preservation of the Soft Protein Corona in Distinct Flow Allows Identification of Weakly Bound Proteins. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docter, D.; Distler, U.; Storck, W.; Kuharev, J.; Wünsch, D.; Hahlbrock, A.; Knauer, S.K.; Tenzer, S.; Stauber, R.H. Quantitative Profiling of the Protein Coronas that Form around Nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2030–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkarran, A.A.; Gharibi, H.; Voke, E.; Landry, M.P.; Saei, A.A.; Mahmoudi, M. Measurements of Heterogeneity in Proteomics Analysis of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona across Core Facilities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V. Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.; Andreozzi, P.; Dal Magro, R.; Fiordaliso, F.; Corbelli, A.; Talamini, L.; Chinello, C.; Raimondo, F.; Magni, F.; Tringali, M.; et al. Evolution of Nanoparticle Protein Corona across the Blood–Brain Barrier. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7292–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, P.; Butner, J.D.; Chuang, Y.; Caserta, S.; Goel, S.; Brinker, C.J.; Cristini, V.; Wang, Z. Mathematical Modeling in Cancer Nanomedicine: A Review. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Orco, D.; Lundqvist, M.; Oslakovic, C.; Cedervall, T.; Linse, S. Modeling the Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona in a Body Fluid. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, O.; Mittag, J.J.; Kelly, P.M.; Milani, S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J.O.; Franzese, G. Understanding the Kinetics of Protein–Nanoparticle Corona Formation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10842–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, H.; Liu, X.; Austin, L.; Maes, G.; Huo, Q. Dynamic Light Scattering as a Powerful Tool for Gold Nanoparticle Bioconjugation and Biomolecular Binding Studies. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9425–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Saccardo, A.; Roccatano, D.; Aboagye-Mensah, D.; Alkaseem, M.; Jewkes, M.; Di Nezza, F.; Baron, M.; Soloviev, M.; Ferrari, E. Modular Assembly of Proteins on Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soloviev, M.; Siligardi, G.; Roccatano, D.; Ferrari, E. Modelling the Adsorption of Proteins to Nanoparticles at the Solid-Liquid Interface. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, H.P. Size and Shape of Protein Molecules at the Nanometer Level Determined by Sedimentation, Gel Filtration, and Electron Microscopy. Biol. Proced. Online 2009, 11, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piella, J.; Bastús, N.G.; Puntes, V. Size-Dependent Protein–Nanoparticle Interactions in Citrate-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: The Emergence of the Protein Corona. Bioconjug Chem. 2017, 28, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Fang, Q. Interaction of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles with Human Plasma: Analysis of Protein Corona Reveals Specific Binding Patterns. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancolini, G.; Maschio, M.C.; Cantarutti, C.; Corazza, A.; Fogolari, F.; Bellotti, V.; Corni, S.; Esposito, G. Citrate Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles Interfere with Amyloid Fibril Formation: D76N and ΔN6 Β2-Microglobulin Variants. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4793–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaspina, D.C.; Faraudo, J. Computer Simulations of the Interaction between SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Different Surfaces. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 051008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A Worldwide Hub of Protein Knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.C.G.; Krüger, K.; Besford, Q.A.; Schlenk, M.; Kempe, K.; Förster, S.; Caruso, F. In Situ Characterization of Protein Corona Formation on Silica Microparticles Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Combined with Microfluidics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Liu, R.; Deng, Z.; Ge, G.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L. Quantitative Study of Protein Coronas on Gold Nanoparticles with Different Surface Modifications. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzen, S.; Schoettler, S.; Baier, G.; Rosenauer, C.; Mailaender, V.; Landfester, K.; Mohr, K. Complementary Analysis of the Hard and Soft Protein Corona: Sample Preparation Critically Effects Corona Composition. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotnikov, D.V.; Berlina, A.N.; Ivanov, V.S.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Adsorption of Proteins on Gold Nanoparticles: One or More Layers? Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColman, S.; Li, R.; Osman, S.; Bishop, A.; Wilkie, K.P.; Cramb, D.T. Serum Proteins on Nanoparticles: Early Stages of the “Protein Corona”. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 20550–20563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, R.; Nienhaus, K.; Nienhaus, G.U. Formation of a Monolayer Protein Corona around Polystyrene Nanoparticles and Implications for Nanoparticle Agglomeration. Small 2019, 15, 1900974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Nienhaus, G.U. In Situ Characterization of Protein Adsorption onto Nanoparticles by Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yu, S. Probing the Binding Affinity of Plasma Proteins Adsorbed on Au Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4787–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi Sahneh, F.; Scoglio, C.; Riviere, J. Dynamics of Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Complex Formation: Analytical Results from Population Balance Equations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, V.P.; Cho, N.J. Kinetics of the Formation of a Protein Corona around Nanoparticles. Math. Biosci. 2016, 282, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioletti-Uberti, S.; Ballauff, M.; Dzubiella, J. Dynamic Density Functional Theory of Protein Adsorption on Polymer-Coated Nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 7932–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Luan, Y.; Dai, W. Dynamic Process, Mechanisms, Influencing Factors and Study Methods of Protein Corona Formation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


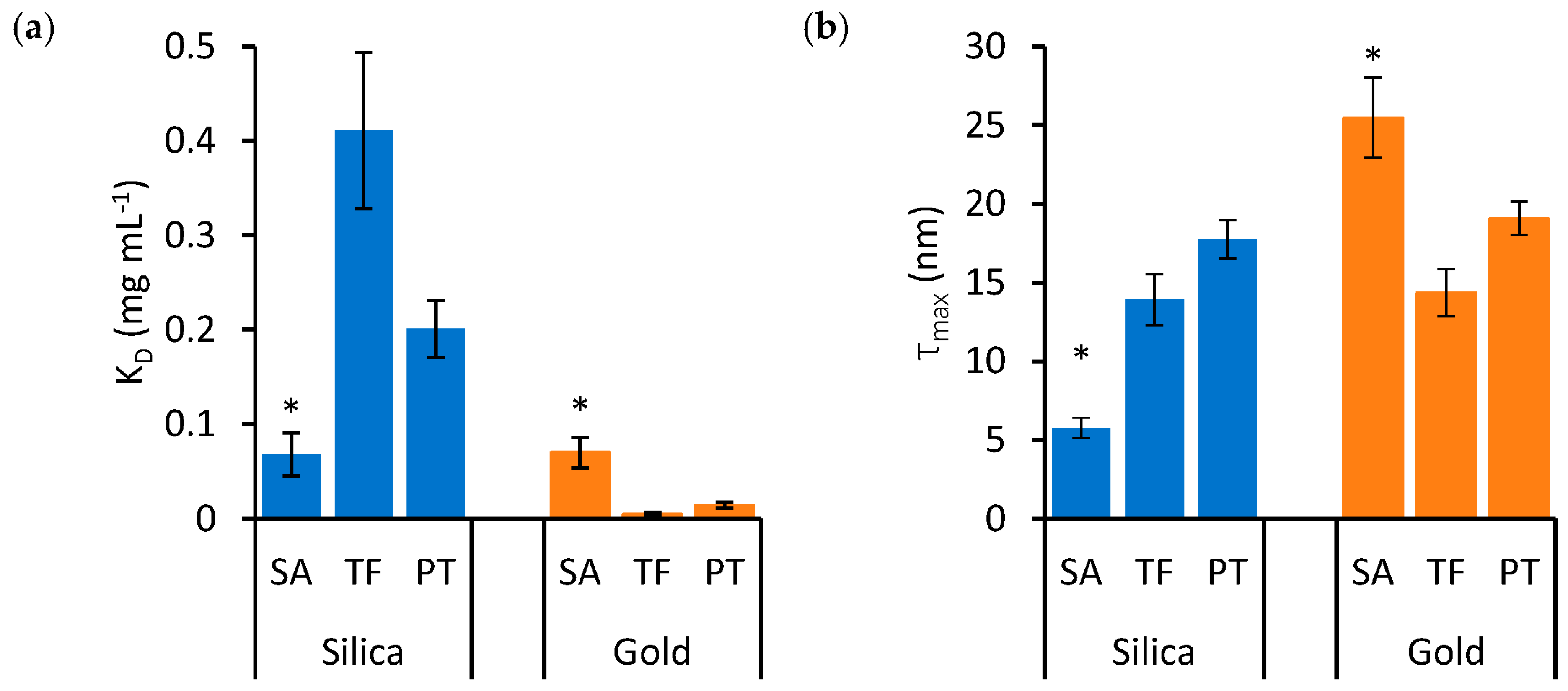

| Protein Type | Nanoparticle Material | KD ± se (mg mL−1) | τmax ± se (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SA | Silica | 0.068 ± 0.023 | 5.8 ± 0.7 |
| Gold | 0.070 ± 0.016 | 25.5 ± 2.5 | |
| TF | Silica | 0.411 ± 0.083 | 13.9 ± 1.6 |
| Gold | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 14.3 ± 1.5 | |
| PT | Silica | 0.201 ± 0.030 | 17.8 ± 1.2 |
| Gold | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 19.1 ±1.1 |
| Protein Type | UniProt ID | Mr (kDa) | pI | Gravy Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | P02768 | 67 | 6.67 | −0.395 |
| TF | P02787 | 80 | 6.70 | −0.411 |
| PT | P00734 | 72 | 5.23 | −0.606 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cornwell, S.E.; Okocha, S.O.; Ferrari, E. Multivariate Analysis of Protein–Nanoparticle Binding Data Reveals a Selective Effect of Nanoparticle Material on the Formation of Soft Corona. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212901
Cornwell SE, Okocha SO, Ferrari E. Multivariate Analysis of Protein–Nanoparticle Binding Data Reveals a Selective Effect of Nanoparticle Material on the Formation of Soft Corona. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(21):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212901
Chicago/Turabian StyleCornwell, Susannah Emily, Sarah Ogechukwu Okocha, and Enrico Ferrari. 2023. "Multivariate Analysis of Protein–Nanoparticle Binding Data Reveals a Selective Effect of Nanoparticle Material on the Formation of Soft Corona" Nanomaterials 13, no. 21: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212901
APA StyleCornwell, S. E., Okocha, S. O., & Ferrari, E. (2023). Multivariate Analysis of Protein–Nanoparticle Binding Data Reveals a Selective Effect of Nanoparticle Material on the Formation of Soft Corona. Nanomaterials, 13(21), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212901