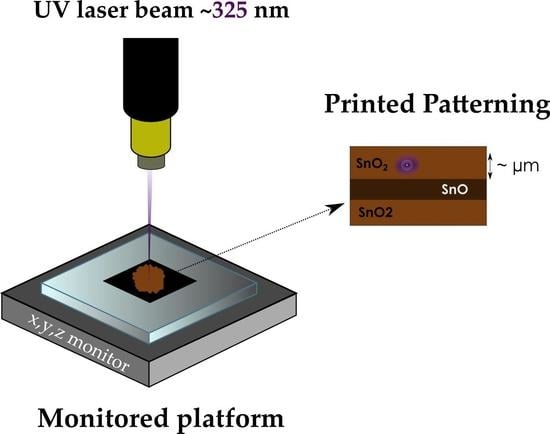
In Situ Local Oxidation of SnO Induced by Laser Irradiation: A Stability Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of SnO Nanoparticles and Nanostructures
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results
3.1. TEM and XRD
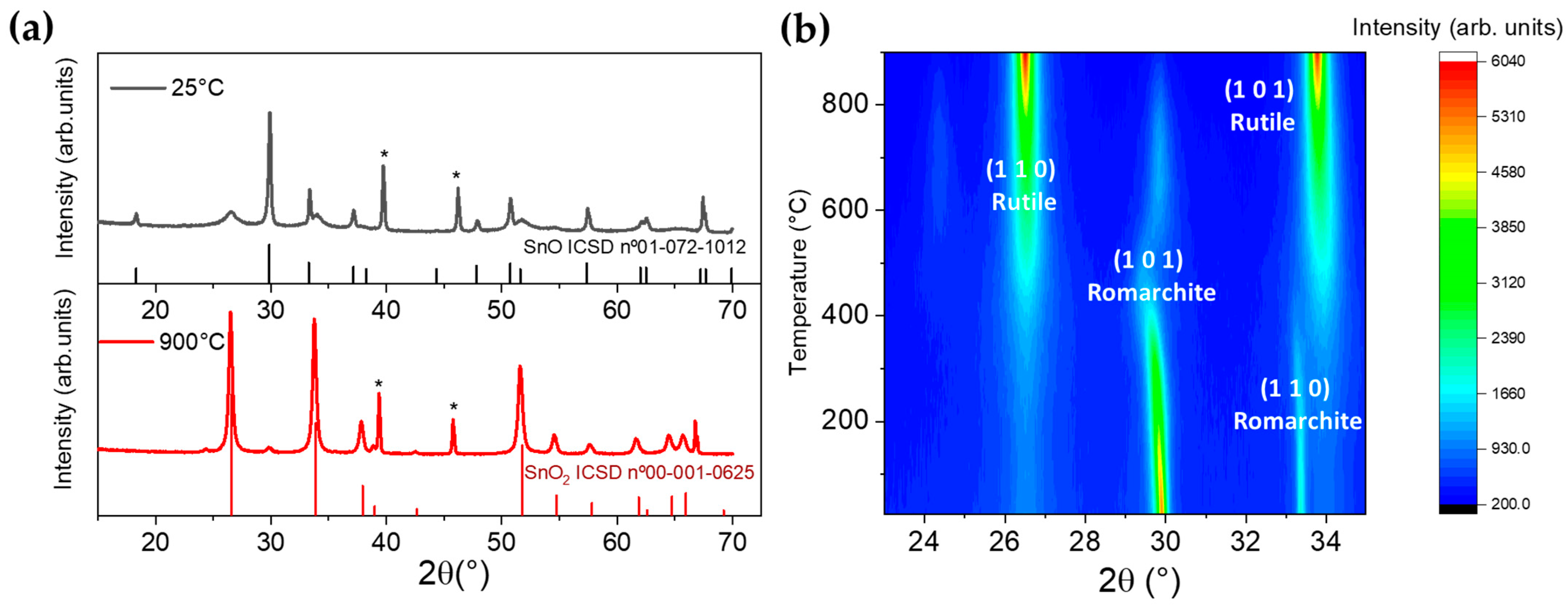
3.2. Thermo XRD
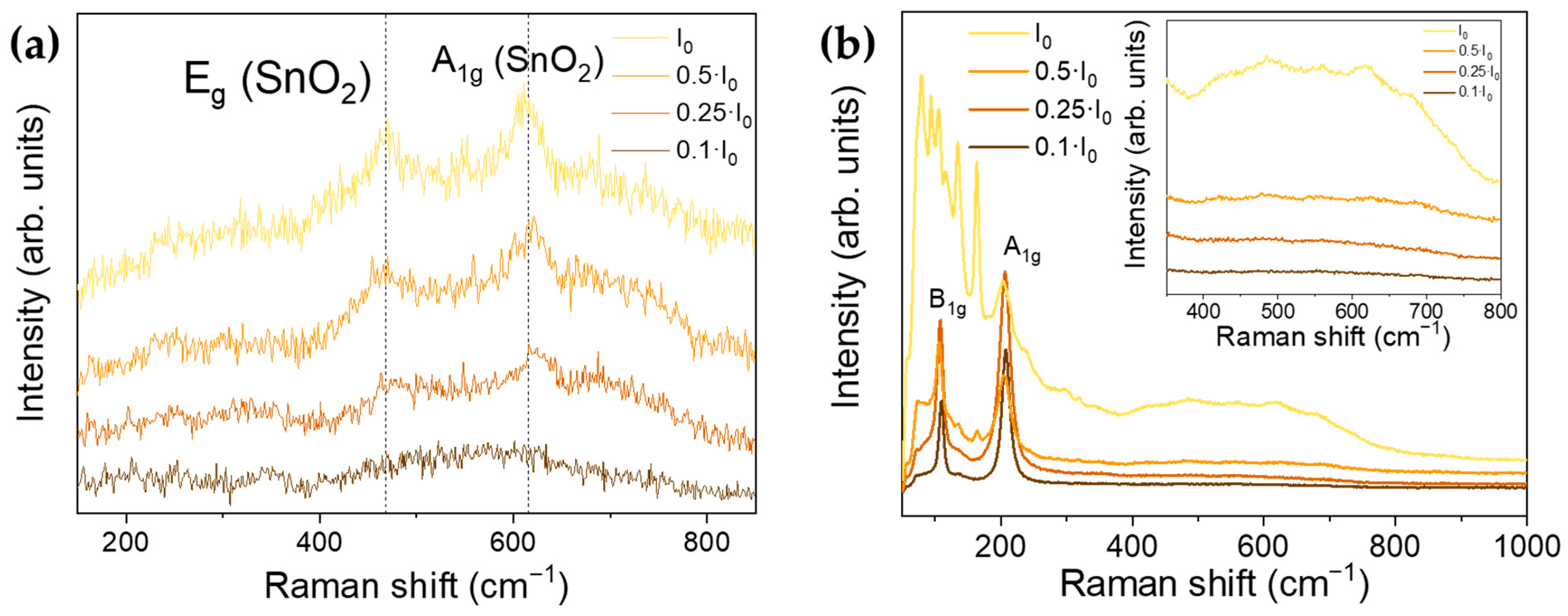
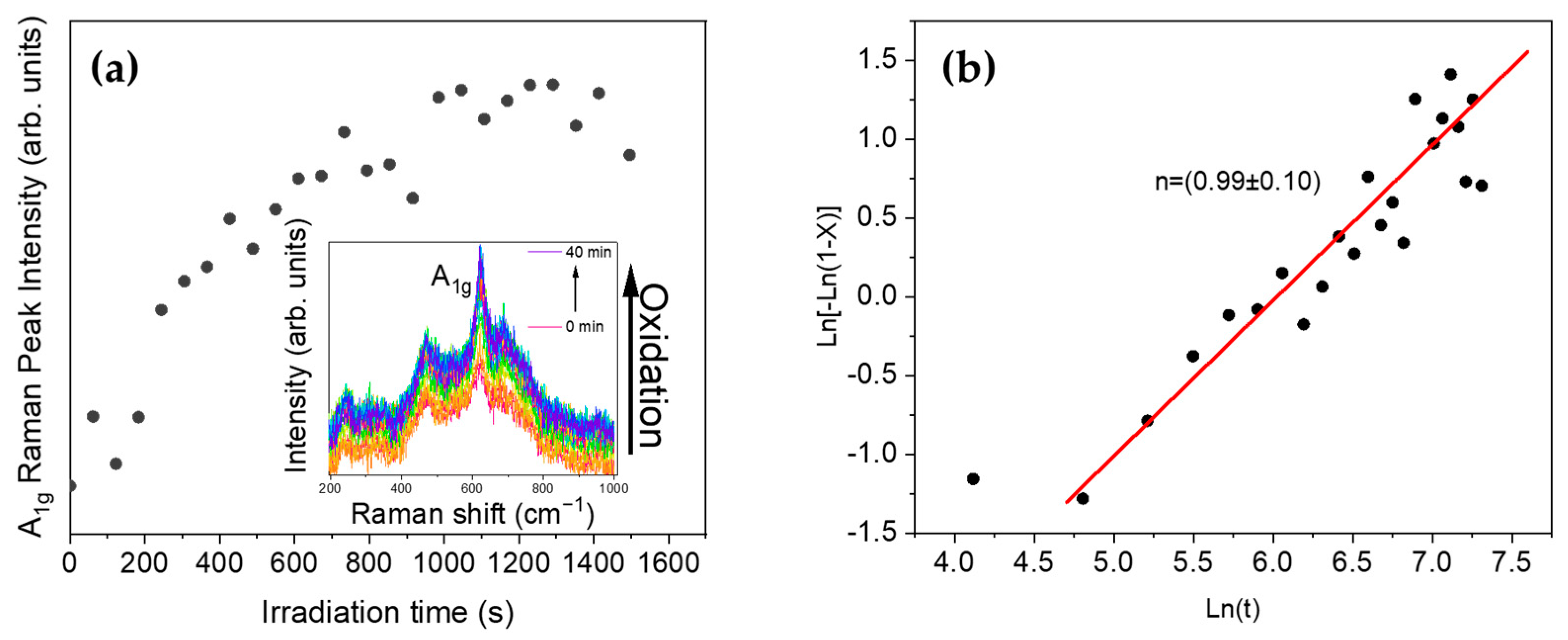
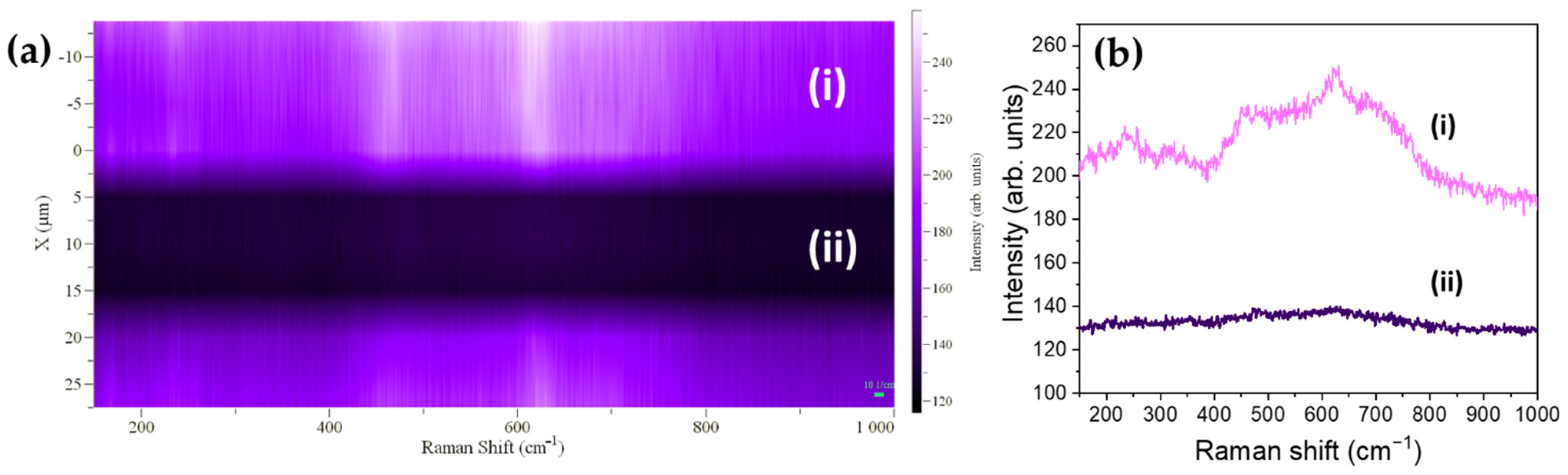
3.3. Raman Spectroscopy
3.4. Laser-Induced Phase Transition
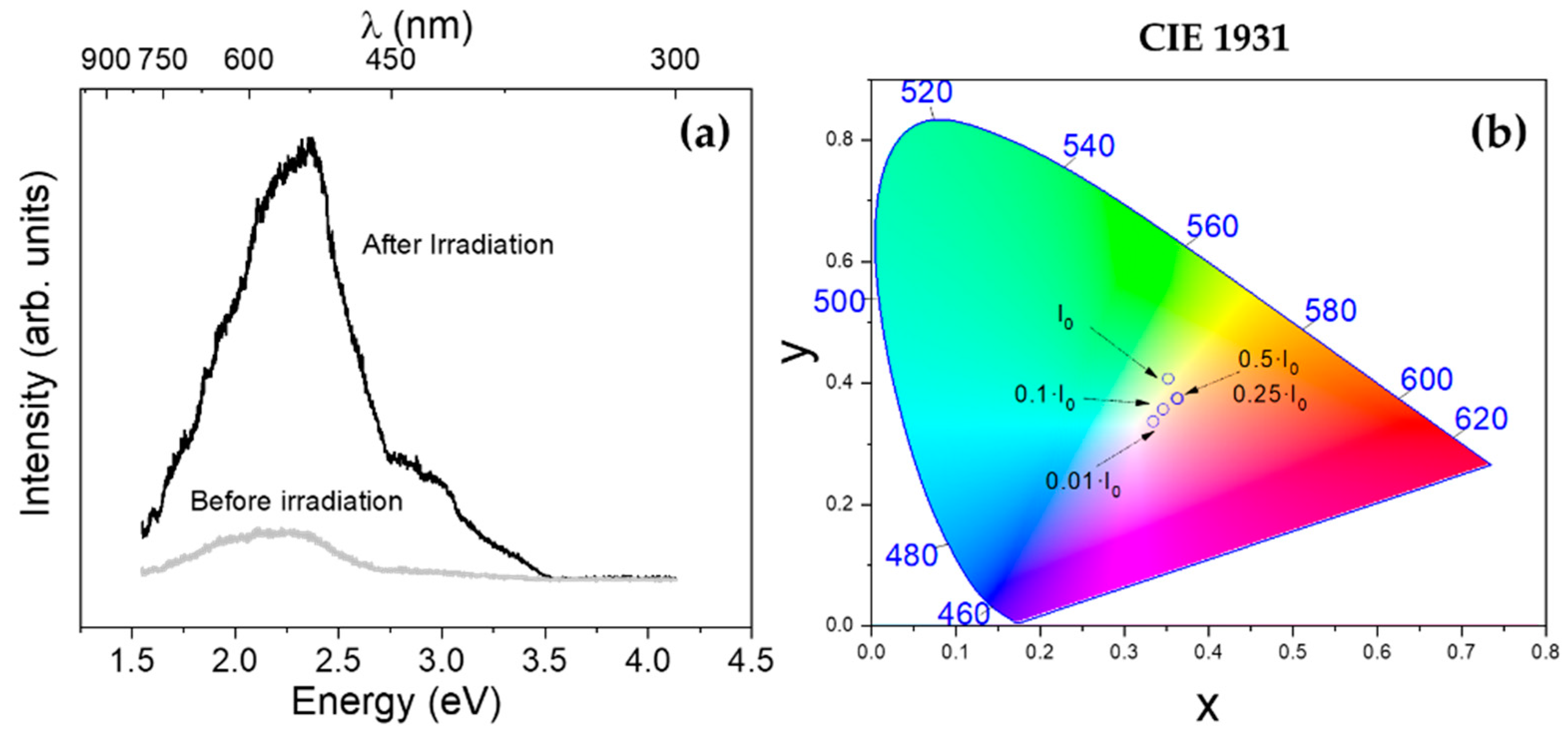
3.5. Photoluminescence
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batzill, M.; Diebold, U. The surface and materials science of tin oxide. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2005, 79, 47–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-López, A.; Maestre, D.; Ramírez-Castellanos, J.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Pis, I.; Nappini, S.; Yuca, N.; Cremades, A. Influence of Doping and Controlled Sn Charge State on the Properties and Performance of SnO2 Nanoparticles as Anodes in Li-Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 18490–18501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.S.; Batista, F.R.M.; Bacani, R.; Triboni, E.R. Structural characterization of SnO nanoparticles synthesized by the hydrothermal and microwave routes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomé, J.; Taeño, M.; Vázquez-lópez, A.; Prado, F.; García-Tecedor, M.; Cristian, G.; Ramírez-Castellanos, J.; Cremades, A. Oxide-Based Materials and Structures; Savkina, R., Khomenkova, L., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.S.; Lou, X.W.D. SnO2 -Based Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Application in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Small 2013, 9, 1877–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Jayaraman, V. SnO2: A comprehensive review on structures and gas sensors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 66, 112–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.D.; Reddy, S.P.; Deepthi, A. Synthesis, Characterization of Tin Oxide (SnO) Nanoparticles via Autoclave synthesis protocol for H2 sensing. Int. J. Nanotechnol. Appl. 2017, 11, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-López, A.; Yaseen, A.; Maestre, D.; Ramírez-Castellanos, J.; Marstein, E.S.; Karazhanov, S.Z.; Cremades, A. Synergetic Improvement of Stability and Conductivity of Hybrid Composites formed by PEDOT: PSS and SnO Nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Yin, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Cao, W. One-step synthesis of SnO hierarchical architectures under room temperature and their photocatalytic properties. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 284002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, S.; Cao, W. Morphology modulation of SnO photocatalyst: From microplate to hierarchical architectures self-assembled with thickness controllable nanosheets. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 4651–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solola, G.T.; Klopov, M.; Akinami, J.O.; Afolabi, T.A.; Karazhanov, S.Z.; Adebayo, G. First principle calculations of structural, electronic, optical and thermoelectric properties of tin (II) oxide. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Gorai, P.; Aydemir, U.; Mason, T.O.; Stevanović, V.; Toberer, E.S.; Snyder, G.J. SnO as a potential oxide thermoelectric candidate. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 8854–8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, A.; Handoko, C.T.; Bustan, M.D.; Yudono, B.; Gulo, F. New route in the synthesis of Tin (II) oxide micro-sheets and its thermal transformation. Mater. Lett. 2018, 211, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, F.I.; Joanni, E.; Savu, R.; Zaghete, M.A.; Longo, E.; Varela, J.A. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nanocrystalline SnO powders. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervillié, C.; Boisard, A.; Labbé, J.; Berthon-Fabry, S.; Guérin, K. Influence upon cycling of oxygen amount in tin-based compound used as negative electrode in lithium-ion battery. Synth. Met. 2020, 267, 116477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaśkaniec, S.; Kavanagh, S.R.; Coelho, J.; Ryan, S.; Hobbsb, C.; Walsh, A.; Scanlon, D.O.; Valeria, N. Solvent Engineered Synthesis of Layered SnO Nanoparticles for High-Performance Anodes. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2020, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, D.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Alshareef, H.N. Two-Dimensional SnO Anodes with a Tunable Number of Atomic Layers for Sodium Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, K.M.; Park, J.S.; Kang, Y.C. Excellent Li-ion storage performances of hierarchical SnO-SnO2 composite powders and SnO nanoplates prepared by one-pot spray pyrolysis. J. Power Sources 2017, 359, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W. Fabrication of SnO2-SnO nanocomposites with p–n heterojunctions for the low-temperature sensing of NO2 gas. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12133–12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, A.; Basak, P.; Satyanarayana, L.; Manorama, S.V. Hierarchical SnO/SnO2 nanocomposites: Formation of in situ p–n junctions and enhanced H2 sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Yu, W.; Peng, F.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Lu, J.; Luo, C.; et al. Enhanced gas selectivity induced by surface active oxygen in SnO/SnO2 heterojunction structures at different temperatures. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Fan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. A low temperature formaldehyde gas sensor based on hierarchical SnO/SnO2 nano-flowers assembled from ultrathin nanosheets: Synthesis, sensing performance and mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palneedi, H.; Park, J.H.; Maurya, D.; Peddigari, M.; Hwang, G.-T.; Annapureddy, V.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, J.-J.; Hahn, B.-D.; Priya, S.; et al. Laser Processing of Metal Oxides: Laser Irradiation of Metal Oxide Films and Nanostructures: Applications and Advances. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1870094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vila, M.; Díaz-Guerra, C.; Piqueras, J. Laser irradiation-induced α to δ phase transformation in Bi2O3 ceramics and nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 71905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, M.Z.; Wang, F.; Zhao, H.; Rafique, M.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Structural and electrochemical properties of SnO nanoflowers as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Dong, P.P.; Lang, X.; Nan, J.M. A novel rose flower-like SnO hierarchical structure synthesized by a hydrothermal method in an ethanol/water system. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2014, 25, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Q.; Fu, L. Oxidation and phase transitions of epitaxial tin oxide thin films on (1012) sapphire. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 6048–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, C.M.; Rodríguez, J.E.; Ramírez, A.E. Thermal behaviour of romarchite phase SnO in different atmospheres: A hypothesis about the phase transformation. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leitner, J.; Sedmidubský, D. Thermodynamic Modeling of Oxidation of Tin Nanoparticles. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2019, 40, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahen, S.; David, N.; Fiorani, J.M.; Maître, A.; Vilasi, M. Thermodynamic modelling of the O-Sn system. Thermochim. Acta 2003, 403, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.; Sham, T.K.; Ding, Z. Observation of single tin dioxide nanoribbons by confocal raman microspectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 18839–18843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diéguez, A.; Romano-Rodríguez, A.; Vilà, A.; Morante, J.R. The complete Raman spectrum of nanometric SnO2 particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.X.; Loa, I.; Syassen, K.; Hanfland, M.; Mathis, Y.-L. Structural properties, infrared reflectivity, and Raman modes of SnO at high pressure. Phys. Status Solidi 2004, 241, 3168–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Grandbois, M. In situ Raman spectroscopic observation of sequential hydrolysis of stannous chloride to abhurite, hydroromarchite, and romarchite. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, C.; Herrero, J. P-type SnO thin films prepared by reactive sputtering at high deposition rates. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1706–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eifert, B.; Becker, M.; Reindl, C.T.; Giar, M.; Zheng, L.; Polity, A.; He, Y.; Heiliger, C.; Klar, P.J. Raman studies of the intermediate tin-oxide phase. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2017, 1, 14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebanova, O.N.; Lazor, P. Raman study of magnetite (Fe3O4): Laser-induced thermal effects and oxidation. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre, D.; Cremades, A.; Piqueras, J. Cathodoluminescence of defects in sintered tin oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 3027–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mingzhe, Z. Effect of Gd3+ doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of SnO crystals. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 17529–17535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prado, F.; Taeño, M.; Maestre, D.; Ramírez-Castellanos, J.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Cremades, A. Effect of the synthesis method on the properties of lithium doped graphene oxide composites with tin oxide nanoparticles: Towards white luminescence. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 129, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanda, J. Colorimetry: Understanding the CIE System; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-04904-4. [Google Scholar]
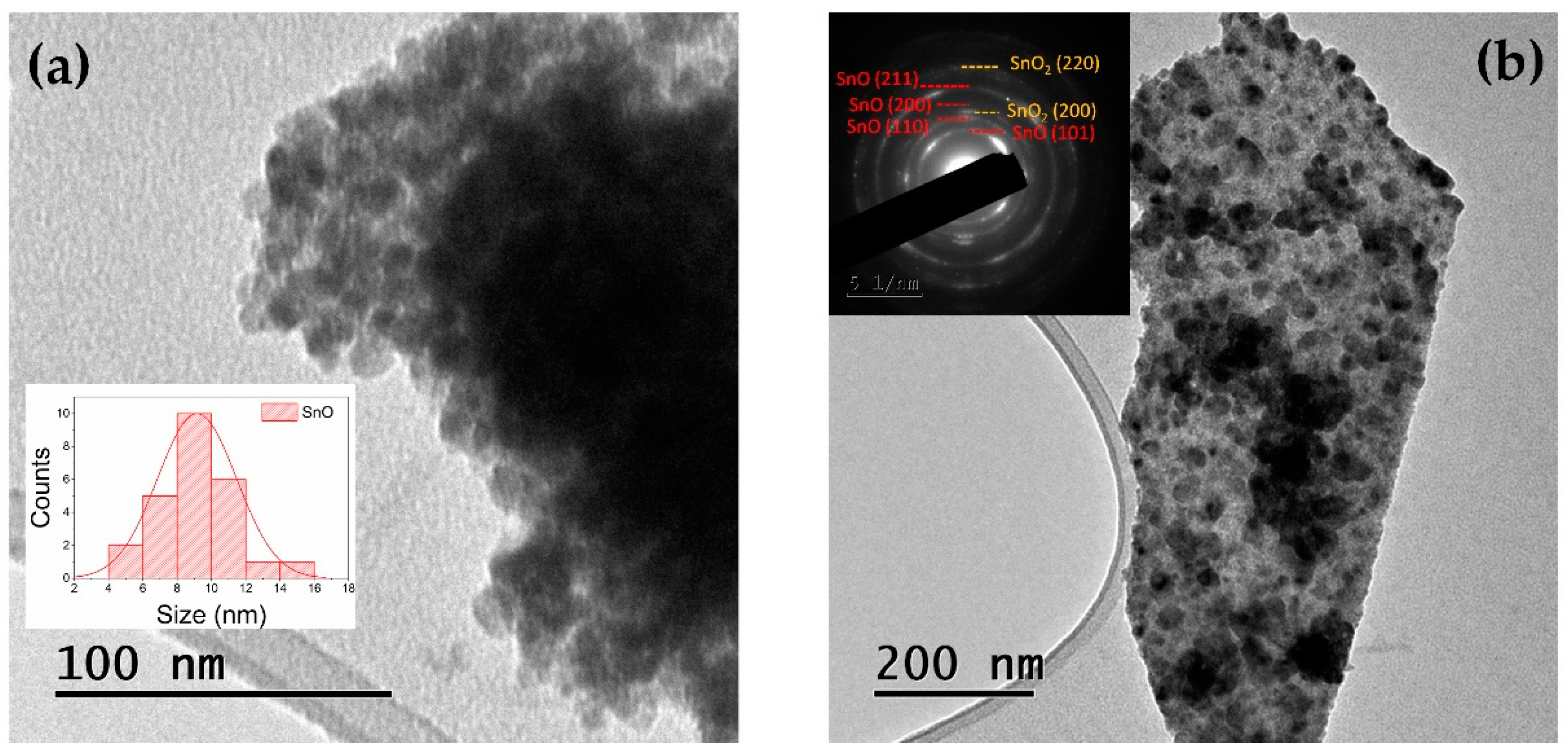
| D(nm) (By TEM) | a(Å) (By XRD) | c(Å) (By XRD) |
|---|---|---|
| 9.14 ± 2.58 | 3.80(1) | 4.83(7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez-López, A.; Maestre, D.; Ramírez-Castellanos, J.; Cremades, A. In Situ Local Oxidation of SnO Induced by Laser Irradiation: A Stability Study. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040976
Vázquez-López A, Maestre D, Ramírez-Castellanos J, Cremades A. In Situ Local Oxidation of SnO Induced by Laser Irradiation: A Stability Study. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040976
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez-López, Antonio, David Maestre, Julio Ramírez-Castellanos, and Ana Cremades. 2021. "In Situ Local Oxidation of SnO Induced by Laser Irradiation: A Stability Study" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040976
APA StyleVázquez-López, A., Maestre, D., Ramírez-Castellanos, J., & Cremades, A. (2021). In Situ Local Oxidation of SnO Induced by Laser Irradiation: A Stability Study. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040976