In Vitro Assessment of the Genotoxic Potential of Pristine Graphene Platelets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Graphene Platelets
Contamination of Graphene Platelets (Endotoxin Content)
2.2. Exposure of Human THP-1 Cell Line to GP
2.3. Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity
2.3.1. WST-1
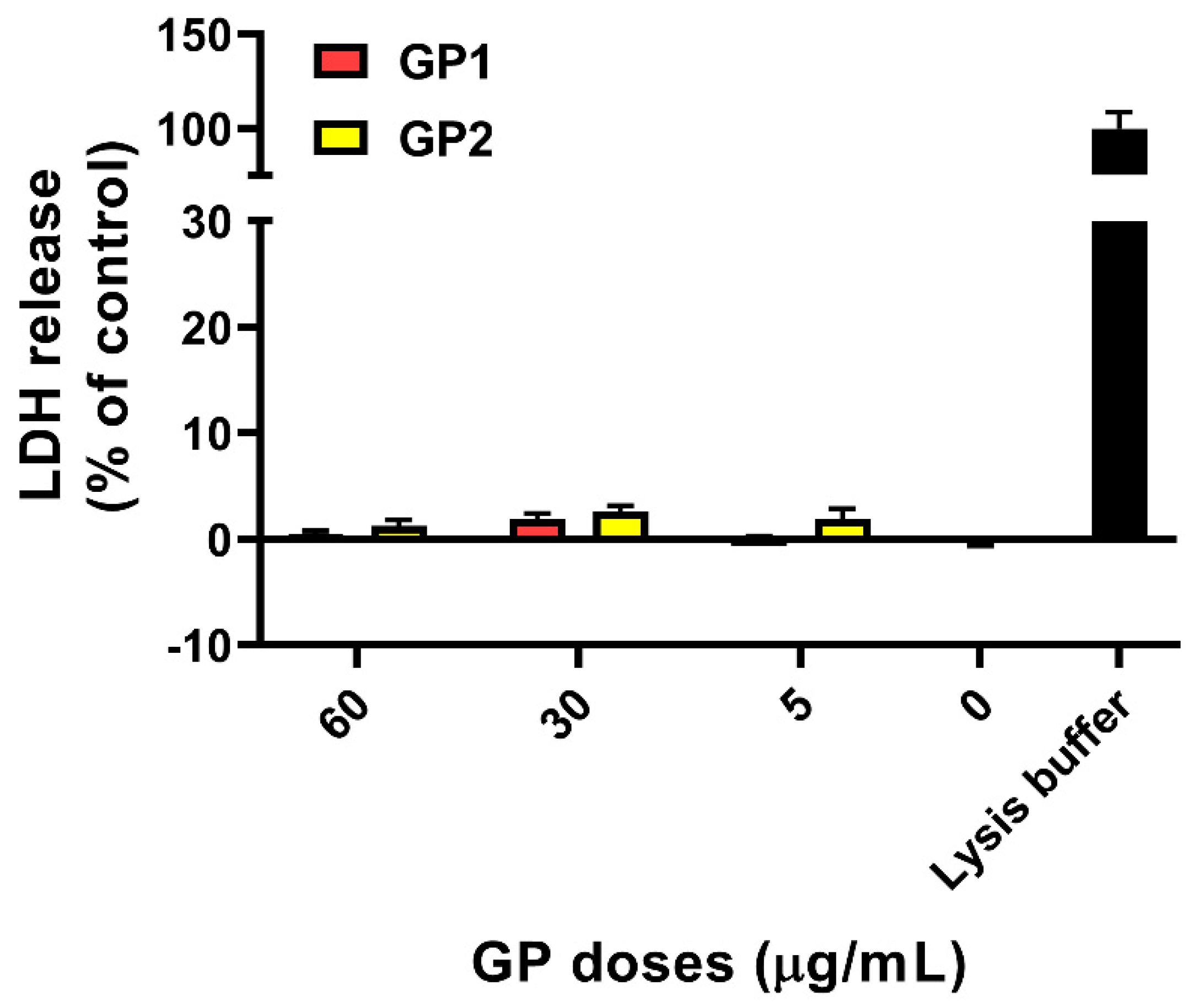
2.3.2. Cell Membrane Integrity
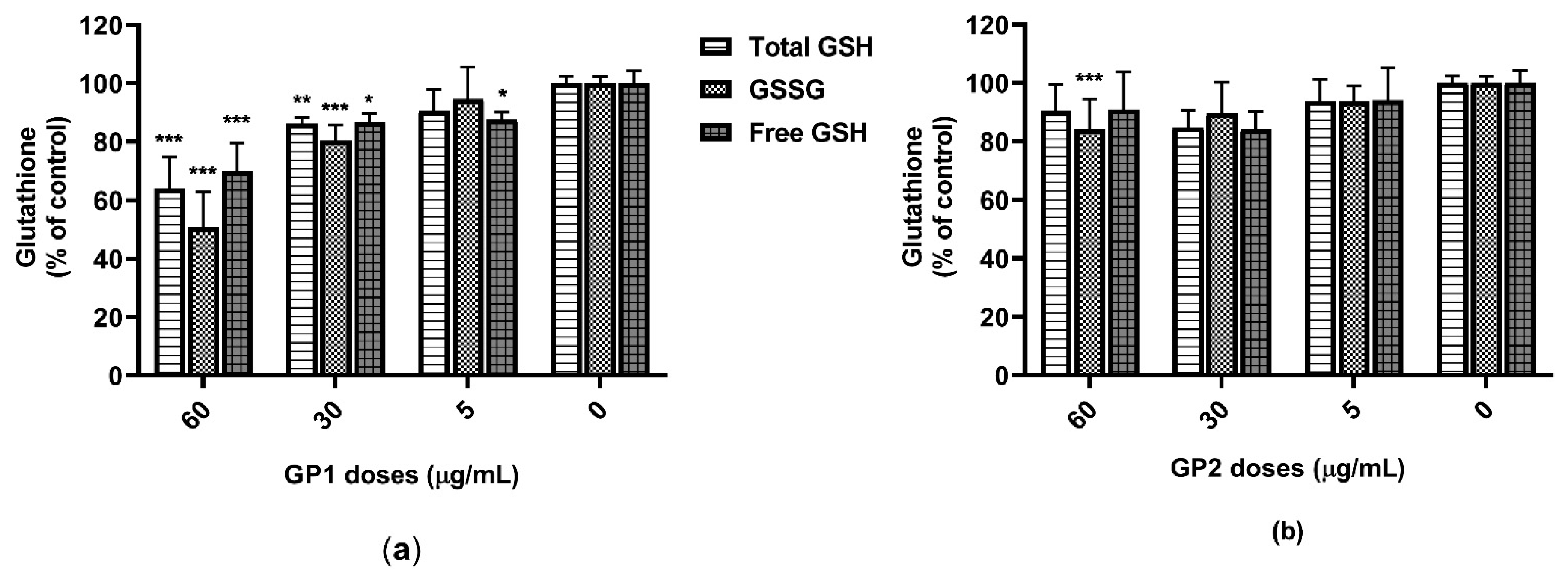
2.4. Oxidative Stress
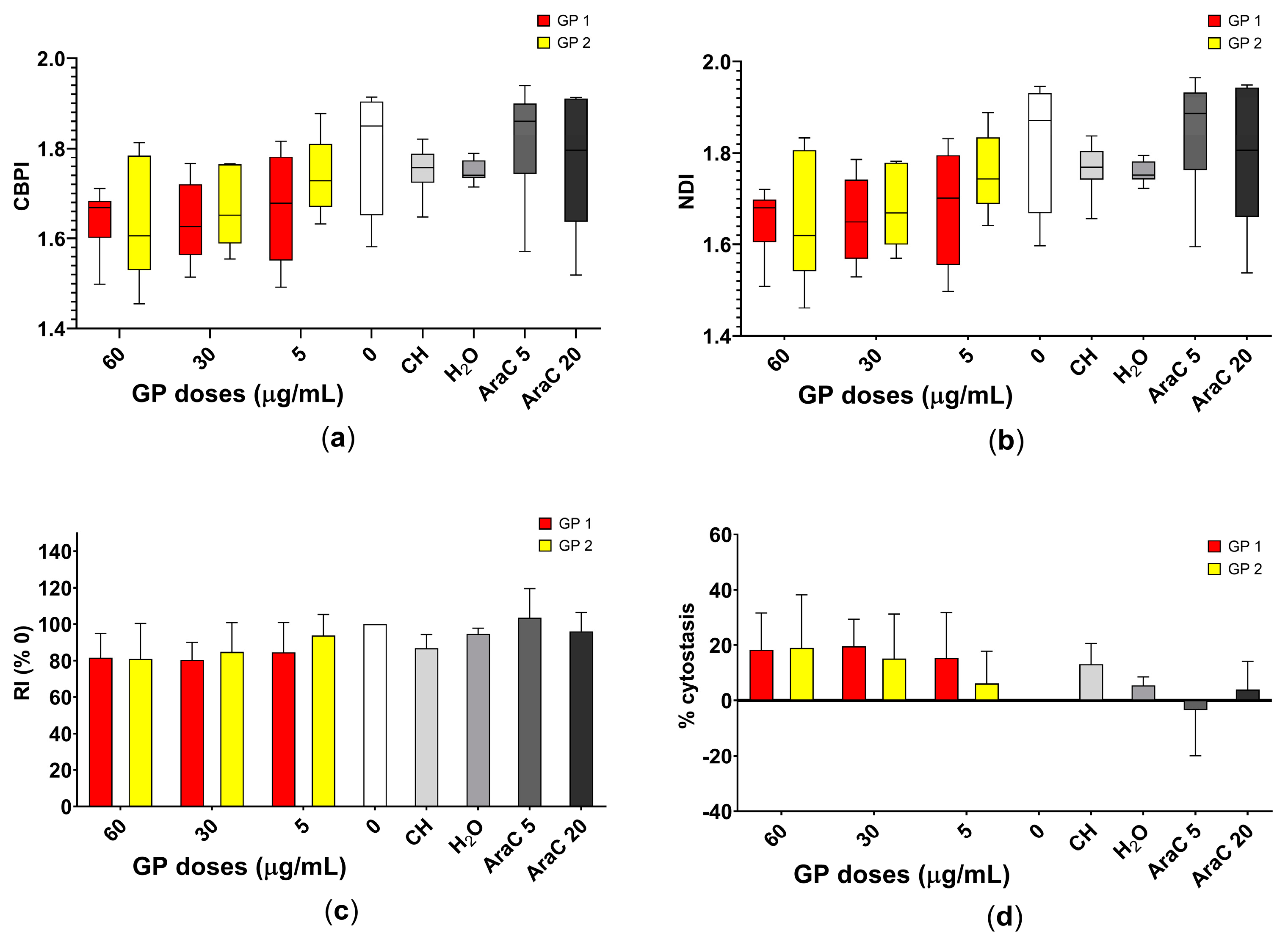
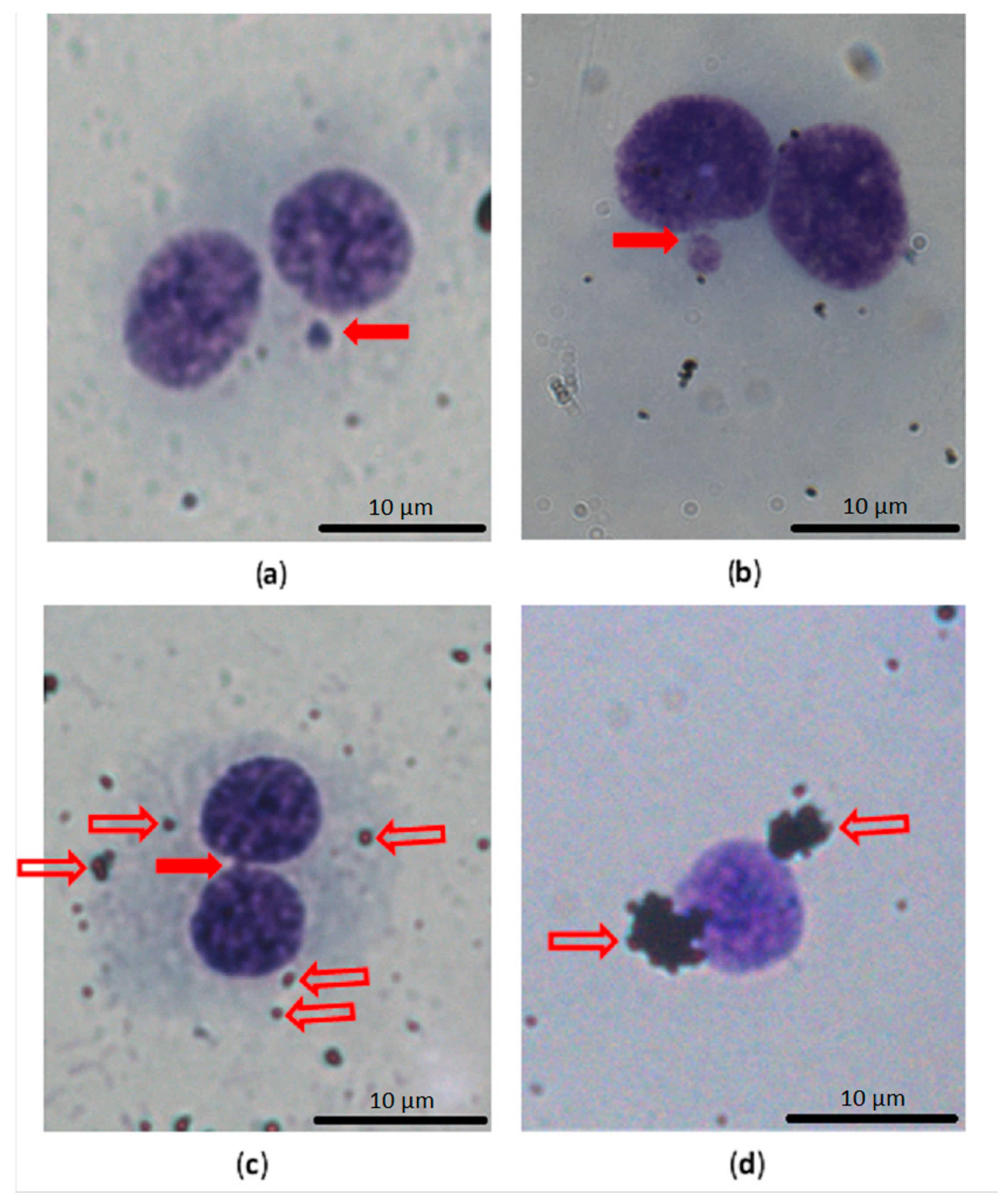
2.5. Cytokinesis Block Micronucleus Test
2.6. Cytokine Secretion
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability/Cytotoxicity
3.2. ROS Generation
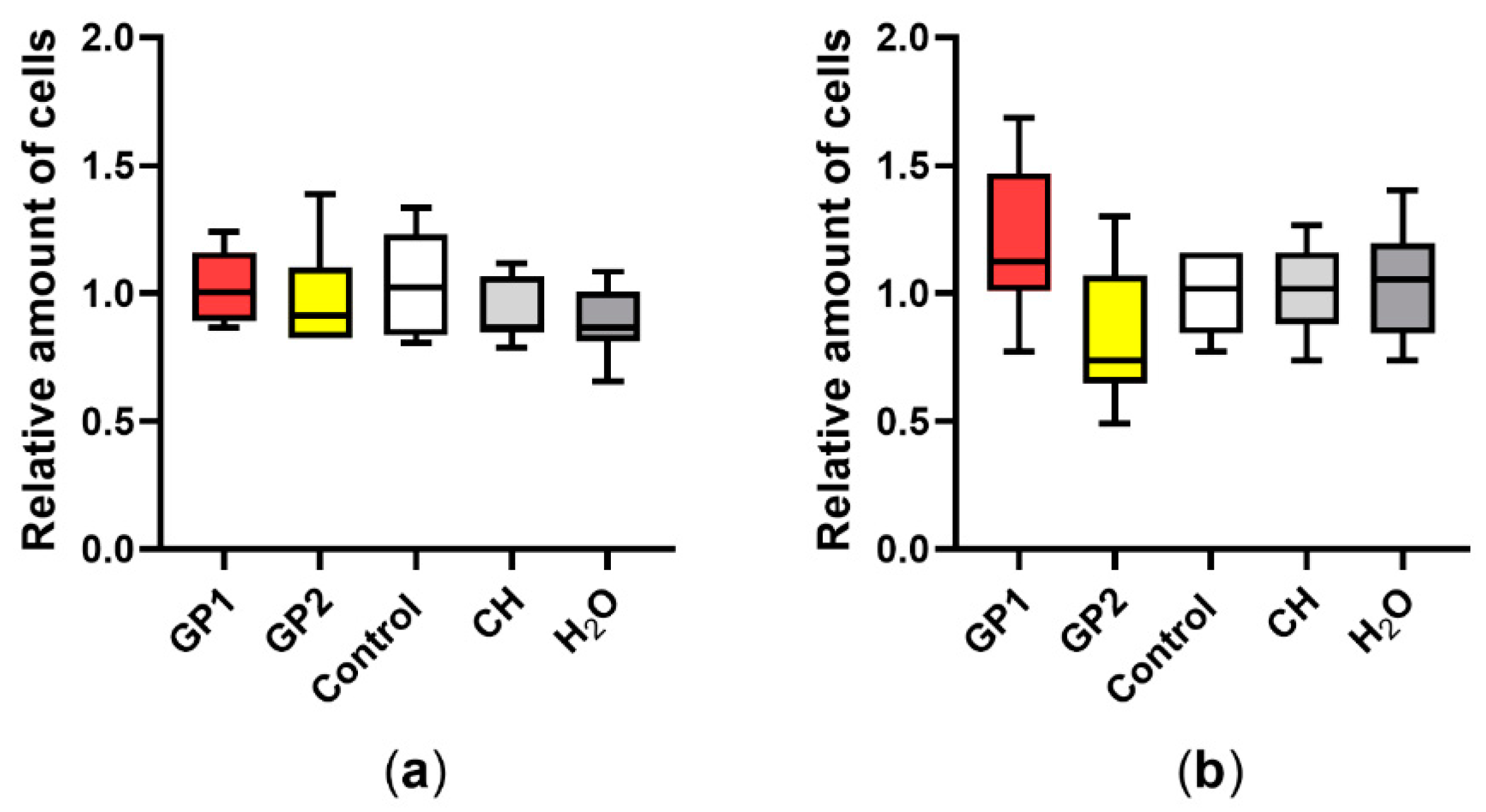
3.3. Cytostasis
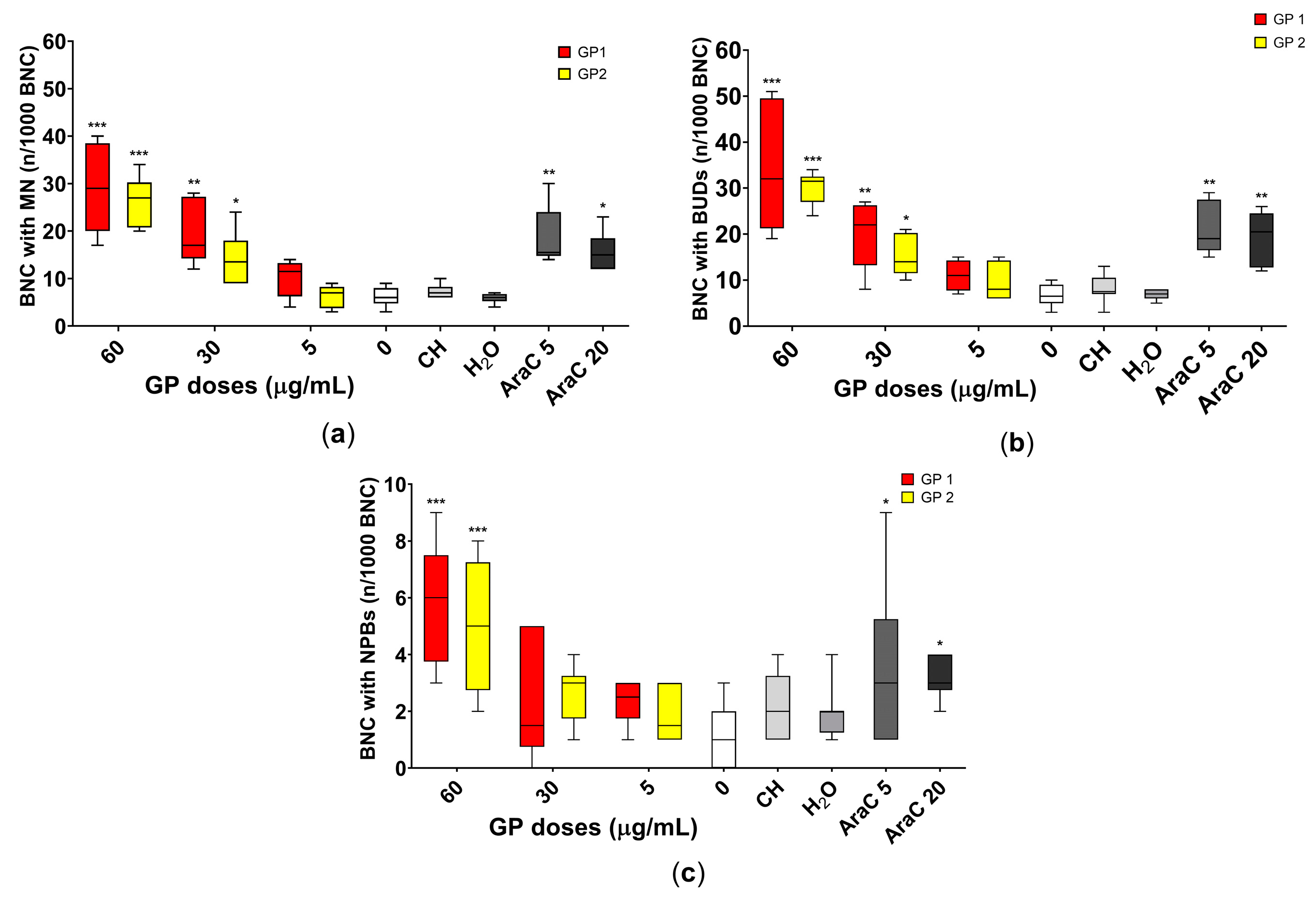
3.4. Genotoxicity
3.5. Inflammatory Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Cytotoxicity of GP
4.1.1. Interference between GP and Cytotoxicity Assays
4.1.2. Cytotoxic Potential of GP
4.2. Oxidative Stress
4.3. Cytostatic and Genotoxic Potential
4.3.1. Cytostatic Potential
4.3.2. Genotoxic Potential
4.4. Inflammatory Potential
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fadeel, B.; Bussy, C.; Merino, S.; Vázquez, E.; Flahaut, E.; Mouchet, F.; Evariste, L.; Gauthier, L.; Koivisto, A.J.; Vogel, U.; et al. Safety Assessment of Graphene-Based Materials: Focus on Human Health and the Environment. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10582–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalwani, G.; D’Agati, M.; Khan, A.M.; Sitharaman, B. Toxicology of graphene-based nanomaterials. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 109–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Yang, M. Recent advances in graphene-based nanomaterials: Properties, toxicity and applications in chemistry, biology and medicine. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Kim, J.H. Differential Immunomodulatory Effect of Graphene Oxide and Vanillin-Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Acute Monocytic Leukemia Cell Line (THP-1). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Graphene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Biocompatibility, and Cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, W.; Yang, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wei, T. The interactions between pristine graphene and macrophages and the production of cytokines/chemokines via TLR- and NF-kappaB-related signaling pathways. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6933–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Luan, B.; Weber, J.K.; Zhou, R.W.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhou, R. Graphene-Induced Pore Formation on Cell Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yang, Z.; Duan, G.; Wu, A.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Ge, C.; Zhou, R. Graphene Oxide Nanosheets Retard Cellular Migration via Disruption of Actin Cytoskeleton. Small 2017, 13, 1602133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Peng, J.; Huang, C.; Cao, Y. Graphene oxide size-dependently altered lipid profiles in THP-1 macrophages. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 199, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Chandran, P.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Rao, C.N.R.; Koyakutty, M. Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzynska, M.; Cendrowski, K.; Barylak, M.; Tkacz, M.; Piotrowska, K.; Kurzawski, M.; Mijowska, E.; Drozdzik, M. Comparative in vitro study of single and four layer graphene oxide nanoflakes—Cytotoxicity and cellular uptake. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 41, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Kim, H.D.; Han, S.S. Biocompatibility and hemocompatibility of hydrothermally derived reduced graphene oxide using soluble starch as a reducing agent. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, T.A.; Pranjol, M.Z.I.; Hayat, H.; Rahat, A.A.M.; Abdullah, T.M.; Whatmore, J.L.; Zhang, S. In vitro toxic effects of reduced graphene oxide nanosheets on lung cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 504001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svadlakova, T.; Hubatka, F.; Turanek Knotigova, P.; Kulich, P.; Masek, J.; Kotoucek, J.; Macak, J.; Motola, M.; Kalbac, M.; Kolackova, M.; et al. Proinflammatory Effect of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: In Vitro Study on Stimulation of Inflammasome NLRP3 via Destabilisation of Lysosomes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ali, S.F.; Dervishi, E.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Casciano, D.; Biris, A.S. Cytotoxicity effects of graphene and single-wall carbon nanotubes in neural phaeochromocytoma-derived PC12 cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W. Trypan Blue Exclusion Test of Cell Viability. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 111, A3.B.1–A3.B.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M. Cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome assay. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 487: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, G.; He, X.; Li, X.; Qiu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S. Limitations of MTT and CCK-8 assay for evaluation of graphene cytotoxicity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53240–53244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Boucetta, H.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Muller, K.H.; Li, S.; Porter, A.E.; Eddaoudi, A.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. Cellular uptake and cytotoxic impact of chemically functionalized and polymer-coated carbon nanotubes. Small 2011, 7, 3230–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagnini, R.; Halamoda Kenzaoui, B.; Walker, L.; Pojana, G.; Magdolenova, Z.; Bilanicova, D.; Saunders, M.; Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Marcomini, A.; Huk, A.; et al. Toxicity screenings of nanomaterials: Challenges due to interference with assay processes and components of classic in vitro tests. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9 (Suppl. 1), 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabra, A.B.; Paula, A.J.; de Lima, R.; Alves, O.L.; Duran, N. Nanotoxicity of graphene and graphene oxide. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, H.; von dem Bussche, A.; Creighton, M.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B.; Gao, H. Graphene microsheets enter cells through spontaneous membrane penetration at edge asperities and corner sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12295–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Emamy, H.; Akhavan, F. Genotoxicity of graphene nanoribbons in human mesenchymal stem cells. Carbon 2013, 54, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shen, H.; Tu, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, J.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Z. The in vitro and in vivo toxicity of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5041–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Gurunathan, S. Biofabrication of a novel biomolecule-assisted reduced graphene oxide: An excellent biocompatible nanomaterial. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6635–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgum, M.J.; Clift, M.J.D.; Evans, S.J.; Hondow, N.; Tarat, A.; Jenkins, G.J.; Doak, S.H. Few-layer graphene induces both primary and secondary genotoxicity in epithelial barrier models in vitro. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Ji, D.-K.; Lucherelli, M.A.; Reina, G.; Ippolito, S.; Samorì, P.; Bianco, A. Comparative Effects of Graphene and Molybdenum Disulfide on Human Macrophage Toxicity. Small 2020, 16, 2002194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasocka, I.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Skibniewski, M.; Skibniewska, E.; Strupinski, W.; Pasternak, I.; Kmieć, H.; Kowalczyk, P. Biocompatibility of pristine graphene monolayer: Scaffold for fibroblasts. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 48, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, E.; Marcos, R. Toxic and genotoxic effects of graphene and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2018, 81, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanagahalli, S.; Murera, D.; Martín, C.; Lin, H.; Wadier, N.; Dumortier, H.; Vázquez, E.; Bianco, A. Few Layer Graphene Does Not Affect Cellular Homeostasis of Mouse Macrophages. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, P.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, T. Interactions of graphene with mammalian cells: Molecular mechanisms and biomedical insights. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Glutathione Homeostasis and Functions: Potential Targets for Medical Interventions. J. Amino Acids 2012, 2012, 736837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgum, M.J.; Clift, M.J.D.; Evans, S.J.; Hondow, N.; Miller, M.; Lopez, S.B.; Williams, A.; Tarat, A.; Jenkins, G.J.; Doak, S.H. In Vitro Primary-Indirect Genotoxicity in Bronchial Epithelial Cells Promoted by Industrially Relevant Few-Layer Graphene. Small 2020, 17, 2002551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Yin, N.; Gao, X.; Xia, T.; Chen, J.J.; et al. Graphene oxide induces toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent necrosis in macrophages. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5732–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, R.; Tsung, A.; Billiar, T. Linking oxidative stress to inflammation: Toll-like receptors. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ruiz, B.; Arellano-García, M.E.; Radilla-Chávez, P.; Salas-Vargas, D.S.; Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Casillas-Figueroa, F.; Luna Vazquez-Gomez, R.; Pestryakov, A.; García-Ramos, J.C.; Bogdanchikova, N. Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus Assay Using Human Lymphocytes as a Sensitive Tool for Cytotoxicity/Genotoxicity Evaluation of AgNPs. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12005–12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Sanderson, B.J.; Kirsch-Volders, M. Adaptations of the in vitro MN assay for the genotoxicity assessment of nanomaterials. Mutagenesis 2011, 26, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, V.A.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, G.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Dhawan, A. ZnO nanoparticles induced inflammatory response and genotoxicity in human blood cells: A mechanistic approach. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 85, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, M. A critique of methods to measure cytotoxicity in mammalian cell genotoxicity assays. Mutagenesis 2012, 27, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Di Bucchianico, S.; Fabbrizi, M.R.; Cirillo, S.; Uboldi, C.; Gilliland, D.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Migliore, L. Aneuploidogenic effects and DNA oxidation induced in vitro by differently sized gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2191–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, C.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Matos, P.; Marques, B.; Jordan, P.; Sousa-Uva, A.; Silva, M.J. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of MWCNT-7 and crocidolite: Assessment in alveolar epithelial cells versus their coculture with monocyte-derived macrophages. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Tan, X.; Feng, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Peng, R. Functionalized graphene oxide triggers cell cycle checkpoint control through both the ATM and the ATR signaling pathways. Carbon 2018, 129, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, G.H.; Han, B.S.; Lee, B.S.; Lee, S.; Cho, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.W. Toxic response of graphene nanoplatelets in vivo and in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinwald, A.; Murphy, F.A.; Jones, A.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Graphene-based nanoplatelets: A new risk to the respiratory system as a consequence of their unusual aerodynamic properties. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, M.; Hajibabae, S.; Barikrow, N. Genotoxicity and Cytotoxicity Assessment of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets on HT29 Cells. J. Kermanshah Univ. Med. Sci. 2018, 22, e69641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, C.L.; Fresegna, A.M.; Ciervo, A.; Maiello, R.; Del Frate, V.; Folesani, G.; Galetti, M.; Poli, D.; Buresti, G.; Di Cristo, L.; et al. Occupational exposure to graphene and silica nanoparticles. Part II: Pilot study to identify a panel of sensitive biomarkers of genotoxic, oxidative and inflammatory effects on suitable biological matrices. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivask, A.; Voelcker, N.H.; Seabrook, S.A.; Hor, M.; Kirby, J.K.; Fenech, M.; Davis, T.P.; Ke, P.C. DNA melting and genotoxicity induced by silver nanoparticles and graphene. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Akhavan, A. Size-dependent genotoxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in human stem cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8017–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallhov, H.; Qin, J.; Johansson, S.M.; Ahlborg, N.; Muhammed, M.A.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. The importance of an endotoxin-free environment during the production of nanoparticles used in medical applications. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiani, M.H.; Gokulan, K.; Williams, K.; Khodakovskaya, M.V.; Khare, S. Graphene and carbon nanotubes activate different cell surface receptors on macrophages before and after deactivation of endotoxins. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostingh, G.J.; Casals, E.; Italiani, P.; Colognato, R.; Stritzinger, R.; Ponti, J.; Pfaller, T.; Kohl, Y.; Ooms, D.; Favilli, F.; et al. Problems and challenges in the development and validation of human cell-based assays to determine nanoparticle-induced immunomodulatory effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Baek, J.E.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, G.H.; et al. 28-Day inhalation toxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in Sprague-Dawley rats. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Lu, C.H.; Chao, Y.C.; Hwang, S.M.; Chen, C.L.; Lo, K.W.; Sung, L.Y.; Luo, W.Y.; Tuan, H.Y.; et al. Simultaneous induction of autophagy and toll-like receptor signaling pathways by graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6559–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinwald, A.; Murphy, F.; Askounis, A.; Koutsos, V.; Sefiane, K.; Donaldson, K.; Campbell, C.J. Minimal oxidation and inflammogenicity of pristine graphene with residence in the lung. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nanomaterial | Particle Size (nm) (Z-Average) | PdI | Average ζ-Potential (mV) | Average ζ-Potential (mV) (in Full RPMI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP1 | 178.5 ± 103 | 0.188 | ≤−50 | ≤−9 |
| GP2 | 332 ± 85 | 0.293 | ≤−47 | ≤−11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malkova, A.; Svadlakova, T.; Singh, A.; Kolackova, M.; Vankova, R.; Borsky, P.; Holmannova, D.; Karas, A.; Borska, L.; Fiala, Z. In Vitro Assessment of the Genotoxic Potential of Pristine Graphene Platelets. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092210
Malkova A, Svadlakova T, Singh A, Kolackova M, Vankova R, Borsky P, Holmannova D, Karas A, Borska L, Fiala Z. In Vitro Assessment of the Genotoxic Potential of Pristine Graphene Platelets. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(9):2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092210
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalkova, Andrea, Tereza Svadlakova, Avni Singh, Martina Kolackova, Radka Vankova, Pavel Borsky, Drahomira Holmannova, Adam Karas, Lenka Borska, and Zdenek Fiala. 2021. "In Vitro Assessment of the Genotoxic Potential of Pristine Graphene Platelets" Nanomaterials 11, no. 9: 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092210
APA StyleMalkova, A., Svadlakova, T., Singh, A., Kolackova, M., Vankova, R., Borsky, P., Holmannova, D., Karas, A., Borska, L., & Fiala, Z. (2021). In Vitro Assessment of the Genotoxic Potential of Pristine Graphene Platelets. Nanomaterials, 11(9), 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092210






