Preparation of Surfactant-Free Nano Oil Particles in Water Using Ultrasonic System and the Mechanism of Emulsion Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Horn, Bath, and Focused Ultrasonic Emulsification
3. Results
3.1. Particle Size Distribution
3.2. Effect of Ultrasonic Frequency on Particle Size
3.3. Emulsion Stability
4. Discussion
Breakdown and Stabilization Mechanisms of O/W-Type Emulsions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padole, A.; Bodhankar, M. Self double-emulsifying drug delivery system (SDEDDS) for oral delivery of vancomycin hydrochloride. Elixir Pharm. 2015, 82, 32184–32188. [Google Scholar]
- Gursoy, R.N.; Benita, S. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2004, 58, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, K.; Chopra, S.; Dhar, D.; Arora, S.; Khar, R.K. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: An approach to enhance oral bioavailability. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Kapil, R.; Singh, R.; Katare, O. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS): Formulation development, characterization, and applications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2009, 26, 427–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schans, C.P.; Postma, D.S.; Koeter, G.H.; Rubin, B.K. Physiotherapy and bronchial mucus transport. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kang, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Sarsenbekuly, B. Emulsification and stabilization mechanism of crude oil emulsion by surfactant synergistic amphiphilic polymer system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2021, 609, 125726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canselier, J.P.; Delmas, H.; Wilhelm, A.M.; Abismail, B. Ultrasound emulsification—An overview. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2002, 23, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, C.; Söllner, K. On the mechanism of emulsification by ultrasonic waves. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1935, 31, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.K.; Fogler, H.S. Acoustic emulsification. Part 2. Breakup of the large primary oil droplets in a water medium. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 88, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, S.A.; Kwak, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, T.G. Novel surfactant-free water dispersion technique of TiO2 NPs using focused ultrasound system. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neduzhii, S.A. Nature of the disturbances giving rise to formation of the disperse phase of an emulsion in an acoustic field. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1965, 10, 390–397. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.Y.; Guo, N.; Teh, C.Y.; Hay, J.X.W. Theory and fundamentals of ultrasound. In Advances in Ultrasound Technology for Environmental Remediation; Springer Briefs in Molecular Science; Wu, T.Y., Guo, N., Teh, C.Y., Hay, J.X.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H. Emulsification: Emulsion Introductory; R D Support Center: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, T. Emulsification and Interface; R D Support Center: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kotronarou, A.; Mills, G.; Hoffmann, M.R. Decomposition of parathion in aqueous solution by ultrasonic irradiation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 1460–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
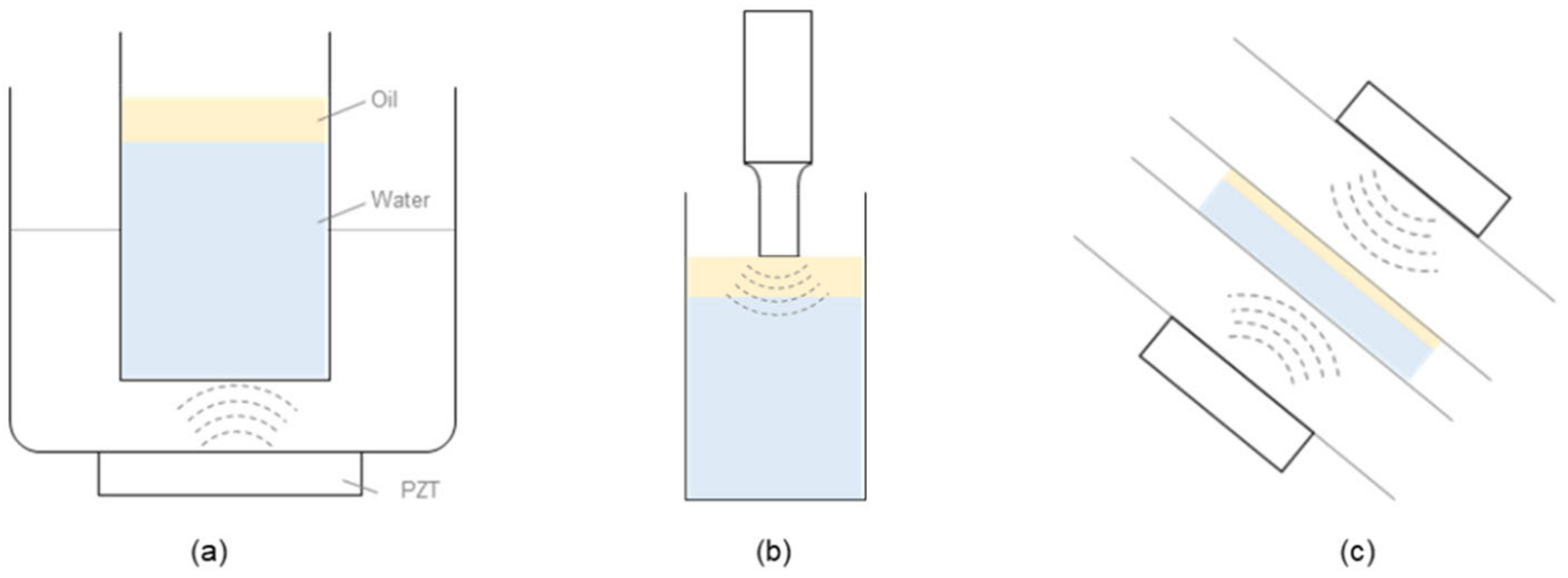
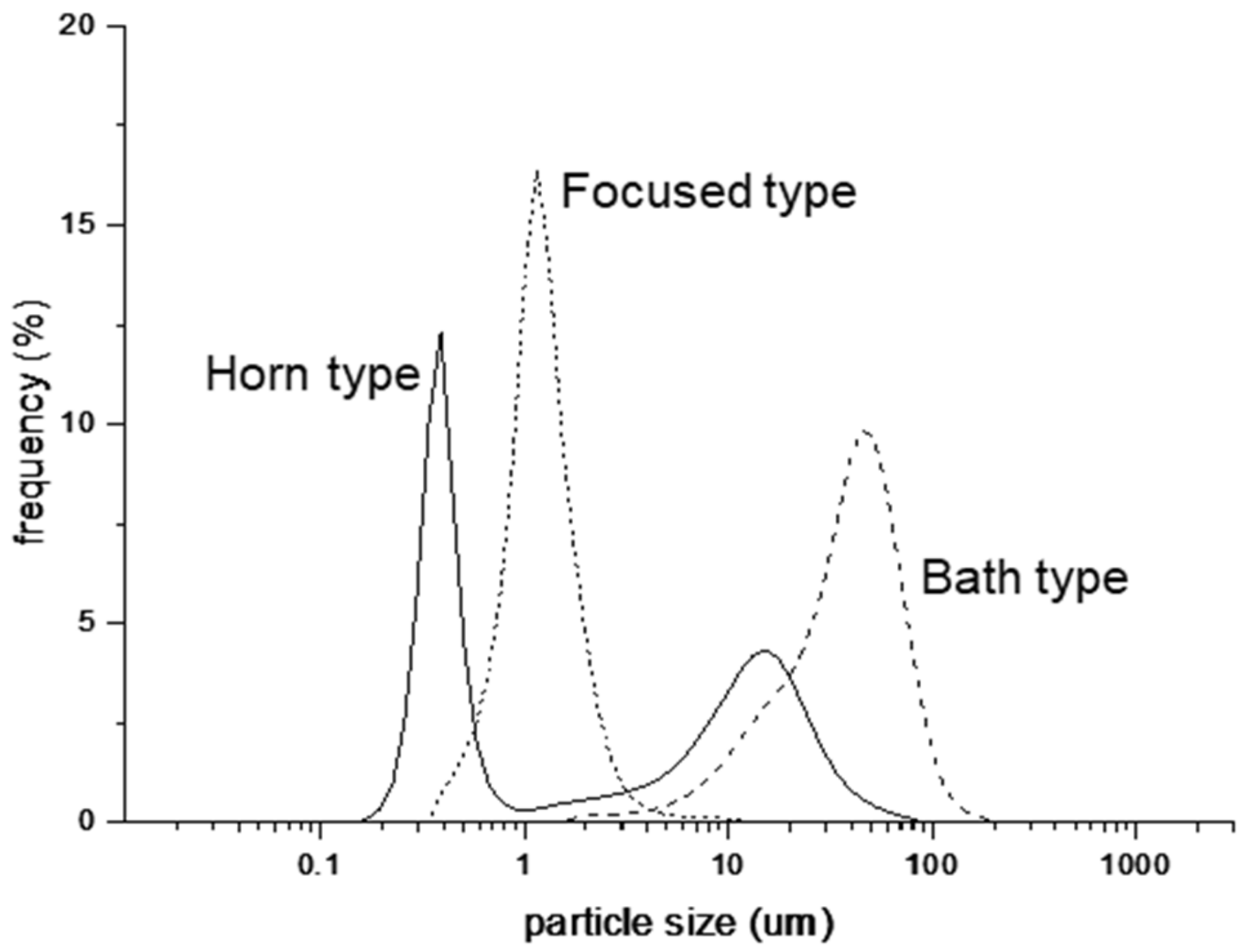
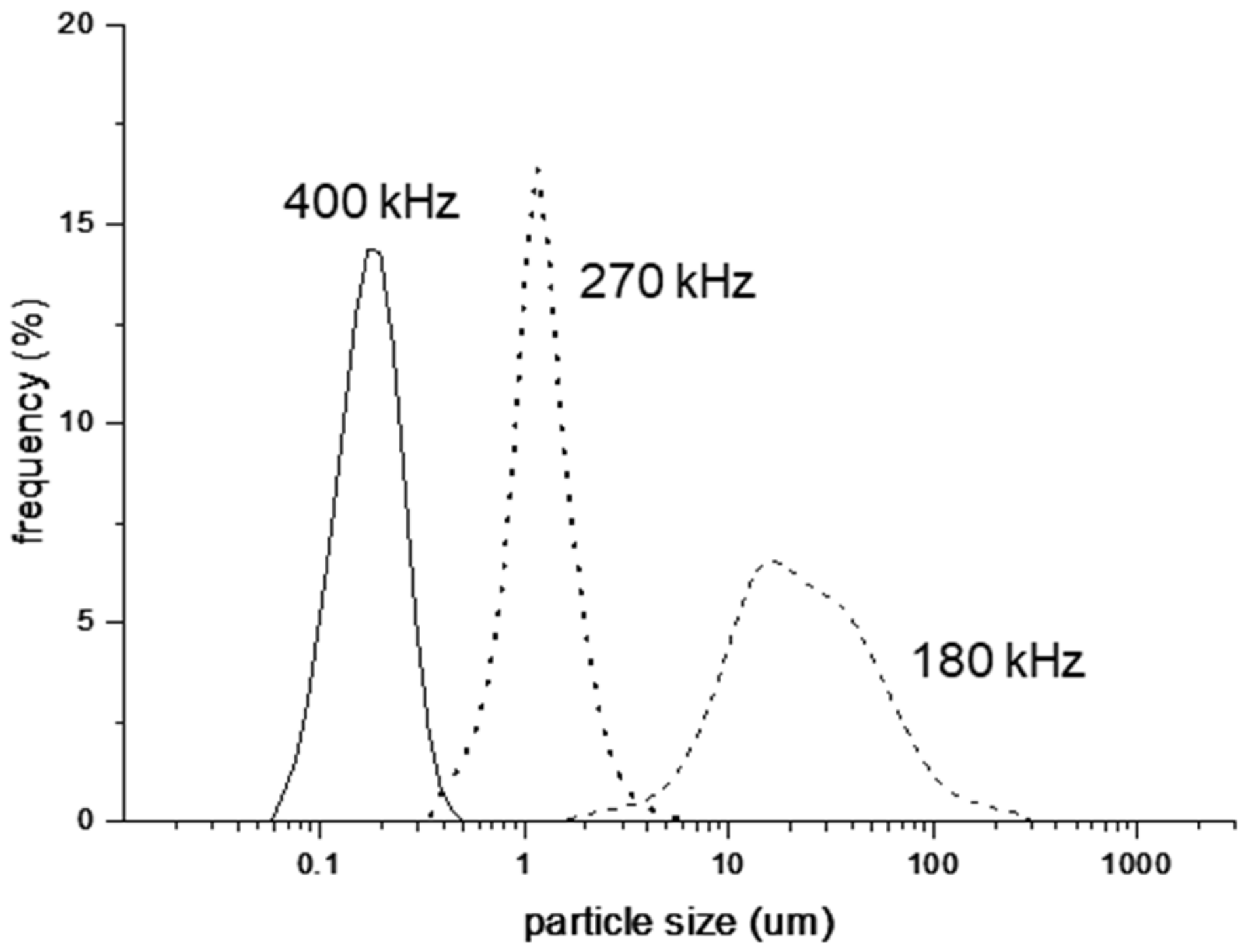
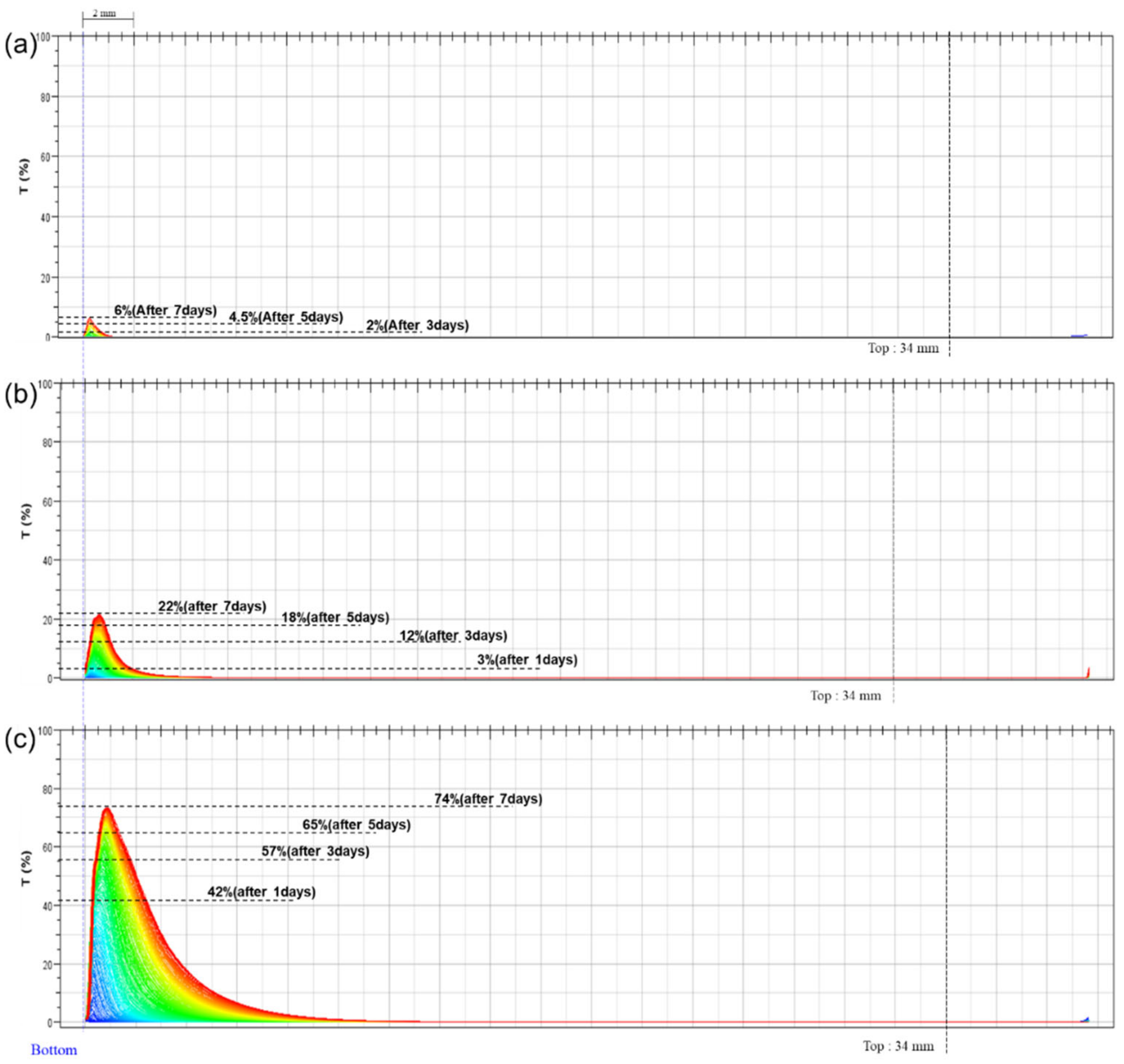
| Dispersion Medium (Continuous Phase) | Dispersed Phase | O/W-Type Emulsion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | 3st water (Deionized Water) | Olive oil | - |
| Specific gravity | 1.0 | 0.915 | - |
| Model or manufacturer | Milli-Q Direct(Merck Millipore, Massachusetts, USA) | F. FAIGES S.L.(Spain) | - |
| Concentration (wt.%) | - | - | 1 |
| Volume (mL) | 99 | 1 | 100 |
| Type | Frequency (kHz) | Power (W) | Irradiation Time (min) | Sample Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bath type (JAC-4020) | 40 | 400 | 30 | 100 |
| Horn type (Sonifier 450) | 20 | 400 | 30 | 100 |
| Focused type (developed in our laboratory) | 400 | 100 | 30 | 100 |
| No. | Dispersion Method | Frequency (kHz) | Power (W) | Irradiation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Focused | 180 | 100 | 60 |
| 2 | Focused | 270 | 100 | 60 |
| 3 | Focused | 400 | 100 | 60 |
| Sample No. | Emulsion A | Emulsion B | Emulsion C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size range | 0.06–0.49 µm | 0.22–7 µm | 2–320 µm |
| After 1 d | 2% | 3% | 42% |
| After 3 d | 2% | 12% | 57% |
| After 5 d | 4.5% | 18% | 65% |
| After 7 d | 6% | 22% | 74% |
| Sedimentation (Rising) Displacement of Particles (20 °C, Underwater, ρ = 0.9 g/cm3) | Particle Displacement by Brownian Motion (20 °C, Underwater) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Size (µm) | Displacement after 1 s (µm) | Particle Size (µm) | Displacement after 1 s (µm) | |
| 0.01 | 2.18 × 10−5 | < | 0.01 | 6.55 |
| 0.1 | 2.18 × 10−3 | < | 0.1 | 2.07 |
| 0.35 | 2.67 × 10−2 | < | 0.35 | 1.11 |
| 0.5 | 5.44 × 10−2 | < | 0.5 | 0.93 |
| 1 | 2.18 × 10−1 | < | 1 | 6.55 × 10−3 |
| 1.554 | 5.26 × 10−1 | = | 1.554 | 5.26 × 10−1 |
| 3.5 | 2.67 | > | 3.5 | 3.50 × 10−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwangbo, S.-A.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, B.-A.; Moon, C.-K. Preparation of Surfactant-Free Nano Oil Particles in Water Using Ultrasonic System and the Mechanism of Emulsion Stability. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091547
Hwangbo S-A, Lee S-Y, Kim B-A, Moon C-K. Preparation of Surfactant-Free Nano Oil Particles in Water Using Ultrasonic System and the Mechanism of Emulsion Stability. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(9):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091547
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwangbo, Seon-Ae, Seung-Yul Lee, Bu-An Kim, and Chang-Kwon Moon. 2022. "Preparation of Surfactant-Free Nano Oil Particles in Water Using Ultrasonic System and the Mechanism of Emulsion Stability" Nanomaterials 12, no. 9: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091547
APA StyleHwangbo, S.-A., Lee, S.-Y., Kim, B.-A., & Moon, C.-K. (2022). Preparation of Surfactant-Free Nano Oil Particles in Water Using Ultrasonic System and the Mechanism of Emulsion Stability. Nanomaterials, 12(9), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12091547






