Eco-Friendly Sustainable Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Biowaste as a Highly Selective Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
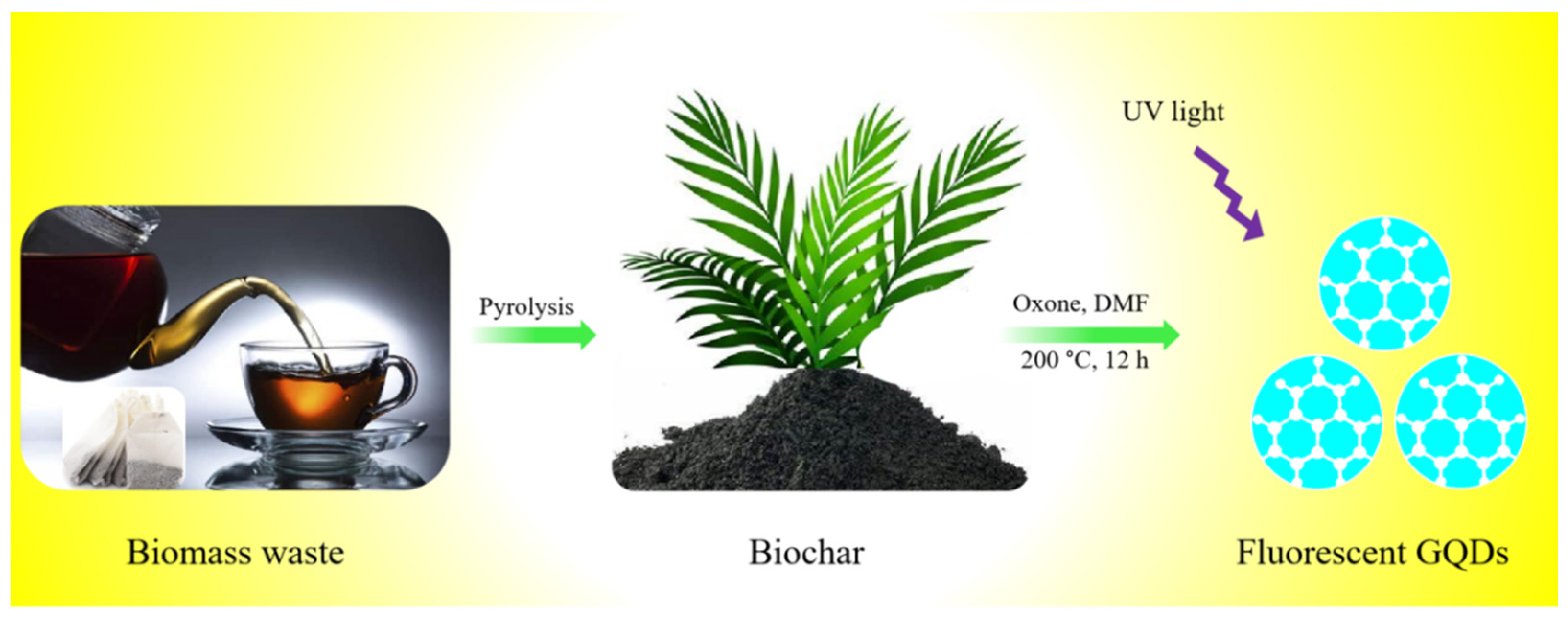
2.2. Preparation of GQDs
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
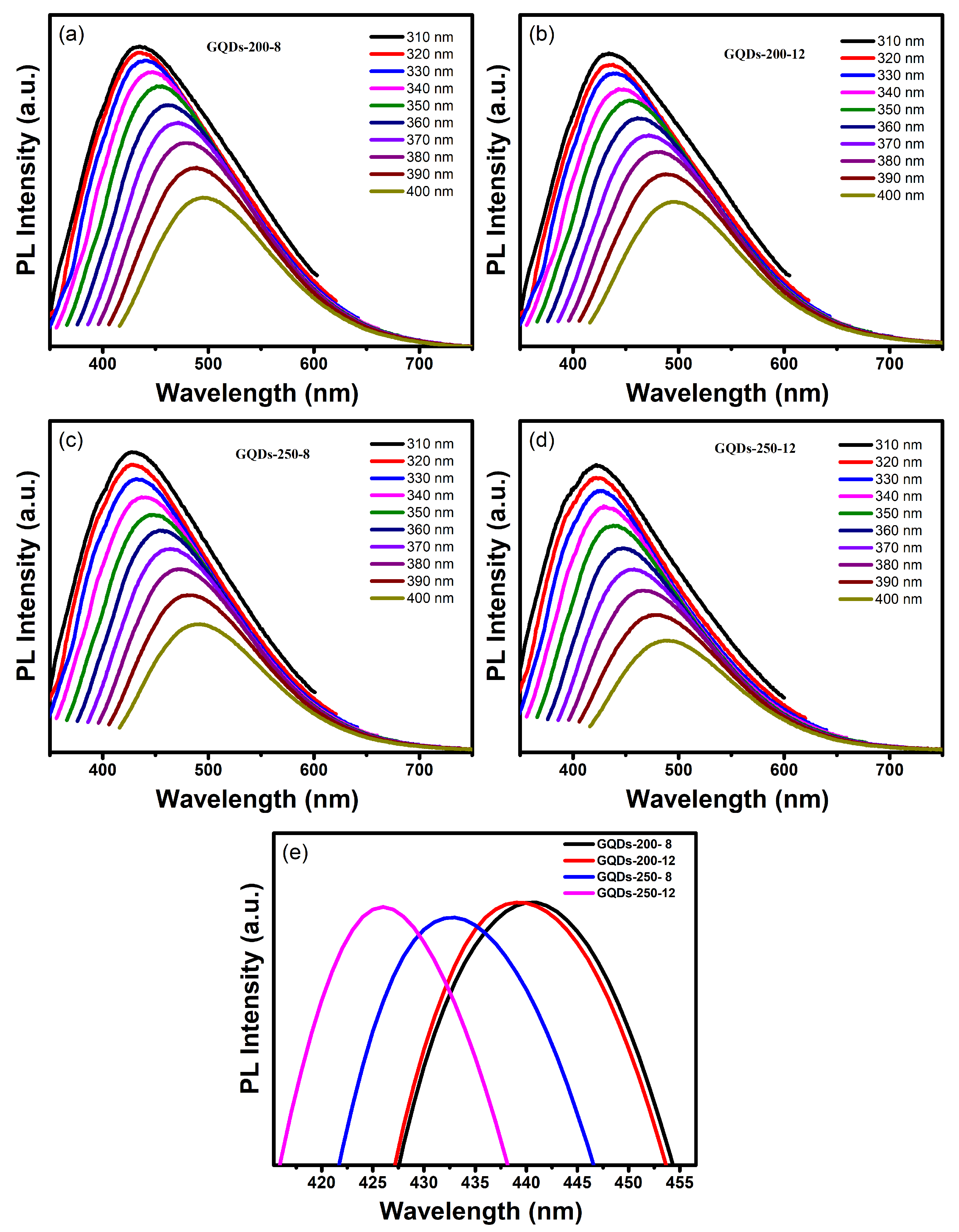
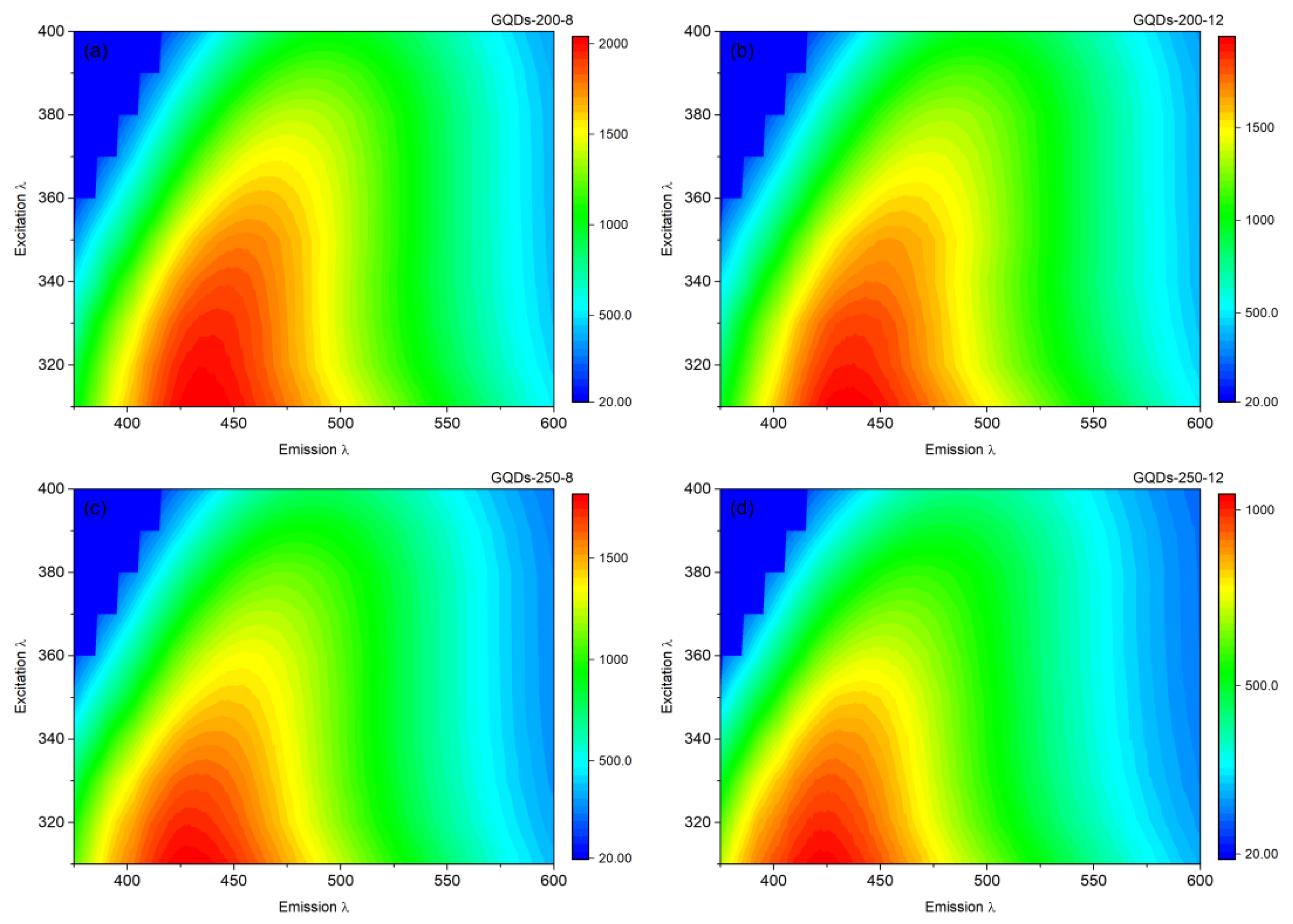
3.1. Optical Property Study
3.2. Morphology Study
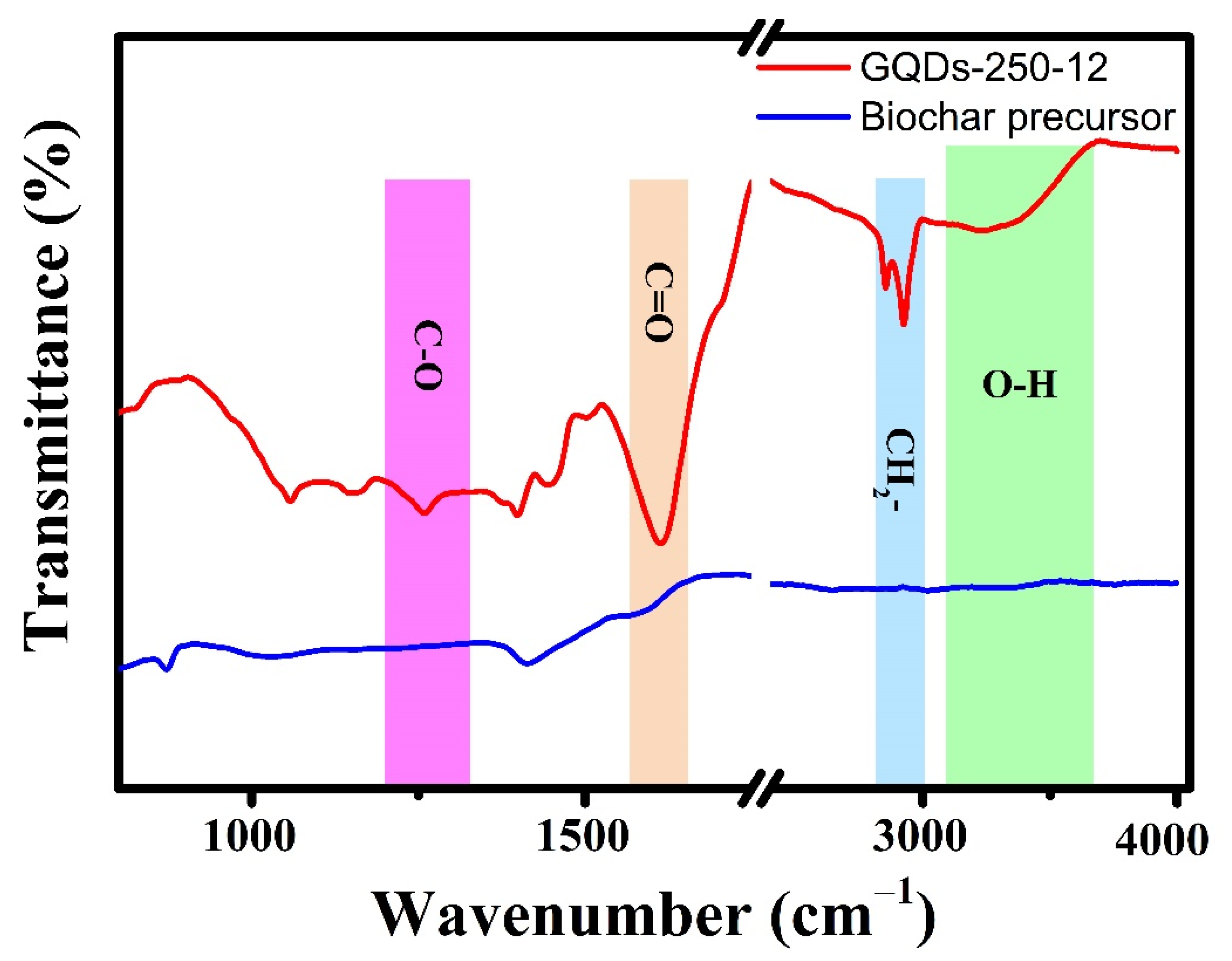
3.3. Structural Examination
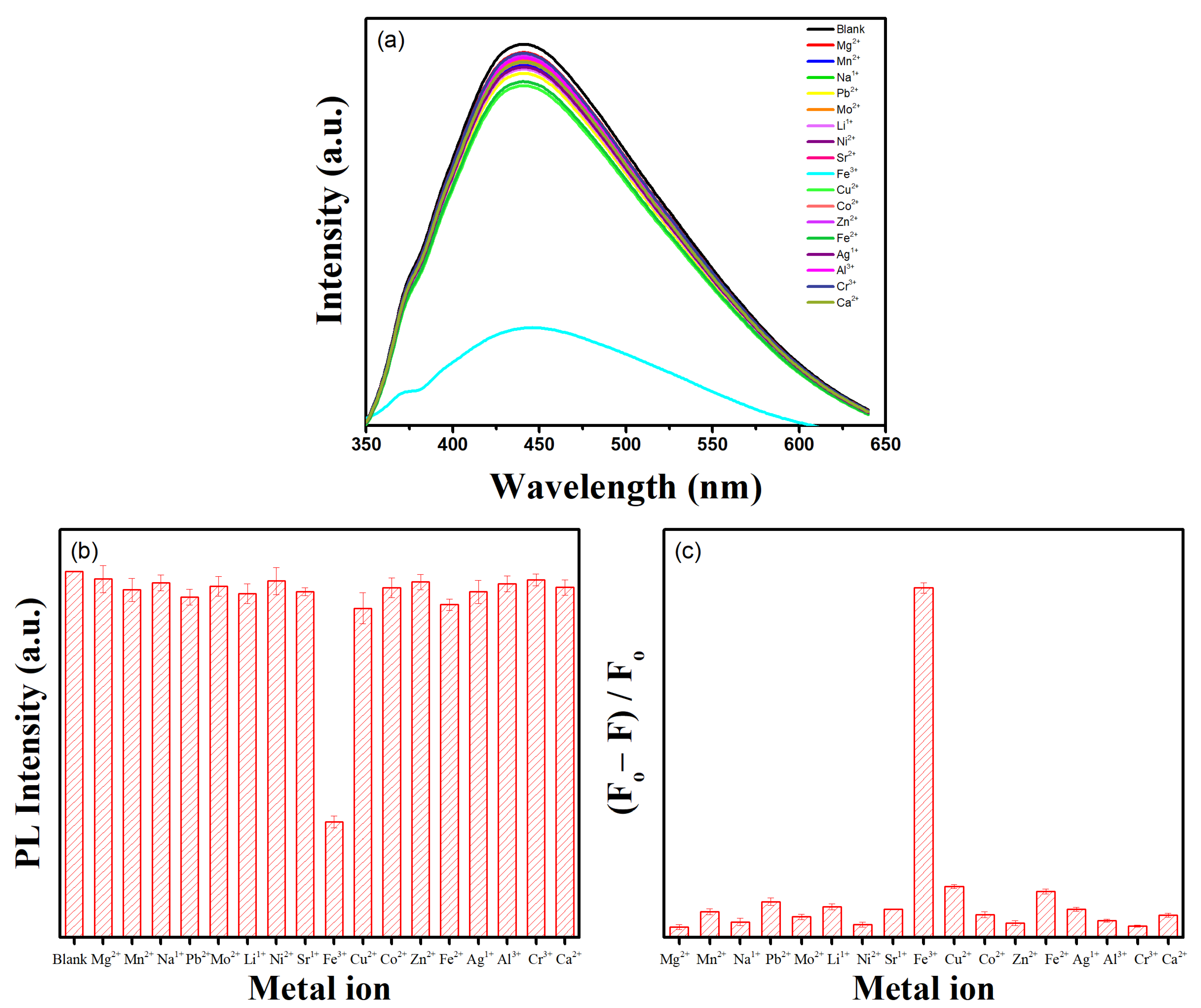
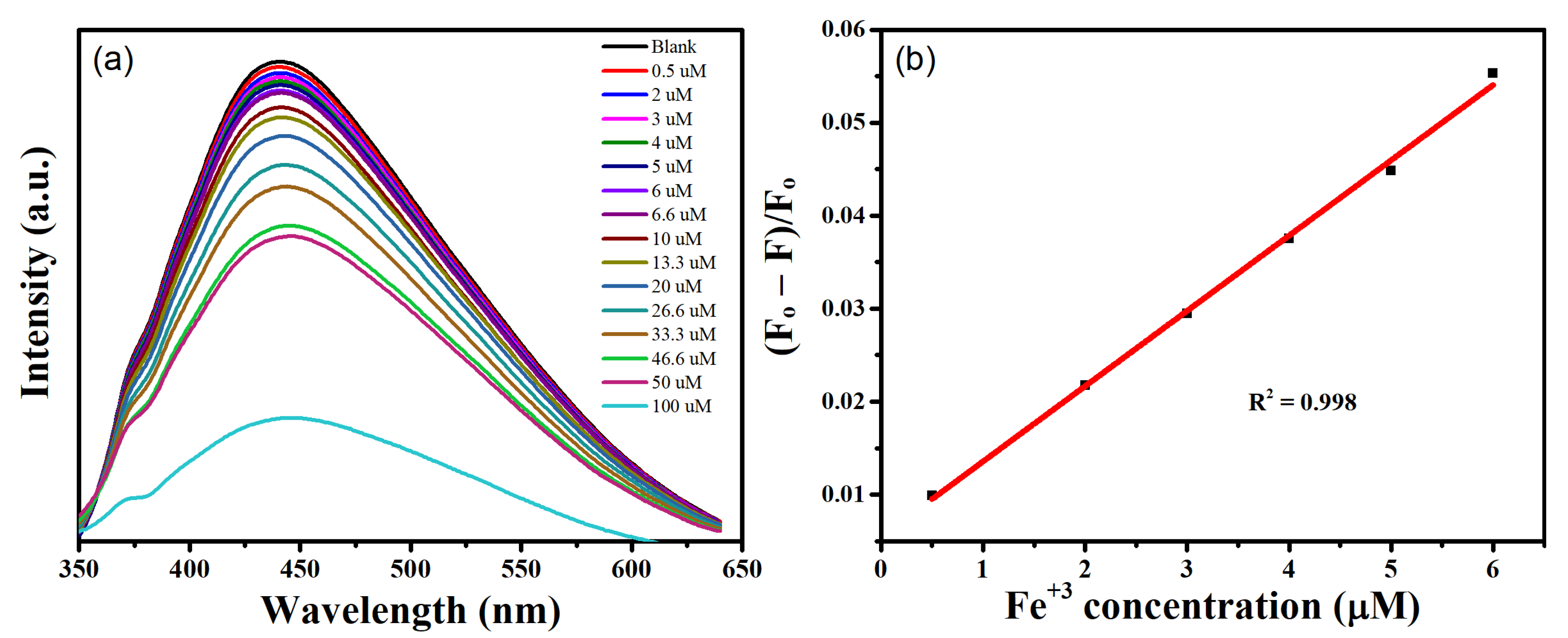
3.4. Application as a PL Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; He, X.; Kang, Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lian, S.; Tsang, C.H.A.; Yang, X.; Lee, S.T. Water-Soluble Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots and Photocatalyst Design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Lifshitz, Y.; Lee, S.T.; Zhong, J.; Kang, Z. Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway. Science 2015, 347, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, N.; Tian, J.; Li, K.; Jiang, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q.; Chen, P. Systematic Bandgap Engineering of Graphene Quantum Dots and Applications for Photocatalytic Water Splitting and CO2 Reduction. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3523–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Zhu, W.; He, B.; Yang, P. Rapid conversion from carbohydrates to large-scale carbon quantum dots for all-weather solar cells. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: Properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: From fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangam, S.; Gupta, A.; Shakeel, A.; Bhattacharya, R.; Sharma, A.K.; Suhag, D.; Chakrabarti, S.; Garg, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Basu, B.; et al. Sustainable synthesis of single crystalline sulphur-doped graphene quantum dots for bioimaging and beyond. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4245–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsuka, H.; Matsui, T. Non-ionic Fluorosurfactant Improves Wettability of Nitrogen-functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Integration with Optoelectronic Devices. Chem. Lett. 2018, 47, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, Y.E.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Carbon dots-Emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yuan, T.; Sui, L.; Wang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Tan, Z.A.; Chen, A.; et al. Engineering triangular carbon quantum dots with unprecedented narrow bandwidth emission for multicolored LEDs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, T.W. Ultrahigh-luminosity white-light-emitting devices based on edge functionalized graphene quantum dots. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Kundu, S.; Roy, C.N.; Das, T.K.; Saha, A. Synthesis of Excitation Independent Highly Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots through Perchloric Acid Oxidation. Langmuir 2017, 33, 14634–14642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B.; Mokaya, R.; Yushin, G. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Abundant Renewable Natural Organic Chemicals for High-Performance Supercapacitor Electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Ji, J.; Fei, R.; Wang, C.Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.R.; Jiang, L.P.; Zhu, J.J. A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, G.; Deng, L.; Hou, Y.; Qu, L. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.W.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Peng, Y.K.; Chou, P.T. Facile synthesis of highly emissive carbon dots from pyrolysis of glycerol; gram scale production of carbon dots/mSiO2 for cell imaging and drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14403–14409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of carbon dots with multiple color emission by controlled graphitization and surface functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wu, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Pan, D.; Wu, M. Facile synthesis of fluorescent graphene quantum dots from coffee grounds for bioimaging and sensing. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, W. Carbon quantum dots displaying dual-wavelength photoluminescence and electrochemiluminescence prepared by high-energy ball milling. Carbon 2015, 94, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Large-scale and controllable synthesis of graphene quantum dots from rice husk biomass: A comprehensive utilization strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Xiang, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Huang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cook, N.P.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Hwang, C.C.; Ruan, G.; et al. Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Park, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, H. Mass Production of Graphene Quantum Dots by One-Pot Synthesis Directly from Graphite in High Yield. Small 2014, 10, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Park, J.; Hyun, D.; Yang, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H. Acid-free and oxone oxidant-assisted solvothermal synthesis of graphene quantum dots using various natural carbon materials as resources. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5633–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, A.; Biswal, M.; Mhamane, D.; Gokhale, R.; Patil, S.; Guin, D.; Ogale, S. Large scale synthesis of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) from waste biomass and their use as an efficient and selective photoluminescence on–off–on probe for Ag+ ions. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11664–11670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Applications in Bioimaging, Biosensing, and Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1904362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Tabish, T.A.; Bull, S.J.; Lim, T.M.; Phan, A.N. High yield synthesis of graphene quantum dots from biomass waste as a highly selective probe for Fe3+ sensing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Sugimoto, H.; Fujii, M.; Giri, P.K. Quantitative Understanding of Charge Transfer Mediated Fe3+ Sensing and Fast Photoresponse by N-doped Graphene Quantum Dots Decorated on Plasmonic Au Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4755–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesani, P.; Singh, G.; Viray, C.M.; Ramaswamy, Y.; Zhu, D.M.; Kingshott, P.; Lu, Z.; Zreiqat, H. Two-Photon Dual-Emissive Carbon Dot-Based Probe: Deep-Tissue Imaging and Ultrasensitive Sensing of Intracellular Ferric Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18395–18406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounsey, R.B.; Teismann, P. Chelators in the treatment of iron accumulation in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 983245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Z.; Huang, C.; Shan, Y.; Liu, C.; Qin, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, T. Understanding the selective detection of Fe3+ based on graphene quantum dots as fluorescent probes: The K sp of a metal hydroxide-assisted mechanism. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12054–12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lei, Y. Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Wang, X.; Routh, P.; Sana, B.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.H.; Lim, K.H.; Li, J.; Chen, P. Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3021–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Peng, Z.; Metzger, A.; Lin, J.; Mann, J.A.; Huang, K.; Xiang, C.; Fan, X.; Samuel, E.L.; Alemany, G.L.B.; et al. Bandgap engineering of coal-derived graphene quantum dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7041–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sk, M.A.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Huang, L.; Lim, K.H.; Chen, P. Revealing the tunable photoluminescence properties of graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6954–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Jin, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, Y.; An, D. Mechanisms behind excitation- and concentration-dependent multicolor photoluminescence in graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cui, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Rong, J. One-step preparation of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots from oxidized debris of graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Samulski, E.T. Synthesis of water soluble graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mo, Z.; Niu, X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Liu, N.; Guo, R. Highly sensitive fluorescence sensor for mercury(II) based on boron- and nitrogen-co-doped graphene quantum dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, M.S.; Schumacher-Schuh, A.; Cardoso, A.M.; Bochi, G.V.; Baldissarelli, J.; Kegler, A.; Santana, D.; Chaves, C.M.M.B.S.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Moresco, R.N.; et al. Iron and Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease: An Observational Study of Injury Biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Ji, J.; Qin, A.; Liao, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, K.; Ou, J. Cane Molasses Graphene Quantum Dots Passivated by PEG Functionalization for Detection of Metal Ions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6763–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, F.; Zou, L.; Chen, D. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding-mediated synthesis of high-quality photoluminescent carbon dots for label-free fluorometric detection of Fe3+ ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Teng, M.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Teng, C.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Shao, Q.; et al. Biomass-derived nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: Highly selective fluorescent probe for detecting Fe3+ ions and tetracyclines. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sensing Material | Synthetic Approach | Detection Range (µM) | LOD (µM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GQDs | Electrochemical exfoliation | 0–80 | 7.22 | [34] |
| PEG-GQDs | Hydrothermal | 0–60 | 5.77 | [46] |
| GQDs | Microwave treatment | 0–50 | 2.5 | [28] |
| GQDs | Chemical oxidation | 0–60 | 0.45 | [32] |
| CQDs | Thermal reaction | 0–20 | 0.041 | [47] |
| N-CQDs | Hydrothermal | 0–250 | 0.75 | [48] |
| GQDs | Hydrothermal | 0–100 | 0.29 | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, A.; Liang, Q.; Abbas, S.; Liaqat, M.; Rubab, S.; Tabish, T.A. Eco-Friendly Sustainable Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Biowaste as a Highly Selective Sensor. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203696
Abbas A, Liang Q, Abbas S, Liaqat M, Rubab S, Tabish TA. Eco-Friendly Sustainable Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Biowaste as a Highly Selective Sensor. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(20):3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203696
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Aumber, Qijie Liang, Saleem Abbas, Maryam Liaqat, Shabnum Rubab, and Tanveer A. Tabish. 2022. "Eco-Friendly Sustainable Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Biowaste as a Highly Selective Sensor" Nanomaterials 12, no. 20: 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203696
APA StyleAbbas, A., Liang, Q., Abbas, S., Liaqat, M., Rubab, S., & Tabish, T. A. (2022). Eco-Friendly Sustainable Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Biowaste as a Highly Selective Sensor. Nanomaterials, 12(20), 3696. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203696






