In Vitro Genotoxicity Evaluation of an Antiseptic Formulation Containing Kaolin and Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Characterization of the Silver-Kaolin Formulation
2.3. Test Compound Preparation
2.4. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.5. Cytotoxicity
2.6. Mouse Lymphoma Assay
2.6.1. Mutant L5178Y TK−/− Cleansing
2.6.2. Mouse Lymphoma Assay
2.6.3. Mouse Lymphoma Assay Calculations
2.7. Micronucleus Test
2.8. Comet Assay
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Silver-Kaolin Formulation
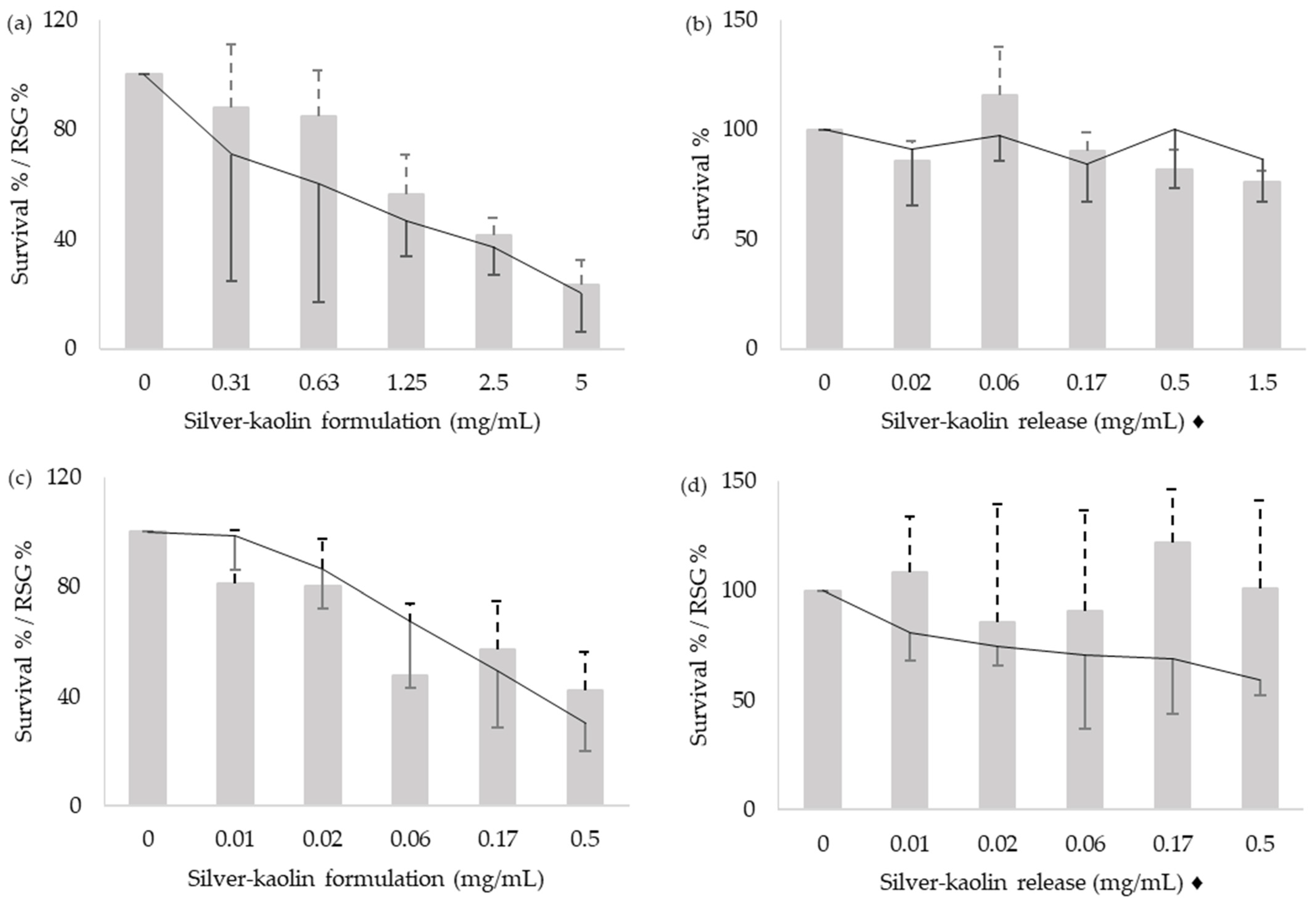
3.2. Cytotoxicity
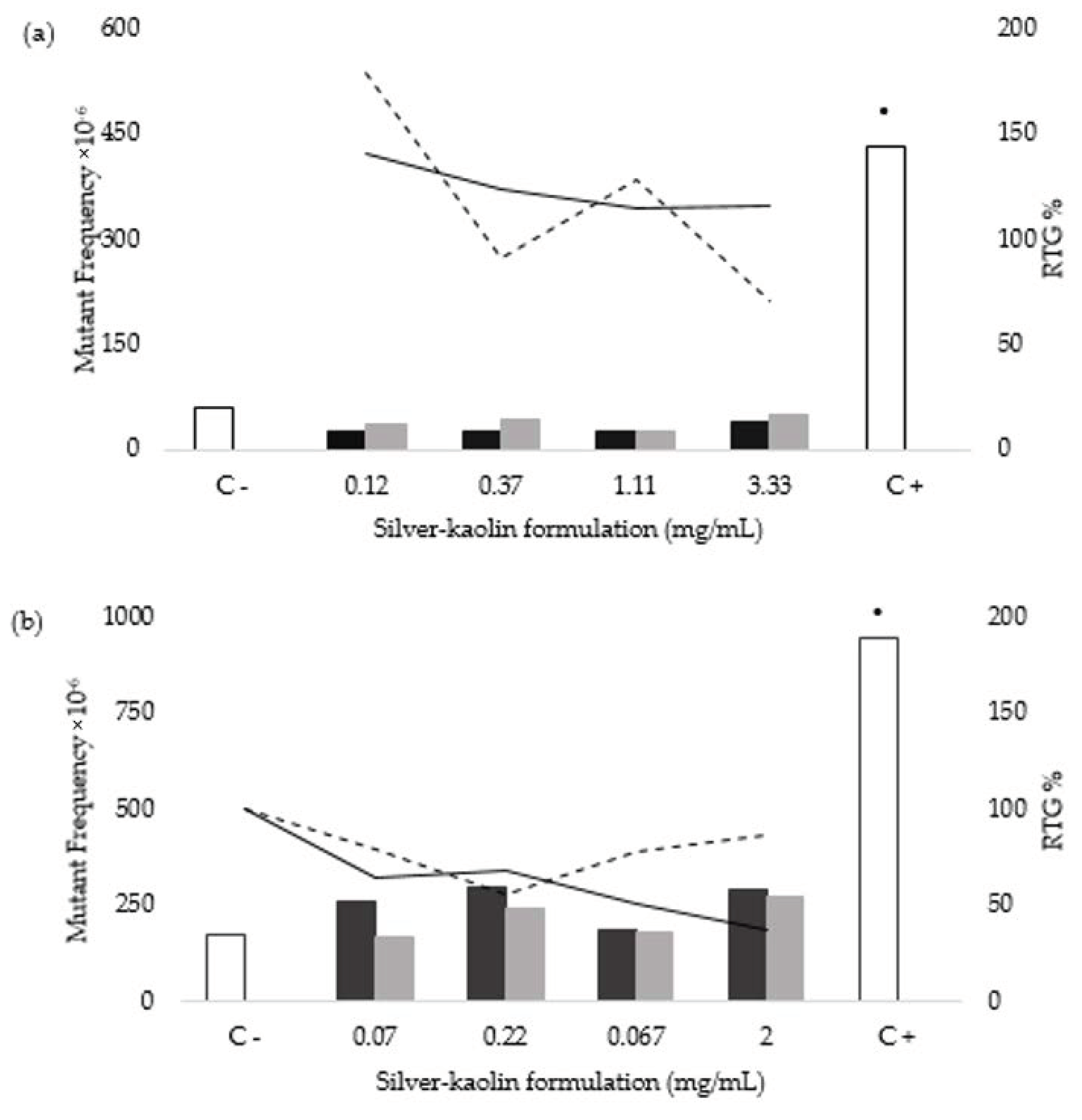
3.3. Mouse Lymphoma Assay
3.4. MN Test
3.5. Comet Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shankar, P. Book review: Tackling drug-resistant infections globally. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. Microbe Mag. 2015, 10, 354–355. [Google Scholar]
- Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial Resistance: Implications and Costs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3903–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Z. Antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in food animals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18377–18384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, E.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P. Antimicrobial resistance in veterinary medicine: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); OIE. Joint FAO/OIE/WHO Expert Workshop on Non-Human Antimicrobial Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance: Scientific Assessment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic, N.; Vidovic, S. Antimicrobial resistance and food animals: Influence of livestock environment on the emergence and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, G.; Ning, J.; Ahmed, S.; Huang, J.; Ullah, R.; An, B.; Hao, H.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Selection and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in Agri-food production. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Parliament; The Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No. 1831/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council on additives for use in animal nutrition. Off. J. Eur. Union 2003, 4, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- UE. Ban on Antibiotics as Growth Promoters in Animal Feed Enters into Effect; UE: Brussels, Belgium, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Arsène, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Andreevna, S.L.; Vladimirovich, E.A.; Carime, B.Z.; Marouf, R.; Khelifi, I. The use of probiotics in animal feeding for safe production and as potential alternatives to antibiotics. Vet. World 2021, 14, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, K.; Mehta, S.; Chavan, R.; Chitalia, V.; Deogharkar, D.; Deshpande, S. Efficiency of Biosynthesized Silver and Zinc Nanoparticles against Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Gomes, D.; Esteruelas, G.; Bonilla, L.; Lopez-Machado, A.L.; Galindo, R.; Cano, A.; Espina, M.; Ettcheto, M.; Camins, A.; et al. Metal-based nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: An overview. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badar, W.; Khan, M.A.U. Analytical study of biosynthesised silver nanoparticles against multi-drug resistant biofilm-forming pathogens. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnhoven, S.W.P.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Herberts, C.A.; Hagens, W.I.; Oomen, A.G.; Heugens, E.H.W.; Roszek, B.; Bisschops, J.; Gosens, I.; Van De Meent, D.; et al. Nano-silve—A review of available data and knowledge gaps in human and environmental risk assessment. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethalakshmi, R. Sarada Gold and silver nanoparticles from Trianthema decandra: Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Mahdy, M.M.; Eldin, T.A.S.; Aly, H.S.; Mohammed, F.F.; Shaalan, M.I. Evaluation of hepatotoxic and genotoxic potential of silver nanoparticles in albino rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 67, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, T.; Jyoti, K.; Patnaik, A.; Singh, A.; Chauhan, R.; Chandel, S.S. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles using an endophytic fungal supernatant of Raphanus sativus. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.M. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhailov, O.V.; Mikhailova, E.O. Elemental Silver Nanoparticles: Biosynthesis and Bio Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subashini, J.; Gopiesh Khanna, V.; Kannabiran, K. Anti-ESBL activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using soil Streptomyces species. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.D.; Kuppusamy, P.; Kim, D.H.; Govindan, N.; Maniam, G.P.; Choi, K.C. Forage Crop Lolium multiflorum Assisted Synthesis of AgNPs and Their Bioactivities Against Poultry Pathogenic Bacteria in in vitro. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondevila, M.; Herrer, R.; Casallas, M.C.; Abecia, L.; Ducha, J.J. Silver nanoparticles as a potential antimicrobial additive for weaned pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 150, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Etayo, L.; González, D.; Leiva, J.; Díez-Leturia, M.; Ezquerra, A.; Lostao, L.; Vitas, A.I. Antibacterial Activity of Kaolin–Silver Nanomaterials: Alternative Approach to the Use of Antibiotics in Animal Production. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.S.; Abou-El-Sherbini, K.S.; Hamzawy, E.M.A.; Amr, M.H.A.; El-Dafrawy, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nano-particles by Macrococcus bovicus and Its Immobilization onto Montmorillonite Clay for Antimicrobial Functionality. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 2225–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.; Patil, S.D.; Jeevanandam, P.; Navani, N.K.; Singla, M.L. Synthesis, characterization and bactericidal activity of silica/silver core–shell nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassouna, M.E.M.; ElBably, M.A.; Mohammed, A.N.; Nasser, M.A.G. Assessment of carbon nanotubes and silver nanoparticles loaded clays as adsorbents for removal of bacterial contaminants from water sources. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosoky, W.M.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Alwan, A.B.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Taha, A.E.; Ghareeb, R.Y.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Khafaga, A.F. Dietary supplementation of silver-silica nanoparticles promotes histological, immunological, ultrastructural, and performance parameters of broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiao, S.-H.; Lin, S.-H.; Shen, C.-I.; Liao, J.-W.; Bau, I.-J.; Wei, J.-C.; Tseng, L.-P.; Hsu, S.-h.; Lai, P.-S.; Lin, S.-Z.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nanohybrids comprising silver nanoparticles and silicate clay for controlling Salmonella infection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA Scientific Committee; Hardy, A.; Benford, D.; Halldorsson, T.; Jeger, M.J.; Knutsen, H.K.; More, S.; Naegeli, H.; Noteborn, H.; Ockleford, C.; et al. Guidance on risk assessment of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnologies in the food and feed chain: Part 1, human and animal health. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Garraus, A.; Azqueta, A.; Vettorazzi, A.; de Cerain, A.L. Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.-R.; Wei, J.-C.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Su, H.-L.; Peng, F.-C.; Lin, J.-J. Evaluation on Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of the Exfoliated Silicate Nanoclay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totsuka, Y.; Higuchi, T.; Imai, T.; Nishikawa, A.; Nohmi, T.; Kato, T.; Masuda, S.; Kinae, N.; Hiyoshi, K.; Ogo, S.; et al. Genotoxicity of nano/microparticles in in vitro micronuclei, in vivo comet and mutation assay systems. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawanishi, M.; Yoneda, R.; Totsuka, Y.; Yagi, T. Genotoxicity of micro- And nano-particles of kaolin in human primary dermal keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Genes Environ. 2020, 42, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Toyooka, T.; Ibuki, Y.; Masuda, S.; Watanabe, M.; Totsuka, Y. Effect of physicochemical character differences on the genotoxic potency of kaolin. Genes Environ. 2017, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OECD. OECD Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals–In Vitro Mammalian Cell Gene Mutation Tests Using the Thymidine Kinase Gene (TG 490); OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, J.; Moore, M.M.; Clive, D.; Hozier, J. Cytogenetic characterization of the L5178Y TK+/− 3.7.2C mouse lymphoma cell line. Mutat. Res. Mutagen. Relat. Subj. 1985, 147, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, M.D.; McDermott, A.; Clare, K.R.; Doherty, A.; Aardema, M.J. The Spectral Karyotype of L5178Y TK+/− Mouse Lymphoma Cells Clone 3.7.2C and Factors Affecting Mutant Frequency at the Thymidine Kinase (tk) Locus in the Microtitre Mouse Lymphoma Assay. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2014, 55, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals–In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test (OECD TG 487); OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2014.
- Bryce, S.M.; Bemis, J.C.; Avlasevich, S.L.; Dertinger, S.D. In vitro micronucleus assay scored by flow cytometry provides a comprehensive evaluation of cytogenetic damage and cytotoxicity. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007, 630, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, A.R.; Azqueta, A. Single-Cell Gel Electrophoresis Combined with Lesion-Specific Enzymes to Measure Oxidative Damage to DNA. In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 112, pp. 69–92. ISBN 9780124059146. [Google Scholar]
- Muruzabal, D.; Langie, S.A.S.; Pourrut, B.; Azqueta, A. The enzyme-modified comet assay: Enzyme incubation step in 2 vs 12-gels/slide systems. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 845, 402981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, P.; Azqueta, A.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Koppen, G.; Bonassi, S.; Milić, M.; Gajski, G.; Costa, S.; Teixeira, J.P.; Costa Pereira, C.; et al. Minimum Information for Reporting on the Comet Assay (MIRCA): Recommendations for describing comet assay procedures and results. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, S.H.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Singh, N. In vitro genotoxicity testing strategy for nanomaterials and the adaptation of current OECD guidelines. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 745, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Genotoxicity of Manufactured Nanomaterials: Report of the OECD Expert Meeting; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2014; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Chen, T. Progress in Genotoxicity Evaluation of Engineered Nanomaterials. In Nanomaterials-Toxicity and Risk Assessment; InTech: Hong Kong, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, S.J.; Clift, M.J.D.; Singh, N.; De Oliveira Mallia, J.; Burgum, M.; Wills, J.W.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Doak, S.H. Critical review of the current and future challenges associated with advanced in vitro systems towards the study of nanoparticle (secondary) genotoxicity. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azqueta, A.; Arbillaga, L.; López De Cerain, A.; Collins, A. Enhancing the sensitivity of the comet assay as a genotoxicity test, by combining it with bacterial repair enzyme FPG. Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muruzabal, D.; Sanz-Serrano, J.; Sauvaigo, S.; Treillard, B.; Olsen, A.K.; López de Cerain, A.; Vettorazzi, A.; Azqueta, A. Validation of the in vitro comet assay for DNA cross-links and altered bases detection. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Park, Y.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Oh, S.M.; Chung, K.H. Appropriate In Vitro Methods for Genotoxicity Testing of Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2013, 28, e2013003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, X.; Takemura, T.; Hanagata, N.; Wu, G.; Chou, L. Genotoxicity and molecular response of silver nanoparticle (NP)-based hydrogel. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OECD (2018) Guidance Document on Good In Vitro Method Practices (GIVIMP), OECD Series on Testing and Assessment, No. 286; OECD Series on Testing and Assessment; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018; ISBN 9789264311008.
- El Yamani, N.; Collins, A.R.; Rundén-Pran, E.; Fjellsbø, L.M.; Shaposhnikov, S.; Zienolddiny, S.; Dusinska, M. In vitro genotoxicity testing of four reference metal nanomaterials, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, cerium oxide and silver: Towards reliable hazard assessment. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huk, A.; Izak-Nau, E.; el Yamani, N.; Uggerud, H.; Vadset, M.; Zasonska, B.; Duschl, A.; Dusinska, M. Impact of nanosilver on various DNA lesions and HPRT gene mutations-effects of charge and surface coating. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huk, A.; Izak-Nau, E.; Reidy, B.; Boyles, M.; Duschl, A.; Lynch, I.; Dušinska, M. Is the toxic potential of nanosilver dependent on its size? Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azqueta, A.; Dusinska, M. The use of the comet assay for the evaluation of the genotoxicity of nanomaterials. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ISO/TR 10993-32; Part 22 Guidance on Nanomaterials. International Organization of Standarization Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Butler, K.S.; Peeler, D.J.; Casey, B.J.; Dair, B.J.; Elespuru, R.K. Silver nanoparticles: Correlating nanoparticle size and cellular uptake with genotoxicity. Mutagenesis 2015, 30, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.C.; Njoroge, J.; Bryce, S.M.; Zheng, J.; Ihrie, J. Flow cytometric evaluation of the contribution of ionic silver to genotoxic potential of nanosilver in human liver HepG2 and colon Caco2 cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Test 1 | Test 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silver-kaolin release ♦ (mg/mL) 3 h treatment | MN/1000 Nuclei | RS % | MN/1000 Nuclei | RS % |
| 0 | 1.18 | 100 | 0.49 | 100 |
| 0.07 | 0.94 | 112 | 0.29 | 87 |
| 0.22 | 1.15 | 93 | 0.79 | 97 |
| 0.67 | 0.93 | 103 | 0.63 | 89 |
| 2 | 1.64 | 128 | 0.75 | 67 |
| MMS 150 µM | 16.77 ** | 38 | 7.53 ** | 47 |
| Silver-kaolin formulation (mg/mL) 24 h treatment | MN/1000 Nuclei | RS % | MN/1000 Nuclei | RS % |
| 0 | 1.71 | 100 | 3.40 | 100 |
| 0.02 | 3.65 * | 85 | 4.60 | 177 |
| 0.05 | 4.07 * | 93 | 3.21 | 109 |
| 0.17 | 3.21* | 90 | 7.35 ** | 133 |
| 0.5 | 1.30 | 85 | 7.21 ** | 65 |
| Colchicine 10 ng/mL | 55.25 ** | 38 | 78.40 ** | 74 |
| Silver-kaolin release ♦ (mg/mL) 24 h treatment | MN/1000 Nuclei | RS % | MN/1000 Nuclei | RS % |
| 0 | 3.74 | 100 | 1.73 | 100 |
| 0.02 | 3.34 | 102 | 4.36 ** | 89 |
| 0.05 | 5.52 ** | 93 | 1.27 | 75 |
| 0.17 | 3.44 | 81 | 1.32 | 77 |
| 0.5 | 2.64 | 93 | 2.25 | 73 |
| Colchicine 10 ng/mL | 42.28 ** | 59 | 95.90 ** | 23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Garraus, A.; Azqueta, A.; Laborda, F.; Gimenez-Ingalaturre, A.C.; Ezquerra, A.; Lostao, L.; Lopez de Cerain, A. In Vitro Genotoxicity Evaluation of an Antiseptic Formulation Containing Kaolin and Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060914
Rodriguez-Garraus A, Azqueta A, Laborda F, Gimenez-Ingalaturre AC, Ezquerra A, Lostao L, Lopez de Cerain A. In Vitro Genotoxicity Evaluation of an Antiseptic Formulation Containing Kaolin and Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(6):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060914
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Garraus, Adriana, Amaya Azqueta, Francisco Laborda, Ana C. Gimenez-Ingalaturre, Alba Ezquerra, Luis Lostao, and Adela Lopez de Cerain. 2022. "In Vitro Genotoxicity Evaluation of an Antiseptic Formulation Containing Kaolin and Silver Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 6: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060914
APA StyleRodriguez-Garraus, A., Azqueta, A., Laborda, F., Gimenez-Ingalaturre, A. C., Ezquerra, A., Lostao, L., & Lopez de Cerain, A. (2022). In Vitro Genotoxicity Evaluation of an Antiseptic Formulation Containing Kaolin and Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 12(6), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060914







