Covalent Organic Framework/Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Trace Quinolones in Food Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Characterization and HPLC Conditions
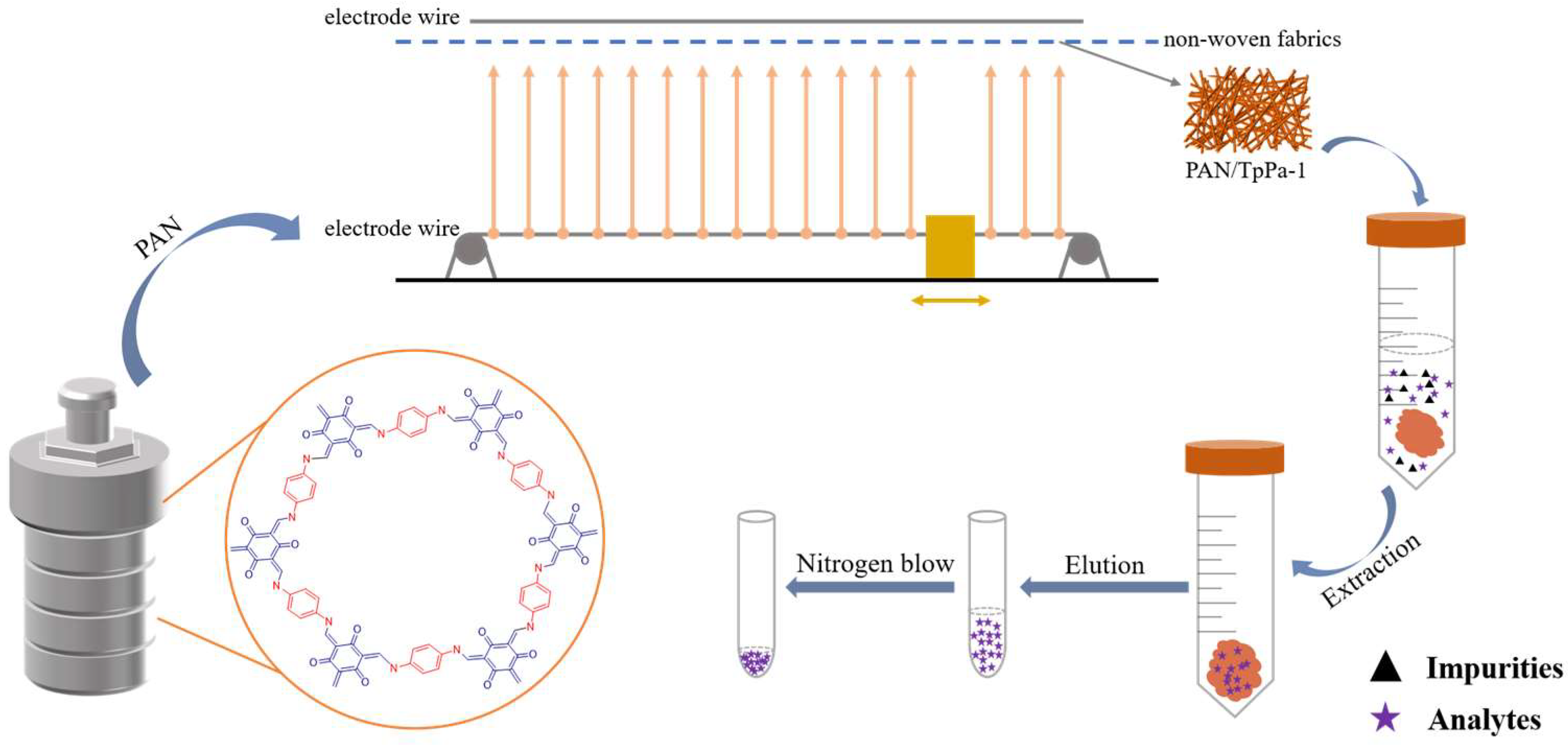
2.3. Preparation of TpPa–1
2.4. Preparation of PAN/TpPa–1 Nanofiber
2.5. Samples Preparation
2.6. dSPE Procedure
3. Results and Discussions
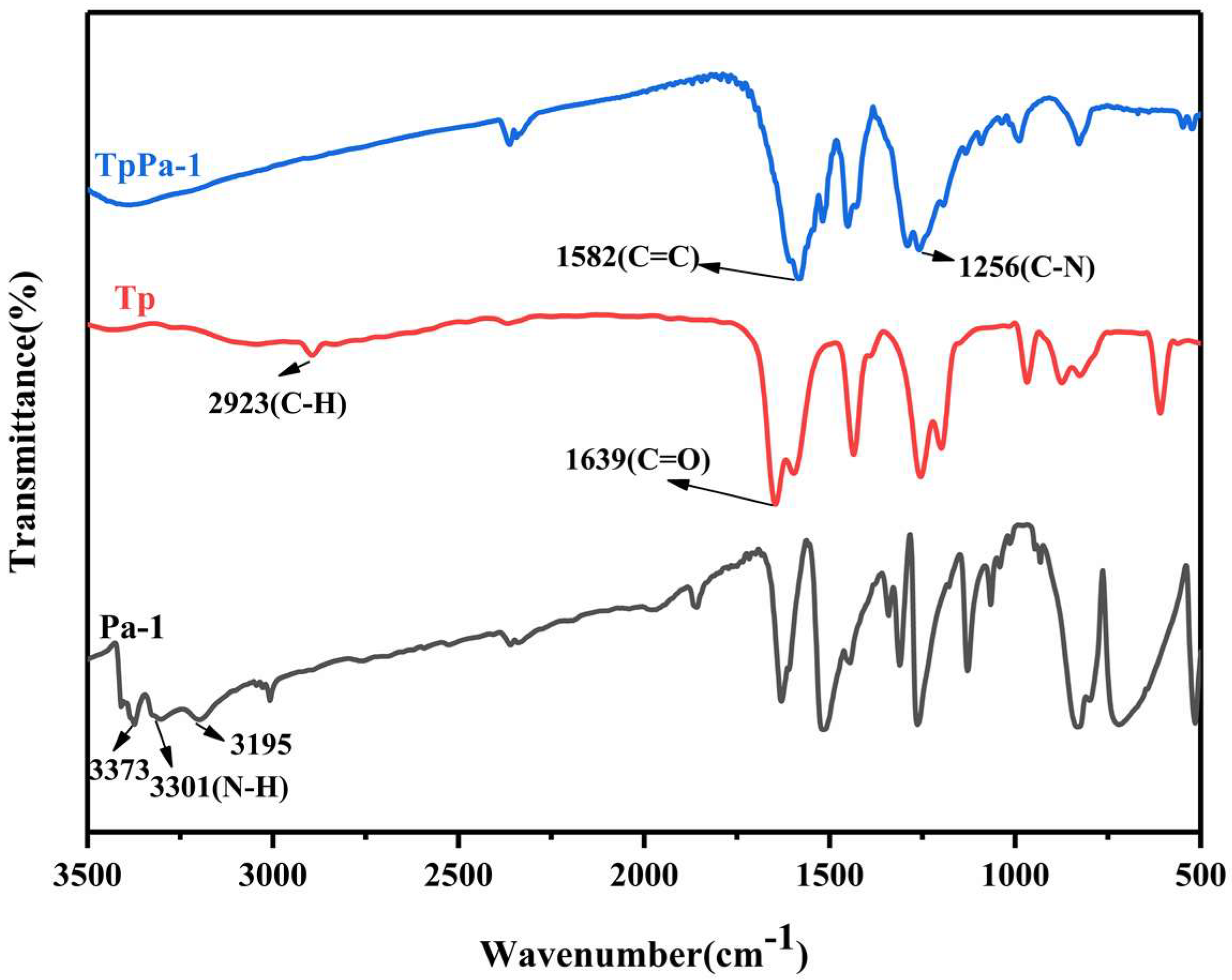
3.1. Characterization of PAN/TpPa–1 Nanofiber
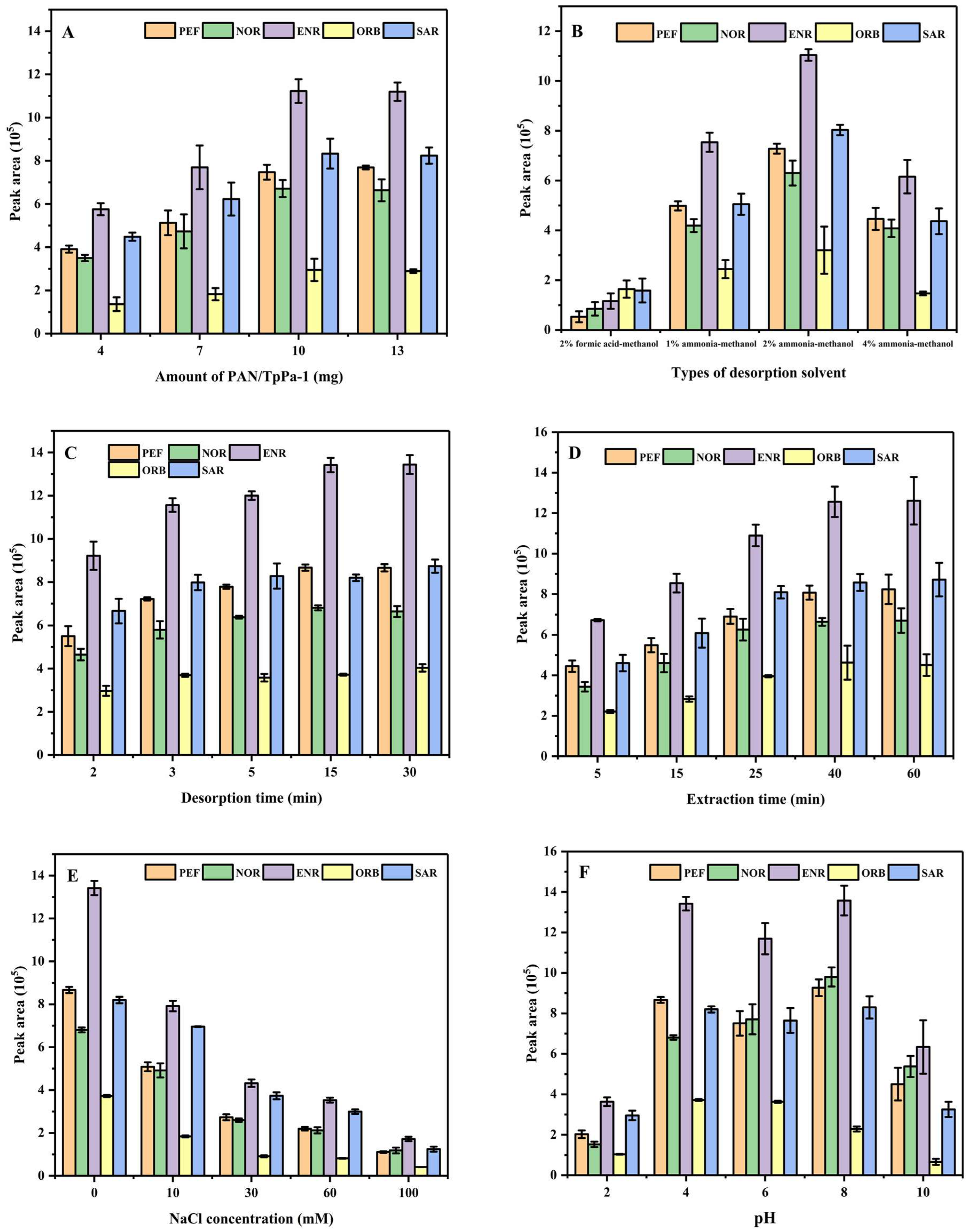
3.2. Optimization of dSPE
3.2.1. Effect of Amount of PAN/TpPa–1 Nanofiber on the Extraction of QAs
3.2.2. Effect of Desorption Solvent and Desorption Time on the Extraction of QAs
3.2.3. Effect of Extraction Time on the Extraction of QAs
3.2.4. Effect of Ionic Strength of Sample Solution
3.2.5. Effect of pH Value of Sample Solution
3.3. Reproducibility and Reusability of PAN/TpPa–1 Nanofiber
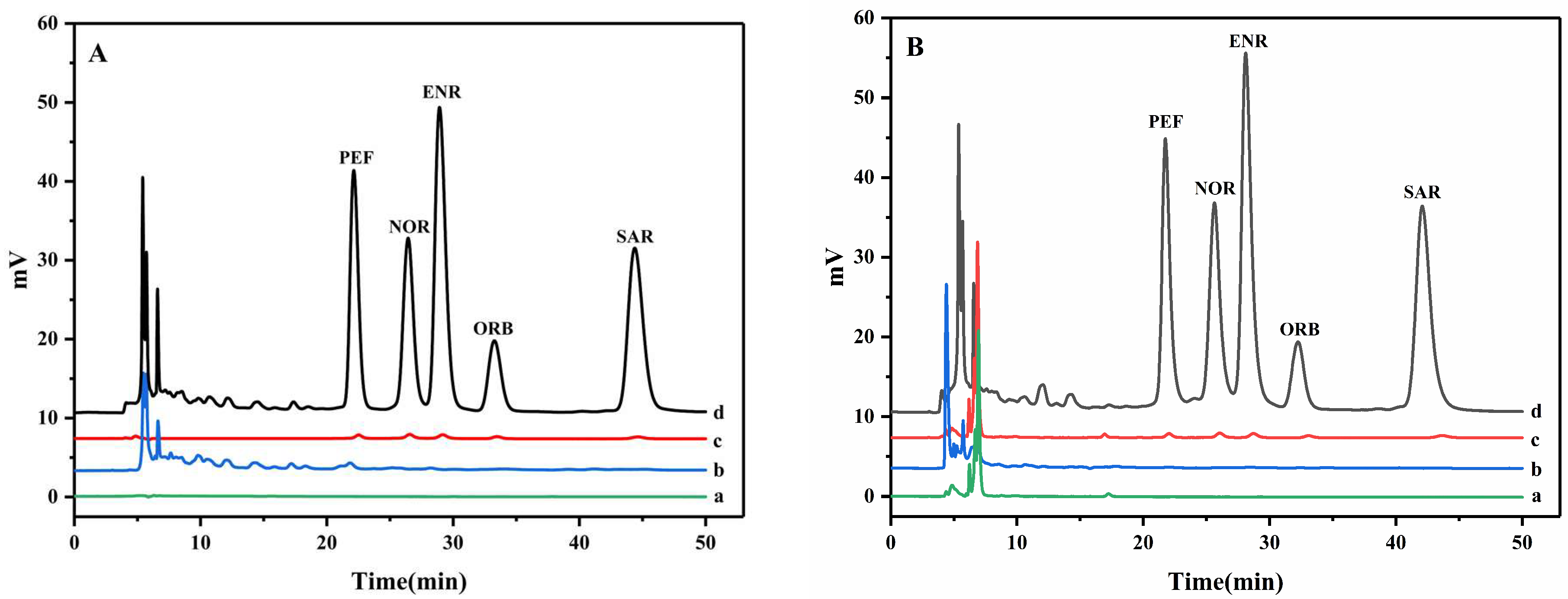
3.4. Method Validation and Application in Real Sample
3.5. Comparison with Other Reported Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greulich, P.; Doležal, J.; Scott, M.; Evans, M.R.; Allen, R.J. Predicting the dynamics of bacterial growth inhibition by ribosome-targeting antibiotics. Phys. Biol. 2017, 14, 065005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.C.; Goyal, R.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, D.; Saini, N.; Rajak, H.; Sharma, S.; Thakur, V.K. Insights on fluoroquinolones in cancer therapy: Chemistry and recent developments. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apreja, M.; Sharma, A.; Balda, S.; Kataria, K.; Capalash, N.; Sharma, P. Antibiotic residues in environment: Antimicrobial resistance development, ecological risks, and bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3355–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, C.; Tertis, M.; Galatus, R. Magnetic nanoparticles for antibiotics detection. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L15, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- GB 31650-2019; National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits for Veterinary Drugs in Foods. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/64074.html (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Pagani, A.P.; Ibañez, G.A. Analytical approach for the simultaneous determination of quinolones in edible animal products. Modeling pH-modulated fluorescence excitation–emission matrices four–way arrays. Talanta 2019, 192, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Deng, R.; Teng, M.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G. A SERS-based multiple immuno-nanoprobe for ultrasensitive detection of neomycin and quinolone antibiotics via a lateral flow assay. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakh, C.; Pochivalov, A.; Koronkiewicz, S.; Kalinowski, S.; Postnov, V.; Bulatov, A. A chemiluminescence method for screening of fluoroquinolones in milk samples based on a multi-pumping flow system. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahouidak, S.; Soriano, M.L.; Salghi, R.; Zougagh, M.; Ríos, Á. Graphene quantum dots for enhancement of fluorimetric detection coupled to capillary electrophoresis for detection of ofloxacin. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2336–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Huo, Y.; Guan, S.P. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on g-C3N4/Fe3O4/MoS2 as a magnetic adsorbent for HPLC-UV determination of fluoroquinolones in chicken and eggs. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. Preparation of highly fluorinated and boron-rich adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in water and milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D. Porous electrospun microfibers for low flow-resistant solid phase extraction of fluoroquinolones in tap water, egg and milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1661, 462719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Xie, K.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Dai, G. Development of a UPLC-FLD method for quantitative analysis of three tetracyclines and two fluoroquinolones in chicken muscle. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Zou, X.; Wang, J. Simultaneous determination of the four key fluoroquinolones and two antipsychotics in fish and shrimp by LC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Liu, T.; Mu, G.; Chen, F.; He, M.; You, S.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F. Rapid and sensitive determination of trace fluoroquinolone antibiotics in milk by molecularly imprinted polymer-coated stainless steel sheet electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Talanta 2020, 219, 121282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, D.; Yan, P. Development of a pH-dependent homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction by cold-induced phase separation in acetonitrile/water mixtures for determination of quinolone residues in animal-derived foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1649, 462235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lin, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, M. A Simple and Fast Extraction Method for the Determination of Multiclass Antibiotics in Eggs Using LC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5064–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashile, G.P.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. Magnetic mesoporous carbon/β-cyclodextrin–chitosan nanocomposite for extraction and preconcentration of multi-class emerging contaminant residues in environmental samples. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Dong, X.; Hou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Ma, H.; Zhao, R.-S. Room-temperature synthesis of flower-shaped covalent organic frameworks for solid-phase extraction of quinolone antibiotics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1126, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z. In situ immobilization of layered double hydroxides onto cotton fiber for solid phase extraction of fluoroquinolone drugs. Talanta 2018, 186, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, G. Rapid in vivo determination of fluoroquinolones in cultured puffer fish (Takifugu obscurus) muscle by solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 175, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzajani, R.; Kardani, F. Fabrication of ciprofloxacin molecular imprinted polymer coating on a stainless steel wire as a selective solid-phase microextraction fiber for sensitive determination of fluoroquinolones in biological fluids and tablet formulation using HPLC-UV detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 122, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, R.; García-Córcoles, M.T.; Çipa, M.; Barrón, D.; Navalón, A.; Zafra-Gómez, A. Determination of quinolone residues in raw cow milk. Application of polar stir-bars and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X. Dissolvable layered double hydroxide as a sorbent in dispersive micro-solid phase extraction for the determination of acidic quinolones in honey by HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, R.; Chen, X.; Chan, T.-W.D. Water-dispersible pH/thermo dual-responsive microporous polymeric microspheres as adsorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from environmental water samples and food samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1601, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.; Li, G.; Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, N.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y. Sulphonate functionalized covalent organic framework-based magnetic sorbent for effective solid phase extraction and determination of fluoroquinolones. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1612, 460651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, B.; Lou, D. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from water samples using titanium-based metal-organic framework functionalized magnetic microspheres. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1579, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Shang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Tan, J. Determination of quinolones in environmental water and fish by magnetic metal organic frameworks based magnetic solid-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, H. Recent development in sample preparation and analytical techniques for determination of quinolone residues in food products. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Mathe, S.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Covalent organic frameworks: From materials design to biomedical application. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, Y.-K.; Shen, S.; Liang, S.-X. Recent advances in porous organic frameworks for sample pretreatment of pesticide and veterinary drug residues: A review. Analyst 2021, 146, 7374–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.-L.; Yang, C.-X.; Wang, W.-L.; Yang, C.; Yan, X.-P. Advances in covalent organic frameworks in separation science. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1542, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Du, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, N.; Sun, Z.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Recent advances in facile synthesis and applications of covalent organic framework materials as superior adsorbents in sample pretreatment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 54–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun nanofibers: New concepts, materials, and applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Hu, B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Pang, J.; Wu, C. Facile synthesis of covalent organic framework incorporated electrospun nanofiber and application to pipette tip solid phase extraction of sulfonamides in meat samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1584, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Lv, F.; Yan, Z. Electrospinning fabrication of covalent organic framework composite nanofibers for pipette tip solid phase extraction of tetracycline antibiotics in grass carp and duck. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kong, R.-M.; Xia, L.; Kong, C.; Li, G. Combination of pipette tip solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography for determination of plant growth regulators in food samples based on the electrospun covalent organic framework/polyacrylonitrile nanofiber as highly efficient sorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1661, 462692. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Guo, H.; Luan, J.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. The electrospun polyacrylonitrile/covalent organic framework nanofibers for efficient enrichment of trace sulfonamides residues in food samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1668, 462917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers Coated with Covalent Organic Frameworks for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 3925–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandambeth, S.; Mallick, A.; Lukose, B.; Mane, M.V.; Heine, T.; Banerjee, R. Construction of Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks with Remarkable Chemical (Acid/Base) Stability via a Combined Reversible and Irreversible Route. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19524–19527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J. Selective extraction and determination of fluoroquinolones in bovine milk samples with montmorillonite magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers and capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, B. Molecularly imprinted polymer coating on metal-organic frameworks for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones from water. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3277–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L. Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by magnetic solid-phase extraction for determination of quinolones. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Ma, N.; Zang, X.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, J.P.; Wu, N.P. Determination of fluoroquinolones in chicken muscle by molecularly imprinted graphitic carbon nitride-based solid-phase extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.-B.; Dong, C.; Li, B.; Dong, J.-P.; Bo, T.-Y.; Wang, T.-L.; Yu, Q.-W.; Feng, Y.-Q. Fabrication of enrofloxacin imprinted organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous sorbent from nanomagnetic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes for the selective extraction of fluoroquinolones in milk samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1361, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Y.-F.; Omer, A.M.; Ouyang, X.-K. Fabrication of novel surface-imprinted magnetic graphene oxide-grafted cellulose nanocrystals for selective extraction and fast adsorption of fluoroquinolones from water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6643–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analytes | Linear Range (ng·mL−1) | R2 | LODs (ng·mL−1) | LOQs (ng·mL−1) | RSDs (%) (n = 3) (50 ng·mL−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |||||
| PEF | 0.5–200 | 0.9946 | 0.039 | 0.110 | 4.0 | 4.8 |
| NOR | 1.0–200 | 0.9967 | 0.069 | 0.233 | 4.3 | 8.2 |
| ENR | 0.5–200 | 0.9972 | 0.030 | 0.086 | 2.8 | 3.0 |
| ORB | 0.5–200 | 0.9951 | 0.133 | 0.288 | 2.9 | 8.8 |
| SAR | 1.0–200 | 0.9974 | 0.073 | 0.226 | 3.9 | 6.3 |
| Analytes | Added (ng·mL−1) | Honey | Pork | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found (ng·mL−1) | Recovery (%) | RSDs (%) | Found (ng·mL−1) | Recovery (%) | RSDs (%) | ||
| PEF | 0 | ND | – | – | ND | – | – |
| 5 | 4.7 | 93.8 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 | 7.9 | |
| 10 | 55.7 | 111.3 | 6.4 | 42.9 | 85.7 | 5.6 | |
| 100 | 87.2 | 87.2 | 1.0 | 95.7 | 95.7 | 8.4 | |
| NOR | 0 | ND | – | – | ND | – | – |
| 5 | 5.6 | 112.6 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 119.0 | 9.2 | |
| 10 | 54.4 | 108.7 | 9.1 | 45.0 | 89.9 | 6.4 | |
| 100 | 82.7 | 82.7 | 3.0 | 101.9 | 101.9 | 6.2 | |
| ENR | 0 | ND | – | – | ND | – | – |
| 5 | 4.8 | 96.1 | 6.5 | 5.4 | 108.6 | 4.5 | |
| 10 | 55.3 | 110.6 | 2.6 | 44.1 | 88.3 | 5.6 | |
| 100 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 3.1 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 5.8 | |
| ORB | 0 | ND | – | – | ND | – | – |
| 5 | 4.1 | 82.6 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 88.9 | 6.9 | |
| 10 | 52.0 | 104.0 | 9.8 | 40.8 | 81.6 | 4.8 | |
| 100 | 83.7 | 83.7 | 6.7 | 86.3 | 86.3 | 4.8 | |
| SAR | 0 | ND | – | – | ND | – | – |
| 5 | 6.0 | 119.7 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 107.6 | 9.8 | |
| 10 | 53.7 | 107.4 | 8.3 | 44.6 | 89.1 | 8.6 | |
| 100 | 86.2 | 86.2 | 5.0 | 107.1 | 107.1 | 7.0 |
| Method | Adsorbent | LOD (μg·kg−1 or μg·L−1) | Recovery (%) | Elution Volume | Amount of Adsorbent (mg) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE-UV | MMMIPs | 12.9–8.8 | 92.7–108.6 | – | 30 mg | [42] |
| HPLC-UV | MIP@UiO-66-NH2 | 0.19–0.39 | 92.6–100.5 | 3 mL | 20 mg | [43] |
| HPLC-DAD | MWCNTs-Fe3O4@SiO2-CS | 1.5–3 | 81.2–109 | 5 mL | 30 mg | [44] |
| HPLC-FD | MIM/C3N4 | 0.2–0.8 | 92.1–99.4 | 1 mL | 30 mg | [45] |
| HPLC-UV | Fe3O4@MI-POSS | 1.76–12.42 | 75.6–108.9 | 2 mL | 60 mg | [46] |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Fe3O4@COF(TpBD)@Au-MPS | 0.1–1.0 | 82–110.2 | 1 mL | 10 mg | [27] |
| HPLC-DAD | Mag@GO-g-CNCs@MIPs | 6.5–51 | 79.2–96.1 | 2 mL × 3 | 20 mg | [47] |
| HPLC-UV | PAN/TpPa–1 | 0.03–0.133 | 81.6–119.7 | 1 mL | 10 mg | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Chen, A.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Covalent Organic Framework/Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Trace Quinolones in Food Samples. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142482
Zhou J, Chen A, Guo H, Li Y, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y. Covalent Organic Framework/Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Trace Quinolones in Food Samples. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(14):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142482
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jinghui, An Chen, Hongying Guo, Yijun Li, Xiwen He, Langxing Chen, and Yukui Zhang. 2022. "Covalent Organic Framework/Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Trace Quinolones in Food Samples" Nanomaterials 12, no. 14: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142482
APA StyleZhou, J., Chen, A., Guo, H., Li, Y., He, X., Chen, L., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Covalent Organic Framework/Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Trace Quinolones in Food Samples. Nanomaterials, 12(14), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12142482






