Bio-Fabrication of Bio-Inspired Silica Nanomaterials from Orange Peels in Combating Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Collection of Orange Peel and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Orange Peel Extract
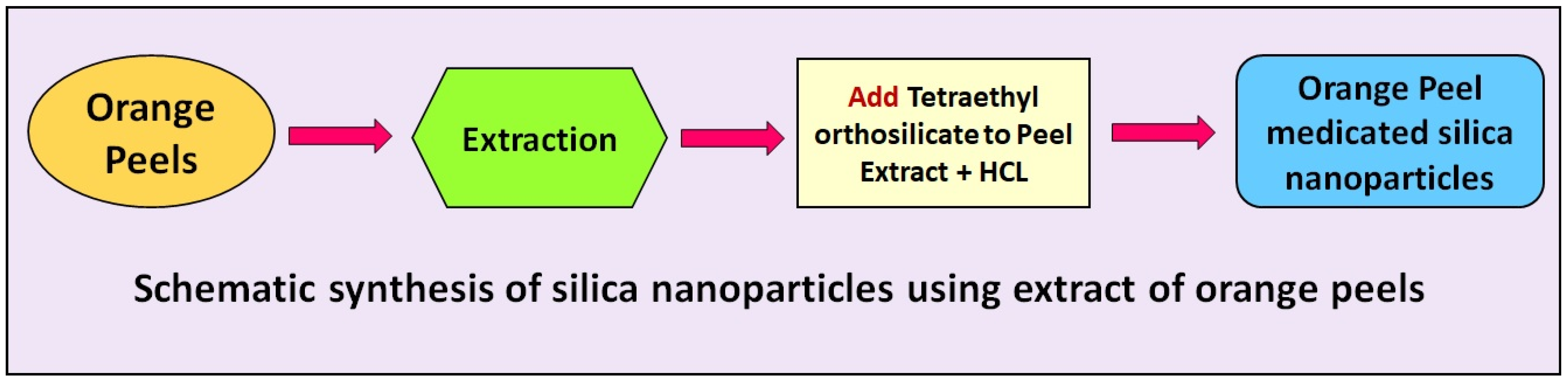
2.3. Biogenic Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles
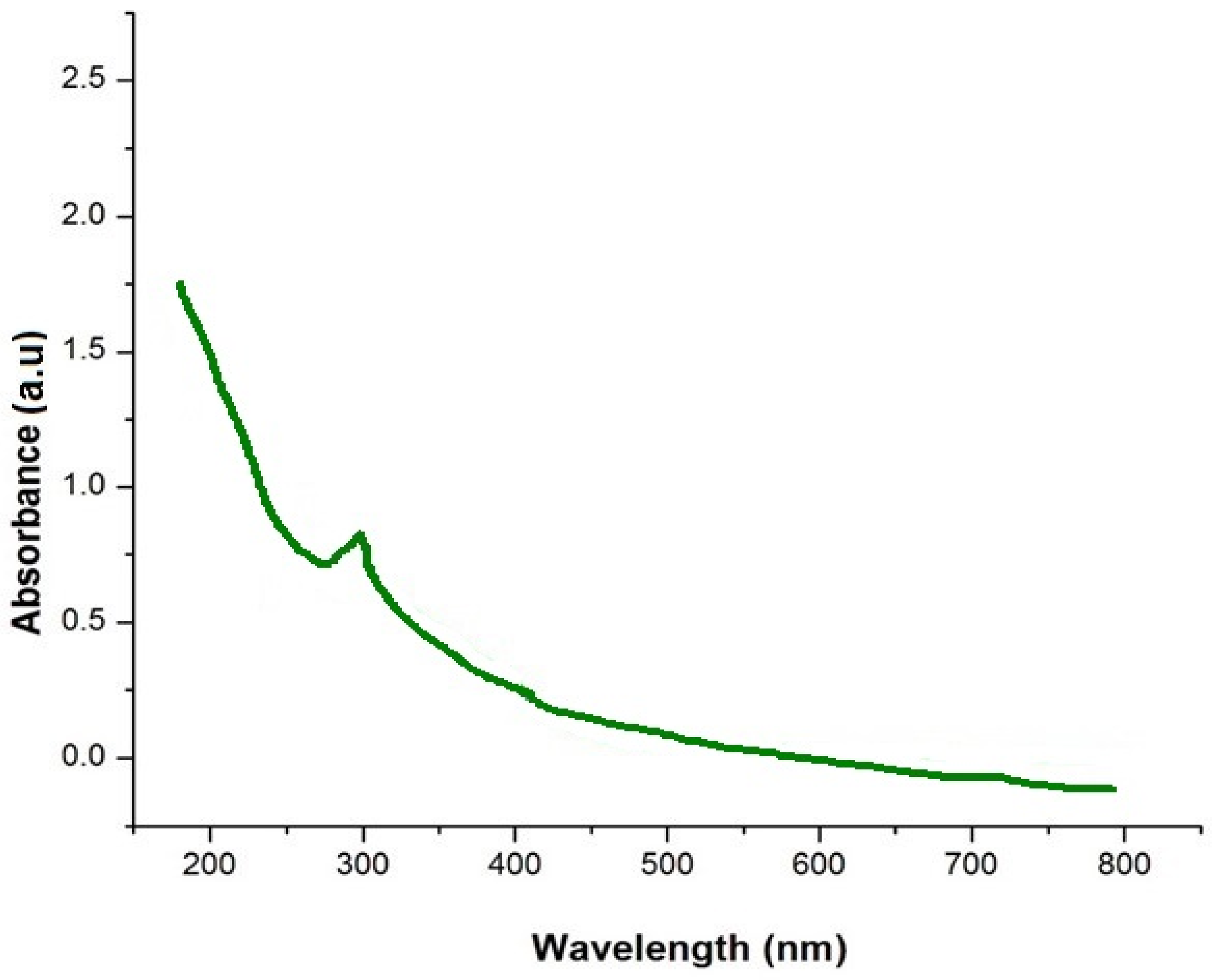
2.4. Analysis of Optical Property and Functional Groups
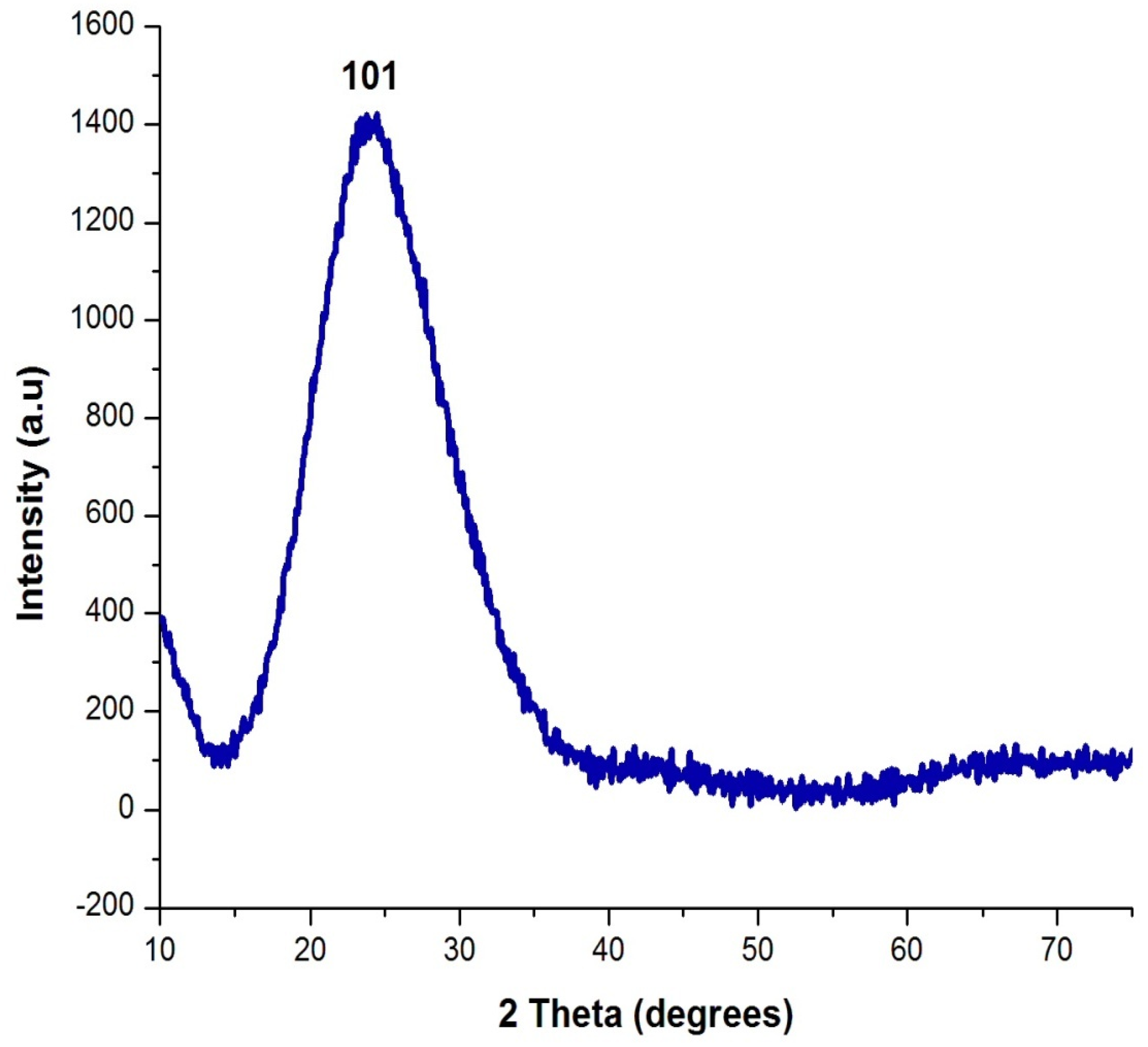
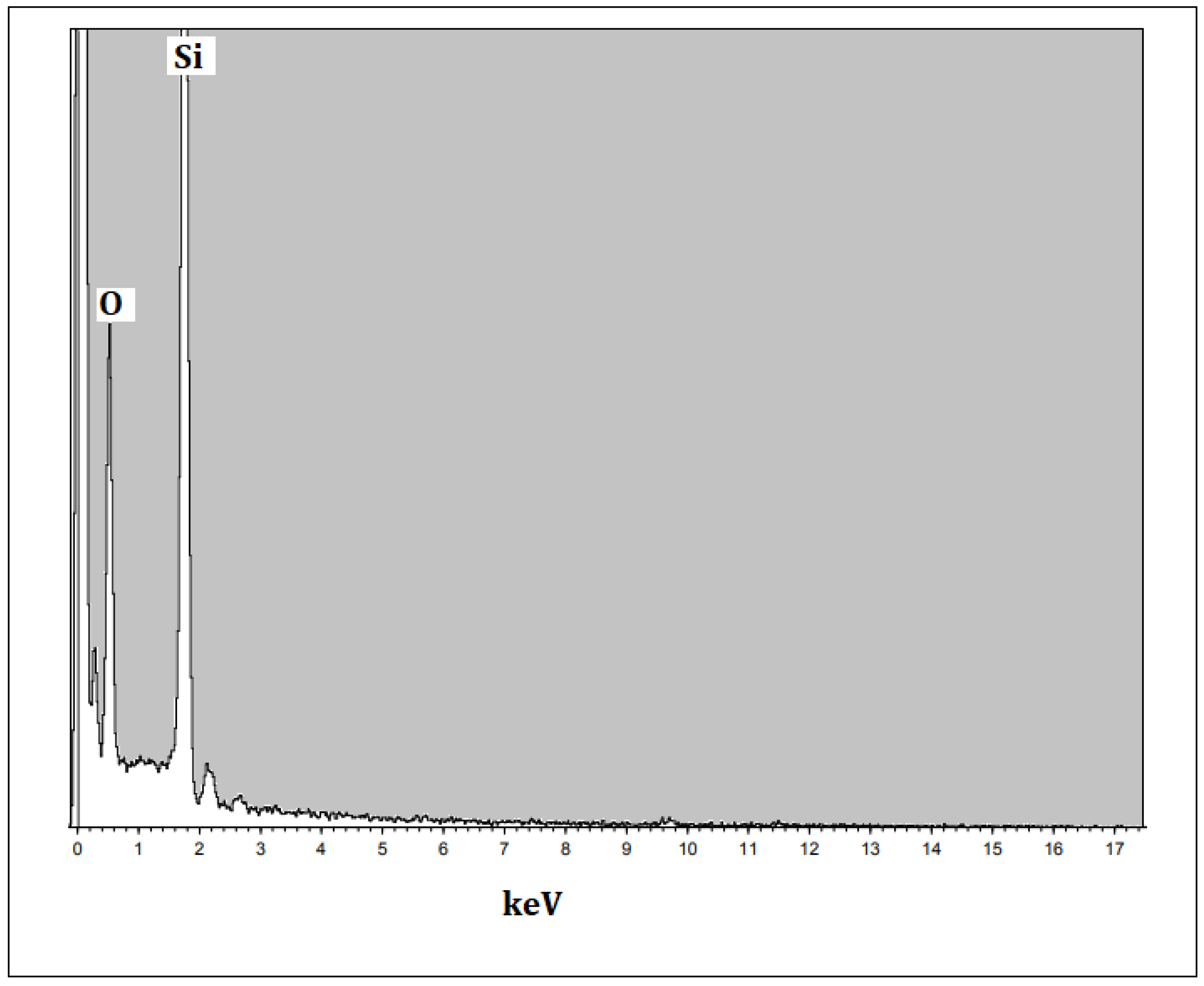
2.5. Analysis of Shape, Elemental Composition and Nature of Silica Nanoparticles
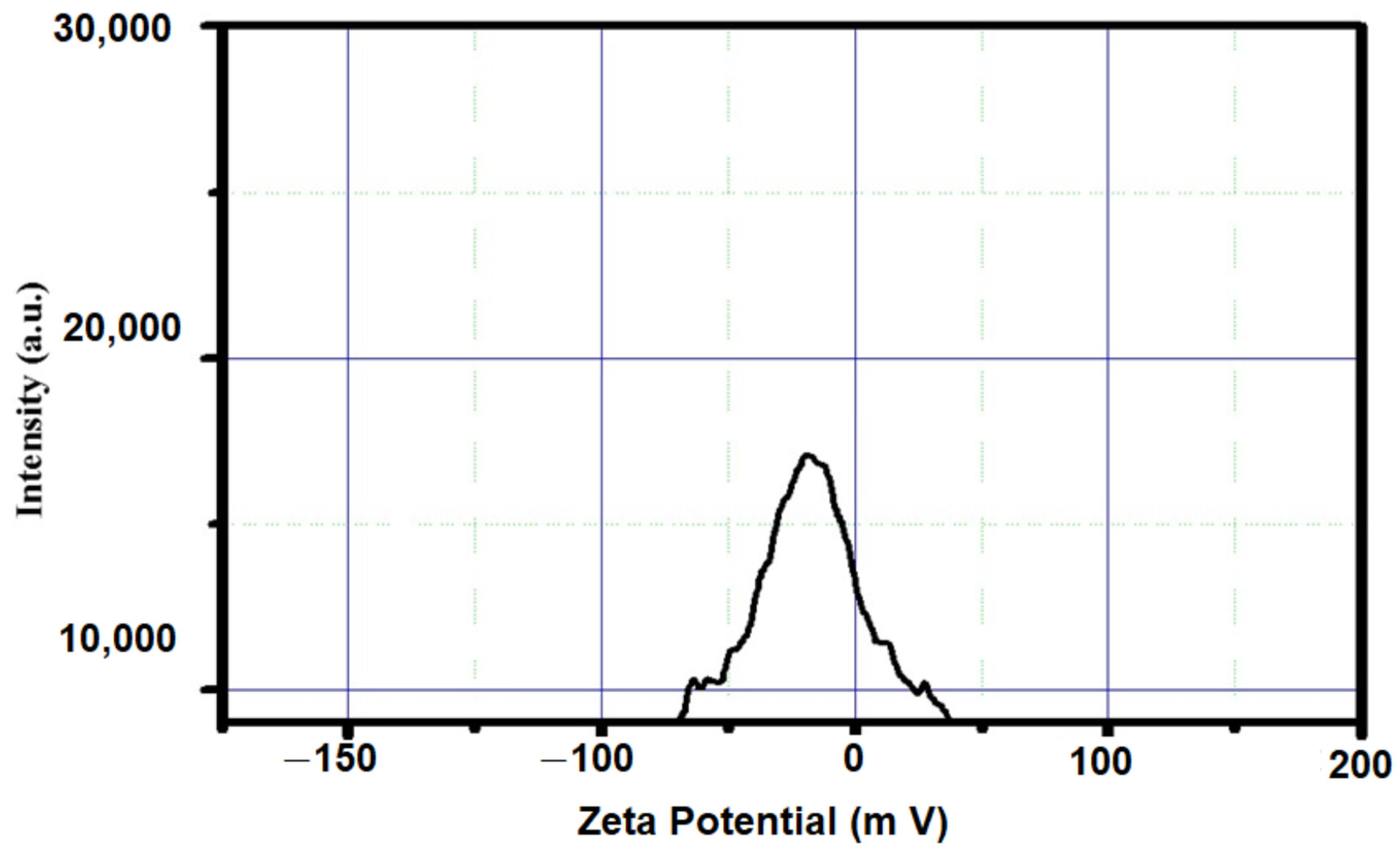
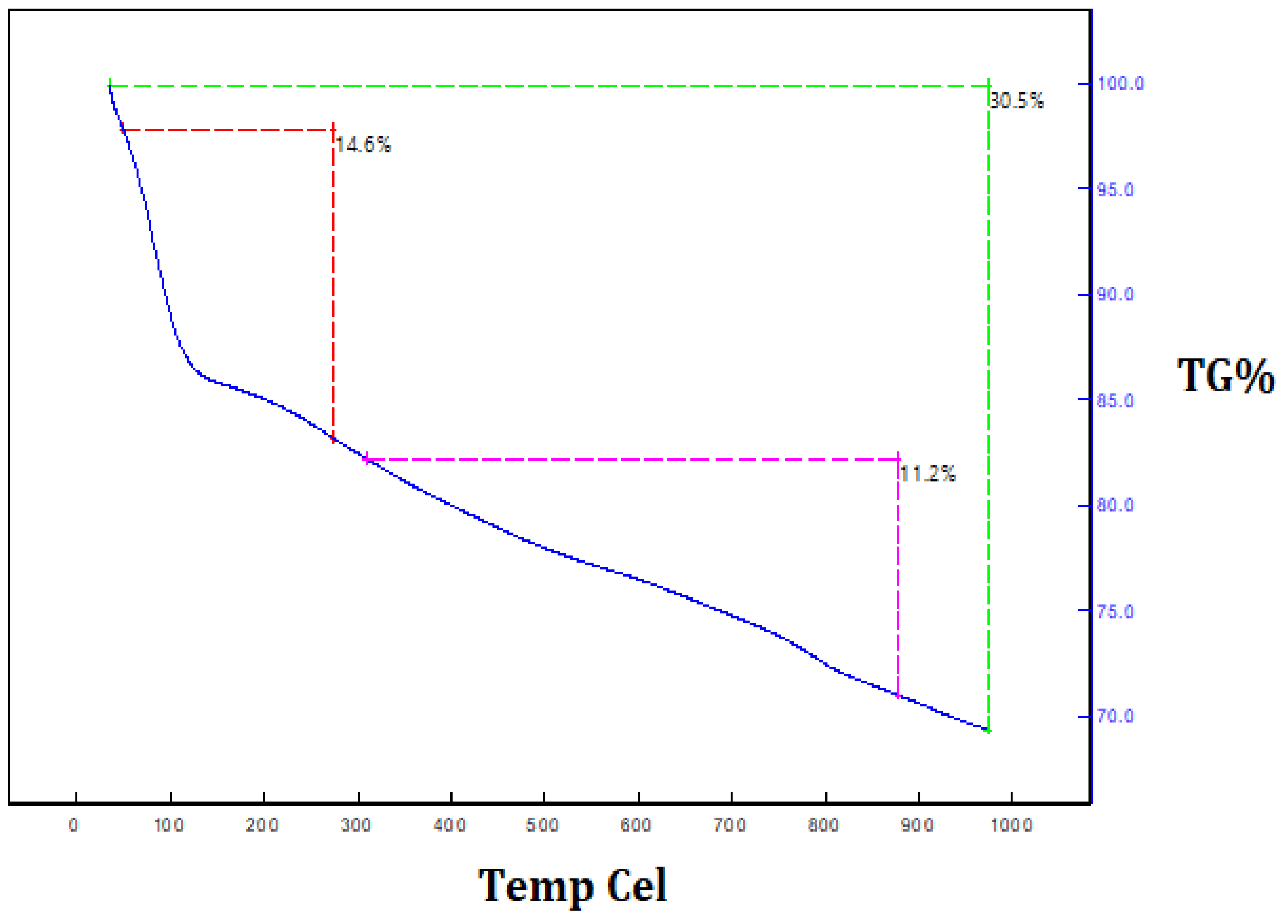
2.6. Zeta Potential and Thermal Stability Analysis
2.7. Antioxidant Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Silica Nanoparticles
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, I.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G. Green synthesis of nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.; Tripathy, S.K.; Poinern, G.E.J. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials 2015, 8, 7278–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: An overview. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 344–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles. A review. Silicon 2020, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.S.; El-Hami, K.; Kodaki, T.; Matsushige, K.; Makino, K. A novel method for synthesis of silica nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 289, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Che, E.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and clearance of silicon, organosilica, silsesquioxane, silica mixed oxide, and mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahrilas, G.A.; Wally, L.M.; Fredrick, S.J.; Hiskey, M.; Prieto, A.L.; Owens, J.E. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using orange peel extract. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.Á.; Ballester, A. Biosynthesis of silver and platinum nanoparticles using orange peel extract: Characterisation and applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A. Cadmium removal and recovery from aqueous solutions by novel adsorbents prepared from orange peel and Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanulla, A.M.; Sundaram, R.J.M.T.P. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using orange peel extract for antibacterial, cytotoxicity and humidity sensor applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 8, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.S.; Aziz, M.H.; Fatima, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Idrees, M.; Rana, S.; Shaheen, F.; Ahmed, A.; Javed, M.Q.; Huang, Q. Green synthesis, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of CeO2 nanoparticles mediated via orange peel extract (OPE). Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0950a4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, A.M.; Cortés, S.; Salgado, J.M.; Max, B.; Rodríguez, N.; Bibbins, B.P.; Converti, A.; Domínguez, J.M. Citric acid production from orange peel wastes by solid-state fermentation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, C.H.N.; Cruz, G.C.F.; Mayrink, W.; Tasic, L. Bio-based synthesis of silver nanoparticles from orange waste: Effects of distinct biomolecule coatings on size, mor-phology, and antimicrobial activity. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2018, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Nhi, T.T.Y.; Van Nhi, N.T.; Cuc, T.T.T.; Tuan, P.M.; Nguyen, D.H. Comparative Study of the Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis Ability and Antibacterial Activity of the Piper betle L.; Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Extracts. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 5518389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Bhattacharya, A. Analysis on synthesis of silica nanoparticles and its effect on growth of T. harzianum & Rhizoctonia species. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 10, 7890–7897. [Google Scholar]
- Niluxsshun, M.C.D.; Masilamani, K.; Mathiventhan, U. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the extracts of fruit peel of Citrus tangerina, Citrus sinensis, and Citrus limon for antibacterial activities. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2021, 2021, 6695734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, R.; Nesaraj, A.S. Effect of surfactants on the wet chemical synthesis of silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Appl. Sci. 2014, 12, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Azawi, M.T.; Hadi, S.M.; Mohammed, C.H. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles via green approach by using hot aqueous extract of and their effect on biofilm formation. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 50, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, N.N.A.; Saeed, M.A.; Hashim, I.H. Thermoluminescence (TL) response of silica nanoparticles subjected to 50 Gy gamma irradiation. Malays J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2017, 13, 178–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pieła, A.; Żymańczyk-Duda, E.; Brzezińska-Rodak, M.; Duda, M.; Grzesiak, J.; Saeid, A.; Mironiuk, M.; Klimek-Ochab, M. Biogenic synthesis of silica nanoparticles from corn cobs husks. Dependence of the productivity on the method of raw material processing. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, R.H.; Yugandhar, P.; Savithramma, N. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of bio silica nanoparticles prepared from Cynodon dactylon L.: A green approach. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2018, 41, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Maroušková, A.; Periakaruppan, R.; Gokul, G.M.; Anbukumaran, A.; Bohatá, A.; Kříž, P.; Bárta, J.; Černý, P.; Olšan, P. Silica Nanoparticles from Coir Pith Synthesized by Acidic Sol-Gel Method Improve Germination Economics. Polymers 2022, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Su, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D.; Cheng, L.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F. Characterization and antioxidant properties of chitosan film incorporated with modified silica nanoparticles as an active food packaging. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S.No. | Concentration of Orange-Peel-Mediated Silica Nanoparticles (µg/mL) | Free Radical Scavenging Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 22.5 ± 0.12 |
| 2 | 100 | 36.7 ± 0.28 |
| 3 | 200 | 65.35 ± 0.32 |
| 4 | 500 | 90.72 ± 0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abomughaid, M.M. Bio-Fabrication of Bio-Inspired Silica Nanomaterials from Orange Peels in Combating Oxidative Stress. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183236
Abomughaid MM. Bio-Fabrication of Bio-Inspired Silica Nanomaterials from Orange Peels in Combating Oxidative Stress. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183236
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbomughaid, Mosleh Mohammad. 2022. "Bio-Fabrication of Bio-Inspired Silica Nanomaterials from Orange Peels in Combating Oxidative Stress" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183236
APA StyleAbomughaid, M. M. (2022). Bio-Fabrication of Bio-Inspired Silica Nanomaterials from Orange Peels in Combating Oxidative Stress. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183236








