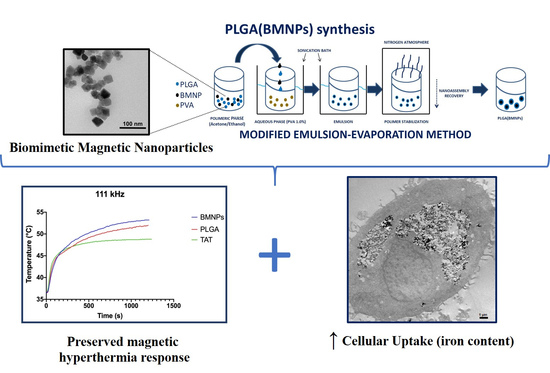
Improving the Cellular Uptake of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles Synthesis
2.3. PLGA Empty Nanoparticles Synthesis
2.4. PLGA Encapsulation of BMNPs and TAT Peptide Functionalization
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering and Zeta Potential
2.6. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.7. Hysteresis Cycle at 5 and 300 K and Magnetic Hyperthermia
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Analysis of Nanoparticle Internalization
2.10. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.11. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of the Nanoformulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles (BMNPs) and the Nanoformulations of PLGA (BMNPs) and TAT-PLGA(BMNPs)
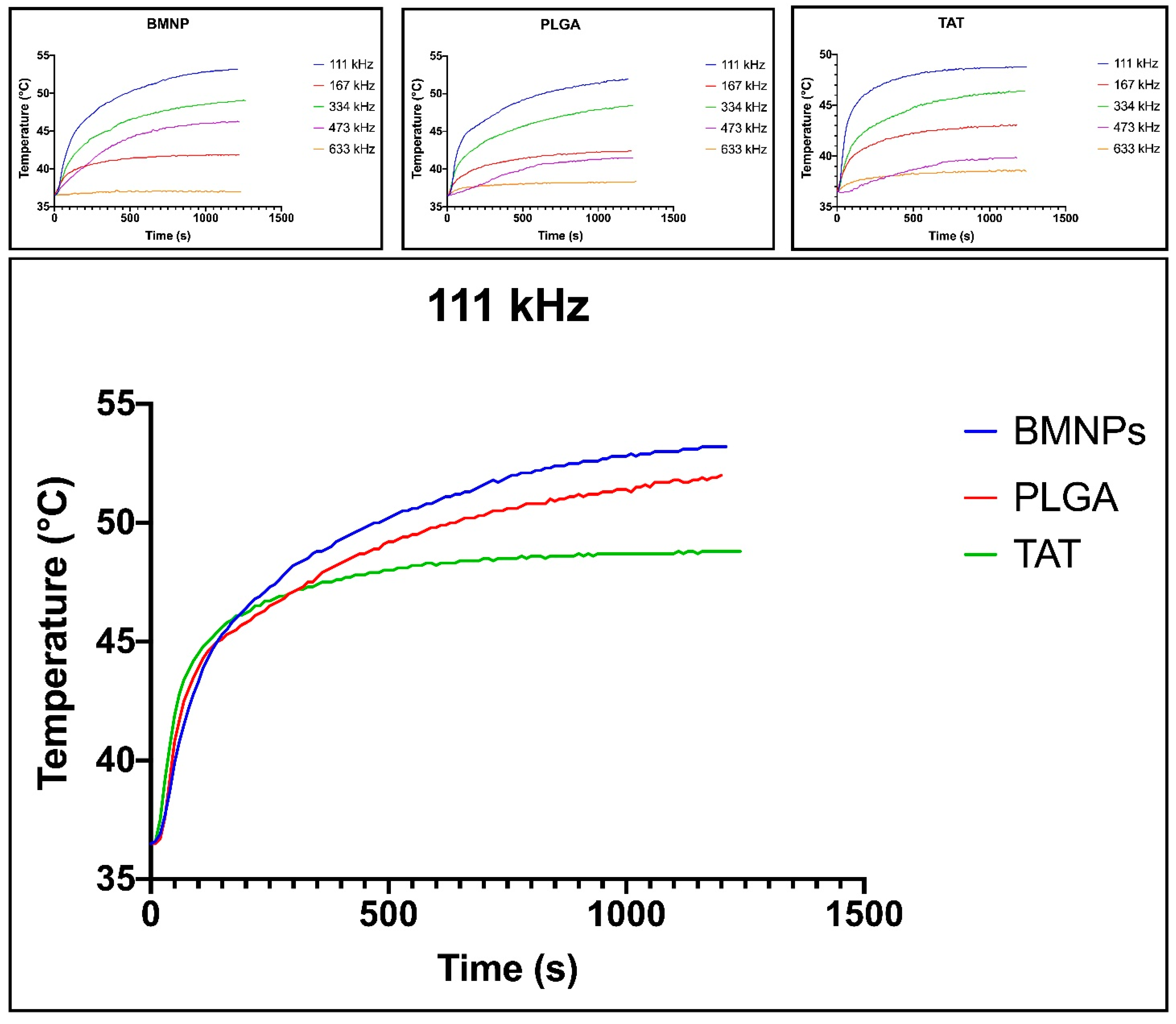
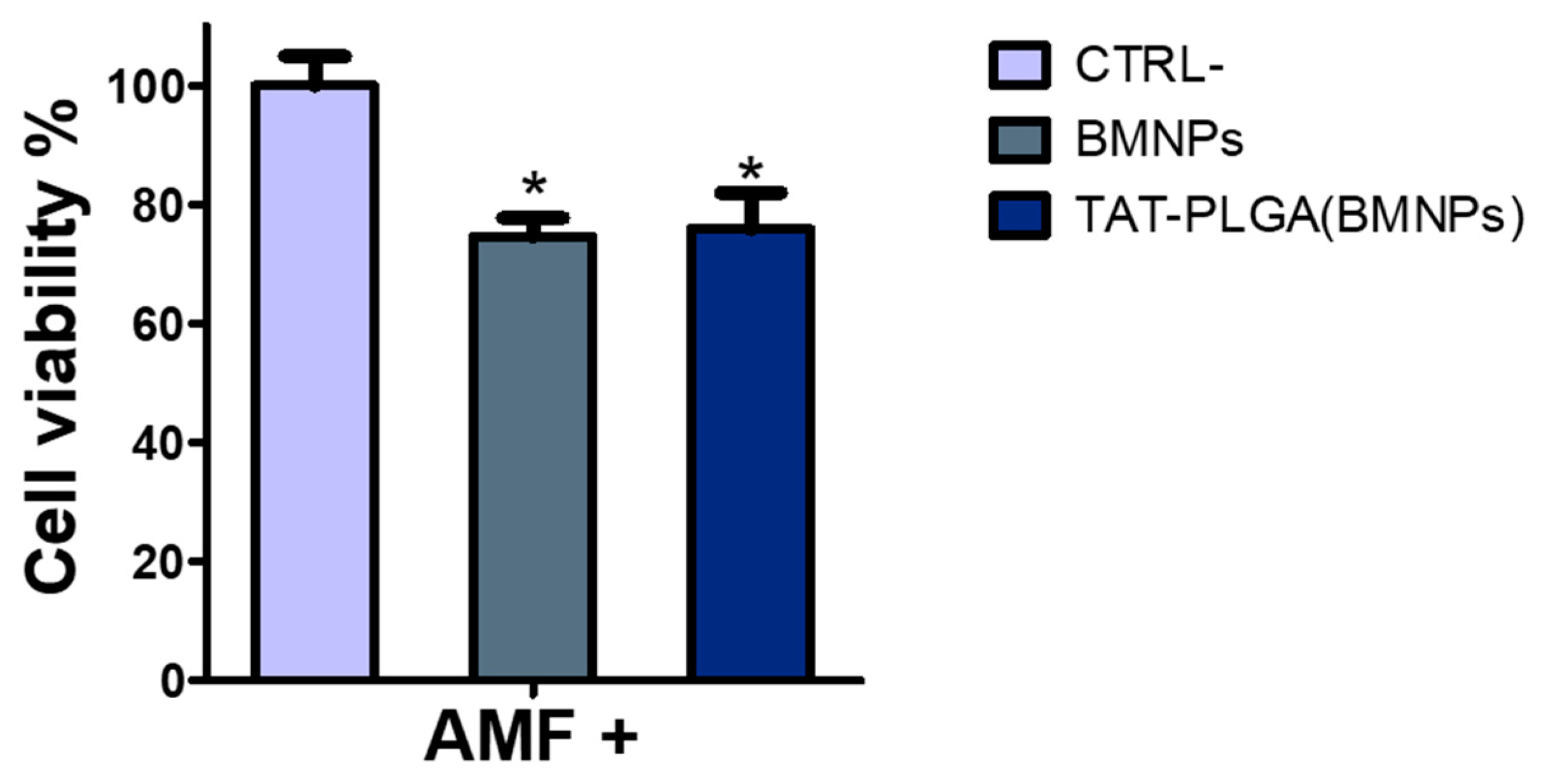
3.2. Magnetic Saturation and Magnetic Hyperthermia of the Nanoformulations
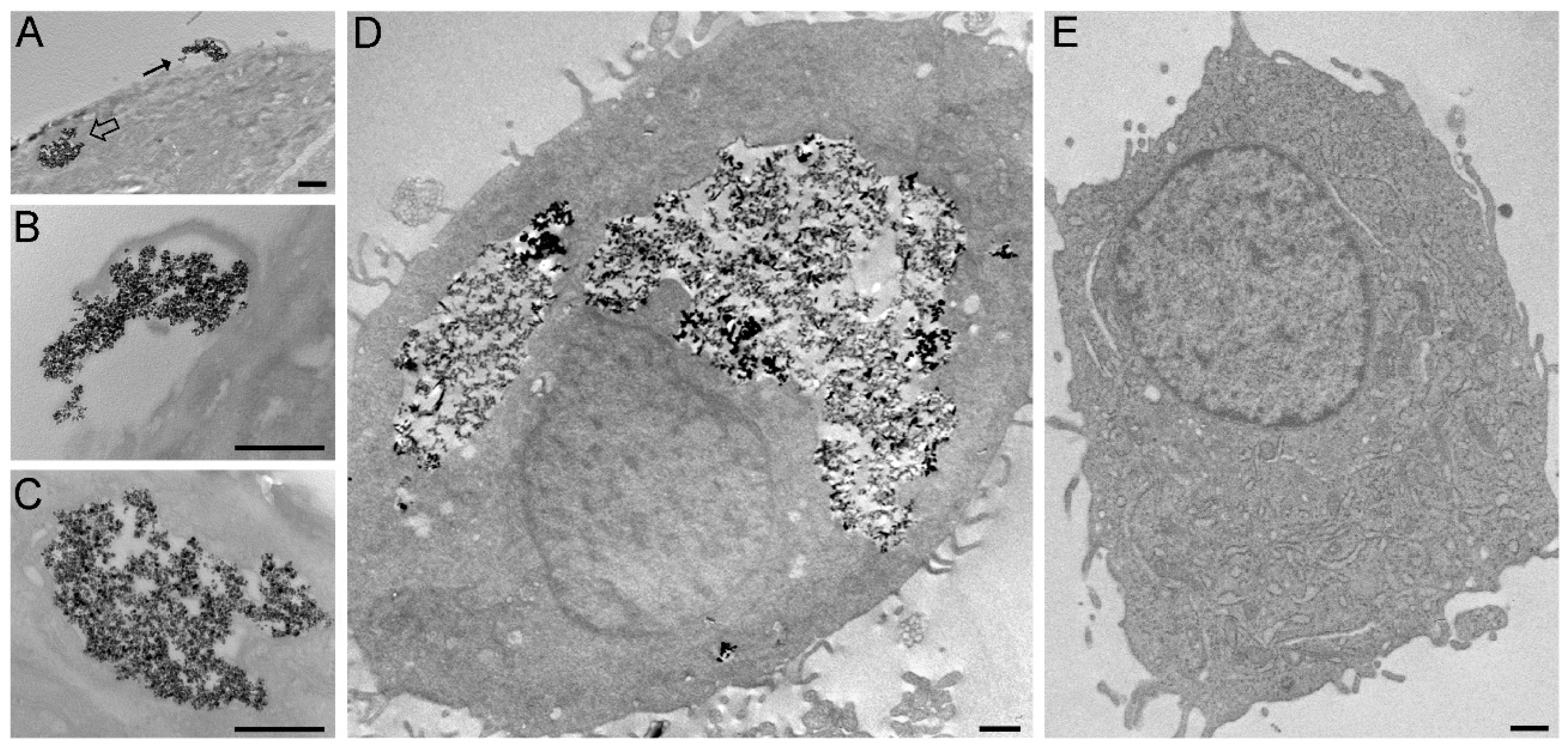
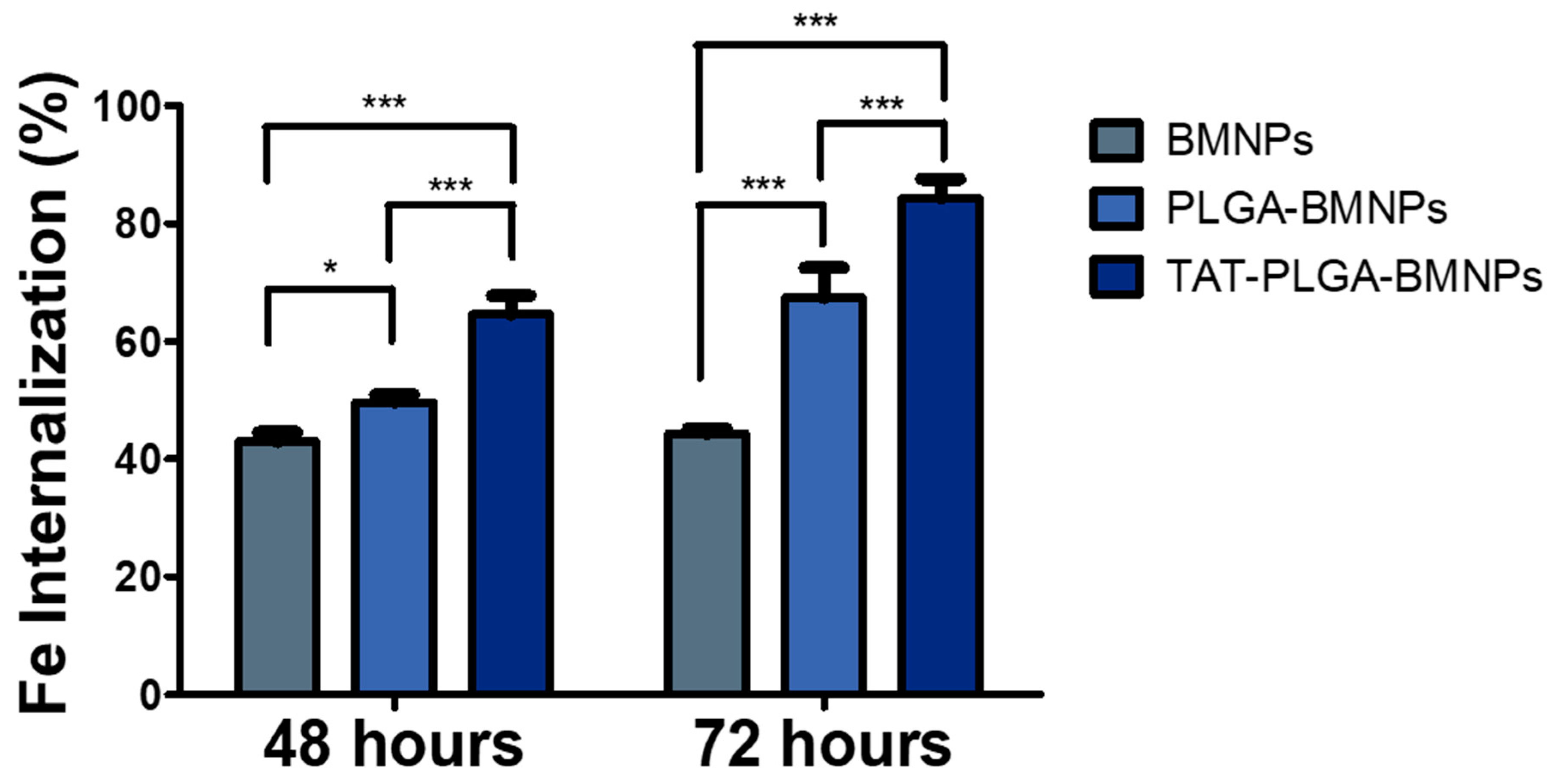
3.3. Enhanced Cellular Uptake of the Nanoformulations versus BMNPs
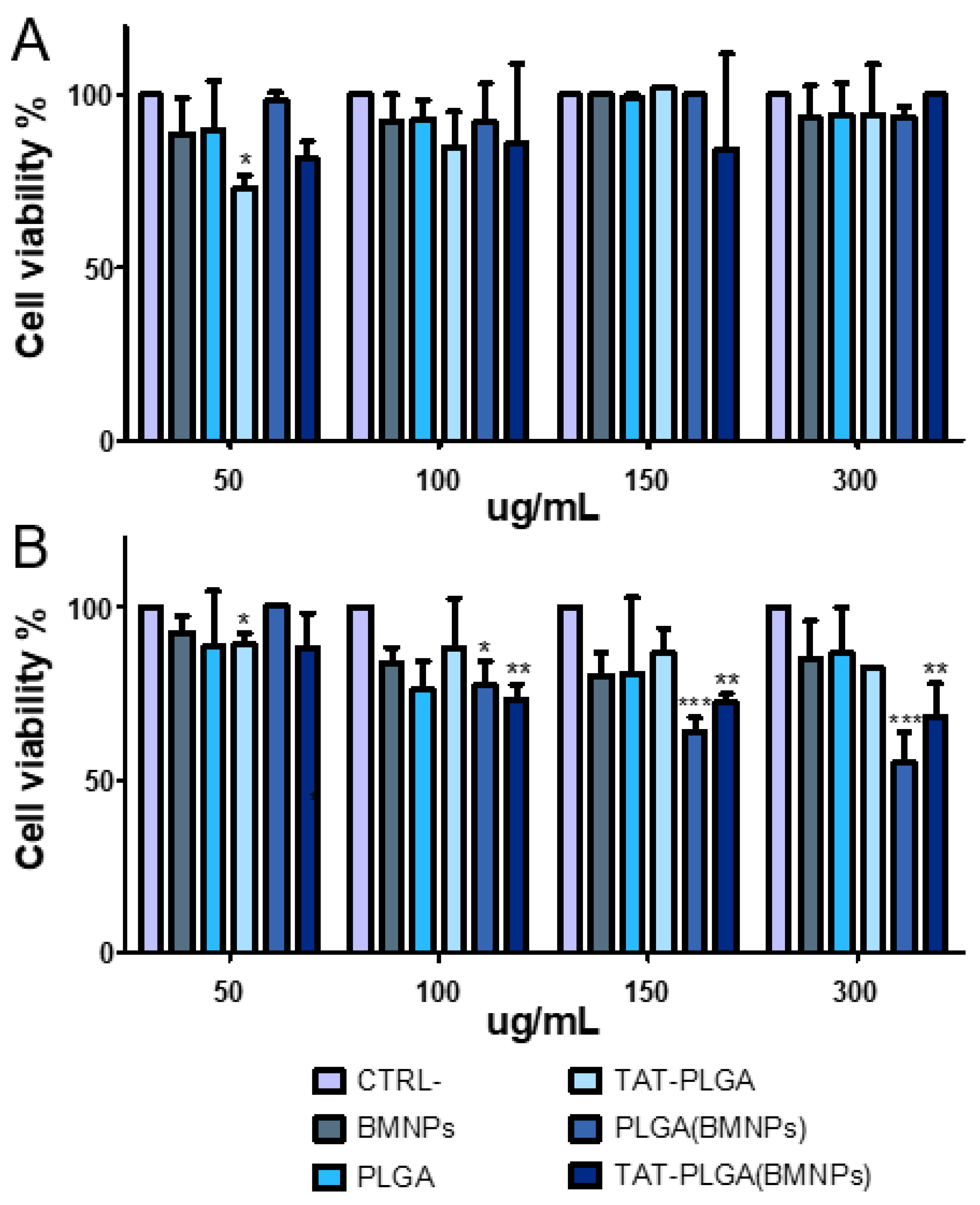
3.4. Cytocompatibility of PLGA(BMNPs)
3.5. Cytotoxicity of PLGA(BMNPs)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Glasgow, M.D.K.; Chougule, M.B. Recent Developments in Active Tumor Targeted Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Combination Chemotherapy in Cancer Treatment and Imaging. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1859–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabalera, Y.; Oltolina, F.; Peigneux, A.; Sola-Leyva, A.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P.; Prat, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Iglesias, G.R. Nanoformulation Design Including MamC-Mediated Biomimetic Nanoparticles Allows the Simultaneous Application of Targeted Drug Delivery and Magnetic Hyperthermia. Polymers 2020, 12, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Pinel, B.; Jabalera, Y.; Ortiz, R.; Cabeza, L.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Biomimetic Magnetoliposomes as Oxaliplatin Nanocarriers: In Vitro Study for Potential Application in Colon Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabalera, Y.; Sola-Leyva, A.; Peigneux, A.; Vurro, F.; Iglesias, G.R.; Vilchez-Garcia, J.; Pérez-Prieto, I.; Aguilar-Troyano, F.J.; López-Cara, L.C.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P.; et al. Biomimetic Magnetic Nanocarriers Drive Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor inside Cancer Cells for Combined Chemo-Hyperthermia Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltolina, F.; Peigneux, A.; Colangelo, D.; Clemente, N.; D’Urso, A.; Valente, G.; Iglesias, G.R.; Jiménez-Lopez, C.; Prat, M. Biomimetic Magnetite Nanoparticles as Targeted Drug Nanocarriers and Mediators of Hyperthermia in an Experimental Cancer Model. Cancers 2020, 12, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Drug Carriers: Preparation, Conjugation and Delivery. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 929–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozorov, T.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Mallapragada, S.K.; Prozorov, R. Novel Magnetic Nanomaterials Inspired by Magnetotactic Bacteria: Topical Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2013, 74, 133–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J. Magnetic Micro- and Nano-Particle-Based Targeting for Drug and Gene Delivery. Nanomedicine 2006, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between Particle Size/Domain Structure and Magnetic Properties of Highly Crystalline Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde-Tercedor, C.; Montalbán-López, M.; Perez-Gonzalez, T.; Sanchez-Quesada, M.S.; Prozorov, T.; Pineda-Molina, E.; Fernandez-Vivas, M.A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.B.; Trubitsyn, D.; Bazylinski, D.A.; et al. Size Control of in Vitro Synthesized Magnetite Crystals by the MamC Protein of Magnetococcus Marinus Strain MC-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5109–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigneux, A.; Jabalera, Y.; Vivas, M.A.F.; Casares, S.; Azuaga, A.I.; Jimenez-Lopez, C. Tuning Properties of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles by Combining Magnetosome Associated Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabalera, Y.; Garcia-Pinel, B.; Ortiz, R.; Iglesias, G.; Cabeza, L.; Prados, J.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Melguizo, C. Oxaliplatin–Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticle Assemblies for Colon Cancer-Targeted Chemotherapy: An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabalera, Y.; Fernández-Vivas, A.; Iglesias, G.R.; Delgado, Á.V.; Jimenez-Lopez, C. Magnetoliposomes of Mixed Biomimetic and Inorganic Magnetic Nanoparticles as Enhanced Hyperthermia Agents. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Rubia, G.; Peigneux, A.; Jabalera, Y.; Puerma, J.; Oltolina, F.; Elert, K.; Colangelo, D.; Gómez Morales, J.; Prat, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C. PH-Dependent Adsorption Release of Doxorubicin on MamC-Biomimetic Magnetite Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13713–13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.G.; Han, S.I.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, H.S. Cellular Responses to Mild Heat Stress. CMLS Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettaieb, A.; Wrzal, K.P.; Averill-Bates, A.D. Hyperthermia: Cancer Treatment and Beyond. In Cancer Treatment—Conventional and Innovative Approaches; Rangel, L., Ed.; InTech Open: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1098-9. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Colombo, M.; Prosperi, D. Recent Advances in Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia for Cancer Therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Foy, S.P.; Jain, T.K.; Labhasetwar, V. PEG-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, M.; Rossotti, B.; Arosio, P.; Ferretti, A.M.; Panigati, M.; Ranucci, E.; Ferruti, P.; Salvati, A.; Maggioni, D. A New Catechol-Functionalized Polyamidoamine as an Effective SPION Stabilizer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Yu, J.-H.; Jang, T.; Kim, B.-K. Enhanced Oxidation Resistance of Iron Nanoparticles via Surface Modification in Chemical Vapor Condensation Process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ladani, R.B.; Zhang, J.; Kinloch, A.J.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Mouritz, A.P.; Ghorbani, K.; Wang, C.H. Epoxy Nanocomposites Containing Magnetite-Carbon Nanofibers Aligned Using a Weak Magnetic Field. Polymer 2015, 68, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.C.; Zhang, J.; Min, K.A.; Lee, K.; Byun, Y.; David, A.E.; He, H.; Yang, V.C. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: Achievements and Challenges in Application for Cancer Treatment: Cell-Penetrating Peptides. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2014, 102, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshankhah, H.; Jafari, S. Cell Penetrating Peptides: A Concise Review with Emphasis on Biomedical Applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosafer, J.; Teymouri, M. Comparative Study of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide/Doxorubicin Co-Loaded Poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Nanospheres Prepared by Different Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Methods. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.; Bovi, M.; Romeo, A.; Guzzo, F.; Chiamulera, C.; Perduca, M. Ketamine Nano-Delivery Based on Poly-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) Nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubin, A.; Destefanis, L.; Bovi, M.; Perozeni, F.; Bargigia, I.; de la Cruz Valbuena, G.; D’Andrea, C.; Romeo, A.; Ballottari, M.; Perduca, M. Encapsulation of Photosystem I in Organic Microparticles Increases Its Photochemical Activity and Stability for Ex Vivo Photocatalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 10435–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery Systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-Based Nanoparticles: An Overview of Biomedical Applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.-M.; Wang, X.; Marin-Muller, C.; Wang, H.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Current Advances in Research and Clinical Applications of PLGA-Based Nanotechnology. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, D.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic) Acid-Controlled-Release Systems: Experimental and Modeling Insights. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2013, 30, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Pourcelle, V.; Marchand-Brynaert, J.; Jérôme, C.; Feron, O.; Préat, V. Targeting of Tumor Endothelium by RGD-Grafted PLGA-Nanoparticles. Meth. Enzymol. 2012, 508, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portioli, C.; Bovi, M.; Benati, D.; Donini, M.; Perduca, M.; Romeo, A.; Dusi, S.; Monaco, H.L.; Bentivoglio, M. Novel Functionalization Strategies of Polymeric Nanoparticles as Carriers for Brain Medications: Peptidic Moieties Enable BBB Traversal of the NPs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2017, 105, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wu, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Xin, H. Enhanced Anti-Tumor of Pep-1 Modified Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide/PTX Loaded Polymer Nanoparticles. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantelmo, A.R.; Cammarota, R.; Noonan, D.M.; Focaccetti, C.; Comoglio, P.M.; Prat, M.; Albini, A. Cell Delivery of Met Docking Site Peptides Inhibit Angiogenesis and Vascular Tumor Growth. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Choi, Y.-S.; Suh, J.-S.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Yang, V.C.; Lee, S.-J.; Chung, C.-P.; Park, Y.-J. Cell-Penetrating Chitosan/Doxorubicin/TAT Conjugates for Efficient Cancer Therapy: Cell-Penetrating Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Yang, H.; Stanley, J.T.; Holloway, P.H.; Moudgil, B.M.; Walter, G.; Mericle, R.A. Rapid and Effective Labeling of Brain Tissue Using TAT-Conjugated CdS∶Mn/ZnS Quantum Dots. Chem. Commun. 2005, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Guo, K.; Lu, J.; He, B.; Moochhala, S.; Kan, L. Polymeric Micelles Anchored with TAT for Delivery of Antibiotics across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Biopolymers 2008, 90, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Tan, J.P.K.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, W.; Wei, Z.; Sheng, J.; Yang, Y.-Y.; et al. The Efficacy of Self-Assembled Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide Nanoparticles against Cryptococcus Neoformans for the Treatment of Meningitis. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2874–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, S.R.; Hruska, K.A.; Dowdy, S.F. Protein Transduction: Unrestricted Delivery into All Cells? Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, I.M.; Wadia, J.S.; Dowdy, S.F. Cationic TAT Peptide Transduction Domain Enters Cells by Macropinocytosis. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, H.; Lebleu, B.; Vives, E. Tat Peptide-Mediated Cellular Delivery: Back to Basics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadia, J.S.; Stan, R.V.; Dowdy, S.F. Transducible TAT-HA Fusogenic Peptide Enhances Escape of TAT-Fusion Proteins after Lipid Raft Macropinocytosis. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadia, J.; Dowdy, S. Transmembrane Delivery of Protein and Peptide Drugs by TAT-Mediated Transduction in the Treatment of Cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.-L.; Lai, C.-H.; Chu, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Tseng, Y.-C.; Chiu, S.-C.; Lin, Y.-H. Nanotheranostics With the Combination of Improved Targeting, Therapeutic Effects, and Molecular Imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 570490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, J.; Castanares, M.A.; Collins, D.S.; Yeo, Y. Magnetophoretic Delivery of a Tumor-Priming Agent for Chemotherapy of Metastatic Murine Breast Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, F.; Wu, J.; Fu, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Brain-Targeted Delivery of Trans-Activating Transcriptor-Conjugated Magnetic PLGA/Lipid Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gonzalez, T.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Neal, A.L.; Rull-Perez, F.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A.; Fernandez-Vivas, A.; Iañez-Pareja, E. Magnetite Biomineralization Induced by Shewanella Oneidensis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglio, S.C.; De Rosa, C.; Piccinelli, F.; Romeo, A.; Perduca, M. Complexes of Rare Earth Ions Embedded in Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) Nanoparticles: Characterization and Spectroscopic Study. Opt. Mater. 2019, 94, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predescu, A.M.; Matei, E.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Pantilimon, C.; Drăgan, C.; Vidu, R.; Predescu, C.; Kuncser, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Dextran-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotin, G.; Blanco-Andujar, C.; Nguyen, D.-V.; Affolter, C.; Boutry, S.; Boos, A.; Ronot, P.; Uring-Lambert, B.; Choquet, P.; Zorn, P.E.; et al. Dendron Based Antifouling, MRI and Magnetic Hyperthermia Properties of Different Shaped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 374002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Malatesta, M. Embedding Cell Monolayers to Investigate Nanoparticle-Plasmalemma Interactions at Transmission Electron Microscopy. Eur. J. Histochem. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Gong, E.-Y.; Romanelli, M.G.; Lee, K. Suppression of Estrogen Receptor-Alpha Transactivation by Thyroid Transcription Factor-2 in Breast Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gneveckow, U.; Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Brüß, V.; Waldöfner, N.; Ricke, J.; Feussner, A.; Hildebrandt, B.; Rau, B.; Wust, P. Description and Characterization of the Novel Hyperthermia- and Thermoablation-System MFH®300F for Clinical Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vurro, F.; Jabalera, Y.; Mannucci, S.; Glorani, G.; Sola-Leyva, A.; Gerosa, M.; Romeo, A.; Romanelli, M.G.; Malatesta, M.; Calderan, L.; et al. Improving the Cellular Uptake of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030766
Vurro F, Jabalera Y, Mannucci S, Glorani G, Sola-Leyva A, Gerosa M, Romeo A, Romanelli MG, Malatesta M, Calderan L, et al. Improving the Cellular Uptake of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030766
Chicago/Turabian StyleVurro, Federica, Ylenia Jabalera, Silvia Mannucci, Giulia Glorani, Alberto Sola-Leyva, Marco Gerosa, Alessandro Romeo, Maria Grazia Romanelli, Manuela Malatesta, Laura Calderan, and et al. 2021. "Improving the Cellular Uptake of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030766
APA StyleVurro, F., Jabalera, Y., Mannucci, S., Glorani, G., Sola-Leyva, A., Gerosa, M., Romeo, A., Romanelli, M. G., Malatesta, M., Calderan, L., Iglesias, G. R., Carrasco-Jiménez, M. P., Jimenez-Lopez, C., & Perduca, M. (2021). Improving the Cellular Uptake of Biomimetic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 766. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030766