Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Burley Tobacco Stems towards Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal: Performance and Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
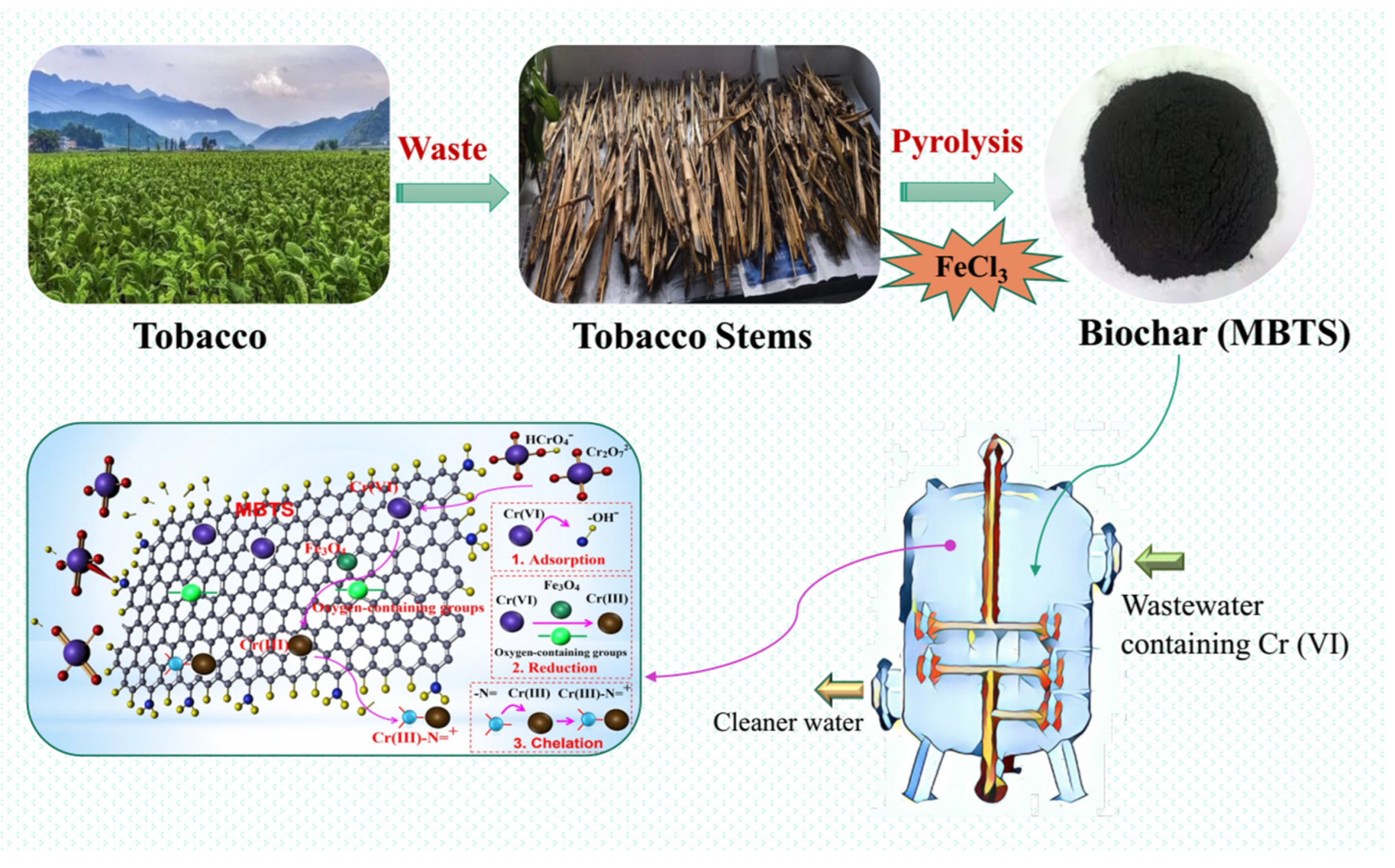
2.1. Synthesis of MBTS Magnetic Biochar
2.2. Batch Adsorptions
2.3. Characterization of MBTS
2.4. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Synthesized Biochar
3.2. Adsorption Isotherm and Kinetics
3.3. Effect of pH on the Adsorption of Cr(VI) on MBTS
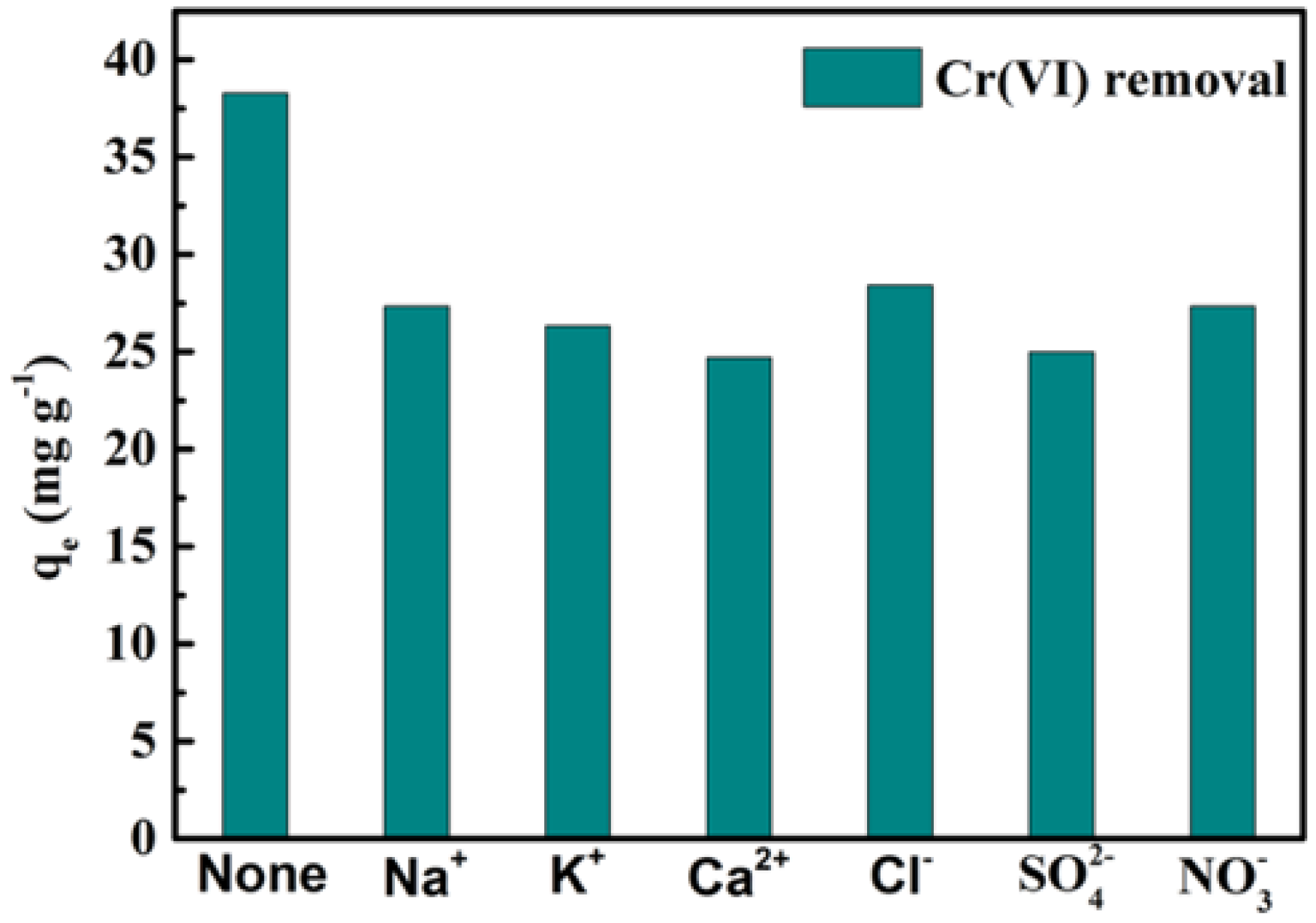
3.4. Effect of Coexisting Ions
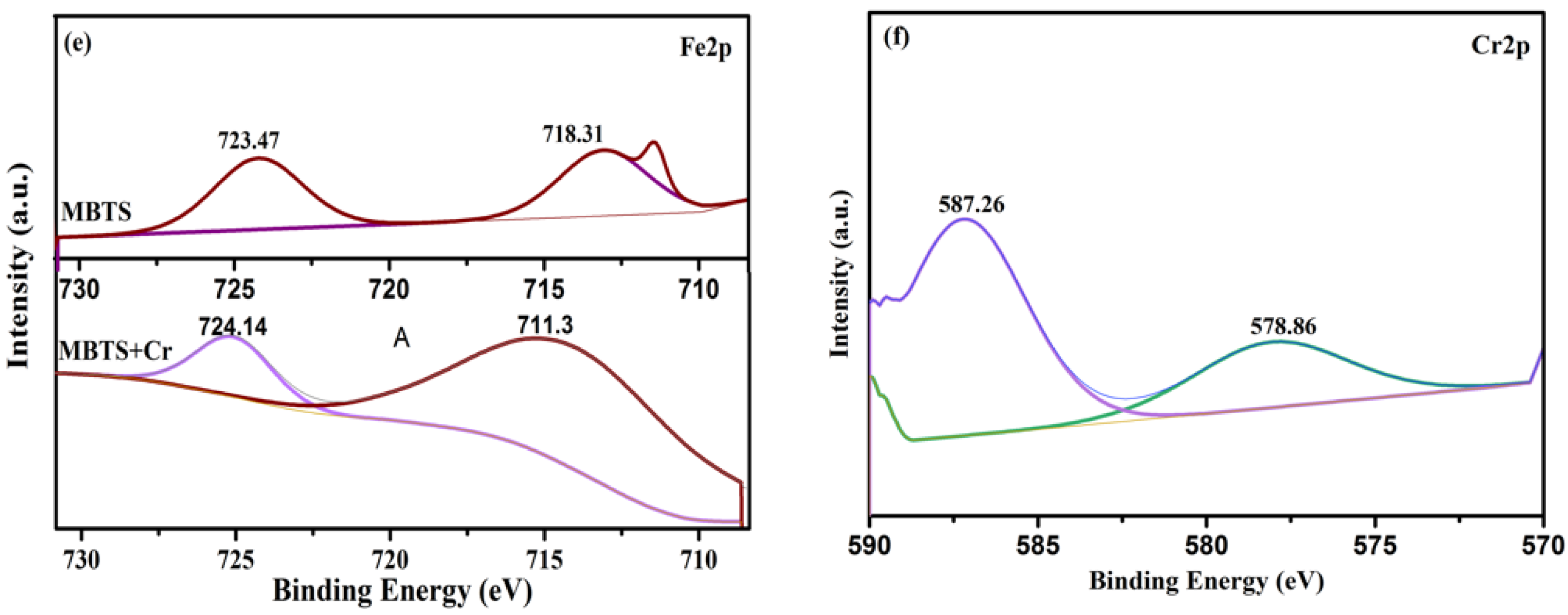
3.5. Adsorption Mechanism
3.6. Engineering Implication
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miretzky, P.; Cirelli, A.F. Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Miao, C.; Ruan, X. Occurrence and environmental impact of industrial agglomeration on regional soil heavy metalloid accumulation: A case study of the Zhengzhou Economic and Technological Development Zone (ZETZ), China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhu, X.; Satpathy, A.; Li, W.; Fortner, J.D.; Giammar, D.E. Cr(VI) Adsorption on Engineered Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Exploring Complexation Processes and Water Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11913–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Li, Y.; Cui, B.; Hu, M.; Luo, S.; Ji, B.; Liu, Y. Natural adsorption of methylene blue by waste fallen leaves of Magnoliaceae and its repeated thermal regeneration for reuse. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shan, R.; Lu, L.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. High-efficiency removal of Cr(VI) by modified biochar derived from glue residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Ji, B.; Cui, B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Luo, S.; Guo, D. Almond Shell-Derived, Biochar-Supported, Nano-Zero-Valent Iron Composite for Aqueous Hexavalent Chromium Removal: Performance and Mechanisms. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, B.; Chen, Z.; Guo, D.; Liu, Y. Investigations on the pyrolysis of microalgal-bacterial granular sludge: Products, kinetics, and potential mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 349, 126328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, G.; Gao, Y.; Fu, W.; Irfan, M.; Mu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A. High-yield and high-performance porous biochar produced from pyrolysis of peanut shell with low-dose ammonium polyphosphate for chloramphenicol adsorption. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; An, Q.; Jin, L.; Luo, N.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J. Unraveling sorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by FeCl3 and ZnCl2-modified corn stalks biochar: Implicit mechanism and application. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.; Shao, Y.; Huang, W.; Cheng, X. Different adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of a novel amino-functionalized hydrothermal biochar for hexavalent chromium and pentavalent antimony. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasozi, G.N.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Gao, B. Catechol and Humic Acid Sorption onto a Range of Laboratory-Produced Black Carbons (Biochars). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6189–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Huang, L. Removal and reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) in simulated wastewater using magnetic biochar prepared by co-pyrolysis of nano-zero-valent iron and sewage sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ma, L.Q.; Li, Y. Characteristics and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium removal by biochar from sugar beet tailing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xing, B.; Ding, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, S. A critical review of the production and advanced utilization of biochar via selective pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.G.; Gloy, B.A.; Joseph, S.; Scott, N.R.; Lehmann, J. Life cycle assessment of biochar systems- estimating the energetic, economic, and climate change potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azazy, M.; Nabil, I.; Hassan, S.S.; El-Shafie, A.S. Adsorption Characteristics of Pristine and Magnetic Olive Stones Biochar with Respect to Clofazimine. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Rong, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Guo, D.; Laghari, M.; Ruan, R. Gas-carrying enhances the combustion temperature of the biomass particles. Energy 2022, 239, 121956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, S. Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from tobacco stem by chemical activation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Niazi, N.K.; Man, Y.B.; Christie, P.; Shan, S.; Wong, M.H. Effect of tobacco stem-derived biochar on soil metal immobilization and the cultivation of tobacco plant. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumba, P.; Phiri, R. Environmental impact assessment of tobacco waste disposal. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2008, 2, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Trubetskaya, A.; Kling, J.; Ershag, O.; Attard, T.M.; Schroder, E. Removal of phenol and chlorine from wastewater using steam activated biomass soot and tire carbon black. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, U.K.; Kumar, B. Pathways of heavy metals contamination and associated human health risk in Ajay River basin, India. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, D.; Deng, S.; Zhao, T.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Winglee, J.; Wiesner, M.R. Preparation of ultrafine magnetic biochar and activated carbon for pharmaceutical adsorption and subsequent degradation by ball milling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 305, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Gu, H.; Rapole, S.B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Haldolaarachchige, N.; Young, D.P.; Guo, Z. One-pot synthesis of magnetic graphene nanocomposites decorated with core@double-shell nanoparticles for fast chromium removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Senan, P. Adsorptive Characteristics of Chromium(VI) Ions from Aqueous Phase by Iron(III) Coordinated Amino-Functionalized Poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-Grafted Cellulose: Equilibrium Kinetics and Thermodynamic Study. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1430–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhan, J. Aerosol-Assisted Self-Assembly of Reticulated N-Doped Carbonaceous Submicron Spheres for Effective Removal of Hexavalent Chromium. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16699–16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, F.; DuChene, J.S.; Qiu, J.; Graham, J.O.; Engelhard, M.H.; Cao, G.; Gai, Z.; Wei, W.D. A Facile Solvothermal Synthesis of Octahedral Fe3 O4 Nanoparticles. Small 2015, 11, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Li, M.; Gan, Q.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal from acidic solutions using biochar modified by Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Typical IR Absorption Frequencies For Common Functional Groups. Available online: https://www.niu.edu/clas/chembio/research/analytical-lab/ftir/ir-frequencies-table.shtml (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- The Nature of Vibrational Spectroscopy. Available online: https://www2.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty/reusch/virttxtjml/spectrpy/infrared/irspec1.htm (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Sha, O.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction Using Fe3O4@SiO2 Magnetic Nanoparticles Followed by UV-Vis Spectrometry for Determination of Paraquat in Plasma and Urine Samples. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 8704639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Ultrafast removal of radioactive strontium ions from contaminated wastewater by nanostructured layered sodium vanadosilicate with high adsorption capacity and selectivity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yuan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Tan, M.; Li, H. Activated biochar with iron-loading and its application in removing Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, J.; He, F.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, F.; Bashir, M.A.; et al. Ball milling biochar iron oxide composites for the removal of chromium (Cr(VI)) from water: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Ma, B.; Chen, S. Carbothermal preparation of porous carbon-encapsulated iron composite for the removal of trace hexavalent chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Is the Free Energy Change of Adsorption Correctly Calculated? J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 84, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Xia, C.; Song, N.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Ge, S.; Wu, C.; Lam, S.S. Phenol removal via activated carbon from co-pyrolysis of waste coal tar pitch and vinasse. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhu, C.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D.; Ma, J. N-doped porous carbon with magnetic particles formed in situ for enhanced Cr(VI) removal. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, M.; Jia, X.; Chen, Z. Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a magnetic biochar derived from Melia azedarach wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ren, H.; Kruse, A.; Cui, R. Polyethylene imine modified hydrochar adsorption for chromium (VI) and nickel (II) removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollavelli, G.; Chang, C.-C.; Ling, Y.-C. Facile Synthesis of Smart Magnetic Graphene for Safe Drinking Water: Heavy Metal Removal and Disinfection Control. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ji, M.; Zhang, Z. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cr(VI) using Sakura waste from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xiao, D.; Ji, L.; Jin, D.; Dai, K.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H. Simple fabrication of Fe3O4:C:gC3N4 two-dimensional composite by hydrothermal carbonization approach with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 3484–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Scudiero, L.; Espinal, J.; McEwen, J.-S.; Garcia-Perez, M. Improving the deconvolution and interpretation of XPS spectra from chars by ab initio calculations. Carbon 2016, 110, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Magnetic Porous Carbonaceous Material Produced from Tea Waste for Efficient Removal of As(V), Cr(VI), Humic Acid, and Dyes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.Y.; Qu, J.; Yan, W.S.; Zhu, J.F.; Wu, Z.Y.; Song, W.G. Low-cost synthesis of flowerlike alpha-Fe2O3 nanostructures for heavy metal ion removal: Adsorption property and mechanism. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4573–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Song, T.; Tang, C.; Meng, Y.; Dai, S.; Wang, H.; Chai, L.; et al. Synthesis of Core-Shell Magnetic Fe3O4@poly(m-Phenylenediamine) Particles for Chromium Reduction and Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5654–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, P. Chemical processes of Cr(VI) removal by Fe-modified biochar under aerobic and anaerobic conditions and mechanism characterization under aerobic conditions using synchrotron-related techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, N.; Chen, N.; Lei, Z.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z. Efficient phosphate removal from wastewater by MgAl-LDHs modified hydrochar derived from tobacco stalk. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 8, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Sun, M.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Shi, L. Life-cycle assessment of tobacco stalk utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Lun, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Comparative study on synergistic effects in co-pyrolysis of tobacco stalk with polymer wastes: Thermal behavior, gas formation, and kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zu, J.; Feng, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Zhong, M.-E.; Zhou, Z.; Zhuang, S. Effect of pyrolysis condition on the adsorption mechanism of heavy metals on tobacco stem biochar in competitive mode. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26947–26962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahori, A.H.; Zhang, Z.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, R.; Mahar, A.; Wang, Z.; Ren, C.; Mi, S.; et al. Mono-and co-applications of Ca-bentonite with zeolite, Ca-hydroxide, and tobacco biochar affect phytoavailability and uptake of copper and lead in a gold mine-polluted soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 374, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
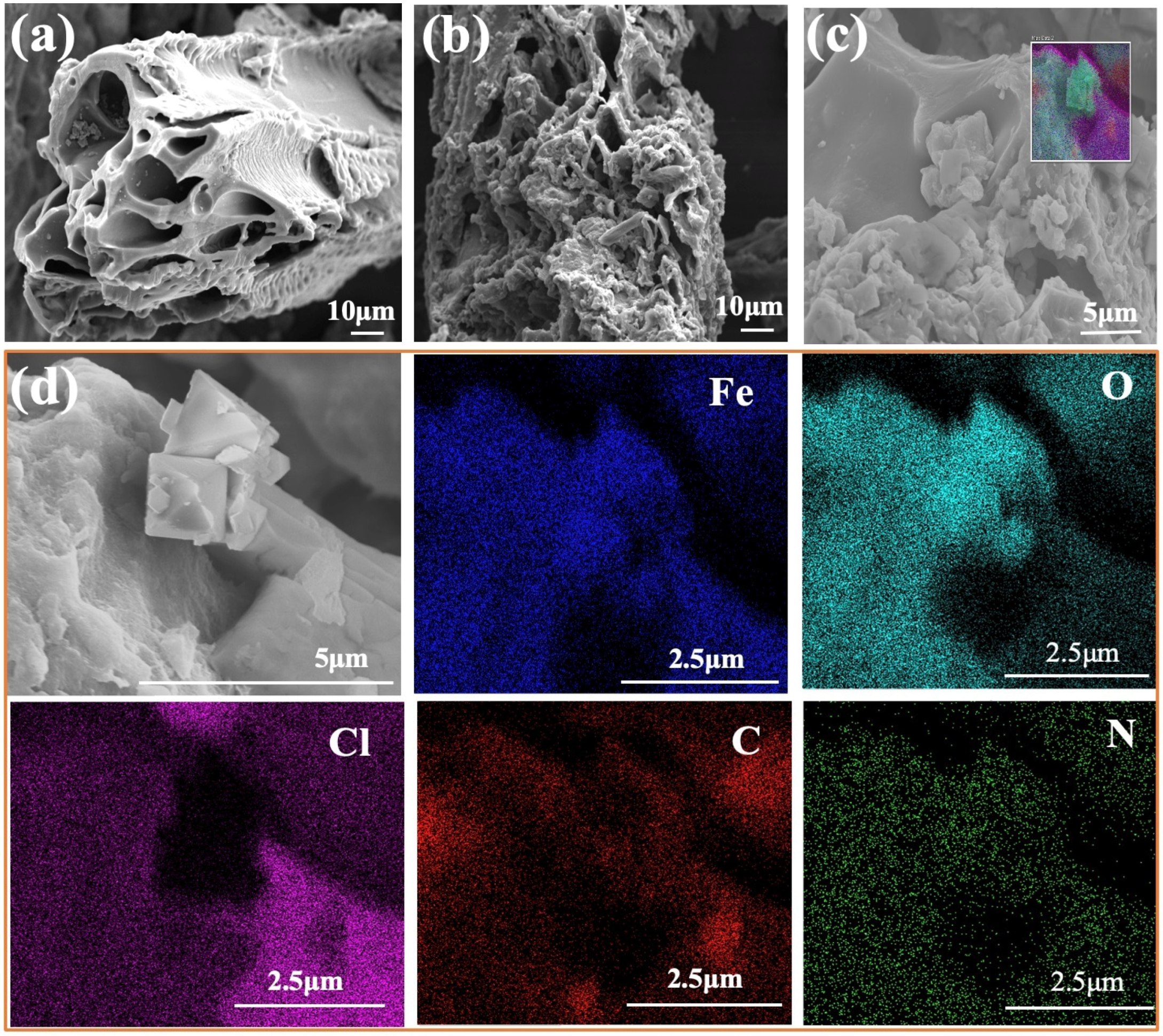
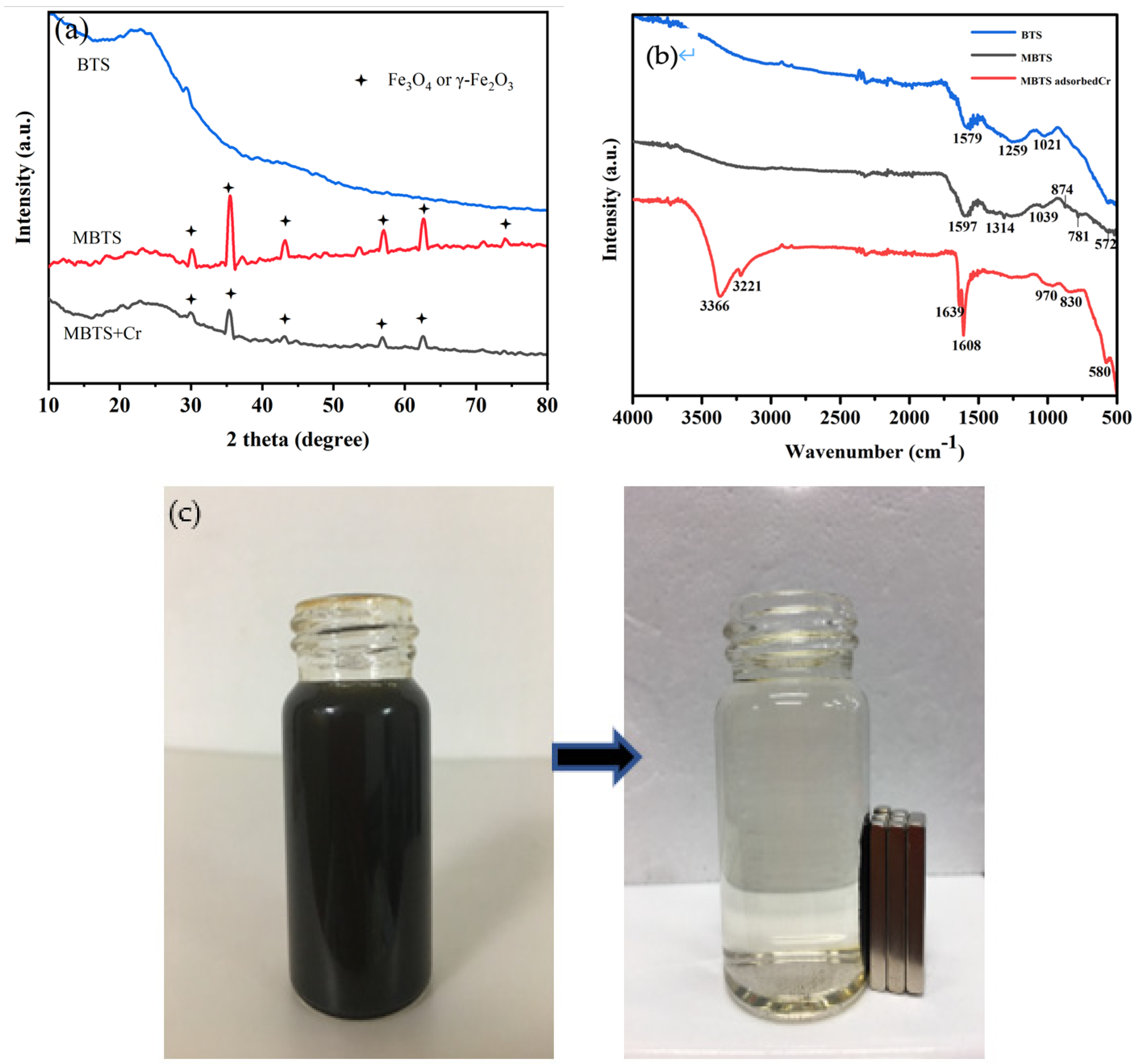
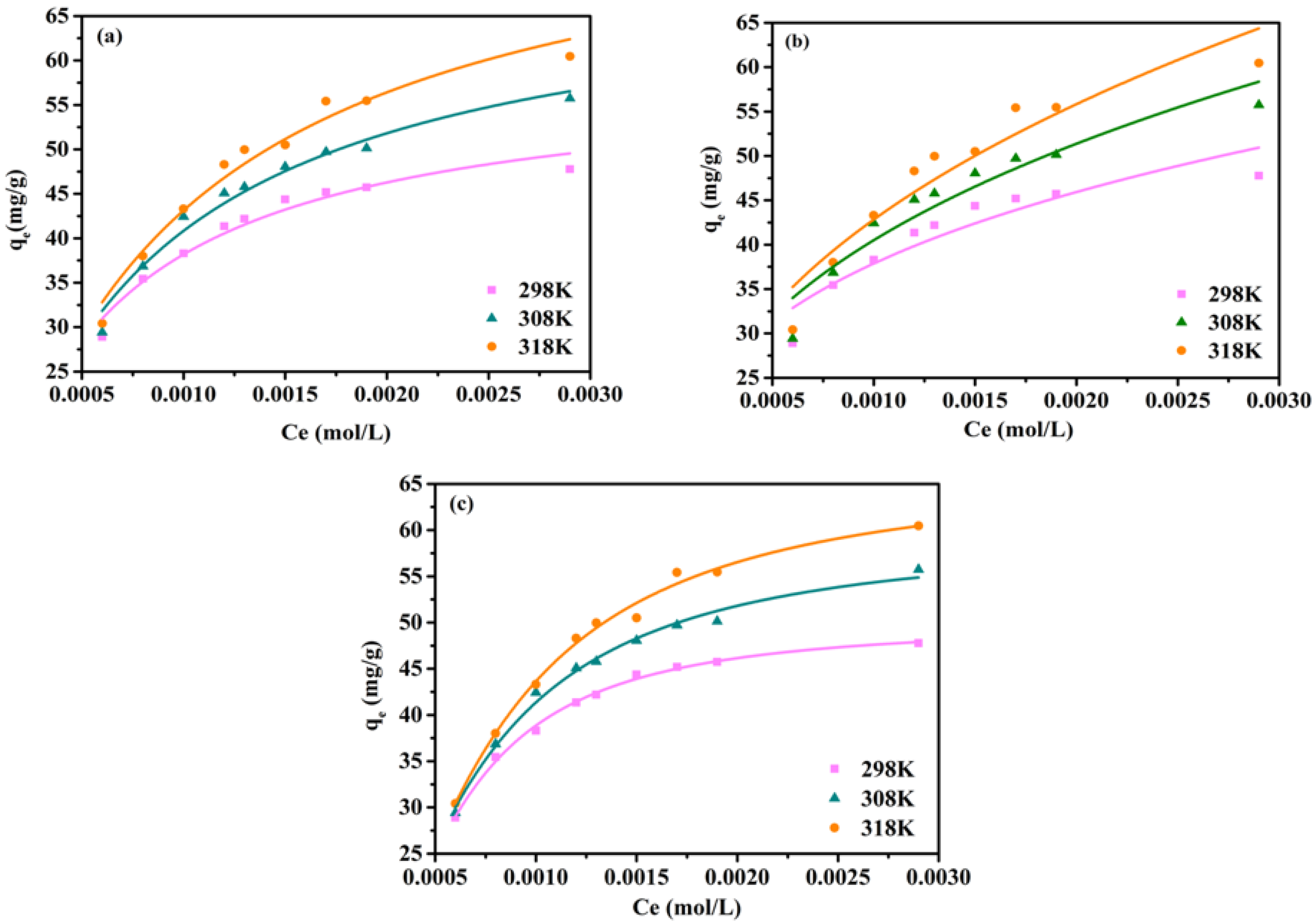

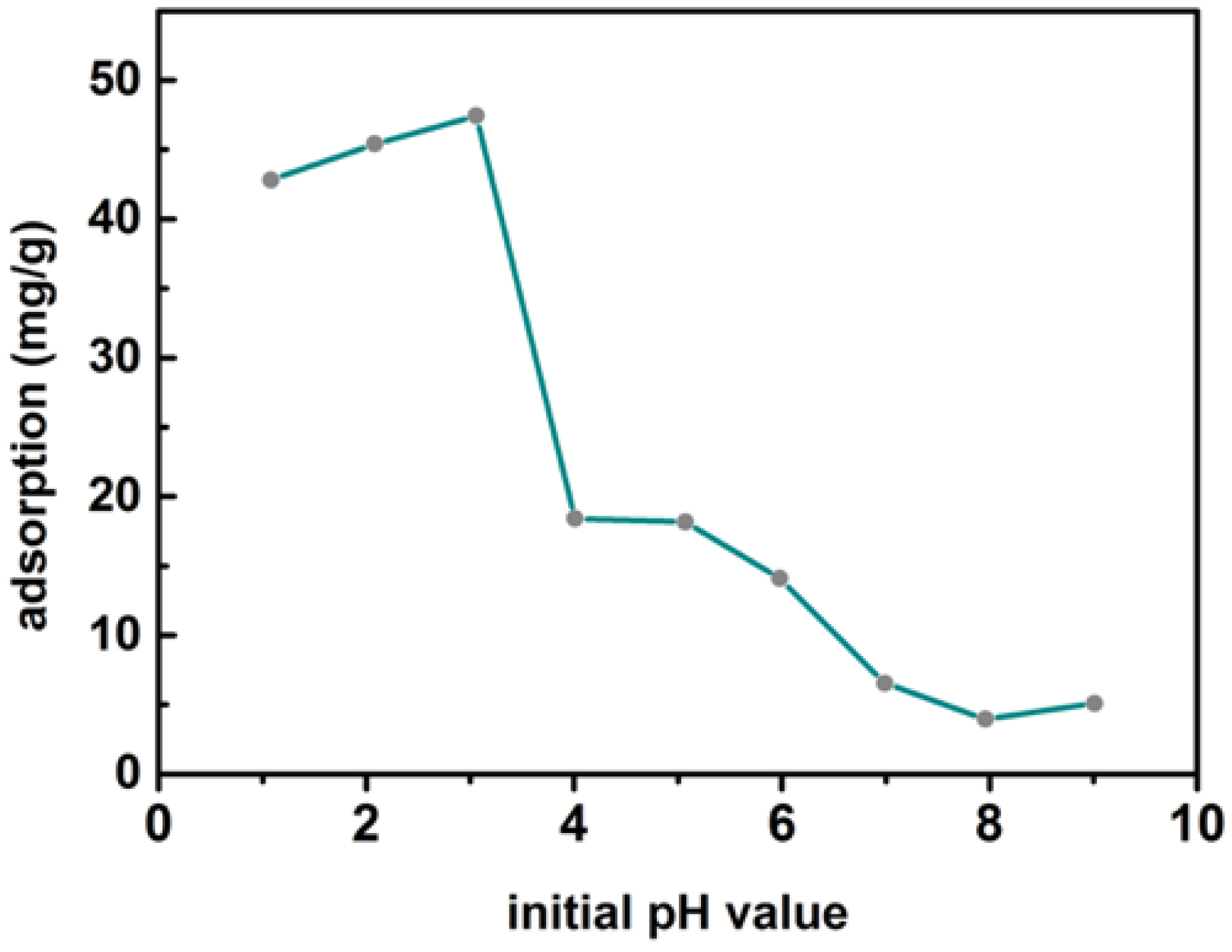

| Adsorbent | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Radius (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTS | 32.78 | 0.072 | 1.631 |
| MBTS before adsorption | 4.33 | 0.008 | 1.633 |
| MBTS after adsorption | 13.83 | 0.039 | 1.637 |
| T(K) | qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mol) | Kf ((mg/g)/ (mol/L)1/n) | Kg (L/mol) | R2 | 1/nF | nL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir model | 298 | 58.74 | 1856.77 | 0.959 | ||||
| 308 | 70.89 | 1358.20 | 0.973 | |||||
| 318 | 70.89 | 1121.19 | 0.970 | |||||
| Freundlich model | 298 | 258.66 | 0.860 | 0.28 | ||||
| 308 | 433.26 | 0.903 | 0.34 | |||||
| 318 | 602.06 | 0.900 | 0.38 | |||||
| Sips isotherm | 298 | 49.83 | 1998.19 | 0.996 | 1.83 | |||
| 308 | 59.24 | 1692.24 | 0.990 | 1.59 | ||||
| 318 | 65.97 | 1512.75 | 0.991 | 1.62 |
| Absorbent | Modified Method | qm (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTS | Biochar derived from tobacco stems | 3.84 | This study |
| MBTS | BTS modified with FeCl3 | 54.92 | This study |
| PBC-ND | Biochar derived from bamboo and poplar | 5.4 | [33] |
| Fe/PBC-ND | PBC-ND modified with Fe (NO3)3 | 25.68 | [33] |
| BM-Fe-HC | Biochar modified with FeCl3 | 48.1 | [34] |
| PC | Porous carbon | 2.50 | [35] |
| Fe@PC | PC modified with Fe (NO3)3 | 10.07 | [35] |
| Magnetic biochar | Biochar modified with FeCl3 | 27.2 | [28] |
| Adsorbent | ΔH0 (KJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol K) | ΔG0 (KJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | |||
| MBTS | 2.842 | 9.903 | −0.109 | −0.208 | −0.307 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Guo, D.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y. Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Burley Tobacco Stems towards Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal: Performance and Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040678
Cui B, Chen Z, Wang F, Zhang Z, Dai Y, Guo D, Liang W, Liu Y. Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Burley Tobacco Stems towards Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal: Performance and Mechanism. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(4):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040678
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Baihui, Zhihua Chen, Feihua Wang, Zihan Zhang, Yanran Dai, Dabin Guo, Wei Liang, and Yu Liu. 2022. "Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Burley Tobacco Stems towards Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal: Performance and Mechanism" Nanomaterials 12, no. 4: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040678
APA StyleCui, B., Chen, Z., Wang, F., Zhang, Z., Dai, Y., Guo, D., Liang, W., & Liu, Y. (2022). Facile Synthesis of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Burley Tobacco Stems towards Enhanced Cr(VI) Removal: Performance and Mechanism. Nanomaterials, 12(4), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12040678








