Hydrogel Contact Lenses Embedded with Amine-Functionalized Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Extended Hyaluronic Acid Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
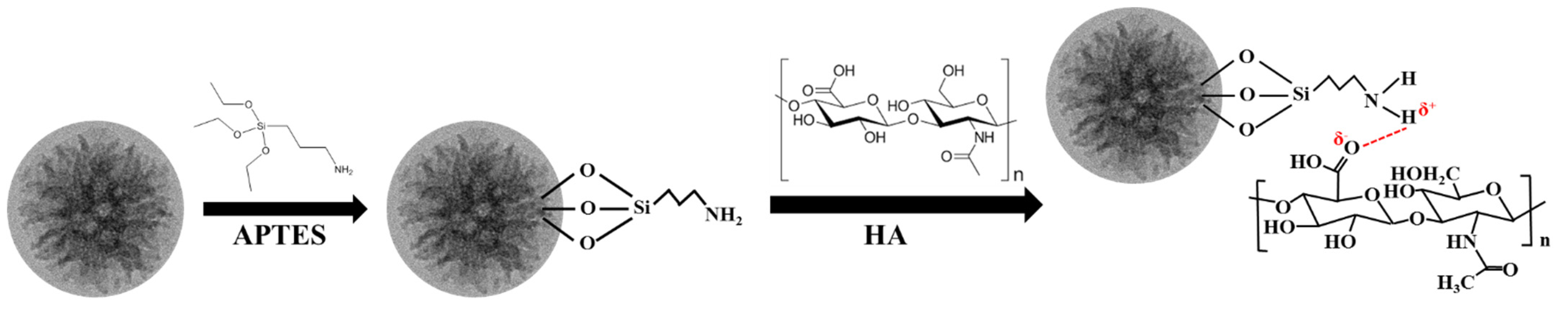
2.2. Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized LPMSNs
2.3. Hydrogel CLs Embedded with LPMSNs
2.4. Measurement of HA Load and Release
2.5. Release Kinetics Mechanism for LPMSN-Laden CLs
2.6. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Functionalized LPMSNs
3.2. Characterization of LPMSN-Laden CLs
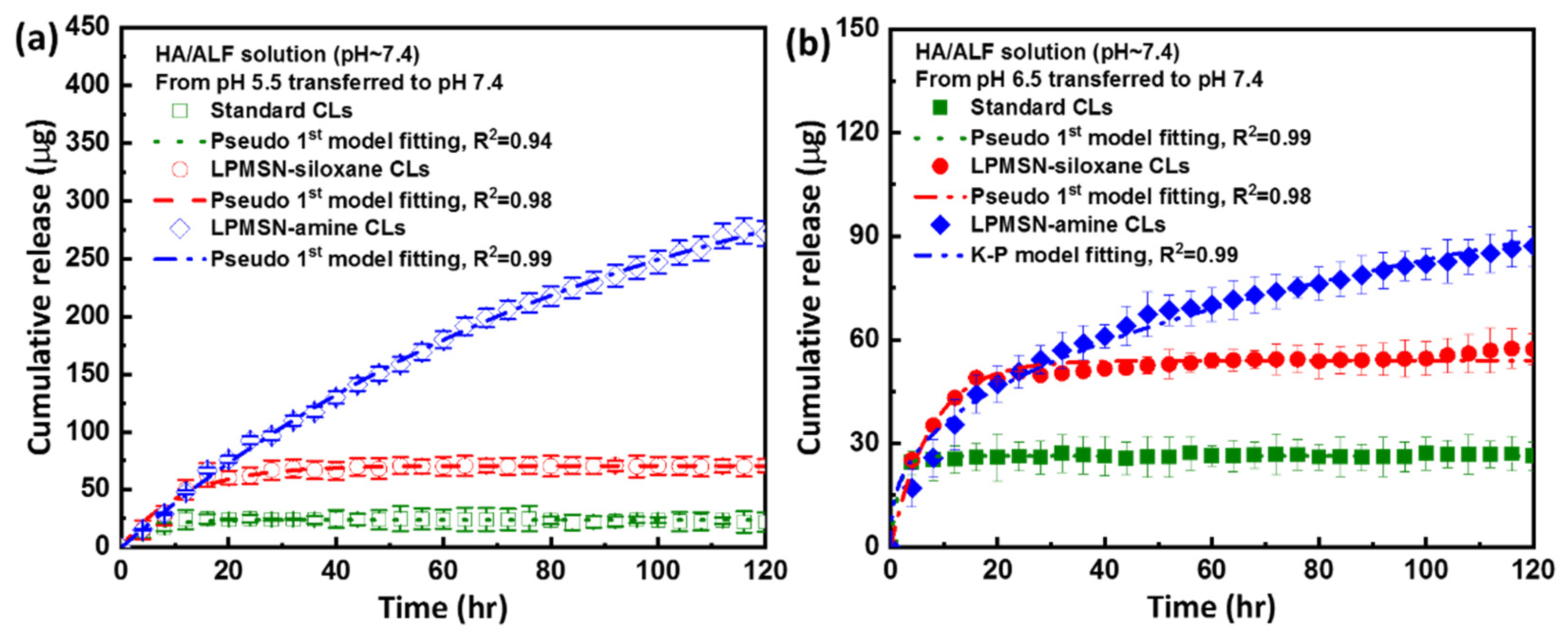
3.3. HA Loaded and Released of LPMSN-Laden CLs
3.4. HA Released Kinetics Mechanism of LPMSN-Laden CLs
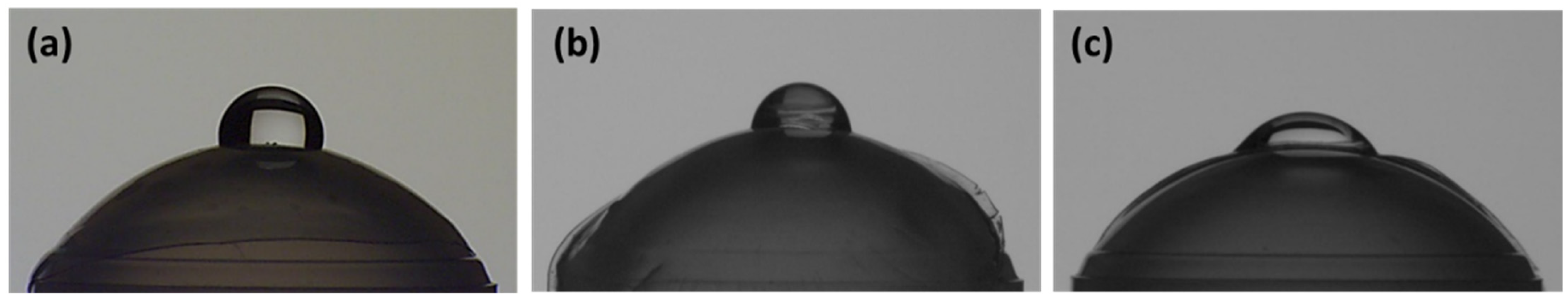
3.5. Wetting Angle of LPMSN-Laden CLs with HA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farandos, N.M.; Yetisen, A.K.; Monteiro, M.J.; Lowe, C.R.; Yun, S.H. Contact lens sensors in ocular diagnostics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 792–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Horikawa, S.; Venkatesh, S.; Saha, J.; Hong, J.W.; Byrne, M.E. Zero-order therapeutic release from imprinted hydrogel contact lenses within in vitro physiological ocular tear flow. J. Control. Release 2007, 124, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.C.; Yang, H. Hydrogel-based ocular drug delivery systems: Emerging fabrication strategies, applications, and bench-to-bedside manufacturing considerations. J. Control. Release 2019, 306, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Luna, C.; Hu, N.; Tammareddy, T.; Domszy, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, N.S.; Yang, A. Extended delivery of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs through contact lenses loaded with Vitamin E and cationic surfactants. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2019, 42, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, P.; Serro, A.P.; Saramago, B.; Colaço, R.; Chauhan, A. Controlled release of antibiotics from vitamin E–loaded silicone-hydrogel contact lenses. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Yang, K.; Kang, B.; Lee, C.; Song, I.T.; Byun, E.; Park, K.I.; Cho, S.W.; Lee, H. Hyaluronic acid catechol: A biopolymer exhibiting a pH-dependent adhesive or cohesive property for human neural stem cell engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulsen, D.; Chauhan, A. Ophthalmic drug delivery through contact lenses. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.H.; Carbia, B.E.; Plummer, C.; Chauhan, A. Dual drug delivery from vitamin E loaded contact lenses for glaucoma therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvi, F.A.; Soni, T.G.; Shah, D.O. A review on therapeutic contact lenses for ocular drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulvi, F.A.; Mangukiya, M.A.; Patel, P.A.; Vaidya, R.J.; Koli, A.R.; Ranch, K.M. Extended release of ketotifen from silica shell nanoparticle-laden hydrogel contact lenses: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripongpreda, T.; Pongsachareonnont, P.; Chanajaree, R.; Rodthongkum, N. Theranostic contact lens based on cellulose nanofibrils/levofloxacin nanocomposite for ocular bacterial infection. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7141–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Jin, X.T.; Zhang, S.X.; Xue, C.; Liu, M.; Luo, Y.H. Colored contact lens with all-weather humidity-triggered discoloration. Dye. Pigment. 2023, 218, 111483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisham, M.; Salih, A.E.; Butt, H. 3D Printing of Multimaterial Contact Lenses. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 4381–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jooken, S.; Deschaume, O.; Bartic, C. Nanocomposite Hydrogels as Functional Extracellular Matrices. Gels 2023, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Alsehli, M.; AI-Enizi, A.; Nafady, A. Recent advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery applications. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Tian, B.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Han, J. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with tumor-shedable hyaluronic acid as carriers for doxorubicin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B. Two-pronged strategy of biomechanically active and biochemically multifunctional hydrogel wound dressing to accelerate wound closure and wound healing. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9937–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.F.; Shiau, F.J. Enhanced and Extended Ophthalmic Drug Delivery by pH-Triggered Drug-Eluting Contact Lenses with Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 18630–18638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Lu, T.; Yu, S.; Hu, H. Fetal milieu-simulating hyaluronic acid-dopamine-chondroitin sulfate hydrogel promoting angiogenesis and hair regeneration for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; Qin, M.Z.; Yang, Y.Y.; Liu, B.W.; Zhang, D.J.; Jiang, C.H.; Yin, Z.Q.; Lu, M.; et al. A comparative study of the ameliorative effects of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides and hyaluronic acid on DSS-induced colitis in mice and research on relevant mechanisms. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 6482–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.F.; Li, J.S.; Fang, Y.T.; Chien, C.J.; Lee, C.H. UV and Blue−Light Anti−Reflective Structurally Colored Contact Lenses based on a Copolymer Hydrogel with Amorphous Array Nanostructures. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4006–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Ding, H.; Deng, D.; Xie, Z. Self-reporting colorimetric analysis of drug release by molecular imprinted structural color contact lens. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34611–34617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, R.; Pereira, A.d.E.S.; Melo, N.F.S.d.; Porto, R.M.; Feitosa, L.O.; Tonello, P.S.; Filho, N.L.D.; Rosa, A.H.; Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Controlled release system for ametryn using polymer microspheres: Preparation, characterization and release kinetics in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieppo, A.; Boggs, A.C.; Pourjavad, P.; Byrne, M.E. Analysis of release kinetics of ocular therapeutics from drug releasing contact lenses: Best methods and practices to advance the field. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2014, 37, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Xue, C.; Shao, K.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; Pan, J.; Lin, D. Photonic Crystal−Embedded Molecularly Imprinted Contact Lenses for Controlled Drug Release. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Derami, H.G.; Gupta, P.; Singamaneni, S.; Jun, Y.S. Ionic surface propensity controls pH in nanopores. Chem 2022, 8, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaleva, E.G.; Molochnikov, L.S.; Venkatesan, U.; Marek, A.; Stepanova, D.P.; Kozhikhova, K.V.; Mironov, M.A.; Smirnov, A.I. Acid–base properties of nanoconfined volumes of anodic aluminum oxide pores by EPR of pH-sensitive spin probes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Widejko, R.G.; Yang, Z.; Nguyen, K.T.; Chen, H.; Fernando, L.P.; Christensen, K.A.; Anker, J.N. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of pH with silica-encapsulated 4-mercaptobenzoic acid-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8013–8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-F.; Shiau, F.-J. Hydrogel Contact Lenses Embedded with Amine-Functionalized Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Extended Hyaluronic Acid Release. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172441
Lai C-F, Shiau F-J. Hydrogel Contact Lenses Embedded with Amine-Functionalized Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Extended Hyaluronic Acid Release. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(17):2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172441
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Chun-Feng, and Fu-Jia Shiau. 2023. "Hydrogel Contact Lenses Embedded with Amine-Functionalized Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Extended Hyaluronic Acid Release" Nanomaterials 13, no. 17: 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172441
APA StyleLai, C.-F., & Shiau, F.-J. (2023). Hydrogel Contact Lenses Embedded with Amine-Functionalized Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Extended Hyaluronic Acid Release. Nanomaterials, 13(17), 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172441






