Abstract
The requirement of simple, efficient and accurate detection of tetracycline (TC) in water environments poses new challenges for sensing platform development. Here, we report a simple method for TC sensing via fluorescence detection based on metal–organic coordination polymers (MOCPs, (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26)) coated with nitrogen-doped carbon dots (NCDs). These NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) composites showed excellent luminescence features of NCDs with stable bright-blue emission under UV light. The results of the sensing experiment showed that the fluorescence of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) can be quenched by TC (166 µM) with 94.1% quenching efficiency via the inner filter effect (IFE) in a short time (10 s), with a detection limit (LOD) of 33.9 nM in a linear range of 8–107 µM. More significantly, NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) showed a high selectivity for TC sensing in the presence of anions and metal cations commonly found in water environments and can be reused in at least six cycles after washing with alcohol. The potential practicality of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was verified by sensing TC in real water samples with the standard addition method, and satisfactory recoveries from 91.95% to 104.72% were obtained.
1. Introduction
Because of its advantages of low cost and effective treatment for bacterial pathogens, antibiotics are widely used in agriculture, animal husbandry, aquaculture and other fields [1]. It is estimated that the global use of antibiotics is expected to reach 225,000 tons by 2020 [2], of which China is the world’s largest user, accounting for about 45% of global consumption each year [3]. However, studies have shown that about 30–70% of antibiotics are not metabolized sufficiently by humans and animals and thus released into the environment in their original form. In recent years, the presence of antibiotics has been found in surface waters in East Asia, Southeast Asia, the United States, Europe and other places at concentrations between ng·L−1 and mg·L−1 [4,5]. Despite the low concentration, long-term exposure to antibiotics is harmful to microbial, plant, animal and human health. Based on the investigation of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, tetracycline (TC) is one of the most commonly used antibiotics in veterinary treatment and animal growth [6]. Considering that the long-term existence of TC in the environment may pose potential risks to organisms such as endocrine disruption, neurotoxicity and genotoxicity, the accurate and quick identification of the concentration of TC in water environments is imperative.
For more effective monitoring of TC in water environments, a number of analytical techniques have been developed in recent years [7,8,9]. As the fluorescent sensing method can avoid the complex operation of traditional large-scale instrumental detection methods, the detection of antibiotics with the fluorescence sensing method has attracted increasing attention recently. Usually, the fluorescence method is based on materials including rare earth metals, fluorescent dyes and some quantum dots [10,11]. However, such fluorescent molecules usually have small sizes and high solubility, which make them difficult to recover in aqueous environments.
Metal–organic coordination polymers (MOCPs) composed of metal ions and organic ligands have attracted much attention due to their diverse structures and abundant active sites [12]. The unique structure and properties give MOCPs broad application prospects in the fields of catalysis [13,14,15], drug delivery [16,17], adsorption [18,19], gas storage [20,21] and sensing [22,23]. At present, there are studies on the application of MOCPs in the field of TC detection. Wang’s group studied the luminescence performance of ZIF-8 and realized the detection of TC in water by ZIF-8 based on the aggregation-induced emission effect [24]. Li’s group fabricated a Zn(bix) coordination polymer (bix = 1,4-bis(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene) and achieved the quantitative detection of TC based on the luminescence of Zn(bix) turned on [25]. However, the intrinsic luminescence of MOCPs usually comes from the charge transfer between the metal and the ligand, or from the luminescence of the metal and organic ligand, which often has low quantum yields and weak luminescence, thus limiting their further practical application. The post-synthetic modification (PSM) method can enhance the luminescence properties of the original MOCPs by loading fluorescence functional materials while retaining the properties of the original MOCPs. In recent years, carbon dots (CDs), a kind of fluorescence material with high quantum yield and long lifetime, have attracted wide attention due to their strong chemical inertness and low toxicity, making them ideal luminescent guests to improve the luminescence performance of MOCPs.
In this study, a simple strategy at room temperature was used to fabricate a fluorescence sensor (NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26)) by introducing nitrogen-doped carbon dots (NCDs) onto a polyoxomolybdate-based coordination polymer ((4-Hap)4(Mo8O26)) for efficient, sensitive and selective detection of TC in aqueous solution. NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) exhibits bright-blue fluorescence emission derived from the NCDs and can be quenched with the addition of TC, which is caused by the inner filter effect (IFE). In addition, NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) can achieve quantitative detection of TC in a wide linear range (8–107 µM) with a detection limit (LOD) of 33.9 nM. Significantly, NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) has been successfully used in sensing TC in real water samples (i.e., river water and tap water), suggesting great practical application potential in the detection of water-environment contaminants.
2. Experiment and Method
2.1. Materials
All chemical reagents used in this work were analytically pure chemicals that did not require further purification. Chemicals used for (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) preparation, namely, ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate, cadmium chloride hemi(pentahydrate), 4-aminopyridine and antibiotics including tetracycline (TC), ciprofloxacin (CIP), chloramphenicol (CAP), sulfadiazine (SDZ), sulfamethazine (SMZ), thiamphenicol (THI), metronidazole (MDZ) and ornidazole (ODZ), were purchased from Aladdin Industrial Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The other chemicals used in this work were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
2.2. Instrumentation
The microstructure was determined by a scanning electron microscope (SEM), JSM-IT500HR, Tokyo, Japan. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were examined on a Bruker D8 X-ray diffractometer (Billerica, MA, USA) with CuKα line as radiation source. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were recorded on a Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS 5, Waltham, MA, USA. X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) were measured by a Thermo Scientific K-Alpha, Waltham, MA, USA to determine the surface element composition of the samples. The fluorescence spectra and luminescent lifetimes were acquired on a FS5 Fluorescence Spectrometer (Edinburgh, UK), and the lifetime was obtained by the luminescent decay fitting. UV-vis absorption spectra were measured by a HACH DR-6000 UV-visible spectrophotometer (Loveland, CA, USA).
2.3. Fabrication of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26)
NCDs were synthesized according to a previous work [26]. In detail, 1.05 g citric acid was dispersed in 10 mL deionized H2O, and then, 0.335 mL ethylenediamine was added. The mixture was stirred for 30 min and then added to a 25 mL Teflon-lined autoclave and heated at 473.15 K for 5 h. After it was cooled down to room temperature, a brown-black solution was obtained and then centrifuged to remove large particles.
A hydrothermal method was used to synthesize (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) according to a previous work [19]. First, 0.0685 g cadmium chloride hydrate (CdCl2·2.5H2O), 0.028 g 4-aminopyridine (4-ap, C5H6N2) and 0.7415 g ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate (H24Mo7N6O24·4H2O) were blended and added to 20 mL deionized water. Then, after 10 min ultrasound treatment, the mixture was encapsulated in a 25 mL Teflon-lined autoclave at 443 K, reacting for 72 h. After being filtered and washed with ethanol three times, (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was obtained after being dried in an oven at 60 °C for 6 h.
The prepared (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (10 mg) and NCDs (1 mL) were dispersed in 10 mL deionized water, stirring after 24 h, then centrifugated (8000 r/min) for 5 min and washed twice with methanol. After being dried at 60 °C overnight, the NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was obtained.
2.4. Fluorescence Sensing of TC
The luminescence performance of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was investigated. First, 2 mg NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was added to 2.5 mL deionized water, and the stability of the luminescence was confirmed by recording the fluorescence emission intensity at different time intervals over 7 days. Moreover, the fluorescence emission intensity was measured by immersing 2 mg NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in 2.5 mL deionized water with different pH (3.0–12.0) to investigate the effects of different pH levels in aqueous solution. The response kinetics were further explored with fluorescence intensity measurement by mixing 2 mg NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and 300 µL TC aqueous solution (1 mM) in 2.5 mL deionized water at room temperature for different incubation times.
Under optimized conditions, the sensing performance of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in relation to TC was studied. In detail, 2 mg NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was dispersed in 2.5 mL deionized water, followed by adding TC aqueous solution (1 mM, 20 µL addition each time) to form solutions with different TC concentrations. After 10 s at room temperature, the emission spectra under 380 nm excitation were recorded. Afterward, the selectivity and anti-interference capability of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in relation to TC was further investigated. In detail, 2 mg NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was added to 2.5 mL of solutions containing various kinds of antibiotics (100 µM, CIP, CAP, SDZ, SMZ, THI, MDZ, ODZ), anions (100 µM, F−, NO2−, S2O32−, SO3−, HSO3−, HCO3−, HSO4−, CO32−, NO3−, SO42−, PO43−, S2O82−) and metal ions (100 µM, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Fe2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Al3+, Ba2+, Fe3+). The fluorescence emission intensities of the solutions with and without 100 µM TC were measured separately after incubating for 10 s at room temperature.
In addition, after the detection of TC, NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was collected, immersed in alcohol for 12 h, then washed and centrifuged for recovery. After being dried in a vacuum at 60 °C for 6 h, NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was obtained and further reused in the detection of TC to explore the reusability.
2.5. Detection of TC in Environmental Samples
Environmental samples were obtained from river water in Changzhou and tap water in the laboratory of Changzhou University in Jiangsu. These collected samples were filtered with 0.45 µm pore size membrane. Then, the spiking method was used to prepared TC solution with various concentrations. The emission intensity was recorded after immersing 2 mg NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in 2.5 mL of the above-described solutions after 10 s incubation time.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Materials
The crystal structure of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) prepared in this work was characterized with XRD patterns. As described in a previous study, the basic structure of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) consisted of a dissociative β-octamolybdate anion and four discrete 4-ap ions protonated at nitrogen atom of the pyridine ring, which further construct the three-dimensional structure of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) via the hydrogen bonds. Moreover, (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) demonstrates an overall negative surface charge in the pH range from 2 to 9 [19]. As depicted in Figure 1a, the major sharp diffraction peaks of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) were in line with the simulated pattern [19], indicating that the crystalline phase of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was pure. In the XRD pattern of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), no obvious change in peaks emerged after NCDs were loaded onto (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (Figure 1a), indicating that the framework of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) remained intact in the post-synthetic loading process. The SEM images of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) without and with loading of NCDs were captured. As illustrated in Figure 1b,c, both (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) showed irregular stone shape, but compared to the pure (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) had a rougher surface, indicating that NCDs attached onto the surface of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). The FTIR spectra were measured to study the chemical composition of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (Figure 1d). In the FTIR spectra of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), the peaks in the range of 600–1000 cm−1 were assigned to v (Mo=O) and v (Mo-O-Mo) in β-octamolybdate, the peaks at 3265 and 3434 cm−1 were the non-coordinating -NH2 functions, the adsorption bands at 1346 and 1625 cm−1 related to the stretching vibration of C-N and the N-H bend vibration, respectively, and the peak at 1000 cm−1 was associated with C=N. In the FTIR spectra of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), the adsorption bands of C-N and N-H were enhanced, and the bands assigned to -COO- of the NCDs at 1700, 1098 and 1053 cm−1 were visible, indicating the successful introduction of NCDs onto (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). Moreover, the peaks associated with -NH2 shifted to a lower wavenumber at 3263 and 3433 cm−1 compared to (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), and the peaks associated with -COO- shifted to a lower wavenumber than that of pristine NCDs at 1723, 1169 and 1092 cm−1 [27], which indicate that hydrogen bonding may be formed between -NH2 of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and -COOH of NCDs. XPS was further investigated to manifest the chemical states and composition of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). All binding energies presented in XPS were modified based on C1s of 284.8 eV. As shown in Figure 1e, four main elements, namely, C, N, O and Mo, existed in the XPS survey of both (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), but the content of O was increased from 24.66 to 36.17% and the content of Mo was decreased from 8.79 to 6.06% after the induction of NCDs by (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), which further confirm that the NCDs were coated on the (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). In the C1s spectra of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (Figure 1f), the chemical bond of C=O with content of 12.45% emerged at 288.09 eV. Moreover, the content of C-C/C=C and C-N decreased from 66.31% and 33.69% to 55.08% and 32.49%, respectively, compared to that of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (Figure 1g). These results suggest that NCDs were coated on the (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and π–π interactions may exist between NCDs and (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26).
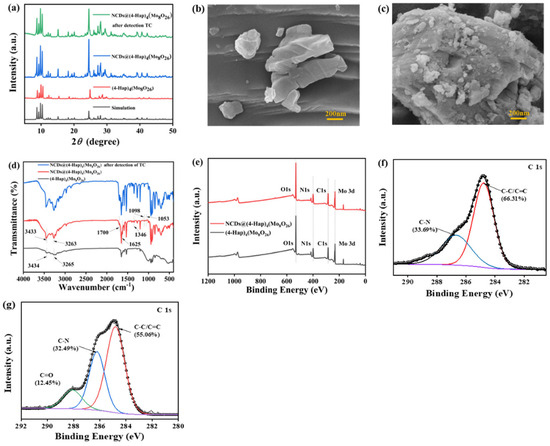
Figure 1.
(a) XRD patterns of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) after the detection of TC; SEM images of 4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (b) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (c); (d) FTIR spectra of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) after the detection of TC; (e) Full range XPS of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26); the C1s spectra of (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (f) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (g).
3.2. Luminescence of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26)
As shown in Figure S1a, (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) is a light-yellow powder under natural light, and it showed a broad, weak fluorescence emission peak at 468 nm (Figure 2a) under UV light excitation (Ex = 363 nm). NCDs exhibited a blue fluorescence emission at 445 nm under excitation of 365 nm (Figure 2a), and situated in the blue region at point a (X = 0.15, Y = 0.12) in the CIE chromaticity diagram (Figure 2b). After loading of NCDs onto (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) turned brown (Figure S1b) under natural light. Similar to other quantum dots reported in the literature [28,29], the fluorescence emission of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) exhibited a strong blue emission at 465 nm (Ex = 380 nm) (Figure 2a), and showed typical excitation-dependent emission, which enhanced with the excitation wavelength increased from 340 to 390 nm and gradually decreased with longer excitation wavelength (Figure S2). The strong blue fluorescence is visible to the naked eye and situated at point b (X = 0.15, Y = 0.18) in the CIE chromaticity diagram (Figure 2b). Compared to NCDs, the emission peak of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) showed a red shift of 20 nm, indicating that the hydrogen bonds may exist between NCDs and (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) [30].
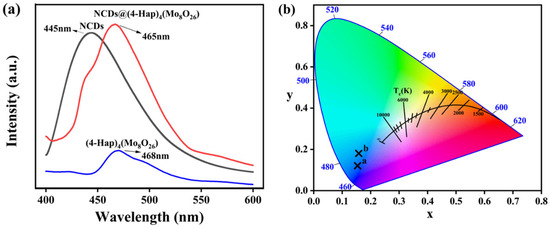
Figure 2.
(a) The emission spectra of NCDs (black line, Ex = 365 nm), (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (blue line, Ex = 363 nm) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (red line, Ex = 380 nm); (b) The chromaticity diagram of NCDs and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) excited at 365 nm.
As depicted in Figure S3, no obvious decline in the fluorescence emission intensity at 465 nm was observed after immersing the NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in water for 7 days, validating the excellent fluorescence stability of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). In addition, the fluorescence emission of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) can be kept stable in the pH range from 3 to 12 (Figure S4), suggesting the potential application of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) as a fluorescent sensor in water.
3.3. Sensing of TC
The results of the response kinetics study of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) for TC sensing are illustrated in Figure 3a. In the study, the fluorescence was quenched in 10 s and reached equilibrium. Based on the rapid response time, all TC sensing experiments with NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in this study were taken in real time.
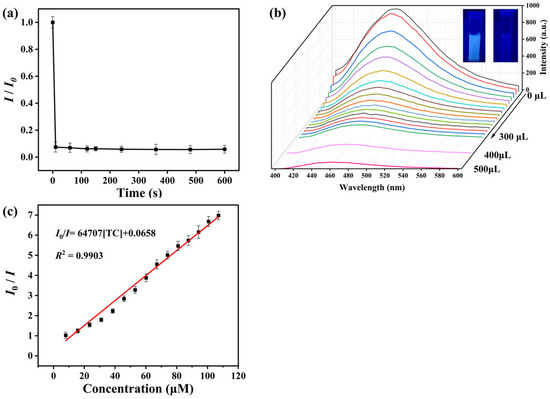
Figure 3.
(a) Fluorescence intensity of the mixed solution of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and TC (2.5 mL, 107 µM) at 465 nm (Ex = 380 nm) at different times; (b) Fluorescent spectra (Ex = 380 nm) of the mixed solution of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and different concentrations of TC; (c) Calibration plot of the fluorescence intensity ratio (I0/I) versus concentrations of TC.
Further, the performance of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in detecting different concentrations of TC was studied. As illustrated in Figure 3b, under excitation of 380 nm, the fluorescence emission was quenched with the addition of TC solution (1 mM) from 0 to 300 µL (20 µL increase each time). The quenching efficiency could reach 85.7% with 300 µL TC solution (1 mM) addition, and further increased to 94.1% with the 500 µL TC solution (1 mM) addition, and the blue fluorescence under UV light was visible to the naked eye from bright to dark (Figure 3b inset). The Stern–Volmer (S-V) formula [31] (Equation (1)) was used to explore the quantitative relationship between the fluorescence emission and the concentration of TC. A good linear relationship with the linear correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.9903 in an 8–107 µM concentration range was found, as shown in Figure 3c, and the Ksv value was calculated as 6.47 × 104 M−1. According to the 3σ IUPAC criteria (3σ/slope) (σ is the standard deviation of three blank measurements) [32], the LOD of TC sensing was estimated to be 33.9 nM. Moreover, as shown in Table 1, the LOD for TC sensing in this work is better than most other TC-detection platforms. In addition, the performance for the detection of TC with the concentration from 0 to 8 µM, as seen in Figure S5, showed a relatively low linear correlation of 0.9299 with a Ksv value of 2.69 × 104 M−1, indicating a higher LOD in practical sensing application than the calculated LOD of 33.9 nM, which may be due to the large error in the detection of trace TC in water.
where I0 and I are the emission intensities of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) before and after the detection of TC, respectively; Ksv represents the S-V constant (M−1); [M] is the molar concentration of TC (µM).
I0/I = Ksv[M] + 1

Table 1.
Comparison of the fluorescence-sensing performance for sensing TC.
3.4. Selectivity and Anti-Interference
The current bottleneck that limits the application of chemical sensors in real water environments is the fact that the fluorescence signal can be interfered with by other species. Thus, the selectivity and anti-interference experiments were conducted with other antibiotics and common ions in a water environment. As depicted in Figure 4a–c, with the addition of TC and other selected species in NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) suspension, only TC quenched the fluorescence of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), whereas other antibiotics and the studied ions showed little effect on the fluorescence emission of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), suggesting the high selectivity of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) for TC sensing. Moreover, the other antibiotics and common ions were mixed with TC and added to the NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) suspension; then, the fluorescence of the mixed solution was monitored. The results in Figure 4d–f show that TC can still quench the fluorescence of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) with similar quenching efficiency in the presence of the other antibiotics and common ions, suggesting excellent anti-interference of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) as a TC sensor.
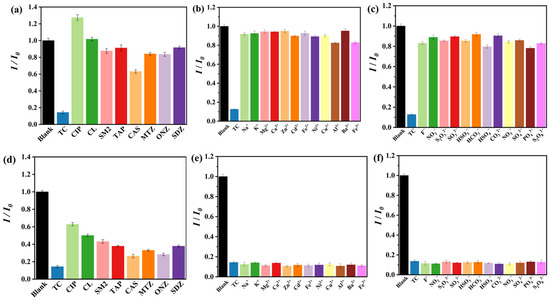
Figure 4.
Fluorescence intensities at 465 nm of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in different (a) antibiotics (100 µM), (b) metal ions (100 µM) and (c) anions (100 µM) in aqueous solutions; fluorescence intensities of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (Ex = 380 nm) at 465 nm with the coexistence of TC (100 µM) and different (d) antibiotics (100 µM), (e) metal ions (100 µM) and (f) anions (100 µM) in aqueous solutions.
3.5. Mechanism of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) for TC Detection
Studies have shown that the reasons for fluorescence quenching of sensing materials caused by the detected substance mainly include the following aspects: (i) The target detection substance interacts with the sensing material, resulting in the structural collapse of the sensing material [40]. (ii) The organic ligands or metal ions in the sensing material react with the target detection substance, destroying the original energy transfer [41]. (iii) The UV-vis spectrum of the target detection substance overlaps with the fluorescence excitation spectrum of the sensing material, resulting in fluorescence quenching by IFE [42]. To investigate the mechanism, the structure of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was first explored. As depicted in Figure 1a, compared to the XRD patterns of the original NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), there was no significant change in NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) after sensing TC, indicating that the structure remained intact; thus, the fluorescence quenching caused by structural damage was excluded. Since the resonance energy transfer during the quenching process can lead to a significant decrease in the fluorescence lifetime, the lifetime of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in aqueous solutions before and after sensing TC was investigated. As illustrated in Figure 5a, the average lifetime of the NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) before and after the detection of TC was 10.86 ns and 10.58 ns, respectively, which remained stable, indicating that the quenching process is static and the resonance energy transfer is not the dominant reason for the fluorescence quenching. Further, the UV-vis absorption spectra of TC and the fluorescence excitation/emission spectrum of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) were recorded. As shown in Figure 5b, the UV-vis absorption spectra of TC overlaps with the excitation spectrum of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), which means that some UV light was absorbed by TC and shielded the excitation light of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), causing the fluorescence to be quenched through the IFE, which usually shows a higher selectivity and shorter response time than other mechanisms [43]. Moreover, TC molecules existed in four distinct species at different pH levels. At a pH lower than 3.3 and in a pH range from 3.3 to 7.7, the dominant species of TC was TC cationic species (TCH3+) and the nearly neutral or zwitterionic species (TCH2±), respectively, which leads to favorable electrostatic attractions between TC and (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) with a negatively charged surface. This can pre-concentrate TC on NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and thereby improve the sensitivity and shorten the response time of TC detection. Additionally, no new adsorption peak on the FTIR spectra of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) was observed after the detection of TC, indicating no chemical interactions between NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and TC. The above speculation was evidenced by the good recyclability of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), as shown in Figure S6, which could be reused in the next six runs after it was washed with alcohol.
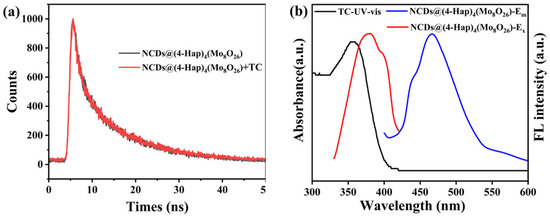
Figure 5.
(a) The fluorescence decay curve of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) (black line) and NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) after detection of TC (red line); (b) The UV-vis adsorption spectra of TC (black line), and the excitation spectra (red line, Em = 465 nm) and emission spectra (blue line, Ex = 380 nm) of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26).
3.6. Sensing TC in Environmental Samples
The feasibility of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) used for sensing TC in environmental water samples was investigated. Two samples, one from tap water and the other from river water, were used as the solvent to prepare TC solutions with various concentrations based on the standard addition method. Recoveries of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) for TC sensing were calculated by Equation (2).
where Cd (mg·L−1) represents the detected concentration of TC, and Cs (mg·L−1) is the spiked concentration of TC.
Recovery = Cd/Cs × 100%
As shown in Table 2, the recoveries were obtained from 91.95% to 104.72%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) were calculated to be in the range from 1.24% to 5.93%, suggesting the accuracy and reliability of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in TC sensing in water environments.

Table 2.
Determination of TC in environmental water samples.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) with satisfactory fluorescence performance for sensitivity and selective sensing of the trace amount of TC in aqueous solutions was fabricated via post-synthetic modification of NCDs on (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). NCDs were successfully coated on (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) and provide a strong and stable blue emission to NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26). NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) can be used for sensing TC with fluorescence quenching in 10 s, and the LOD can reach 33.9 nM with a linear range in 8–107 µM. In particular, the change of the fluorescent signal from bright blue to dark blue under UV light is visible to the naked eye, making NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) more practical in TC sensing. The potential practical application was further verified by the standard addition experiments with good recoveries in real water samples. In addition, mechanism studies showed that the fluorescence quenching may be attributed to the inner filter effect, which usually provides high sensitivity and quick response for sensing. It is believed that this strategy can provide a new viewpoint in constructing reliable methods for TC sensing in water environments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nano13192676/s1: Figure S1: Photographs of (a) (4-Hap)4(Mo8O26), (b) NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) under natural light; Figure S2: Emission spectra for NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in water at different wavelengths; Figure S3: Relative fluorescence intensity of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) with excitation at 380 nm in 7 days; Figure S4: The relative fluorescence intensity of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) in water under different pH levels (Ex = 380 nm); Figure S5: Calibration plot of the fluorescence intensity ratio (I0/I) versus concentrations of TC in 0–8 µM; Figure S6: Recovery tests of NCDs@(4-Hap)4(Mo8O26) for TC sensing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and M.P.; methodology, Y.Z. and M.P.; software, M.S.; validation, Y.L., E.D. and X.X.; formal analysis, M.S.; investigation, M.S.; resources, Y.Z. and M.P.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z. and M.P.; visualization, M.S.; supervision, Y.L., E.D. and X.X.; project administration, Y.Z. and M.P.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20210856), the Science and Technology Project of Changzhou City (CJ20210117) and Science and Technology Project of China Petroleum and Changzhou University Innovation Consortium (research on key supporting technologies for multi-element thermal fluid heavy oil production).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Analysis and Testing Center of Changzhou University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, R.; Tan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Sources, Environmental Fate, and Ecological Risks of Antibiotics in Sediments of Asia’s Longest River: A Whole-Basin Investigation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14439–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy. The State of the World’s Antibiotics. 2021. Available online: https://cddep.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/The-State-of-the-Worlds-Antibiotics-in-2021.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, M.-C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Yee Leung, K.M.; Snyder, S.A.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Which Micropollutants in Water Environments Deserve More Attention Globally? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, X.; Gu, C.; Chen, Z. Tetracycline photolysis revisited: Overlooked day-night succession of the parent compound and metabolites in natural surface waters and associated ecotoxicity. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leichtweis, J.; Vieira, Y.; Welter, N.; Silvestri, S.; Dotto, G.L.; Carissimi, E. A review of the occurrence, disposal, determination, toxicity and remediation technologies of the tetracycline antibiotic. Process Saf. Environ. 2022, 160, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.E.C.; de Faria, L.V.; Araújo, D.A.G.; Richter, E.M.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Dantas, L.M.F.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; da Silva, I.S. Lab-made 3D-printed electrochemical sensors for tetracycline determination. Talanta 2023, 259, 124536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Gu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Qian, T. Novel preparation of red fluorescent carbon dots for tetracycline sensing and its application in trace determination. Talanta 2023, 253, 123975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullam, E.M.; Adam, K.M.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Xiao, J. Silicon quantum dots-based fluorescent sensor for the detection of cobalt with high sensitivity and selectivity. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 108476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, K.; Tan, R.; Hao, R.; Miao, L.; He, Y.; Xianghua, W.; Zhang, J.; Rui, X. A carbazole-hemicyanine dye based ratiometric fluorescent probe for selective detection of bisulfite (HSO3−) in cells and C. elegans. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshevoi, E.I.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Dorovatovskii, P.V.; Lazarenko, V.A.; Fedin, V.P. Crystal Structure of Metal-Organic Coordination Polymers Based on Potassium and Barium Cations with α-Cyclodextrin. J. Struct. Chem. 2020, 61, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-X.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Wang, C.-C. Selective oxidation of aqueous organic pollutants over MOFs-based catalysts: A mini review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, S.-S.; Feng, Z.; Fu, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.-C. High-efficient peroxymonosulfate activation for rapid atrazine degradation by FeSx@MoS2 derived from MIL-88A(Fe). J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-C.; Ren, X.; Wang, P.; Chang, C. The state of the art review on photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction over MOFs-based photocatalysts: From batch experiment to continuous operation. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Matzger, A.J. Enhanced Drug Delivery by Dissolution of Amorphous Drug Encapsulated in a Water Unstable Metal–Organic Framework (MOF). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16790–16794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Wen, N.; Xiong, H.; Cai, S.; He, Q.; Hu, Y.; Peng, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Metal-organic frameworks for stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Biomaterials 2020, 230, 119619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Zeng, X.; Sun, X.-Z.; Zhao, C.; Fu, H.; Wang, P. Seignette salt induced defects in Zr-MOFs for boosted Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption: Universal strategy and mechanism insight. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wang, C.-C.; Zhu, T.; Wang, P.; Gao, S.-J. Ultra-high uptake and selective adsorption of organic dyes with a novel polyoxomolybdate-based organic–inorganic hybrid compound. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45688–45692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, B. Metal–Organic Framework Based on α-Cyclodextrin Gives High Ethylene Gas Adsorption Capacity and Storage Stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34095–34104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Ben-Mansour, R.; Habib, M.A. An efficient CO2 adsorptive storage using MOF-5 and MOF-177. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Zhang, X.-W.; Ren, X.-Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.-X.; Fu, H. A new Eu-MOF for ratiometrically fluorescent detection toward quinolone antibiotics and selective detection toward tetracycline antibiotics. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, M.; Peng, M.; Du, E.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.-C. The fabrication strategies and enhanced performances of metal-organic frameworks and carbon dots composites: State of the art review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Dai, W.; Wang, H. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for ratiometric fluorescence sensing tetracyclines in environmental water based on AIE effects. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1199, 339576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, F.; Zhao, X.J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.F. Visual detection of tetracycline antibiotics with the turned on fluorescence induced by a metal–organic coordination polymer. Talanta 2013, 107, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gong, J.; Wei, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, G.; Tong, Y.; He, W. Metal organic framework loaded fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme with light regulating redox ability for detection of ferric ion and glutathione. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 618, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: Facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, C.-F.; Yu, Z.-Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, S. Facile access to versatile fluorescent carbon dots toward light-emitting diodes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2692–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Meziani, M.J.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Luo, P.G.; Lin, Y.; Harruff, B.A.; Veca, L.M.; Murray, D.; et al. Carbon Dots for Multiphoton Bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11318–11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-F.; Gao, S.-Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, T.-F.; Cao, R. C-QDs@UiO-66-(COOH)2 Composite Film via Electrophoretic Deposition for Temperature Sensing. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Lu, R.; Tang, S.; Liu, X. Highly cross-linked fluorescent poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-curcumin) microspheres for the selective detection of picric acid in solution phase. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4604–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Li, L.; Yuan, D.-Q.; Huang, Y.-B.; Cao, R. Fast, highly selective and sensitive anionic metal-organic framework with nitrogen-rich sites fluorescent chemosensor for nitro explosives detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, D.; Domini, C.; Garrido, M. New carbon dots based on glycerol and urea and its application in the determination of tetracycline in urine samples. Talanta 2019, 201, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Q. Ratio fluorescence detection of tetracycline by a Eu3+/NH2-MIL-53(Al) composite. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gan, N.; Li, Q.; Cuan, J. Detection and removal of antibiotic tetracycline in water with a highly stable luminescent MOF. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.J.; Wang, Z.G.; Su, M.; Liu, X.T.; Shen, S.G.; Dong, J.X. A dual-signal fluorescent colorimetric tetracyclines sensor based on multicolor carbon dots as probes and smartphone-assisted visual assay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1247, 340843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lan, C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, N.; Wu, Y. A novel ratiometric fluorescence probe for highly sensitive and specific detection of chlorotetracycline among tetracycline antibiotics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1089, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sianglam, P.; Ngamdee, K.; Ittisanronnachai, S.; Promarak, V.; Ren, X.-K.; Ngeontae, W. An effective strategy for the detection of tetracycline by N,S-doped carbon nanodots after preconcentration with a hybrid functional nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 108025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, S.; Yin, K.; Ng, W.J. Nitrogen-Doped Durian Shell Derived Carbon Dots for Inner Filter Effect Mediated Sensing of Tetracycline and Fluorescent Ink. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Yan, B. Novel core–shell structure microspheres based on lanthanide complexes for white-light emission and fluorescence sensing. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.-l.; Shi, Y.-X.; Chen, H.-H.; Lang, J.-P. A Zn(ii) coordination polymer and its photocycloaddition product: Syntheses, structures, selective luminescence sensing of iron(iii) ions and selective absorption of dyes. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 18795–18803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, H.; Yang, Y.; Wong, W.-T. Luminescent lanthanide metal-organic framework test strip for immediate detection of tetracycline antibiotics in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Zheng, M.; Qin, M.; Wei, W. Dual-emission of Eu based metal-organic frameworks hybrids with carbon dots for ratiometric fluorescent detection of Cr(VI). Talanta 2019, 191, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).