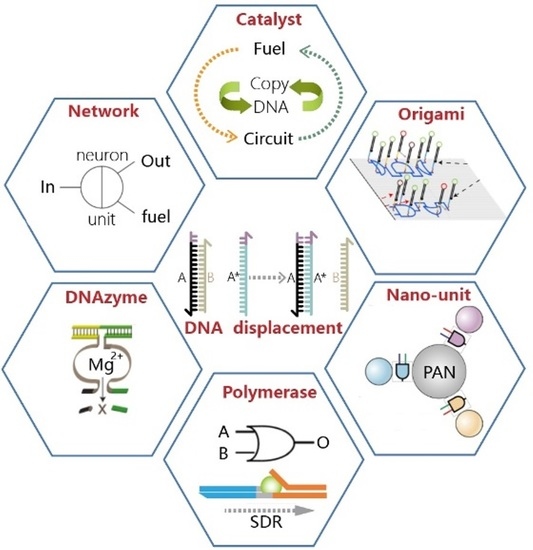
Development of Synthetic DNA Circuit and Networks for Molecular Information Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
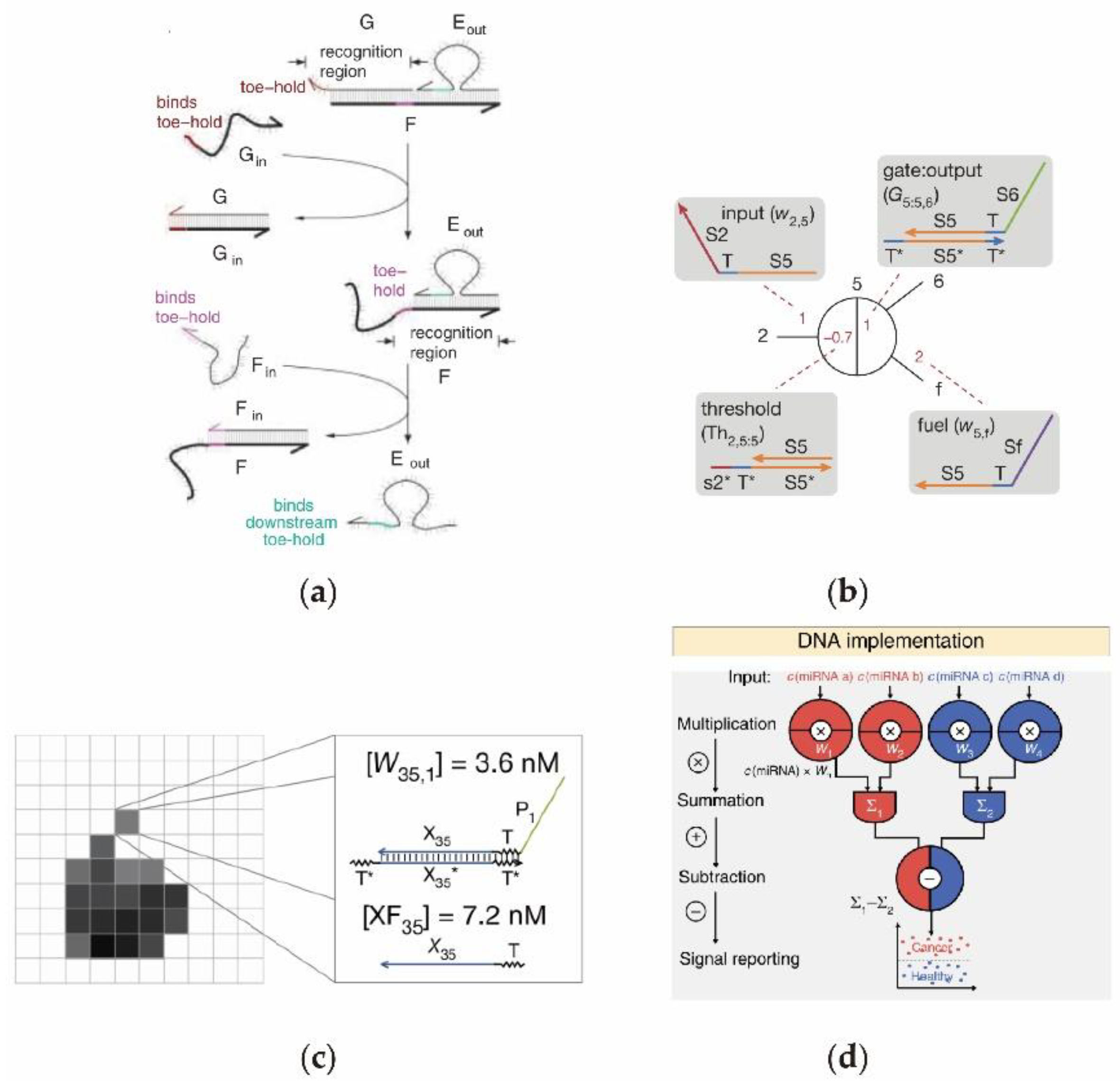
2. The Research Studies on DNA Circuits
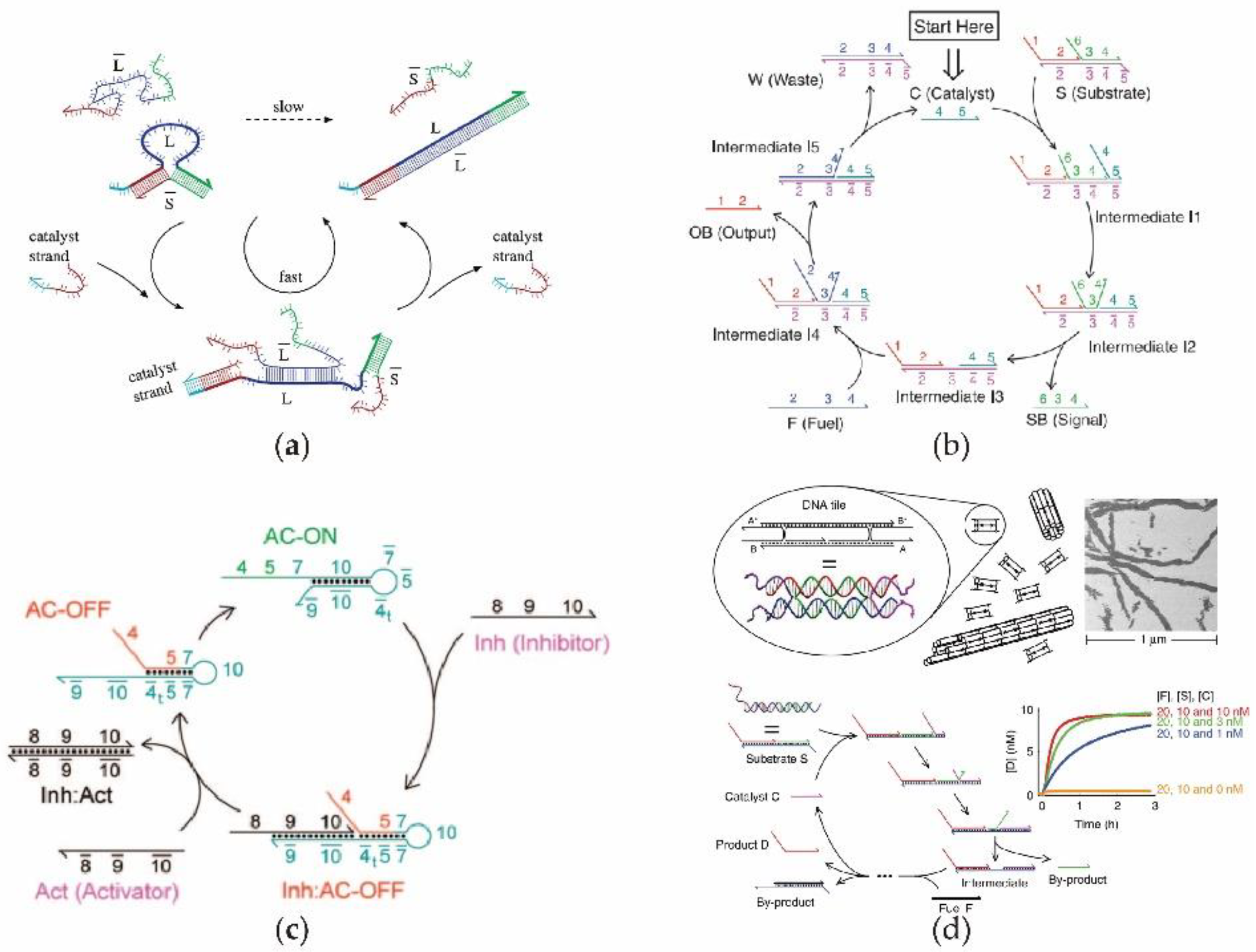
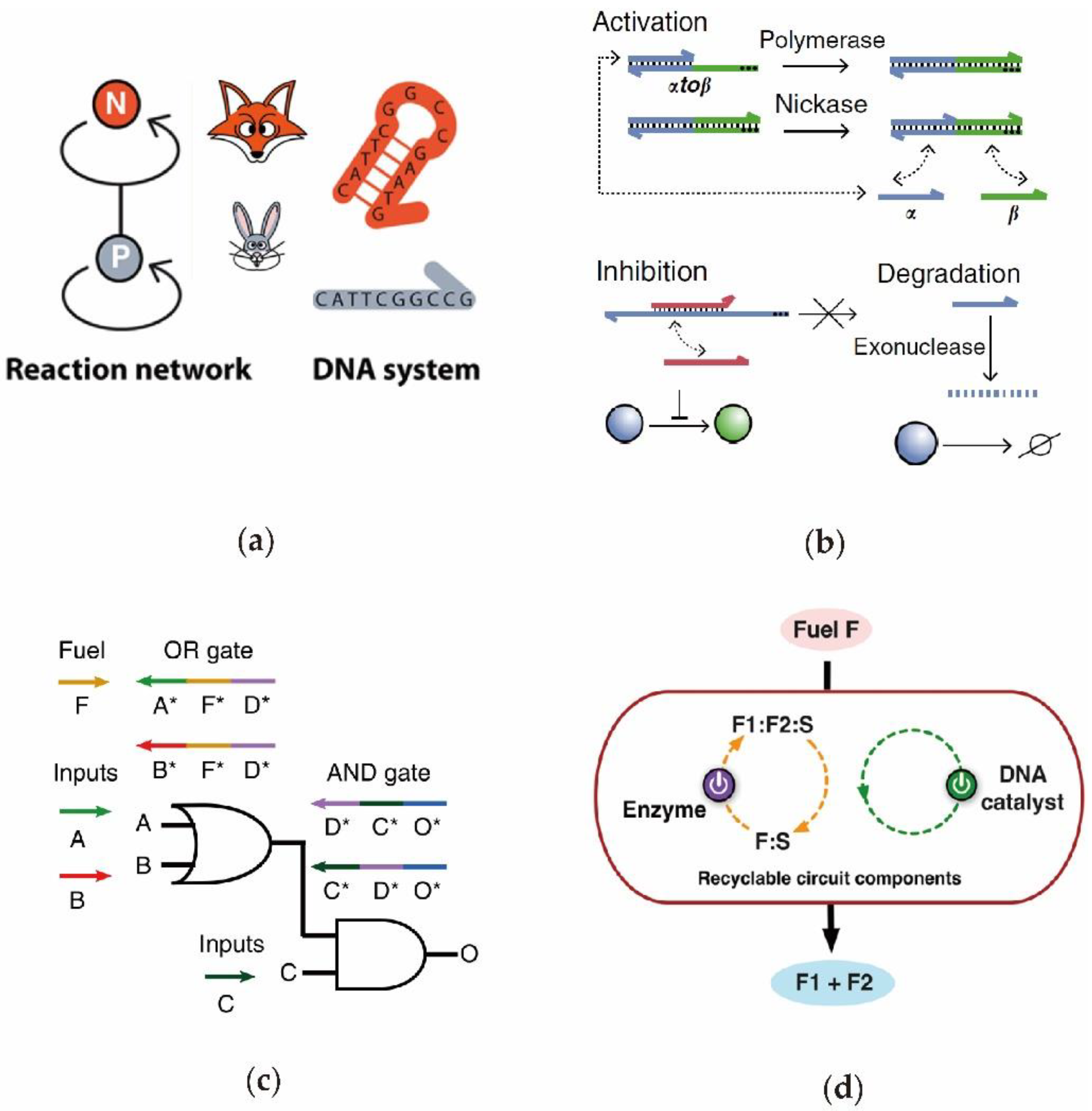
2.1. Cascading DNA Circuits In Vitro
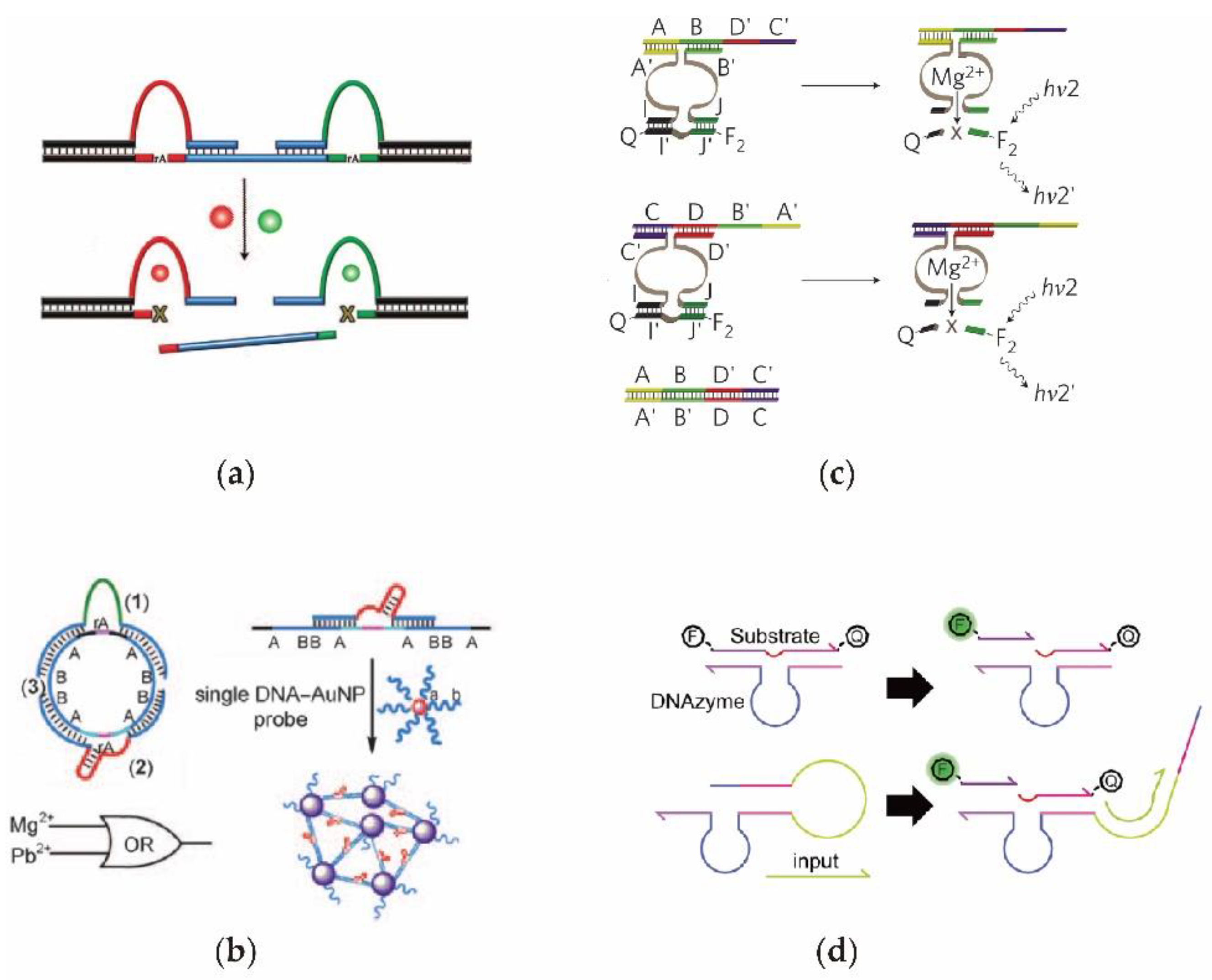
2.2. Enzyme-Free Catalytic DNA Circuit
2.3. DNAzyme-Based DNA Circuit
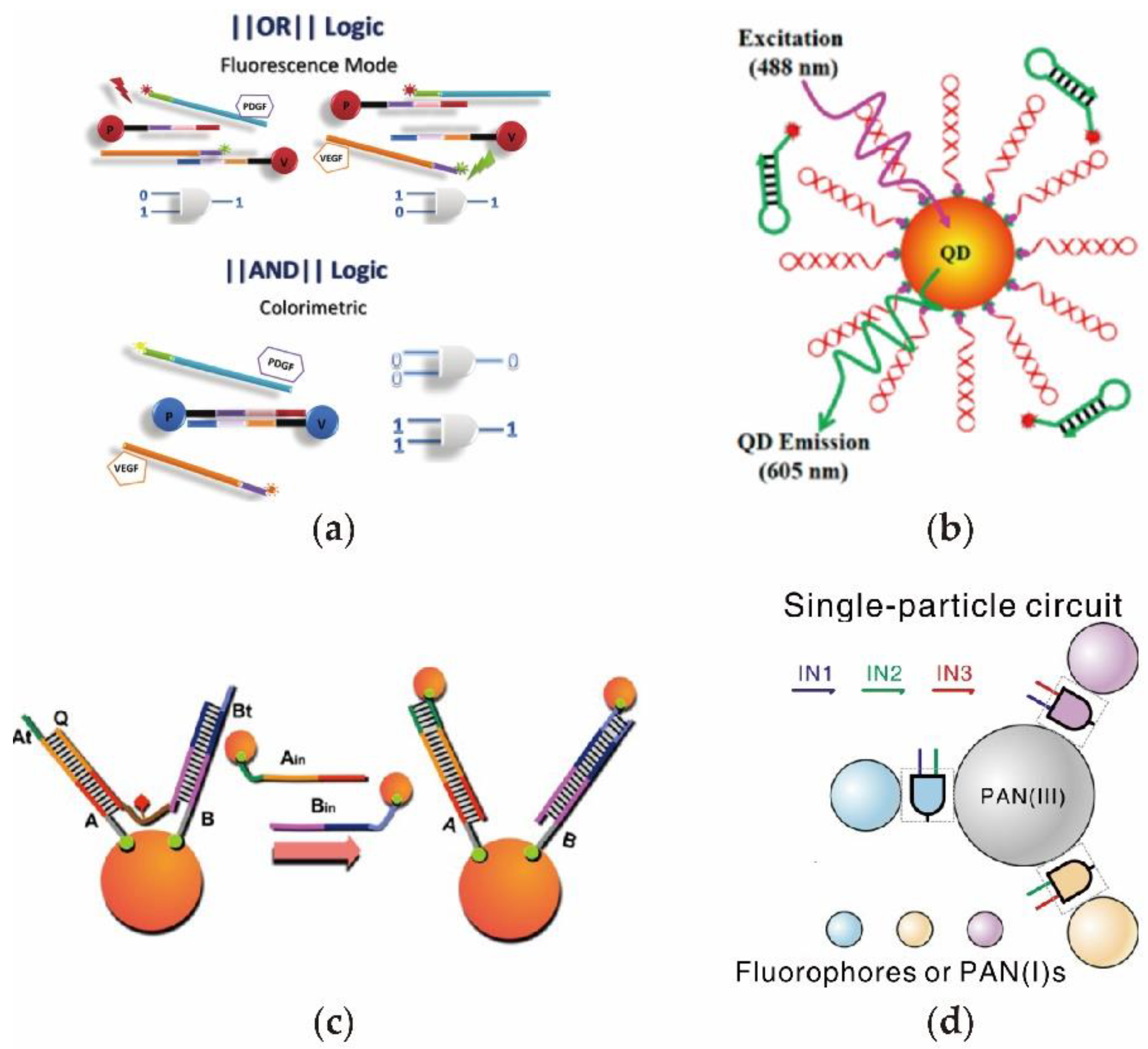
2.4. Protein Enzyme-Assiste d DNA Circuit
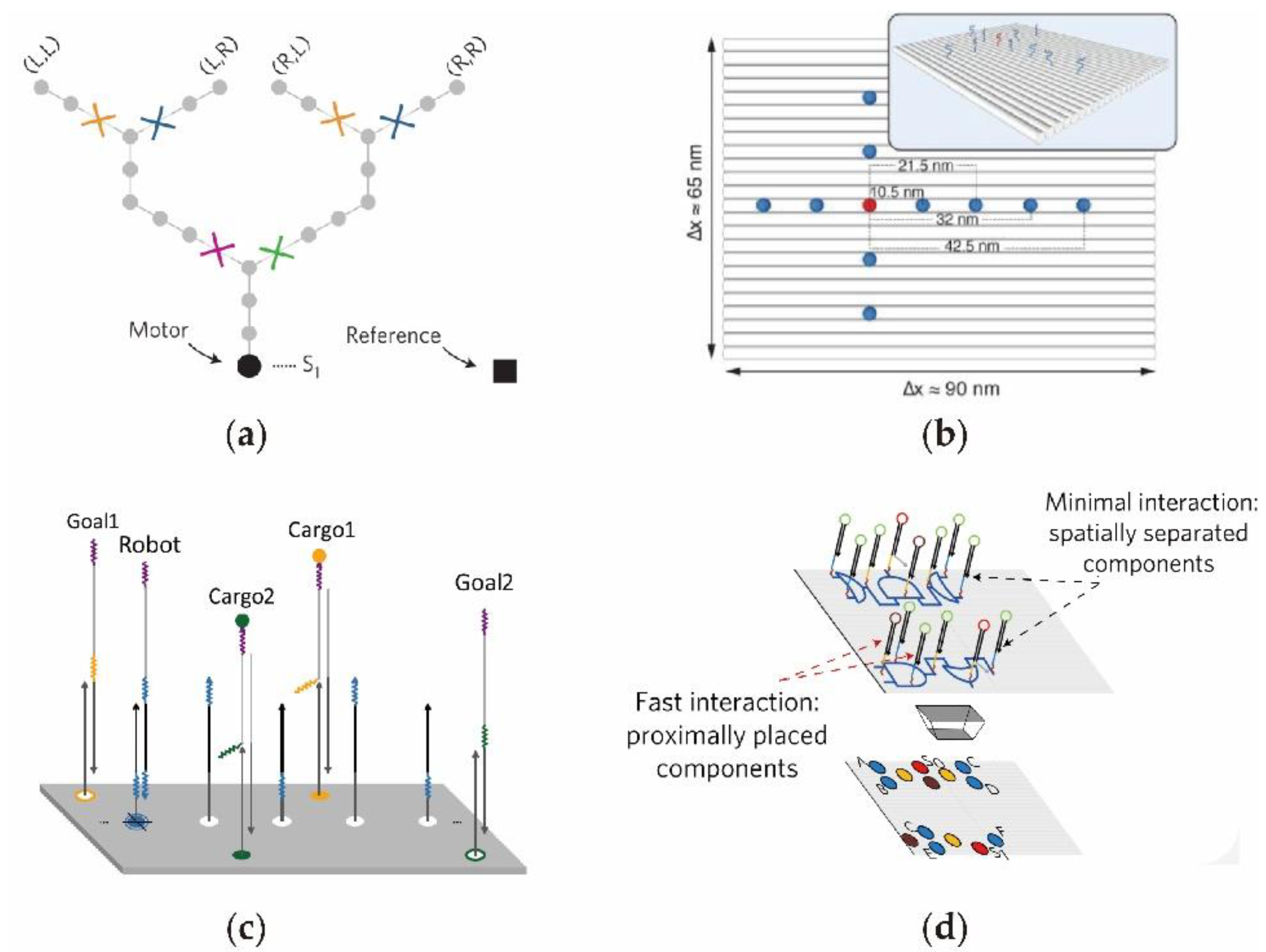
2.5. The DNA Circuits on Origami Surface
2.6. The DNA Circuits Combined with Nanoparticles
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Y.C.; Cui, Y.X.; Li, X.Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Tang, A.N.; Kim, K.; Kong, D.M. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase and T7 Exonuclease-Aided Amplification Strategy for Ultrasensitive Detection of Uracil-DNA Glycosylase. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8629–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, F.; Wang, F.B.; Yuan, Q. Rapid and Selective Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Bloodstream Infections with Aptamer-Based Recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19371–19378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Li, N.; Dai, L.; Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Ding, B.; et al. DNA Origami as an In Vivo Drug Delivery Vehicle for Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6633–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organick, L.; Ang, S.D.; Chen, Y.J.; Lopez, R.; Yekhanin, S.; Makarychev, K.; Racz, M.Z.; Kamath, G.; Gopalan, P.; Nguyen, B.; et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Rondelez, Y. Predator-Prey Molecular Ecosystems. Acs Nano 2013, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.Y.; Chang, W.L.; Ho, M.C.; Lu, J.; Cao, J.N. Is optimal solution of every NP-complete or NP-hard problem determined from its characteristic for DNA-based computing. Biosystems 2005, 80, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Duan, X.Y.; Liu, N. A plasmonic nanorod that walks on DNA origami. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; White, K.S.; Winfree, E. Construction of an in vitro bistable circuit from synthetic transcriptional switches. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Liu, S.J.; Bleris, L.; Benenson, Y. Logic integration of mRNA signals by an RNAi-based molecular computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2692–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Ren, J.; Fan, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, E. Integration of graphene oxide and DNA as a universal platform for multiple arithmetic logic units. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14390–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.B.; Zhang, L.B.; Dong, S.J.; Wang, E.K. Four-Way Junction-Driven DNA Strand Displacement and Its Application in Building Majority Logic Circuit. Acs Nano 2013, 7, 10211–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fern, J.; Schulman, R. Design and Characterization of DNA Strand-Displacement Circuits in Serum-Supplemented Cell Medium. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, K. A DNA nanowire based localized catalytic hairpin assembly reaction for microRNA imaging in live cells. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7802–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prokup, A.; Hemphill, J.; Deiters, A. DNA Computation: A Photochemically Controlled AND Gate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3810–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, A.A.; Kim, J.; Ma, D.; Silver, P.A.; Collins, J.J.; Yin, P. Complex cellular logic computation using ribocomputing devices. Nature 2017, 548, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinaudo, K.; Bleris, L.; Maddamsetti, R.; Subramanian, S.; Weiss, R.; Benenson, Y. A universal RNAi-based logic evaluator that operates in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, J.; Deiters, A. DNA computation in mammalian cells: microRNA logic operations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10512–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Lyu, C.; Ji, X.; Hou, J.; Guo, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Lou, C. Insulated transcriptional elements enable precise design of genetic circuits. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, A.; Cardelli, L. A programming language for composable DNA circuits. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6 (Suppl. S4), 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Kong, J.; Zhu, J.; Ermann, N.; Predki, P.; Keyser, U.F. Digital Data Storage Using DNA Nanostructures and Solid-State Nanopores. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, R.; Chen, Y.J.; Dumas Ang, S.; Yekhanin, S.; Makarychev, K.; Racz, M.Z.; Seelig, G.; Strauss, K.; Ceze, L. DNA assembly for nanopore data storage readout. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fern, J.; Scalise, D.; Cangialosi, A.; Howie, D.; Potters, L.; Schulman, R. DNA Strand-Displacement Timer Circuits. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Winfree, E. Dynamic allosteric control of noncovalent DNA catalysis reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13921–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graugnard, E.; Kellis, D.L.; Bui, H.; Barnes, S.; Kuang, W.; Lee, J.; Hughes, W.L.; Knowlton, W.B.; Yurke, B. DNA-Controlled Excitonic Switches. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2117–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Briggs, N.; McLain, J.R.; Ellington, A.D. Stacking nonenzymatic circuits for high signal gain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5386–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Elbaz, J.; Willner, I. Enzyme-free amplified detection of DNA by an autonomous ligation DNAzyme machinery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5504–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yue, L.; Shpilt, Z.; Cecconello, A.; Kahn, J.S.; Lehn, J.M.; Willner, I. Controlling the Catalytic Functions of DNAzymes within Constitutional Dynamic Networks of DNA Nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9662–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Mao, C. Molecular gears: A pair of DNA circles continuously rolls against each other. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11410–11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Elbaz, J.; Orbach, R.; Magen, N.; Willner, I. Amplified analysis of DNA by the autonomous assembly of polymers consisting of DNAzyme wires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17149–17151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Elbaz, J.; Teller, C.; Willner, I. Amplified detection of DNA through an autocatalytic and catabolic DNAzyme-mediated process. Angew. Chem. 2011, 50, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Y.; Fan, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, D.; Hong, W.; Liu, Y. A DNA arithmetic logic unit for implementing data backtracking operations. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlyahovsky, B.; Li, Y.; Lioubashevski, O.; Elbaz, J.; Willner, I. Logic Gates and Antisense DNA Devices Operating on a Translator Nucleic Acid Scaffold. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.; Shang, S.; Kolpashchikov, D.M. Molecular Logic Gates Connected through DNA Four-Way Junctions. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 4459–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y. DNA based arithmetic function: A half adder based on DNA strand displacement. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chen, J.Z.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, C.N. A simple three-input DNA-based system works as a full-subtractor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Fan, D.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, E. Enzyme-free and DNA-based multiplexer and demultiplexer. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15940–15943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Enzyme-Free Unlabeled DNA Logic Circuits Based on Toehold-Mediated Strand Displacement and Split G-Quadruplex Enhanced Fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Expanding the rule set of DNA circuitry with associative toehold activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Winfree, E. Control of DNA Strand Displacement Kinetics Using Toehold Exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17303–17314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. A Responsive Hidden Toehold To Enable Controllable DNA Strand Displacement Reactions. Angew. Chem. 2011, 50, 11934–11936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, K.M.; Qian, L. Scaling up molecular pattern recognition with DNA-based winner-take-all neural networks. Nature 2018, 559, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Eshra, A.; Shah, S.; Bui, H.; Fu, D.; Yang, M.; Mokhtar, R.; Reif, J. Fast and compact DNA logic circuits based on single-stranded gates using strand-displacing polymerase. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A.; Dehankar, A.; Winter, J.O.; Castro, C.E. Reciprocal Control of Hierarchical DNA Origami-Nanoparticle Assemblies. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 8469–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Nguyen, M.K.; Natarajan, A.K.; Nguyen, V.H.; Kuzyk, A. A DNA Origami-Based Chiral Plasmonic Sensing Device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44221–44225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Gibson, K.J.; Liu, D.; Rees, H.C.; Lee, J.H.; Xia, W.; Lin, R.; Xin, H.L.; Gang, O.; Weizmann, Y. Regioselective surface encoding of nanoparticles for programmable self-assembly. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Mitta, S.B.; Song, Y.; Son, J.; Park, S.; Ha, T.H.; Park, S.H. 3-Input/1-Output Logic Implementation Demonstrated by DNA Algorithmic Self-Assembly. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 4369–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, J. A molecular logical switching beacon controlled by thiolated DNA signals. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11308–11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Both, S.; Weiss, T.; Liu, N. DNA-Assembled Multilayer Sliding Nanosystems. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6385–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, G.; Dalchau, N.; Muscat, R.A.; Phillips, A.; Seelig, G. A spatially localized architecture for fast and modular DNA computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, N.; Ouldridge, T.E.; Sulc, P.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Yurke, B.; Louis, A.A.; Doye, J.P.; Winfree, E. On the biophysics and kinetics of toehold-mediated DNA strand displacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 10641–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, B.M.; Cockroft, S.L.; Ghadiri, M.R. Modular multi-level circuits from immobilized DNA-Based logic gates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14875–14879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seelig, G.; Soloveichik, D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Winfree, E. Enzyme-free nucleic acid logic circuits. Science 2006, 314, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkataraman, S.; Dirks, R.M.; Rothemund, P.W.; Winfree, E.; Pierce, N.A. An autonomous polymerization motor powered by DNA hybridization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Winfree, E. Scaling Up Digital Circuit Computation with DNA Strand Displacement Cascades. Science 2011, 332, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, R.; Li, H.; Teng, X.; Du, Y.; Miao, Y.; Lin, H.C.; Han, D. Cancer diagnosis with DNA molecular computation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Lubrich, D.; Turberfield, A.J. DNA hairpins: Fuel for autonomous DNA devices. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seelig, G.; Yurke, B.; Winfree, E. Catalyzed relaxation of a metastable DNA fuel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12211–12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Turberfield, A.J.; Yurke, B.; Winfree, E. Engineering entropy-driven reactions and networks catalyzed by DNA. Science 2007, 318, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Hariadi, R.F.; Choi, H.M.; Winfree, E. Integrating DNA strand-displacement circuitry with DNA tile self-assembly. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, J.; Moshe, M.; Shlyahovsky, B.; Willner, I. Cooperative multicomponent self-assembly of nucleic acid structures for the activation of DNAzyme cascades: A paradigm for DNA sensors and aptasensors. Chemistry 2009, 15, 3411–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbach, R.; Mostinski, L.; Wang, F.; Willner, I. Nucleic acid driven DNA machineries synthesizing Mg2+-dependent DNAzymes: An interplay between DNA sensing and logic-gate operations. Chemistry 2012, 18, 14689–14694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.J.; Lin, J.; Cao, J.; Vazin, M.; Liu, J. Ultrasensitive DNAzyme beacon for lanthanides and metal speciation. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Willner, I. DNAzyme-Controlled Cleavage of Dimer and Trimer Origami Tiles. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2867–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Emura, T.; Hidaka, K.; Wang, F.; Willner, I.; Sugiyama, H. Single-Molecule Visualization of the Activity of a Zn(2+)-Dependent DNAzyme. Angew. Chem. 2015, 54, 10550–10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleman-Garcia, M.A.; Orbach, R.; Willner, I. Ion-responsive hemin-G-quadruplexes for switchable DNAzyme and enzyme functions. Chem. 2014, 20, 5619–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Orbach, R.; Willner, I. Detection of metal ions (Cu2+, Hg2+) and cocaine by using ligation DNAzyme machinery. Chem. 2012, 18, 16030–16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, C. Entropy-driven DNA logic circuits regulated by DNAzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 8532–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orbach, R.; Willner, B.; Willner, I. Catalytic nucleic acids (DNAzymes) as functional units for logic gates and computing circuits: From basic principles to practical applications. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4144–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moshe, M.; Elbaz, J.; Willner, I. Sensing of UO22+ and Design of Logic Gates by the Application of Supramolecular Constructs of Ion-Dependent DNAzymes. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Yan, Y.; Hao, S.; Zhang, S. Colorimetric logic gates based on supramolecular DNAzyme structures. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, J.; Lioubashevski, O.; Wang, F.; Remacle, F.; Levine, R.D.; Willner, I. DNA computing circuits using libraries of DNAzyme subunits. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, J.; Wang, F.A.; Remacle, F.; Willner, I. pH-Programmable DNA Logic Arrays Powered by Modular DNAzyme Libraries. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6049–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, B.I.; Pollak, N.M.; Stefanovic, D.; Macdonald, J. Repeated Reuse of Deoxyribozyme-Based Logic Gates. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 7655–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enghiad, B.; Zhao, H.M. Programmable DNA-Guided Artificial Restriction Enzymes. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.L.; Tang, Y.A.; Mason, S.D.; Chen, J.B.; Li, F. Enzyme-Powered Three-Dimensional DNA Nanomachine for DNA Walking, Payload Release, and Biosensing. Acs Nano 2016, 10, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zahid, O.K.; Swain, B.E.; Parsonage, D.; Hollis, T.; Harvey, S.; Perrino, F.W.; Kohli, R.M.; Taylor, E.W.; Hall, A.R. Solid-State Nanopore Analysis of Diverse DNA Base Modifications Using a Modular Enzymatic Labeling Process. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7110–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esadze, A.; Rodriguez, G.; Weiser, B.P.; Cole, P.A.; Stivers, J.T. Measurement of nanoscale DNA translocation by uracil DNA glycosylase in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12413–12424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, L.; Joesaar, A.; Steur, E.; Engelen, W.; van Santen, R.A.; Merkx, M.; de Greef, T. Hierarchical control of enzymatic actuators using DNA-based switchable memories. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Ke, Y.; Yan, H. Nicking-Assisted Reactant Recycle To Implement Entropy-Driven DNA Circuit. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17189–17197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Willner, I. Active generation of nanoholes in DNA origami scaffolds for programmed catalysis in nanocavities. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhomirov, G.; Petersen, P.; Qian, L. Triangular DNA Origami Tilings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17361–17364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Xin, H.L.; Li, H.; Ke, Y.; Shih, W.M.; Gang, O. Prescribed nanoparticle cluster architectures and low-dimensional arrays built using octahedral DNA origami frames. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, C.E.; Kilchherr, F.; Kim, D.N.; Shiao, E.L.; Wauer, T.; Wortmann, P.; Bathe, M.; Dietz, H. A primer to scaffolded DNA origami. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Ouyang, X.; Kopperger, E.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; et al. Solving mazes with single-molecule DNA navigators. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, S.F.; Bath, J.; Katsuda, Y.; Endo, M.; Hidaka, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Turberfield, A.J. A DNA-based molecular motor that can navigate a network of tracks. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichmann, M.; Kopperger, E.; Simmel, F.C. Robustness of Localized DNA Strand Displacement Cascades. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8487–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thubagere, A.J.; Li, W.; Johnson, R.F.; Chen, Z.; Doroudi, S.; Lee, Y.L.; Izatt, G.; Wittman, S.; Srinivas, N.; Woods, D.; et al. A cargo-sorting DNA robot. Science 2017, 357, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lan, X.; Lu, X.; Shen, C.; Ke, Y.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q. Au nanorod helical superstructures with designed chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Govorov, A.O.; Yan, H.; Liu, Y. DNA-Guided Plasmonic Helix with Switchable Chirality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11763–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thacker, V.V.; Herrmann, L.O.; Sigle, D.O.; Zhang, T.; Liedl, T.; Baumberg, J.J.; Keyser, U.F. DNA origami based assembly of gold nanoparticle dimers for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kühler, P.; Roller, E.M.; Schreiber, R.; Liedl, T.; Lohmüller, T.; Feldmann, J. Plasmonic DNA-Origami Nanoantennas for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2914–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Lu, M.; Both, S.; Pfeiffer, M.; Urban, M.J.; Zhou, C. Watching a Single Fluorophore Molecule Walk into a Plasmonic Hotspot. Acs Photonics 2019, 6, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, M.J.; Zhou, C.; Duan, X.; Liu, N. Optically Resolving the Dynamic Walking of a Plasmonic Walker Couple. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8392–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyriazi, M.E.; Giust, D.; El-Sagheer, A.H.; Lackie, P.M.; Muskens, O.L.; Brown, T.; Kanaras, A.G. Multiplexed mRNA Sensing and Combinatorial-Targeted Drug Delivery Using DNA-Gold Nanoparticle Dimers. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chai, H.; Miao, P. Bipedal DNA Walker Based Electrochemical Genosensing Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4953–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Corn, R.M. DNAzyme footprinting: Detecting protein-aptamer complexation on surfaces by blocking DNAzyme cleavage activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2072–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Chai, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, W.; Yuan, R. DNA Cascade Reaction with High-Efficiency Target Conversion for Ultrasensitive Electrochemiluminescence microRNA Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10258–10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lai, W.; Zhuang, J.; Tang, J.; Tang, D. Nanogold-functionalized DNAzyme concatamers with redox-active intercalators for quadruple signal amplification of electrochemical immunoassay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, F.; Bai, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, D. Gene Circuit Compartment on Nanointerface Facilitatating Cascade Gene Expression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19171–19177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Quan, K.; Xie, N.; Ou, M.; Wang, K. Gold Nanoparticle Based Hairpin-Locked-DNAzyme Probe for Amplified miRNA Imaging in Living Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5850–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.P.; Ma, P.Q.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Yin, B.C.; Ye, B.C. Rational Engineering of a Dynamic, Entropy-Driven DNA Nanomachine for Intracellular MicroRNA Imaging. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 9077–9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gines, G.; Zadorin, A.S.; Galas, J.C.; Fujii, T.; Estevez-Torres, A.; Rondelez, Y. Microscopic agents programmed by DNA circuits. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, F.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Nucleic acid-mesoporous silica nanoparticle conjugates for keypad lock security operation. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2305–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Lam, J.C.; Chiuman, W.; Brook, M.A.; Li, Y. Enzymatic cleavage of nucleic acids on gold nanoparticles: A generic platform for facile colorimetric biosensors. Small 2008, 4, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukoor, M.I.; Altman, M.O.; Han, D.; Bayrac, A.T.; Ocsoy, I.; Zhu, Z.; Tan, W. Aptamer-nanoparticle assembly for logic-based detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3007–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.Y. Catalytic Self-Assembly of Quantum-Dot-Based MicroRNA Nanosensor Directed by Toehold-Mediated Strand Displacement Cascade. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6370–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shen, L.; Ma, J.; Schlaberg, H.I.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C. Fluorescent nanoparticle beacon for logic gate operation regulated by strand displacement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5392–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Qu, Z.; Ge, Z.; Narayanan, R.P.; Williams, D.; et al. Programming nanoparticle valence bonds with single-stranded DNA encoders. Nat. Mater. 2019, 19, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C. Development of Synthetic DNA Circuit and Networks for Molecular Information Processing. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112955
Zhang Y, Feng Y, Liang Y, Yang J, Zhang C. Development of Synthetic DNA Circuit and Networks for Molecular Information Processing. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112955
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yongpeng, Yuhua Feng, Yuan Liang, Jing Yang, and Cheng Zhang. 2021. "Development of Synthetic DNA Circuit and Networks for Molecular Information Processing" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112955
APA StyleZhang, Y., Feng, Y., Liang, Y., Yang, J., & Zhang, C. (2021). Development of Synthetic DNA Circuit and Networks for Molecular Information Processing. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112955