Biomedical and Textile Applications of Alternanthera sessilis Leaf Extract Mediated Synthesis of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Pathogenic Strains
2.2. Isolation and Screening
2.3. Floral Collections
2.4. AS-AgNPs Synthesis (A. sessilis Mediated Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis)
2.5. Antibacterial Activity
2.6. Embedding Synthesized As-AgNPs to Fabrics
Fabric Sensitivity Test
2.7. Conformational Study of AS-AgNPs Coated on Fabrics
2.7.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
2.7.2. FTIR
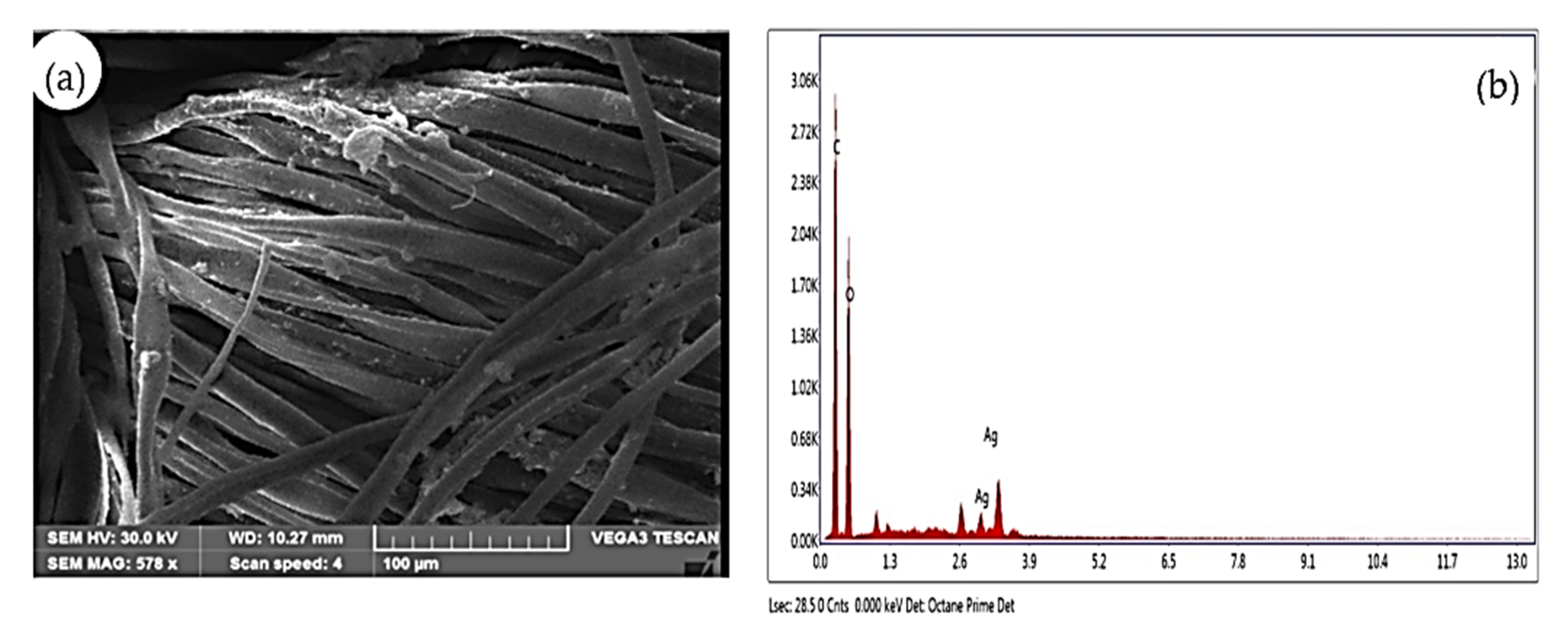
2.7.3. SEM with EDAX (Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis)
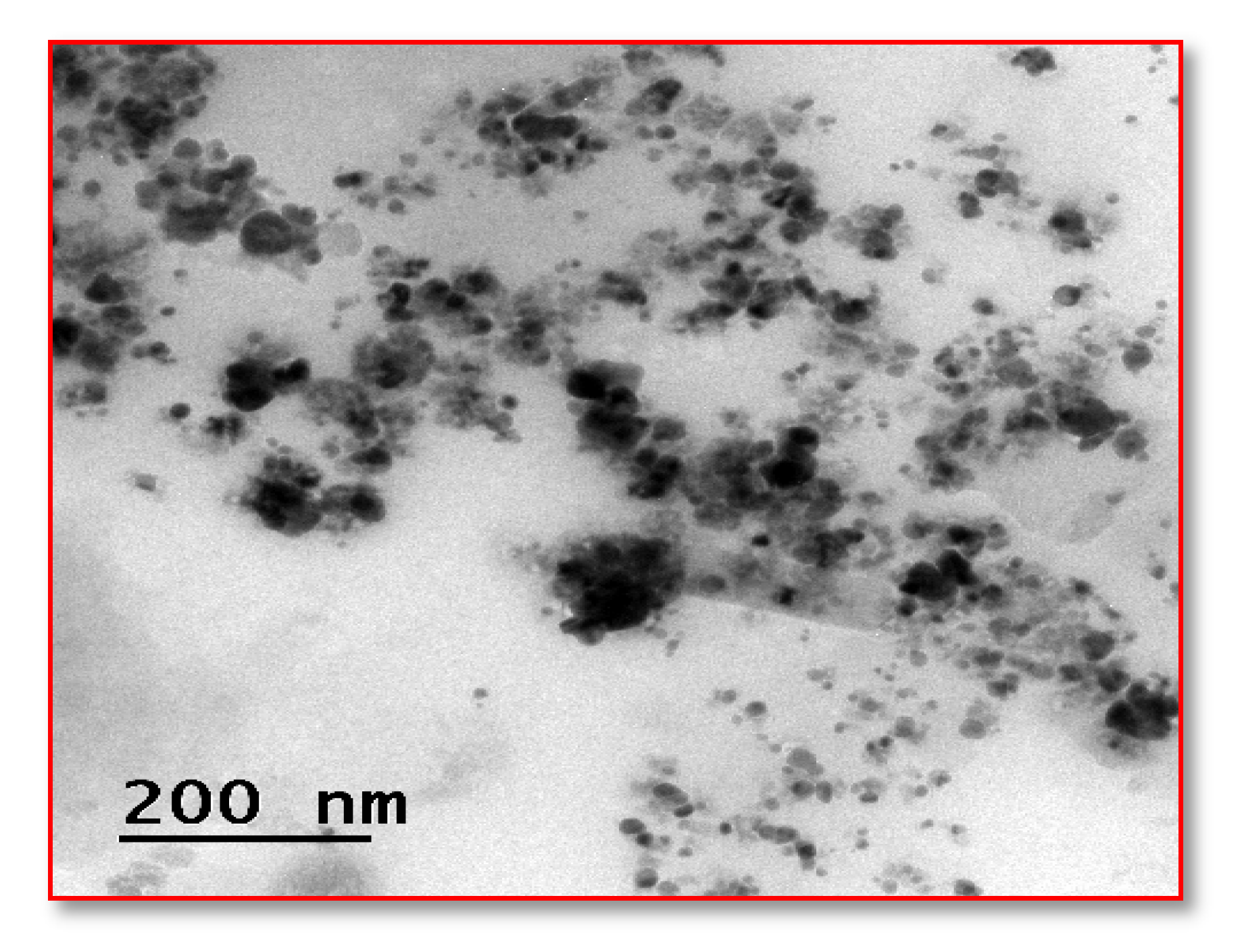
2.7.4. HR-TEM
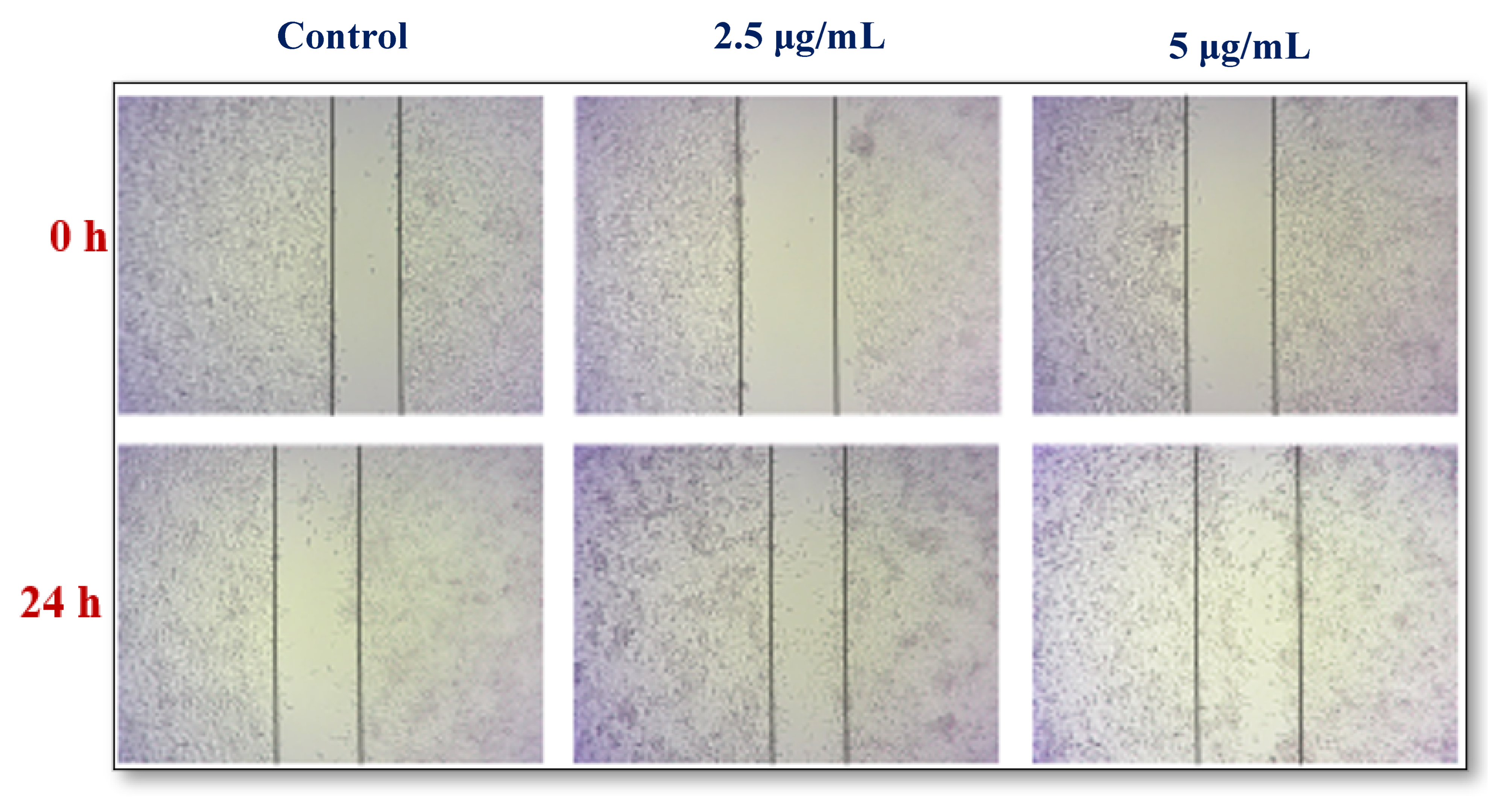
2.7.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.7.6. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolated Strains
3.2. AS-AgNPs Synthesis
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
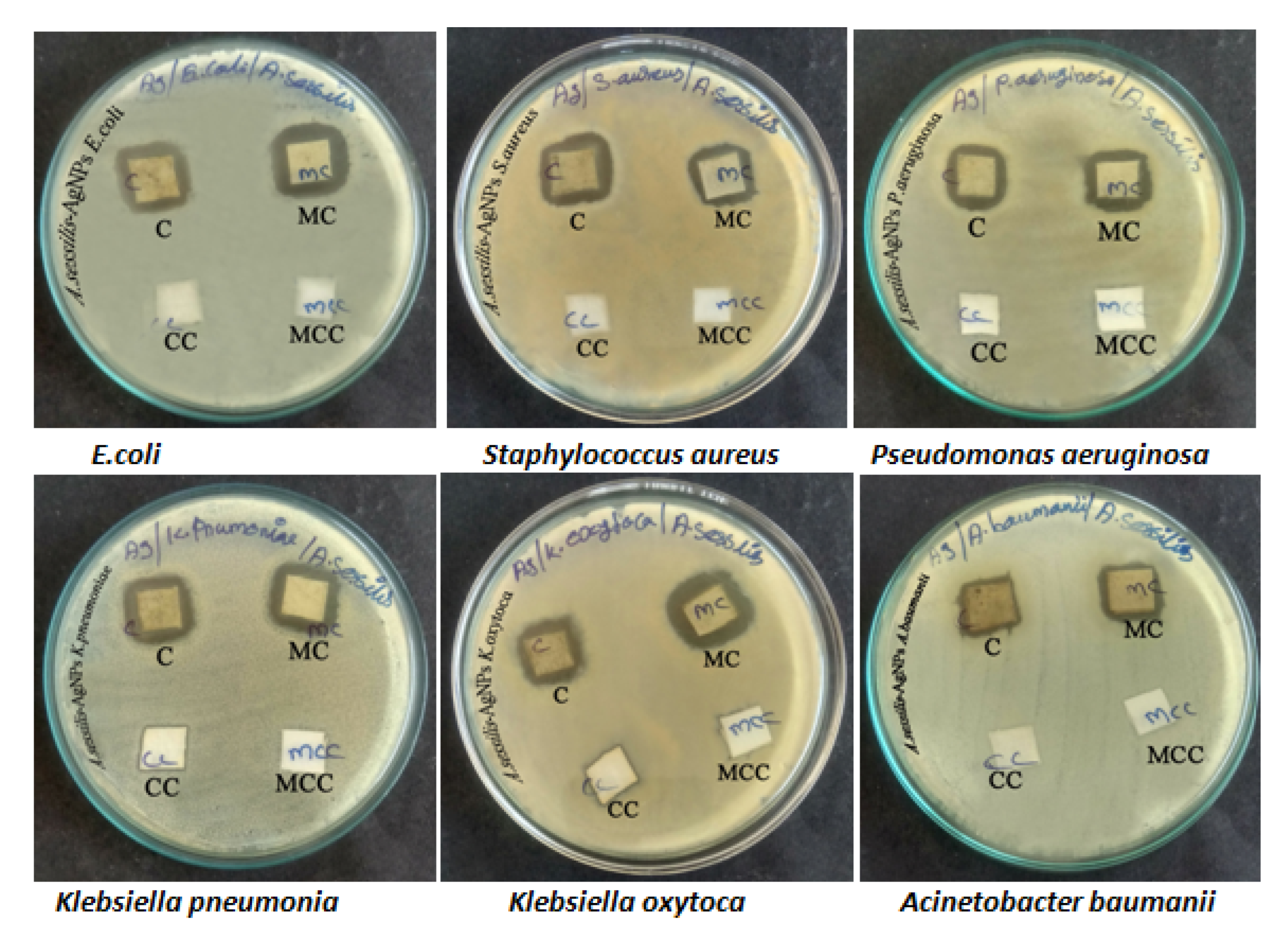
3.4. Fabric Sensitivity Test
3.5. Conformational Study of AS-AgNPs Coated on Fabrics
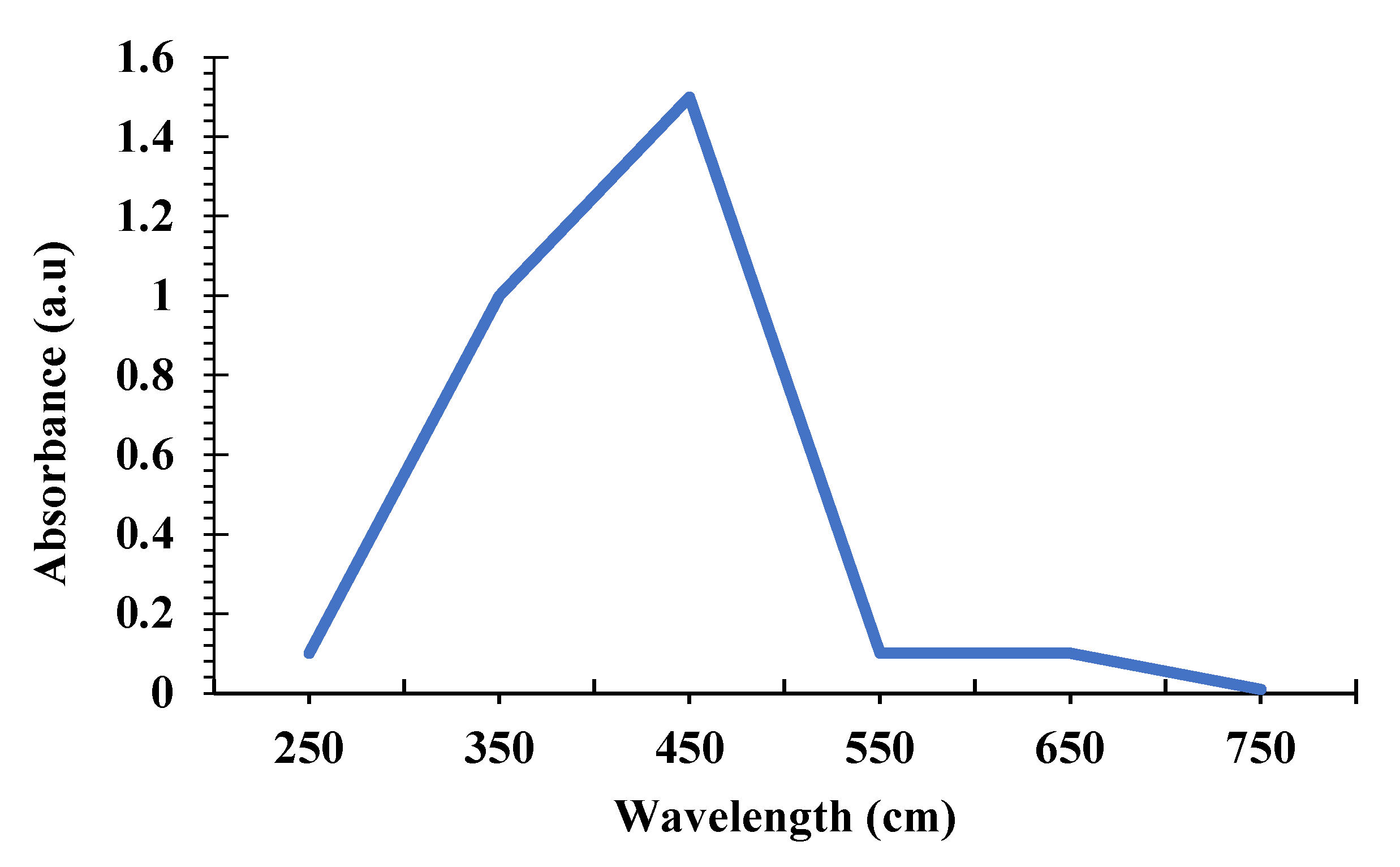
3.5.1. UV-Visible Spectrum
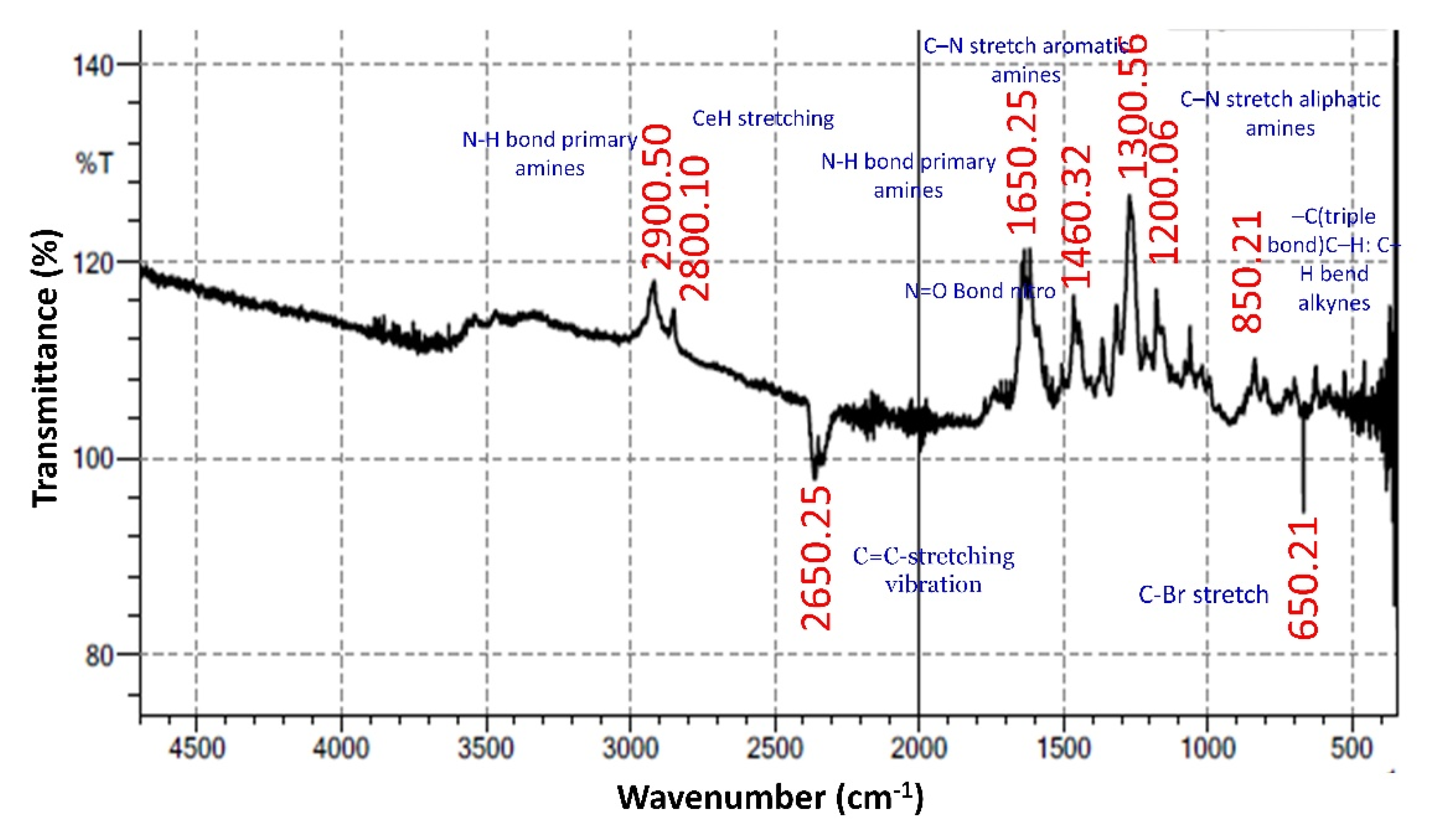
3.5.2. FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy)
3.5.3. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDAX)
3.5.4. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HR-TEM)
3.5.5. MTT Cell Viability Assay
3.5.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Shmgani, H.S.A.; Mohammed, W.H.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Saadoon, A.H. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus leaf extract and assessing their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and wound-healing activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghimaa, M.; Alharbi, S.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Curcuma longa L. and coating on the cotton fabrics for antimicrobial applications and wound healing activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 204, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Sajankila, S.P.; Rao, C.V.; Hegde, A.R.; Mutalik, S. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Jatropha curcas seed cake extract and characterization: Evaluation of its antibacterial activity. Energy Sources Part A 2021, 43, 3415–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, T.R.; Parvathy, S.; Veettil, M.V.; Rosemary, J.; Ansalna, T.H.; Shahzabanu, M.M.; Devika, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Aloe vera leaf extract and its antimicrobial activity. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 3956–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraimathi, K.L.; Sudha, V.; Lavanya, R.; Brindha, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alternanthera sessilis (Linn.) extract and their antimicrobial, antioxidant activities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, S.; Govada, V.R.; Anantha, R.K.; Verma, M.K. An Investigation into phytochemical constituents, antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-cataract activity of Alternanthera sessilis, a predominant wild leafy vegetable of South India. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunmathi, D.; Sivakumar, R.; Ravikumar, K. In vitro Anti-inflammatory and antiarthritic activity of ethanolic leaf extract of Alternanthera sessilis (L.) R. BR. ex DC and Alternanthera philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2016, 5, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M. Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing Application: Progress and Future Trends. Materials 2019, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniandy, K.; Gothai, S.; Tan, W.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Esa, N.M.; Chandramohan, G.; Al-Numair, K.S.; Arulselvan, P. In vitro wound healing potential of stem extract of Alternanthera sessilis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 3142073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtz, N.; Penant, G.; Jardot, P.; Duclos, N.; La Scola, B. Culture of SARS-CoV-2 in a panel of laboratory cell lines, permissivity, and differences in growth profile. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakayil, R.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Anbazhagan, M.; Kumar, N.; Mathanmohun, M. Antibacterial Potential of Acorus Calamus Extracts Against the Multi-Drug Resistant Nosocomial Pathogens. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2021, 24, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kabeerdass, N.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Anbazhagan, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Nachimuthu, S.; Rajendran, M.; Mathanmohun, M. Screening, detection and antimicrobial susceptibility of multi-drug resistant pathogens from the clinical specimens. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburam, S.; Ramasamy, S.; Shanmugam, G.; Mathanmohun, M. Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Potential and Molecular Docking Studies of Phyllanthus emblica Phytochemicals Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakayil, R.; Nazeer, T.A.; Mathanmohun, M. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Extracts from Acorus calamus Rhizome against Multidrug-resistant Nosocomial Pathogens. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 12, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Nikparast, Y.; Saliani, M. Synergistic Effect between Phyto-Syntesized Silver Nanoparticles and Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic on some Pathogenic Bacterial Strains. J. Med. Bacteriol. 2018, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Vanlalveni, C.; Lallianrawna, S.; Biswas, A.; Selvaraj, M.; Changmai, B.; Rokhum, S.L. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts and their antimicrobial activities: A review of recent literature. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2804–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdhouse, M.J.; Lalitha, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the extract of Alternanthera sessilis—antiproliferative effect against prostate cancer cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakshayani, S.S.; Marulasiddeshwara, M.B.; Kumar, S.; Golla, R.; Devaraja, S.R.H.K.; Hosamani, R. Antimicrobial, anticoagulant and antiplatelet activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Selaginella (Sanjeevini) plant extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 787–797. [Google Scholar]
- Vakayil, R.; Muruganantham, S.; Kabeerdass, N.; Rajendran, M.; Ramasamy, S.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Almoallim, H.S.; Manikandan, V.; Mathanmohun, M. Acorus calamus-zinc oxide nanoparticle coated cotton fabrics shows antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities against skin cancer cells. Process Biochem. 2021, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeerdass, N.; Al Otaibi, A.; Rajendran, M.; Manikandan, A.; Kashmery, H.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Madhu, P.; Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Mathanmohun, M. Bacillus-Mediated Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis and Its Antagonistic Activity against Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczuk, D.; Pitucha, M. Application of FTIR method for the assessment of immobilization of active substances in the matrix of biomedical materials. Materials 2019, 12, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Femi-Adepoju, A.G.; Dada, A.O.; Otun, K.O.; Adepoju, A.O.; Fatoba, O.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using terrestrial fern (Gleichenia Pectinata (Willd.) C. Presl.): Characterization and antimicrobial studies. Heliyon 2019, 5, e0154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.J.; Shameli, K.; Sazili, A.Q.; Selamat, J.; Kumari, S. Rapid green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles arbitrated by curcumin in an alkaline medium. Molecules 2019, 24, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakayil, R.; Anbazhagan, M.; Shanmugam, G.; Ramasamy, S.; Mathanmohun, M. Molecular docking and in vitro analysis of phytoextracts from B. serrata for antibacterial activities. Bioinformation 2021, 17, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdhouse, J.; Lalitha, P. Apoptotic efficacy of biogenic silver nanoparticles on human breast cancer MCF-7 cell lines. Prog. Biomater. 2015, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Selvaraj, R. Green synthesis, structural characterization, and catalytic activity of silver nanoparticles stabilized with Bridelia retusa leaf extract. Green Process. Synth. 2018, 7, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, B.; Tafvizi, F.; Bostanabad, S.Z. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia turcomanica leaf extract and the study of anti-cancer effect and apoptosis induction on gastric cancer cell line (AGS). Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.A.; Yousuf, R.I.; Shoaib, M.H.; Asghar, M.A. Antibacterial, anticoagulant and cytotoxic evaluation of biocompatible nanocomposite of chitosan loaded green synthesized bioinspired silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ho, W.; Zhang, X.; Bertrand, N.; Farokhzad, O. Cancer nanomedicine: From targeted delivery to combination therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
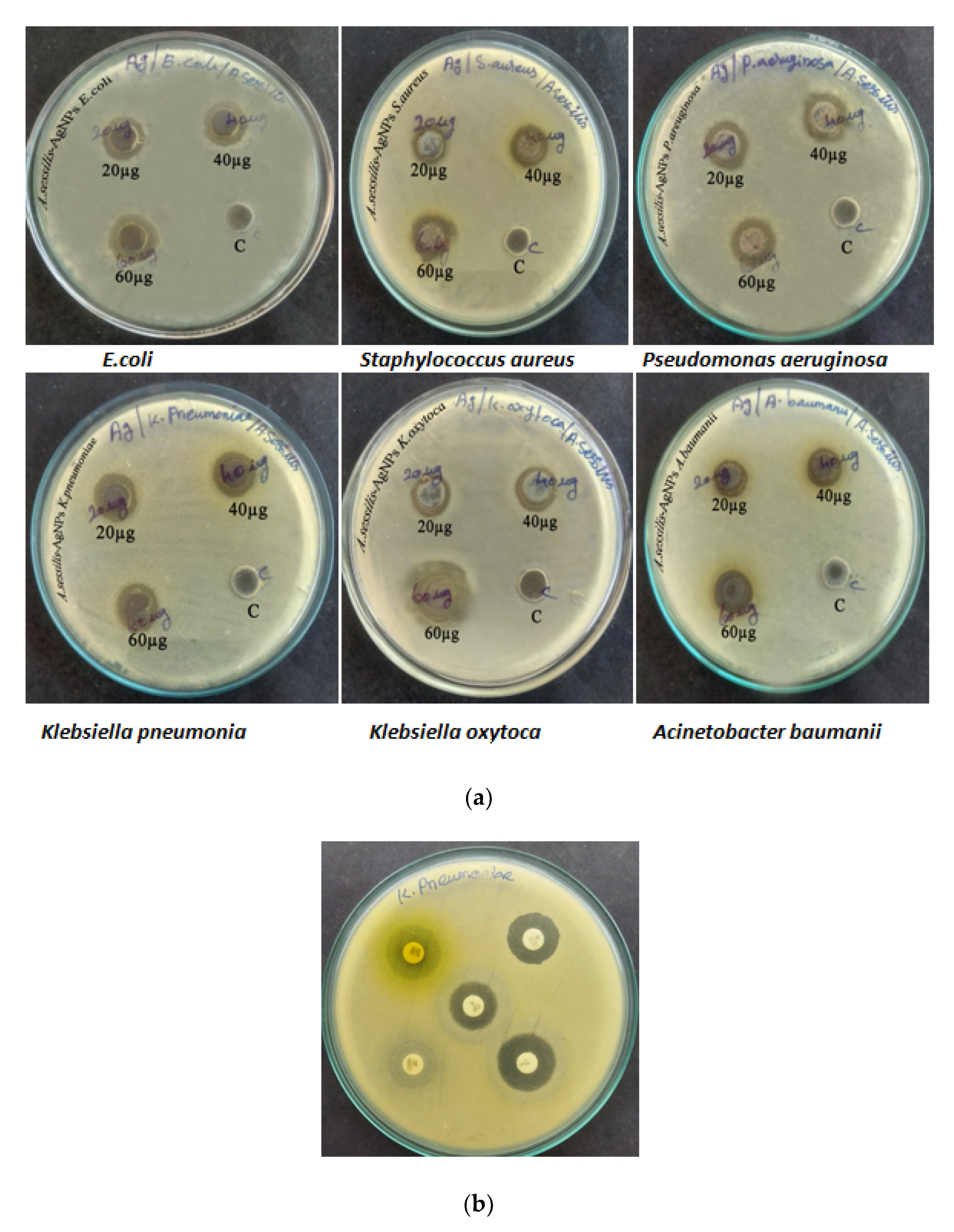

| S. No | Name of the Organism | Zone Diameter (20 µg/mL) | Zone Diameter (40 µg/mL) | Zone Diameter (60 µg/mL) | Zone Diameter (Clarithromycin CLR 15 µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Escherichia coli | 8 mm | 10 mm | 12 mm | 19 mm |
| 2. | Staphylococcus aureus | 6 mm | 9 mm | 11 mm | 18 mm |
| 3. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 4 mm | 6 mm | 9 mm | 28 mm |
| 4. | Klebsiella pneumoniae | 9 mm | 10 mm | 12 mm | 17 mm |
| 5. | Klebsiella oxytoca | 10 mm | 11 mm | 13 mm | 19 mm |
| 6. | Acinetobacter baumanii | 11 mm | 12 mm | 13 mm | 6 mm |
| S.No. | Name of the Organism | Cotton Fabrics | Mixed Cotton Fabrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | E. coli | 09 mm | 13 mm |
| 2. | Staphylococcus aureus | 10 mm | 10 mm |
| 3. | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 09 mm | 11 mm |
| 4. | Klebsiella pneumoniae | 08 mm | 12 mm |
| 5. | Klebsiella oxytoca | 08 mm | 10 mm |
| 6. | Acinetobacter baumanii | 06 mm | 08 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabeerdass, N.; Murugesan, K.; Arumugam, N.; Almansour, A.I.; Kumar, R.S.; Djearamane, S.; Kumaravel, A.K.; Velmurugan, P.; Mohanavel, V.; Kumar, S.S.; et al. Biomedical and Textile Applications of Alternanthera sessilis Leaf Extract Mediated Synthesis of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticle. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162759
Kabeerdass N, Murugesan K, Arumugam N, Almansour AI, Kumar RS, Djearamane S, Kumaravel AK, Velmurugan P, Mohanavel V, Kumar SS, et al. Biomedical and Textile Applications of Alternanthera sessilis Leaf Extract Mediated Synthesis of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticle. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162759
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabeerdass, Nivedhitha, Karthikeyan Murugesan, Natarajan Arumugam, Abdulrahman I. Almansour, Raju Suresh Kumar, Sinouvassane Djearamane, Ashok Kumar Kumaravel, Palanivel Velmurugan, Vinayagam Mohanavel, Subbiah Suresh Kumar, and et al. 2022. "Biomedical and Textile Applications of Alternanthera sessilis Leaf Extract Mediated Synthesis of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticle" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162759
APA StyleKabeerdass, N., Murugesan, K., Arumugam, N., Almansour, A. I., Kumar, R. S., Djearamane, S., Kumaravel, A. K., Velmurugan, P., Mohanavel, V., Kumar, S. S., Vijayanand, S., Padmanabhan, P., Gulyás, B., & Mathanmohun, M. (2022). Biomedical and Textile Applications of Alternanthera sessilis Leaf Extract Mediated Synthesis of Colloidal Silver Nanoparticle. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162759







