Abstract
Nanosponges with three-dimensional (3D) porous structures, narrow size distribution, and high entrapment efficiency are widely engineered for cancer therapy and drug delivery purposes. They protect the molecular agents from degradation and help to improve the solubility of lipophilic therapeutic agents/drugs with targeted delivery options in addition to being magnetized to attain suitable magnetic features. Nanosponge-based delivery systems have been applied for cancer therapy with high specificity, biocompatibility, degradability, and prolonged release behavior. In this context, the drug loading within nanosponges is influenced by the crystallization degree. Notably, 3D printing technologies can be applied for the development of novel nanosponge-based systems for biomedical applications. The impacts of polymers, cross-linkers, type of drugs, temperature, loading and mechanism of drug release, fabrication methods, and substitution degree ought to be analytically evaluated. Eco-friendly techniques for the manufacturing of nanosponges still need to be uncovered in addition to the existing methods, such as solvent techniques, ultrasound-assisted preparation, melting strategies, and emulsion solvent diffusion methods. Herein, the recent advancements associated with the drug delivery and cancer therapy potential of nanosponges (chiefly, cyclodextrin-based, DNAzyme, and ethylcellulose nanosponges) are deliberated, focusing on the important challenges and future perspectives.
1. Introduction
Nanomaterials have been widely explored as potential drug delivery and cancer therapy agents; however, detailed studies are still required to find efficient delivery systems with high biocompatibility and biodegradability properties for specific and targeted therapy [1,2,3,4]. Additionally, the interactions of these nanomaterials with physiological environments, along with their nanotoxicological assessments, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic issues, metabolism, and drug release mechanisms (e.g., diffusion, erosion, targeting, swelling, dissolution, and osmosis), still need to be comprehensively addressed, especially for clinical translation studies [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Among these created nanomaterials, nanosponges with suitable penetration, absorption, biocompatibility, bioavailability, and stability have been studied for targeted and sustained drug delivery and cancer therapy [10]. Nanosponges are solid, crosslinked, polymeric, nano-sized, porous structures; these can be defined as hydrophilic, water-insoluble, and supramolecular three-dimensional (3D) hyper-reticulated nanoporous structures, exhibiting significant stability over a wide range of temperatures and pH levels. They have shown attractive benefits, such as high biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low cytotoxicity, making them suitable for biomedical applications [11]. For instance, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges have excellent potential for the production of inclusion and non-inclusion complexes with a variety of drugs/active molecules, offering an effective therapeutic vehicle for transferring drugs with low bioavailability. In inclusion complex nanosponges, the drug forms an inclusion complex with the cyclodextrin molecule. However, in non-inclusive complex nanosponges, the drug molecule becomes entrapped or imbibed into their porous nanostructures. Among nanosponges, cyclodextrin-based structures have been widely explored for drug delivery, remediation, sensing, and catalytic applications (Figure 1) [12]. The cavity of nanosponges permits the addition of hydrophobic molecules, and the more hydrophilic outer polymeric network enables it to accommodate less lipophilic molecules. It has been revealed that the solubility/degradability of the drugs can be improved when they are incorporated into the nanosponges, thus enhancing their bioavailability. As an example, nanosponges have been formulated to enhance the solubility and bioavailability and to reduce the oral dose of the anticancer drug, lapatinib [13]. On the other hand, one of the disadvantages of these nanostructures is their ability to include only small molecules. Indeed, the application of nanosponges is still at an early stage, and future explorations ought to focus on designing innovative nanosponge-based systems (either alone or in the presence of other polymers) with potential pharmaceutical and biomedical applications [12,14,15,16]. An assortment of nanosponges has been created, namely titanium-based, metallic, β-cyclodextrin, hyper-crosslinked polystyrene, silicon-based, DNAzyme, and ethylcellulose nanosponges [17]. The mesh-like/colloidal structures of nanosponges make them ideal candidates for the encapsulation of different compounds, including drugs, phytochemicals, volatile oils, antineoplastic agents, genetic substances, and proteins/peptides, among others [18,19,20]. As an example, peptide nanosponges (~80 nm) were designed for cell-based cancer therapy [19]. Furthermore, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges were introduced as effective and safer alternatives for removing toxic molecules such as indole in the body, reducing the dialysis frequency and avoiding the hepatic and cardiac toxicity [21].
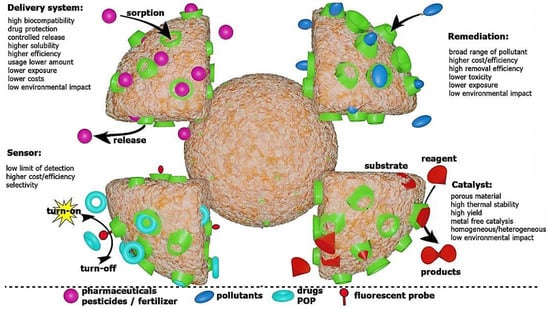
Figure 1.
Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges with their advantages and applications. Adapted from [12] with permission. Copyright 2022 Frontiers (CC BY 4.0).
Nanosponges (~200–300 nm) exist in both crystalline and para-crystalline forms, which mostly depend on the reaction/synthesis and processing conditions. The property pertaining to the crystallization of nanosponges can help in controlling and governing their drug-loading capacity [17]. Several techniques have been introduced for the synthesis of nanosponges, such as the interfacial phenomenon, hot melting process, hyper-crosslinked cyclodextrin, ultrasound-assisted, solvent condensation, microwave (MW)-assisted synthesis, interfacial condensation, mechanochemical synthesis, chain-growth poly-condensation, and emulsion solvent evaporation methods [22]. Notably, greener approaches with safety, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendliness for the synthesis of nanosponges still need to be attended to [23,24,25,26,27]. For instance, the MW synthesis technique was deployed to synthesize crystalline cyclodextrin nanosponges with a narrow particle size distribution via the reaction of cyclodextrin with suitable cross-linkers in polar aprotic solvents (e.g., dimethylformamide) [28]. In addition, the ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of nanosponges with uniform spherical sizes was reported, with the benefits of solvent-free processes and environmentally benign features [12,29]. Widely explored nanosponges such as the cyclodextrin-based nanosponges have been synthesized under different types of stimuli-responsive methods that allow the acquisition of molecularly imprinted, plain, and modified nanosponges [30]. For instance, cyclodextrin nanosponges obtained via the molecularly imprinted approaches have shown remarkable selectivity/specificity towards molecular agents, making them suitable for various biomedical applications [31]. Cyclodextrin nanosponges have presented the alluring benefits of unique architectures, a high crosslinked 3D network, negligible toxicity, sustainability, environmental friendliness, low cost, and hosting potentials for a variety of molecular agents, which renders them suitable for the fields of bio- and nanomedicine [32]. The formation of assorted complexes of nanosponges with hydrophilic or lipophilic molecules has been explored for targeted delivery, along with their protection from degradability [16,22,33].
The surface functionalization/modification of these nanosponges can be performed by applying carbon nanotubes, silver nanowires, and titanium dioxide (TiO2), among others [34,35]. As an example, the cyclodextrin-based nanosponges were surface functionalized with cholesterol; these are dispersible in the cells and are responsible for different protein bindings or cell interactions. After that, doxorubicin was loaded into the functionalized nanosponges to improve the bioavailability and targeted release of this anticancer drug [36]. Indeed, several studies have shown the excellent potential of nanosponges with their special porous structures for entrapping or encapsulating drugs/therapeutic agents, thereby reducing their toxicity and possible side effects [37]. They have also shown a programmable and sustained release of drugs compared to the conventional drug delivery systems [38]. In one study, chitosan nanosponges were designed for improving the drug penetration through skin, with no noticeable toxicity. Accordingly, the skin permeation was enhanced compared to the free model drug, providing efficient trans-epidermal drug delivery [39]. There are still some crucial factors that should be systematically evaluated, particularly in the clinical translation studies of nanosponge-based dosage forms, encompassing pharmacokinetics, recyclability, targeting behaviors, adsorption or encapsulation processes, bioavailability, biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, and histopathological assessments, among others [40]. Herein, the drug delivery and cancer therapy applications of nanosponge-based systems (mostly, cyclodextrin-based, DNAzyme, and ethylcellulose nanosponges) are deliberated, with a focus on the crucial challenges and future directions.
2. Drug Delivery and Cancer Therapy
2.1. Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges
Cyclodextrin nanosponges with unique properties, such as biocompatibility, porous structures, controlled-release behavior, and enhanced oral bioavailability, have been introduced as safe carriers of drugs/therapeutic agents for the treatment of various diseases (especially cancers/tumors) [14,41]. Although numerous in vitro cellular studies have been reported so far, further explorations ought to be focused on in vivo evaluations of these nanosponges (Table 1) [42]. Cyclodextrins have shown significant reactivity and can be directly co-polymerized with other monomers or grafted onto organic/inorganic compounds due to the presence of hydroxyl groups with the capability of a substitution/elimination process [43]. Cyclodextrin nanosponges with varying lipophilic cavities and a hydrophilic network based on the nature of cross-linkers can be considered as ideal alternates to improve the stability of compounds (e.g., volatile compounds) and the solubility of drugs/therapeutic agents (Figure 2) [44]. Notably, the porosity and surface area of nanosponges can be affected by the amount of cross-linkers; typically, with an increase in the amount of cross-linker usage, nanosponges with smaller sizes and greater porosity can be obtained. These nanosystems are resistant to organic solvents and can show good thermal stability (up to 300 °C), which makes them attractive candidates for a variety of nanoformulations [12]. For instance, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges have been designed to enhance the aqueous solubility of kynurenic acid as an antioxidant with therapeutic activities. Accordingly, the solubility of this antioxidant was highly enhanced, and higher drug-loading (~19.06%) and encapsulation proficiency (~95.31%) could also be obtained [45]. In addition, hyper-branched cyclodextrin-based nanosponges with high encapsulation efficiency (~80%) were developed for improving the physicochemical properties of norfloxacin (an antibiotic), thus facilitating its oral absorption; improved antimicrobial activity in sepsis models (in vivo) was discerned [46].

Table 1.
Some selected examples of nanosponges in biomedicine with attractive benefits.
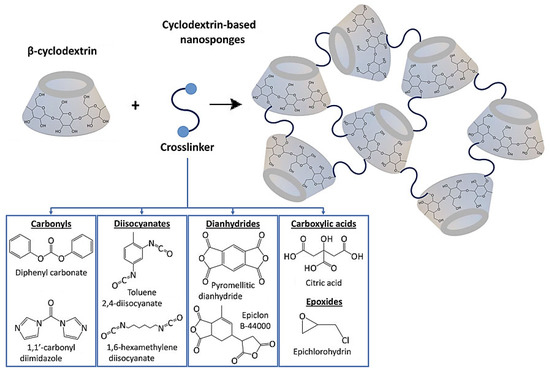
Figure 2.
Assorted cross-linkers applied for manufacturing cyclodextrin nanosponge-based systems. Adapted from [12] with permission. Copyright 2022 Frontiers (CC BY 4.0).
Glutathione-responsive cyclodextrin nanosponges have been designed for the targeted drug delivery of doxorubicin with improved anti-tumoral activity (in vitro and in vivo) (Figure 3). These nanosystems with good biosafety exhibited reduced drug resistance properties as they could be taken up via the active mechanisms and circumvent the efflux drug pump [60]. Similarly, glutathione bio-responsive nanosponges with high degradability, pH-responsive behavior, and efficient drug-loading capacity (~22.6%) were fabricated utilizing β-cyclodextrin-appended hyper-crosslinked polymer via the oligomerization of acryloyl-6-ethylenediamine-6-deoxy-β-cyclodextrin, acrylic acid, with N,N-bis (acryloyl)-cystamine (as a cross-linker) for the targeted delivery of doxorubicin. As a result, the release of doxorubicin was highly enhanced (~77.0%) in acidic (pH = 5.0) and cytosolic reducing (10 mM glutathione) environments, offering promising platforms for the targeted drug transport in tumor therapy [61].
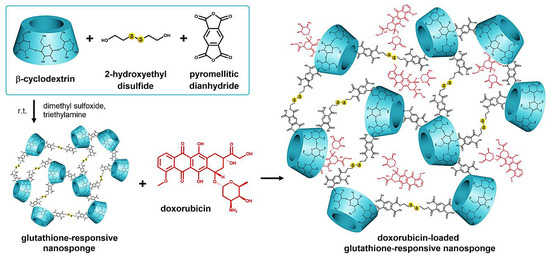
Figure 3.
Preparative process for doxorubicin-loaded glutathione-responsive nanosponges with antitumor effects. Adapted from [60] with permission. Copyright 2020 Elsevier.
Hyper-crosslinked cyclodextrin nanosponges (~316.4 ± 8.5 nm) synthesized via a solvent evaporation technique were loaded with artemether and lumefantrine (antimalarial agents) to improve their solubility and to acquire a controlled-release profile. In vitro evaluations illustrated the controlled-release behaviors of these nanosponges for 24 h; they exhibited good stability at 40°C for 3 months [62]. Additionally, β-cyclodextrin nanosponges were designed for transferring lipophilic drugs (e.g., dexibuprofen) and providing efficient delivery systems for improving the drug solubility [63]. Nanosponges were also constructed for improving the solubility of docetaxel in aqueous media with targeted delivery benefits [30,64,65]. Palminteri et al. [66] constructed a novel system using cyclodextrin-centered nanosponges for transferring the glutathione-mediated transport of resveratrol into the targeted cancerous cells. In addition, the oral bioavailability of avanafil and dapoxetin was improved by applying cyclodextrin-based nanosponges [67]. Magnetic nanosponges have shown great potential for targeted drug delivery as well [68]. These nanosystems were prepared after the addition of magnetite nanomaterial to the polymers of cyclodextrin and maltodextrin, crosslinked with 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole. One study reported the design of magnetic nanosponges for the targeted delivery of doxorubicin with the loading capacity of ~3 wt%, wherein the loaded anticancer drug could be released with sustained kinetics over a prolonged period of time [68].
2.2. DNAzyme Nanosponges
The developments in bioinspired, self-catabolic DNAzyme nanosponges with controllable drug delivery behaviors and suitable gene silencing functions have been reported, thereby opening a new window in designing smart nanosystems with gene therapeutic and personalized biomedical commitments [69]. For instance, bioinspired self-catabolic DNAzyme nanosponges were fabricated with multifunctionality for controllable and targeted drug delivery and gene silencing with high efficiency [70]. Wang et al. [71] developed a DNAzyme-driven drug transport system containing the rolling circle oligomerized DNAzyme-substrate frameworks and the captured pH-receptive ZnO nanomaterials (Figure 4). The designed DNAzyme nanosponges could be encoded with multivalent tandem aptamer arrangements for targeted delivery into cancerous cells. Accordingly, the dissolution of ZnO into Zn2+ ions was stimulated by the acidic endo/lysosomal microenvironment to perform as co-factors of DNAzyme and the creators of therapeutic reactive oxygen species (ROS) [71].
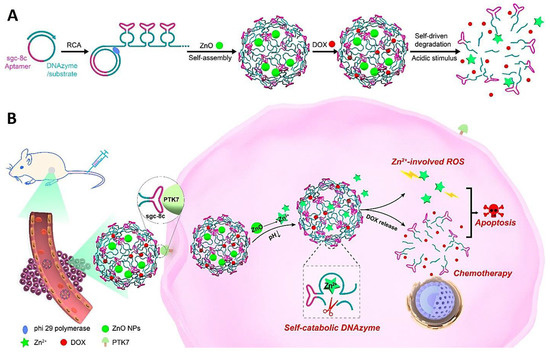
Figure 4.
(A) Isothermal rolling circle amplification (RCA)-based assembly and acid-stimulated disassembly of nanosponge-based delivery systems containing doxorubicin (DOX), DNAzyme, and ZnO nanomaterials. (B) The intracellular dissolution of ZnO into Zn2+ ions can induce the formation of ROS and activate the cleavage of DNAzyme along with the stimulated release of the anticancer drug after specific uptake by cells. Adapted from [71] with permission. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.
Self-assembled DNA nanosponges were designed with multivalent tumor cell-fastening ligands to enable the tumor-explicit drug release with high efficacy (Figure 5) [72]. These nanosponges were applied for adsorption and clearance of intracellular miRNA-21 and could be damaged under acidic pH conditions in endo/lysosomes to provide plentiful miRNA-21 binding sites and induce the discharge of doxorubicin. They triggered synergistic antitumor chemotherapy, which ensued as a result of the co-delivery of doxorubicin and antisense oligonucleotides for miRNA-21. The improvement of antitumor chemotherapy by DNA nanosponges could be attained via the modification of the cell apoptosis-associated gene expression triggered by them [72].
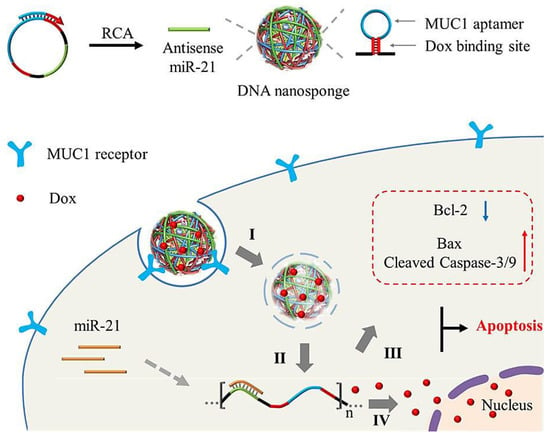
Figure 5.
DNA nanosponges created for the clearance and adsorption of intracellular miRNA-21 (miR-21), along with regulatory effects of gene expression in tumor cells for synergistic and specific antitumor chemotherapy (I-IV). RCA: rolling circle amplification; Dox: doxorubicin. Adapted from [72] with permission. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.
Dynamic DNA nanosponges with appropriate stability and biocompatibility were designed for DNAzyme-mediated gene regulation and programmable tumor-targeted delivery with high efficiency [73]. After environmental stimulation, the performance of DNAzyme was increased and the cleavage of RNA was accelerated by a supplementary catalytic co-factor. Notably, the generation of O2 and 1O2 was accelerated as a supplementary treatment, providing concurrently self-enhanced gene-photodynamic cancer therapy [73]. Future studies ought to focus on the clinical translation of these oligonucleotide-based drugs for cancer therapy. Sponge-like nanoplatforms were developed via the simple assembly of a cationic polymer and a long single strand of DNA encoded with sequences of multivalent deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme) (Figure 6) [69]. These nanosponges were employed for the photothermal therapy of cancers to overcome thermal resistance. The DNAzymes catalytically cleaved the HSP70 mRNAs and downregulated the expression of the subsequent proteins to obtain protection effects towards the cancer cells (MCF-7) from destruction by hyperthermia, sensitizing these cancerous cells to heat via the overexpression inhibition of HSP70. These nanosponges could be applied for multimodal imaging due to their efficient tumoral accumulation capabilities with an enhanced permeability and retention effect [69].
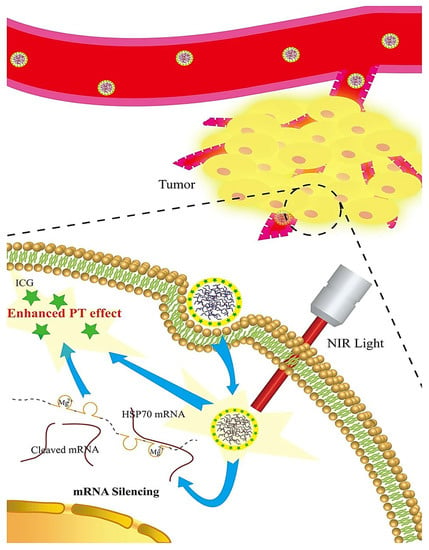
Figure 6.
DNAzyme-based nanosponges applied for targeted photothermal therapy of tumors with multimodal imaging potentials. PT: photothermal; NIR: near-infrared; ICG: indocyanine green (photothermal small molecule). Adapted from [69] with permission. Copyright 2018 Springer Nature (CC BY 4.0).
2.3. Ethylcellulose Nanosponges
Ethylcellulose nanosponges were constructed via an ultrasonic-assisted emulsion solvent evaporation method for the targeted delivery of withaferin-A with anticancer properties [74]. Accordingly, the examined drug was successfully entrapped (~85 ± 11%) into the nanosponges (~117 ± 4 nm) for anticancer activity against MCF-7 cells (the half-maximal inhibitory concentration = ~1.57 ± 0.091 µM). The possible mechanism for the elimination of cancer cells was based on apoptosis. After the in vivo evaluation of the nanosponge-based system, the results were consistent with those obtained with cisplatin [74]. In addition, to improve the bioavailability of Abemaciclib (an anticancer drug against breast cancer), ethylcellulose nanosponges were created with sustained-release behavior via an emulsion solvent diffusion technique [75]. Consequently, the nanosponges exhibited high stability and sustained release of the drug (~77.12 ± 2.54%) in 24 h, with efficient cytotoxic activity versus MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancerous cells [75]. Spherical ethylcellulose nanosponges with sustained-release behavior were prepared via a quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion technique and could be deployed for the delivery of hesperetin with anti-carcinogenic, tumor necrosis, and antioxidant effects [76]. These nanosponges could retard the drug discharge (~39.98%) for up to 8 h relative to the neat drug (~70.74%) and the physical blend (~73.72%), with robust downregulating influences on cytokines [76].
Almutairy et al. [77] developed ethylcellulose nanosponges for improving the oral bioavailability of olmesartan medoxomil with antihypertensive potentials (in vivo). This nanosystem with sustained-release behavior exhibited higher cytotoxicity against A549 lung cell lines in relation to the neat drug and, additionally, could significantly reduce the systolic blood pressure compared to the control and pure drug [77]. In addition, lemongrass-loaded ethylcellulose nanosponges were formulated via an emulsion solvent evaporation method, which displayed enhanced in vivo antifungal activity against Candida albicans strain ATC 100,231 and reduced irritation [78]. Ethylcellulose nanosponges (~272.92 ± 12.31 nm) fabricated by the double emulsion solvent evaporation technique exhibited the entrapment efficiency for carboplatin of ~56.27 ± 2.52%. The designed nanosponges had sustained drug releases of 79.03% (pH = 4.5) and 95.94% (pH = 6.8) within 12 h, making them efficient nanocarriers with the sustained release of hydrophilic therapeutic agents [79].
Nanosponges have been synthesized through an emulsion solvent evaporation technique deploying polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and ethylcellulose for the targeted delivery of ribociclib, a kinase inhibitor against metastatic breast cancer [80]. Consequently, the encapsulation of the drug was successfully accomplished within the porous polymeric matrix. After in vitro analyses, it was revealed that the drug release was highly accelerated, with a maximum drug release through the ribociclib-loaded nanosponges (~81.85 ± 0.37%). This nanosystem exhibited high cytotoxic effects against MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancerous cell lines, with a higher degree of apoptosis compared to the free ribociclib, offering promising platforms for targeted drug delivery against metastatic cancers, with a higher safety and efficacy profile [80]. Additionally, nanosponge-based platforms (~261.0 ± 3.5 nm) endowed with a sustained mode were constructed from ethylcellulose and PVA via an emulsion solvent evaporation method for targeted delivery of brigatinib as tyrosine kinase inhibitors against lung cancer cells [81]; the entrapment efficiency was ~85.69 ± 0.04% and the drug loading was ~17.69 ± 0.01%. The nanosystems exhibited sustained drug release (~86.91 ± 2.12%) for ~12 h, thereby efficiently reducing the cell viability of the human lung cancer cell line A549 [81].
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Nanosponge-based systems endowed with remarkable porosity, simple functionalization processes, unique architectures, eco-friendliness, and cost-effectiveness have been explored as promising alternatives to targeted drug delivery and cancer therapy. Among them, cyclodextrin nanosponges exhibited unique properties, high biocompatibility, negligible toxicity, and ease of surface modifications, which renders them the predominantly evaluated nanosponges in bio- and nanomedicine. Future studies ought to be directed towards the efficient functionalization of nanosponges for the reduction in possible toxicity, the improvement of their biosafety, and the enhancement of their specificity/selectivity. These structures can be applied to improve the solubility of the drugs/therapeutic agents and protect them from degradation; by changing the concentration of polymers/other materials and the cross-linker ratio, innovative nanosponges can be obtained endowed with multifunctionality and different properties. Notably, additional explorations need to focus on their biodistribution and biocompatibility. To better improve the physicochemical properties and functionality of nanosponges, further optimization studies are still necessary; their complexation performances, structural variations, commercialization, long-term biosafety analyses, low-cost/large-scale production, and specific nanotoxicological assessments ought to be comprehensively focused on in future explorations. Additional studies are warranted to focus on the specific surface functionalization or modification of nanosponges using distinct materials, such as fluorescent compounds, magnetite nanoparticles, folic acid, etc., to fabricate multifunctional systems with cancer/tumor theranostic applications.
Author Contributions
S.I. and R.S.V.: conceptualization, writing—reviewing and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Joseph, X.; Akhil, V.; Arathi, A.; Mohanan, P.V. Nanobiomaterials in support of drug delivery related issues. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 279, 115680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, M.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Jaleh, B.; Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, S. Carbon-based nanomaterials for targeted cancer nanotherapy: Recent trends and future prospects. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 716–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrion, C.C.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Jaleh, B.; Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, S. Lignin, lipid, protein, hyaluronic acid, starch, cellulose, gum, pectin, alginate and chitosan-based nanomaterials for cancer nanotherapy: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 178, 193–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Plant pollen grains: A move towards green drug and vaccine delivery systems. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Important Roles of Oligo- and Polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2: Recent Advances. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Nanosponges for water treatment: Progress and challenges. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pisapati, A.V.; Zhang, X.F.; Cheng, X. Recent developments in nanomaterial-based shear-sensitive drug delivery systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2002196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Nano- and biosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: Challenges and opportunities. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 3092–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Nanophotocatalysts against viruses and antibiotic-resistant bacteria: Recent advances. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, R.A.M.; Hani, U.; Bhosale, R.R.; Kulkarni, P.K.; Shanmuganathan, S. Nanosponge carriers-an archetype swing in cancer therapy: A comprehensive review. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyari, S.; Zahednezhad, F.; Khatami, M.; Hashemzadeh, N.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Trotta, F. Cyclodextrin nanosponges as potential anticancer drug delivery systems to be introduced into the market, compared with liposomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 67, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzeri, G.; Matias, P.M.C.; Murtinho, D.; Valente, A.J.M. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: Overview and opportunities. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 859406. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, P.P.; Prathvi; Gujaran, T.V.; Mehta, C.H.; Suresh, A.; Koteshwara, K.B.; Pai, K.G.; Nayak, U.Y. Development of lapatinib nanosponges for enhancing bioavailability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 102684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lembo, D.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges as vehicles for antiviral drugs: Challenges and perspectives. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, V.; Sartini, S.; Quattrini, L.; Baraldi, C.; Gamberini, M.C.; La Motta, C. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for the targeted delivery of the anti-restenotic agent DB103: A novel opportunity for the local therapy of vessels wall subjected to percutaneous intervention. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherje, A.P.; Dravyakar, B.R.; Kadam, D.; Jadhav, M. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: A critical review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Bhattacharya, S. The ascension of nanosponges as a drug delivery carrier: Preparation, characterization, and applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2022, 33, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, Q.J.; Li, W.; Zuberi, Z.; Feng, J.X.; Lin, Q.L.; Ren, J.L.; Luo, F.J.; Ding, Q.M.; Zeng, X.X.; et al. Toward improvements for carrying capacity of the cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: Recent progress from a material and drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 5995–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yapa, A.S.; Kariyawasam, N.L.; Shrestha, T.B.; Kalubowilage, M.; Wendel, S.O.; Yu, J.; Pyle, M.; Basel, M.T.; Malalasekera, A.P.; et al. Rationally designed peptide nanosponges for cell-based cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 2555–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailaja, D.; Pramodkumar, S. Nanosponges Encapsulated Phytochemicals for Targeting Cancer: A Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 443–462. [Google Scholar]
- Varan, C.; Anceschi, A.; Sevli, S.; Bruni, N.; Giraudo, L.; Bilgiç, E.; Korkusuz, P.; İskit, A.B.; Trotta, F.; Bilensoy, E. Preparation and characterization of cyclodextrin nanosponges for organic toxic molecule removal. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 585, 119485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.; Shende, P. A Comprehensive Patent Review on β-cyclodextrin Cross-linked Nanosponges for Multiple Applications. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 14, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Greener approach to nanomaterials and their sustainable applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Journey on greener pathways: From the use of alternate energy inputs and benign reaction media to sustainable applications of nano-catalysts in synthesis and environmental remediation. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2027–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Greener and sustainable chemistry. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varma, R.S. Greener and Sustainable Trends in Synthesis of Organics and Nanomaterials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5866–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, R.S. Biomass-Derived Renewable Carbonaceous Materials for Sustainable Chemical and Environmental Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6458–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Kadian, V.; Kumar, A.; Mahant, S.; Rao, R. Evaluation of Solubility, Photostability and Antioxidant Activity of Ellagic Acid Cyclodextrin Nanosponges Fabricated by Melt Method and Microwave-Assisted Synthesis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 59, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, A.; Ciesielski, W.; Girek, B.; Girek, T.; Koziel, K.; Kulawik, D.; Lagiewka, J. Biomedical application of cyclodextrin polymers cross-linked via dianhydrides of carboxylic Acids. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, F.; Tannous, M.; Cavalli, R.; Zanetti, M.; Trotta, F. Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Prajapati, S.K.; Kumari, A.; Mody, N.; Bajpai, M. Engineered nanosponges as versatile biodegradable carriers: An insight. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Singh, P.; Singhal, A.; Alka. Cyclodextrin-based nanostructured materials for sustainable water remediation applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32432–32448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei Monfared, Y.; Mahmoudian, M.; Cecone, C.; Caldera, F.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Matencio, A.; Trotta, F. Stabilization and Anticancer Enhancing Activity of the Peptide Nisin by Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges against Colon and Breast Cancer Cells. Polymers 2022, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taka, A.L.; Pillay, K.; Mbianda, X.Y. Nanosponge cyclodextrin polyurethanes and their modification with nanomaterials for the removal of pollutants from waste water: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkas, M.; Allabashi, R.; Tsiourvas, D.; Mattausch, E.-M.; Perfler, R. Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Filters Based on Dendritic and Cyclodextrin “Nanosponges” for the Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Ren, X.; Guo, T.; Wu, L.; Shakya, S.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Maharjan, A.; Singh, V.; Zhang, J. Biofunctionalization of β-cyclodextrin nanosponges using cholesterol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, R.K.; Patel, N.; Patel, Z.; Chakraborthy, G.S.; Upadhye, V. Nanosponges as a biocatalyst carrier—An innovative drug delivery technology for enzymes, proteins, vaccines, and antibodies. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 102329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.D.P.; Andrade, T.d.A.; Frank, L.A.; Soares de Souza, E.P.B.S.; Trindade, G.d.G.G.; Trindade, I.A.S.; Serafini, M.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Araújo, A.A.d.S. Advances of nanosystems containing cyclodextrins and their applications in pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Oh, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Shin, Y.C.; Choi, W.I. A Novel Chitosan Nanosponge as a Vehicle for Transepidermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taka, A.L.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Pillay, K.; Yangkou Mbianda, X. Metal nanoparticles decorated phosphorylated carbon nanotube/cyclodextrin nanosponge for trichloroethylene and Congo red dye adsorption from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torne, S.; Darandale, S.; Vavia, P.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: Effective nanocarrier for tamoxifen delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyari, S.; Trotta, F.; Valizadeh, H.; Jelvehgari, M.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges as promising carriers for active agents. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 2019, 16, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, D.A.; Bolaños, K.; Priotti, J.; Yutronic, N.; Kogan, M.J.; Sierpe, R.; Donoso-González, O. Cyclodextrin-Modified Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery: Classification and Advances in Controlled Release and Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asela, I.; Donoso-González, O.; Yutronic, N.; Sierpe, R. β-Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges functionalized with drugs and gold nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, N.K.; Caldera, F.; Bessone, F.; Cecone, C.; Pedrazzo, A.R.; Cavalli, R.; Dianzani, C.; Trotta, F. Evaluation of solubility enhancement, antioxidant activity, and cytotoxicity studies of kynurenic acid loaded cyclodextrin nanosponge. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, C.; Meirelles, G.C.; Barp, C.G.; Assreuy, J.; Silva, M.A.; Ponchel, G. Cyclodextrin based nanosponge of norfloxacin: Intestinal permeation enhancement and improved antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, F.; Argenziano, M.; Trotta, F.; Dianzani, C.; Gigliotti, L.; Tannous, M.; Pastero, L.; Aquilano, D.; Nishimoto, T.; Higashiyama, T.; et al. Cyclic nigerosyl-1,6-nigerose-based nanosponges: An innovative pH and time-controlled nanocarrier for improving cancer treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, C.P.; Trotta, F.; Kushwah, V.; Devasari, N.; Singh, C.; Suresh, S.; Jain, S. Potential of erlotinib cyclodextrin nanosponge complex to enhance solubility, dissolution rate, in vitro cytotoxicity and oral bioavailability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, R.; Cavalli, R.; Ellis, L.; Pettazzoni, P.; Trotta, F.; Ciamporcero, E.; Barrera, G.; Fantozzi, R.; Dianzani, C.; Pili, R. Nanosponge-encapsulated camptothecin exerts anti-tumor activity in human prostate cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torne, S.J.; Ansari, K.A.; Vavia, P.R.; Trotta, F.; Cavalli, R. Enhanced oral paclitaxel bioavailability after administration of paclitaxel-loaded nanosponges. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyari, S.; Esmailnezhad, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Jelvehgari, M.; Ghazi, F.; Zakeri-Milani, P. In-vitro characterization and cytotoxicity study of flutamide loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, C.L.; Ferrara, B.; Occhipinti, S.; Boggio, E.; Barrera, G.; Pizzimenti, S.; Giovarelli, M.; Fantozzi, R.; Chiocchetti, A.; Argenziano, M.; et al. Enhanced cytotoxic effect of camptothecin nanosponges in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells in vitro and in vivo on orthotopic xenograft tumors. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pushpalatha, R.; Selvamuthukumar, S.; Kilimozhi, D. Cross-linked, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for curcumin delivery-physicochemical characterization, drug release, stability and cytotoxicity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shringirishi, M.; Mahor, A.; Gupta, R.; Prajapati, S.K.; Bansal, K.; Kesharwani, P. Fabrication and characterization of nifedipine loaded β-cyclodextrin nanosponges: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; Pai, J.-Y.; Du, P.; Liu, P. Facile synthesis of fluorescent hyper-cross-linked β-cyclodextrin-carbon quantum dot hybrid nanosponges for tumor theranostic application with enhanced antitumor efficacy. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4084–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rao, R. Novel dithranol loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges for augmentation of solubility, photostability and cytocompatibility. Cnano 2021, 17, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.M.; Ibrahim, F.; Ismail, A. Formulation and evaluation of cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of griseofulvin as pediatric oral liquid dosage form for enhancing bioavailability and masking bitter taste. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.K.; Trotta, F.; Gaud, R.; Deshmukh, K.; Cavalli, R.; Biasizzo, M. Influence of different techniques on formulation and comparative characterization of inclusion complexes of ASA with β-cyclodextrin and inclusion complexes of ASA with PMDA cross-linked β-cyclodextrin nanosponges. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 74, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Bajaj, A.; Khole, I.; Munjapara, G.; Trotta, F. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of b-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of telmisartan. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 77, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daga, M.; de Graaf, I.A.M.; Argenziano, M.; Barranco, A.S.M.; Loeck, M.; Al-Adwi, Y.; Cucci, M.A.; Caldera, F.; Trotta, F.; Barrera, G.; et al. Glutathione-responsive cyclodextrin-nanosponges as drug delivery systems for doxorubicin: Evaluation of toxicity and transport mechanisms in the liver. Toxicol. Vitr. 2020, 65, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Shi, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W. Smart GSH/pH dual-bioresponsive degradable nanosponges based on β-CD-appended hyper-cross-linked polymer for triggered intracellular anticancer drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.; Shende, P. Dual drug delivery of cyclodextrin cross-linked artemether and lumefantrine nanosponges for synergistic action using 23 full factorial designs. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 602, 125049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, Q.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Batool, F.; Malik, N.S.; Rehman, M. Novel β-cyclodextrin nanosponges by chain growth condensation for solubility enhancement of dexibuprofen: Characterization and acute oral toxicity studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.S.B.; Akhtar, N.; Minhas, M.U.; Mahmood, A.; Khan, K.U. Synthesis and Characterization of Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanosponges with Cyclodextrin Blends for Drug Solubility Improvement. Gels 2022, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabicová, I.; Appleton, S.L.; Tannous, M.; Hoti, G.; Caldera, F.; Pedrazzo, A.R.; Cecone, C.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F. History of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Polymers 2020, 12, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palminteri, M.; Dhakar, N.K.; Ferraresi, A.; Caldera, F.; Vidoni, C.; Trotta, F.; Isidoro, C. Cyclodextrin nanosponge for the GSH-mediated delivery of Resveratrol in human cancer cells. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardouh, A.R.; Elhusseiny, S.; Gad, S. Mixed Avanafil and Dapoxetin Hydrochloride cyclodextrin nano-sponges: Preparation, in-vitro characterization, and bioavailability determination. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, F.; Nisticò, R.; Magnacca, G.; Matencio, A.; Monfared, Y.K.; Trotta, F. Magnetic Composites of Dextrin-Based Carbonate Nanosponges and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Potential Application in Targeted Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liang, L.; Sun, X.; Yu, G.; Chen, S.; Shi, S.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Ge, K.; Liu, D.; et al. Deoxyribozyme-nanosponges for improved photothermal therapy by overcoming thermoresistance. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Gong, X.; He, S.; Shang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, F. A self-catabolic multifunctional DNAzyme nanosponge for programmable drug delivery and efficient gene silencing. Angew Chem. 2021, 60, 10766–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; He, S.; Li, R.; Deng, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, F. Nonviolent Self-Catabolic DNAzyme Nanosponges for Smart Anticancer Drug Delivery. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5852–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Song, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z. DNA Nanosponge for Adsorption and Clearance of Intracellular miR-21 and Enhanced Antitumor Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 46604–46613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J.; Mo, F.; Song, G.; Zou, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. A dynamic DNA nanosponge for triggered amplification of gene-photodynamic modulation. Chem. Sci 2022, 13, 5155–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.S.; Nasrullah, U.; Zaib, S.; Usman, F.; Khan, A.; Gohar, U.F.; Uddin, J.; Khan, I.; Al-Harrasi, A. Preparation, Characterization, and Pharmacological Investigation of Withaferin-A Loaded Nanosponges for Cancer Therapy; In Vitro, In Vivo and Molecular Docking Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Fatima, F.; Ahmed, M.M.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alali, A.S.; Kalam, M.A.; Alshamsan, A.; Alkholief, M.; Malik, A.; Az, A.; et al. Abemaciclib-loaded ethylcellulose based nanosponges for sustained cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells lines. Saudi Pharm. J. 2022, 30, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.; Nadaf, S.; Rarokar, N.; Gurav, N.; Jagtap, P.; Mali, P.; Ayyanar, M.; Kalaskar, M.; Gurav, S. QBD approach for the development of hesperetin loaded colloidal nanosponges for sustained delivery: In-vitro, ex-vivo, and in-vivo assessment. OpenNano 2022, 7, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairy, B.K.; Alshetaili, A.; Alali, A.S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Anwer, M.K.; Aboudzadeh, M.A. Design of olmesartan medoxomil-loaded nanosponges for hypertension and lung cancer treatments. Polymers 2021, 13, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr-Eldin, S.M.; Labib, G.S.; El-Kamel, A.H. Design and formulation of a topical hydrogel integrating lemongrass-loaded nanosponges with an enhanced antifungal effect: In vitro/in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Hafiz, M.A.; Abbas, N.; Bukhari, N.I. Quality by design approach for formulation development and evaluation of carboplatin loaded ethylcellulose nanosponges. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2022, 71, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Fatima, F.; Alali, A.; Kalam, M.A.; Alhazzani, K.; Bhatia, S.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M. Ribociclib-loaded ethylcellulose-based nanosponges: Formulation, physicochemical characterization, and cytotoxic potential against breast cancer. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 1922263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Fatima, F.; Anwer, M.K.; Ansari, M.J.; Das, S.S.; Alshahrani, S.M. Development and characterization of ethyl cellulose nanosponges for sustained release of brigatinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Polym. Eng. 2020, 40, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).