Room Temperature Magnetic Memory Effect in Nanodiamond/γ-Fe2O3 Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Structural Properties
3.2. Magnetic Properties
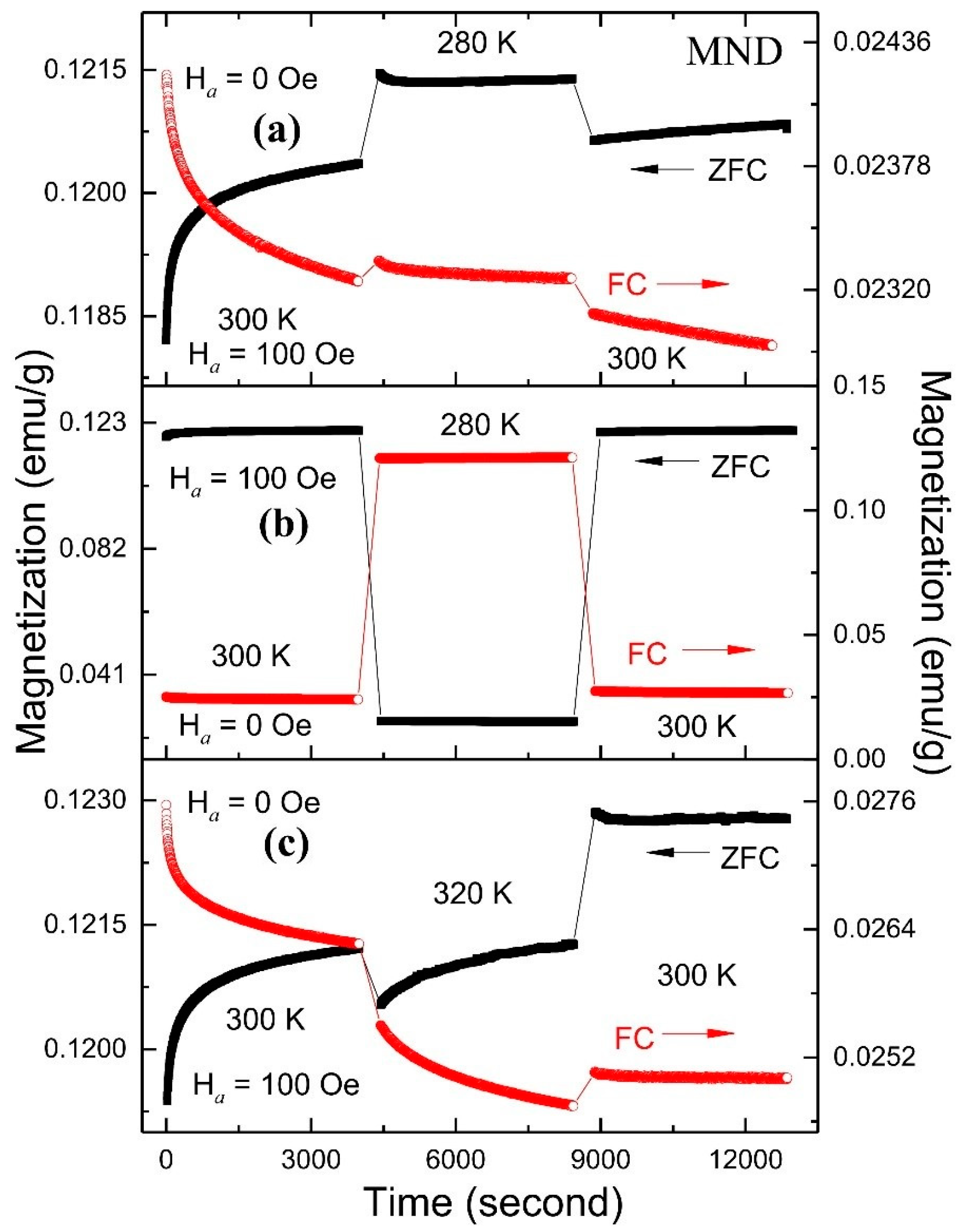
3.3. Magnetic Memory Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; Salamon, M.B.; Garnier, K.; Averback, R.S. Memory Effects in an Interacting Magnetic Nanoparticle System. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Jönsson, P.E.; Takayama, H.; Mamiya, H. Aging and memory effects in superparamagnets and superspin glasses. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, M.; Dattagupta, S. Memory in nanomagnetic systems: Superparamagnetism versus spin-glass behavior. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, H.; Kelley, L.P.; Iglesias, Ò.; Alonso, J.; Phan, M.H.; Sun, C.J.; Saboungi, M.L.; Srikanth, H. Spin-glass-like freezing of inner and outer surface layers in hollow γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Sabyasachi, S.; Bhaumik, A.; Ray, R. Magnetic Memory Effects in Fe/γ-Fe2O3 Nanostructures. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 50, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, G.M.; Senaratne, U.; Tackett, R.J.; Buc, E.C.; Naik, R.; Vaishnava, P.P.; Naik, V.M.; Wenger, L.E. Memory effects and magnetic interactions in a γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticle system. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10J507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Xu, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Xia, Z. Magnetic memory effect at room temperature in exchange coupled NiFe2O4-NiO nanogranular system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, S.; Chowdhury, R.; Bandyopadhyay, B. Strong memory effect at room temperature in nanostructured granular alloy Co0.3Cu0. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95695–95702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gao, Y.; Malik, A.; Liu, Y.; Gong, G.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Yuan, S. Field pulse induced magnetic memory effect at room temperature in exchange coupled NiFe2O4/NiO nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.C.; Li, T.Y.; Kumar, B.V.; Reddy, P.M.; Peng, J.C.; Wu, C.M.; Wu, S.Y. Room Temperature Magnetic Memory Effect in Cluster-Glassy Fe-doped NiO Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevedentseva, E.; Karmenyan, A.; Lin, Y.C.; Song, C.Y.; Lin, Z.R.; Ahmed, A.I.; Chang, C.C.; Norina, S.; Bessalova, V.; Perov, N.; et al. Multifunctional biomedical applications of magnetic nanodiamond. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 1404. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhani, P.; Singh, R.N. Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized Magnetic Fe3O4 and Nanodiamond Particles as a Platform for Amoxicillin Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 3957–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasraghi, S.S.; Shojaei, A.; Sundararaj, U. Highly biocompatible multifunctional hybrid nanoparticles based on Fe3O4 decorated nanodiamond with superior superparamagnetic behaviors and photoluminescent properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbiero, M.; Castelletto, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Charnley, M.; Russell, S.; Gu, M. Nanoscale magnetic imaging enabled by nitrogen vacancy centres in nanodiamonds labelled by iron–oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 8847–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, D.E.J.; Boele, T.; Rej, E.; McCamey, D.R.; King, N.J.C.; Gaebel, T.; Reilly, D.J. Phase-Encoded Hyperpolarized Nanodiamond for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Samuely, T.; Iwahara, N.; Kačmarčík, J.; Wang, C.; May, P.W.; Jochum, J.K.; Onufriienko, O.; Szabó, P.; Zhou, S.; et al. Yu-Shiba-Rusinov bands in ferromagnetic superconducting diamond. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrich, P.; Casas, C.F.D.L.; Liu, X.; Bretscher, H.L.; Berman, J.R.; Heremans, F.J.; Nealey, P.F.; Awschalom, D.D. Long-range spin wave mediated control of defect qubits in nanodiamonds. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2017, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPMS 3. User’s Manual, 1500-100, Rev. F1; MPMS 3: Atwood, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Osipov, V.Y.; Shakhov, F.M.; Bogdanov, K.V.; Takai, K.; Hayashi, T.; Treussart, F.; Baldycheva, A.; Hogan, B.T.; Jentgens, C. High-Quality Green-Emitting Nanodiamonds Fabricated by HPHT Sintering of Polycrystalline Shockwave Diamonds. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toby, B.H.; Von Dreele, R.B. GSAS-II: The genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krezhov, K.; Nedkov, I.; Somogyváari, Z.; Svab, E.; Mészáros, G.; Sajó, I.; Bouree, F. Vacancy ordering in nanosized maghemite from neutron and X-ray powder diffraction. Appl. Phys. A 2002, 74, s1077–s1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevedentseva, E.; Peer, D.; Uvarov, V.; Zousman, B.; Levinson, O. Nanodiamonds of Laser Synthesis for Biomedical Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, K.; Krenn, H.; Szabó, D.V. Memory effect versus exchange bias for maghemite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 393, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xiao, X.H.; Zhang, S.F.; Peng, T.C.; Zhou, J.; Ren, F.; Jiang, C.Z. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) Short-Nanotubes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardis, M.; Douvalis, A.P.; Tsitrouli, D.; Rabias, I.; Stamopoulos, D.; Kehagias, T.; Karakosta, E.; Diamantopoulos, G.; Bakas, T.; Papavassiliou, G.; et al. Structural, static and dynamic magnetic properties of dextran coated γ-Fe2O3nanoparticles studied by57Fe NMR, Mössbauer, TEM and magnetization measurements. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24, 6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Quaresma, P.; Tavares, P.B.; Pereira, E.; Araújo, J.P.; Freire, C. Superparamagnetic γ-Fe2O3@SiO2 nanoparticles: A novel support for the immobilization of [VO (acac) 2]. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 2842–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, P.; Baral, P.R.; Nath, R. Cluster spin-glass behavior and memory effect in Cr0.5Fe0.5Ga. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Mandal, P.; Prabhakaran, D. Memory effects and magnetic relaxation in single-crystallineLa0.9Sr0.1CoO. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, D.; Karmakar, A.; Bhunia, M.K.; Bhaumik, A.; Majumdar, S.; Giri, S. Memory effects in superparamagnetic and nanocrystalline Fe50Ni50 alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.S.; Singh, V.; Somesh, K.; Mukharjee, P.K.; Jain, A.; Yusuf, S.M.; Nath, R. Unconventional superparamagnetic behavior in the modified cubic spinel compound LiNi0.5Mn1.5O. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, M.; Otero, G.J.; Rivas, J.; Bunde, A. Slow relaxation in ferromagnetic nanoparticles: Indication of spin-glass behavior. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, N.A.; Serebryakova, O.N. Equilibrium properties of assembly of interacting superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G. Infinite Number of Order Parameters for Spin-Glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1979, 43, 1754–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
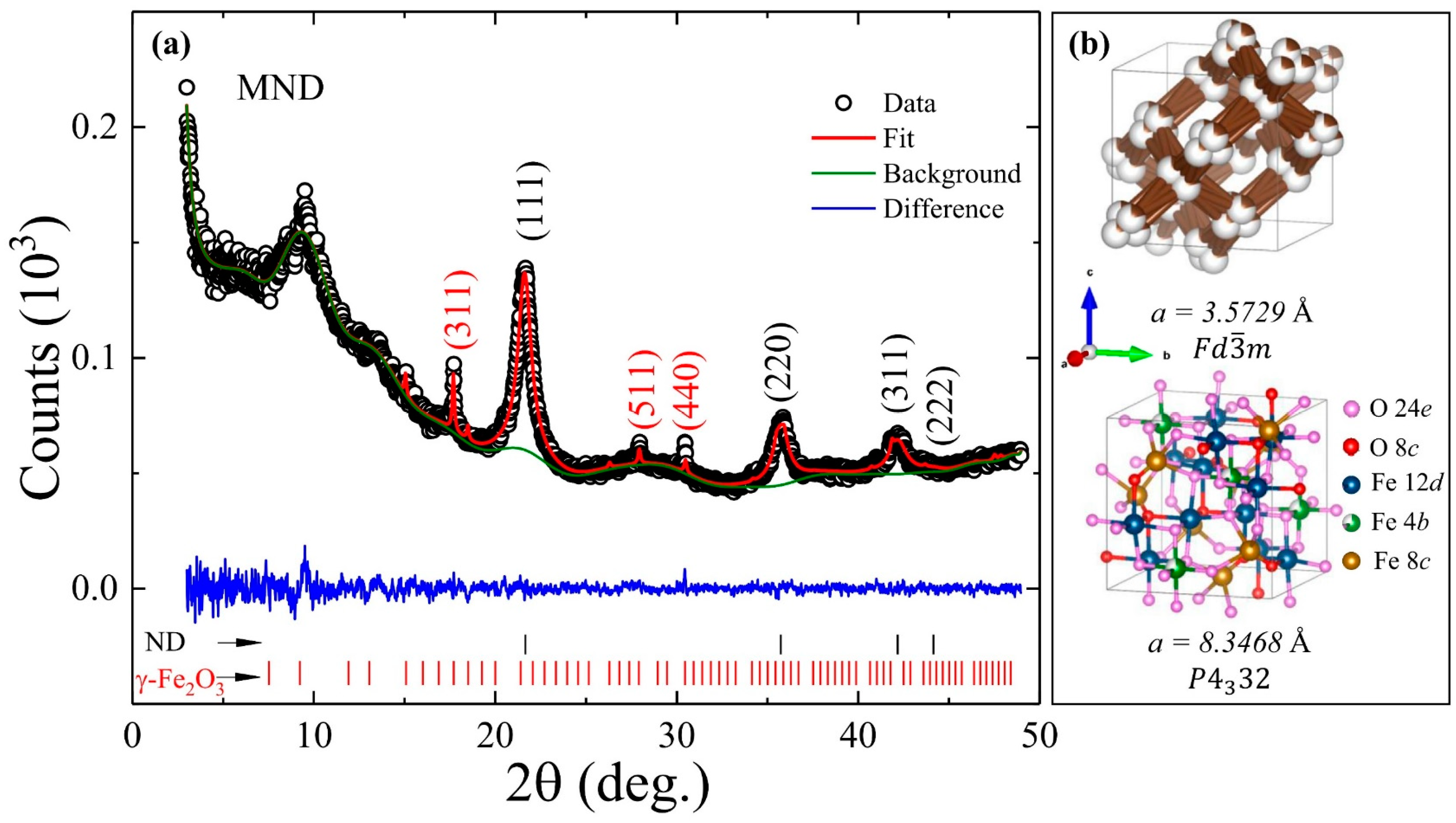
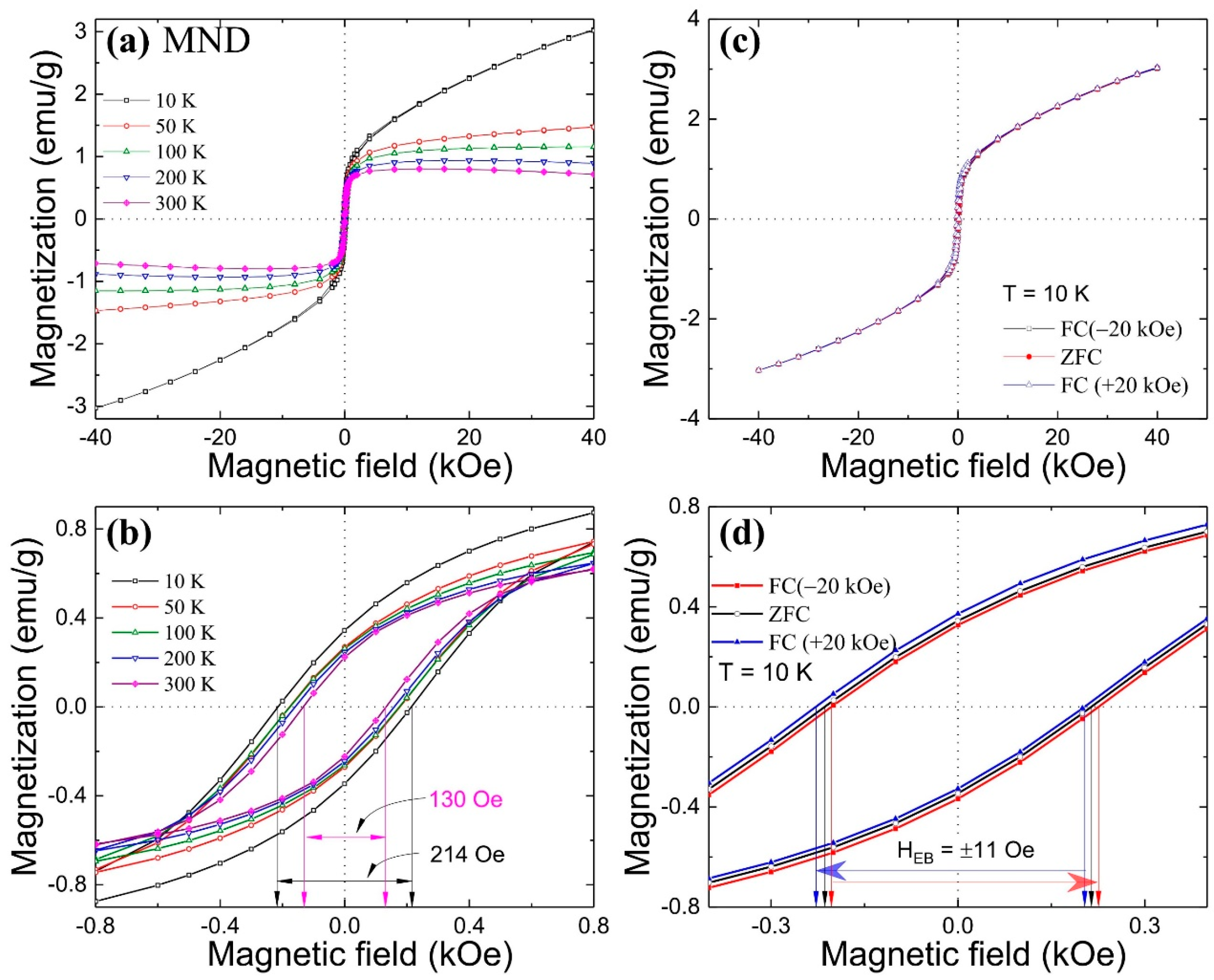
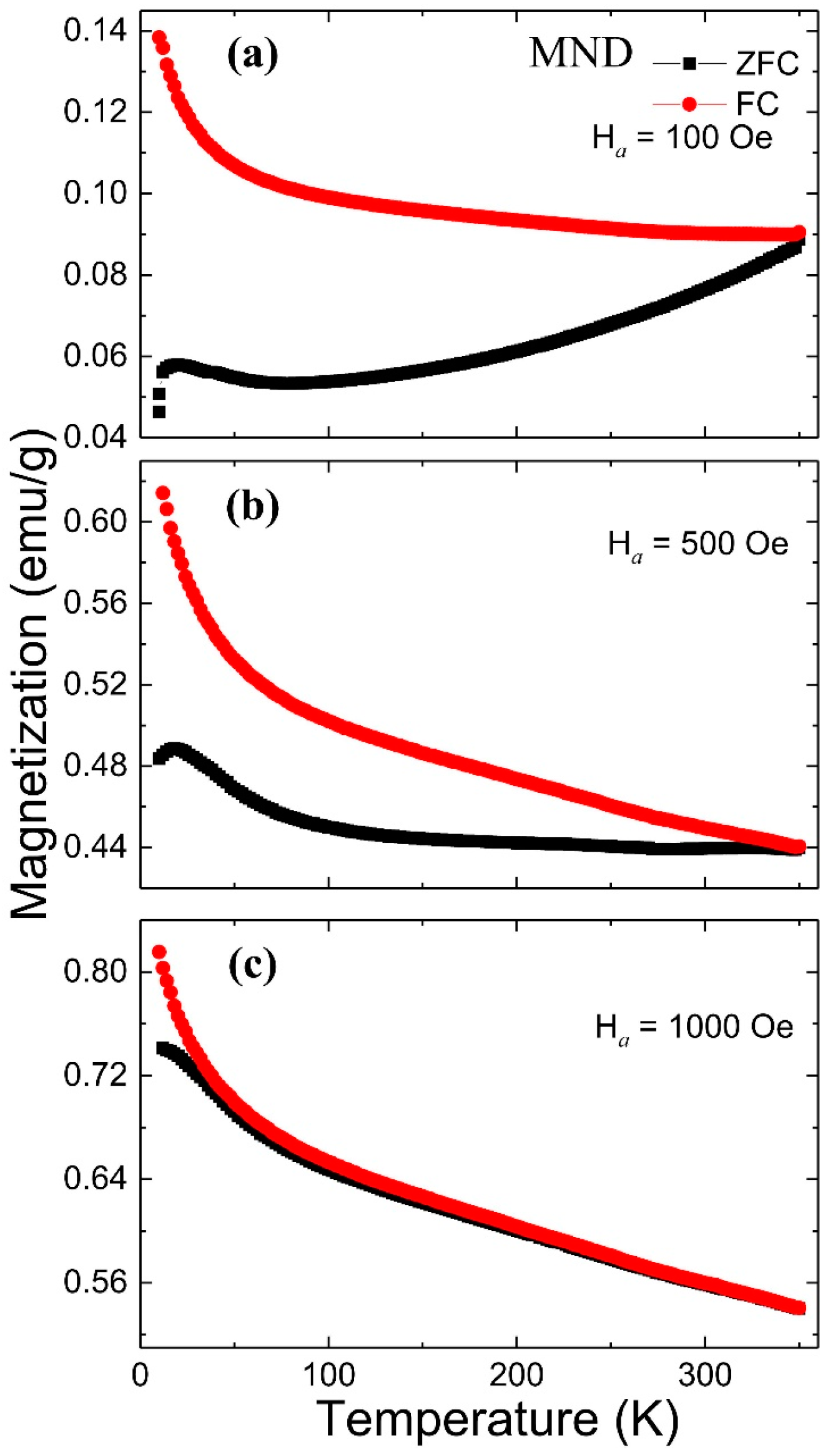
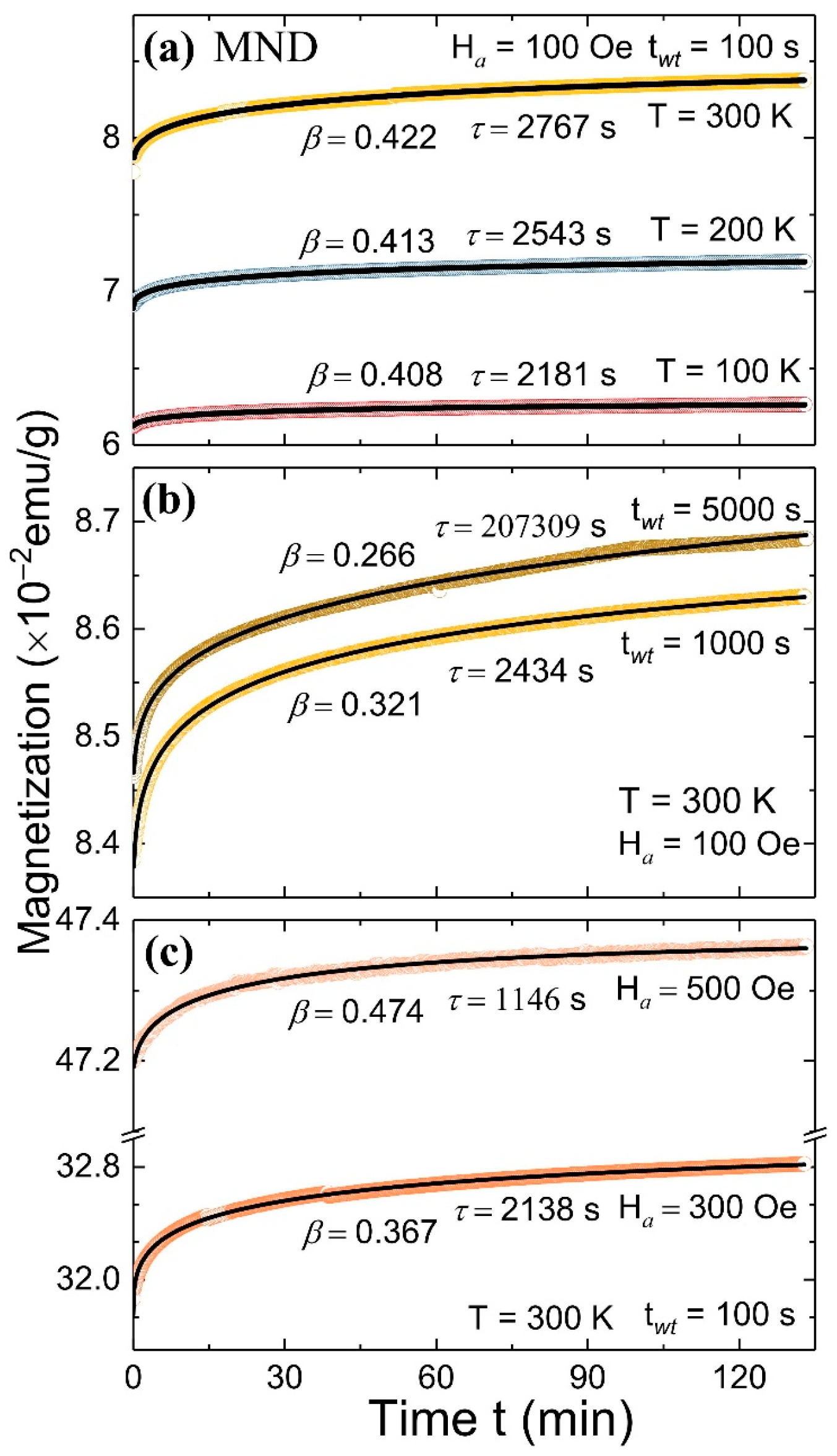

| Parameter | MND | ND-Wash | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase | ND | γ-Fe2O3 | ND | |
| a = b = c (Å) | 3.5729(12) | 8.3468(14) | 3.5579(6) | |
| V (Å3) | 45.612(46) | 581.5(3) | 45.037(22) | |
| C | (x = y = z) (Å) | 0.8301(88) | - | 0.8203(8) |
| Occupancy | 0.214(4) | - | 0.219(1) | |
| Fe 4b | (x = y = z) (Å) | - | 0.625 | - |
| Occupancy | - | 0.717(203) | - | |
| ρ (g/cm3) | 2.9979 | 5.1044 | 3.1021 | |
| Weight fraction (%) | 98.89 | 1.11 | 100 | |
| Grain size (nm) | 4.74 | 43 | 4.90 | |
| wR (%) | 2.77 | 1.69 | ||
| GOF | 0.25 | 0.35 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandhi, A.C.; Selvam, R.; Cheng, C.-L.; Wu, S.Y. Room Temperature Magnetic Memory Effect in Nanodiamond/γ-Fe2O3 Composites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030648
Gandhi AC, Selvam R, Cheng C-L, Wu SY. Room Temperature Magnetic Memory Effect in Nanodiamond/γ-Fe2O3 Composites. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(3):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030648
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandhi, Ashish Chhaganlal, Rajakar Selvam, Chia-Liang Cheng, and Sheng Yun Wu. 2021. "Room Temperature Magnetic Memory Effect in Nanodiamond/γ-Fe2O3 Composites" Nanomaterials 11, no. 3: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030648
APA StyleGandhi, A. C., Selvam, R., Cheng, C.-L., & Wu, S. Y. (2021). Room Temperature Magnetic Memory Effect in Nanodiamond/γ-Fe2O3 Composites. Nanomaterials, 11(3), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11030648









