Wettability of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Reinforced with TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles at Different Reflow Times
Abstract
1. Introduction
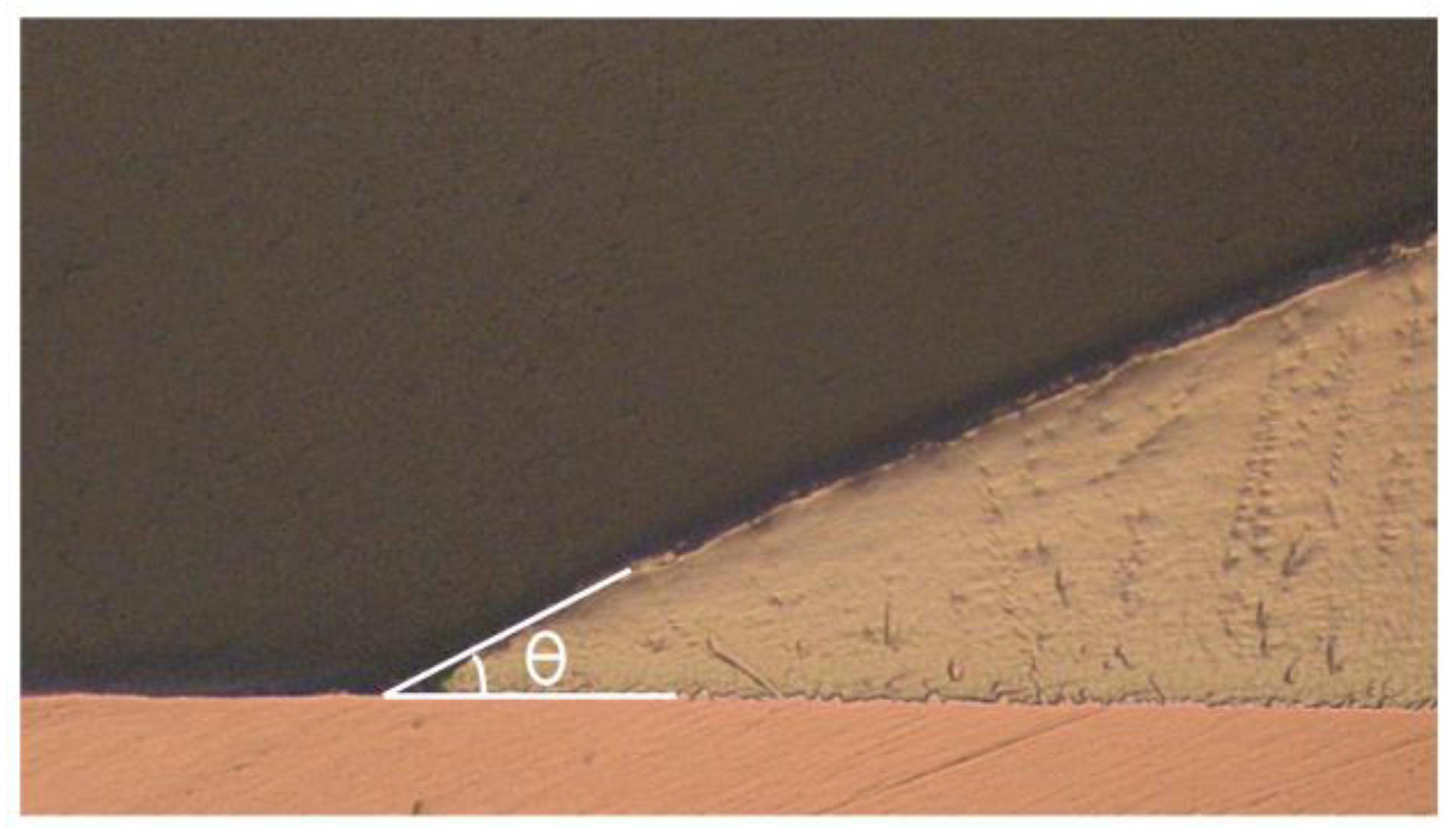
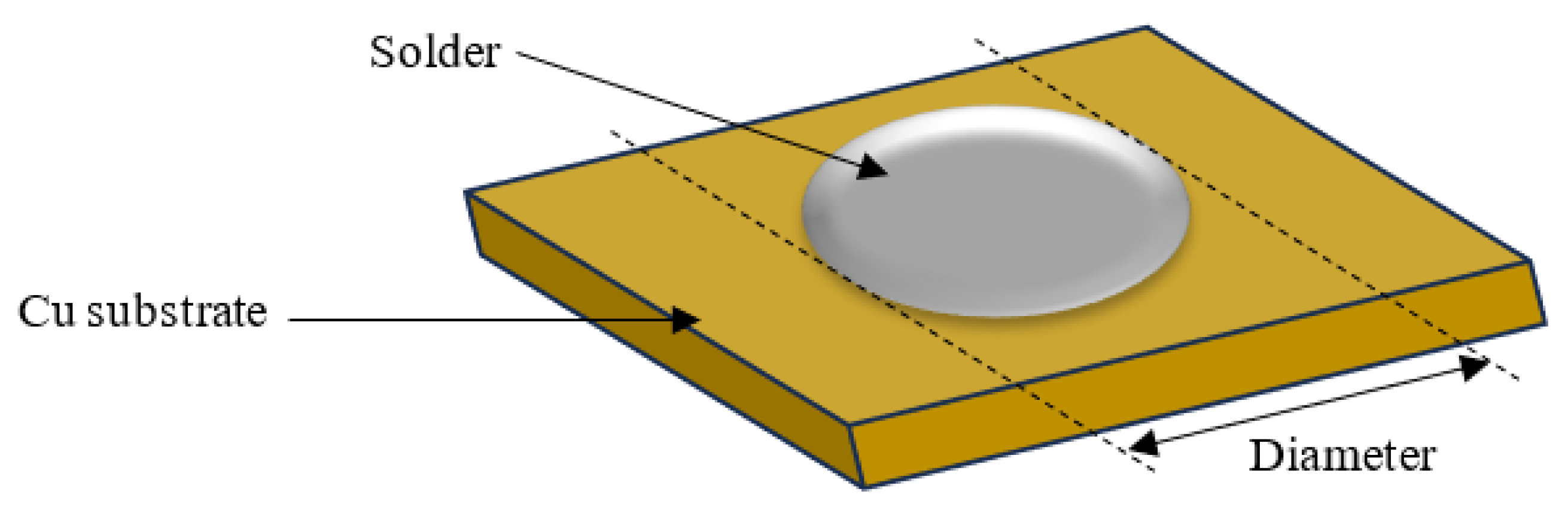
2. Methodology
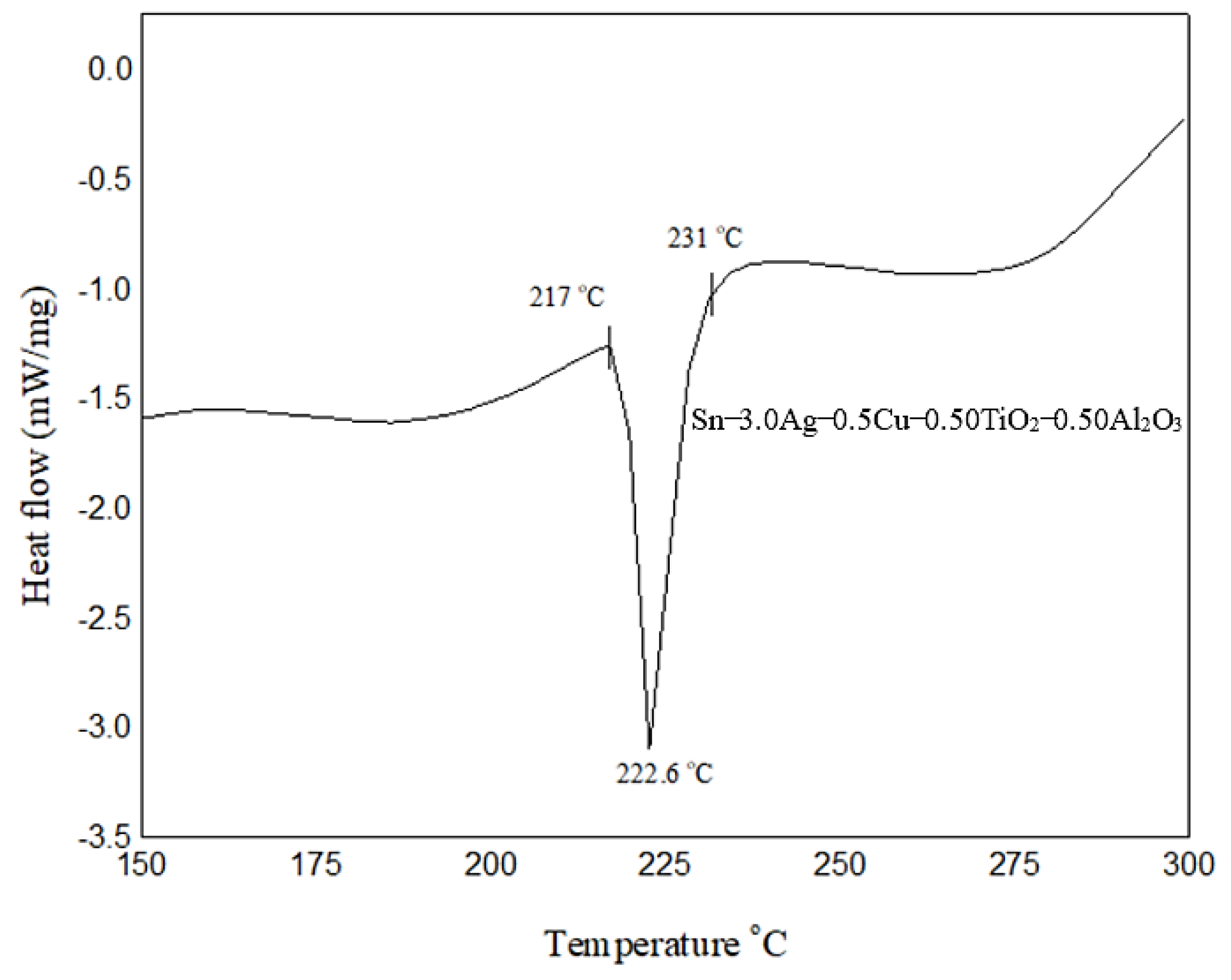
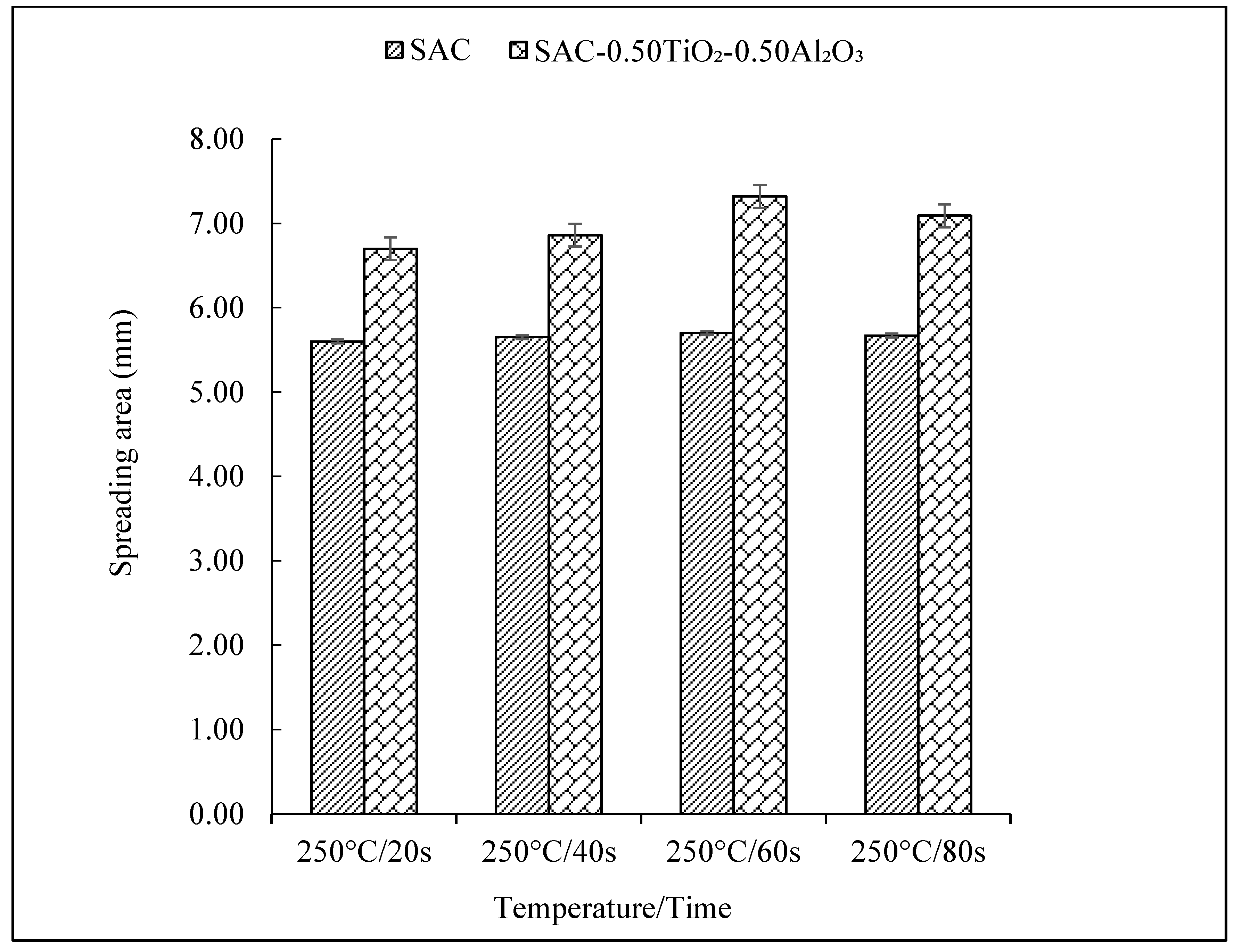
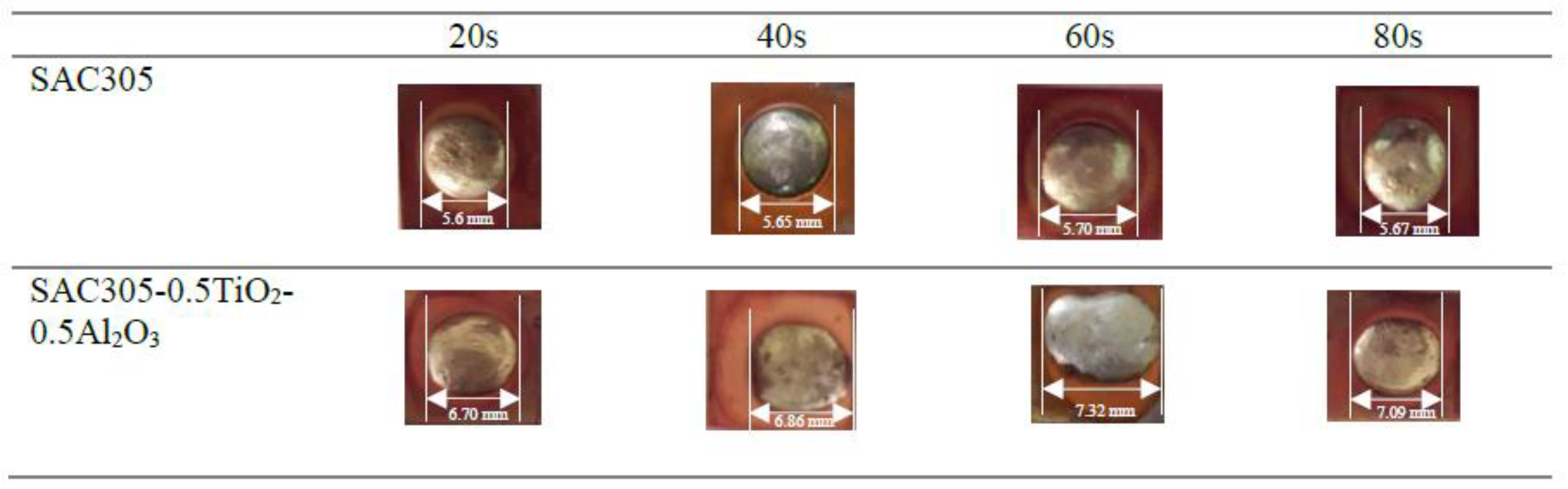
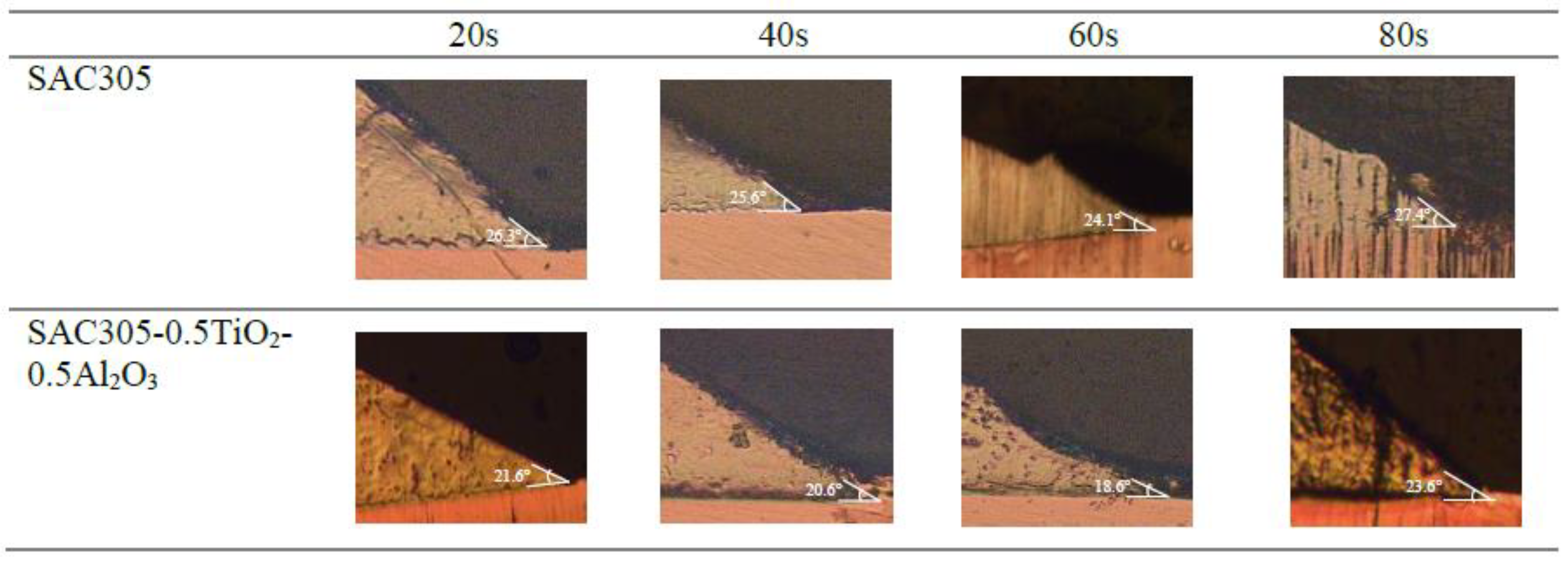
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S.K.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Amalina, A. Effects of metallic nanoparticle doped flux on interfacial intermetallic compounds between Sn3.0Ag-0.5Cu and copper substrate. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC 2013), Singapore, 11–13 December 2013; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, S.; Liang, Z. Properties and Microstructures of Sn-Ag-Cu-X Lead-Free Solder Joints in Electronic Packaging. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 639028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, T.; Mattila, T.; Vuorinen, V.; Karppinen, J.; Li, J.; Sippola, M.; Kivilahti, J.K. Evolution of microstructure and failure mechanism of lead-free solder interconnections in power cycling and thermal shock tests. Microelectron. Reliab. 2007, 47, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zou, C.; Yang, B.; Zhai, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhuravlev, E.; Schick, C. Nanoparticles of SnAgCu lead-free solder alloy with an equivalent melting temperature of SnPb solder alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Madureira, M.A.; Bonilla, S.H.; Giannetti, B.F. Assessing the replacement of lead in solders: Effects on resource use and human health. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazal, M.A.; Liyana, N.K.; Rubaiee, S.; Anas, A. A critical review on performance, microstructure and corrosion resistance of Pb-free solders. Measurement 2019, 134, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Sun, L.; Long, W.M.; He, P.; Xiong, M.Y.; Zhao, M. Reliability issues of lead-free solder joints in electronic devices. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 876–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, M.K.; Gergely, G.; Koncz-Horváth, D.; Gácsi, Z. Investigation of microstructure and wetting behavior of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu (SAC305) lead-free solder with additions of 1.0 wt % SiC on copper substrate. Intermetallics 2021, 128, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Haslinda, M.M.; Ervina Efzan, M.N.; Mohd Mustafa, A.A.; Canan, A. Effects of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles addition on the thermal properties and wettability of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xTiO2-xAl2O3. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2169, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Chan, Y.C. The influence of a small amount of Al and Ni nano-particles on the microstructure, kinetics and hardness of Sn-Ag-Cu solder on OSP-Cu pads. Intermetallics 2012, 29, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Han, Y.D.; Jing, H.Y.; Wei, J.; Xu, L.Y. Effect of graphene nanosheets reinforcement on the performance of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 562, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervina, E.M.N.; Amares, S. Review on the effect of alloying element and nanoparticle additions on the properties of Sn-Ag-Cu solder alloys. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2014, 26, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, D.; Sarmento, M.; Barros, D.; Peixoto, H.; Cerqueira, F. The effect of Bi addition on the electrical and microstructural properties of SAC405 soldered structure. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2021, 33, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles size on the properties of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu nano-composite solders and joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 662, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikale, S.; Prabhu, K.N. Effect of multiple reflow cycles and Al2O3 nanoparticles reinforcement on performance of SAC305 lead-free solder alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 3102–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Cao, T.; Cui, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiao, Z. Effect of nano-ZnO particles on wettability, interfacial morphology and growth kinetics of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-xAnO composite solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 19214–19226. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10854-019-02279-9 (accessed on 12 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Effect of TiO2 addition concentration on the wettability and intermetallic compounds growth of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu–xTiO2 nano-composite solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 3816–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, J. Effects of α-Al2O3 nanoparticles-doped on microstructure and properties of Sn–0.3Ag–0.7Cu low-Ag solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 7372–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amares, S.; Rajkumar, D.; Ervina, E.M.N.; Sia, Y.Y. Reliability Study of Lead Free Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu and Copper (Cu) Substrate based on the Microstructure, Physical and Mechanical Properties. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 5, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, L.C.; Chang, S.Y.; Lee, C.I.; Sun, W.H.; Huang, C.H. Effects of nano-Al2O3 additions on microstructure development and hardness of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu solder. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4831–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Fouzder, T.; Chan, Y.C.; Yung, W.K.C. Microstructure, kinetic analysis and hardness of Sn–Ag–Cu–1wt% nano-ZrO2 composite solder on OSP-Cu pads. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3319–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sohn, H.R.; Jung, J.P. Effect of Graphene Nanoplatelets on Wetting, Microstructure, and Tensile Characteristics of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu (SAC) Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Sharma, A.; Lim, D.U.; Yun, J.H.; Jung, J.P. Effects of AlN Nanoparticles on the Microstructure, Solderability, and Mechanical Properties of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 4372–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukpimai, K.; Suwannakrue, W.; Kanlayasiri, K. Wettability and printability of SAC305-xTiO2 Pb-free solder paste on Cu substrate. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. 2019, 635, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C.; Wu, R.W.; Cheng, T.-H.; Fan, K.-H.; Chen, R.S. Effects of nano-Al2O3 particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu composite solder ball grid array joints on Sn/Cu pads. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.T.; Tan, A.W.; Farazila, Y. Influence of nanoparticle addition on the formation and growth of intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in Cu/Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu solder joint during different thermal conditions. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 033505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xue, S.; Wang, J.; Xue, P.; Zhong, S.; Long, W. Effect of Nanoparticles Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of Lead-Free Solders: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, S. Materials modification of the lead-free solders incorporated with micro/nano-sized particles: A review. Mater. Des. 2020, 197, 109224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Zhang, L. Microstructure, mechanical and electrical performances of zirconia nanoparticles-doped tin-silver-copper solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 7524–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Xu, A.; Rosei, F.; Ma, D.; Chen, G. Interfacial reaction-directed synthesis of a ceria nanotube-embedded ultra-small Pt nanoparticle catalyst with high catalytic activity and thermal stability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14148–14154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.Y.; Zhang, L. Interface reaction and intermetallic compound growth behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder joints on different substrates in electronic packaging. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1741–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathian, Z.; Maleki, A.; Niroumand, B. Synthesis and characterization of ceramic nanoparticles reinforced lead-free solder. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5302–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenyu, Z.; Lei, L.; Hyun, S.C.; Jian, C.; Qian, W.; Yuming, W.; Guisheng, Z. Effect of nano-Al2O3 reinforcement on the microstructure and reliability of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 60, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, T.Y. Effect of nano-TiO2 particles and cooling rate on the thermal, microstructure and mechanical properties of novel low-ag Sn1.5Sb1Ag solders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of nano-Fe2O3 additions on wettability and interfacial intermetallic growth of low-Ag content Sn–Ag–Cu solders on Cu substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 627, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, Z.; Saad, A.; Abas, M.; Ali, M.; Fakpan, K. Structural analysis on nanocomposites lead free solder using nanoindentation. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. (JAMT) 2022, 16, 15–28. Available online: https://jamt.utem.edu.my/jamt/article/view/6383/3991 (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Tikale, S.; Prabhu, K.N. Development of low-silver content SAC0307 solder alloy with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 787, 139439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sorory, H.; Gumaan, M.S.; Shalaby, R.M. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure, mechanical and thermal properties of rapid quenching SAC355 lead-free solder alloy. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2023, 35, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.K.; Chan, Y.C. Growth mechanism of intermetallic compounds and damping properties of Sn–Ag–Cu-1wt% nano-ZrO2 composite solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 2014, 54, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C.; Chang, S.Y. Effects of Nano-TiO2 additions on thermal analysis, microstructure and tensile properties of Sn3.5Ag0.25Cu solder. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Jain, C.C.; Chuang, T.H.; Feng, L.P.; Tsao, L.C. Effect of addition of TiO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure, microhardness and interfacial reactions of Sn3.5AgxCu solder. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4720–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amares, S.; Rajkumar, D. Effect on the wettability, hardness and shear strength properties of 3%-nano Titanium Oxide (TiO2) added Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu (SAC)/Copper (Cu) solder joint. MATEC Web Conf. 2014, 237, 02013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erer, A.M.; Oguz, S.; Türen, Y. Influence of bismuth (Bi) addition on wetting characteristics of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy on Cu substrate. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bian, X.; Qiu, X.; Jia, Y.; Yi, J.; Wang, G. Investigation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SAC105 Solders with Sb, In, Ni, and Bi Additions. Materials 2023, 16, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervina, E.M.N.; Zuhailawati, H.; Radzali, O. Low temperature In–Bi–Zn solder alloy on copper substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efzan, E.M.N.; Aisyah, M. A review of solder evolution in electronic application. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2012, 1, 1–10. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=3de96da6928bdb6155646f71375087cabe11f7a0 (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Noor, E.E.M.; Sharif, N.M.; Yew, C.K.; Ariga, T.; Ismail, A.B.; Hussain, Z. Wettability and strength of In–Bi–Sn lead-free solder alloy on copper substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 507, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tu, K.N. Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2014, 82, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chan, Y.C. Research advances in nano-composite solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, K. Lead-Free Soldering in Electronics: Science, Technology and Environmental Impact, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Interfacial IMC growth of SAC305/Cu joint with a novel dual-layer of Ni(P)/Cu plating during solid-state aging. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 199, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.D.; Huang, M.L.; Zhou, S.M. Effect of electromigration on intermetallic compound formation in line-type Cu/Sn/Cu interconnect. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 504, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Duh, J.G.; Kao, C.R. Direct evidence for a Cu-enriched region at the boundary between Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn during Cu/Sn reaction. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.Q.; Wu, C.M.L.; Law, C.M.T.; Wang, L.; Lai, J.K.L. Intermetallic compounds growth between Sn-3.5Ag lead-free solder and Cu substrate by dipping method. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 392, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.Q.; Wang, L. The growth and roughness evolution of intermetallic compounds of Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu interface during soldering reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 458, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wilding, I.J.; Collins, M.N. Alloying influences on low melt temperature SnZn and SnBi solder alloys for electronic interconnections. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 665, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, K.; Khodabakhshi, F.; Zareh, E.; Shahbazkhan, A.; Simchi, A. Effect of alumina nanoparticles on the microstructure and mechanical durability of meltspun lead-free solders based on tin alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688 Pt A, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, G.Y.; Pan, Y.C. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles on IMC growth in Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu–xTiO2 solder joints in reflow process. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 554, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, L.C. Suppressing effect of 0.5 wt.% nano-TiO2 addition into Sn–3.5Ag–0.5Cu solder alloy on the intermetallic growth with Cu substrate during isothermal aging. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 8441–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.H.; Wu, M.W.; Chang, S.Y.; Ping, S.F.; Tsao, L.C. Strengthening mechanism of nano-Al2O3 particles reinforced Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu lead-free solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed Muzni, N.H.; Mhd Noor, E.E.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B. Wettability of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Reinforced with TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles at Different Reflow Times. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202811
Mohamed Muzni NH, Mhd Noor EE, Abdullah MMAB. Wettability of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Reinforced with TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles at Different Reflow Times. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(20):2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202811
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed Muzni, Nur Haslinda, Ervina Efzan Mhd Noor, and Mohd Mustafa Al Bakri Abdullah. 2023. "Wettability of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Reinforced with TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles at Different Reflow Times" Nanomaterials 13, no. 20: 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202811
APA StyleMohamed Muzni, N. H., Mhd Noor, E. E., & Abdullah, M. M. A. B. (2023). Wettability of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Reinforced with TiO2 and Al2O3 Nanoparticles at Different Reflow Times. Nanomaterials, 13(20), 2811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13202811





