Nano-MIL-88A(Fe) Enabled Clear Cellulose Films with Excellent UV-Shielding Performance and Robust Environment Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
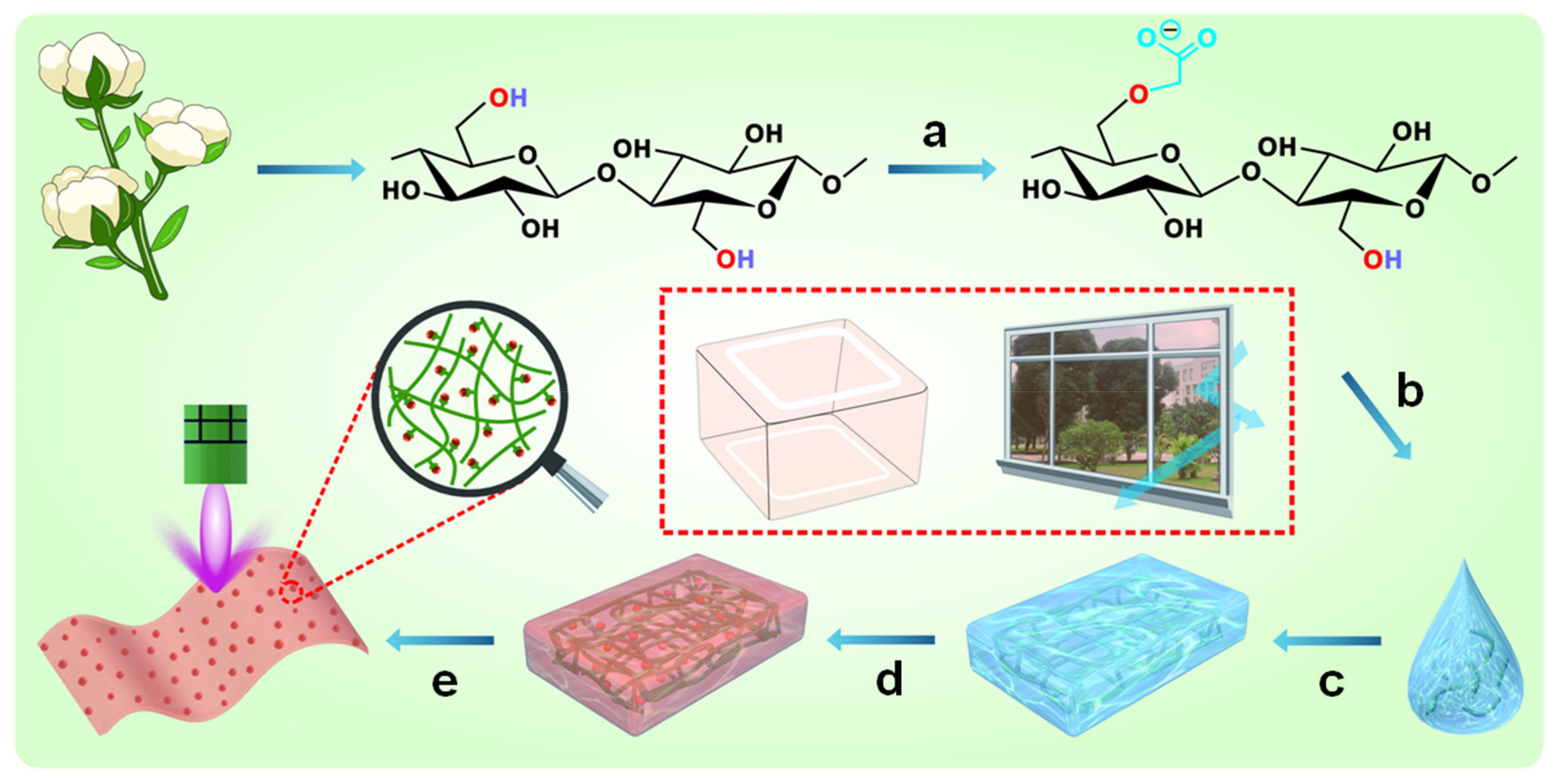
2.2. Fabrication of Carboxymethylated Cellulose Fibers
2.3. Fabrication of MIL-88A(Fe)@Carboxymethylated Cellulose Films (M(Fe)CCFs)
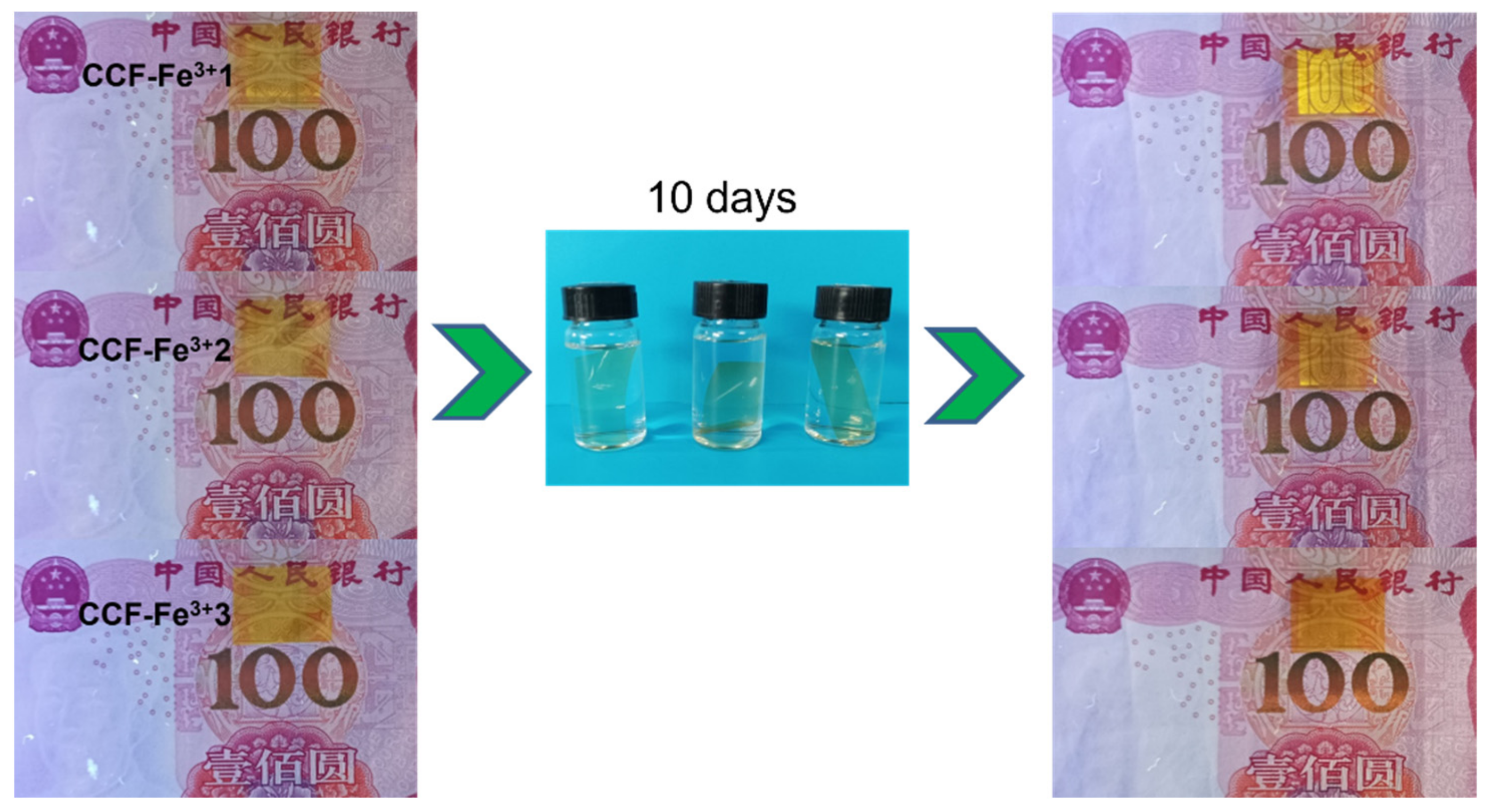
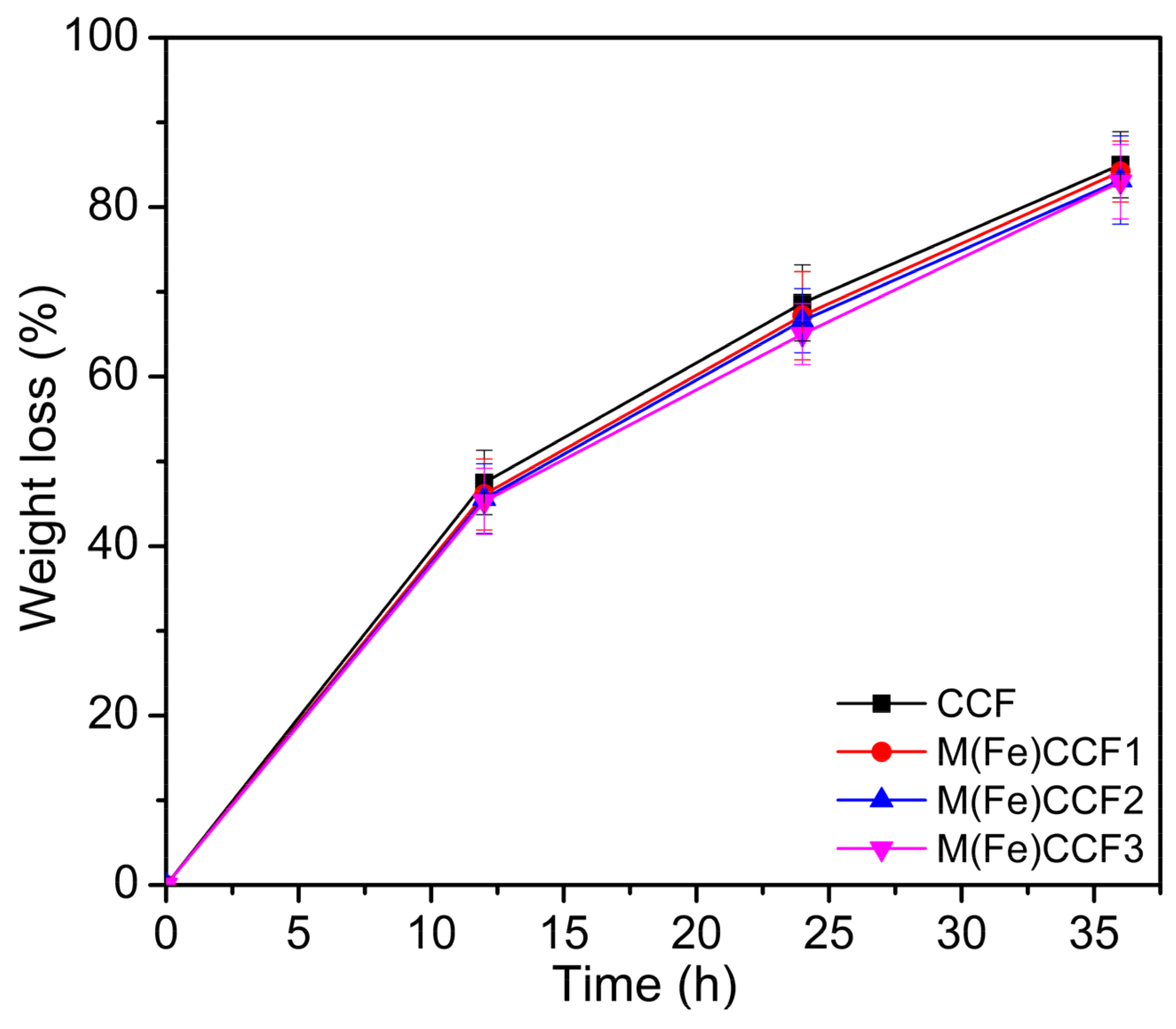
2.4. Environmental Resistance Test
2.5. Biodegradability Test
2.6. Characterization
3. Results
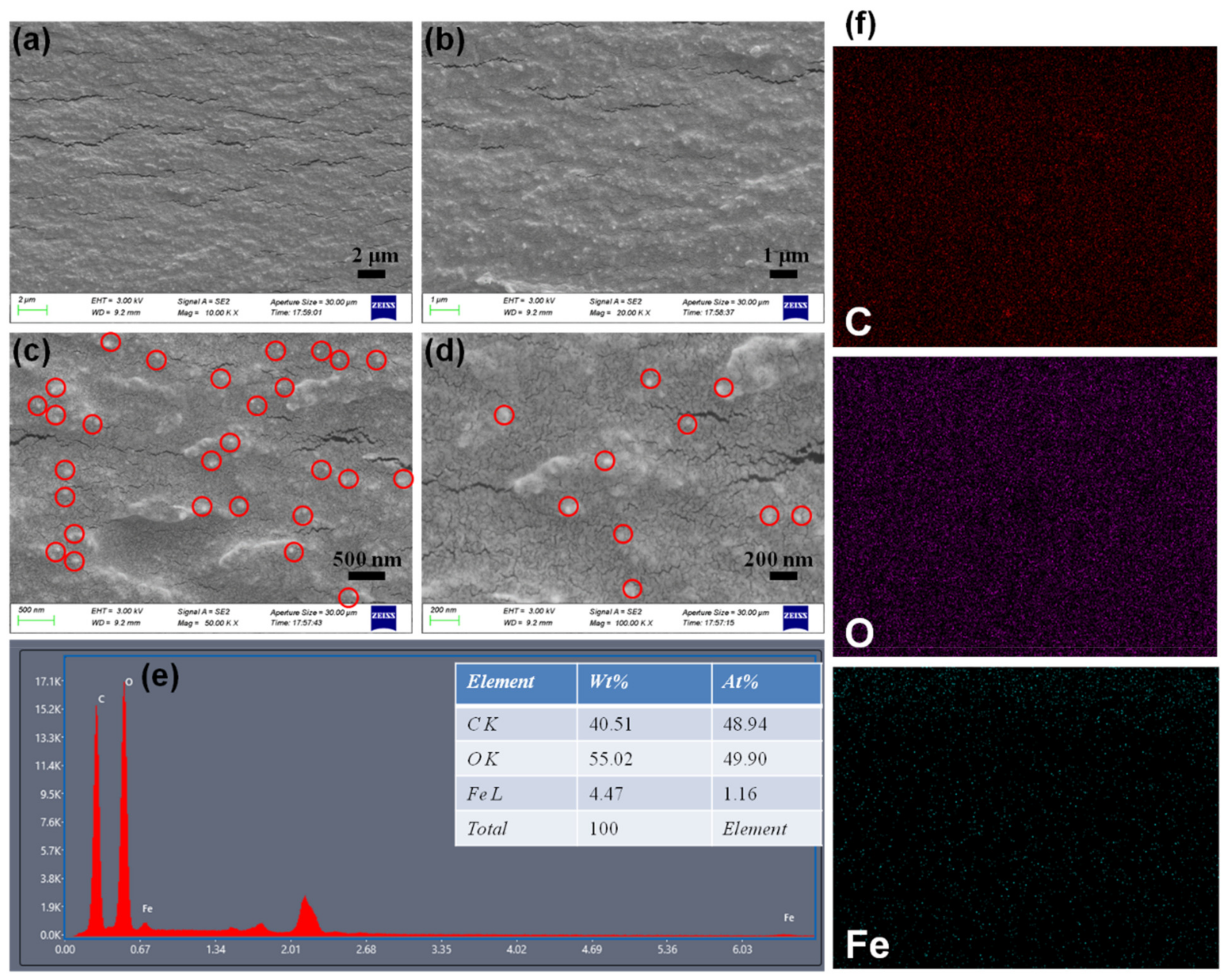
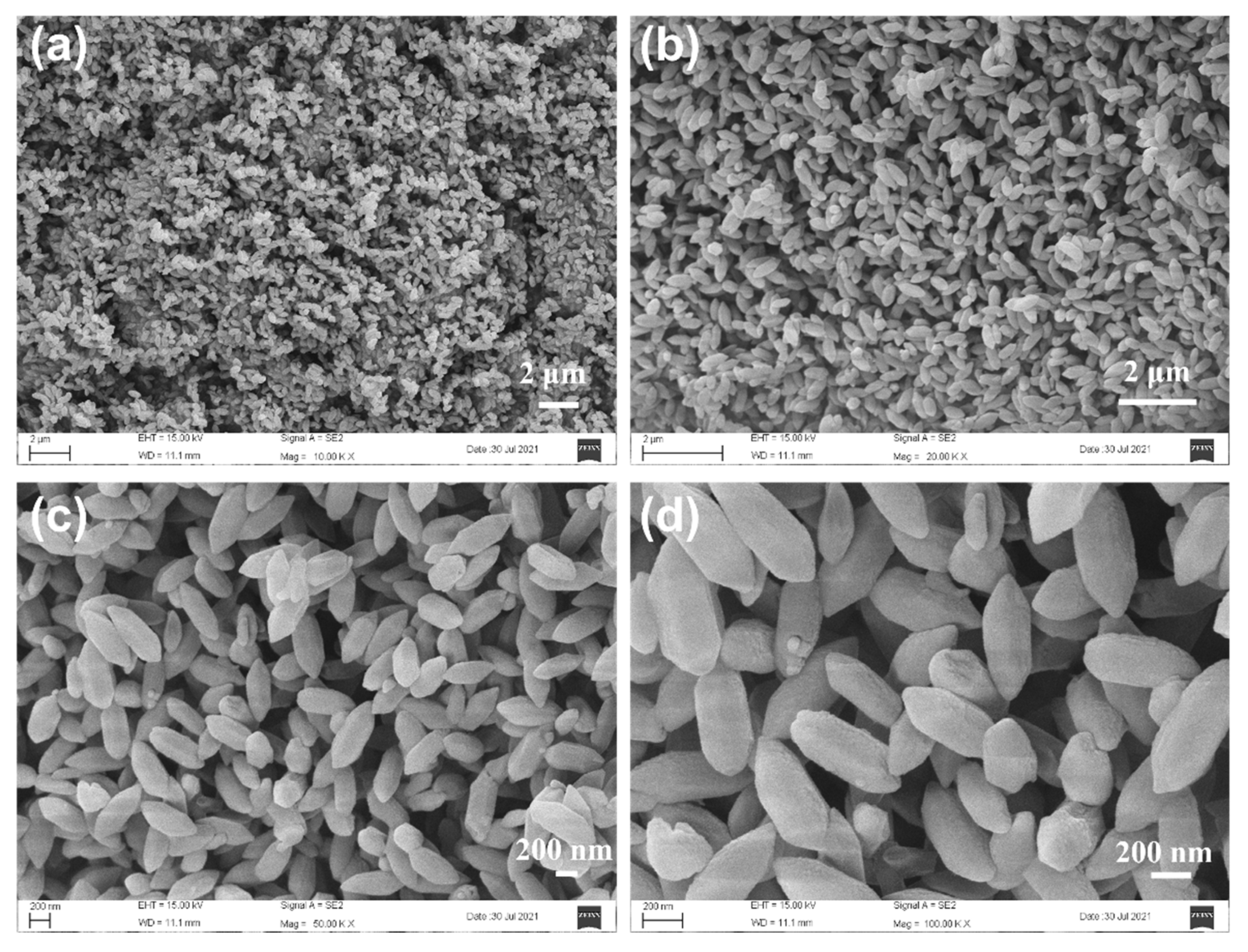
3.1. Structure and Morphology of M(Fe)CCFs
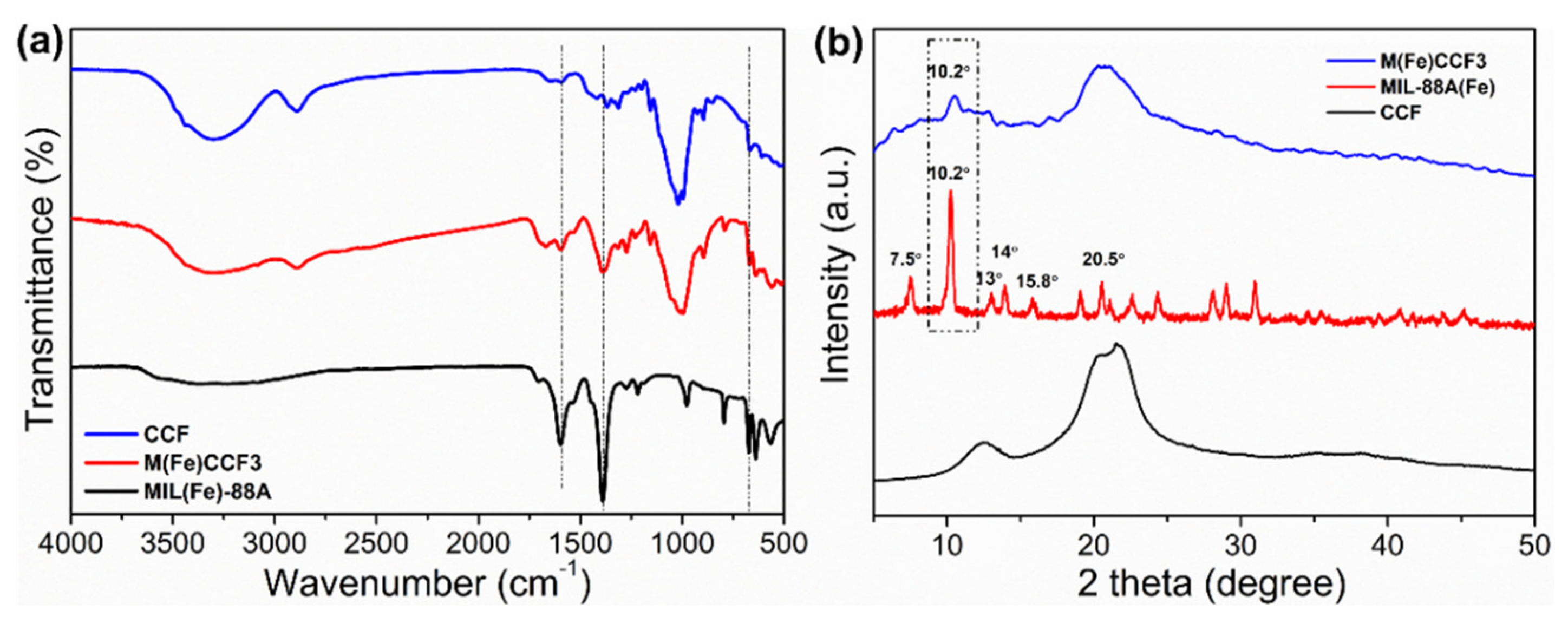
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. XRD Analysis
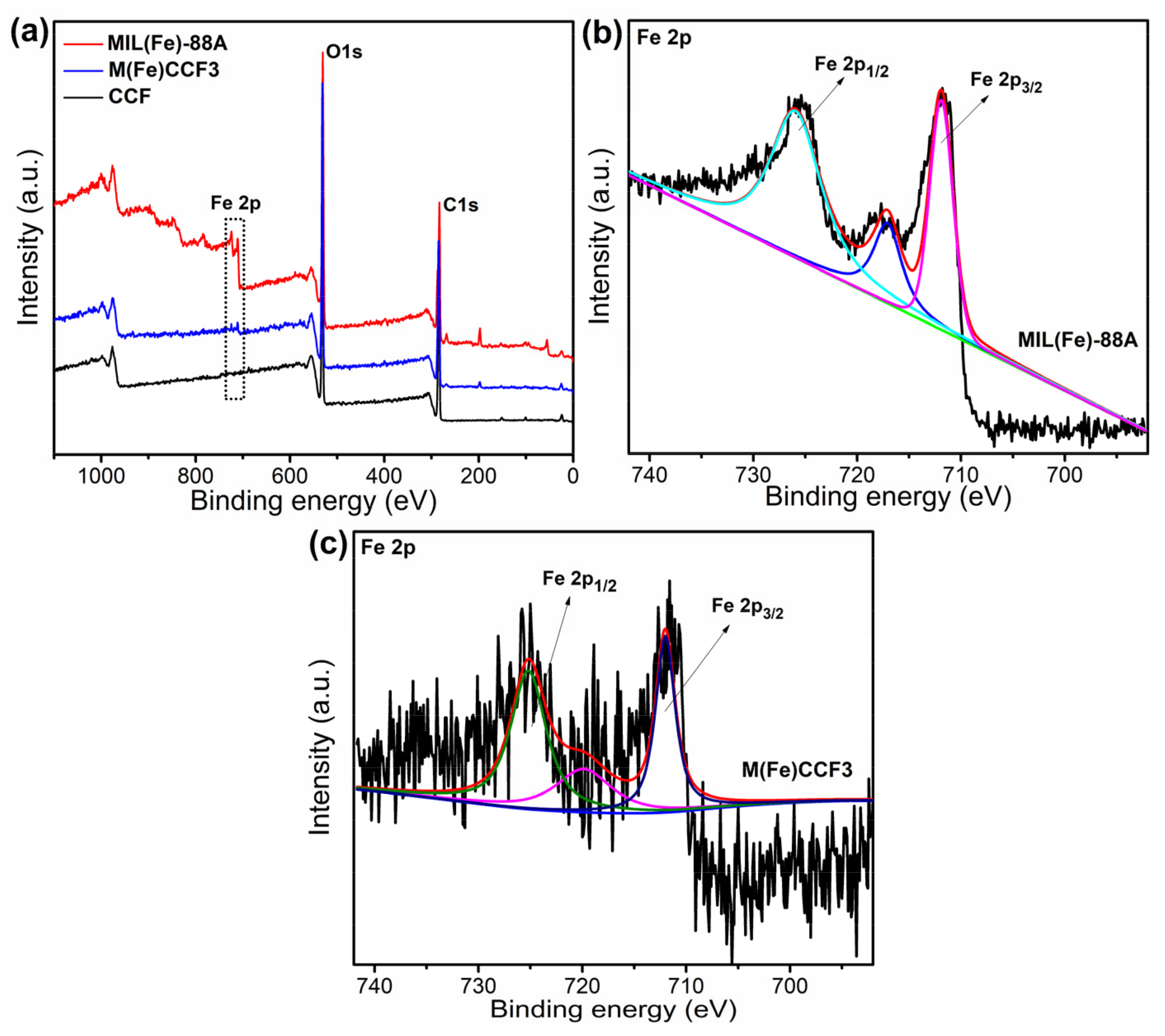
3.4. XPS Analysis
3.5. TG Analysis
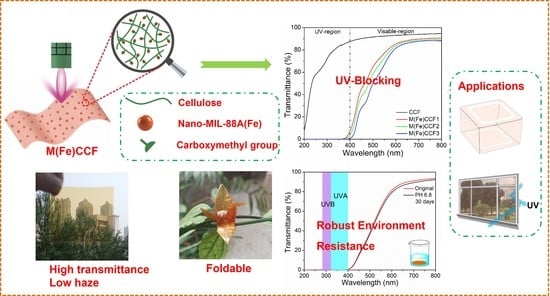
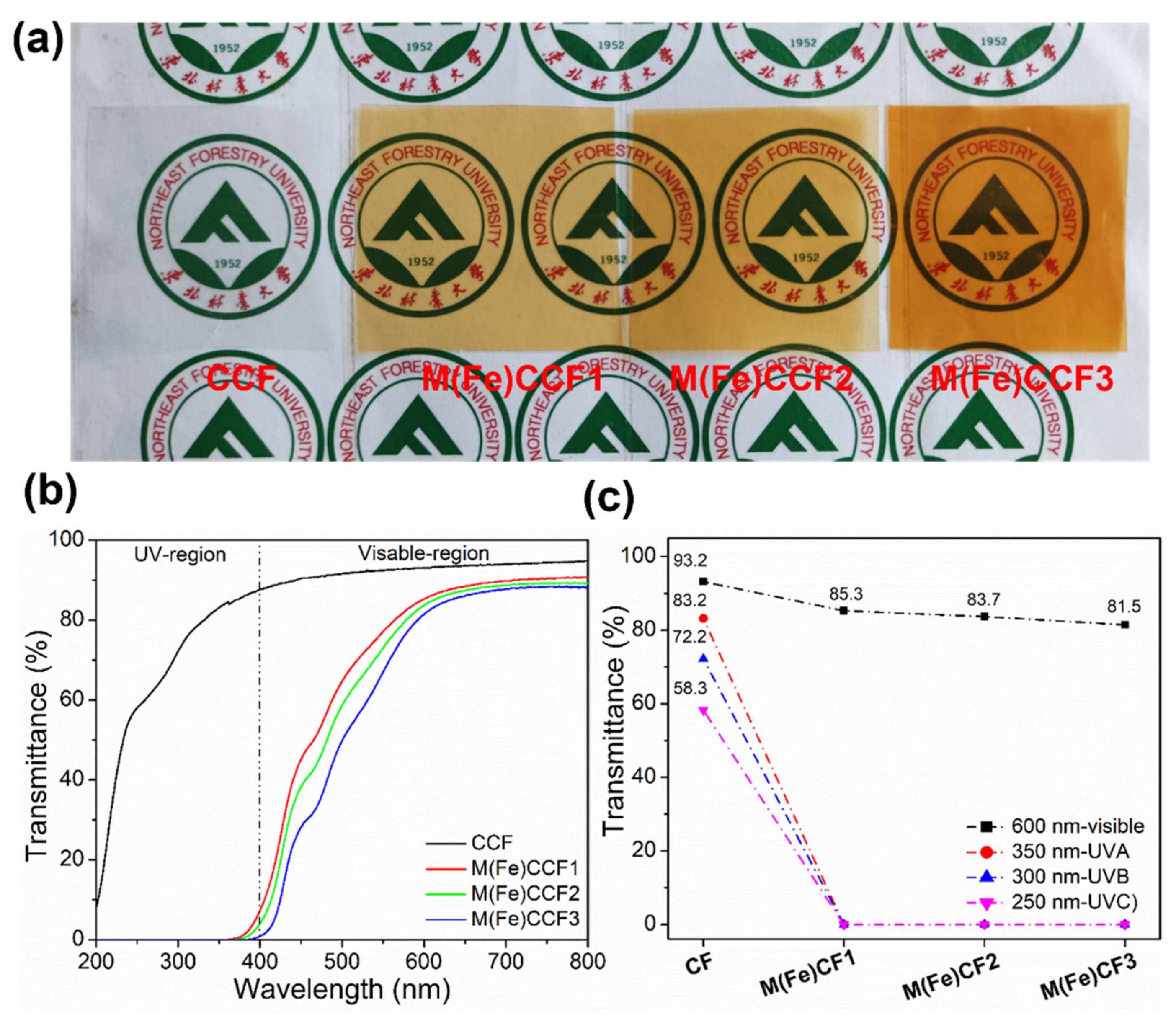
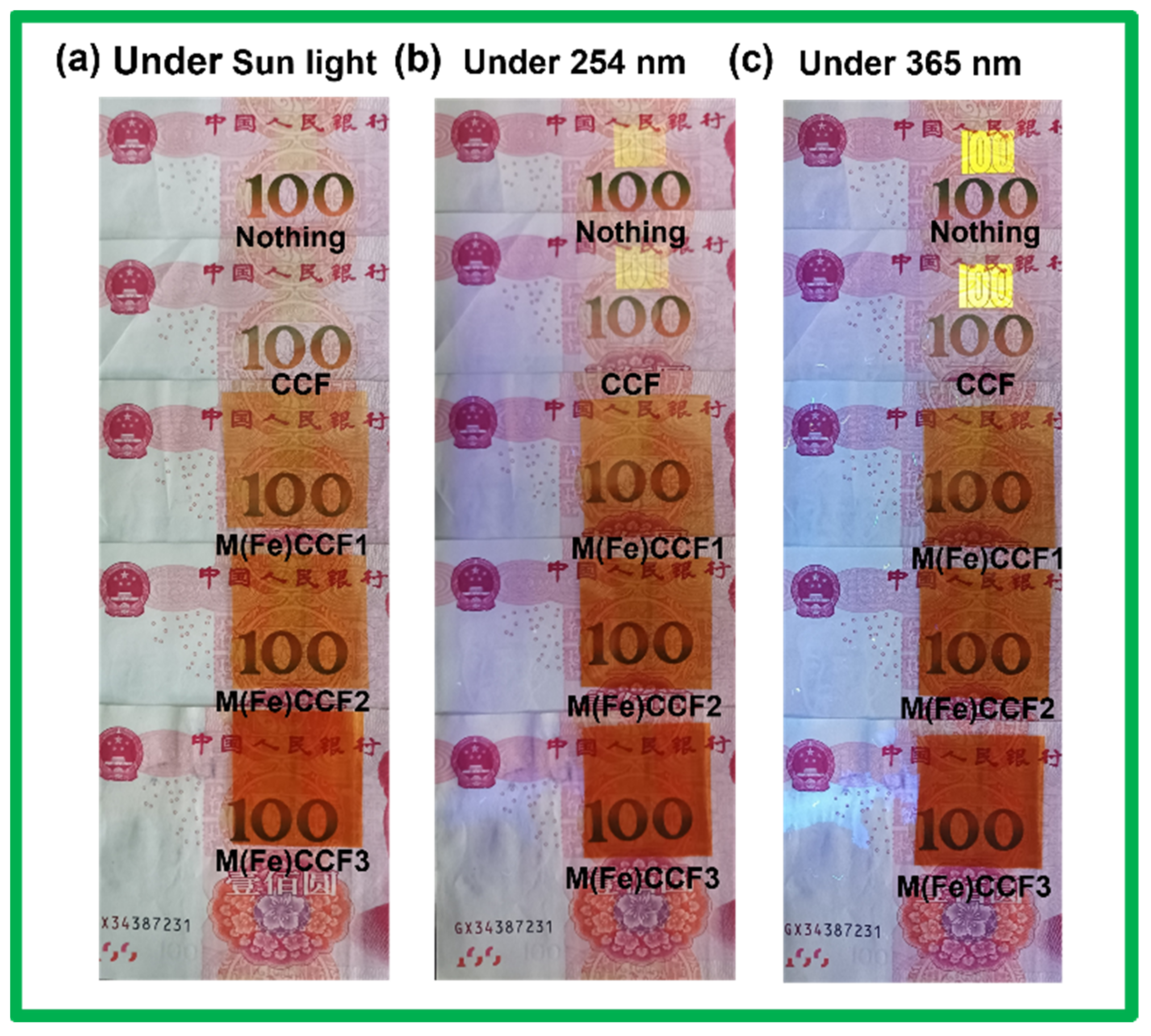
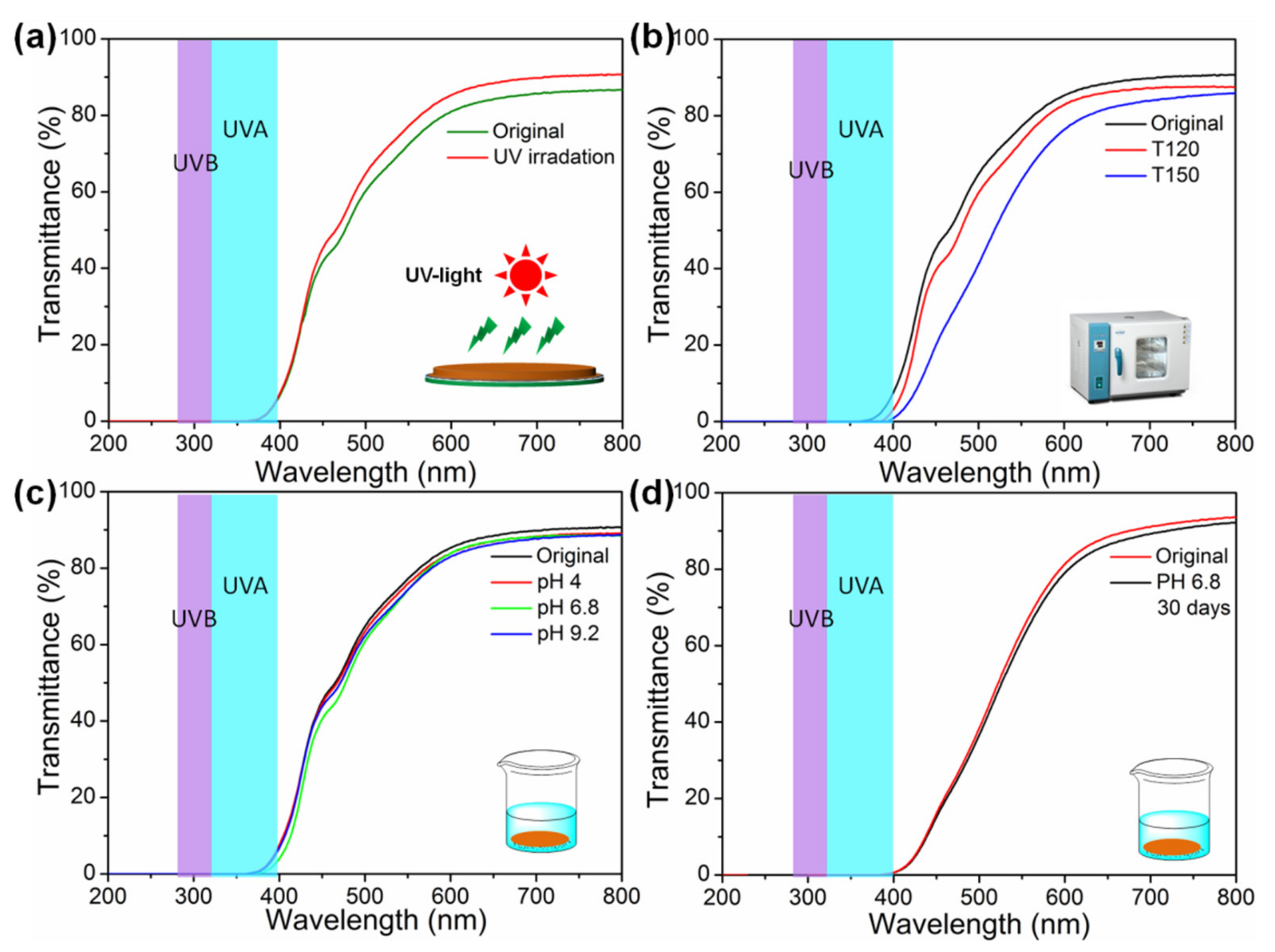
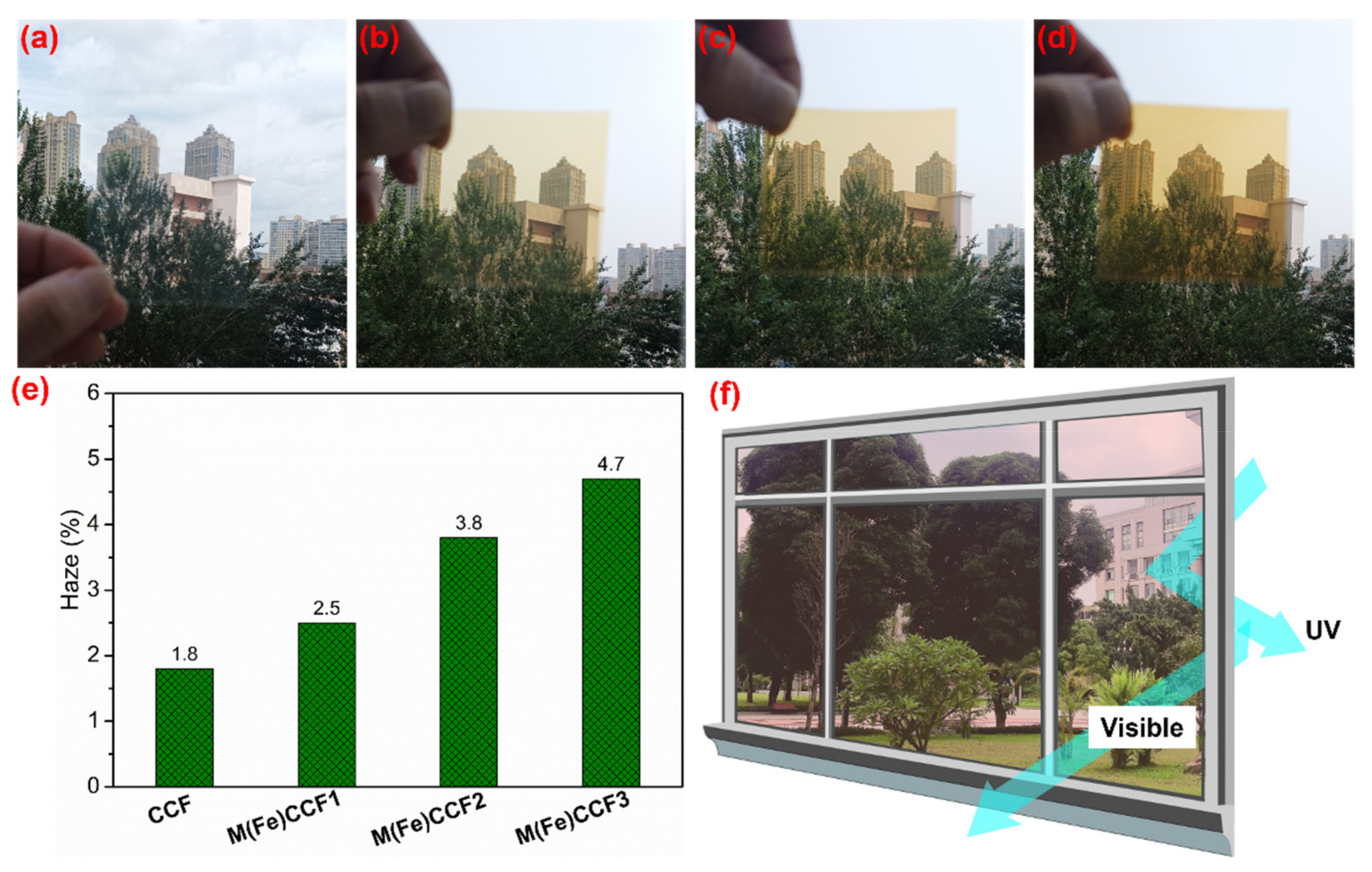
3.6. UV Light Blocking Performance of M(Fe)CCFs
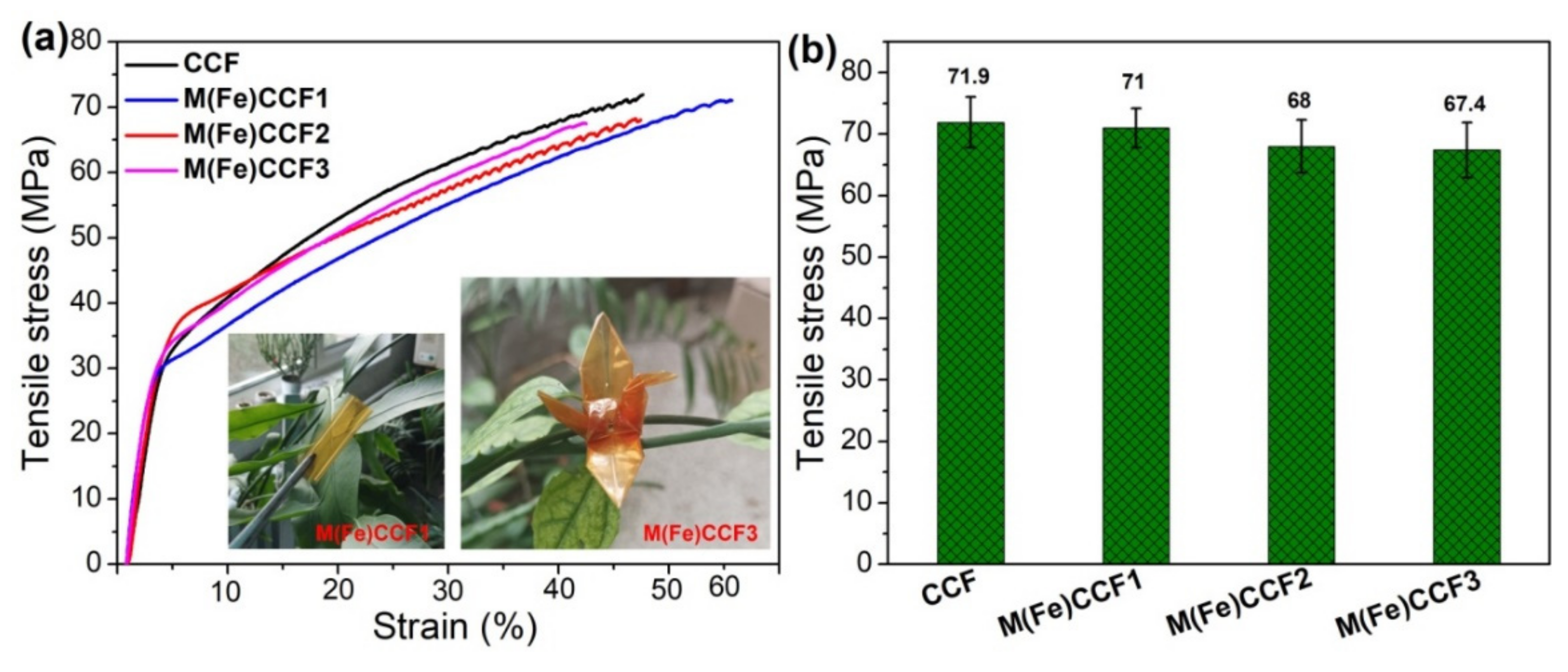
3.7. Mechanical Property of M(Fe)CCFs
3.8. Biodegradability of M(Fe)CCFs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olson, E.; Li, Y.; Lin, F.-Y.; Miller, A.; Liu, F.; Tsyrenova, A.; Palm, D.; Curtzwiler, G.W.; Vorst, K.L.; Cochran, E. Thin biobased transparent UV-blocking coating enabled by nanoparticle self-assembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 24552–24559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, L.; An, X.; Qian, X. Nano-metal organic framework for enhanced mechanical, flame retardant and ultraviolet-blue light shielding properties of transparent cellulose-based bioplastics. Polymers 2021, 13, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Adak, B.; Bansala, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Green solvent processed cellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposite films with superior mechanical, thermal, and ultraviolet shielding properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Song, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wan, L.; Yao, J. Highly transparent graphene oxide/cellulose composite film bearing ultraviolet shielding property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huang, J.; He, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, X.; Wu, W.; Li, R.K. Biodegradable and renewable UV-shielding polylactide composites containing hierarchical structured POSS functionalized lignin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Ji, X.; Zheng, B.; Wang, C.; Hao, W.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Xia, G.; Ji, X.; Zhang, J. Eco-friendly and complete recycling of waste bamboo-based disposable paper cups for value-added transparent cellulose-based films and paper plastic composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirviö, J.A.; Ismail, M.Y.; Zhang, K.; Tejesvi, M.V.; Ämmälä, A. Transparent lignin-containing wood nanofiber films with UV-blocking, oxygen barrier, and anti-microbial properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 7935–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, W.; Yan, L. Preparation of flexible, highly transparent, cross-linked cellulose thin film with high mechanical strength and low coefficient of thermal expansion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fukuzumi, H.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A.; Zhang, L. Transparent cellulose films with high gas barrier properties fabricated from aqueous alkali/urea solutions. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2766–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghifar, H.; Venditti, R.; Jur, J.; Gorga, R.E.; Pawlak, J.J. Cellulose-lignin biodegradable and flexible UV protection film. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, S.; Bai, H.; Zhang, S. Use of CeO2 nanoparticles to enhance UV-shielding of transparent regenerated cellulose films. Polymers 2019, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Tang, W.; Yong, Q. Tuning the cellulose nanocrystal alignments for supramolecular assembly of chiral nematic films with highly efficient UVB shielding capability. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuoriluoto, M.; Hokkanen, A.; Mäkelä, T.; Harlin, A.; Orelma, H. Optical properties of an organic-inorganic hybrid film made of regenerated cellulose doped with light-scattering TiO2 particles. Opt. Mater. 2022, 123, 111882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabani, I.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Yoo, J.; Hussain, S.; Maqbool, T.; Seo, Y.-S. Engineering-safer-by design ZnO nanoparticles incorporated cellulose nanofiber hybrid for high UV protection and low photocatalytic activity with mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, H.E.; Abdelhameed, R.M. Anti-UV radiation textiles designed by embracing with nano-MIL(Ti, In)–metal organic framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28034–28045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P.; Cao, F.; Zhang, K.; Hou, L.; Gao, R.C.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.Y. Design of anti-UV radiation textiles with self-assembled metal–organic framework coating. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Gu, S. Robust fluorine-free colorful superhydrophobic PDMS/NH2-MIL-125(Ti)@cotton fabrics for improved ultraviolet resistance and efficient oil–water separation. Cellulose 2019, 26, 9335–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, H.; Ye, D.; Xu, W.; Gu, S. Multi-functional cotton textiles design using in situ generating zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67) for effective UV resistance, antibacterial activity, and self-cleaning. Cellulose 2021, 28, 5923–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Xing, Y. Multi-functional finishing of cotton fabrics by water-based layer-by-layer assembly of metal–organic framework. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4223–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.; Mao, X.; Chen, X.-L.; Li, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y. Multifunctional textiles/metal−organic frameworks composites for efficient ultraviolet radiation blocking and noise reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55316–55323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Fu, X.; Gao, X.; Mao, X.; Li, Z. UV-shielding alginate films crosslinked with Fe3+ containing EDTA. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 115480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Gogoi, P.; Bian, H.; Dai, H. Highly transparent and thermally stable cellulose nanofibril films functionalized with colored metal ions for ultraviolet blocking activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Fang, H.; Gosztola, D.J.; Jiang, Z.; Jena, P.; Wang, W.-N. Mechanistic insight into photocatalytic pathways of MIL-100(Fe)/TiO2 composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12516–12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Bo, Y.; Hui, Z.; Xu, Z. A g-C3N4/MIL-101(Fe) heterostructure composite for highly efficient BPA degradation with persulfate under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23703–23711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G. Hexagonal microspindle of NH2-MIL-101(Fe) metal–organic frameworks with visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of toluene. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4289–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z. Anchoring NaYF4:Yb,Tm Upconversion Nanocrystals on concave MIL-53(Fe) octahedrons for NIR-light enhanced photocatalysis. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pu, M.; Guan, Z. Metal–organic frameworks MIL-88A with suitable synthesis conditions and optimal dosage for effective catalytic degradation of Orange G through persulfate activation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 112502–112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasevani, S.G.; Mohaghegh, N.; Gholami, M. Kinetic study of navy blue photocatalytic degradation over Ag3PO4/BiPO4@ MIL-88B(Fe)@gC3N4 core@shell nanocomposite under visible light irradiation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10390–10396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yang, H.; Cai, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, C. Preparation and photocatalytic property of spindle-like MIL-88B(Fe) nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2016, 67, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hori, N.; Takemura, A. Synthesis and characterization of Cu-BTC metal–organic frameworks onto lignocellulosic fibers by layer-by-layer method in aqueous solution. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of lignin on the performance of biodegradable cellulose aerogels made from wheat straw pulp-LiCl/DMSO solution. Cellulose 2020, 27, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Cai, Y.; Yao, Y.; Teng, B.-T.; Hao, Q.; Shuxiang, L. Synthesis of (100) surface oriented MIL-88A-Fe with rod-like structure and its enhanced fenton-like performance for phenol removal. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 259, 118064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Song, X.X.; Wu, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.C. Room-temperature preparation of MIL-88A as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for degradation of rhodamine B and bisphenol a under visible light. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 125, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Cai, W. Coupling of heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes and photocatalysis in efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by Fe-based MOFs: Synergistic effect and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.A.; Chang, H.-A.; Hsu, C.-J. Iron-based metal organic framework, MIL-88A, as a heterogeneous persulfate catalyst for decolorization of Rhodamine B in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32520–32530. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hori, N.; Takemura, A. A comparative study of depositing Cu-BTC metal–organic framework onto cellulosic filter paper via different procedures. Cellulose 2020, 27, 6537–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M. Ultrathin graphene oxide encapsulated in uniform MIL-88A(Fe) for enhanced visible light-driven photodegradation of RhB. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 221, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Gahete, J.; Klee, R.; Esquivel, D.; Ruiz, J.R.; Jimenez-Sanchidrian, C.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Fast ultrasound-assisted synthesis of highly crystalline MIL-88A particles and their application as ethylene adsorbents. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 50, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Fu, H.; Zhao, C. Superior removal of inorganic and organic arsenic pollutants from water with MIL-88A(Fe) decorated on cotton fibers. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pi, Y.; Wu, L.; Xia, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Facilitation of the visible light-induced Fenton-like excitation of H2O2 via heterojunction of g-C3N4/NH2-Iron terephthalate metal-organic framework for MB degradation. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 202, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Gou, L.; Zhou, X.; Bao, N.; Gu, H. Chitosan–Fe3O4 nanocomposite based electrochemical sensors for the determination of bisphenol A. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9056–9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Du, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, G.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Peng, H. Flexible cellulose nanopaper with high wet tensile strength, high toughness and tunable ultraviolet blocking ability fabricated from tobacco stalk via a sustainable method. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13021–13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Zuo, C.; Deng, Y.; Dai, H. Thermally-induced cellulose nanofibril films with near-complete ultraviolet-blocking and improved water resistance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; An, X.; Qian, X. Nano-MIL-88A(Fe) Enabled Clear Cellulose Films with Excellent UV-Shielding Performance and Robust Environment Resistance. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111891
Sun L, An X, Qian X. Nano-MIL-88A(Fe) Enabled Clear Cellulose Films with Excellent UV-Shielding Performance and Robust Environment Resistance. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(11):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111891
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lijian, Xianhui An, and Xueren Qian. 2022. "Nano-MIL-88A(Fe) Enabled Clear Cellulose Films with Excellent UV-Shielding Performance and Robust Environment Resistance" Nanomaterials 12, no. 11: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111891
APA StyleSun, L., An, X., & Qian, X. (2022). Nano-MIL-88A(Fe) Enabled Clear Cellulose Films with Excellent UV-Shielding Performance and Robust Environment Resistance. Nanomaterials, 12(11), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12111891