Effective Magnetic MOFs Adsorbent for the Removal of Bisphenol A, Tetracycline, Congo Red and Methylene Blue Pollutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
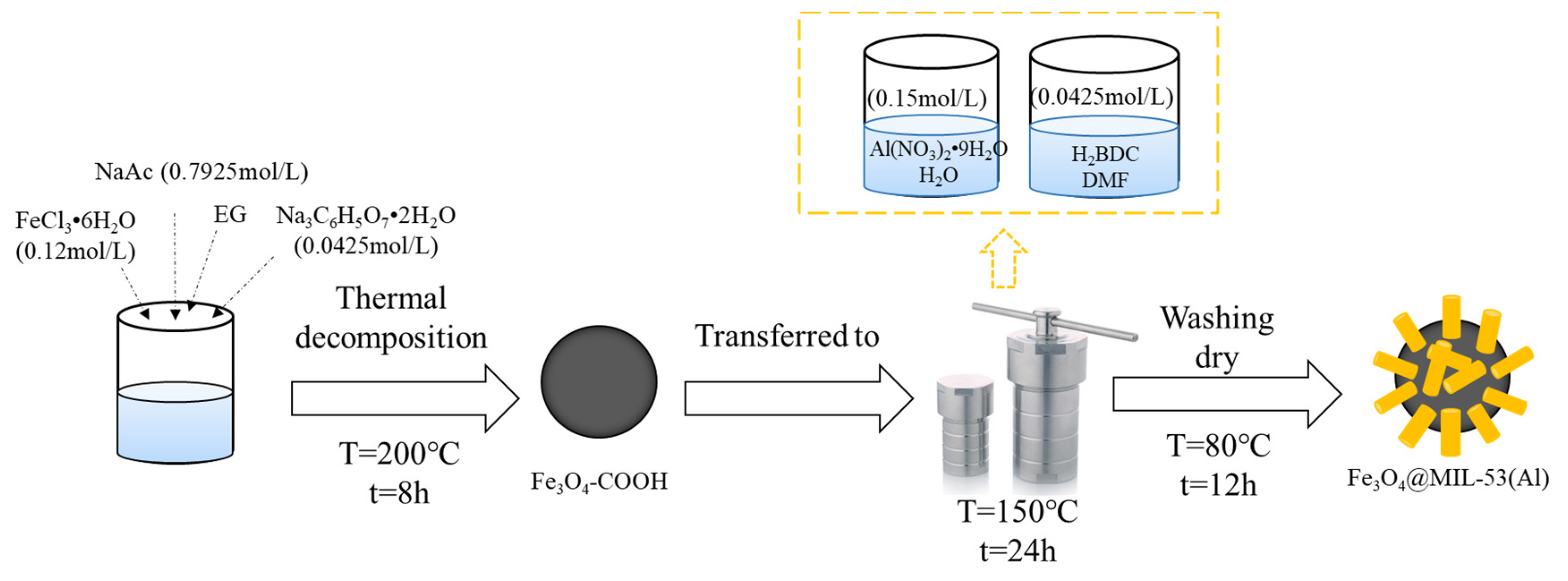
2.3. Preparation of Fe3O4@MIL-53(Al)
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Regeneration Experiments
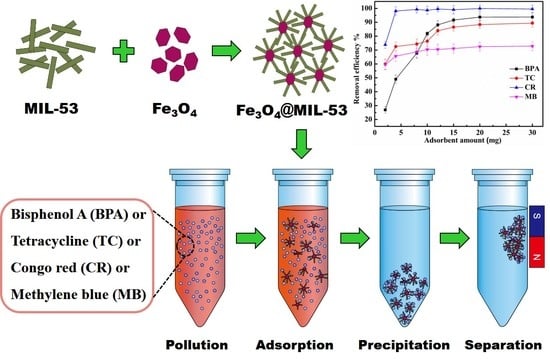
3. Results and Discussion
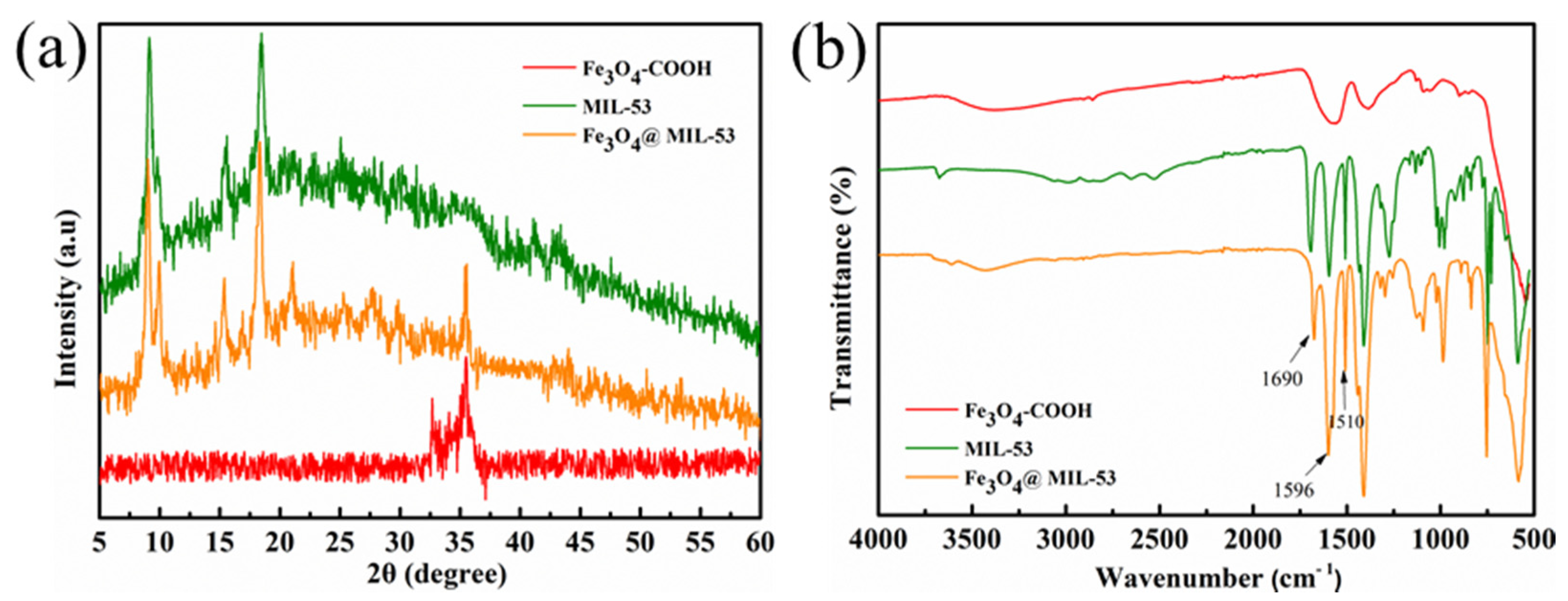
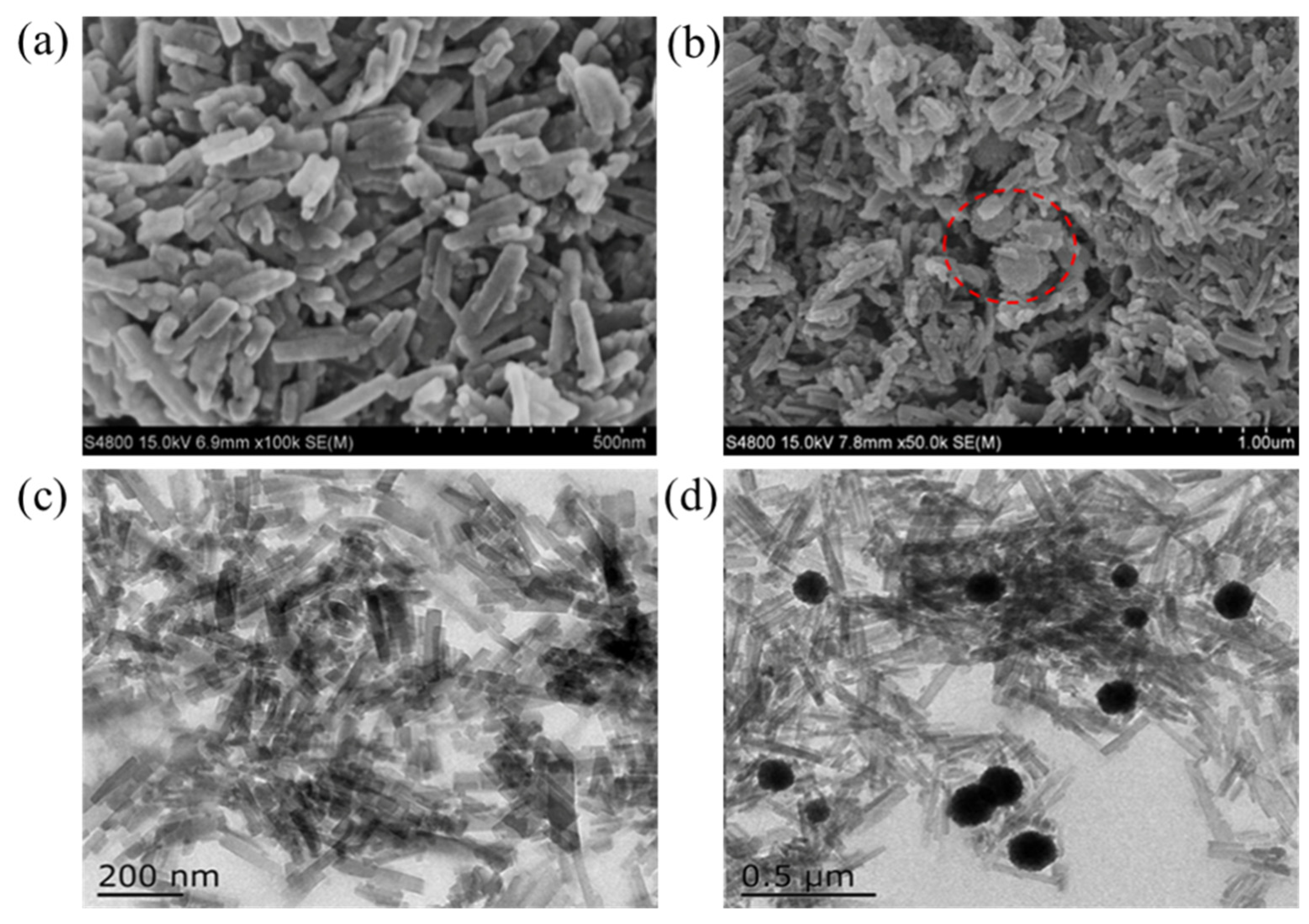
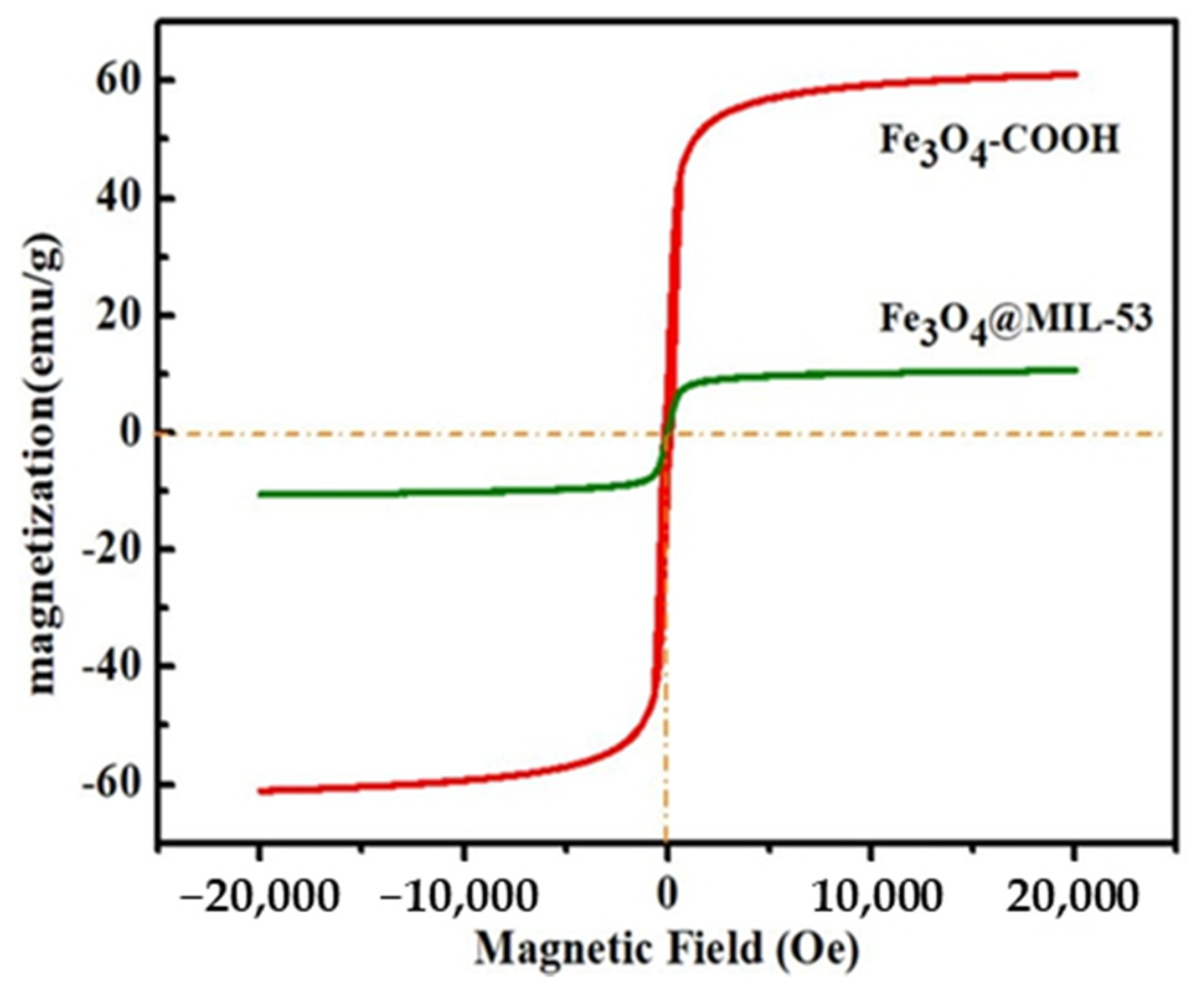
3.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@MIL-53(Al)
3.2. Adsorption of BPA, TC, CR, and MB
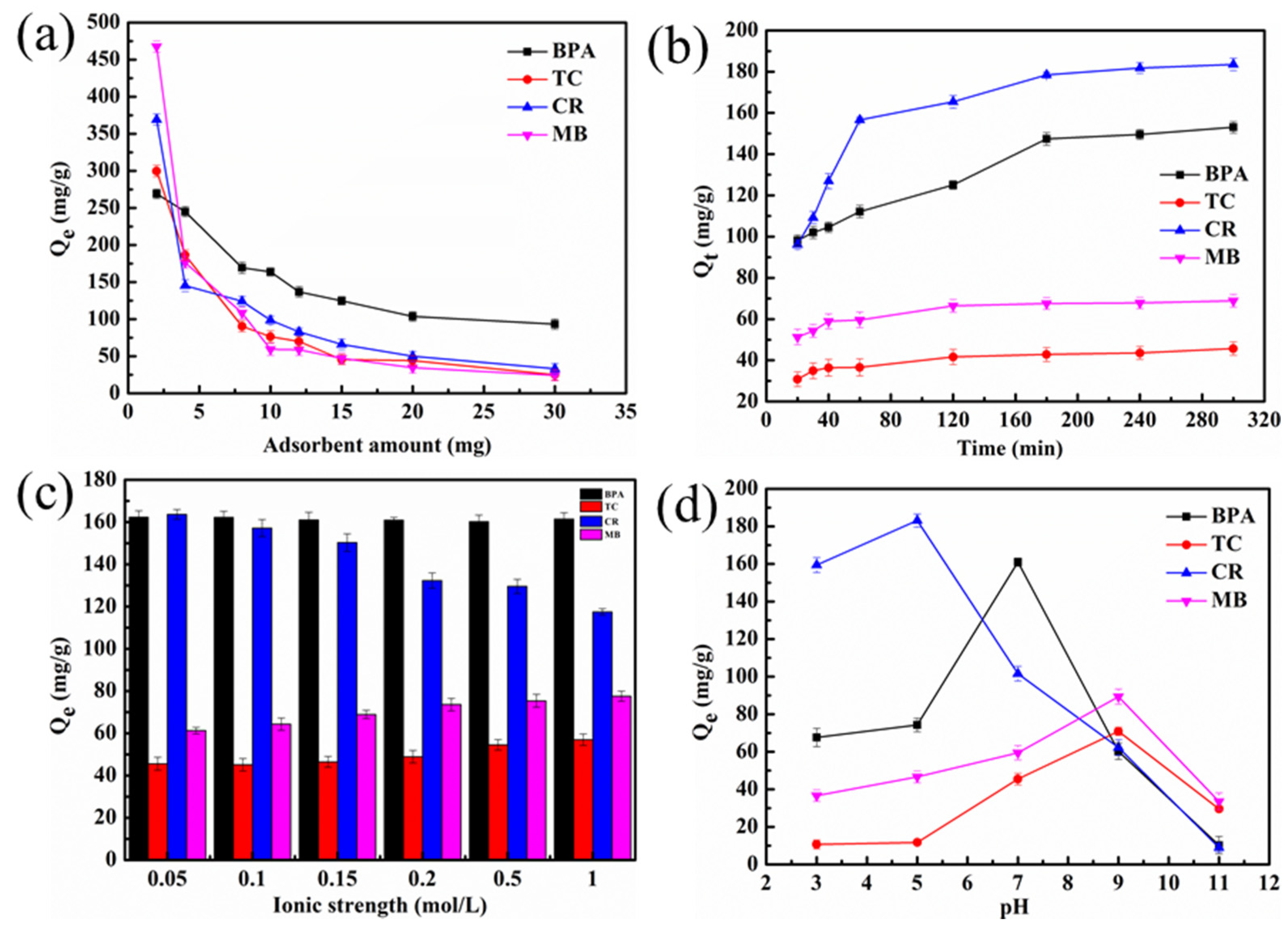
3.2.1. Influence of Adsorbent Amounts
3.2.2. Influence of Adsorption Time
3.2.3. Influence of Ionic Strength
3.2.4. Influence of pH
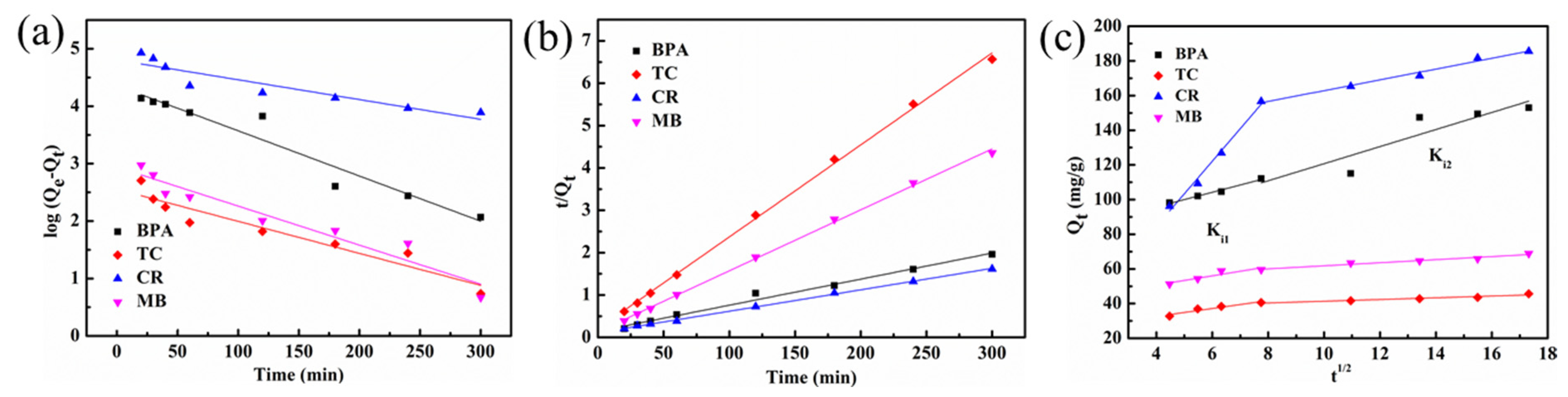
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
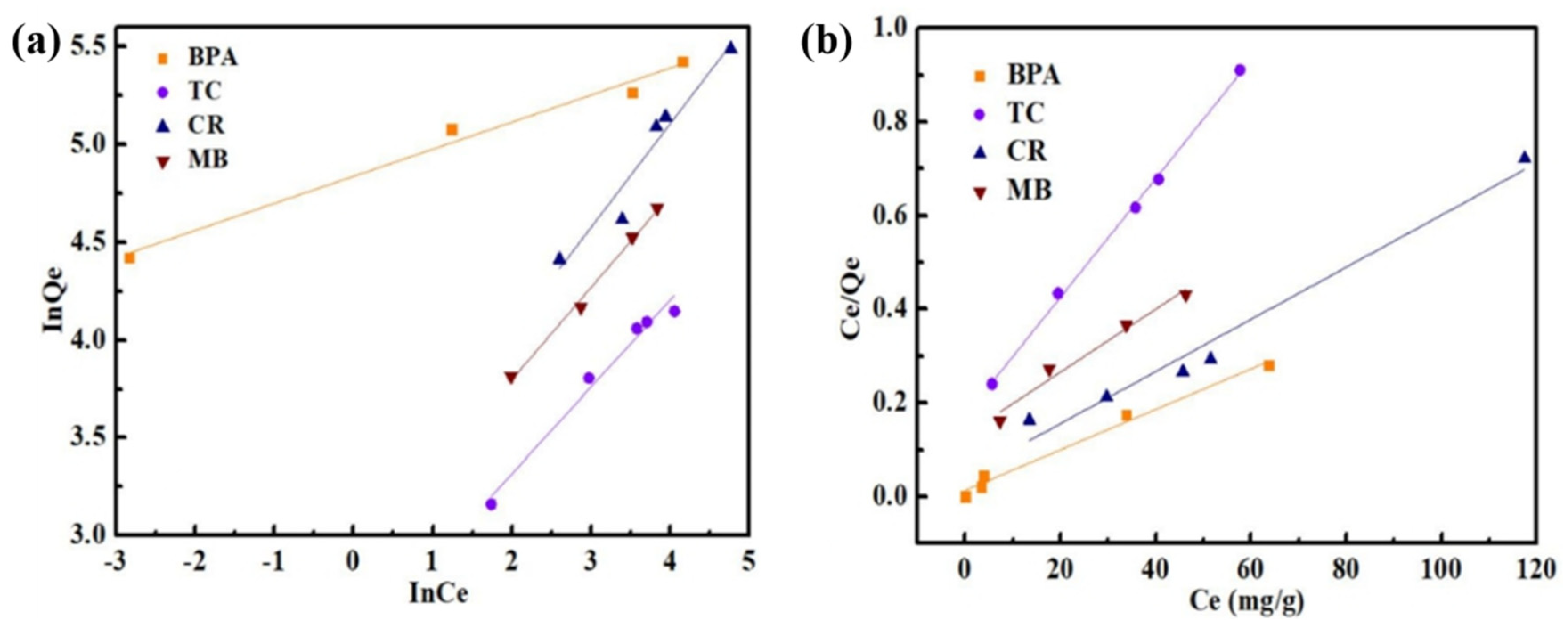
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bakker, K. Water Security: Research Challenges and Opportunities. Science 2012, 337, 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, C.; Dias, E.M. Towards the use of metal-organic frameworks for water reuse: A review of the recent advances in the field of organic pollutants removal and degradation and the next steps in the field. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2015, 3, 22484–22506. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Salam, O.E.; Abou Taleb, E.M.; Afify, A.A. Electrochemical treatment of chemical oxygen demand in produced water using flow-by porous graphite electrode. Water Environ. J. 2018, 32, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykovsky, N.A.; Bykovsky, N.A.; Kantor, E.A.; Rahman, P.A.; Puchkova, L.N.; Fanakova, N.N. Electrochemical treatment of waste water from nickel in galvanic production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 350, 12026–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, B.; Kanaga, P. Waste Water Treatment by Electrochemical Oxidation of Organic Pollutants. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Li, X.; Ling, Y.; Li, L. Efficient degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by photocatalytic ozonation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 296, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, L.; Wei, B. Redox sculptured dual-scale porous nickel-iron foams for efficient water oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 309, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhou, D.; Fan, W.; Huo, M.; Crittenden, J.; Yu, Z.; Ju, P.; Wang, Y. The effectiveness of coagulation for water reclamation from a wastewater treatment plant that has a long hydraulic and sludge retention times: A case study. Chemosphere 2016, 157, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Troyer, L.; Catalano, J.; Giammar, D. Dynamics of Chromium(VI) Removal from Drinking Water by Iron Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13502–13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Cai, Y.; Tang, J.; Pang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Simultaneous removal of lead and phenol contamination from water by nitrogen-functionalized magnetic ordered mesoporous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horovitz, I.; Gitis, V.; Avisar, D.; Mamane, H. Ceramic-based photocatalytic membrane reactors for water treatment—Where to next. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2020, 36, 593–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, P.I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low Cost Adsorbents for Removal of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113C, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, T.; Dutta, J. Applications of Nanotechnology in Wastewater Treatment—A Review. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, X.R.; Sun, B.J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W.; Chen, C.T.; Sun, D.P. Bacterial cellulose/attapulgite magnetic composites as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions and dye treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Tan, L.; Liu, J.; Tan, B.; Yang, X.; Xu, H. Triptycene-Based Hyper-Cross-Linked Polymer Sponge for Gas Storage and Water Treatment. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 8509–8514. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Pournara, A.; Kim, K.; Bansal, V.; Rapti, S.; Manos, M. Metal-organic frameworks: Challenges and opportunities for ion-exchange/sorption applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 86, 25–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, C.; Chen, S.; Song, L.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Thouvenot, C.; Nogues, M.; Marsolier, G.; Louer, D.; Ferey, G. Very Large Breathing Effect in the First Nanoporous Chromium(III)-Based Solids: MIL-53 or CrIII(OH)·{O2C−C6H4−CO2}·{HO2C−C6H4−CO2H}x·H2Oy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13519–13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, T.; Serre, C.; Huguenard, C.; Fink, G.; Taulelle, F.; Henry, M.; Bataille, T.; Férey, G. A Rationale for the Large Breathing of the Porous Aluminum Terephthalate (MIL-53) Upon Hydration. Chem. A Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Qiu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, J. Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres with a designable metal–organic framework shell. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9497–9500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, X.C.A.N. Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, C.; Guan, H.; Li, L.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, R. Magnetic Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Composite for Removal of Lead and Malachite Green in Wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 539, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Qiu, H.; Liu, L. Preparation of Magnetic Fe3O4/MIL-88A Nanocomposite and Its Adsorption Properties for Bromophenol Blue Dye in Aqueous Solution. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, M.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xu, Y. A unique coordination-driven route for the precise nanoassembly of metal sulfides on metal–organic frameworks. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, W.; Yang, Q.; Kaneti, Y.V.; Xu, X.; Alshehri, S.M.; Ahamad, T.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Na, J.; Tang, J.; et al. Core-shell motif construction: Highly graphitic nitrogen-doped porous carbon electrocatalysts using MOF-derived carbon@COF heterostructures as sacrificial templates. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantulnikovs, K.; Glushkova, A.; Kollár, M.; Forró, L.; Horváth, E.; Sienkiewicz, A. Differential Response of the Photoluminescence and Photocurrent of Polycrystalline CH3NH3PbI3 and CH3NH3PbBr3 to the Exposure to Oxygen and Nitrogen. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Vaidya, L.; Rathod, V.K. Enzyme embedded metal organic framework (enzyme–MOF): De novo approaches for immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Huo, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J. Metal-organic framework-based composite Ni@MOF as Heterogenous catalyst for ethylene trimerization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 594, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, W.; Tang, J.; Tan, H.; Wang, J.; Kaneti, Y.V.; Bando, Y.; Wang, T.; He, J.; Yamauchi, Y. MOF nanoleaves as new sacrificial templates for the fabrication of nanoporous Co–Nx/C electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Yadian, B.; Wu, R.; Long, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y. Structure stability of metal-organic framework MIL-53 (Al) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energ. 2013, 38, 16710–16715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Li, G.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.N.; Qiao, J.; McDonald, A. The removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by MIL-53(Al) and mesostructured MIL-53(Al). J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 405, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jv, X.; Zhao, X. A Simplified Method for Synthesis of l-Tyrosine Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles and Its Application for the Removal of Organic Dyes. J. Chem. Eng. Data ACS J. Data 2017, 62, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Qi-bin, S.; Zi-dan, L.; Xiao-ying, Y.; Tai-ping, Z.; Zhi-zhong, L. Preparation of Two Kinds of Biochar and the Factors Influencing Tetracycline Removal from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Xiong, Z. Removal of bisphenol A in aqueous solutions by core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Water Stability and Competition Effects toward CO2 Adsorption on Metal Organic Frameworks. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2015, 44, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; Wei, F.; Chen, N.; Liang, Z.; Luo, Y. Synthesis of graphene oxide/metal–organic frameworks hybrid materials for enhanced removal of Methylene blue in acidic and alkaline solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Ding, C.; Wei, F.; Chen, N.; Liang, Z.; Luo, Y. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with nickel-based metal-organic framework/graphene oxide composites prepared by ultrasonic wave-assisted ball milling. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshraja, D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Kushwaha, J.P.; Mall, I.D. Quinoline adsorption onto granular activated carbon and bagasse fly ash. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C. The Strengthening Role of the Amino Group in Metal–Organic Framework MIL-53 (Al) for Methylene Blue and Malachite Green Dye Adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 3414–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, J.; Jia, M.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Y. Mn-doped zirconium metal-organic framework as an effective adsorbent for removal of tetracycline and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 290, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.X.; Chen, W.J.; Wu, Y.Y.; Wu, X.X.; Zhao, Q.R. Highly efficient adsorption capacity of MIL-53(Fe) metal organic framework material for congo red. Ind. Water Treat. 2017, 37, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.M.; Jhung, S.H. A remarkable adsorbent for removal of bisphenol S from water: Aminated metal-organic framework, MIL-101-NH2. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Fu, J. Adsorptive removal of tetracycline by sustainable ceramsite substrate from bentonite/red mud/pine sawdust. Sci. Rep. UK 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Cai, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Faraj, Y.; Ju, X.; Xie, R.; Chu, L. β-Cyclodextrin-modified graphene oxide membranes with large adsorption capacity and high flux for efficient removal of bisphenol A from water. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Holtzl, T.; Szekely, G. Scavenging organic micropollutants from water with nanofibrous hypercrosslinked cyclodextrin membranes derived from green resources. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xiong, Z. Adsorption Behavior of Three Nitroimidazoles in Aqueous Solutions to Magnetic-modified Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes. Acta Chim. Sinica 2013, 71, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wo, R.; Li, Q.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, G.; Lei, K.; Du, P.; Jiang, W. Preparation and Characterization of Functionalized Metal–Organic Frameworks with Core/Shell Magnetic Particles (Fe3O4@SiO2@MOFs) for Removal of Congo Red and Methylene Blue from Water Solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Chemicals | Molecular Weight(g/mol) | Suppliers | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferric chloride | FeCl3·6H2O | 270.3 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| ethylene glycol | C2H6O2 | 62.1 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| anhydrous sodium acetate | CH3COONa | 82.1 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| Trisodium citrate dihydrate | Na3C6H5O7·2H2O | 294.1 | Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| N, N-dimethylformamide | C3H7NO | 73.1 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| aluminum nitrate nonahydrate | H18AlN3O18 | 375.1 | Xilong Scientific Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| 1,4-Dicarboxybenzene | C8H6O4 | 166.1 | Nanjing Wanqing Pharm. Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| methyl alcohol | CH3OH | 32.1 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| Bisphenol A | C15H16O2 | 228.3 | Aladdin BioChem Technology Co., Ltd. | G.C |
| Tetracycline | C22H24N2O8 | 444.4 | Nanjing Jia Nanjing Jiaozi Rattan Scientific ozi Rattan Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd. | C.P |
| Congo red | C32H22N6Na2O6S2 | 696.7 | Chengdu Kelong Chemical Industry | A.R |
| methylene blue | C₁₆H₁₈ClN₃S | 319.8 | Chengdu Kelong Chemical Industry | A.R |
| sodium chloride | NaCl | 58.4 | Chengdu Kelong Chemical Industry | A.R |
| sodium hydroxide | NaOH | 40.0 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| hydrochloric acid | HCl | 36.5 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| deionized water | H2O | 18.0 | Laboratory provision | A.R |
| Absolute ethyl alcohol | C2H6O | 46.1 | Nanjing Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. | A.R |
| Kinetics | Parameters | Dyes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | TC | CR | MB | ||
| Qcala (mg/g) | 162.6 | 46.1 | 200.0 | 69.9 | |
| Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Qexpb (mg/g) | 160.9 | 47.8 | 234.4 | 70.8 |
| k2 (g/mg/min) | 2.62 × 10−4 | 2.35 × 10−3 | 2.26 × 10−4 | 1.54 × 10−3 | |
| R2 | 0.9897 | 0.9984 | 0.9988 | 0.9986 | |
| Qcala (mg/g) | 78.1 | 12.8 | 122.0 | 18.9 | |
| Pseudo-First-Order Model | k1 (min−1) | 0.0079 | 0.0055 | 0.0034 | 0.0068 |
| R2 | 0.9332 | 0.9047 | 0.8343 | 0.9236 | |
| ki1 (mg/g/min1/2) | 2.65 | 2.28 | 18.79 | 1.75 | |
| C1 (mg/g) | 87.9 | 23.5 | 18.8 | 45.2 | |
| Intraparticle Diffusion Models | R2 | 0.8657 | 0.8971 | 0.9801 | 0.8249 |
| ki2 (mg/g/min1/2) | 1.43 | 0.50 | 3.11 | 0.82 | |
| C2 (mg/g) | 127.9 | 36.4 | 131.7 | 53.9 | |
| R2 | 0.9329 | 0.9129 | 0.9845 | 0.8599 | |
| Dyes | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | |
| BPA | 205.0 | 0.3077 | 0.9835 | 0.1380 | 126.2 | 0.9758 |
| TC | 78.9 | 0.0735 | 0.9978 | 0.4441 | 11.4 | 0.9726 |
| CR | 179.5 | 0.1253 | 0.9670 | 0.5303 | 19.8 | 0.9262 |
| MB | 148.8 | 0.0511 | 0.9611 | 0.4711 | 17.4 | 0.9924 |
| Adsorbent | Qmax (mg/g) | Target Pollutant | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@MIL-53(Al) | 160.9 mg/g | BPA | This Work |
| 47.8 mg/g | TC | ||
| 234.4 mg/g | CR | ||
| 70.8 mg/g | MB | ||
| MIL-53(Al) | 329.2 ± 16.5 mg/g | BPA | [31] |
| MIL-53(Fe) | 247.7 mg/g | TC | [41] |
| 1 482 mg/g | CR | [42] | |
| MIL-101-NH2 | Less than 100 mg/g | BPA | [43] |
| CWs Ben-Rm-Ps ceramsite | 2.56 mg/g | TC | [44] |
| CDGO nanosheets | 23.1 mg/g | BPA | [45] |
| HP-β-CD | 186.9 ± 7.9 mg/g | MB | [46] |
| Dyes | T (K) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAP | 298 | −8.23 | - | - |
| 308 | −9.04 | −34.1 | −81.5 | |
| 318 | −9.86 | - | - | |
| TC | 298 | −2.62 | - | - |
| 308 | −3.37 | 19.7 | 74.9 | |
| 318 | −4.12 | - | - | |
| CR | 298 | −3.67 | - | - |
| 308 | −6.07 | 67.8 | 240.0 | |
| 318 | −8.47 | - | - | |
| MB | 298 | −2.48 | - | - |
| 308 | −2.96 | 11.8 | 47.9 | |
| 319 | −3.44 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Wo, R.; Sun, Z.; Hao, G.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Jiang, W. Effective Magnetic MOFs Adsorbent for the Removal of Bisphenol A, Tetracycline, Congo Red and Methylene Blue Pollutions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081917
Zhang G, Wo R, Sun Z, Hao G, Liu G, Zhang Y, Guo H, Jiang W. Effective Magnetic MOFs Adsorbent for the Removal of Bisphenol A, Tetracycline, Congo Red and Methylene Blue Pollutions. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081917
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guangpu, Rong Wo, Zhe Sun, Gazi Hao, Guigao Liu, Yanan Zhang, Hu Guo, and Wei Jiang. 2021. "Effective Magnetic MOFs Adsorbent for the Removal of Bisphenol A, Tetracycline, Congo Red and Methylene Blue Pollutions" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081917
APA StyleZhang, G., Wo, R., Sun, Z., Hao, G., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., Guo, H., & Jiang, W. (2021). Effective Magnetic MOFs Adsorbent for the Removal of Bisphenol A, Tetracycline, Congo Red and Methylene Blue Pollutions. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11081917