High Performance and Self-Humidifying of Novel Cross-Linked and Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Sulfonated Polysulfone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
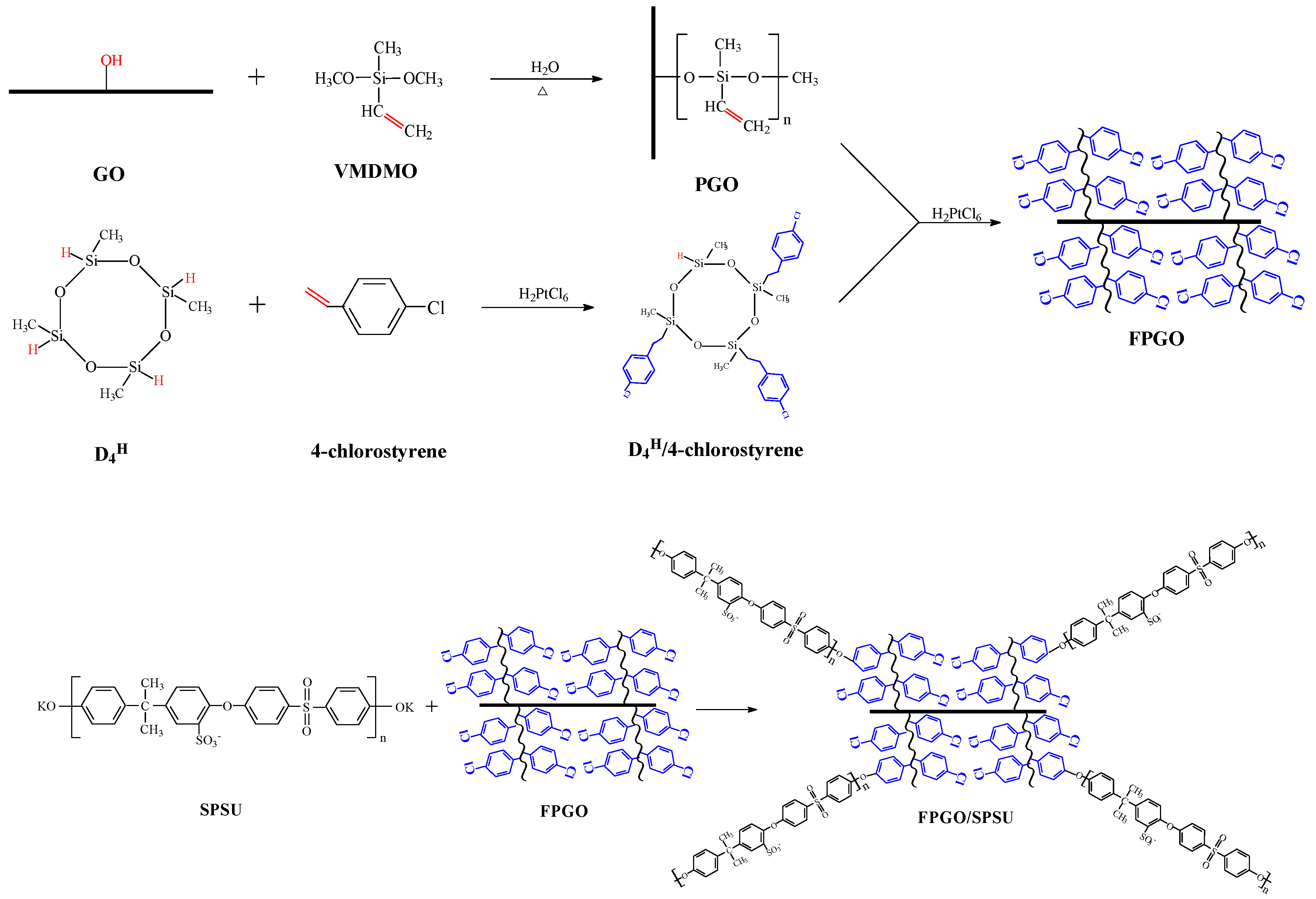
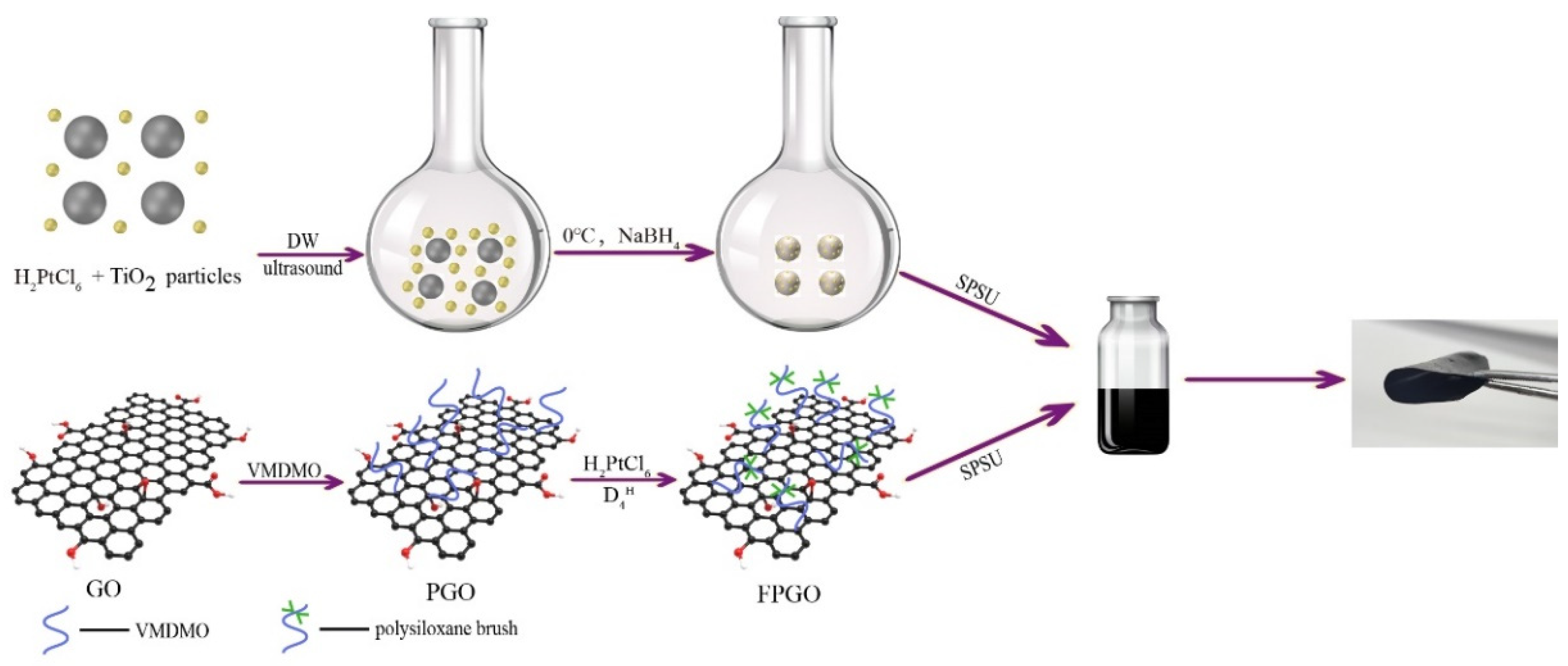
2.2. Preparation of GO Polymeric Brushes
2.3. Preparation of Pt-TiO2 Nanoparticles
2.4. Preparation of the Cross-Linked PEM and Nanocomposite PEMs
2.5. Characterization
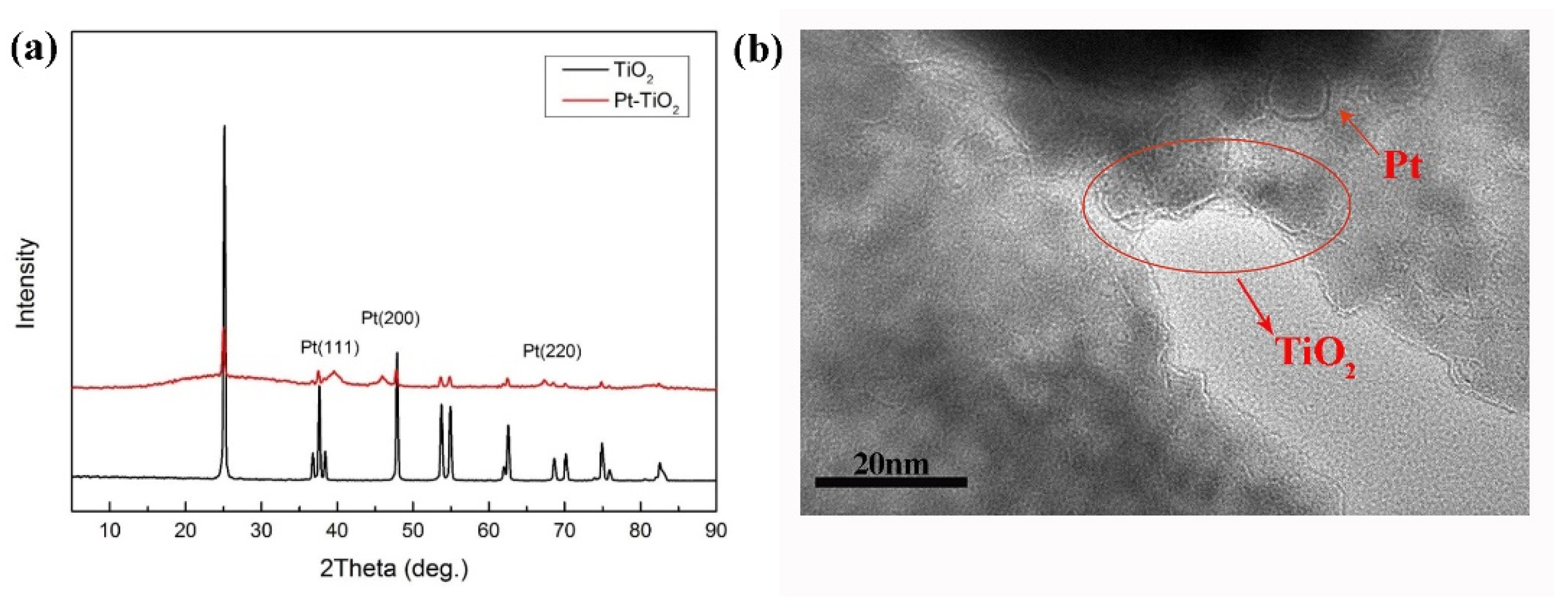
2.5.1. Characterization of Pt-TiO2 Nanoparticles
2.5.2. The Morphology of the Nanocomposite PEM
2.5.3. Measurement of Water Uptake (WU) and Swelling Ratio (SR)
2.5.4. Measurement of Ion Exchange Capacity (IEC)
2.5.5. Measurement of Thermal Stability
2.5.6. Measurement of Mechanical Properties
2.5.7. Measurement of Oxidation Stability
2.5.8. Measurement of Proton Conductivity
2.5.9. Measurement of Methanol Permeability and Selectivity
3. Results
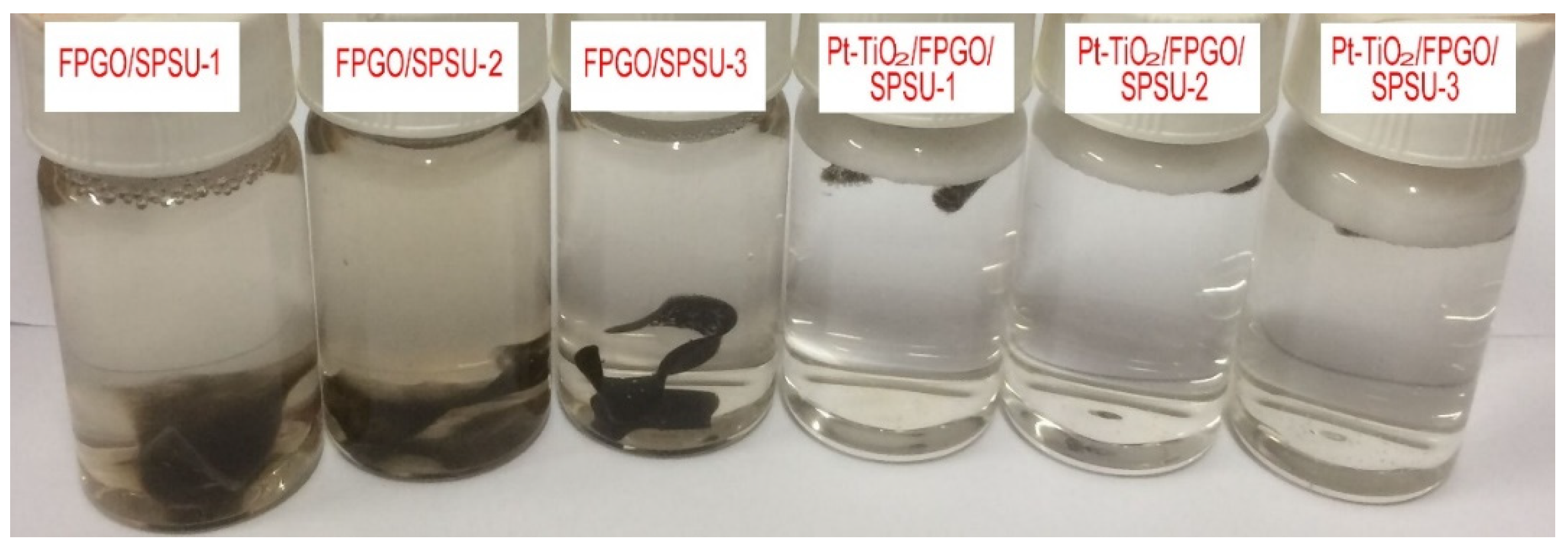
3.1. Preparation Process of the Cross-Linked PEM and the Nanocomposite PEMs
3.2. Characterization of Pt-TiO2 Nanoparticles
3.3. Characterization of the Cross-Linked PEM and the Nanocomposite PEMs
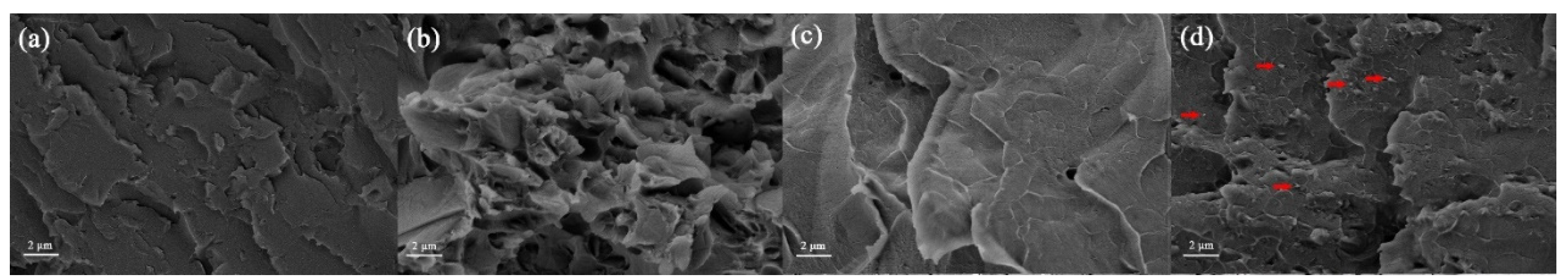
3.3.1. Surface Morphology
3.3.2. Mechanical Properties
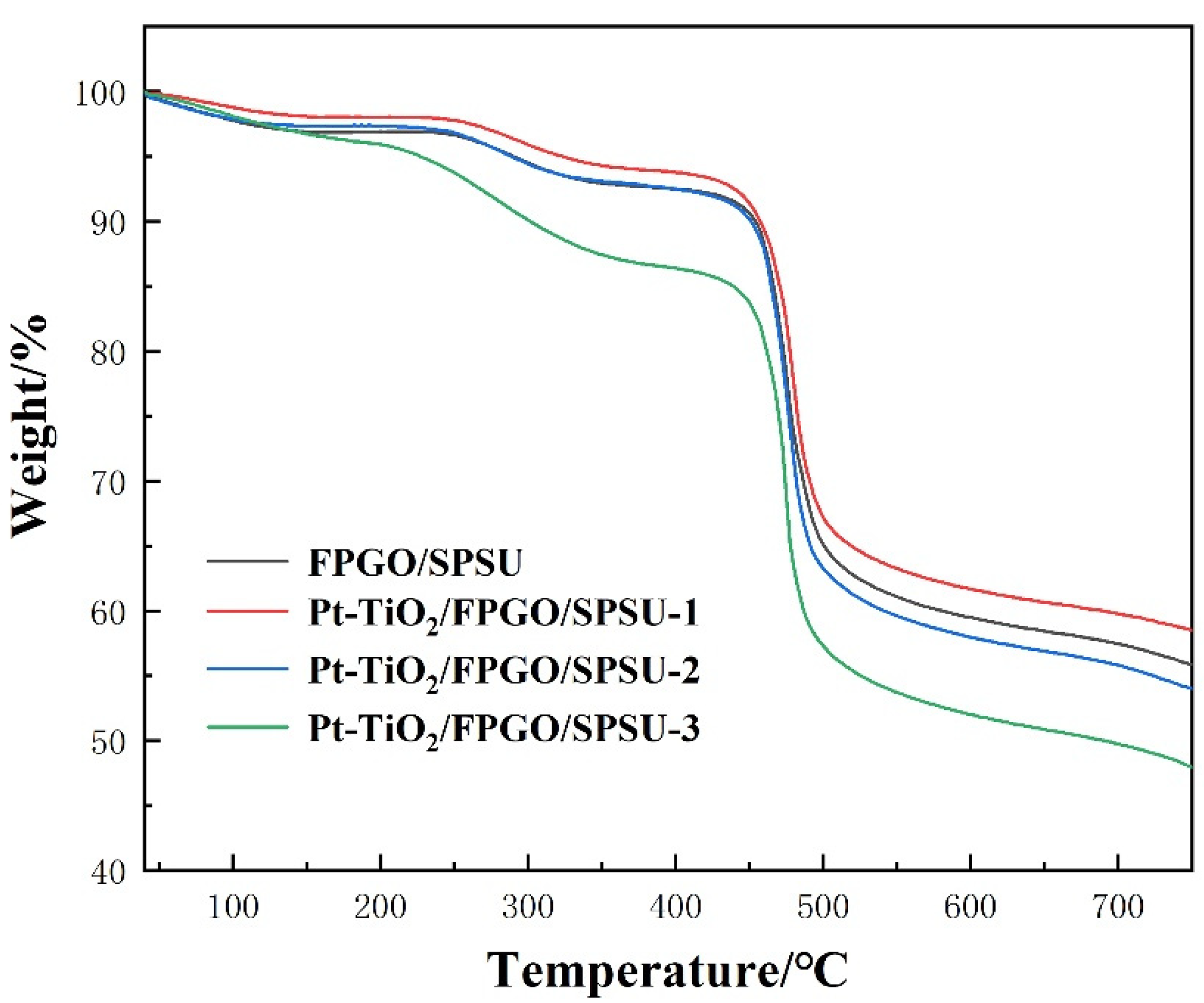
3.3.3. Thermal Stability
3.3.4. Oxidation Stability
3.4. The Performance of the Cross-Linked PEM and the Nanocomposite PEMs
3.4.1. Water Uptake, Swelling Ratio and Ion Exchange Capacity
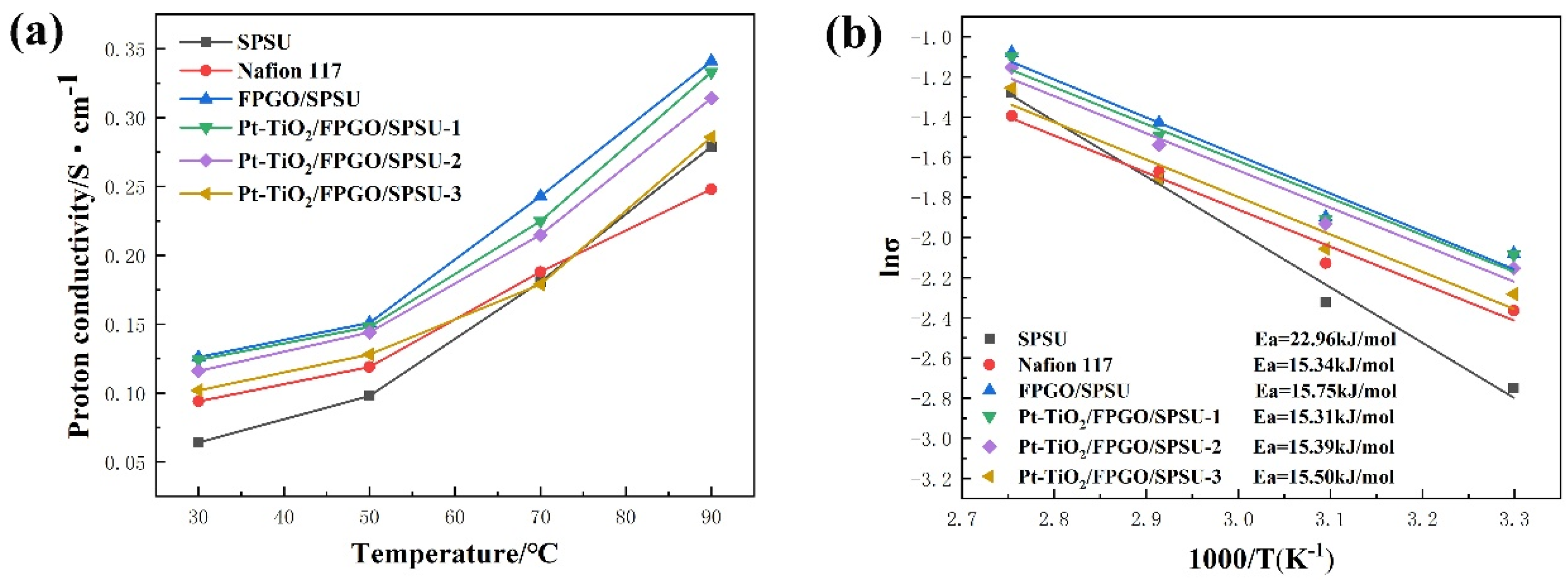
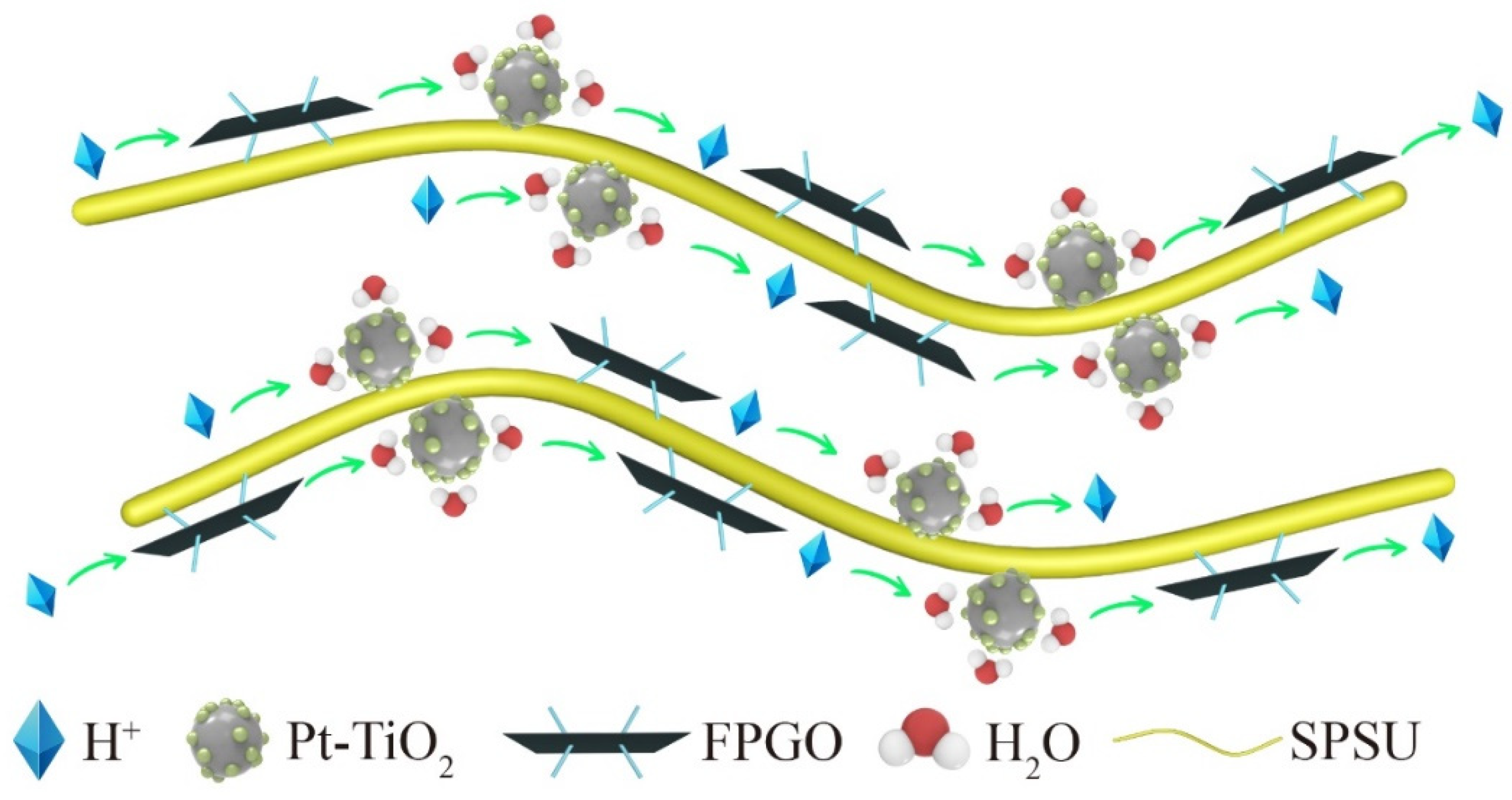
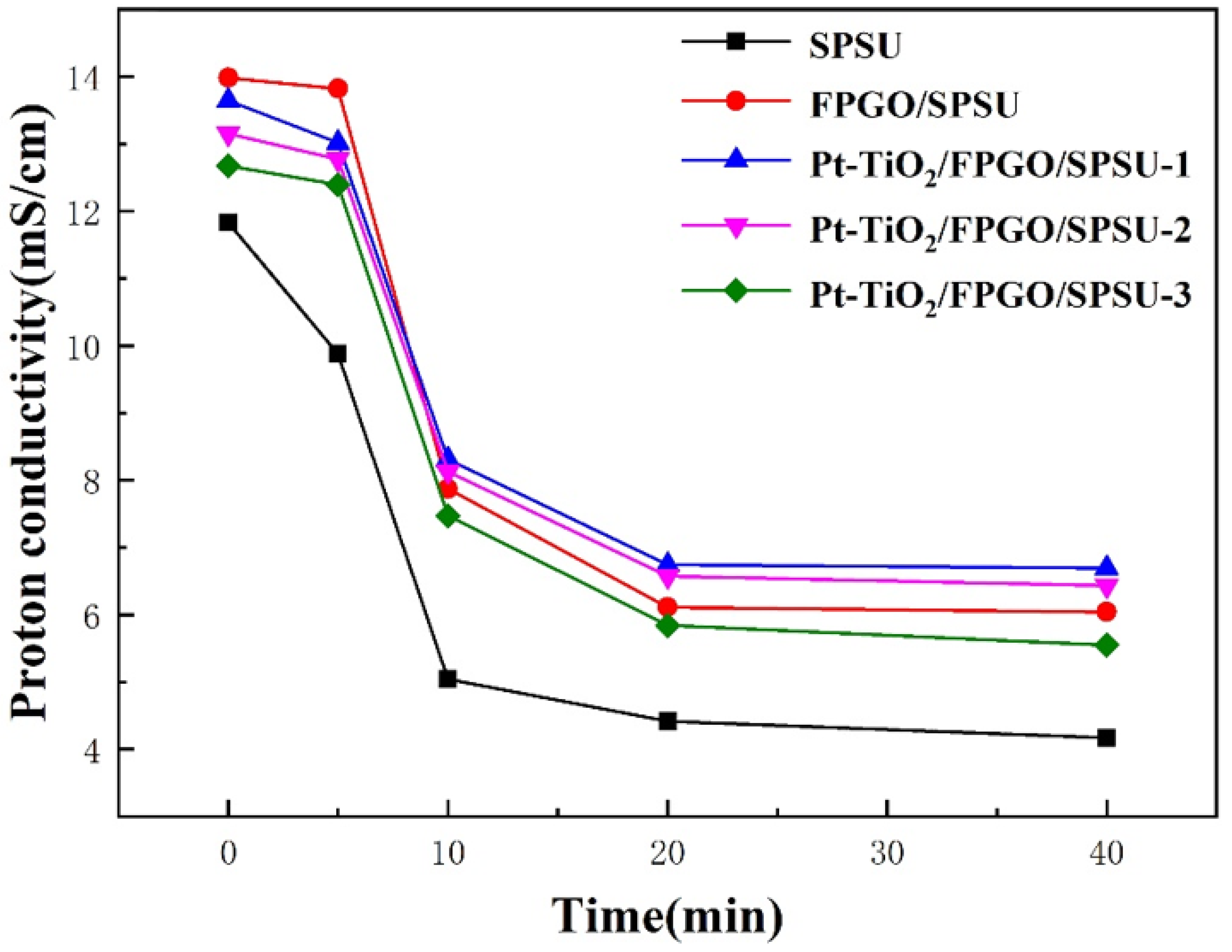
3.4.2. Proton Conductivity
3.4.3. Methanol Permeability and Selectivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinothkannan, M.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, H.K.; Yoo, D.J. Ceria stabilized by titanium carbide as a sustainable filler in the nafion matrix improves the mechanical integrity, electrochemical durability, and hydrogen impermeability of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells: Effects of the filler content. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 5704–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, R.; Wen, Y.; Ma, Z.F.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J. High temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Progress in advanced materials and key technologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1138–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lan, F.; Chen, J.; Zeng, C.; Wang, J. A review of proton exchange membrane fuel cell water management: Membrane electrode assembly. J. Power Source 2022, 517, 230723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, H.A.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. A review of proton exchange membranes based on protic ionic liquid/polymer blends for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Source 2021, 484, 229197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Li, H. Polyoxometalate-polymer hybrid materials as proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourzare, K.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, S.; Sadrabadi, M.H.; Ulbricht, M. Improvement of proton conductivity of magnetically aligned phosphotungstic acid-decorated cobalt oxide embedded Nafion membrane. Energy 2022, 239, 121940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourzare, K.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, S.; Sadrabadi, M.M.H.; Frost, I.; Ulbricht, M. Improving the efficiency of Nafion-based proton exchange membranes embedded with magnetically aligned silica-coated Co3O4 nanoparticles. Solid State Ion. 2020, 351, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wan, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhou, X.; Huang, F. Synthesis and performance study of a novel sulfonated polytriazole proton exchange membrane. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanikia, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Amoli, H.S.; Hooshyari, K.; Enhessari, M. Polybenzimidazole/strontium cerate nanocomposites with enhanced proton conductivity for proton exchange membrane fuel cells operating at high temperature. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 154, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomein, P.; Ketelaars, W.; Lap, T.; Liu, G. Sulfonated aromatic polymer as a future proton exchange membrane: A review of sulfonation and crosslinking methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, N.; Gray, E.M.; Webb, C.J. Non-fluorinated polymer composite proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications—A review. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2019, 20, 2016–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, L.; Yue, B. Improving the overall characteristics of proton exchange membranes via nanophase separation technologies: A progress review. Fuel Cells 2017, 17, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, G.G.; Ibrahim, A.; Borello, D.; El-Kharouf, A. Composite polymers development and application for polymer electrolyte membrane technologies—A review. Molecules 2020, 25, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Vona, M.L.; Knauth, P. Sulfonated aromatic polymers as proton-conducting solid electrolytes for fuel cells: A short review. Z. Phys. Chem. 2013, 227, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbanescu, O.S.; Voicu, S.I.; Thakur, V.K. Polysulfone functionalized membranes: Properties and challenges. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.P.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Masdar, M.S. Silica-related membranes in fuel cell applications: An overview. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 16068–16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, N.A.M.; Nakao, H.; Jaafar, J.; Kim, J.D. Crosslinked carbon nanodots with highly sulfonated polyphenylsulfone as proton exchange membrane for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 9979–9988. [Google Scholar]
- Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Brunetti, A.; Barbieri, G.; Nicotera, I. Highly-performing and low-cost nanostructured membranes based on Polysulfone and layered doubled hydroxide for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Source 2020, 471, 228440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chae, S.R.; Hendren, Z.; Park, J.S.; Wiesner, M.R. Recent advances in proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, H.J.; Ren, Q.; Luo, H.B.; Ren, X.M.; Tian, Z.F.; Lu, S. Extra water-and acid-stable MOF-801 with high proton conductivity and its composite membrane for proton-exchange membrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28656–28663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prykhodko, Y.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Hespel, L.; Marais, S. Progress in hybrid composite Nafion®-based membranes for proton exchange fuel cell application. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Jo, M.J.; Nam, S.Y. A review of polymer–nanocomposite electrolyte membranes for fuel cell application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Narducci, R.; Compañ, V.; Costantino, F. Proton conductivity of composite polyelectrolyte membranes with metal-organic frameworks for fuel cell applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.R.; Won, J.H.; Yoon, K.S.; Hong, Y.T.; Lee, S.Y. Multilayer-structured, SiO2/sulfonated poly (phenylsulfone) composite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 6182–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, M.T.; Vatanparast, M. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of ZrO2 nanoparticles and their application to improve the chemical stability of Nafion membrane in proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 483, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Park, J.; Jeon, Y.; Park, J.I.; Einaga, H.; Truong, Y.B.; Shul, Y.G. Phosphate-modified TiO2/ZrO2 nanofibrous web composite membrane for enhanced performance and durability of high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 7645–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonggo, S.T. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonate polystyrene-lignosulfonate-alumina (SPS-LS-Al2O3) polyblends as electrolyte membranes for fuel cell. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1677, p. 120009. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, D.; He, G.; Hou, Z.; Ming, P.; Song, S. Preparation and characterization of a modified montmorillonite/sulfonated polyphenylether sulfone/PTFE composite membrane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Su, H.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Arpornwichanop, A. Effect of catalyst layer with zeolite on the performance of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell operated under low-humidity conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 15878–15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, C.M.; Sharma, S.; de Camargo Forte, M.M.; Steinberger-Wilckens, R. New approaches towards novel composite and multilayer membranes for intermediate temperature-polymer electrolyte fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Source 2016, 316, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, P. Metal organic frameworks modified proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X. Constructing continuous proton-conducting highways within sulfonated poly (arylene ether nitrile) composite membrane by incorporating amino-sulfo-bifunctionalized GO. Polymers 2018, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.K. Surface and interface engineering for organic–inorganic composite membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9716–9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.Y.; Wong, W.Y.; Loh, K.S.; Daud, W.R.W.; Lim, K.L.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R. Development of poly (vinyl alcohol)-based polymers as proton exchange membranes and challenges in fuel cell application: A review. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 171–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Choi, D.H.; Park, C.H.; Nam, S.Y. Characterization of the sulfonated PEEK/sulfonated nanoparticles composite membrane for the fuel cell application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 5793–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Sun, G.; Jin, W.; Hou, H.; Wang, S.; Xin, Q. Nafion® and nano-size TiO2–SO42− solid superacid composite membrane for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussi, J.M.; Cortez, M.L.; Marmisollé, W.A.; Azzaroni, O. Practical use of polymer brushes in sustainable energy applications: Interfacial nanoarchitectonics for high-efficiency devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 814–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anahidzade, N.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Dinari, M.; Tadavani, K.F.; Zhiani, M. Metal-organic framework anchored sulfonated poly (ether sulfone) as a high temperature proton exchange membrane for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, T.; Wu, L.; Wu, Y. Hybrid acid-base polymer membranes prepared for application in fuel cells. J. Power Source 2009, 186, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Song, M.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Yoo, D.J. Amine functionalized carbon nanotube (ACNT) filled in sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membrane: Effects of ACNT in improving polymer electrolyte fuel cell performance under reduced relative humidity. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 188, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Ding, H. Multi-functionalized acid-base double-shell nanotubes are incorporated into the proton exchange membrane to cope with low humidity conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 30673–30688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, L.; Choe, E.W.; Benicewicz, B.C. Synthesis of Poly (2, 2′-(1, 4-phenylene) 5, 5′-bibenzimidazole)(para-PBI) and Phosphoric Acid Doped Membrane for Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.J.; Li, Z.L.; Lyu, H.L.; Zheng, J.J.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, F.N.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Rao, H.X. A graphene oxide polymer brush based cross-linked nanocomposite proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cells s. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15740–15753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubir, N.A.; Zhang, X.; Yacou, C.; Diniz da Costa, J.C. Fenton-like degradation of acid orange 7 using graphene oxide-iron oxide nanocomposite. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2014, 6, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Yip, H.L.; Chen, K.S.; O’Malley, K.M.; Acton, O.; Sun, Y.; Jen, A.K.Y. Surface doping of conjugated polymers by graphene oxide and its application for organic electronic devices. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; Ye, Y.S.; Yen, Y.C.; Tsai, L.D.; Hwang, B.J.; Chang, F.C. Synthesis and characterization of new sulfonated polytriazole proton exchange membrane by click reaction for direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 15333–15343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wilkie, C.A.; Moore, R.B.; Mauritz, K.A. TGA–FTi. r. investigation of the thermal degradation of Nafion® and Nafion®/[silicon oxide]-based nanocomposites. Polymer 1998, 39, 5961–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mossayebi, Z.; Saririchi, T.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Parnian, M.J. Investigation and optimization of physicochemical properties of sulfated zirconia/sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) nanocomposite membranes for medium temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 12293–12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dang, J.; Wu, W.; Lin, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Nanofiber composite membrane using quantum dot hybridized SPEEK nanofiber for efficient through-plane proton conduction. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 609, 118198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xing, W.; Sun, J. Self-Healing proton-exchange membranes composed of Nafion–poly (vinyl alcohol) complexes for durable direct methanol fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, J. Proton exchange membranes with cross-linked interpenetrating network of sulfonated polyvinyl alcohol and poly (2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid): Excellent relative selectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hoorfar, M.; Shen, K.; Fang, J.; Yue, X.; Jiang, Z. Development of a crosslinked pore-filling membrane with an extremely low swelling ratio and methanol crossover for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PEM Samples | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion 117 | 100.00 a | 28.40 a | 329 a |
| SPSU | 342.30 | 30.15 | 7.29 |
| FPGO/SPSU | 267.50 | 32.60 | 12.37 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-1 | 304.50 | 29.14 | 15.44 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-2 | 671.10 | 30.90 | 13.81 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-3 | 258.05 | 25.44 | 12.82 |
| PEM Samples | Oxidative Stability a (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| τ1 b | τ2 c | Δ = τ2 − τ1 | |
| Nafion 117 | 180 d | >960 d | >780 d |
| SPSU | 75 | 120 | 45 |
| FPGO/SPSU | 90 | 310 | 220 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-1 | 255 | 735 | 480 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-2 | 270 | 630 | 360 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-3 | 240 | 545 | 305 |
| Membrane Samples | WU (%) | IEC (mmol/g) | SR (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 50 °C | 70 °C | 90 °C | |||
| Nafion 117 | 35.60 a | 0.91 a | 13.02 b | 15.88 b | 17.52 b | 20.16 b |
| SPSU | 38.12 | 1.52 | 6.02 | 13.73 | 20.42 | 169.72 |
| FPGO/SPSU | 45.89 | 1.83 | 8.85 | 12.62 | 14.93 | 154.39 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-1 | 46.58 | 1.91 | 9.16 | 13.37 | 15.87 | 172.52 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-2 | 47.85 | 2.23 | 9.21 | 14.25 | 16.74 | 187.36 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-3 | 47.81 | 1.97 | 9.47 | 14.76 | 15.31 | 166.27 |
| Membrane Samples | Methanol Permeability (10−6 cm2 s−1) | Selectivity (104 S s cm−3) |
|---|---|---|
| Nafion 117 | 2.9400 a | 4.2619 |
| SPSU | 2.3407 | 4.7934 |
| FPGO/SPSU | 1.7117 | 7.2267 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-1 | 1.4157 | 8.5117 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-2 | 1.6186 | 7.1667 |
| Pt-TiO2/FPGO/SPSU-3 | 1.6853 | 6.0879 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Guo, X.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Tu, M.; Rao, H. High Performance and Self-Humidifying of Novel Cross-Linked and Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Sulfonated Polysulfone. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050841
Li X, Zhang Z, Xie Z, Guo X, Yang T, Li Z, Tu M, Rao H. High Performance and Self-Humidifying of Novel Cross-Linked and Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Sulfonated Polysulfone. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(5):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050841
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinyu, Zhongxin Zhang, Zheng Xie, Xinrui Guo, Tianjian Yang, Zhongli Li, Mei Tu, and Huaxin Rao. 2022. "High Performance and Self-Humidifying of Novel Cross-Linked and Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Sulfonated Polysulfone" Nanomaterials 12, no. 5: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050841
APA StyleLi, X., Zhang, Z., Xie, Z., Guo, X., Yang, T., Li, Z., Tu, M., & Rao, H. (2022). High Performance and Self-Humidifying of Novel Cross-Linked and Nanocomposite Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Sulfonated Polysulfone. Nanomaterials, 12(5), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12050841






