Highly Sensitive Acetone Gas Sensors Based on Erbium-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Synthesis of Bi1−xErxFeO3 Nanoparticles
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Measurement of Bi1−xErxFeO3 Gas Sensors
3. Results
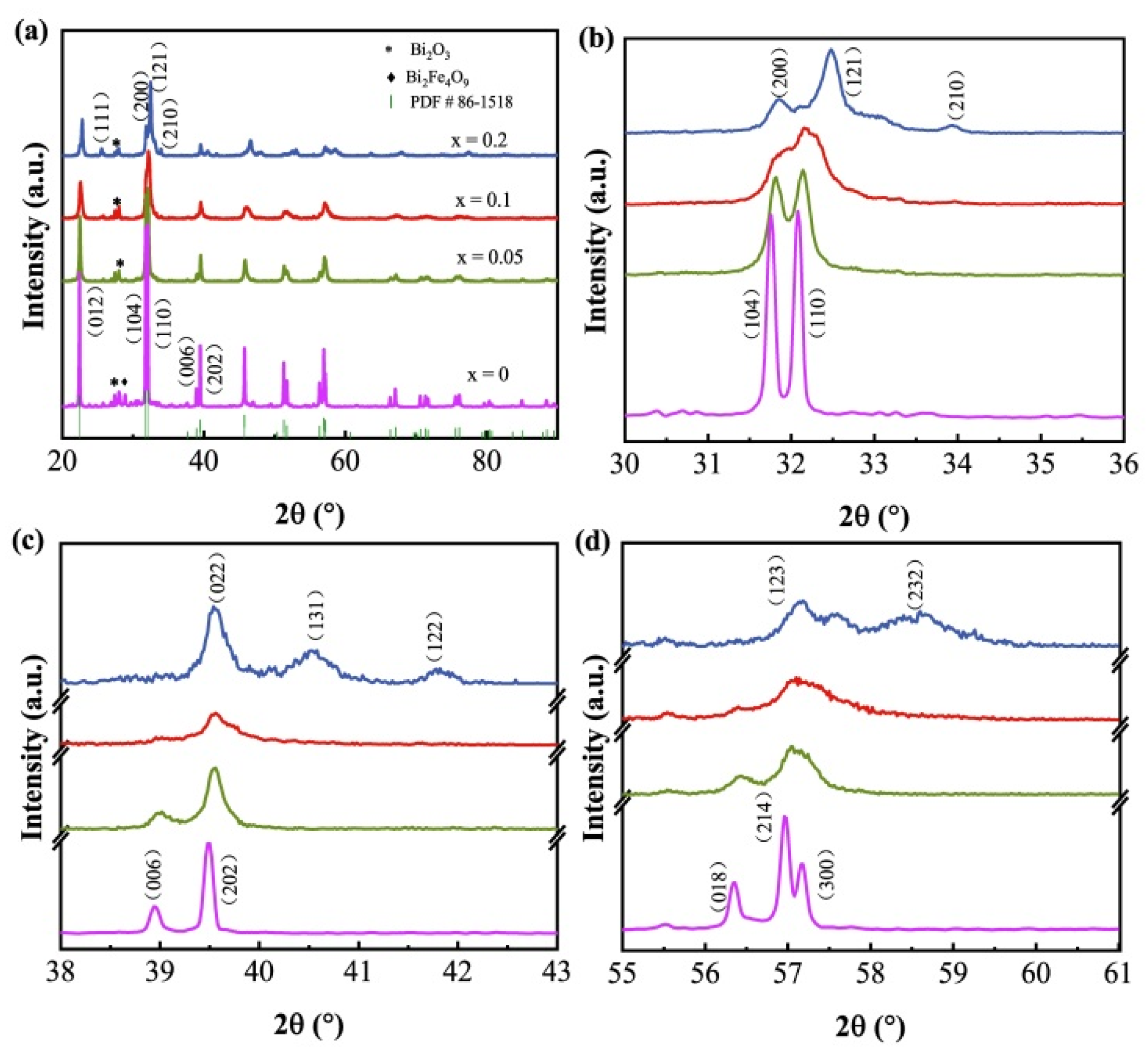
3.1. Structure
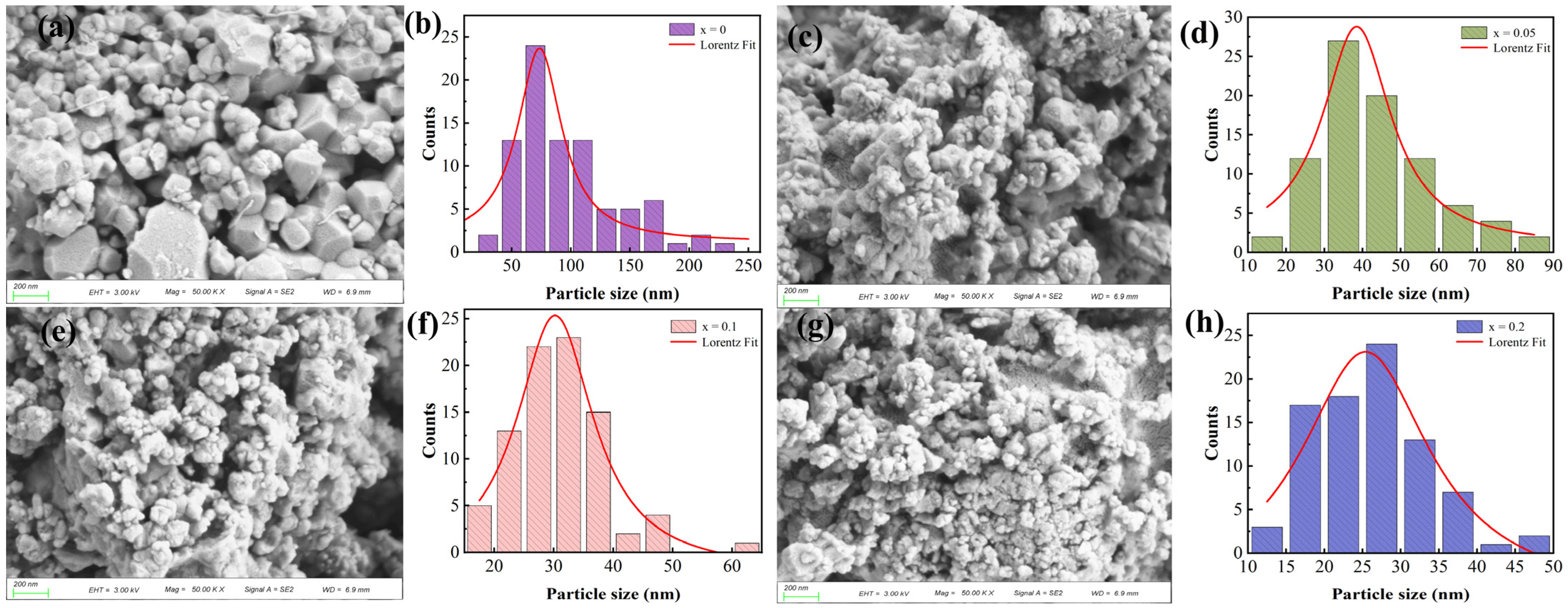
3.2. Morphology
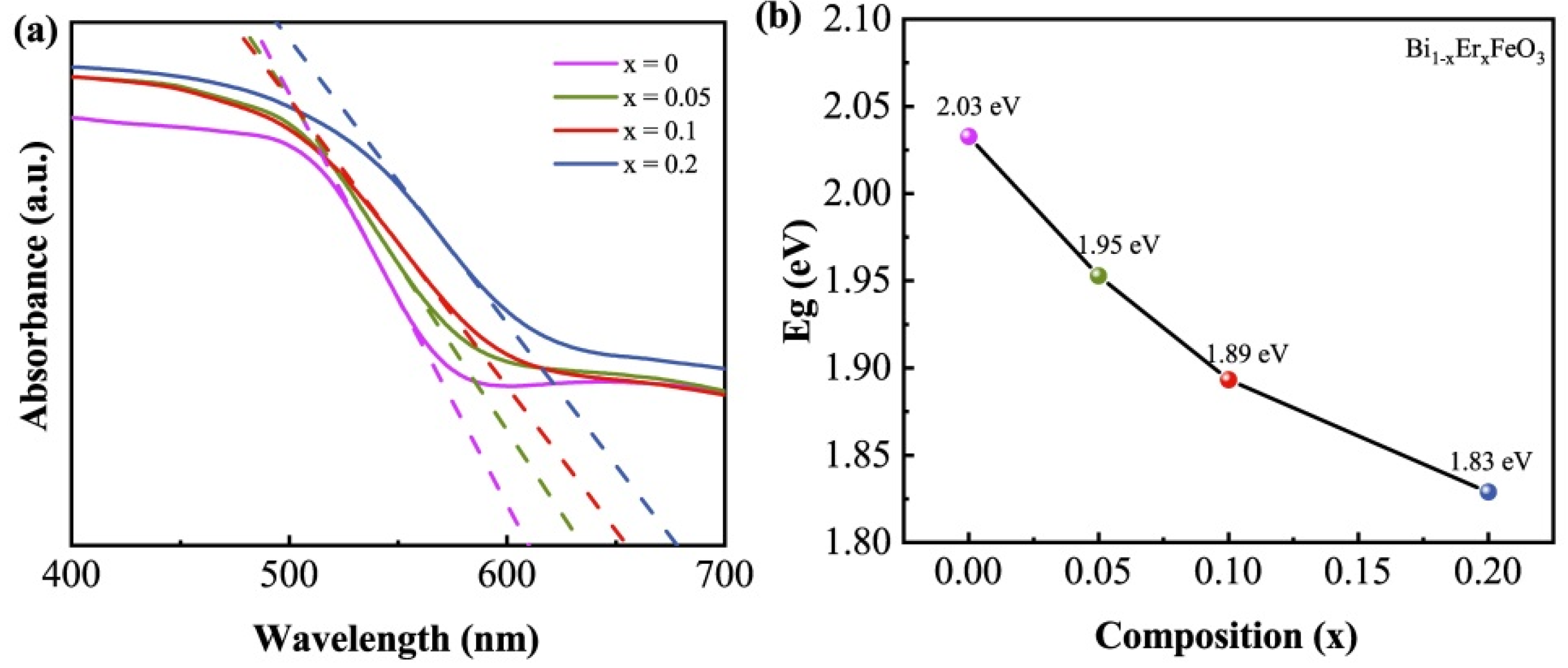
3.3. Band Gap Energy
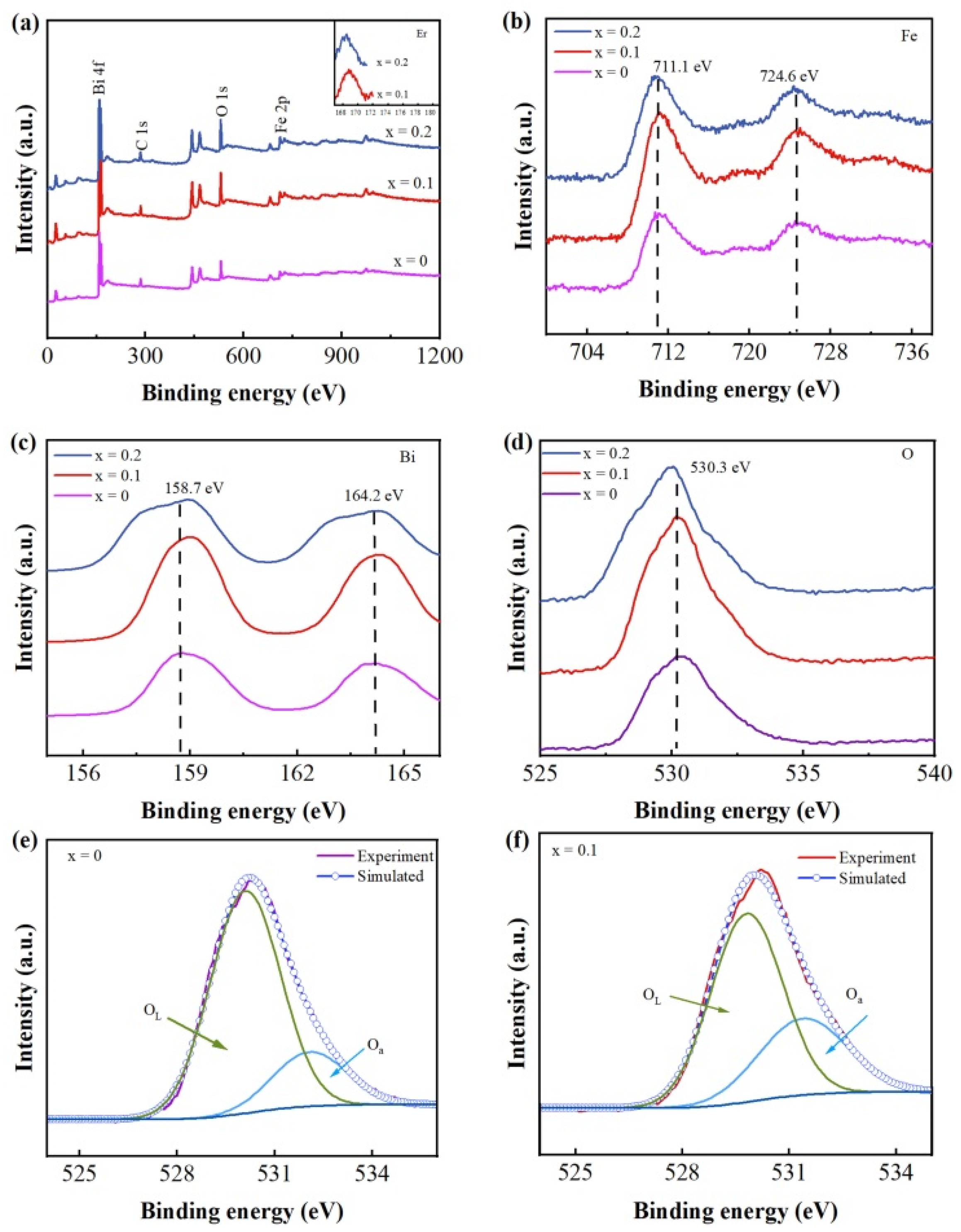
3.4. XPS
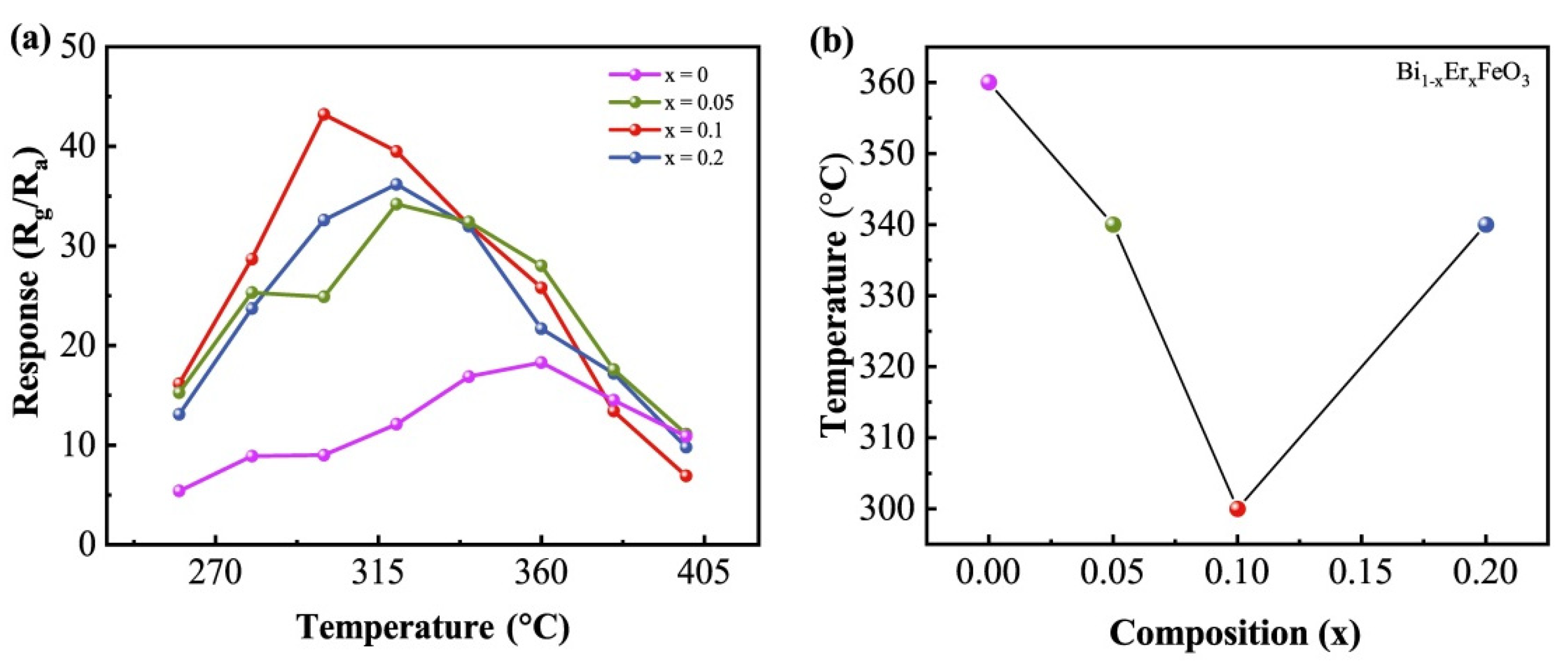
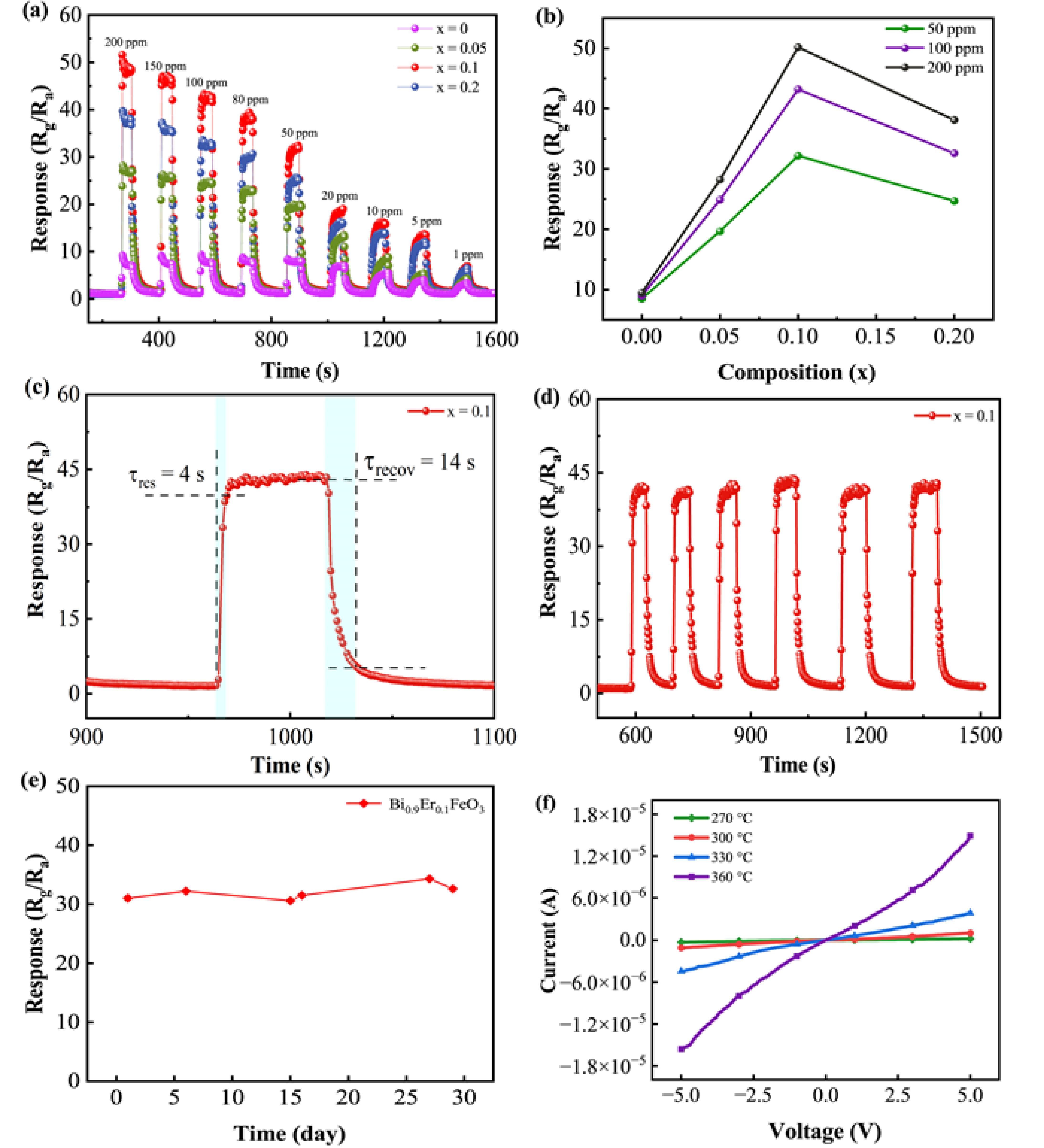
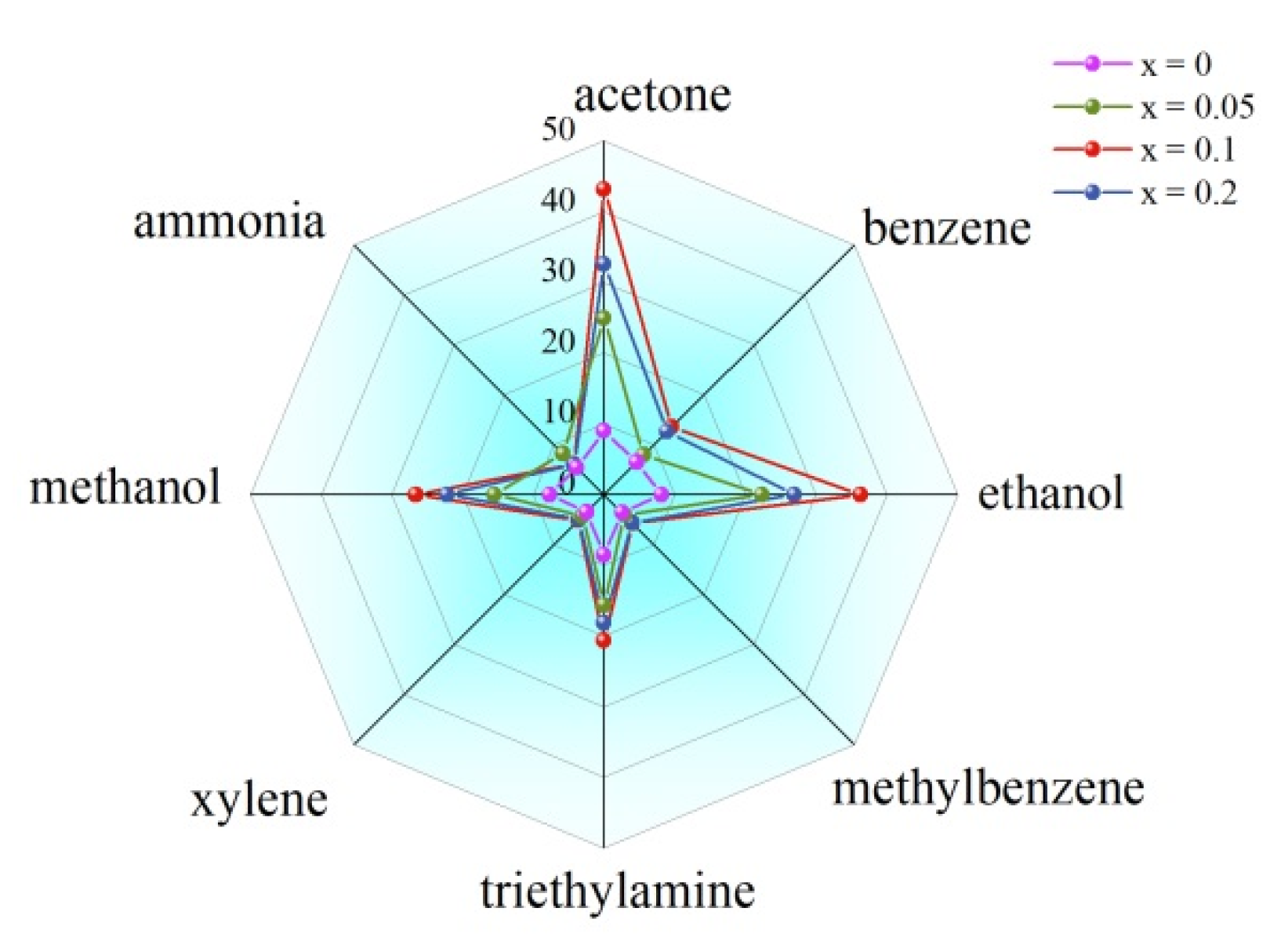
3.5. Gas-Sensing Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amiri, V.; Roshan, H.; Mirzaei, A.; Neri, G.; Ayesh, A.I. Nanostructured metal oxide-based acetone gas sensors: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rydosz, A. Sensors for enhanced detection of acetone as a potential tool for noninvasive diabetes monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.-C.; Fang, T.-H.; Hsiao, Y.-J.; Li, Z.-J. Rapid detection of low concentrations of H2S using CuO-doped ZnO nanofibers. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 852, 157014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Toan, N.; Hung, C.M.; Hoa, N.D.; Van Duy, N.; Thi Thanh Le, D.; Thi Thu Hoa, N.; Viet, N.N.; Phuoc, P.H.; Van Hieu, N. Enhanced NH3 and H2 gas sensing with H2S gas interference using multilayer SnO2/Pt/WO3 nanofilms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Tang, D. Reduced graphene oxide/BiFeO3 nanohybrids-based signal-on photoelectrochemical sensing system for prostate-specific antigen detection coupling with magnetic microfluidic device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of Pd/PdO@ZnO-ZnO nanorods by using metal organic framework templated catalysts for selective detection of triethylamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 350, 130840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Rational design of SnO2 hollow microspheres functionalized with derivatives of Pt loaded MOFs for superior formaldehyde detection. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhang, R.; Meng, F. Perovskite-structured LaCoO3 modified ZnO gas sensor and investigation on its gas sensing mechanism by first principle. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 130015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanocubes and nanospheres and their gas sensing properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, X. Fabrication of hollow In2O3–ZnO microtubules by a simple biotemplate method and their gas-sensing properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 28, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y. Hierarchical magnetic BiFeO3 microcages: Controlling synthesis and visible-light photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Atiq, S.; Mahmood, A.; Ramay, S.M.; Kumail Abbas, S.; Naseem, S. Optimisation of giant magnetoresistance in Mn-substituted BiFeO3 for low field sensors. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 14677–14685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Pu, S.; Hu, Z. Enhanced multiferroic properties of Bi0.85Nd0.15FeO3 ceramics with excess Bi2O3. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 791, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Mi, W. Progress in BiFeO3-based heterostructures: Materials, properties and applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 477–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Dong, S.; Han, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Bu, Q.; Li, X.; Xiang, J. A fast response & recovery acetone gas sensor based on BiFeO3 nanomaterials with high sensitivity and low detection limit. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 29, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisegapriyan, K.S.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Alluri, N.R.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Kim, S.-J. All in one transitional flow-based integrated self-powered catechol sensor using BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Chen, J.; Jin, D.; Cheng, J. Preparation and gas sensing characteristics of BiFeO3 crystallites. Mater. Lett. 2017, 197, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A.S.; Abovian, H.V.; Avakian, P.B.; Mkrtchian, S.H.; Haroutunian, V.M. Bismuth ferrites: New materials for semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 4, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Majumder, S.B.; Dewan, M.; Roy Chaudhuri, A. Hydrogen sensing characteristics of perovskite based calcium doped BiFeO3 thin films. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18648–18656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y. Fast response isopropanol sensing properties with sintered BiFeO3 nanocrystals. Materials 2020, 13, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Hierarchical hollow BiFeO3 microcubes with enhanced acetone gas sensing performance. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 6702–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Pal, M. Highly selective and stable acetone sensor based on chemically prepared bismuth ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 787, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, S.; Ghosh, R. Origin of irreversible to reversible transition in acetone detection for Y-doped BiFeO3 perovskite. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 144501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan, M.; Xu, Q.; Katoch, A.; Anariba, F.; Kim, S.S.; Wu, P. O2 sensing dynamics of BiFeO3 nanofibers: Effect of minor carrier compensation. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 175501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ma, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Bi, J.; Wu, J. Acetone sensing with parts-per-billion limit of detection using a BiFeO3-based solid solution sensor at the morphotropic phase boundary. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 313, 128060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douani, R.; Lamrani, N.; Oughanem, M.H.; Saidi, M.; Guhel, Y.; Chaouchi, A.; Boudart, B. Improvement of humidity sensing performance of BiFeO3 nanoparticles-based sensor by the addition of carbon fibers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 307, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Ma, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, S. Enhanced ferromagnetism of Er-doped BiFeO3 thin films derived from rhombohedral-to-orthorhombic phase transformations. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Sanghi, S.; Agarwal, A.; Kumar, R.; Singh, O. Crystal structure, magnetic and dielectric properties of Er-doped BiFeO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorgu, A.I.; Maxim, F.; Matei, C.; Ferreira, L.P.; Ferreira, P.; Cruz, M.M.; Berger, D. Fast synthesis of rare-earth (Pr3+, Sm3+, Eu3+ and Gd3+) doped bismuth ferrite powders with enhanced magnetic properties. J. Alloy Compd. 2015, 629, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesinska, A.; Khort, A.; Bobowska, I.; Busiakiewicz, A.; Wypych-Puszkarz, A. Influence of the La3+, Eu3+, and Er3+ doping on structural, optical, and electrical properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles synthesized by microwave-assisted solution combustion method. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 5394325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Pu, H.; Wells, S.A.; Wen, Z.; Mao, S.; Chang, J.; Hersam, M.C.; Chen, J. Ultrahigh sensitivity and layer-dependent sensing performance of phosphorene-based gas sensors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, S.; Ma, S.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Almamoun, O. Modulated PrFeO3 by doping Sm3+ for enhanced acetone sensing properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 856, 158274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Leonardi, S.G.; Pistone, A.; Mavilia, L.; Neri, G. Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, J.; Jin, H.; Jin, D.; Peng, X.; Hong, B.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Ge, H.; et al. Calcination-temperature-dependent gas-sensing properties of mesoporous nickel oxides nanowires as ethanol sensors. Powder Technol. 2017, 318, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, G. Highly Sensitive Acetone Gas Sensors Based on Erbium-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203679
Liu X, Li J, Guo L, Wang G. Highly Sensitive Acetone Gas Sensors Based on Erbium-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(20):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203679
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaolian, Jing Li, Lanlan Guo, and Guodong Wang. 2022. "Highly Sensitive Acetone Gas Sensors Based on Erbium-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 20: 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203679
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, J., Guo, L., & Wang, G. (2022). Highly Sensitive Acetone Gas Sensors Based on Erbium-Doped Bismuth Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 12(20), 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203679






