Quantum Dot-Induced Blue Shift of Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
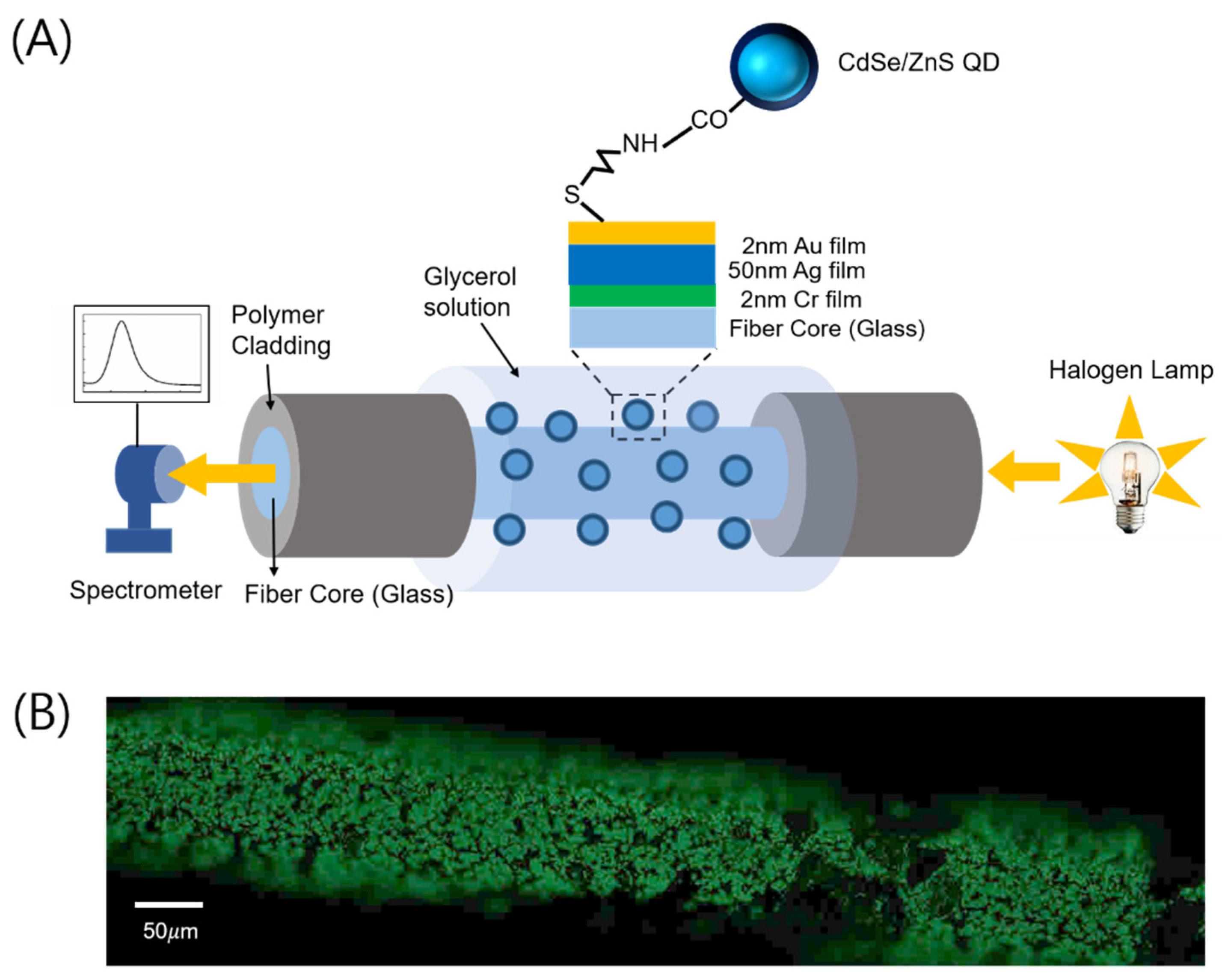
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
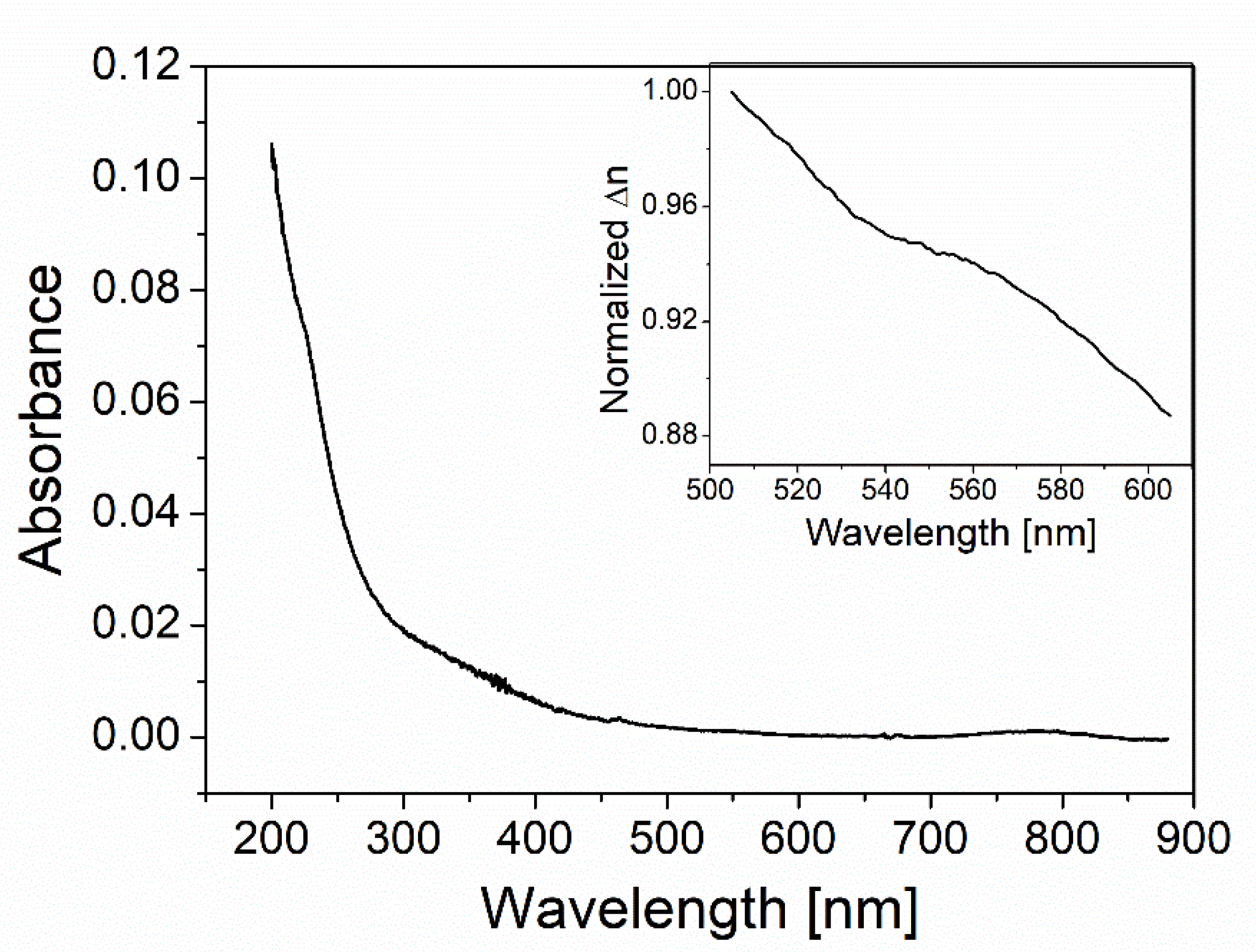
3.1. QDs Absorbance Spectra and KK Relation
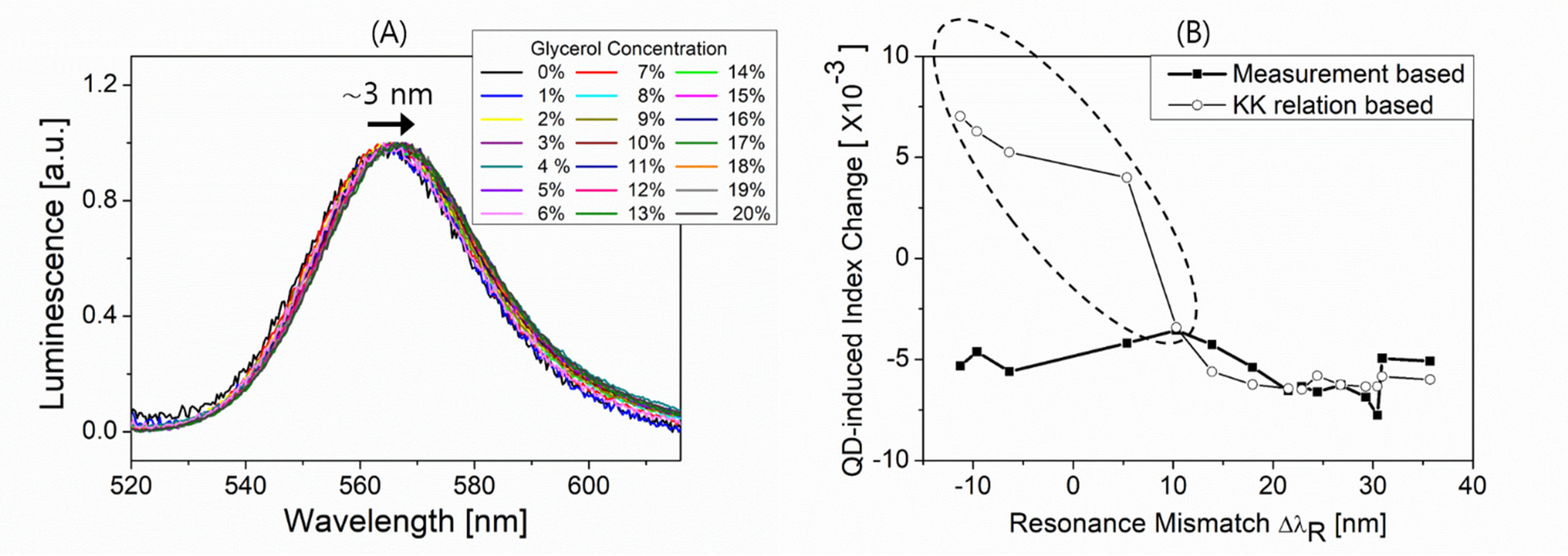
3.2. Coupling of Fiber Surface Plasmons with QDs
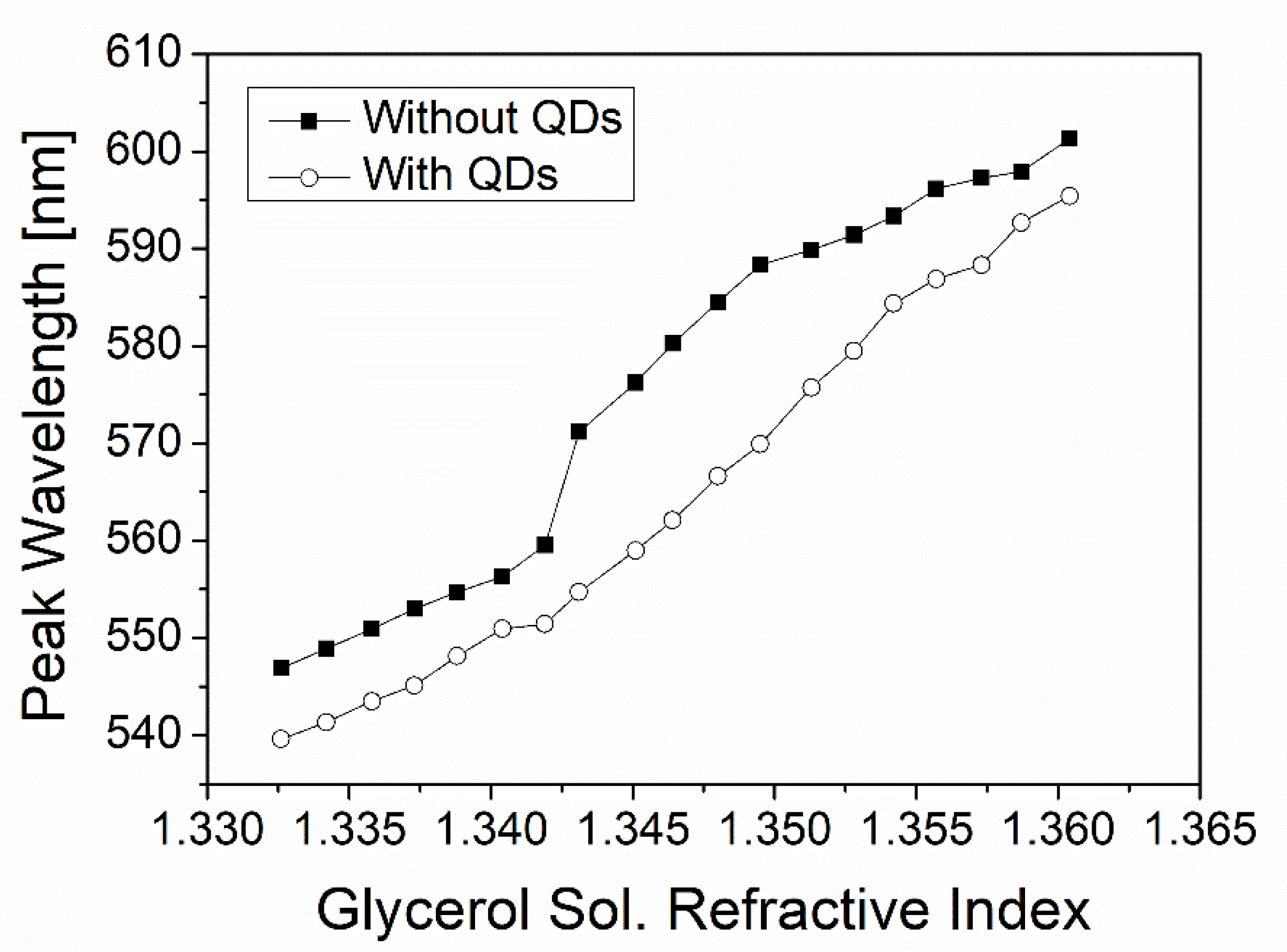
3.3. QD-Induced Blue Shift of Plasmon Resonance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raether, H. Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, S.A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Jha, R.; Gupta, B.D. Fiber-Optic Sensors Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2007, 7, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willets, K.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homola, J. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors for Detection of Chemical and Biological Species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Okamoto, T. Plasmonics: Visit the past to know the future. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 433001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cushing, S.K.; Wu, N. Plasmon-enhanced optical sensors: A review. Analyst 2015, 140, 386–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, T.R.; Duval, M.L.; Kelly, K.L.; Lazarides, A.A.; Schatz, G.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Nanosphere lithography_Effects of the external dielectric medium on the surface plasmon resonance spectrum of a periodic array of silver nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 9846–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, E. Optics; Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Haes, A.J.; Zou, S.; Zhao, J.; Schatz, G.C.; van Duyne, R.P. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy near molecular resonances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10905–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jensen, L.; Sung, J.; Zou, S.; Schatz, G.C.; van Duyne, R.P. Interaction of plasmon and molecular resonances for rhodamine 6G adsorbed on silver nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7647–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, F.; Bohren, D.R.H. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Yariv, A. Optical Electronics in Modern Communications; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, H.; Koch, S.W. Quantum Theory of the Optical and Electronic Properties of Semiconductors, 4th ed.; World Scientific: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, H. Kramers-Kronig Relation for Attenuated Total Reflection from a Metal-Dielectric Interface Where Surface Plasmon Polaritons Are Excited. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, G.; Ogawa, Y.; Minami, F. Density dependence of photoluminescence lifetime of CdSe/ZnS core-shell colloidal quantum dots. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 064323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.D.; Hildebrandt, N. Quantum dots: Bright and versatile in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4792–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nistad, B.; Skaar, J. Causality and electromagnetic properties of active media. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 036603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skaar, J. Causality ans Its Implications for Passive and Active Media, Proceedings of the 2010 URSI International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory (EMTS 2010), Berlin, Germany, 16–19 August 2010; IEEE: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Son, C.; Choi, S.; Yoon, W.J.; Ju, H. A Plasmonic Fiber Based Glucometer and Its Temperature Dependence. Micromachines 2018, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, V.T.; Yoon, W.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Ju, H. DNA sequence-induced modulation of bimetallic surface plasmons in optical fibers for sub-ppq (parts-per-quadrillion) detection of mercury ions in water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23894–23902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, N.J.; Fischer, M.J.E. Surface Plasmon Resonance Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Springer: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yan, Q.; Liu, H.B.; Zhou, X.H.; Xiao, S.J. Different EDC/NHS activation mechanisms between PAA and PMAA brushes and the following amidation reactions. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12058–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingegowda, D.C.; Komal Kumar, J.; Devi Prasad, A.G.; Zarei, M.; Gopal, S. FTIR spectroscopic studies on cleome gynandra-comparative analysis of functional group before and after extraction. Rom. J. Biophys. 2012, 22, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Mahindrakar, J.N.; Patil, Y.S.; Salunkhe, P.H.; Ankushrao, S.S.; Kadam, V.N.; Ubale, V.P.; Ghanwat, A.A. Optically transparent organosoluble poly(ether-amide)s bearing triptycene unit; synthesis and characterization. J. Macrhomol. Sci. Part A-Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 55, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeska, J.; Elert, A.M.; Morawska, M.; Sikorska, W.; Kowalczuk, M.; Rutkowska, M. Branched polyurethanes based on synthetic polyhydroxybutyrate with tunable structure and properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naidoo, C.; Kruger, C.A.; Abrahamse, H. Targeted photodynamic therapy treatment of in vitro A375 metastatic melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 6079–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, H.; Uskov, A.V.; Nötzel, R.; Li, Z.; Molina Vázquez, J.; Lenstra, D.; Khoe, G.D.; Dorren, H.J.S. Effects of two-photon absorption on carrier dynamics in quantum-dot optical amplifiers. Appl. Phys. B 2006, 82, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, V.T.; Seok, J.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Ju, H. Quantum Dot-Induced Blue Shift of Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122076
Nguyen TT, Tran VT, Seok JS, Lee J-H, Ju H. Quantum Dot-Induced Blue Shift of Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(12):2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122076
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Than Thi, Vien Thi Tran, Joo Seon Seok, Jun-Ho Lee, and Heongkyu Ju. 2022. "Quantum Dot-Induced Blue Shift of Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy" Nanomaterials 12, no. 12: 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122076
APA StyleNguyen, T. T., Tran, V. T., Seok, J. S., Lee, J.-H., & Ju, H. (2022). Quantum Dot-Induced Blue Shift of Surface Plasmon Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials, 12(12), 2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122076





