Influences of Cu Doping on the Microstructure, Optical and Resistance Switching Properties of Zinc OxideThin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
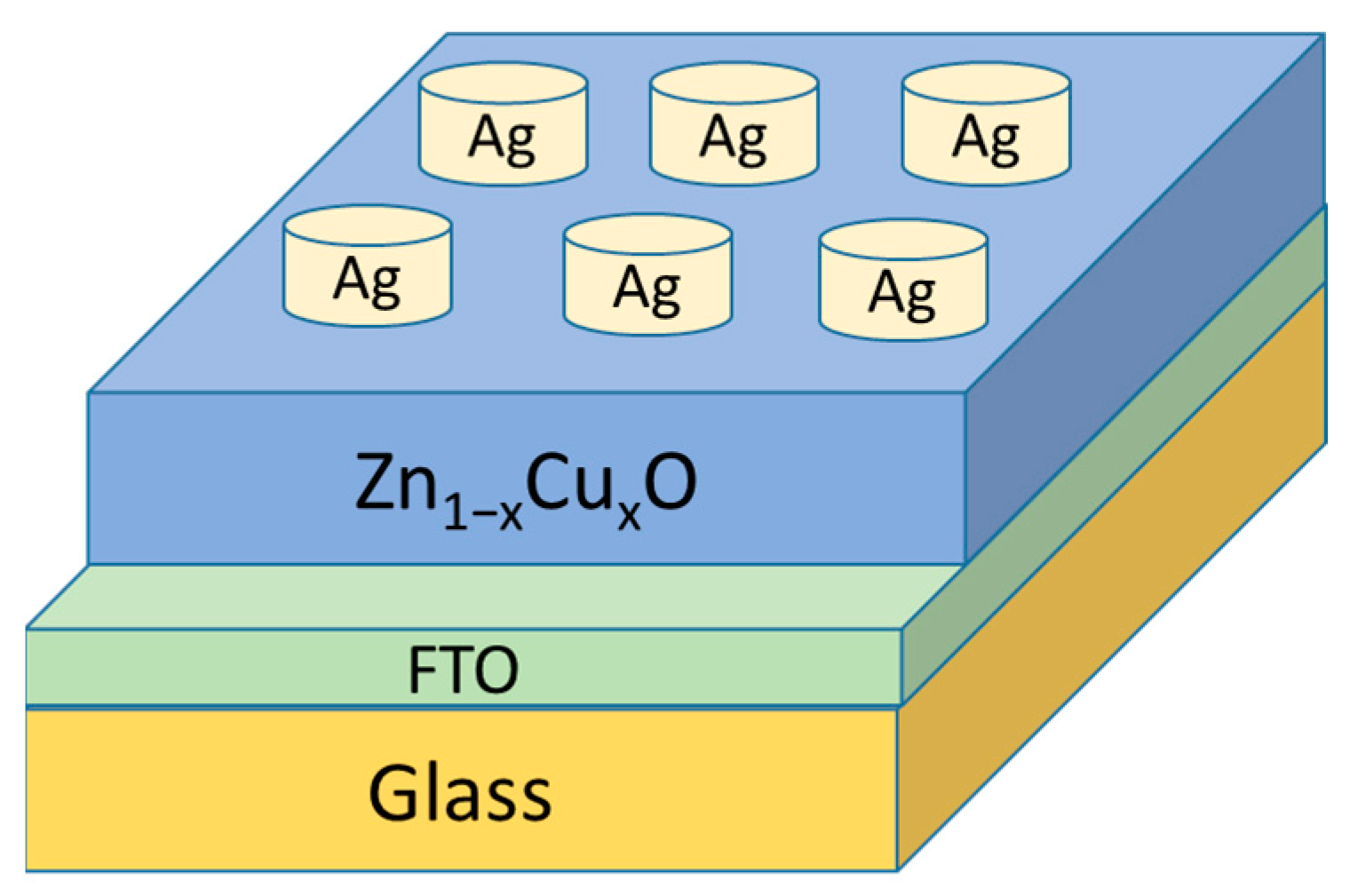
2. Experimental Section
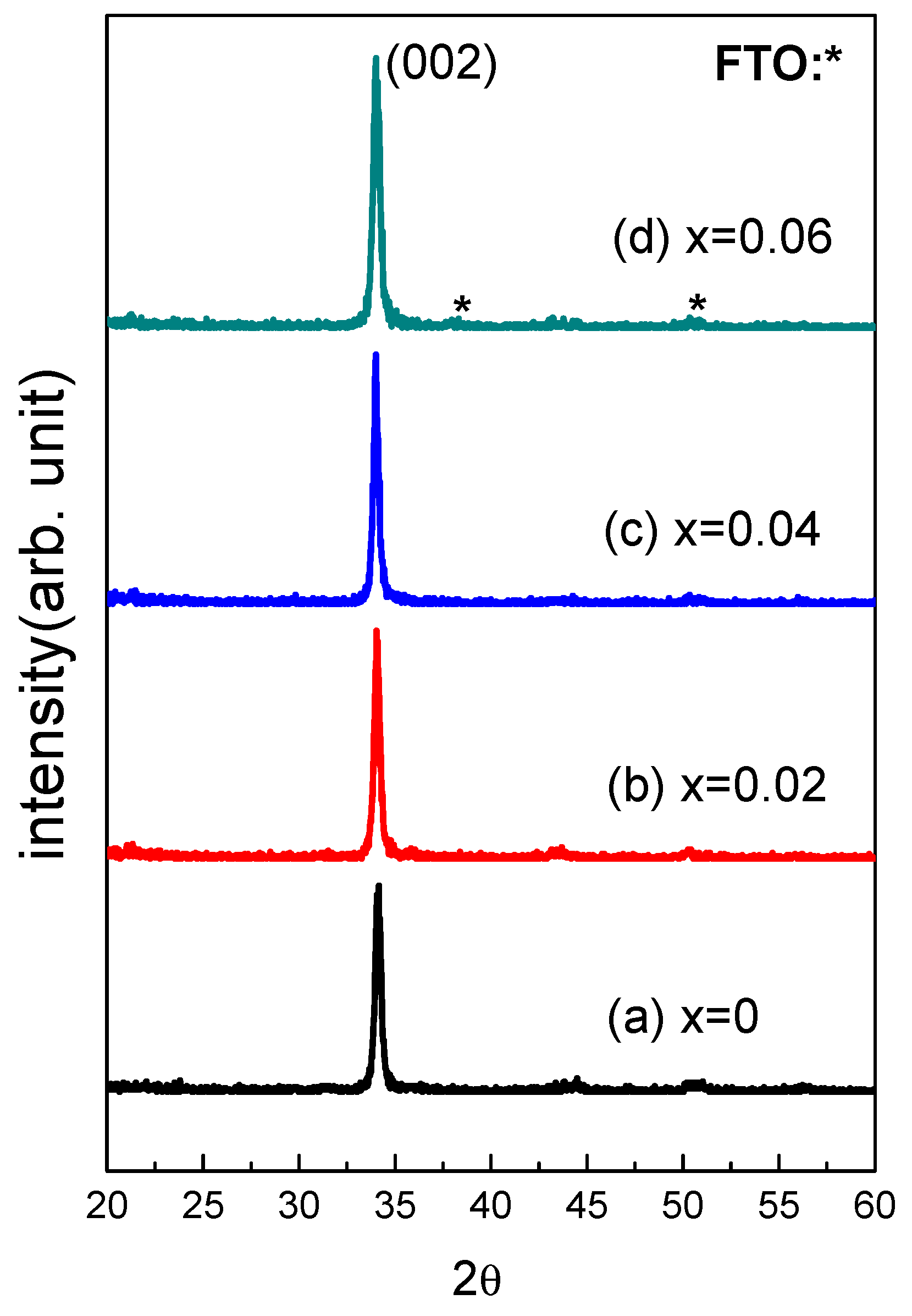
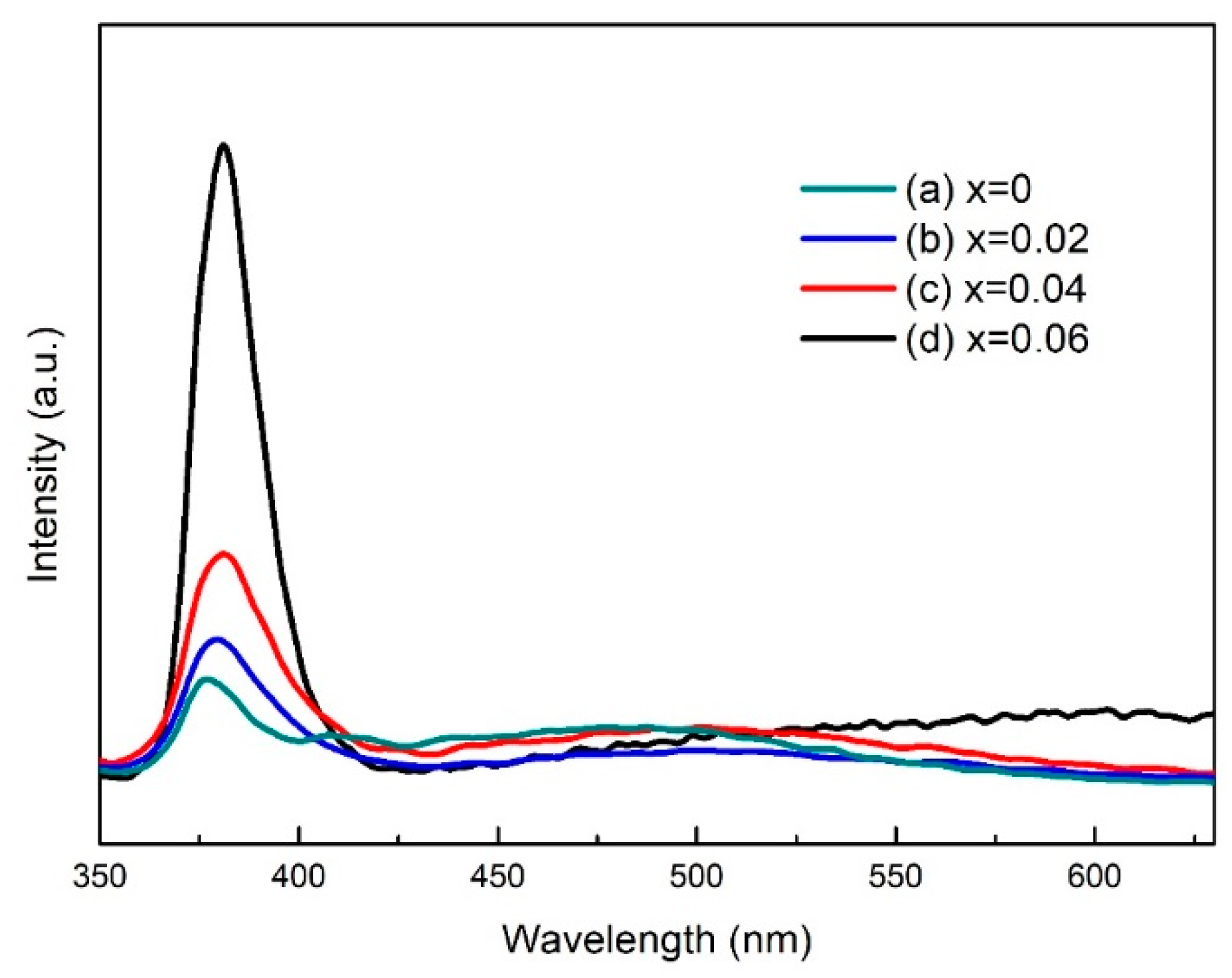
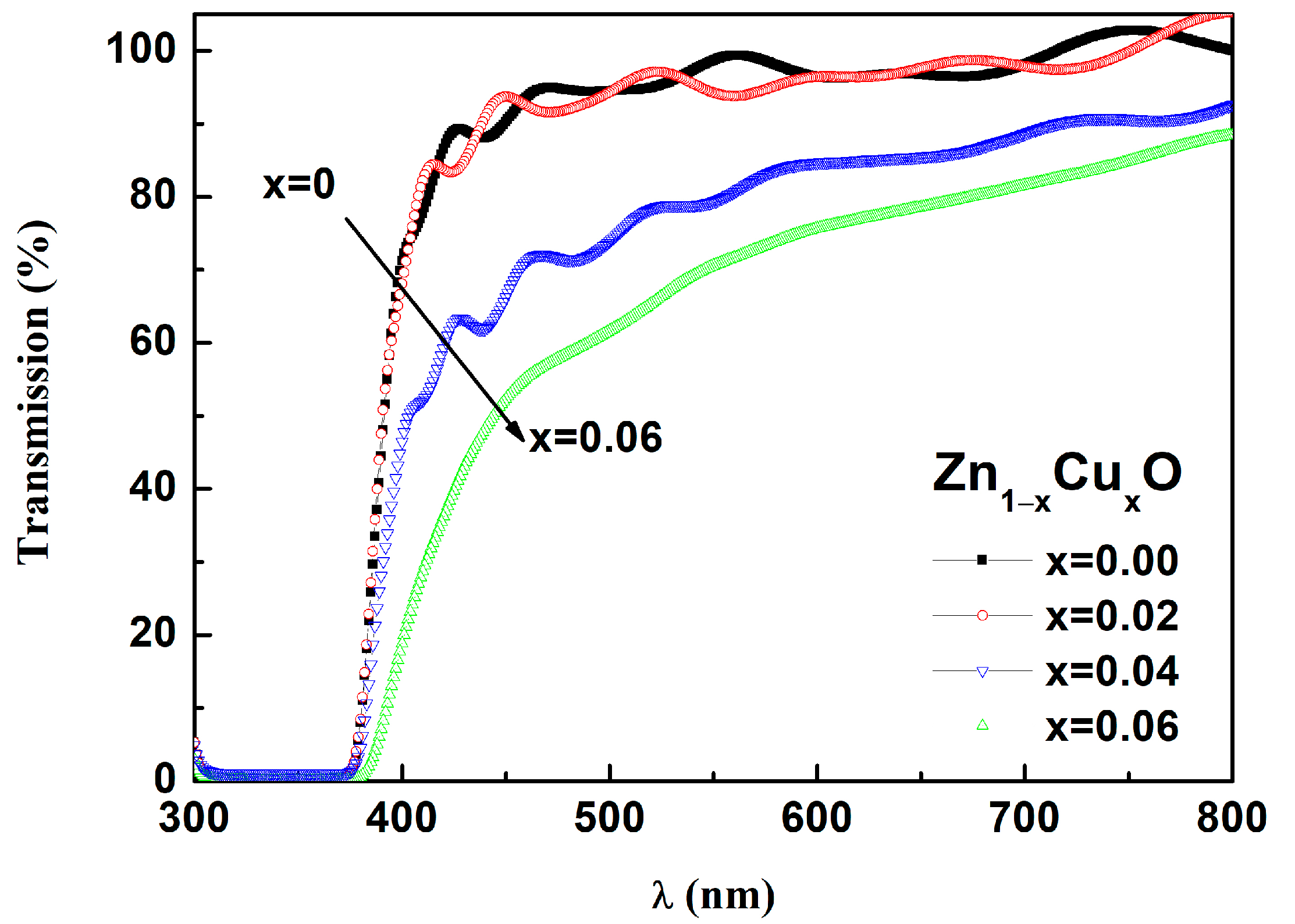
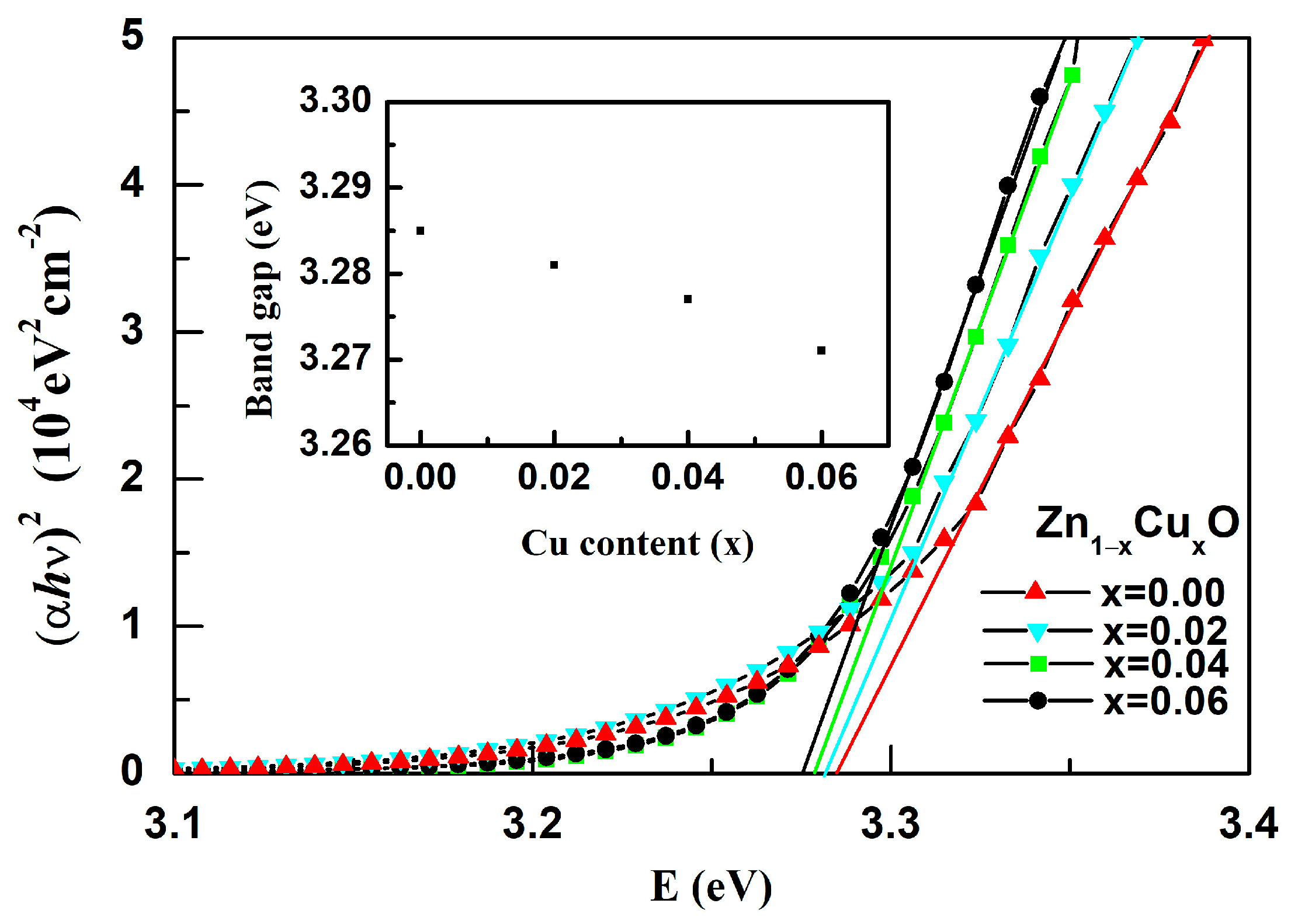
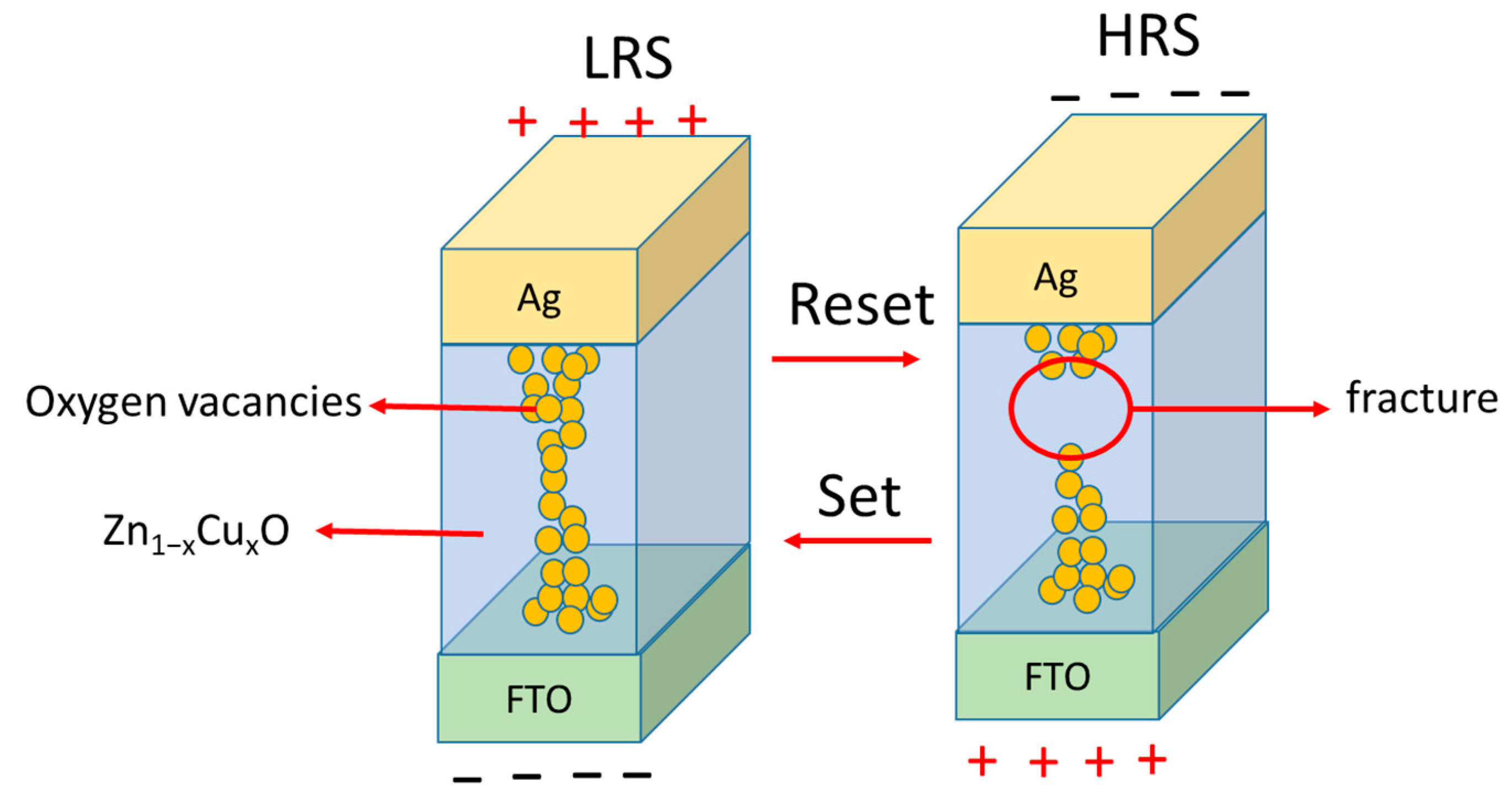
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Li, Y.T.; Long, S.B.; Zhang, M.H.; Liu, Q.; Shao, L.B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, Q.Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, M. Resistive switching properties of Au/ZrO2/Ag structure for low-voltage nonvolatile memory applications. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2010, 31, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Robertson, J. Materials selection for oxide-based resistive random access memories. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 223516–223518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, F.M.; Larcher, L.; Bersuker, G.; Padovani, A.; Pavan, P. An empirical model for RRAM resistance in low- and high-resistance states. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2013, 34, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, F.; Peng, S.; He, C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. Improvement of resistive switching in Cu/ZnO/Pt sandwiches by weakening the randomicity of the formation/rupture of Cu filaments. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 275204–275208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.J.; Wei, T.C.; Tsai, D.S.; Lin, C.H.; He, J.H. Surface effects of electrode-dependent switching behavior of resistive random-access memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 131603–131606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-Y.; Lai, Y.-C.; Wu, S.-F.; Wang, F.; Chen, F.; Tsai, M.-J.; Tsai, M.-J. Unipolar resistive switching characteristics of ZnO thin films for nonvolatile memory applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 022110–022113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Han, D.; Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Kang, J.; Yu, B. Characteristics and mechanism of conduction/set process in TiNZnOPt resistance switching random-access memories. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 92232112–92232113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Moon, H.; Gupt, D.; Yoo, S.; Choi, Y.K. Resistive Switching Characteristics of Sol–Gel Zinc Oxide Films for Flexible Memory Applications. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2009, 56, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, M.; Heluani, S.P.; Juarez, G.; Simonelli, G.; Braunstein, G.; Duhalde, S. Electric-pulse-induced reversible resistance in doped zinc oxide thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 052105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Lu, Y.M.; Shen, D.Z.; Fan, X.W.; Kong, X.G. Structure and photoluminescence of Mn-passivated nanocrystalline ZnO thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 254, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.T.; Kim, D.H.; Zhao, X.H.; Ying, L.; Zhu, M.Y.; Lee, B.; Liu, C. Effect of Co doping on unipolar resistance switching in Pt/Co:ZnO/Pt structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hao, A.; Qin, N.; Bao, D. Unipolar resistive switching properties of Pr-doped ZnO thin films. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S474–S480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, M.; Zeng, B. Top electrode-dependent resistance switching behaviors of lanthanum-doped ZnO film memory devices. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 114, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.C.; Yang, M.Y. Trap characterization and conductance quantization in phosphorus-doped ZnO memory devices. Vacuum 2017, 140, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.J.; Su, W.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Hu, B.L.; Pan, L.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.D.; Li, R.W. Observation of Conductance Quantization in Oxide-Based Resistive Switching Memory. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Li, G.P.; Ye, J.Y.; Wei, Z.P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.D.; Xing, G.Z.; Wu, T. Electrode dependence of resistive switching in Mn-doped ZnO: Filamentary versus interfacial mechanisms. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 192113–192115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Pan, F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Zeng, F. Fully Room-Temperature-Fabricated Nonvolatile Resistive Memory for Ultrafast and High-Density Memory Application. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T.; Ohno, H.; Matsukura, F.; Cibert, J.; Ferrand, D. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 2000, 287, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Hou, T.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Lee, S.T. First-principles study of doping effect on the phase transition of zinc oxide with transition metal doped. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 541, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, A.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Maqueira, L. Structural, chemical and optical evaluation of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by an aqueous solution method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Kim, S.J. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, N.; Revathi, M.; Pachamuthu, P. Surface and optical properties of undoped and Cu doped ZnO nanostructures. Optik 2017, 130, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, A.W. A new method of X-ray crystal analysis. Phys. Rev. 1917, 10, 661–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.L.; Vanalakara, S.A.; Patil, P.S.; Kim, J.H. Fabrication of nanostructured ZnO thin films based NO2 gas sensor via SILAR technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Ambedkar, A.K.; Tyagi, S.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, A.; Gautam, Y.K.; Singh, B.P. Room temperature photoluminescence and spectroscopic ellipsometry of reactive co-sputtered Cu-doped ZnO thin films. Optik 2022, 257, 168860–168871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Srivastava, S.; Aziz, M.K.; Kanaoujiya, R.; Rajkumar, C. Photosensitivity and structural properties of vanadium-doped ZnO and ZnO nanoparticle at various calcined temperature. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ai, X.; Huang, X.; Ma, S. Effects of the substrate and oxygen partial pressure on the microstructure and optical properties of Ti-doped ZnO thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 2011, 50, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbali, R.; Essalah, G.; Ghoudi, A.; Guermazi, H.; Guermazi, S.; El Hdiy, A.; Benhayoune, H.; Duponchel, B.; Oueslati, A.; Leroy, G. The effect of (In, Cu) doping and co-doping on physical properties and organic pollutant photodegradation efficiency of ZnO nanoparticles for wastewater remediation. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 33828–33841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuermeier, J.; Wardenga, H.F.; Morasch, J.; Siol, S.; Nandy, S.; Calmeiro, T.; Klein, A.; Fortunato, E. Highly conductive grain boundaries in copper oxide thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 235303–235308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chuang, P.Y.; Lin, Y.S. Abnormal volatile memory characteristic in normal nonvolatile ZnSnO resistive switching memory. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2018, 65, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanana, R.K. Determination of electron and hole effective masses in thermal oxide utilizing an n-channel silicon MOSFET. IOSR J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Guan, X.; Wong, H.-S.P. Conduction mechanism of TiN/HfOx/Pt resistive switching memory: A trap-assisted-tunneling model. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 063507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, J.-H.; Kao, M.-C.; Chen, K.-H.; Li, M.-Z. Influences of Cu Doping on the Microstructure, Optical and Resistance Switching Properties of Zinc OxideThin Films. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192685
Weng J-H, Kao M-C, Chen K-H, Li M-Z. Influences of Cu Doping on the Microstructure, Optical and Resistance Switching Properties of Zinc OxideThin Films. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(19):2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192685
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Jun-Hong, Ming-Cheng Kao, Kai-Huang Chen, and Men-Zhe Li. 2023. "Influences of Cu Doping on the Microstructure, Optical and Resistance Switching Properties of Zinc OxideThin Films" Nanomaterials 13, no. 19: 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192685
APA StyleWeng, J.-H., Kao, M.-C., Chen, K.-H., & Li, M.-Z. (2023). Influences of Cu Doping on the Microstructure, Optical and Resistance Switching Properties of Zinc OxideThin Films. Nanomaterials, 13(19), 2685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192685








