Release of Nanoparticles in the Environment and Catalytic Converters Ageing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Mineralogical Composition
2.2. Physical Wear and Particle Size
2.3. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
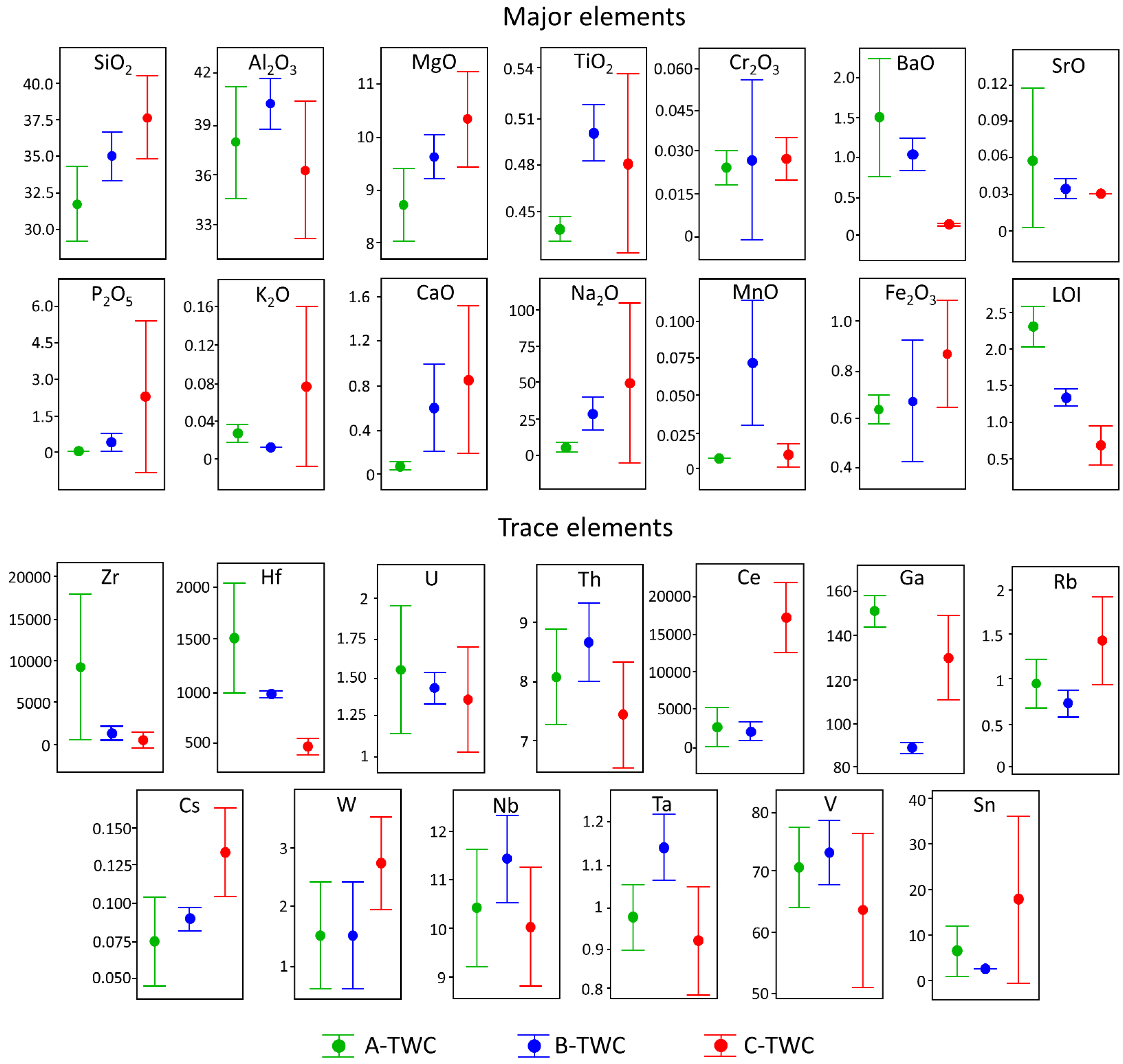
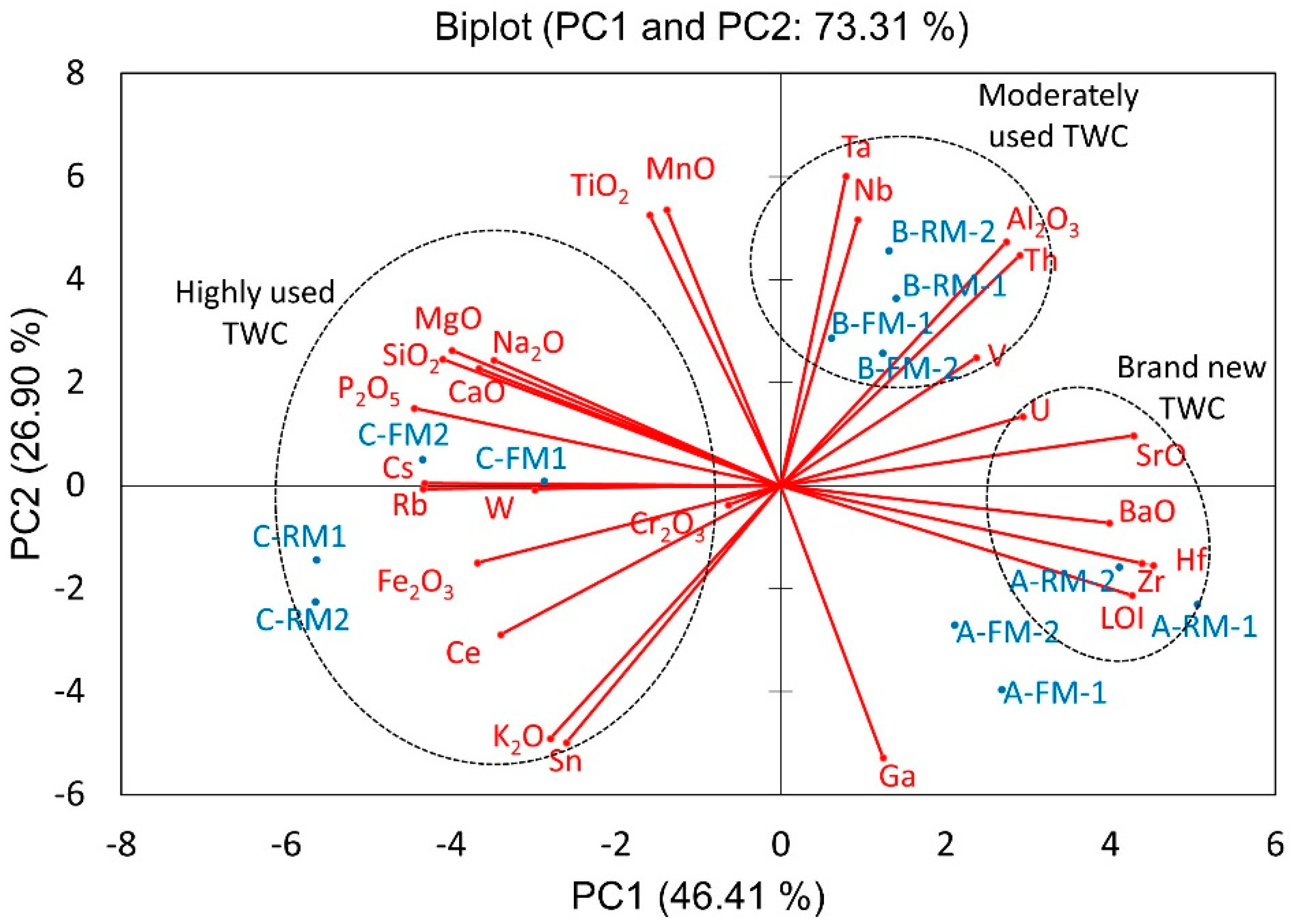
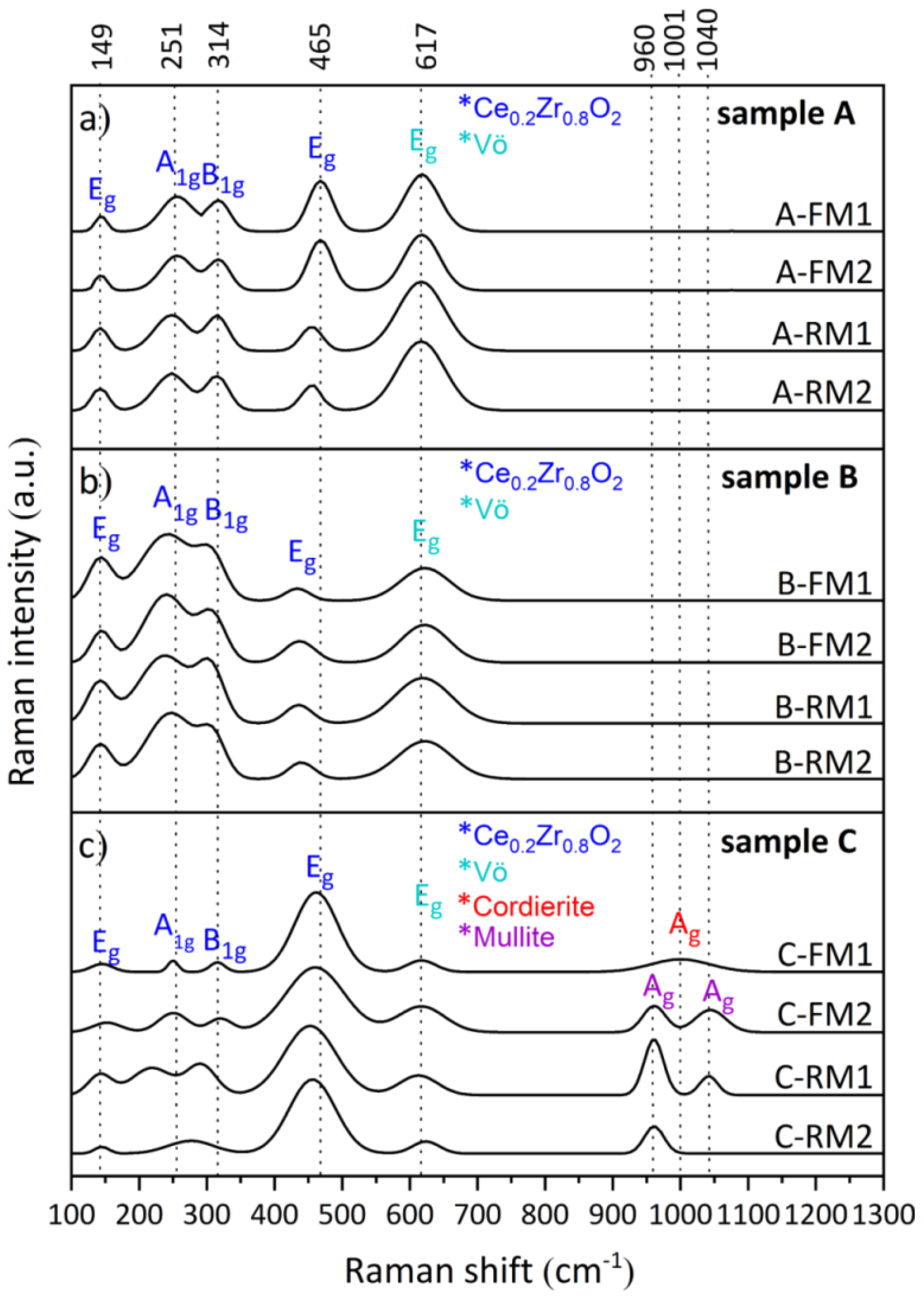
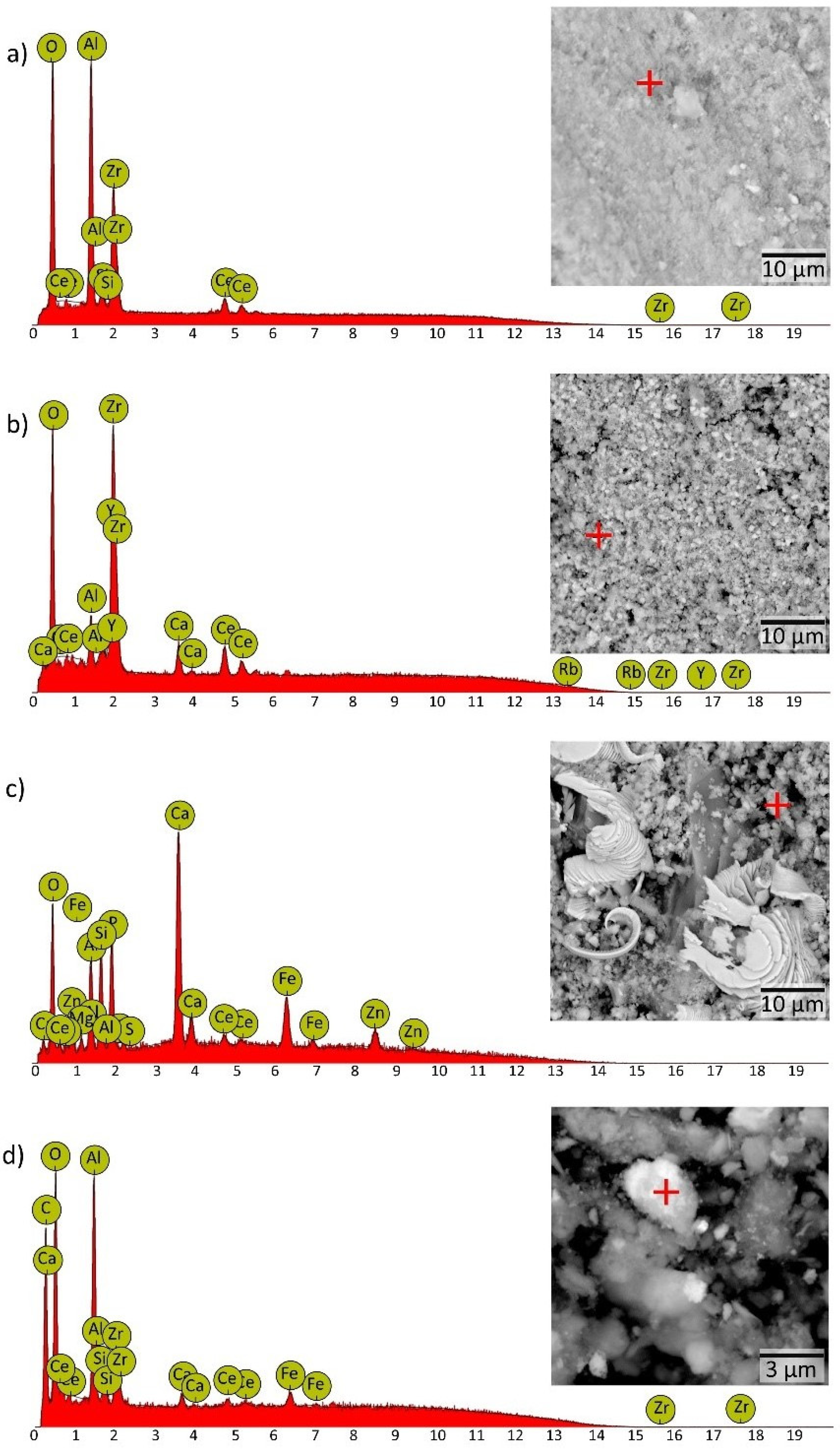
3.1. Chemical and Mineralogical Composition
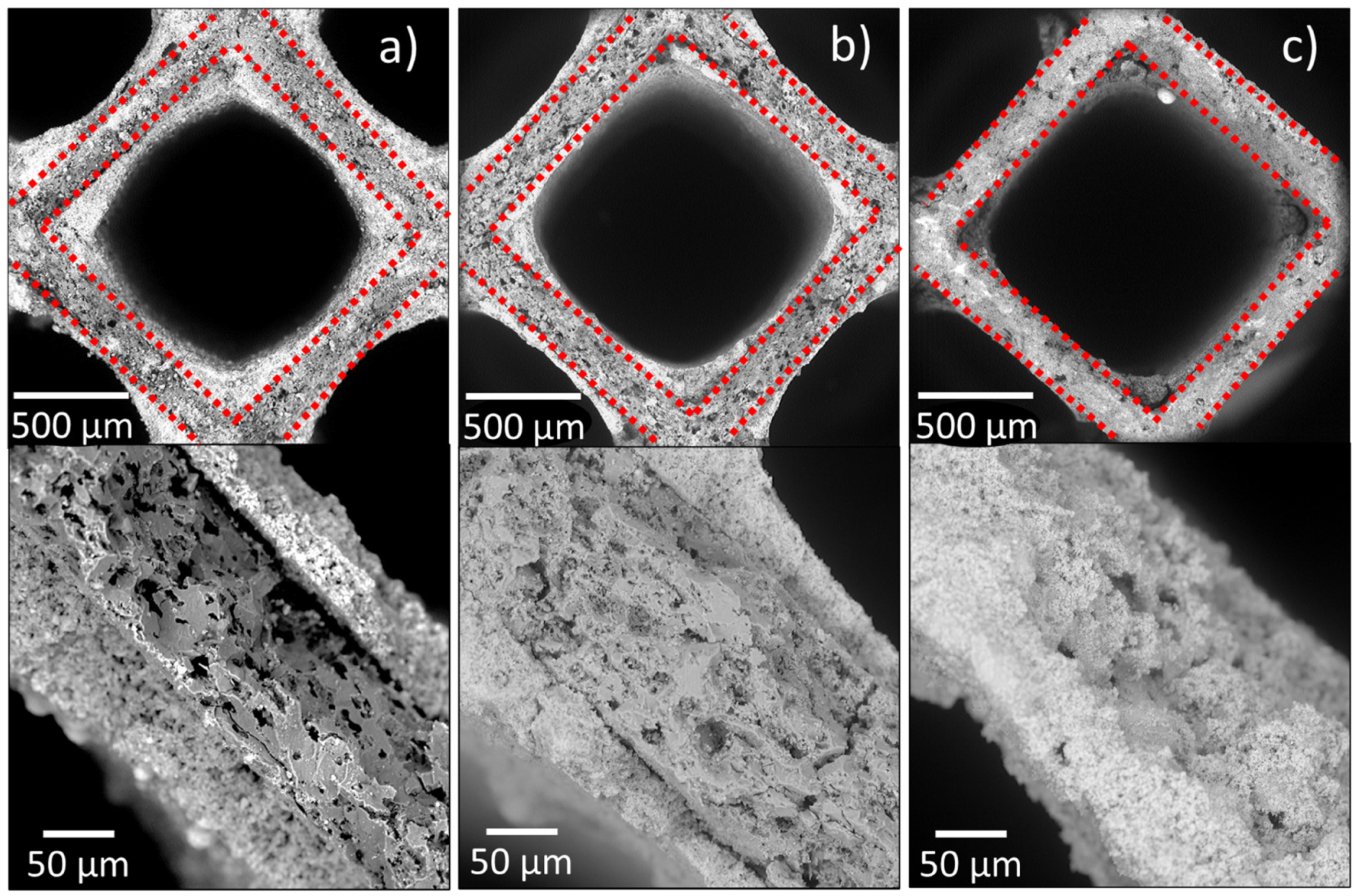
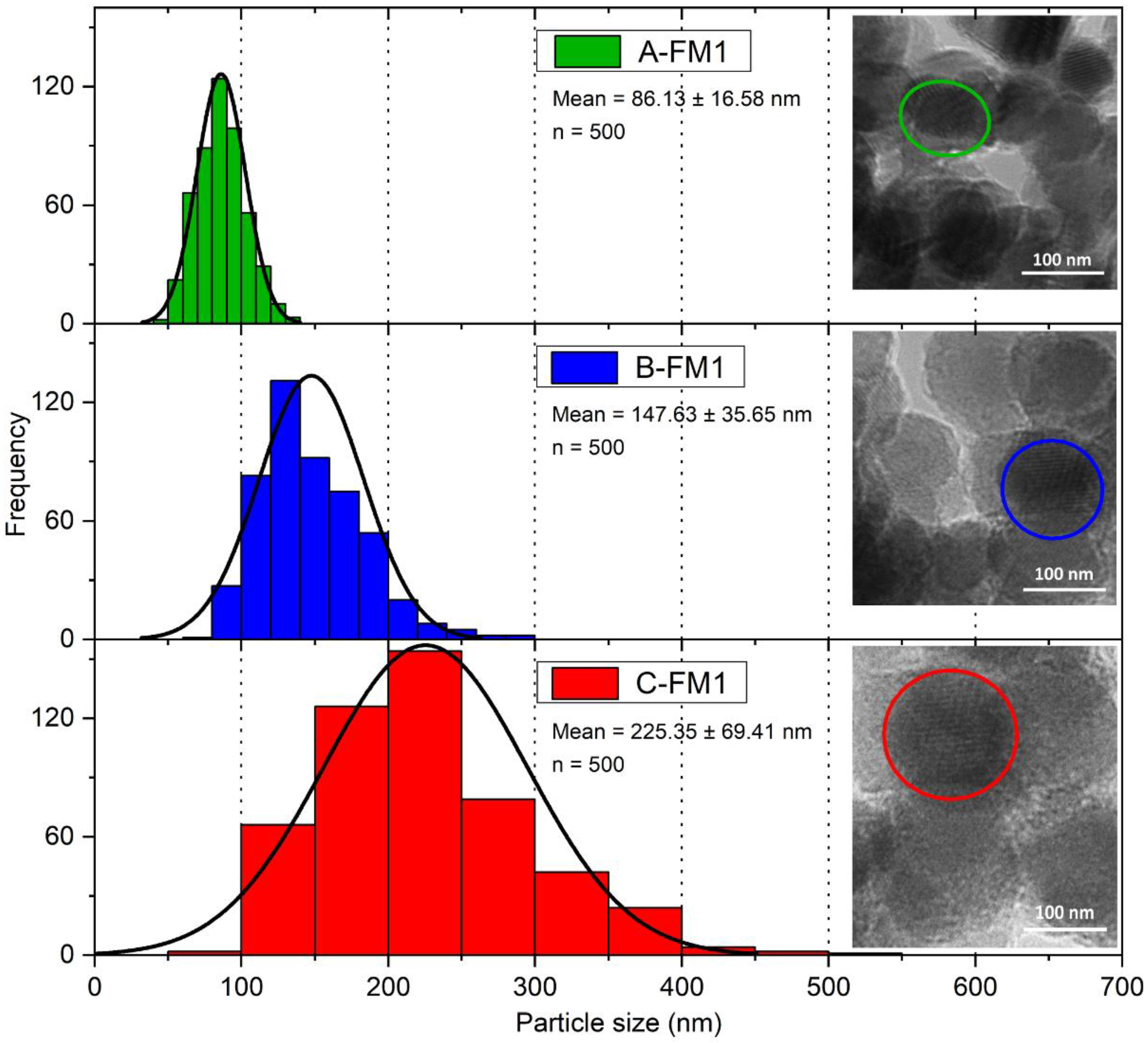
3.2. Wear Degradation and Particle Size
3.3. Limitations of the Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rönkkö, T.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Karjalainen, P.; Keskinen, J.; Hillamo, R.; Niemi, J.V.; Pirjola, L.; Timonen, H.J.; Saarikoski, S.; Saukko, E.; et al. Traffic is a major source of atmospheric nanocluster aerosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7549–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charron, A.; Polo-Rehn, L.; Besombes, J.-L.; Golly, B.; Buisson, C.; Chanut, H.; Marchand, N.; Guillaud, G.; Jaffrezo, J.-L. Identification and quantification of particulate tracers of exhaust and non-exhaust vehicle emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5187–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, S.; Mehta, N.S. Automobile pollution control using catalysis. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acres, G.J.K.; Cooper, B.J. Automobile emission control systems. Platinum Metals Rev. 1972, 16, 74–86. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, S.; Dhal, G.C. Cerium catalysts applications in carbon monoxide oxidations. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.M.; Khan, A. Nanosized CeO2–SiO2, CeO2–TiO2, and CeO2–ZrO2 mixed oxides: Influence of supporting oxide on thermal stability and oxygen storage properties of ceria. Catal. Surv. Asia 2005, 9, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kašpar, J.; Fornasiero, P.; Graziani, M. Use of CeO2-based oxides in the three-way catalysis. Catal. Today 1999, 50, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, R.M.; Farrauto, R.J. Automobile exhaust catalysts. App. Catal. A Gen. 2001, 221, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritsanaviparkporn, E.; Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Reina, T.R. Catalytic converters for vehicle exhaust: Fundamental aspects and technology overview for newcomers to the field. Chemistry 2021, 3, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ullah, H.; Zhou, M.; Peng, L.; He, A.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Spatial distributions, sources, potential risks of multi-trace metal/metalloids in street dusts from barbican downtown embracing by Xi’an ancient city wall (NW, China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ash, P.W.; Boyd, D.A.; Hyde, T.I.; Keating, J.L.; Randlshofer, G.; Rothenbacher, K.; Sankar, G.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Toner, B.M. Local structure and speciation of platinum in fresh and road-aged North American sourced vehicle emissions catalysts: An X-ray absorption spectroscopic study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3658–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruguete, D.M.; Murayama, M.; Blakney, T.; Winkler, C. Enhanced release of palladium and platinum from catalytic converter materials exposed to ammonia and chloride bearing solutions. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkin, D.; Zgorelec, Z.; Rinkovec, J. Concentrations of Pt, Pd and Rh in soil and vegetation: A review. J. Central Eur. Agric. 2019, 20, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Figueroa, D.; Pedroza-Montero, M.; Barboza-Flores, M.; Navarro-Espinoza, S.; Ruiz-Torres, R.; Robles-Morúa, A.; Romero, F.; Schiavo, B.; González-Grijalva, B.; Acosta-Elias, M. Identification of refractory zirconia from catalytic converters in dust: An emerging pollutant in urban environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Antonsson, M.; Eurenius, L.; Olsson, E.; Skoglundh, M. Deactivation of diesel oxidation catalysts: Vehicle- and synthetic aging correlations. App. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 72, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, M.; Ricchiardi, G.; Damin, A.; Sgroi, M.; Nicol, G.; Parussa, F. Thermal ageing effects in a commercial three-way catalyst: Physical characterization of washcoat and active metal evolution. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2020, 21, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Velasco, J.R.; Botas, J.A.; Ferret, R.; González-Marcos, M.P.; Marc, J.-L.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, M.A. Thermal aging of Pd/Pt/Rh automotive catalysts under a cycled oxidizing–reducing environment. Catal. Today 2000, 59, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Granados, M.; Cabello-Galisteo, F.; Mariscal, R.; Alifanti, M.; Gurbani, A.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Fernández-Ruíz, R. Modification of a three-way catalyst washcoat by aging: A study along the longitudinal axis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8442–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyestanaki, A.K.; Klingstedt, F.; Salmi, T.; Murzin, D.Y. Deactivation of postcombustion catalysts, a review. Fuel 2004, 83, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, K.; Oh, S.H. Modeling and analysis of rapid catalyst aging cycles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetten, O.; Pischinger, S.; Küpper, C.; Weinowski, R.; Gian, D.; Ignatov, D.; Betton, W.; Bahn, M. Catalyst aging method for future emissions standard requirements. SAE Int. 2010, 2010, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabatini, S.; Kil, I.; Hamilton, T.; Wuttke, J.; Rio, L.; Smith, M.; Filipi, Z.; Hoffman, M.; Onori, S. Characterization of Aging Effect on Three-Way Catalyst Oxygen Storage Dynamics; SAE Technical Paper No. 2016-01-0971; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Ferri, D.; Hauert, R. Influence of aging effects on the conversion efficiency of automotive exhaust gas catalysts. Catal. Today 2010, 155, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diario Oficial de la Federación (México). PROY-NOM-167-SEMARNAT-2017: Límites máximos permisibles de emisión de contaminantes para los vehículos automotores que circulan en las entidades federativas Ciudad de México, Hidalgo, Estado de México, Morelos, Puebla y Tlaxcala. In Los Métodos de Prueba Para la Evaluación de Dichos Límites y las Especificaciones de Tecnologías de Información y Hologramas; 05-09-2017; Available online: https://www.dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=5496105&fecha=05/09/2017 (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Vlasov, D.; Kosheleva, N.; Kasimov, N. Spatial distribution and sources of potentially toxic elements in road dust and its PM10 fraction of Moscow megacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, T.; Lassi, U.; Rahkamaa-Tolonen, K.; Kinnunen, T.; Keiski, R.L. The effect of barium on the catalytic behaviour of fresh and aged Pd-Ba-OSC/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 298, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Crespo, R.; de Leeuw, N.H.; Hamad, S.; Waghmare, U.V. Phase separation and surface segregation in ceria–zirconia solid solutions. Proc. R. Soc. A 2012, 467, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, S.Y.; García-Rodríguez, S.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Efstathiou, A.M. Deactivation of Pd/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 model three-way catalyst by P, Ca and Zn deposition. App. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 111–112, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larese, C.; Galisteo, F.C.; Granados, M.L.; Mariscal, R.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Furió, M.; Ruiz, R.F. Deactivation of real three way catalysts by CePO4 formation. App. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 40, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosacki, I.; Suzuki, T.; Anderson, H.U.; Colomban, P. Raman scattering and lattice defects in nanocrystalline CeO2 thin films. Solid State Ion. 2002, 149, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Bishop, S.R.; Rupp, J.L.M.; Tuller, H.L. Structural characterization and oxygen nonstoichiometry of ceria-zirconia (Ce1−xZrxO2−δ) solid solutions. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4277–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolon, A.M.; Gentleman, M.M.; Clarke, D.R. Raman spectroscopic bbservations of ferroelastic ewitching in ceria-stabilized zirconia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 4478–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovarelli, A.; de Leitenburg, C.; Dolcetti, G. Design better cerium-based oxidation catalysts. Chemtech 1997, 27. Available online: www.osti.gov/biblio/514757 (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Kaindl, R.; Tobbens, D.M.; Haefeker, U. Quantum-mechanical calculations of the Raman spectra of Mg- and Fe-cordierite. Ame. Mineral. 2011, 96, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, N.; Duraipandian, S.; Guimbretière, G.; Poirier, J. Raman spectra of synthetic and natural mullite. Vib. Spectros. 2016, 82, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P.; Piriou, B. The structures and vibrational spectra of crystals and glasses in the silica-alumina system. J. Non-Crys. Sol. 1982, 53, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüscher, C.H. Phonon spectra of 2:1 mullite in infrared and Raman experiments. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1996, 23, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Bao, H.; Zhao, H.; Ding, Y. Study on the reaction process and mechanism of the system of cordierite with zirconia. Ceram. Inter. 2019, 45, 5066–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, D.J.; Risbud, S.H.; Shackelford, J.F. Mullite. In Ceramic and Glass Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Birke, M.; Rauch, U.; Stummeyer, J.; Lorenz, H.; Keilert, B. A review of platinum group element (PGE) geochemistry and a study of the changes of PGE contents in the topsoil of Berlin, Germany, between 1992 and 2013. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 187, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, P.S.; Miller, A.; Edwards, A.C. The distribution of automobile catalysts-cast platinum, palladium and rhodium in soils adjacent to roads and their uptake by grass. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladonin, D.V. Platinum-Group Elements in soils and street dust of the Southeastern Administrative District of Moscow. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2018, 51, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Álvarez, E.; Ordóñez-Godínez, S.; Beramendi-Orosco, L.E.; Vega-Rodríguez, J.; Amador-Muñoz, O. Increase of the environmental Pt concentration in the metropolitan area of Mexico city associated to the use of automobile catalytic converters. In Platinum Metals in the Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Bocca, B.; Caimi, S.; Smichowski, P.; Gomez, D.; Caroli, S. Monitoring Pt and Rh in urban aerosols from Buenos Aires, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 358, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Galindo, R.; Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Álvarez, E.; Ordoñez-Godínez, S.L.; Amador-Muñoz, O.; Beramendi-Orosco, L.; Retama-Hernández, A.; Miranda, J.; Rosas-Pérez, I. Platinum concentration in PM2.5 in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area: Relationship to meteorological conditions. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 26, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkovec, J. Platinum, palladium, and rhodium in airborne particulate matter. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2019, 70, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moldovan, M.; Palacios, M.A.; Gomez, M.M.; Morrison, G.; Rauch, S.; McLeod, C.; Ma, R.; Caroli, S.; Alimonti, A.; Petrucci, F.; et al. Environmental risk of particulate and soluble platinum group elements released from gasoline and diesel engine catalytic. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 296, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, M.; Goriaux, M.; Liu, Y.; Martinet, S.; Jean-Soro, L.; Ruban, V. Platinum group elements study in automobile catalysts and exhaust gas samples. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.A.; Gómez, M.M.; Moldovan, M.; Morrison, G.; Rauch, S.; McLeod, C.; Ma, R.; Laserna, J.; Lucena, P.; Caroli, S.; et al. Platinum-group elements: Quantification in collected exhaust fumes and studies of catalyst surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 257, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, H. Mechanical stability of monolithic catalysts: Zcattering of washcoat adhesion and failure mechanism of active material. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 14713–14721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.W.; De La Riva, A.T.; Challa, S.R.; Datye, A.K. Sintering of catalytic nanoparticles: Particle migration or ostwald ripening? Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Hernandez, A.L.; Meza-Figueroa, D.; Tanori, J.; Acosta-Elias, M.; Gonzalez-Grijalva, B.; Maldonado-Escalante, J.F.; Rochin-Wong, S.; Soto-Puebla, D.; Navarro-Espinoza, S.; Ochoa-Contreras, R.; et al. Identification of inhalable rutile and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) nanoparticles in the atmospheric dust. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, O.K.; Ergun, D.; Basaran, N. Can the ceramic industry be a new and hazardous sector for work-related asthma? Respir. Med. 2018, 137, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maxim, L.D.; Utell, M.J. Review of refractory ceramic fiber (RCF) toxicity, epidemiology and occupational exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2018, 30, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.G.; Cole, T.B.; Coburn, J.; Chang, Y.C.; Dao, K.; Roque, P.J. Neurotoxicity of traffic-related air pollution. Neurotoxicology 2017, 59, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sett, R. Responses in plants exposed to dust pollution. Hortic. Int. J. 2017, 1, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro-Espinoza, S.; Meza-Figueroa, D.; Guzmán, R.; Duarte-Moller, A.; Esparza-Ponce, H.; Paz-Moreno, F.; González-Grijalva, B.; Álvarez-Bajo, O.; Schiavo, B.; Soto-Puebla, D.; et al. Release of Nanoparticles in the Environment and Catalytic Converters Ageing. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123406
Navarro-Espinoza S, Meza-Figueroa D, Guzmán R, Duarte-Moller A, Esparza-Ponce H, Paz-Moreno F, González-Grijalva B, Álvarez-Bajo O, Schiavo B, Soto-Puebla D, et al. Release of Nanoparticles in the Environment and Catalytic Converters Ageing. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(12):3406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123406
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro-Espinoza, Sofía, Diana Meza-Figueroa, Roberto Guzmán, Alberto Duarte-Moller, Hilda Esparza-Ponce, Francisco Paz-Moreno, Belem González-Grijalva, Osiris Álvarez-Bajo, Benedetto Schiavo, Diego Soto-Puebla, and et al. 2021. "Release of Nanoparticles in the Environment and Catalytic Converters Ageing" Nanomaterials 11, no. 12: 3406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123406
APA StyleNavarro-Espinoza, S., Meza-Figueroa, D., Guzmán, R., Duarte-Moller, A., Esparza-Ponce, H., Paz-Moreno, F., González-Grijalva, B., Álvarez-Bajo, O., Schiavo, B., Soto-Puebla, D., & Pedroza-Montero, M. (2021). Release of Nanoparticles in the Environment and Catalytic Converters Ageing. Nanomaterials, 11(12), 3406. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123406








