Superparamagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characteristics of Magnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles
2.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. In Vivo Toxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
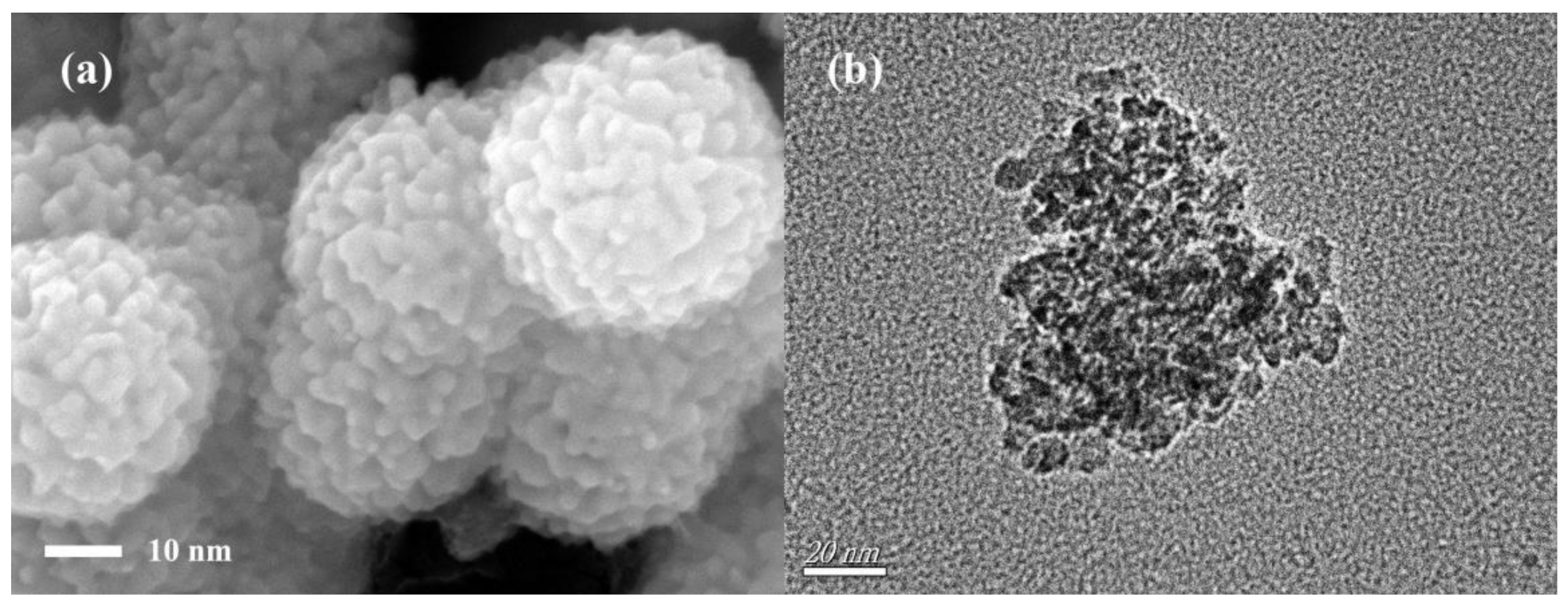
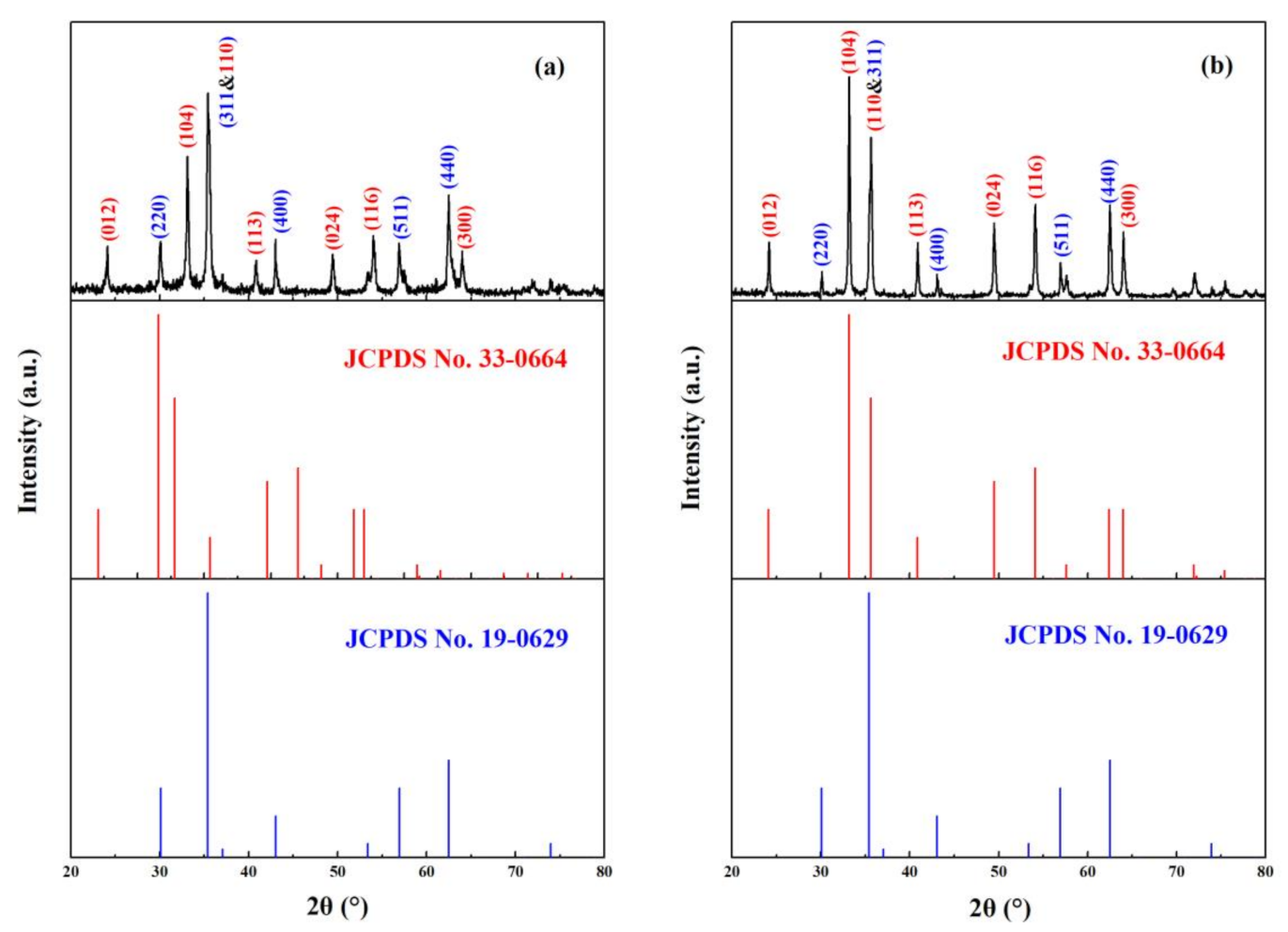
3.1. Characteristics of Magnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles
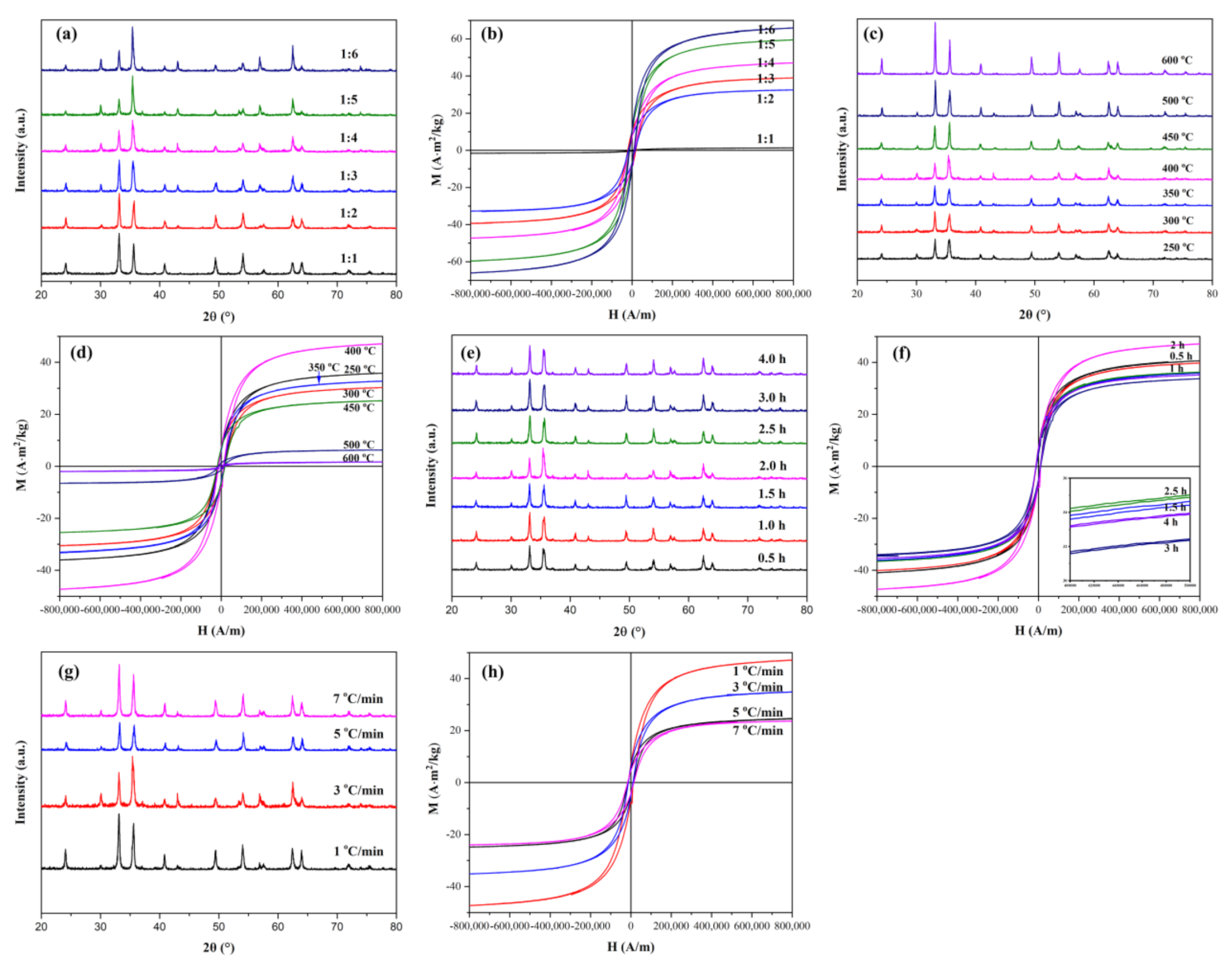
3.2. Effects of Experimental Conditions on the Ratio of α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 in Heterogeneous Nanoparticles
3.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
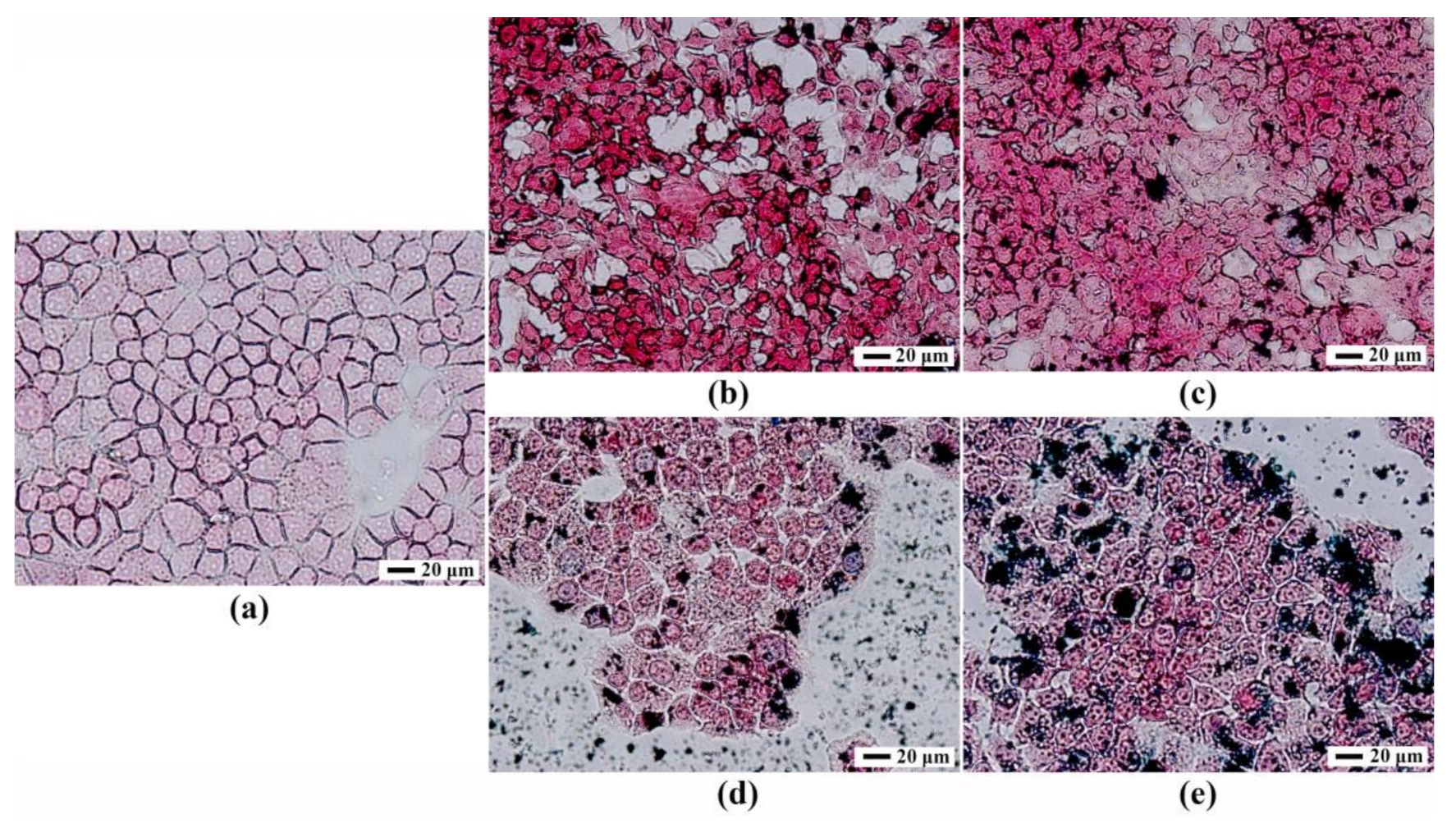
3.4. Prussian Blue Staining
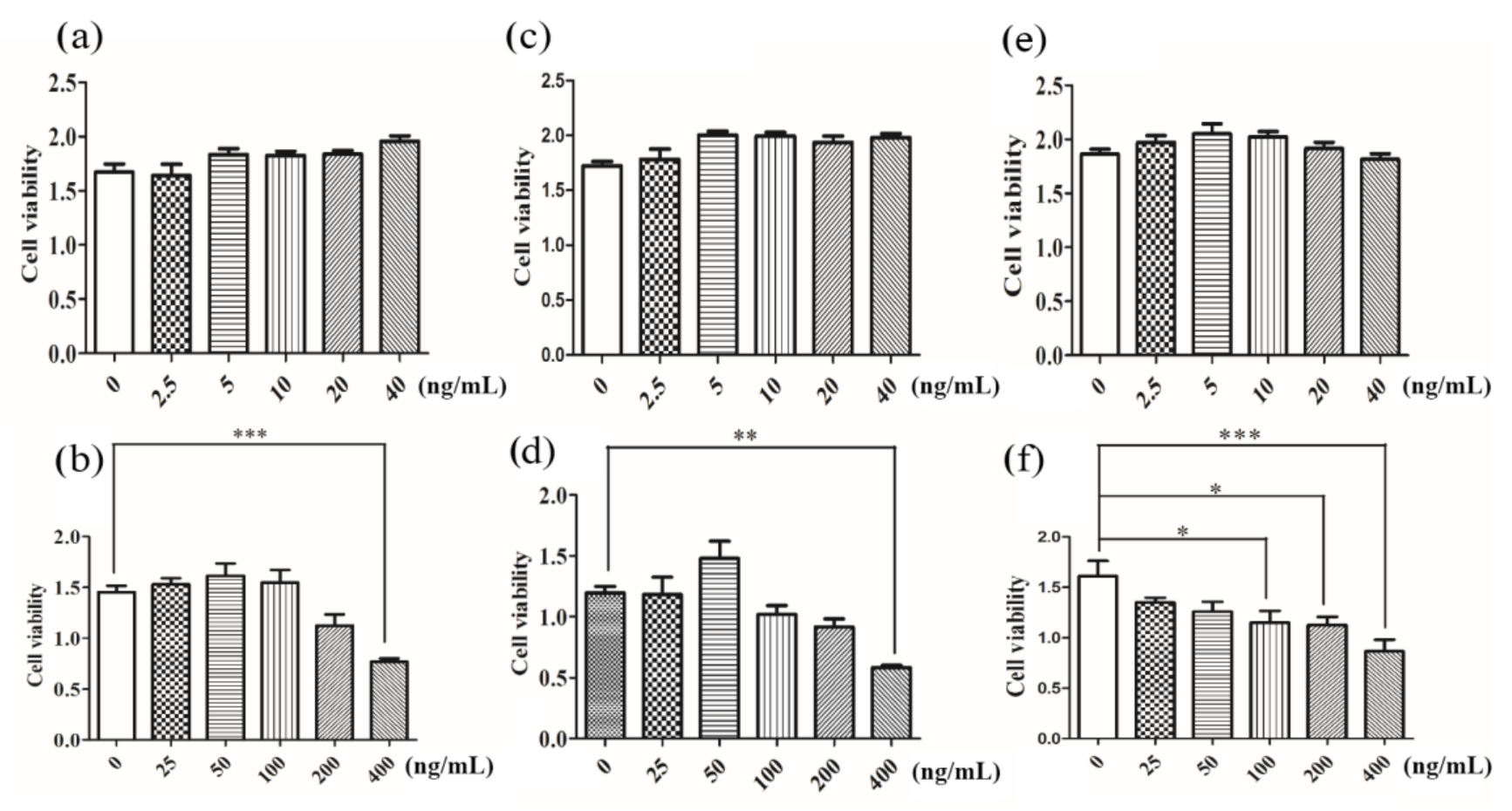
3.5. Cell Counting Kit-8 and LDH Detection of Cell Viability
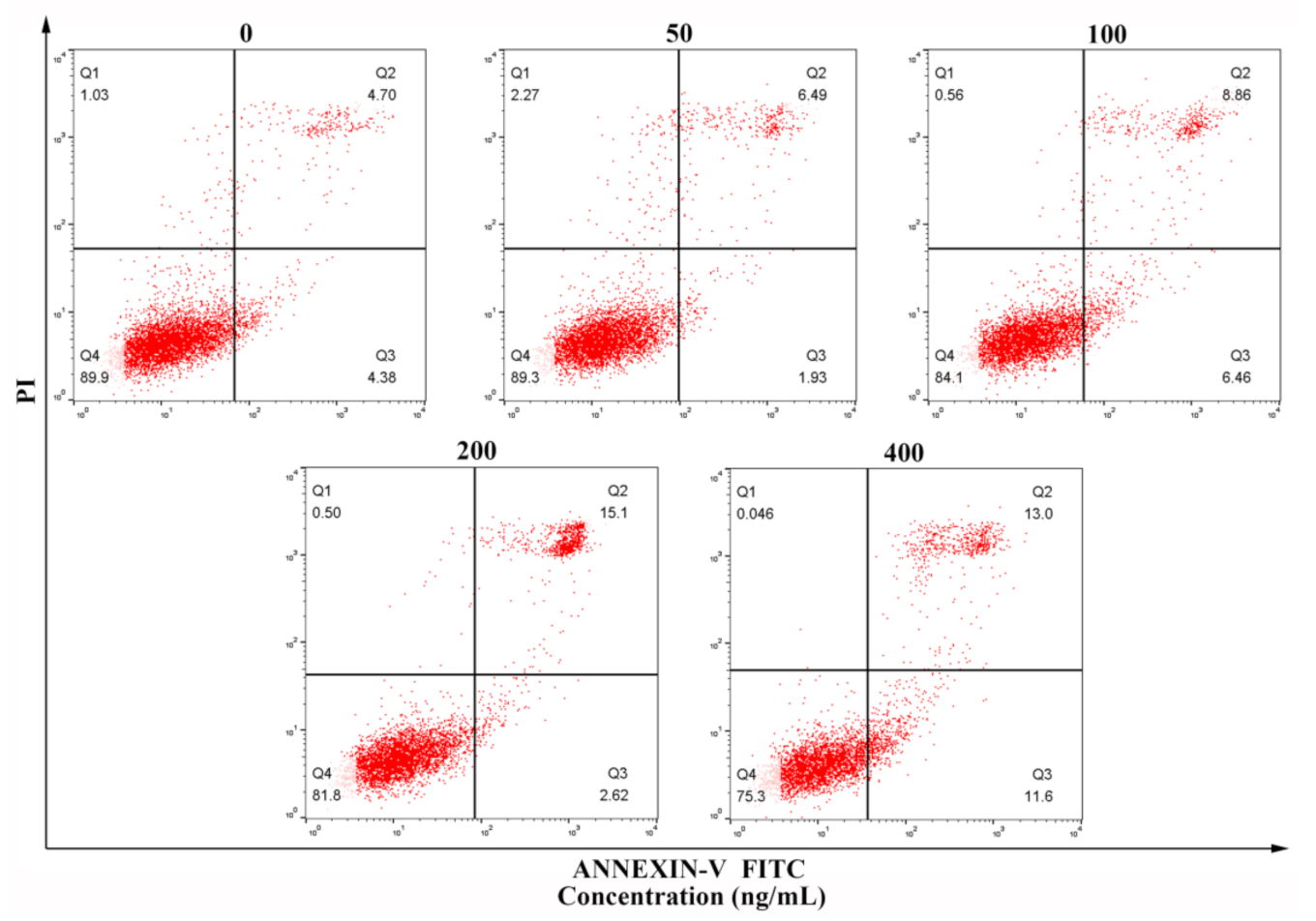
3.6. Flow Cytometry Detection of Apoptosis
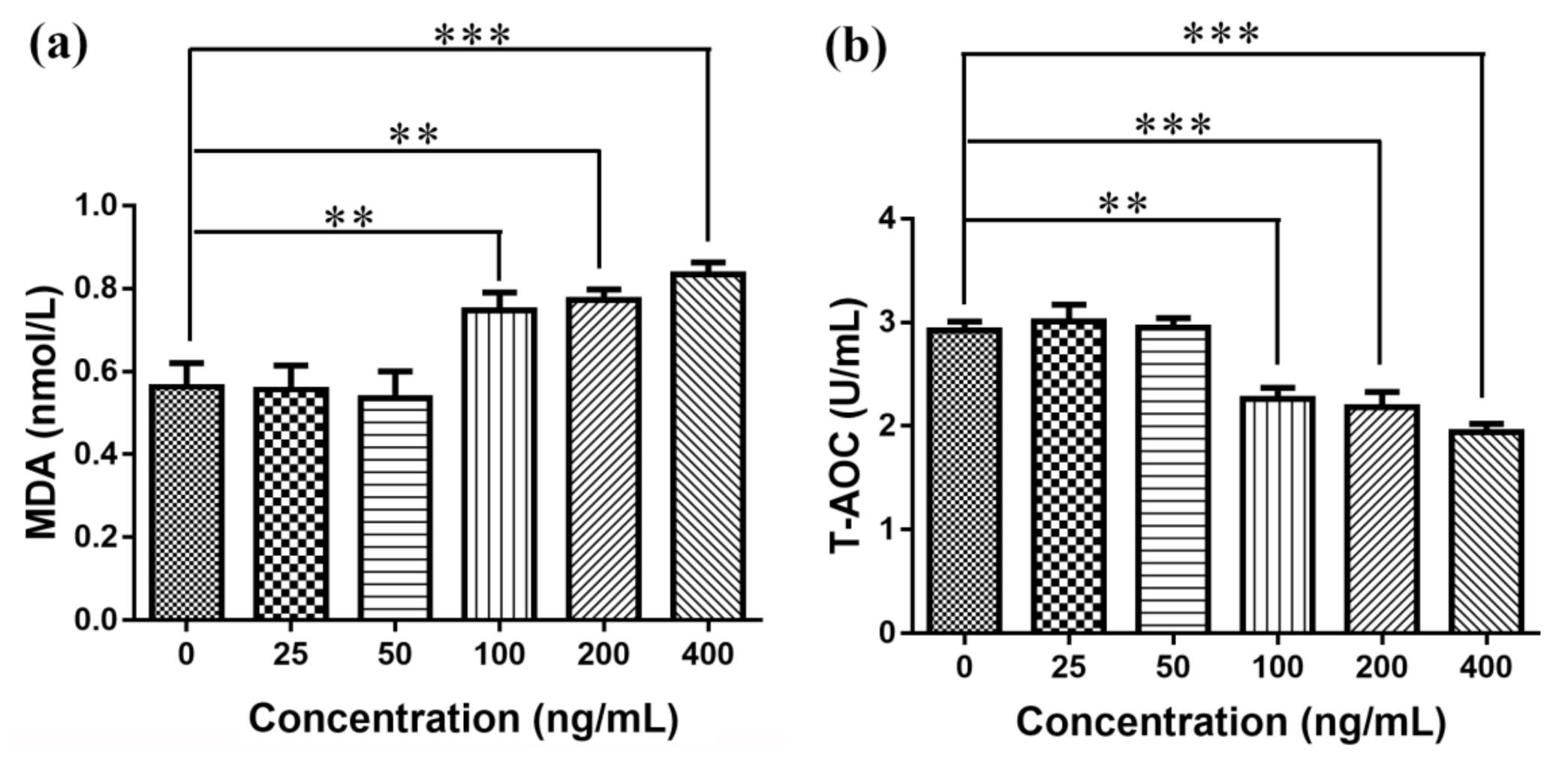
3.7. Elisa Detects MDA Production and T-AOC
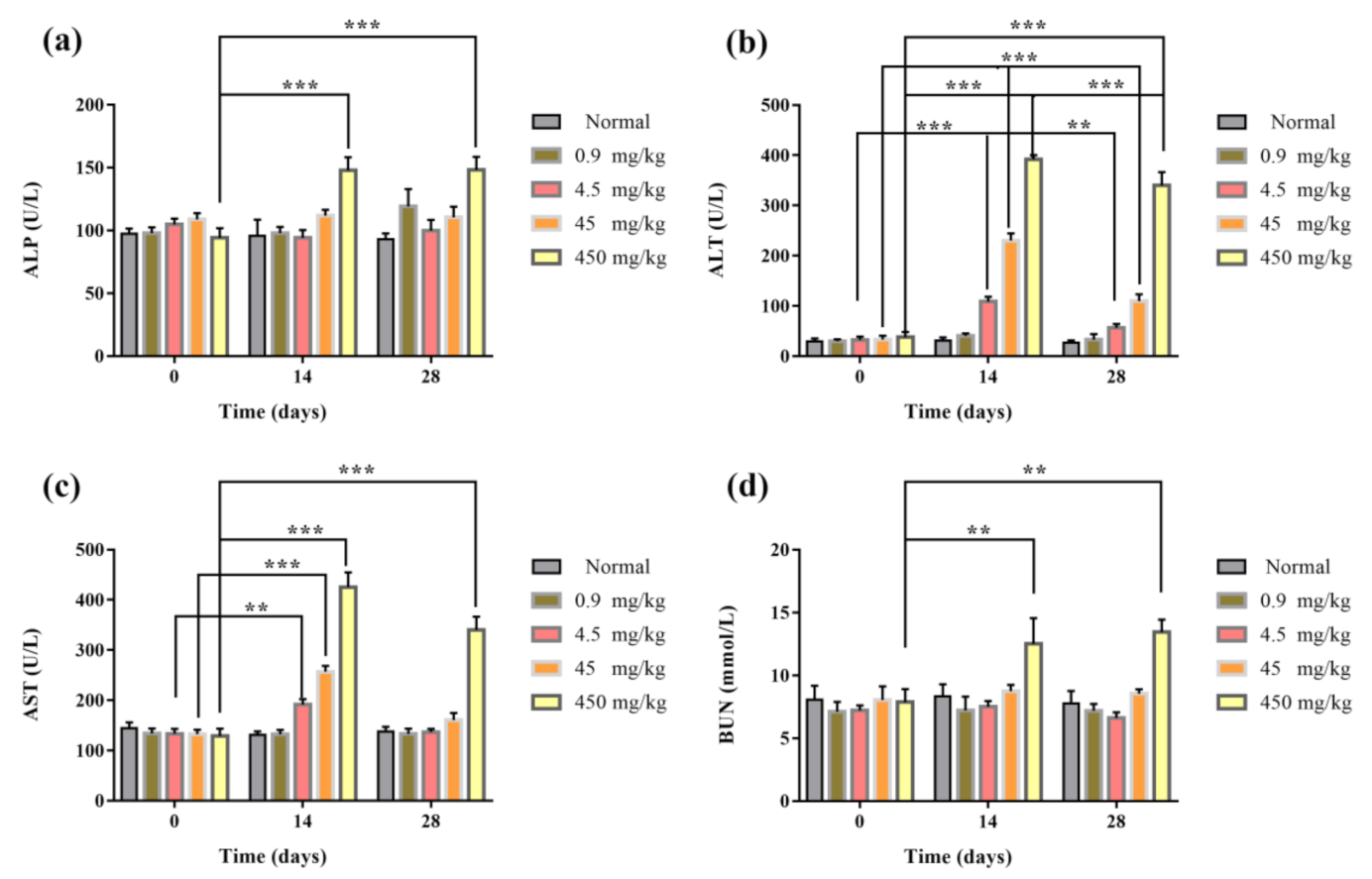
3.8. Blood Routine and Biochemical Assay of Mice
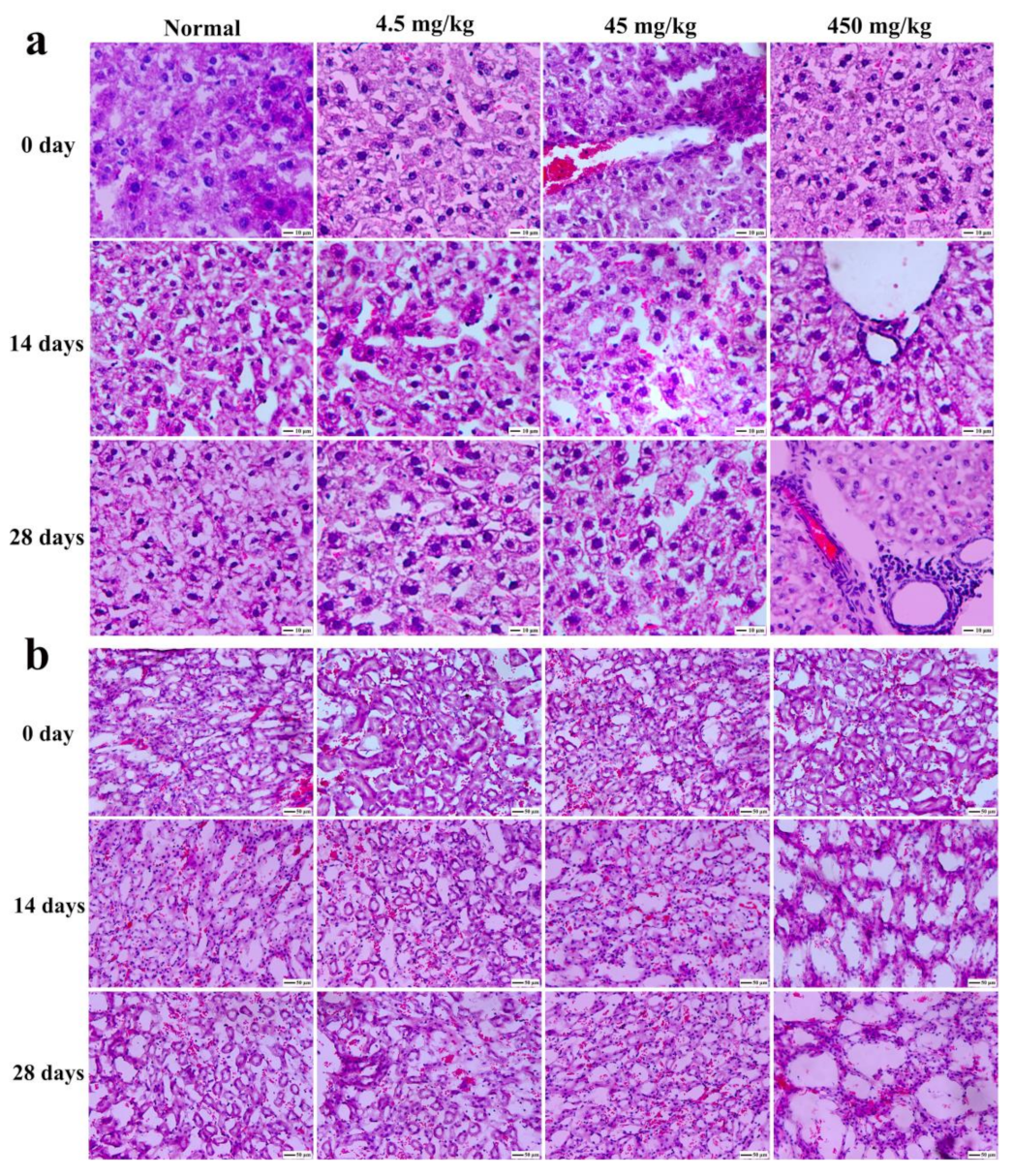
3.9. Histopathological Section Observation of Mice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gujre, N.; Mitra, S.; Soni, A.; Agnihotri, R.; Rangan, L.; Rene, E.R.; Sharma, M.P. Speciation, contamination, ecological and human health risks assessment of heavy metals in soils dumped with municipal solid wastes. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalani, S.; Oliveira, J.; Guidelli, E.J.; Araujo, J.F.D.F.; Wiekhorst, F.; Baffa, O. Synthesis of radioluminescent iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized by anthracene for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 602, 125105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Shapter, J.G.; Qi, W.; Yang, S.; Gao, G. Recent progress in magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 452001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, D.W.; Wang, M.; Chai, X.; Wang, M. The application of resting magnetic resonance imaging in the cognitive judgment of Parkinson. World Neurosurg. 2020, 138, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rost, N.C.V.; Sen, K.; Savliwala, S.; Singh, I.; Liu, S.; Unni, M.; Raniero, L. Magnetic particle imaging performance of liposomes encapsulating iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 504, 166675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.F.; Yang, T.; Yang, J.; Fu, S.; Zhang, S.B. Targeting strategies for superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 102, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Du, Y.M.; Shi, J.; Pong, W.T. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-hollow mesoporous silica Spheres: Fabrication and potential application in drug delivery. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrahman, A.A.A.; Mansour, F.R. Targeted magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation, functionalization and biomedical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Tec. 2019, 52, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Z.; Wu, J.L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, R.L.; Li, Z.H.; Luan, Y.X. Amphiphilic prodrug-decorated graphene oxide as a multi-functional drug delivery system for efficient cancer therapy. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkouli, K.I.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Mosaddegh, E. Synthesis and characterization of aminotetrazole-functionalized magnetic chitosan nanocomposite as a novel nanocarrier for targeted gene delivery. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebrahtu, C.; Abate, S.; Chen, S.M.; Salazar, A.F.S.; Perathoner, S.; Krebs, F.; Palkovits, R. Enhanced catalytic activity of iron-promoted nickel on γ-Al2O3 nanosheets for carbon dioxide methanation. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, S.; Ueda, K.; Ohyama, J.; Satsuma, A. Enhanced three way catalytic activity of NiFe2O4 by physically mixed metal oxides. Cataly. Today 2018, 303, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taebi, S.; Keyhanfar, M.; Noorbakhsh, A. A novel method for sensitive, low-cost and portable detection of hepatitis B surface antigen using a personal glucose meter. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 458, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, W.M.O.S.D.; Caetano, B.L.; Annunzio, S.R.D.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Ménager, C.; Fontana, C.R.; Santilli, C.V. Conjugation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and curcumin photosensitizer to assist in photodynamic therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 196, 111297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Gao, Y. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for controllable photodynamic cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 144, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, A.; Mihailović, J.; Mirković, M.; Radović, M.; Milanović, Z.; Ognjanović, M.; Janković, D.; Antić, B.; Mijović, M.; Vranješ-Đurić, S.; et al. Aminosilanized flower-structured superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coupled to 131I-labeled CC49 antibody for combined radionuclide and hyperthermia therapy of cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlberger, M.; Janko, C.; Unterweger, H.; Band, J.; Schreiber, E.; Lehmann, C.; Dudziak, D.; Lee, G.; Alexiou, C.; Tietze, R. Non-magnetic chromatographic separation of colloidally metastable superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and suspension cells. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1122–1123, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.G.; González-Martínez, E.; Águila, C.R.D.; González-Martínez, D.A.; Ruiz, G.G.; Artalejo, A.G.; Yee-Madeira, H. Chitosan-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for DNA and rhEGF separation. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 591, 124500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, E.; Dantas, J.; Santos, S.P.T.A.D.; Bicalho, M.D.C.M.; Kiminami, R.H.G.A.; Silva, M.R.D.; Costa, A.C.F.D.M. Effect of the surface treatment on the structural, morphological, magnetic and biological properties of MFe2O4 iron spinels (M=Cu, Ni, Co, Mn and Fe). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.Y.; Paknikar, K.M.; Bodas, D.; Gajbhiye, V. Applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in biomedical nanotechnology. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1221–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suturin, S.; Kaveev, A.; Korovin, A.; Fedorov, V.; Sawada, M.; Sokolov, N. Structural transformations and interfacial iron reduction in heterostructures with epitaxial layers of 3d metals and ferrimagnetic oxides. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2018, 51, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassoued, A.; Lassoued, M.S.; Dkhil, B.; Ammar, S.; Gadri, A. Synthesis, structural, morphological, optical and magnetic characterization of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles by precipitation method: Effect of varying the nature of precursor. Phys. E 2018, 97, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Dho, J. Anisotropic lattice disorder and enhanced magnetic anisotropy in Fe3O4 films on (110) SrTiO3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 468, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Akbari, A. Magnetic nanocarriers: Evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloids Interface 2019, 265, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, Z.; Bakhshi, B.; Javidi, J.; Adrangi, S. Synthesis of Silica-coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Preventing Aggregation Without Using Additives or Seed Pretreatment. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-zeid, Y.; Ismail, N.S.M.; McLean, G.R.; Hamdy, N.M. A molecular docking study repurposes FDA approved iron oxide nanoparticles to treat and control COVID-19 infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 153, 105465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.N.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.H. pH-Sensitive tumor-targeted hyperbranched system based on glycogen nanoparticles for liver cancer therapy. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100521. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, J.B.; Fan, Q.Q.; Zhang, C.L.; Lee, J.; Byun, J.; Xing, L.; Gao, X.D.; Oh, Y.K.; Jiang, H.L. Hyperbranched lipoid-based lipid nanoparticles for bidirectional regulation of collagen accumulation in liver fibrosis. J. Control. Releas. 2020, 321, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Pan, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.L.; Liu, R.J. Immobilization and characterization of cellulase on hydroxy and aldehyde functionalized magnetic Fe2O3/Fe3O4 nanocomposites prepared via a novel rapid combustion process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asuha, S.; Suyala, B.; Siqintana, X.; Zhao, S. Direct synthesis of Fe3O4 nanopowder by thermal decomposition of Fe–urea complex and its properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 2870–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Das, A.; Raha, S.; Barui, A. Size-dependent apoptotic activity of gold nanoparticles on osteosarcoma cells correlated with SERS signal. J. Photoch. Photobio. B 2020, 203, 111778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwoko, K.C.; Raab, A.; Cheyne, L.; Dawson, D.; Krupp, E.; Feldmann, J. Matrix-dependent size modifications of iron oxide nanoparticles (Ferumoxytol) spiked into rat blood cells and plasma: Characterisation with TEM, AF4-UV-MALS-ICP-MS/MS and spICP-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1124, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.W.; Viggeswarapu, M.; Habib, M.M.; Beck, G.R. Bioactive effects of silica nanoparticles on bone cells are size, surface, and composition dependent. Acta Biomater. 2018, 82, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catala, L.; Mallah, T. Nanoparticles of Prussian blue analogs and related coordination polymers: From information storage to biomedical applications. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 32–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Xing, F.J.; Cong, Y.W.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, M.X.; Wu, Z.Q.; Yu, S.L.; Wei, H.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Chen, G. Antimony trichloride induces a loss of cell viability via reactive oxygen species-dependent autophagy in A549 cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B. 2017, 93, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, L.; Okazaki, K.; Arias-Barreiro, C.R.; Heng, L.Y.; Mori, I.C. Application of the cellular oxidation biosensor to Toxicity Identification Evaluations for high-throughput toxicity assessment of river water. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Jafari, S.; Saeidi, J.; Mohtashami, M.; Salehi, I. Synthesis and characterization of polyglycerol coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and cytotoxicity evaluation on normal human cell lines. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 551, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.S.; Seo, K.I. Sanggenol L promotes apoptotic cell death in melanoma skin cancer cells through activation of caspase cascades and apoptosis-inducing factor. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 138, 111221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunilkumar, D.; Drishya, G.; Chandrasekharan, A.; Shaji, S.K.; Nair, B.G. Oxyresveratrol drives caspase-independent apoptosis-like cell death in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through the induction of ROS. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 173, 113724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cai, Z.N.; Mehmood, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, W.J.; Zhang, W.N.; Lu, Y.M.; Chen, Y. Polysaccharide FMP-1 from Morchella esculenta attenuates cellular oxidative damage in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells through PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample A (Å) | Sample B (Å) | Fe3O4 (Å) 1 | γ-Fe2O3 (Å) 2 | hkl | α-Fe2O3(Å) 3 | hkl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.9666 | 2.9627 | 2.9670 | 2.9530 | 220 | - | - |
| 2.5322 | 2.5156 | 2.5320 | 2.5177 | 311 | 2.5190 | 110 |
| 2.1008 | 2.0980 | 2.0993 | 2.0886 | 400 | - | - |
| 1.6159 | 1.6144 | 1.6158 | 1.6073 | 511 | - | - |
| 1.4844 | 1.4844 | 1.4845 | 1.4758 | 440 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Superparamagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040834
Li Y, Wang Z, Liu R. Superparamagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(4):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, You, Zhou Wang, and Ruijiang Liu. 2021. "Superparamagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility" Nanomaterials 11, no. 4: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040834
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, Z., & Liu, R. (2021). Superparamagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility. Nanomaterials, 11(4), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040834






