Mechanical and Conductive Properties of Cu Matrix Composites Reinforced by Oriented Carbon Nanotubes with Different Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials and Preparation
2.2. Characterization and Testing
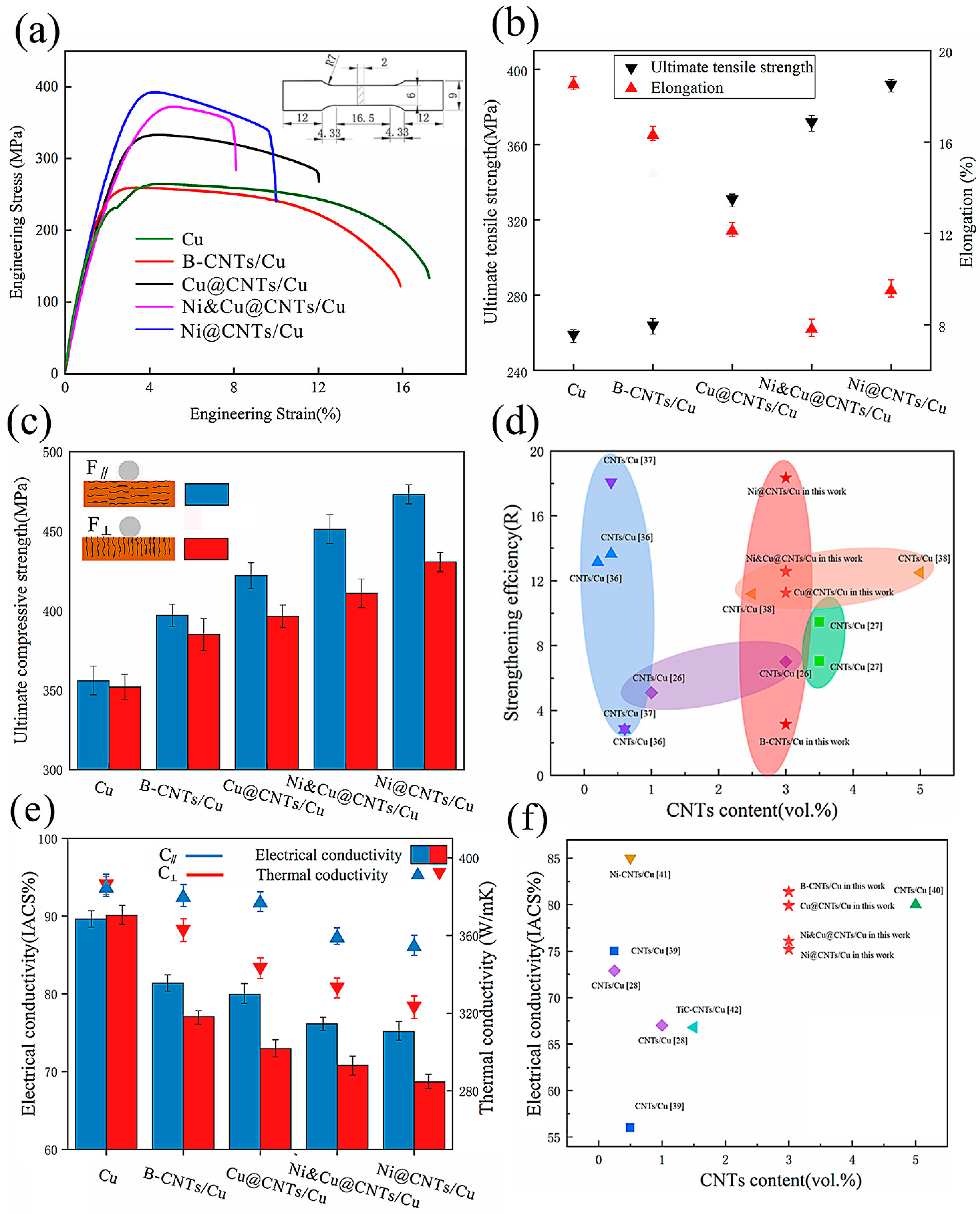
3. Macro Performance Test Results
4. Microscopic Characterization Results
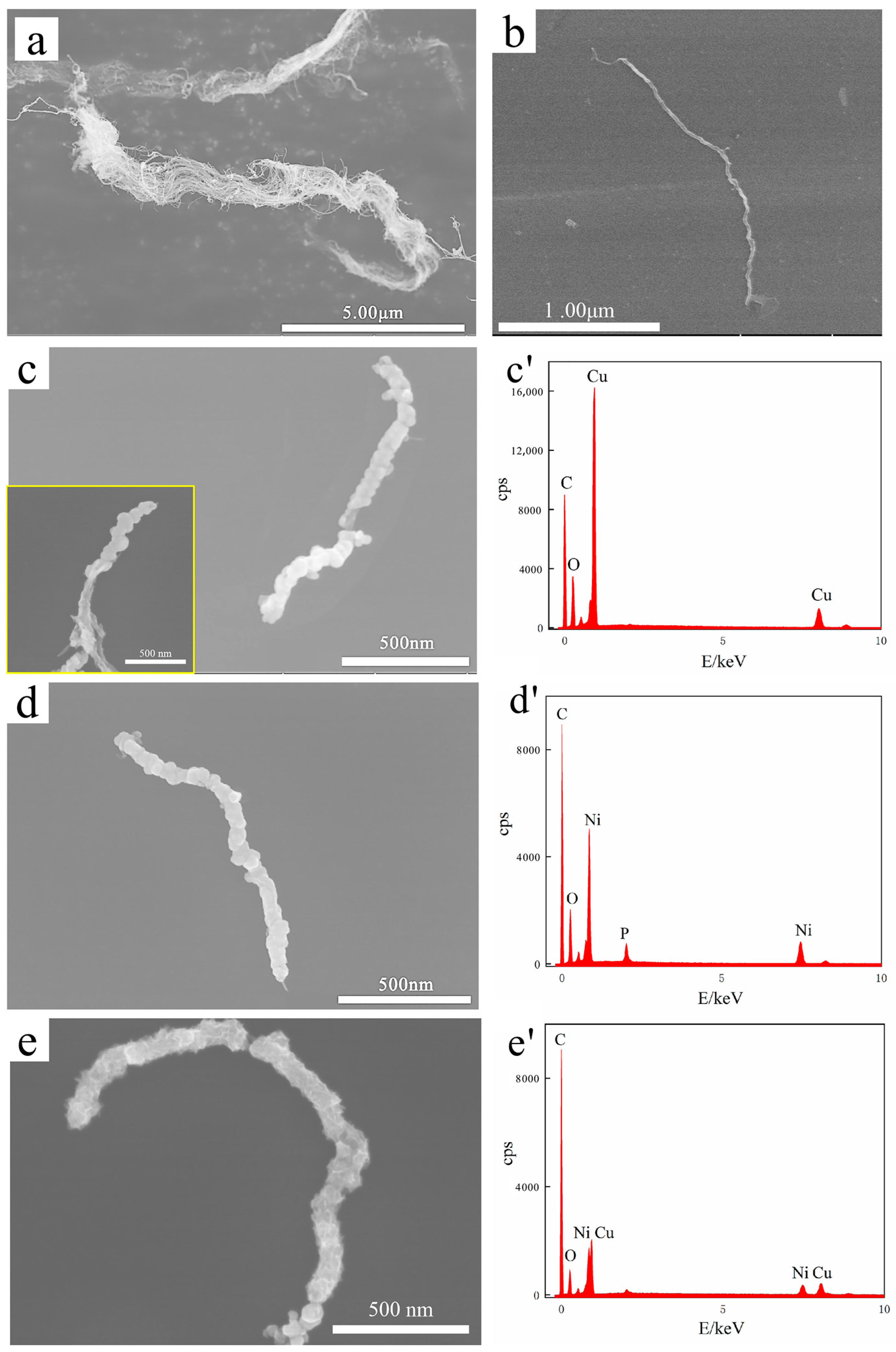
4.1. Coated MWCNTs
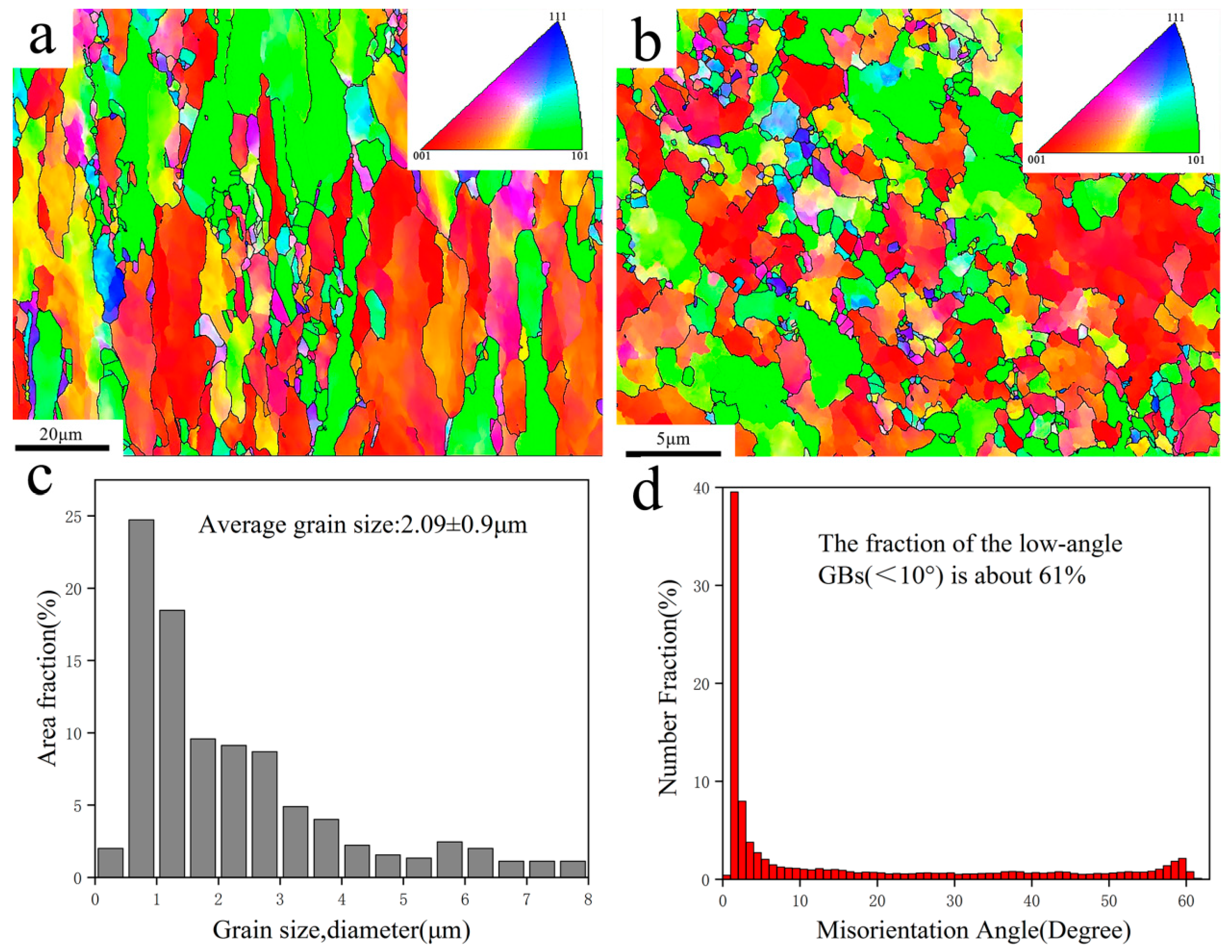
4.2. Orientation of MWCNTs in Composites
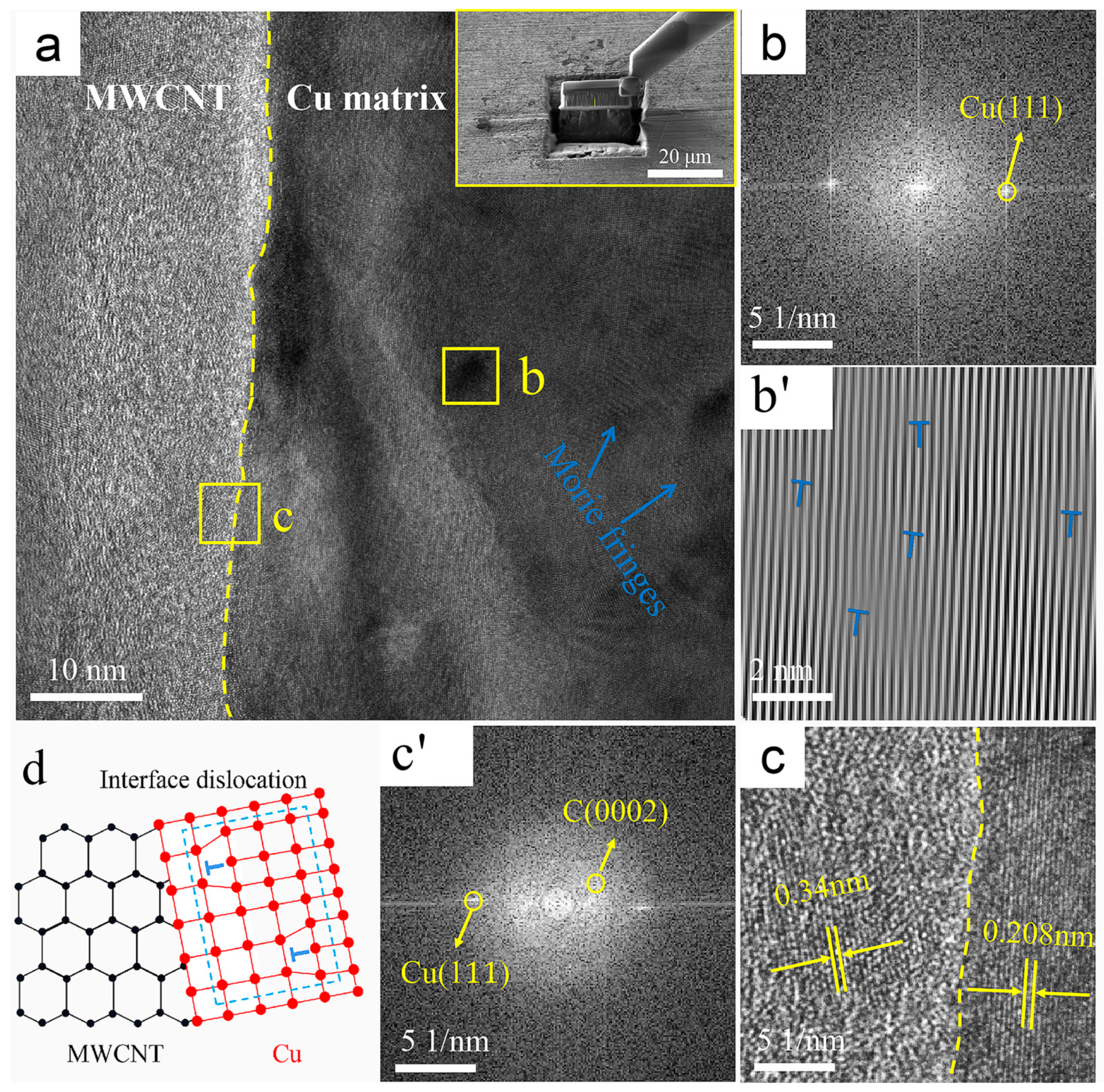
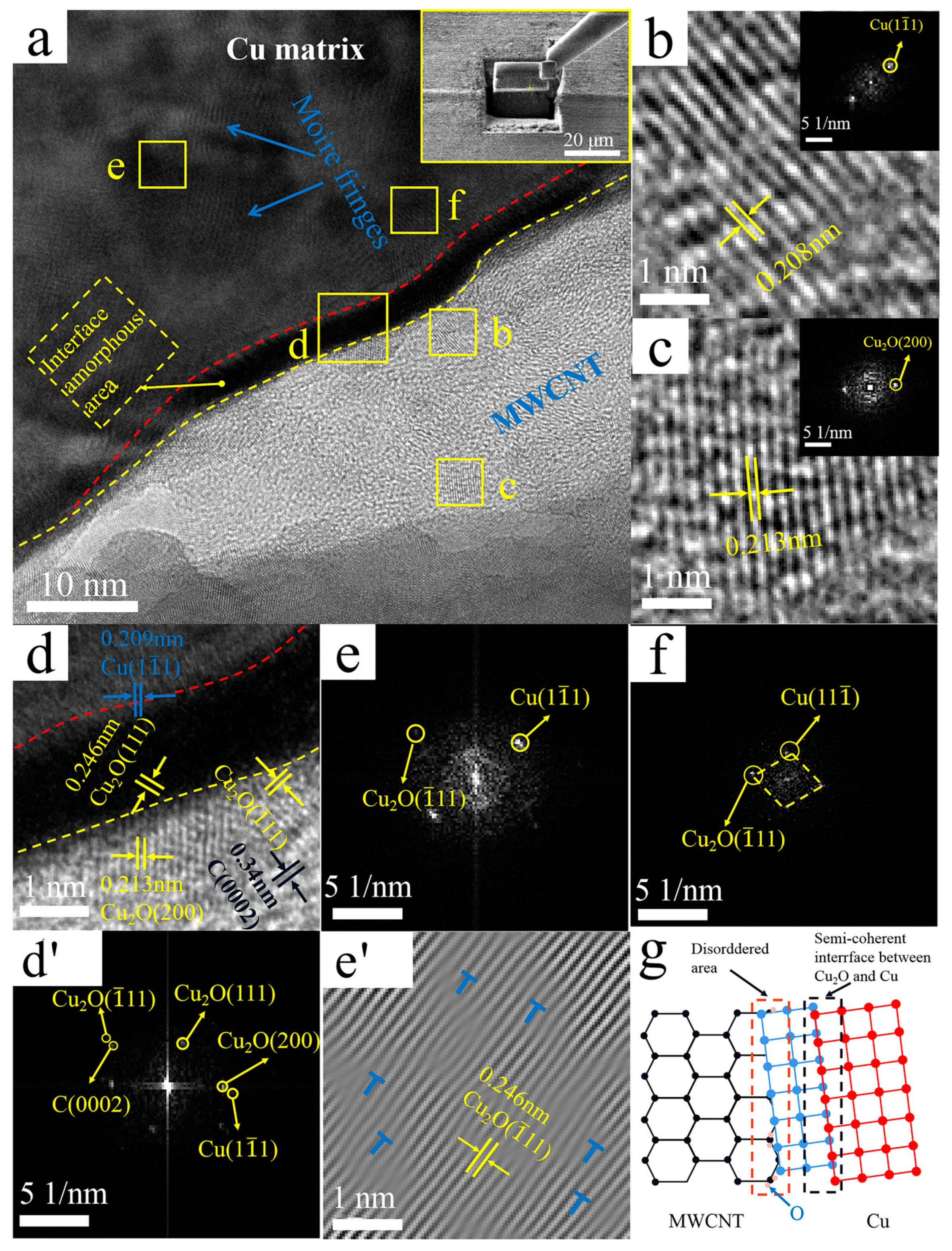
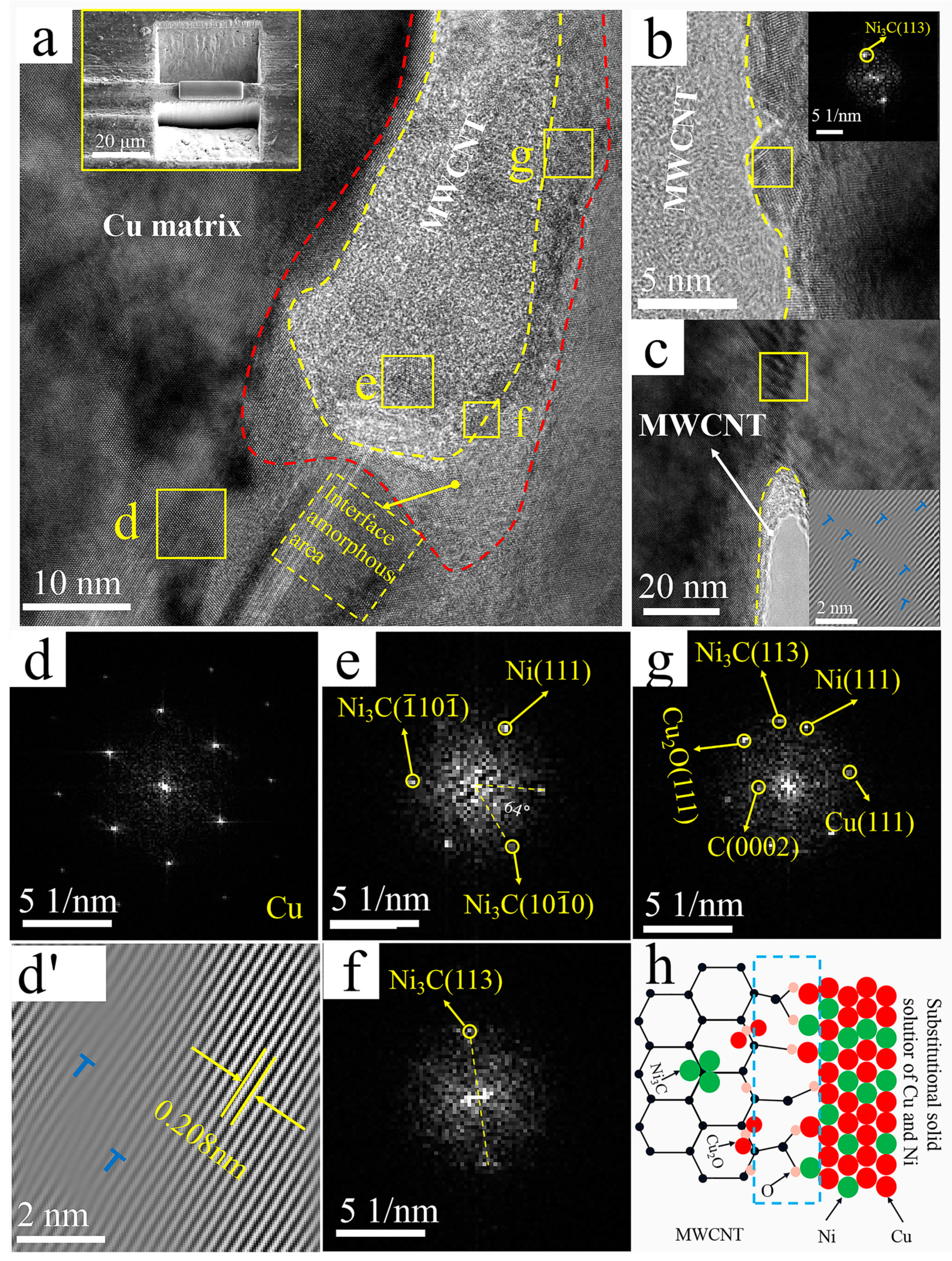
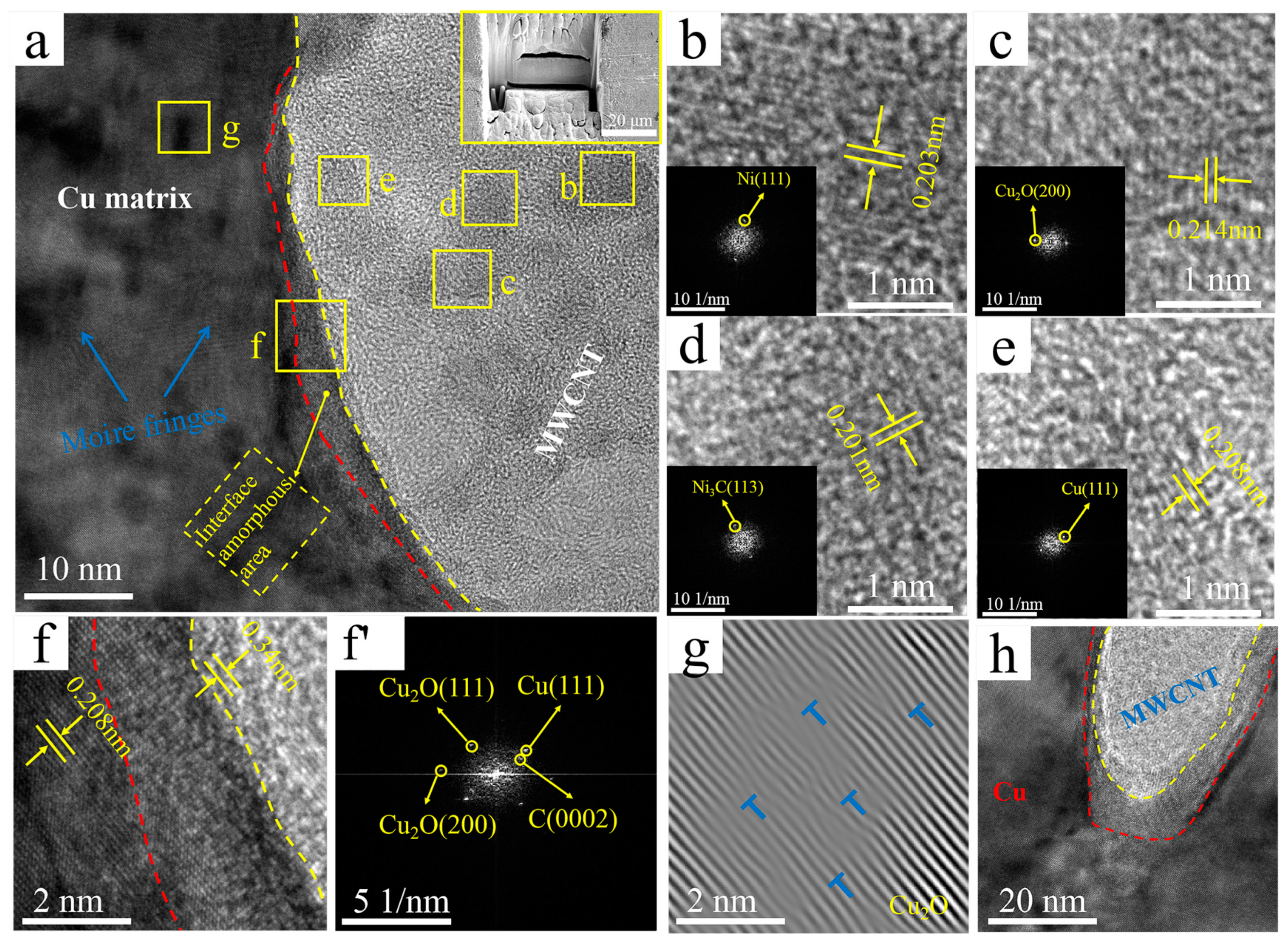
4.3. MWCNTs/Cu Interface
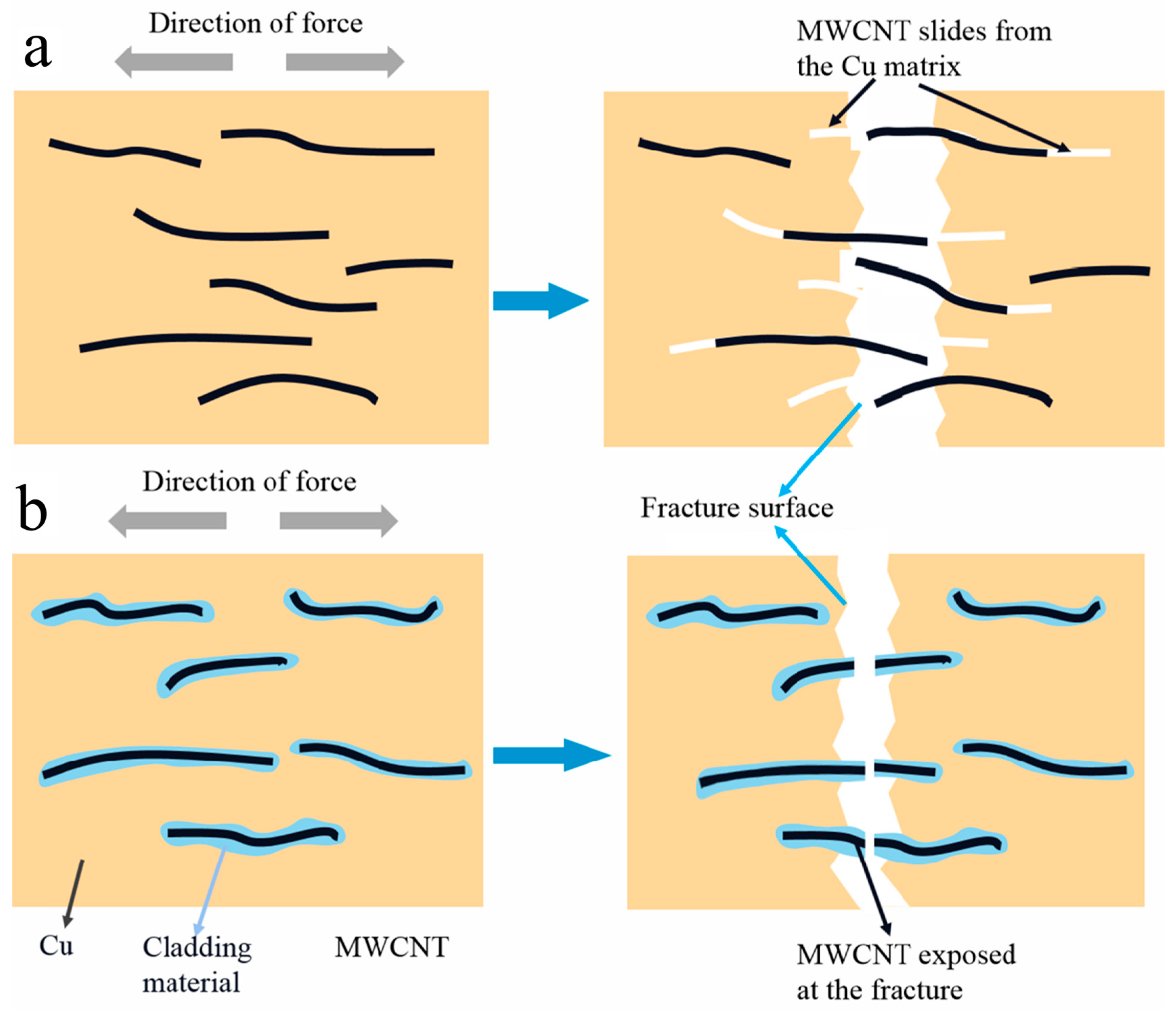
4.4. Tensile Fracture
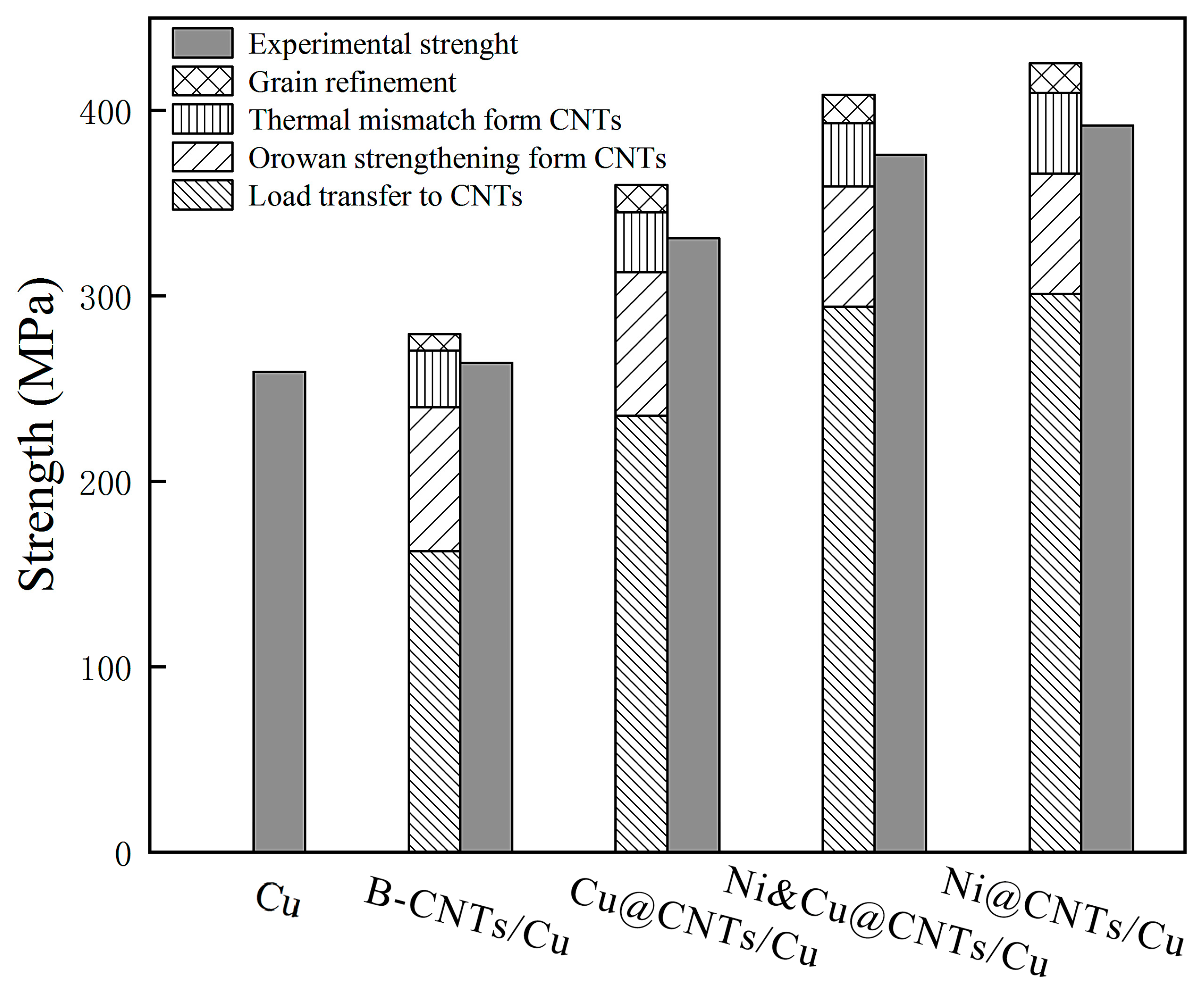
5. Strengthening Mechanism
6. Effect of the Interface on Conductivity
7. Conclusions
- The wettability of MWCNTs with respect to the Cu matrix as limited, resulting in weak mechanical bonding between CNTs and the Cu matrix in the B-MWCNTs/Cu composite. Therefore, its strengthening effect on the matrix was much lower than that of coated MWCNTs. However, the conduction performance of the B-MWCNTs/Cu composite had the minimum reduction, which may be ascribed to the reduction of the energy loss of electron–phonon conversion by the tightly bonded interface. In addition, the low-density dislocation near the interface also reduced the lattice disorder of Cu in amorphous regions.
- There were interfacial products such as Cu2O and Ni3C, solid solutions of Cu and Ni, transitional amorphous areas, and high-density dislocations at interfacial regions in-plated CNT-reinforced Cu composites, forming tight interface bonding, which effectively strengthened the composites. However, these factors also caused the scattering of electrons and phonons, increasing the electrical/thermal resistance of the interface and leading to a decrease in the conductivity of composites. The ductility of the composites decreased, which was attributed to the blocking effect of MWCNTs on the dislocation slip.
- The Ni plating was the most dense, continuous, and complete. The strengthening effect of Ni@CNT with respect to the Cu matrix is the greatest, but its elongation and conductivity decreased greatly. The Cu@CNTs/Cu composite achieved the balance of mechanical properties, ductility, and conductivity/thermal conductivity. Its ultimate tensile strength was 373 MPa, the elongation was 12.1%, and the axial conductivity and thermal conductivity were 79.9 IACS% and 376 W/mK, respectively.
- MWCNTs in the prepared Cu composites remained straight, long, monodispersed, and unidirectionally arranged, which enabled the excellent axial conductivity and mechanical properties of MWCNTs to be exerted, exhibiting orthotropic anisotropy.
- Even if the outermost tubes were damaged by acid treatment, MWCNTs with multilayer nested tube structures could still transmit electrons/phonons axially through inner tubes, which prevented the influence of outer tube damage on the conductivity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Li, T.; Su, W.; Guo, S. Investigation on microstructure and properties of Cu–Al2O3 composites fab-ricated by a novel in-situ reactive synthesis. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Guo, X.; Song, K.; Jia, S.; Yakubov, V.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Liang, S. Synergistic strengthening effect of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and titanium diboride (TiB2) microparticles on mechanical properties of copper matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 7989–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, W.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, F.; Dong, G.; Xiao, P. Microstructures and properties of hybrid copper matrix composites reinforced by TiB whiskers and TiB2 particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Kang, K.; Yin, J.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, H. Microstructural, mechanical and tribological performances of carbon fiber reinforced copper/carbon composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 142, 106247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Sohn, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Han, J.H. Effect of dispersion and alignment of graphite fibers on thermal expansion induced fracture of graphite fiber/copper composite. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yi, M. Preparation and properties of copper-plated expanded graphite/copper composites. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.; Wong, P.; Man, H. Enhancement in corrosion and electrical wear resistance of copper via laser surface alloying with NiTi. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 408, 126804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.R.; Lau, H.C.; Ramakrishna, S. CNT-reinforced metal and steel nanocomposites: A comprehensive assessment of progress and future directions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 114, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, B.; Ni, S.; Yi, J.; Song, M. Acquiring well balanced strength and ductility of Cu/CNTs composites with uniform dispersion of CNTs and strong interfacial bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 733, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Tu, J.; Zhang, X. Mechanical properties and physical properties of Cu-based composite materials reinforced by carbon nanotubes. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 14, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Tao, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bao, R.; Li, F.; Fang, D.; Li, C.; Yi, J. Enhancement of mechanical properties and conductivity in carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/Cu matrix composite by surface and intratube decoration of CNTs. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 816, 141248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantzinos, S.K.; Antoniou, P.A.; Giannopoulos, G.I.; Fatsis, A.; Markolefas, S.I. Design of Laminated Composite Plates with Carbon Nanotube Inclusions against Buckling: Waviness and Agglomeration Effects. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, J.; Yi, J.; Liu, Y.; Bao, R.; Li, C.; Tan, S.; You, X. Enhancing the strength of carbon nanotubes reinforced copper matrix composites by optimizing the interface structure and dispersion uniformity. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 88, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.K.; Thomas, B.; Kar, V.R. A Comprehensive Review on CNTs and CNT-Reinforced Composites: Syntheses, Characteristics and Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varo, T.; Canakci, A. Effect of the CNT Content on Microstructure, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Based Electrical Contact Materials Produced by Flake Powder Metallurgy. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraei, A.A.; Fathi, A.; Givi, M.K.B.; Pashaei, M.H. Fabricating and improving properties of copper matrix nanocomposites by electroless copper-coated MWCNTs. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 116, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, E.; Torikachvili, M.; Meyers, M.; Olevsky, E.A. Magnetic enhancement of thermal conductivity in copper–carbon nanotube composites produced by electroless plating, freeze drying, and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Lett. 2012, 79, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Lopez, A.; Morales-Rodríguez, A.; Vega-Padillo, J.; Poyato, R.; Muñoz, A.; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A. Enhanced carbon nanotube dispersion in 3YTZP/SWNTs composites and its effect on room temperature mechanical and electrical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 682, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiderdoni, C.; Pavlenko, E.; Turq, V.; Weibel, A.; Puech, P.; Estournès, C.; Peigney, A.; Bacsa, W.; Laurent, C. The preparation of carbon nanotube (CNT)/copper composites and the effect of the number of CNT walls on their hardness, friction and wear properties. Carbon 2013, 58, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, K.; Wu, Q.; Jia, C.; Liang, X.; Nie, J.; Tian, W.; Gai, G.; Guo, H. Fabrication and effective thermal conductivity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced Cu matrix composites for heat sink applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhao, S.; Dong, S.; Li, L.; Xiao, A.; Li, S. Preparation of Nickel-Copper Bilayers Coated on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Yang, A.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Lou, D.; Liu, D. Fabrication of carbon nanotubes/Cu composites with orthotropic mechanical and tribological properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 804, 140788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Song, Q.; Yin, S.-P.; Kang, Z.; Li, S.-L. Improvement of interfacial interaction and mechanical properties in copper matrix composites reinforced with copper coated carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, T.; Shi, C.; Liu, E.; He, C.; Zhao, N. Synergistic effect of CNTs reinforcement and precipitation hardening in in-situ CNTs/Al–Cu composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 633, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, C.; Lecouturier, F.; Mesguich, D.; Ferreira, N.; Chevallier, G.; Estournès, C.; Weibel, A.; Laurent, C. High strength–High conductivity double-walled carbon nanotube–Copper composite wires. Carbon 2016, 96, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, S.; Han, S.; Kim, W. A combination of ball milling and high-ratio differential speed rolling for synthesizing carbon nanotube/copper composites. Carbon 2013, 61, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, J.; Xiong, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, W. Enhanced strength and excellent transport properties of a superaligned carbon nanotubes reinforced copper matrix laminar composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Shuai, J.; Liu, K.; Hou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, W. Enhanced mechanical and electrical properties of super-aligned carbon nanotubes reinforced copper by severe plastic deformation. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 160, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Da, B.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, L. Simultaneous improvement of electrical conductivity and mechanical property of Cr doped Cu/CNTs composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Cha, S.I.; Gemming, T.; Eckert, J.; Hong, S.H. The Role of Interfacial Oxygen Atoms in the Enhanced Mechanical Properties of Carbon-Nanotube-Reinforced Metal Matrix Nanocomposites. Small 2008, 4, 1936–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Kim, B.-H.; Kim, S.; Han, D.-S.; Kim, G.; Lee, K.-R. Improved binding between copper and carbon nanotubes in a composite using oxygen-containing functional groups. Carbon 2011, 49, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; You, X.; Yi, J.; Fang, D.; Bao, R.; Shen, T.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Li, C. Influence of dispersion state of carbon nanotubes on electrical conductivity of copper matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 752, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Da, B.; Zhao, X.; Ding, F.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, L. Enhanced electrical conductivity and hardness of Copper/Carbon Nanotubes composite by tuning the interface structure. Mater. Lett. 2020, 280, 128564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Li, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X. Enhanced interfacial strength of carbon nanotube/copper nanocomposites via Ni-coating: Molecular-dynamics insights. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostr. 2017, 88, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.I.; Kim, K.T.; Arshad, S.N.; Mo, C.B.; Hong, S.H. Extraordinary Strengthening Effect of Carbon Nanotubes in Metal-Matrix Nanocomposites Processed by Molecular-Level Mixing. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Bao, R.; Yi, J.; Li, C.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Tan, S.; You, X. Interface optimization of CNT/Cu composite by forming TiC na-noprecipitation and low interface energy structure via spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Bao, R.; Li, F.; Li, C.; Yi, J. Interface interaction and synergistic strengthening behavior in pure copper matrix composites reinforced with functionalized carbon nanotube-graphene hybrids. Carbon 2019, 146, 736–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, J.; Xiong, L.-Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.-Z. Effects of ply-orientation on microstructure and properties of super-aligned carbon nanotube reinforced copper laminar composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y. Effect of CNTs content on the microstructures and properties of CNTs/Cu composite by microwave sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 771, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoush, W.; Lim, B.K.; Mo, C.B.; Nam, D.H.; Hong, S.H. Electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced copper nanocomposites fabricated by electroless deposition process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 513–514, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhan, Z.; Quan, L. Study of the preparation and properties of 0.5 vol% Ni-CNTs/Cu nanocomposites with magnetic alignment. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 781, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bai, F.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Compression Properties and Electrical Conductivity of In-Situ 20 vol.% Nano-Sized TiCx/Cu Composites with Different Particle Size and Morphology. Materials 2017, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, L.; Dong, S.; Xiao, A.; Sun, S.; Li, S. Effects of Two Purification Pretreatments on Electroless Copper Coating over Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.-C.; Jeng, Y.-R.; Lee, J.-T.; Stachiv, I.; Sittner, P. Effects of carbon nanotube reinforcement and grain size refinement mechanical properties and wear behaviors of carbon nanotube/copper composites. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 74, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Study on mechanical properties and wear behavior of in-situ synthesized CNTs/CuCrZrY composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Vacuum 2021, 188, 110180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yi, J.; Xia, C.; Yi, Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure characterization of well-dispersed carbon nanotubes reinforced copper matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 727, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula, P.; Aromaa, J.; Wilson, B.P.; Janas, D.; Koziol, K.; Forsén, O.; Lundström, M. Observations of copper deposition on functionalized carbon nanotube films. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bao, R.; Yi, J.; Fang, D. Fabrication of CNT/Cu composites with enhanced strength and ductility by SP combined with optimized SPS method. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, E.; Kitzmantel, M.; Hulman, M.; Angerer, P. Potential and challenges of metal-matrix-composites reinforced with carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Q.-H.; Zhou, G.-H.; Liao, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, L. Interfacial structure in AZ91 alloy composites reinforced by graphene nanosheets. Carbon 2018, 127, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzumaki, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Ichinose, H.; Ito, K. Processing of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Aluminum Composite. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh-Aghdam, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Ansari, R. A comprehensive predicting model for thermomechanical properties of particulate metal matrix nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 739, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpour, M.; Farvizi, M.; Lee, D.; Rezaei, H.; Kim, H. Effect of high-pressure torsion on the microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of hot-consolidated Cu–CNT nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 638, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shen, J.; Ye, X.; Imai, H.; Umeda, J.; Takahashi, M.; Kondoh, K. Solid-state interfacial reaction and load transfer efficiency in carbon nanotubes (CNTs)-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Carbon 2017, 114, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C. Enhanced strength in reduced graphene oxide/nickel composites prepared by molecular-level mixing for structural applications. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 118, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.-B.; Wang, X.-H.; Huang, D.-J.; Zhang, H. Interface structure and strengthening behavior of graphene/CuCr composites. Carbon 2018, 133, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocks, U.; Mecking, H. Physics and phenomenology of strain hardening: The FCC case. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2003, 48, 171–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Wang, F.-C.; Li, S.-L.; Korznikov, E.; Zhao, X.-C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.-F.; Kang, Z. Synergistic strengthening effect of nanocrystalline copper reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maqbool, A.; Hussain, M.A.; Khalid, F.A.; Bakhsh, N.; Hussain, A.; Kim, M.H. Mechanical characterization of copper coated carbon nanotubes reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Charact. 2013, 86, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Song, M.; Yi, J.; Ni, S.; Shen, T.; Du, Y. Improving the mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced pure alu-minum matrix composites by achieving non-equilibrium interface. Mater. Design 2017, 120, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpour, M.; Salahi, E.; Hesari, F.A.; Simchi, A.; Kim, H. Fabrication, characterization and mechanical properties of hybrid composites of copper using the nanoparticulates of SiC and carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 572, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Weng, L.; Zhu, H.; Fan, T.; Zhang, D. Simultaneously enhancing the strength, ductility and conductivity of copper matrix composites with graphene nanoribbons. Carbon 2017, 118, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, R.E.; Zinkle, S.J. On the relationship between uniaxial yield strength and resolved shear stress in polycrystalline mate-rials. J. Nucl. Mater. 2000, 283, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Geng, L. Effect of heat treatment on interfacial bonding and strengthening efficiency of graphene in GNP/Al composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Park, J.; Keum, D.H.; Lee, Y.H. Strengthening mechanisms in carbon nanotube-reinforced aluminum composites. Carbon 2015, 95, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirasu, K.; Yamamoto, G.; Tamaki, I.; Ogasawara, T.; Shimamura, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Hashida, T. Negative axial thermal expansion coefficient of carbon nanotubes: Experimental determination based on measurements of coefficient of thermal expansion for aligned carbon nanotube reinforced epoxy composites. Carbon 2015, 95, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korb, G.; Koráb, J.; Groboth, G. Thermal expansion behaviour of unidirectional carbon-fibre-reinforced copper-matrix compo-sites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1998, 29, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Young, R.; Kinloch, I.A.; Sun, R.; Zhang, G.; Noé, L.; Monthioux, M. Coefficient of thermal expansion of carbon nanotubes measured by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 051907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Ren, S.; He, X.; Qu, X. Properties and microstructure of nickel-coated graphite flakes/copper composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Carbon 2017, 121, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Pan, B.; Pan, D.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S.; Jia, L.; Kondoh, K. A novel strengthening effect of in-situ nano Al2O3w on CNTs reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites and the matched strengthening mechanisms. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Lu, L.; Suresh, S. Strengthening Materials by Engineering Coherent Internal Boundaries at the Nanoscale. Science 2009, 324, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savvas, D.; Stefanou, G.; Papadopoulos, V.; Papadrakakis, M. Effect of waviness and orientation of carbon nanotubes on random apparent material properties and RVE size of CNT reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2016, 152, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Jia, C.-C.; Li, W.-S. Thermal conductivity enhancement in carbon nanotube/Cu–Ti composites. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 110, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Anderson, I.; Riedemann, T.; Russell, A. Modeling the electrical resistivity of deformation processed metal–metal composites. Acta Mater. 2014, 77, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Q.; Petranovic, D.; Krishnan, S.; Cassell, A.; Ye, Q.; Li, J.; Meyyappan, M.; Yang, C. Electron Transport Through Metal–Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2004, 3, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, L.; Lasserre, F.; Gachot, C.; Grützmacher, P.; MacLucas, T.; Souza, N.; Mücklich, F.; Suarez, S. Long-lasting solid lubrication by CNT-coated patterned surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milowska, K.Z.; Ghorbani-Asl, M.; Burda, M.; Wolanicka, L.; Ćatić, N.; Bristowe, P.D.; Koziol, K.K.K. Breaking the electrical barrier between copper and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8458–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhart, F. Interactions between metals and carbon nanotubes: At the interface between old and new materials. Nanoscale 2009, 1, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purewal, M.S.; Hong, B.H.; Ravi, A.; Chandra, B.; Hone, J.; Kim, P. Scaling of Resistance and Electron Mean Free Path of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 186808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Qu, J.; Yao, M. Electrical resistance at carbon nanotube/copper interfaces: Capped versus open-end carbon nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2012, 82, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formula (g/L) | NiSO4 ·6H2O | 40 |
| C6H5Na3O7 | 60 | |
| NaH2PO2 | 20 | |
| NH4Cl | 35 | |
| Activated MWCNTs | 0.6 | |
| Condition | Temperature (°C) | 20 |
| pH | 8.0 |
| Formula (g/L) | CuSO4·5H2O | 7.5 |
| C2H2O3 (50%) | 27.5 | |
| EDTANa2·2H2O | 89.4 | |
| 2,2′-Dipyridyl | 0.01 | |
| Activated MWCNTs | 0.6 | |
| Condition | Temperature (°C) | 20 |
| pH | 11.5 |
| Formula (g/L) | CuSO4·5H2O | 7.5 |
| NiSO4·6H2O | 0.75 | |
| NaH2PO2 | 0.375 | |
| C2H2O3 | 27.5 | |
| EDTANa2·2H2O | 89.4 | |
| 2,2′-Dipyridyl | 0.01 | |
| Activated MWCNTs | 0.6 | |
| Condition | Temperature (°C) | 20 |
| pH | 11.5 |
| Cu | B-CNTs/Cu Composite | Cu@CNTs/Cu Composite | Ni&Cu@CNTs/Cu Composite | Ni @CNTs/Cu Composite | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTS (MPa) | 259 | 264 | 332 | 373 | 391 | |
| YS (MPa) | 231 | 250 | 309 | 316 | 358 | |
| Elongation (%) | 18.5 | 16.2 | 12.1 | 9.50 | 7.50 | |
| UCS (MPa) | F∥ | 356 | 397 | 422 | 451 | 473 |
| F⊥ | 352 | 385 | 396 | 413 | 430 | |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | C∥ | 386 | 379 | 376 | 358 | 354 |
| C⊥ | 384 | 340 | 328 | 312 | 301 | |
| Electrical Conductivity (IACS%) | C∥ | 90.1 | 81.4 | 79.9 | 76.1 | 75.2 |
| C⊥ | 89.9 | 72.1 | 70.8 | 65.5 | 63.7 | |
| Materials | Average Grain Sizes (μm) | Low-Angle GBs (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cu | 3.21 (±1.1) | 41 |
| B-CNTs/Cu composite | 3.01 (±0.95) | 49 |
| Cu@CNTs/Cu composite | 2.37 (±1.01) | 54 |
| Cu&Ni@CNTs/Cu composite | 2.21 (±0.97) | 57 |
| Ni@CNTs/Cu composite | 2.09 (±0.9) | 61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z.; Yang, A.; Tao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Xue, H. Mechanical and Conductive Properties of Cu Matrix Composites Reinforced by Oriented Carbon Nanotubes with Different Coatings. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020266
Zheng Z, Yang A, Tao J, Li J, Zhang W, Li X, Xue H. Mechanical and Conductive Properties of Cu Matrix Composites Reinforced by Oriented Carbon Nanotubes with Different Coatings. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(2):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020266
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zhong, Anxin Yang, Jiafeng Tao, Jing Li, Wenqian Zhang, Xiuhong Li, and Huan Xue. 2022. "Mechanical and Conductive Properties of Cu Matrix Composites Reinforced by Oriented Carbon Nanotubes with Different Coatings" Nanomaterials 12, no. 2: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020266
APA StyleZheng, Z., Yang, A., Tao, J., Li, J., Zhang, W., Li, X., & Xue, H. (2022). Mechanical and Conductive Properties of Cu Matrix Composites Reinforced by Oriented Carbon Nanotubes with Different Coatings. Nanomaterials, 12(2), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020266






