Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Properties of Zinc Oxide Obtained in the Presence of Nonionic Structure-Forming Compounds
Abstract
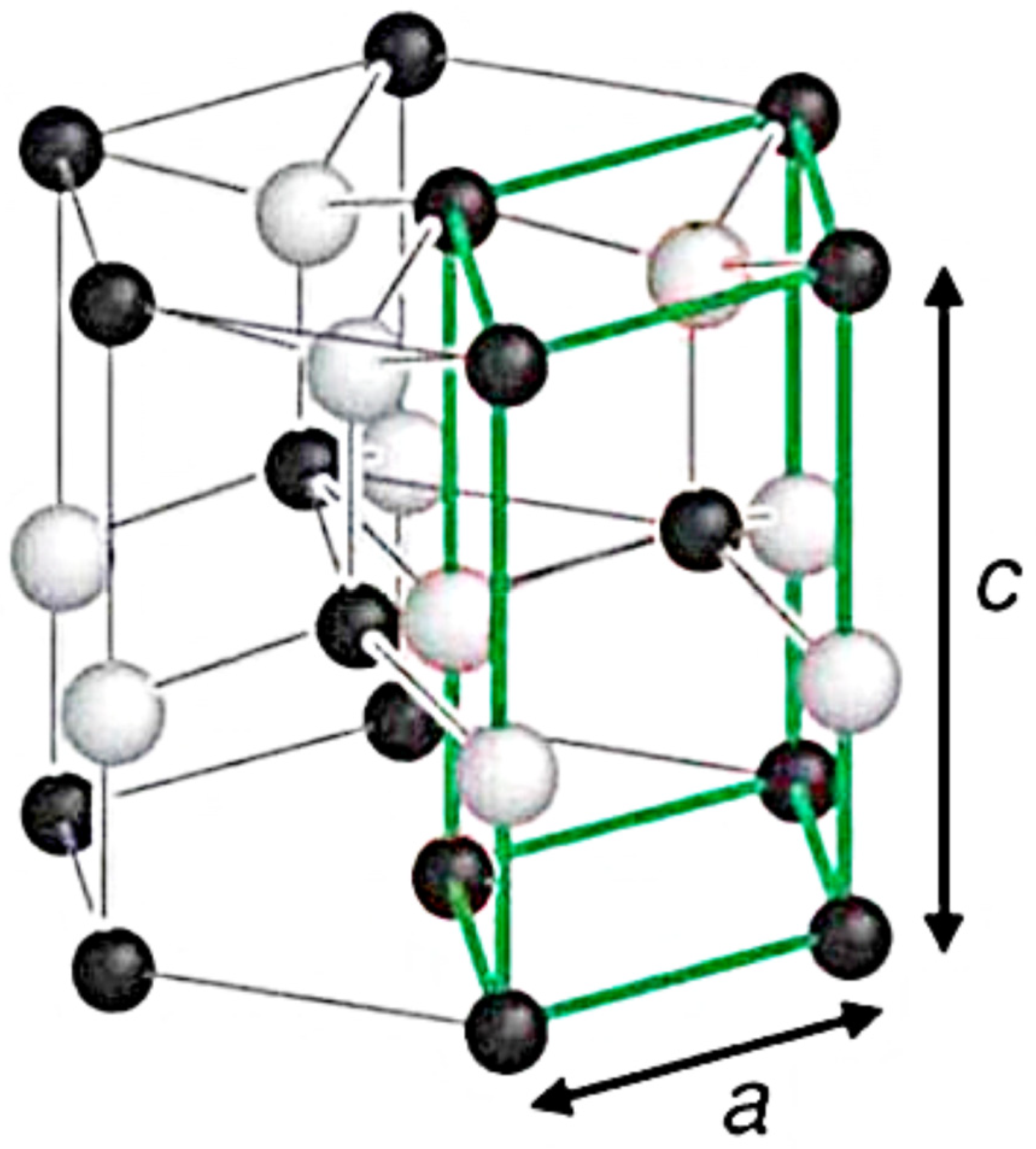
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- The interaction of Zn(NO3)2·6H2O with NH4OH in a medium of nonionic surfactants and further thermolysis of the products of reaction and structure-forming compounds at a temperature of 600 °C—calcination method (C), samples C1–C6, where the number denotes the type of a surfactant according to Table 1;
- The interaction of Zn(NO3)2·6H2O with NH4OH in a medium of nonionic surfactants and aging of washed precipitates under hydrothermal conditions in the presence of a glass substrate—method of hydrothermal synthesis with a glass substrate (HTG), samples HTG1–HTG6;
- The interaction of Zn(NO3)2·6H2O with NH4OH in a medium of nonionic surfactants and aging of the precipitates under hydrothermal conditions in the absence of a glass substrate—HT method, samples HT1–HT6;
- The calcination of the samples obtained by the HT method at a temperature of 600 °C— HTC method, samples HTC1–HTC6.
3. Results
3.1. Study of the Structures of Synthesized Products
3.2. The Morphological Features of Synthesized ZnO Samples
3.3. Determination of Residual Zn2+ Ions in the Supernatant of Synthesized Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.C. Zinc oxide nanostructures: Synthesis, characterizations and device applications. J. Nanoeng. Nanomanuf. 2013, 3, 283–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moezzi, A.; McDonagh, A.M. Zinc oxide particles: Synthesis, properties and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide—From synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, P.; Kaur, A. An overview on uses of zinc oxide nanoparticles. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 4, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, S. A short review on properties and applications of ZnO based thin film and devices. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 2020, 64, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, R.; Jalil, A. Optoelectronic and solar cell applications of ZnO nanostructures. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 2, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uresti-Porras, J.G.; Cabrera-De-La Fuente, M. Foliar application of zinc oxide nanoparticles and grafting improves the bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) productivity grown in NFT system. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2021, 49, 12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Pazirofteh, M. Application of ZnO nanostructures in ceramic and polymeric membranes for water and wastewater technologies: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, J.O.; Bittencourt, C. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by ecofriendly routes: Adsorbent for copper removal from wastewater. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraja, G.; Prasad, C. Application of ZnO nanorods as an adsorbent material for the removal of As (III) from aqueous solution: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2018, 9, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Quan, W. Heterogeneous ZnO-containing catalysts for efficient biodiesel production. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 20465–20478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, L. The applications of morphology controlled ZnO in catalysis. Catalysts 2016, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, M.N.; Ekhator, I. Effect of zinc oxide level as activator on the mechanical properties of natural rubber composite. Niger. J. Technol. 2019, 38, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, M.; Sowińska, A. Zinc complexes with 1,3-diketones as activators for sulfur vulcanization of styrene-butadiene elastomer filled with carbon black. Materials 2021, 14, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, Z.; Ferreira, N.M.; Figueiredo, G.; Mendo, S.; Nunes, C.; Ferreira, P. Electrically Conductive and Antimicrobial Agro-Food Waste Biochar Functionalized with Zinc Oxide Particles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abendrot, M.; Kalinowska-Lis, U. Zinc-containing compounds for personal care applications. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshaykranth, A.; Jayarambabu, N. Antibacterial activity study of ZnO incorporated biodegradable poly (lactic acid) films for food packaging applications. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 1369–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donga, S.; Chanda, S. Caesalpinia Crista seeds mediated green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for antibacterial, antioxidant, and anticancer activities. BioNanoScience 2022, 12, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, B.; Rajeshkumar, S. Biomedical application of chitosan and piper longum-assisted nano zinc oxide–based dental varnish. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Zhong, C. Recent advances in antimicrobial hydrogels containing metal ions and metals/metal oxide nanoparticles. Polymers 2017, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motelica, L.; Ficai, D.; Oprea, O.; Ficai, A.; Trusca, R.-D.; Andronescu, E.; Holban, A.M. Biodegradable Alginate Films with ZnO Nanoparticles and Citronella Essential Oil—A Novel Antimicrobial Structure. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Wu, Z.; Pang, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Pan, Q. Fabrication of ZnO@Plant Polyphenols/Cellulose as Active Food Packaging and Its Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrajhi, A.H.; Ahmed, N.M.; Halim, M.M.; Altowyan, A.S.; Azmi, M.N.; Almessiere, M.A. Distinct Optical and Structural (Nanoyarn and Nanomat-like Structure) Characteristics of Zinc Oxide Nanofilm Derived by Using Salvia officinalis Leaves Extract Made without and with PEO Polymer. Materials 2023, 16, 4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestopino, G.; Orsini, A.; Barettin, D.; Arrabito, G.; Pignataro, B.; Medaglia, P.G. Vertically Aligned Nanowires and Quantum Dots: Promises and Results in Light Energy Harvesting. Materials 2023, 16, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seil, J.T.; Webster, T.J. Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: Methods and literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2767–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T. Size-dependent bacterial growth inhibition and mechanism of antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallo da Silva, B.; Abuçafy, M.P. Relationship between structure and antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: An overview. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9395–9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, B.; Zereffa, E.A. A review on enhancing the antibacterial activity of ZnO: Mechanisms and microscopic investigation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, Y. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, A.; Pomastowski, P. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antiseptic activity and toxicity mechanism. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamimi, N.; Mohammadi Nafchi, A. The effects of nano-zinc oxide morphology on functional and antibacterial properties of tapioca starch bionanocomposite. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4497–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayevska, N.; Przysiecka, Ł. ZnO size and shape effect on antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity profile. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebian, N.; Amininezhad, S.M. Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their morphology-dependent antibacterial and optical properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2013, 120, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, L.C.; Mahmud, S. Effect of surface modification and UVA photoactivation on antibacterial bioac tivity of zinc oxide powder. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droepenu, E.K.; Wee, B.S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesis methods and its effect on morphology: A review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 4261–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivtseva, A.V.; Kondrashova, N.B. Effect of the alkaline agent nature on the microstructure and properties of zinc oxide prepared via precipitation method. Inorg. Mater. 2022, 58, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudukudy, M.; Yaakob, Z. Simple chemical synthesis of novel ZnO nanostructures: Role of counter ions. Solid State Sci. 2014, 30, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Sol gel synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their application as nano-composite electrode material for supercapacitor. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1220, 128654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbreders, V.; Krasovska, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanostructures with controllable morphology change. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurisic, A.B.; Chen, X.Y. Recent progress in hydrothermal synthesis of zinc oxide nanomaterials. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 5, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musić, S.; Šarić, A. Dependence of the microstructural properties of ZnO particles on their synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 448, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozegholami Barmi, M.; Minakshi, M. Tuning the Redox Properties of the Nanostructured CoMoO4 Electrode: Effects of Surfactant Content and Synthesis Temperature. ChemPlusChem 2016, 81, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Behbudi, G. Shape-controlled synthesis of zinc nanostructures mediating macromolecules for biomedical applications. Biomater. Res. 2022, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelsamen, A.; Mahmud, S. Novel Pluronic F-127-coated ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their in-vitro cytotoxicity evaluation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.; Bao, X. The use of PEO-PPO-PEO block copolymers in the synthesis of ZnO via the hydrothermal method. In Proceedings of the 2010 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 21–24 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Liu, F. Zinc oxide nano-and micro-crystals synthesised by co-precipitation and hydrothermal process. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, S4-669–S4-673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, A. Molecular Spectroscopy of Oxide Catalyst Surfaces; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2003; 641p. [Google Scholar]
- Minakshi Sundaram, M.; Appadoo, D. Traditional salt-in-water electrolyte vs. waterin-salt electrolyte with binary metal oxide for symmetric supercapacitors: Capacitive vs. faradaic. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 11743–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccuzzi, F.; Morterra, C. Infrared spectrum of microcrystalline zinc oxide. Electronic and vibrational contributions under different temperature and environmental conditions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1981, 77, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, B.M.; Gedvilas, L.M. Infrared spectroscopy of polycrystalline ZnO and ZnO:N thin films. J. Cryst. Growth. 2005, 281, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccuzzi, F.; Borello, E. Infrared study of ZnO surface properties. I. Hydrogen and deuterium chemisorption at room temperature. J. Catal. 1978, 51, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1986; 484p. [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi, K. Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. Practical; Holden-Day, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA; Nankodo Company Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1962; 233p. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Huang, X. PEG-assisted synthesis of ZnO nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingshirn, C.F.; Waag, A. Zinc Oxide: From Fundamental Properties towards Novel Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ding, Y.L. Investigation into the antibacterial behaviour of suspensions of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO nanofluids). J. Nanopart. Res. 2007, 9, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Mustapha, A. Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| № | Name | Formula | Mean Molecular Weight (MW), g/mol | Ethylene Oxide Concentration, Weight. % | Surfactant Solution Viscosity (C = 0.0085 mol/L), mPa·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Distilled water | H2O | 18 | – | 0.88 |
| 1 | Pluronic F-127 |  | 12,600 | 70 | 5.95 |
| 2 | Pluronic P-123 | 5800 | 30 | 1.60 | |
| 3 | Pluronic L-81 | 2800 | 10 | 1.17 | |
| 4 | Pluronic L-31 | 1100 | 10 | 1.12 | |
| 5 | PE-block-PEG |  | 575 | 20 | 1.19 |
| 6 | PEG |  | 400 | 100 | 1.02 |
| Synthesis Method | Surfactant Removal Technique | Sample | Specific Surface Area, SBET, m2/g | Total Pore Volume, Vtot, cm3/g | Pore Diameter, Dpore, nm | Crystallite Size, nm (XRD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Calcination at 600 °C | C1 | 22.84 | 0.088 | 14.67 | 28.25 |
| C2 | 18.79 | 0.087 | 17.61 | 31.31 | ||
| C3 | 13.23 | 0.067 | 17.38 | 31.80 | ||
| C4 | 10.33 | 0.045 | 18.03 | 34.69 | ||
| C5 | 8.56 | 0.030 | 16.56 | 35.52 | ||
| C6 | 9.82 | 0.041 | 18.75 | 35.87 | ||
| HTG | Ethyl alcohol extraction | HTG1 | 117.79 | 0.605 | 20.542 | 25.99 |
| HTG2 | 19.16 | 0.102 | 21.207 | 26.39 | ||
| HTG3 | 10.44 | 0.043 | 16.636 | 27.34 | ||
| HTG4 | 75.09 | 0.382 | 20.326 | 29.46 | ||
| HTG5 | 8.25 | 0.027 | 12.964 | 32.24 | ||
| HTG6 | 11.54 | 0.030 | 10.372 | 30.65- | ||
| HT | Ethyl alcohol extraction | HT1 | 145.48 | 0.519 | 13.60 | 16.87 |
| HT2 | 24.79 | 0.071 | 16.20 | 27.10 | ||
| HT3 | 21.11 | 0.072 | 15.39 | 28.03 | ||
| HT4 | 35.69 | 0.202 | 23.00 | 28.19 | ||
| HT5 | 38.81 | 0.258 | 23.59 | 27.46 | ||
| HT6 | 34.73 | 0.138 | 14.25 | 33.36 | ||
| HTC | Calcination at 600 °C | HTC1 | 24 | 0.09 | 15 | 33.92 |
| HTC2 | 24 | 0.10 | 14 | 34.84 | ||
| HTC3 | 10 | 0.04 | 14 | 35.76 | ||
| HTC4 | 10 | 0.04 | 14 | 36.18 | ||
| HTC5 | 6 | 0.015 | 12 | 37.96 | ||
| HTC6 | 15 | 0.05 | 13 | 33.42 |
| Synthesis Method | Sample | Mean Particle Size, μm (SEM) | Residual Amount of Zn2+ Ions, mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | C1 | 0.03 | 10.22 |
| C2 | 0.04 | 9.18 | |
| C3 | 0.07 | 8.50 | |
| C4 | 0.08 | 8.06 | |
| C5 | 0.08 | 7.86 | |
| C6 | 0.08 | 7.94 | |
| HTG | HTG1 | 2.0 | 8.69 |
| HTG2 | 0.6 | 6.64 | |
| HTG3 | 0.6 | 6.86 | |
| HTG4 | 1.5 | 5.04 | |
| HTG5 | 1.5 | 5.38 | |
| HTG6 | 1.5 | 5.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valtsifer, V.A.; Sivtseva, A.V.; Kondrashova, N.B.; Shamsutdinov, A.S.; Averkina, A.S.; Valtsifer, I.V.; Feklistova, I.N.; Strelnikov, V.N. Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Properties of Zinc Oxide Obtained in the Presence of Nonionic Structure-Forming Compounds. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13182537
Valtsifer VA, Sivtseva AV, Kondrashova NB, Shamsutdinov AS, Averkina AS, Valtsifer IV, Feklistova IN, Strelnikov VN. Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Properties of Zinc Oxide Obtained in the Presence of Nonionic Structure-Forming Compounds. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(18):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13182537
Chicago/Turabian StyleValtsifer, Viktor A., Anastasia V. Sivtseva, Natalia B. Kondrashova, Artem S. Shamsutdinov, Anastasia S. Averkina, Igor V. Valtsifer, Irina N. Feklistova, and Vladimir N. Strelnikov. 2023. "Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Properties of Zinc Oxide Obtained in the Presence of Nonionic Structure-Forming Compounds" Nanomaterials 13, no. 18: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13182537
APA StyleValtsifer, V. A., Sivtseva, A. V., Kondrashova, N. B., Shamsutdinov, A. S., Averkina, A. S., Valtsifer, I. V., Feklistova, I. N., & Strelnikov, V. N. (2023). Influence of Synthesis Conditions on the Properties of Zinc Oxide Obtained in the Presence of Nonionic Structure-Forming Compounds. Nanomaterials, 13(18), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13182537





