Transformed Filaments by Oxygen Plasma Treatment and Improved Resistance State
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
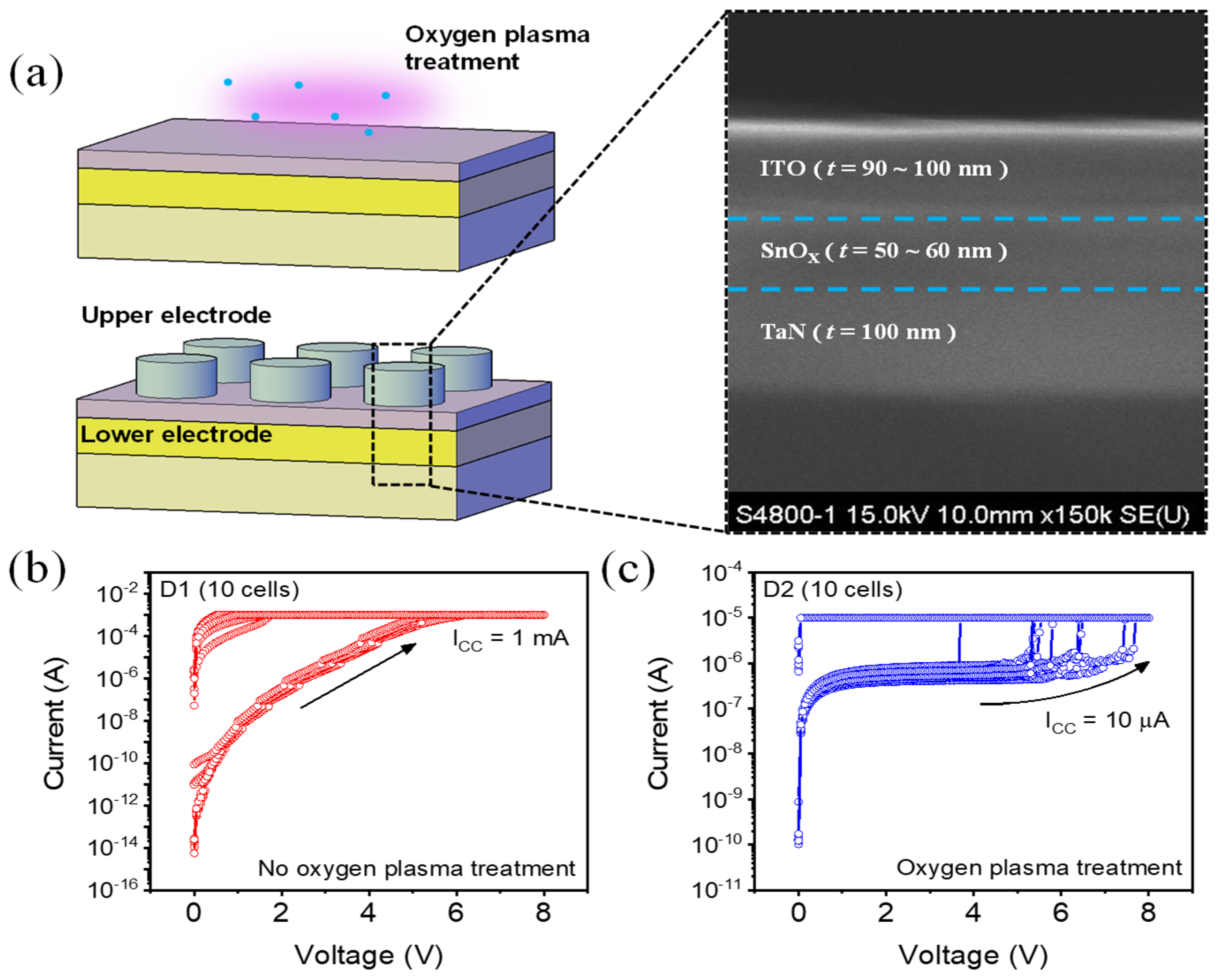
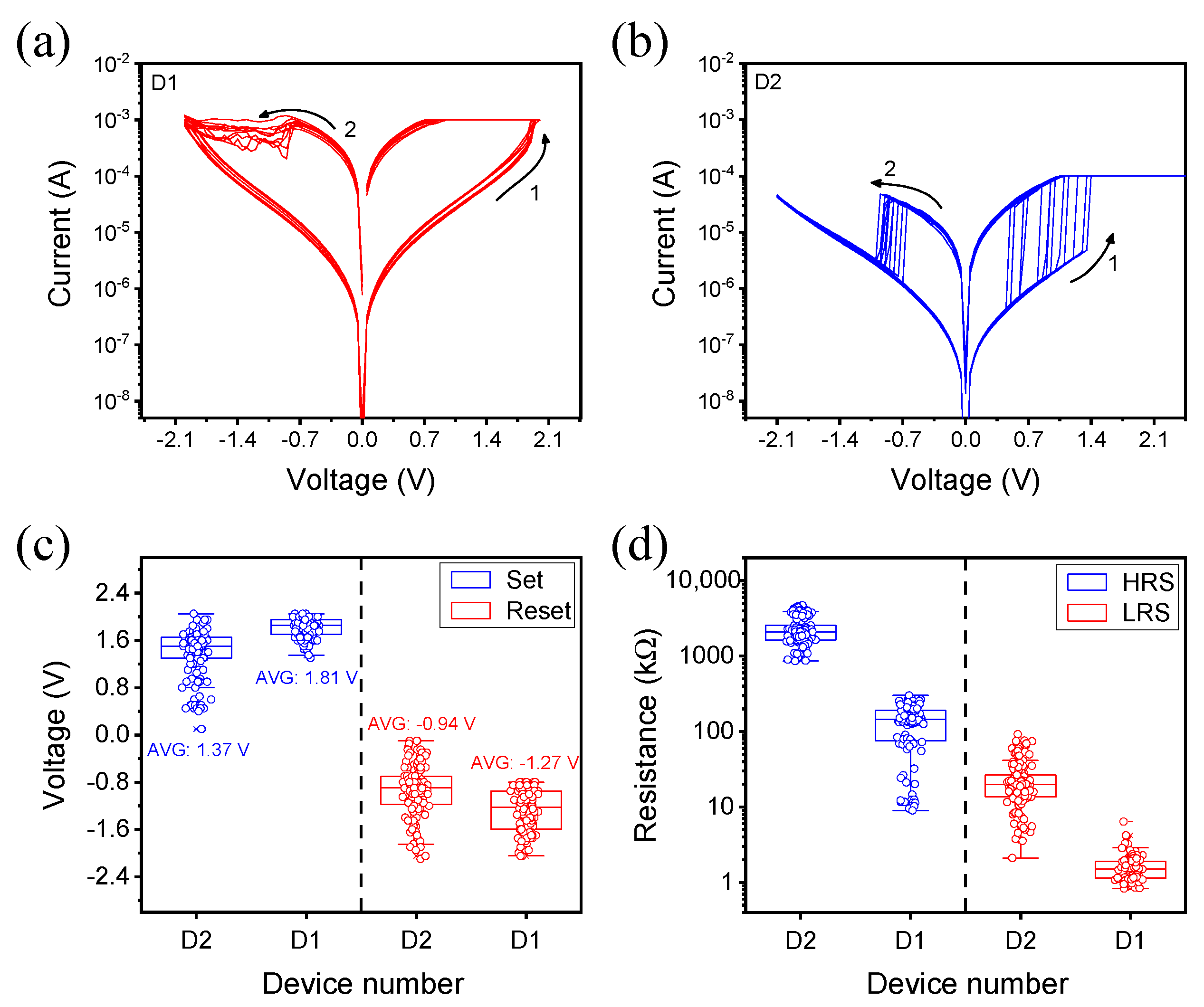
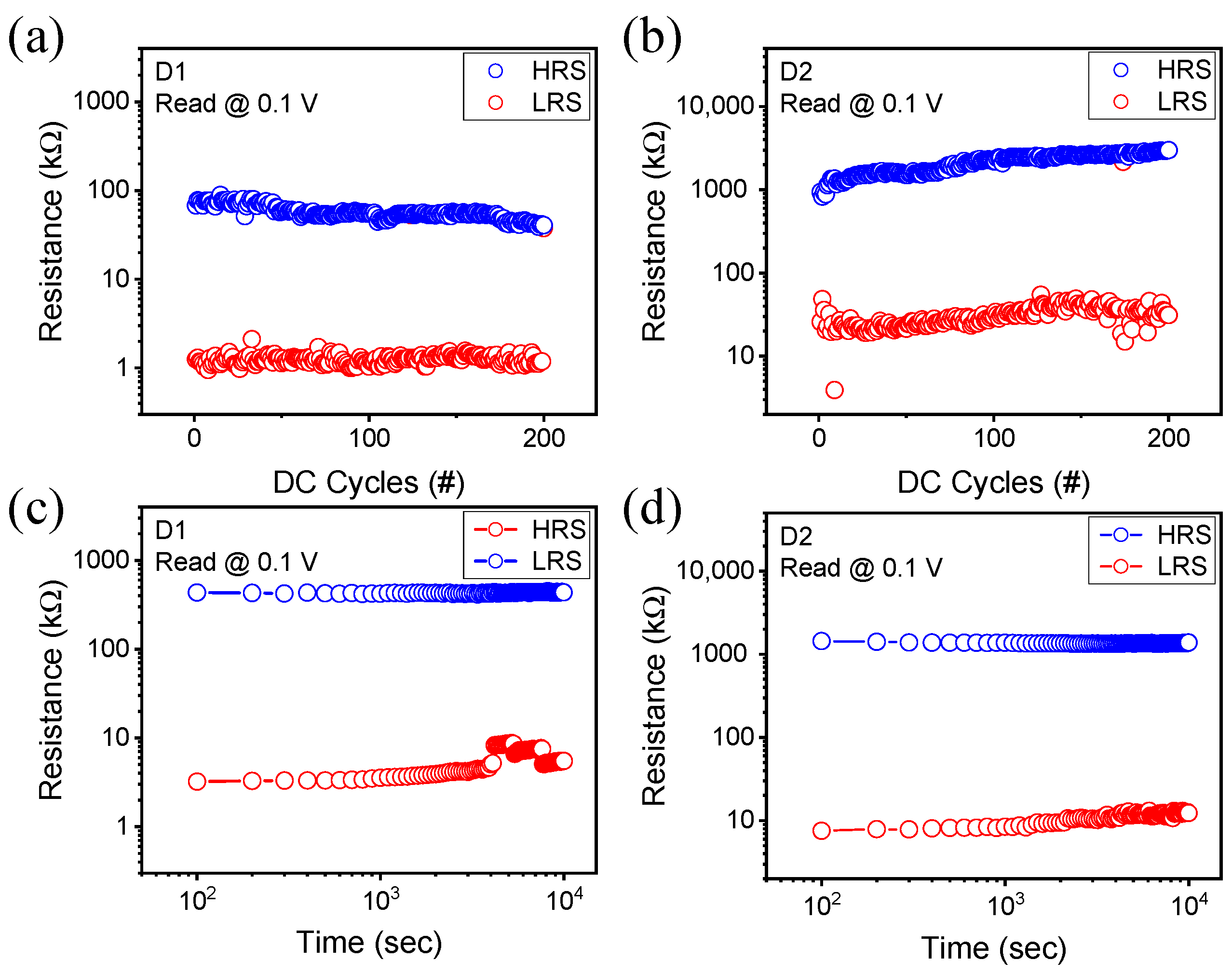
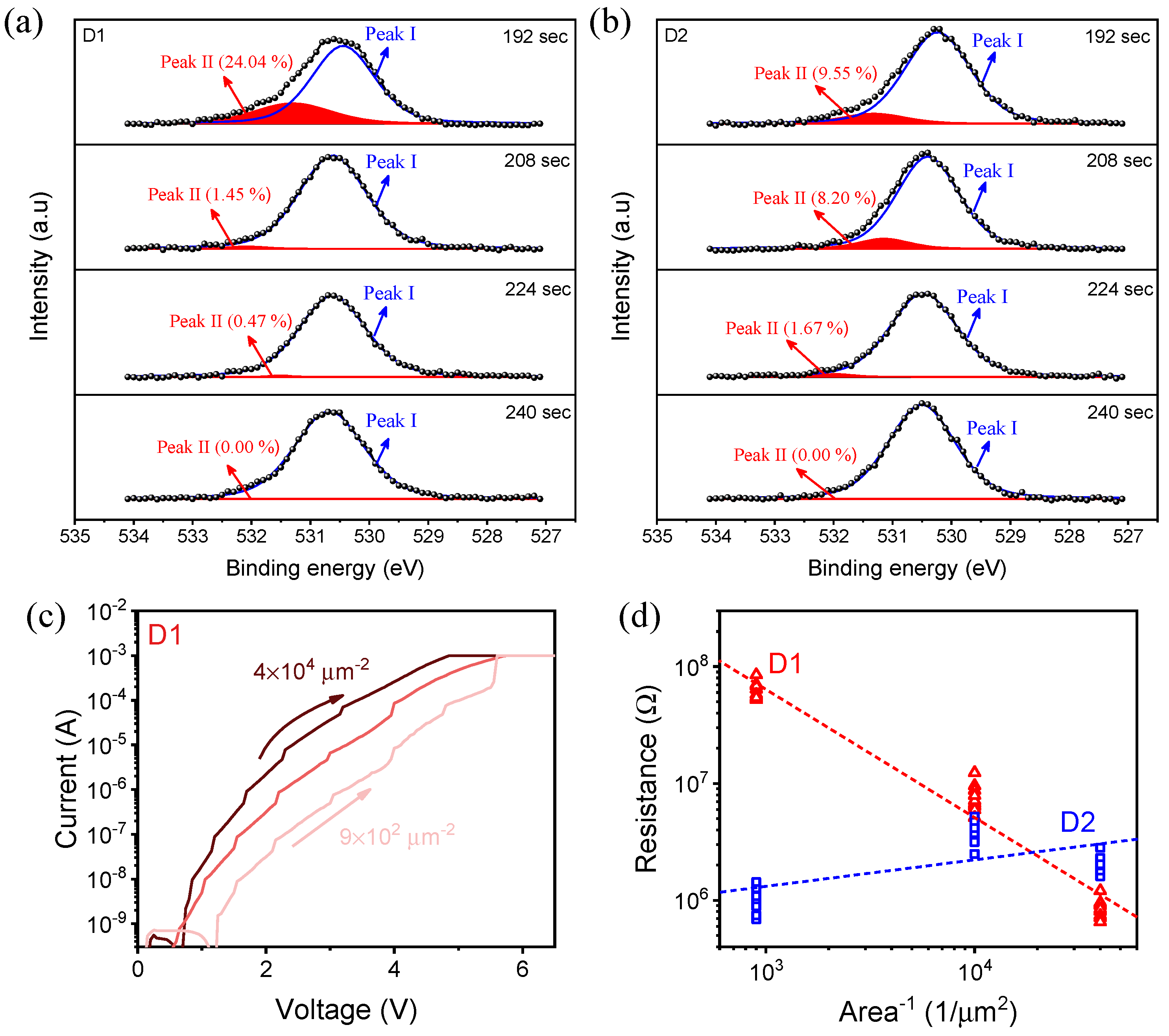
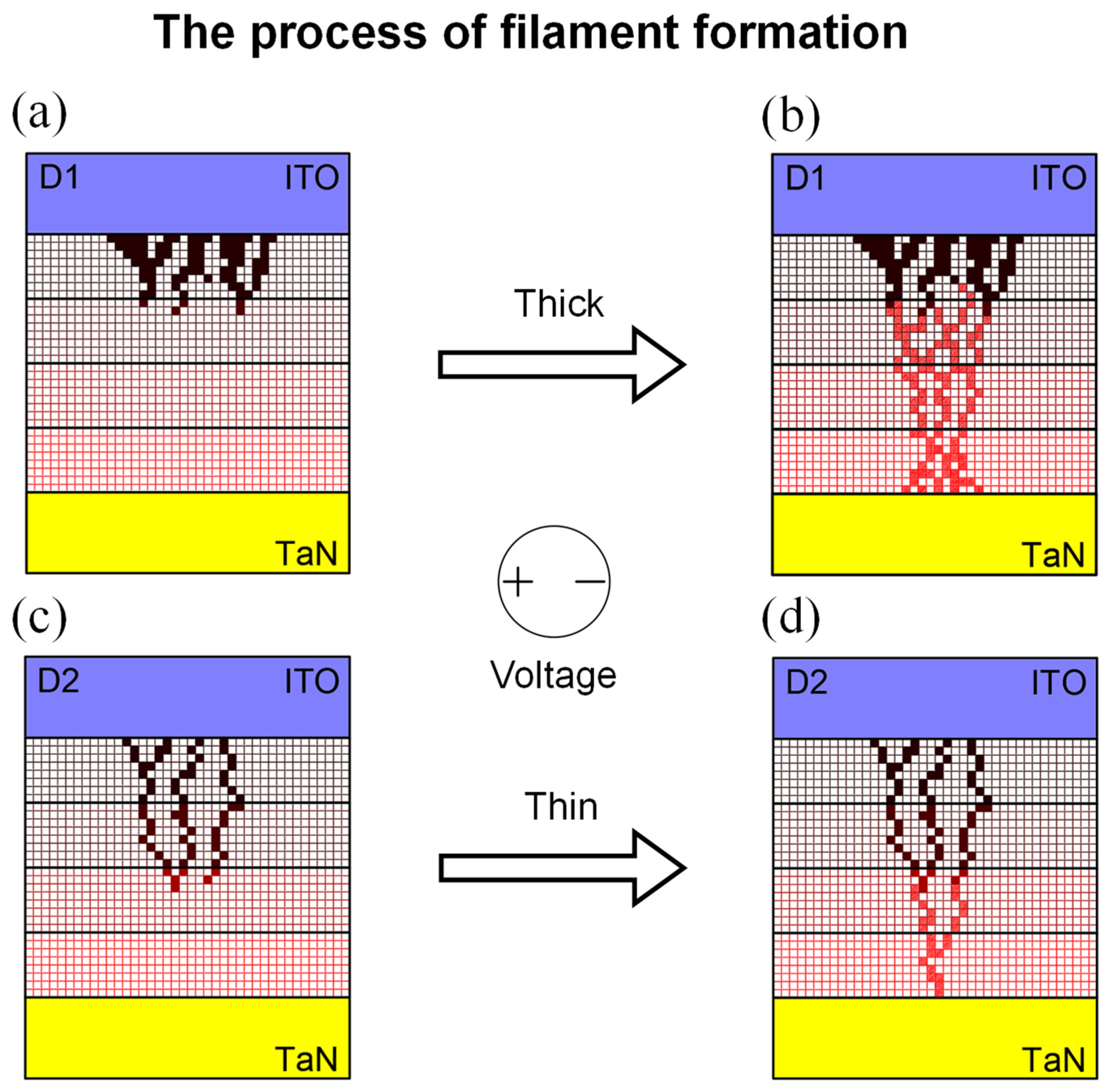
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Long, S.; Liu, Q.; Lv, H.; Liu, M. Resistive switching performance improvement via modulating nanoscale conductive filament, involving the application of two-dimensional layered materials. Small 2017, 13, 1604306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qi, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C. Advances of RRAM devices: Resistive switching mechanisms, materials and bionic synaptic application. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, G.; Yu, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y. Multi-Factor-Controlled ReRAM Devices and Their Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 8895–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Arita, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujiwara, I. In Situ transmission electron microscopy analysis of conductive filament during solid electrolyte resistance switching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 212104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Lv, H.; Long, S.; Yin, K.; Wan, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, M. Real-time observation on dynamic growth/dissolution of conductive filaments in oxide-electrolyte-based ReRAM. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yang, S.; Zeng, M.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Bai, X. Bipolar electrochemical mechanism for mass transfer in nanoionic resistive memories. Adv. Func. Mater. 2014, 26, 3649–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Song, C.; Yang, J.; Zeng, F.; Pan, F. Oxygen migration induced resistive switching effect and its thermal stability in W/TaOX/Pt structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 253509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, W.; Cai, W.F.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Lv, H.; Long, S.; Liu, M. Intrinsic anionic rearrangement by extrinsic control: Transition of RS and CRS in thermally elevated TiN/HfO2/Pt RRAM. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18908–18917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Schell, W.; Zhu, X.; Kioupakis, E.; Lu, W.D. Charge transition of oxygen vacancies during resistive switching in oxide-based RRAM. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11579–11586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Gao, B.; Liu, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Han, R.; Kang, J.; Yu, B. A unified physical model of switching behavior in oxide-based RRAM. In Proceedings of the 2008 Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–19 June 2008; pp. 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Kemal, R.E.; Luo, Y.; Bao, P.; Althobaiti, M.; Hesp, D.; Dhanak, V.R.; Zheng, Z.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; et al. Effects of annealing conditions on resistive switching characteristics of SnOX thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 673, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, M.K.; Hedhili, M.N.; Wang, Q.; Melnikov, V.A.; Mohammed, O.F.; Alshareef, H.N. Nanoscale cross-point resistive switching memory comprising p-Type SnO bilayers. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1400035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liang, L.Y.; Cao, H.T.; Liu, Z.M.; Zhuge, F. Structural, chemical, optical, and electrical evolution of SnOX films deposited by reactive rf magnetron sputtering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5673–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.K.; Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Effect of interlayer on resistive switching properties of SnO2 -based memristor for synaptic application. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Woo, S.-J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S. Demonstration of threshold switching and bipolar resistive switching in Ag/SnOX/TiN memory device. Metals 2021, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Abbas, Y.; Abbas, H.; Jeon, Y.-R.; Hussain, S.; Naqvi, B.A.; Choi, C.; Jung, J. Dependence of InGaZnO and SnO2 thin film stacking sequence for the resistive switching characteristics of conductive bridge memory devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, J.; Singh, R.G.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, V.; Singh, F.; Kumar, R. Effect of annealing on the surface morphology, optical and structural properties of nanodimensional tungsten oxide prepared by coprecipitation technique. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 48, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, W.-Y.; Jang, B.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, K.; Jang, J. Effect of annealing environment on the performance of sol–gel-processed ZrO2 RRAM. Electronics 2019, 8, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, C.P.; Jain, P.K.; Chand, U.; Sharma, S.K.; Birla, S.; Sancheti, S. Effect of annealing temperature on switching characteristics of zinc oxide-based RRAM device. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Innovative Trends and Advances in Engineering and Technology, Shegoaon, India, 27–28 December 2019; pp. 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Srinivas, V.; Ram, S.; De Toro, J.A.; Riveiro, J.M. Effect of interstitial oxygen on the crystal structure and magnetic properties of Ni nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 6782–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, B.; Abbas, Y.; Sokolov, A.S.; Choi, C. Interface engineering of ALD HfO2-based RRAM with Ar plasma treatment for reliable and uniform switching behaviors. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 735, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chang, Y.-F.; Fowler, B.; Lee, J. The effect of plasma treatment on reducing electroforming voltage of silicon oxide RRAM. ECS Trans. 2012, 45, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liao, C.; Cheng, S.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, P. Ultralow switching current in HfOX/ZnO bilayer with tunable switching power enabled by plasma treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 063501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Qiu, W.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, S.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Q. Resistive switching of plasma-treated zinc oxide nanowires for resistive random access memory. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.F.; Xin, P.C.; Cheng, S.Y.; Yu, J.L.; Zheng, Q. Plasma enhanced multistate storage capability of single ZnO nanowire based memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 031603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Chang, T.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Tsai, T.-M.; Pan, C.-H.; Chen, M.-C.; Su, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Huang, H.-C.; et al. Resistance switching characteristics induced by O2 plasma treatment of an indium tin oxide film for use as an insulator in resistive random access memory. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Chang, T.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Tsai, T.-M.; Pan, C.-H.; Shih, C.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Yang, C.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Lin, J.-C.; et al. Effects of plasma treatment time on surface characteristics of indium-tin-oxide film for resistive switching storage applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Chen, M.-C.; Yang, C.-C.; Zheng, H.-X.; Chen, P.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-K.; Chen, J.-J.; et al. Improvement of hafnium oxide resistive memory performance through low-temperature supercritical oxidation treatments. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2021, 68, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Kao, C.-H.; Chan, Y.-T.; Chu, T.-M.; Wang, J.-C. Multilevel resistive switching behaviors of N2-plasma-treated stacked GdOX/SiNX RRAMs. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SBBB13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Lee, D.; Cho, S.-H.; Hur, J.-H.; Lee, S.-M.; Seo, D.H.; Kim, D.-S.; Yang, M.-S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, E.; et al. A plasma-treated chalcogenide switch device for stackable scalable 3D nanoscale memory. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.; Elshekh, H.; Yu, T.; Mao, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z. Photo-Induced Negative Differential Resistance in a Resistive Switching Memory Device Based on BiFeO3/ZnO Heterojunctions. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 14, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H.; Chang, K.-C.; Chang, T.-C.; Tsai, T.-M.; Pan, C.-H.; Chu, T.-J.; Chen, M.-C.; Huang, H.-C.; Lo, I.; Zheng, J.-C.; et al. Bulk oxygen–ion storage in indium–tin–oxide electrode for improved performance of HfO2-based resistive random access memory. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2016, 37, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Choi, J.; Chung, D.; Kim, S. Transformed Filaments by Oxygen Plasma Treatment and Improved Resistance State. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152716
Park J, Choi J, Chung D, Kim S. Transformed Filaments by Oxygen Plasma Treatment and Improved Resistance State. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152716
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jongmin, Jungwhan Choi, Daewon Chung, and Sungjun Kim. 2022. "Transformed Filaments by Oxygen Plasma Treatment and Improved Resistance State" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152716
APA StylePark, J., Choi, J., Chung, D., & Kim, S. (2022). Transformed Filaments by Oxygen Plasma Treatment and Improved Resistance State. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152716







