GO/CNT−OH/Nafion Nanocomposite Humidity Sensor Based on the LC Wireless Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
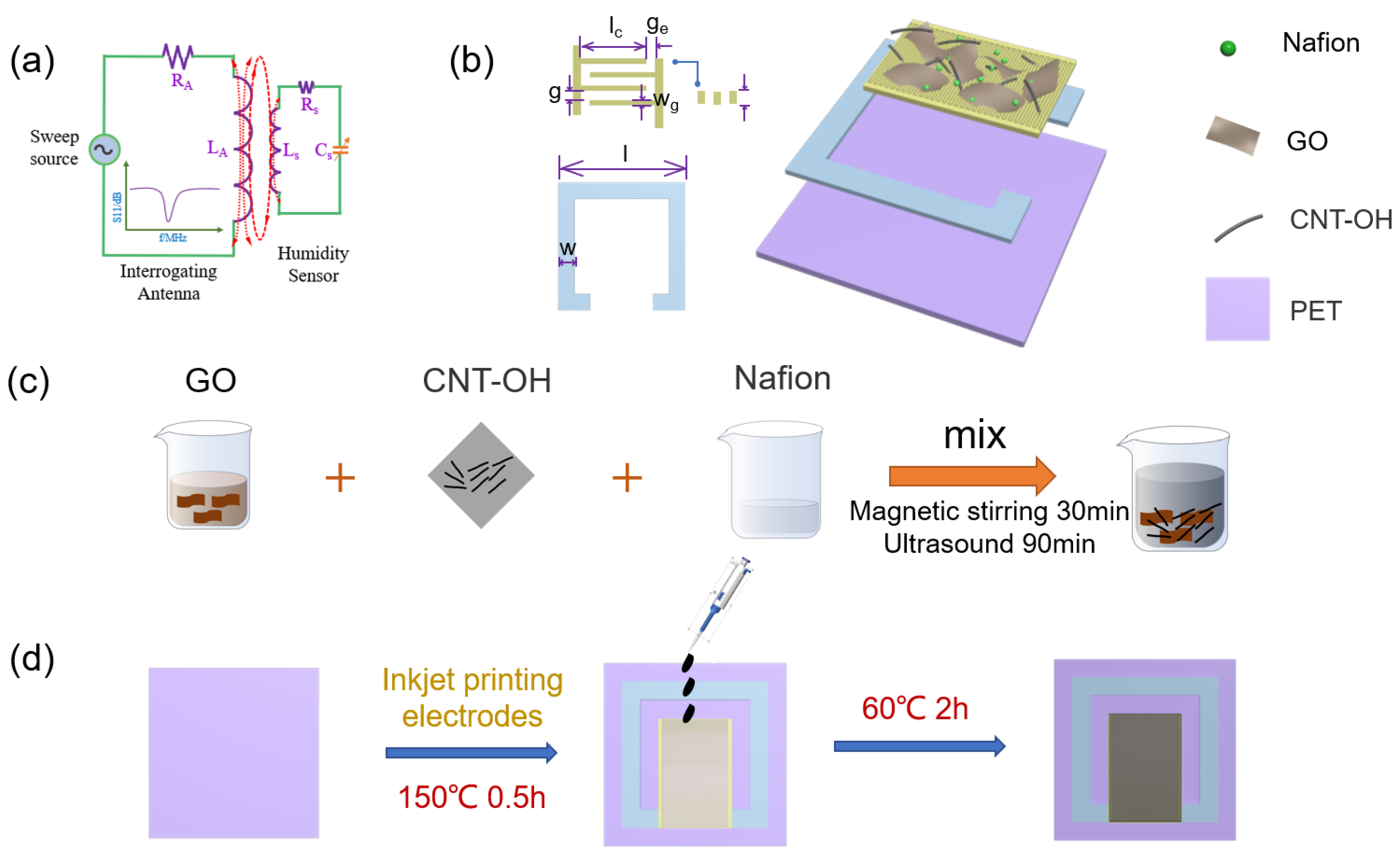
2.2. Sensor Fabrication and Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.2. Humidity-Sensing Performance
3.3. Sensing Mechanism of the Humidity Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, L.; Ravaynia, P.S.; Huang, Q.A.; Hierlemann, A.; Modena, M.M. Parallelized Wireless Sensing System for Continuous Monitoring of Microtissue Spheroids. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Tan, Q.; Jia, P.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Xue, C.; Xiong, J. Review of Research Status and Development Trends of Wireless Passive Lc Resonant Sensors for Harsh Environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 13097–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gu, D.; Li, X.; Lin, S.; Zhao, S.; Rumyantseva, M.N.; Gaskov, A.M. Reduced Graphene Oxide Hybridized with WS2 Nanoflakes Based Heterojunctions for Selective Ammonia Sensors at Room Temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, M.; Tang, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Q. Recent Progress of Diversiform Humidity Sensors Based on Versatile Nanomaterials and Their Prospective Applications. Nano Res. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Han, Y.; Tao, B. ZnO/MoS2/RGO Nanocomposite Non-Contact Passive and Chip-Less LC Humidity Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 13891–13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Petrila, I.; Vigneselvan, S.; Dharmavarapu, R.; Juodkazis, S.; Kavita, S.; Chandrasekaran, J. Efficient Humidity-Sensitive Electrical Response of Annealed Lithium Substituted Nickel Ferrite (Li–NiFe2O4) Nanoparticles under Ideal, Real and Corrosive Environments. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 18660–18667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Pan, J.; Gao, C.; Wang, Q. Finite Element Analysis Model of Electronic Skin Based on Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Hamidon, M.N. Humidity Sensors Principle, Mechanism, and Fabrication Technologies: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittersma, Z.M. Recent Achievements in Miniaturised Humidity Sensors—A Review of Transduction Techniques. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2002, 96, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marcellis, A.; Ferri, G.; Mantenuto, P. A Novel 6-Decades Fully-Analog Uncalibrated Wheatstone Bridge-Based Resistive Sensor Interface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 189, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revuelto, J.; Calvo, B.; Medrano, N.; Zatorre, G.; Celma, S. A Circuit Interface for Resistive Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2009 Spanish Conference on Electron Devices, CDE’09, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 11–13 February 2009; pp. 316–319. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Cabezas, A.L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.R.; Zhang, Z. Bin Flexible UHF Resistive Humidity Sensors Based on Carbon Nanotubes. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jian, J.; Geng, X.; Gou, G.; Cui, W.; Cui, J.; Qiao, Y.; Fu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.L. A Miniaturized Integrated SAW Sensing System for Relative Humidity Based on Graphene Oxide Film. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 9733–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; He, M.; Meng, N.; He, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Shi, T.; Hasan, T.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Y.; et al. Fast Response and High Sensitivity ZnO/Glass Surface Acoustic Wave Humidity Sensors Using Graphene Oxide Sensing Layer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zi, G.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, T. Self-Powered Biosensor for Specifically Detecting Creatinine in Real Time Based on the Piezo-Enzymatic-Reaction Effect of Enzyme-Modified Zno Nanowires. Biosensors 2021, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Shah, M.A.; Ganai, P.A. Nanoporous Anodic Alumina (NAA) Prepared in Different Electrolytes with Different Pore Sizes for Humidity Sensing. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020, 24, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Seo, J.; Park, J.; Hwang, I.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, H.; Yoo, B. Capacitive Humidity Sensing Properties of Freestanding Bendable Porous SiO2/Si Thin Films. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhabi, S.; Jackson, K.J.; Beierle, A.M.; Carr, A.R.; Zellner, E.M.; Reuel, N.F. Monitoring Wound Health through Bandages with Passive LC Resonant Sensors. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martuza, M.A.; Lee, C.H.; Sazonov, A.; Boumaiza, S.; Karim, K.S. Wireless LC-Type Passive Humidity Sensor Using Large-Area RF Magnetron Sputtered ZnO Films. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2018, 65, 3447–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, J.Q.; Huang, Q.A. An LC-Type Passive Wireless Humidity Sensor System with Portable Telemetry Unit. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 24, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim Tan, E.; Ng, W.N.; Shao, R.; Pereles, B.D.; Ghee Ong, K. A Wireless, Passive Sensor for Quantifying Packaged Food Quality. Sensors 2007, 7, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Larsson, O.; Platt, D.; Nordlinder, S.; Engquist, I.; Berggren, M.; Crispin, X. An All-Printed Wireless Humidity Sensor Label. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.R. Low-Cost Printed Chipless RFID Humidity Sensor Tag for Intelligent Packaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.Z.; Wang, L.F.; Dong, L.; Deng, W.J.; Huang, Q.A. Low Cost Paper-Based LC Wireless Humidity Sensors and Distance-Insensitive Readout System. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4717–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, Y.L.; Lu, Y.F.; Ding, X.Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Shi, G.; Wu, W.; Haick, H. Tailor-Made Engineering of Bioinspired Inks for Writing Barcode-like Multifunctional Sensory Electronics. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Salmerón, J.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Rodríguez, M.A.C.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F.; Palma, A.J. HF RFID Tag as Humidity Sensor: Two Different Approaches. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5726–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, D.Z.; Mansouri, A.; Anzi, L.; Sordan, R.; Stojanovic, G.M. Performance Analysis of Flexible Ink-Jet Printed Humidity Sensors Based on Graphene Oxide. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 4378–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Du, A.; Deng, G.; Zhao, X.; Pan, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, Q. Naturally Nitrogen-Doped Self-Encapsulated Biochar Materials Based on Mouldy Wheat Flour for Silicon Anode in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 450, 142269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Yin, K.; Xie, X.; Ji, J.; Wan, S.; Sun, L.; Terrones, M.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Ultrahigh Humidity Sensitivity of Graphene Oxide. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q. One-Step Synthesis Method of Flower-like Si@NiO/RGO Composites as High-Performance Anode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Han, M.; Lee, G.S. Humidity-Sensing Characteristics of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Sheet. Mater. Lett. 2014, 122, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Park, J.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Yao, J. Synthesis of Enhanced Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Graphene Oxide Nanosheets by a Solvothermal Method. Carbon 2009, 47, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, R.; Zhang, Y.; Nayak, S.K.; Ajayan, P.M. Effect of H2O Adsorption on Electron Transport in a Carbon Nanotube. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 2638–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.P.; Zhao, Z.G.; Liu, X.W.; Zhang, Z.X.; Suo, C.G. A Capacitive Humidity Sensor Based on Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs). Sensors 2009, 9, 7431–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z. Facile Fabrication of Graphene Oxide/Nafion/Indium Oxide for Humidity Sensing with Highly Sensitive Capacitance Response. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 292, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Ding, X.; Zhao, X. A QCM Humidity Sensors Based on GO/Nafion Composite Films with Enhanced Sensitivity. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 8874–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Ding, X.; Zhao, X. A High-Sensitive Humidity Sensor Based on Water-Soluble Composite Material of Fullerene and Graphene Oxide. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Ding, X.; Zhao, X. High-Sensitive Humidity Sensor Based on Graphene Oxide with Evenly Dispersed Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 207, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.H.; Zhao, Q.N.; Li, C.Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, B.H.; Tai, H.L. Enhanced Positive Humidity Sensitive Behavior of P-Reduced Graphene Oxide Decorated with n-WS2 Nanoparticles. Rare Met. 2021, 40, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sensing Material | Range (% RH) | Response (s) | Recovery (s) | Sensitivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DuPont 5018 | 20–90 | - | >1800 | 1.1 kHz/%RH | [22] |
| PEL | 30–80 | 240 | 360 | 371 kHz/%RH | [23] |
| Paper | 11–97 | 3600 | 2400 | 140 kHz/%RH | [24] |
| GO/CNT−OH/Nafion | 30–95 | 110 | 115 | 547kHz/%RH | This work |
| Symbol | Unit (mm) |
|---|---|
| L | 40 |
| W | 5 |
| wg | 0.25 |
| g | 0.25 |
| ge | 0.25 |
| lc | 17.75 |
| h | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Jiao, C.; Wang, M.; Pan, J.; Wang, Q. GO/CNT−OH/Nafion Nanocomposite Humidity Sensor Based on the LC Wireless Method. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13131925
Wang C, Jiao C, Wang M, Pan J, Wang Q. GO/CNT−OH/Nafion Nanocomposite Humidity Sensor Based on the LC Wireless Method. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(13):1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13131925
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chengkai, Chunxiao Jiao, Meng Wang, Jinghong Pan, and Qi Wang. 2023. "GO/CNT−OH/Nafion Nanocomposite Humidity Sensor Based on the LC Wireless Method" Nanomaterials 13, no. 13: 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13131925
APA StyleWang, C., Jiao, C., Wang, M., Pan, J., & Wang, Q. (2023). GO/CNT−OH/Nafion Nanocomposite Humidity Sensor Based on the LC Wireless Method. Nanomaterials, 13(13), 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13131925






