Visible-Light Active Sulfur-Doped Titania Nanoparticles Immobilized on a Silica Matrix: Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Degradation of Pollutants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Materials Synthesis and Characterization
2.3. Photocatalytic Evaluation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Powder XRD and Porosity Analysis
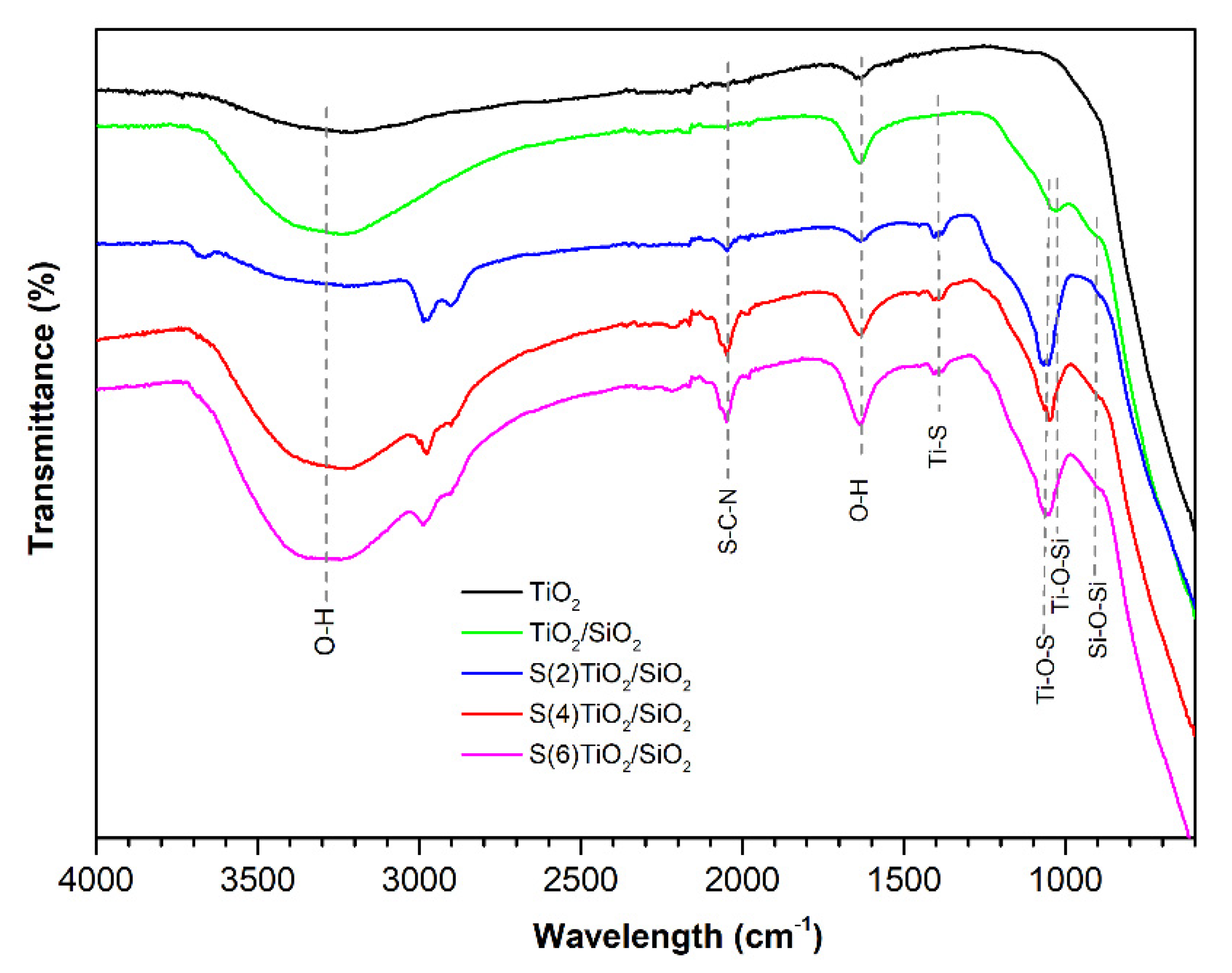
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.3. UV–Vis Diffused Reflectance Spectroscopy: Band Gap Analysis
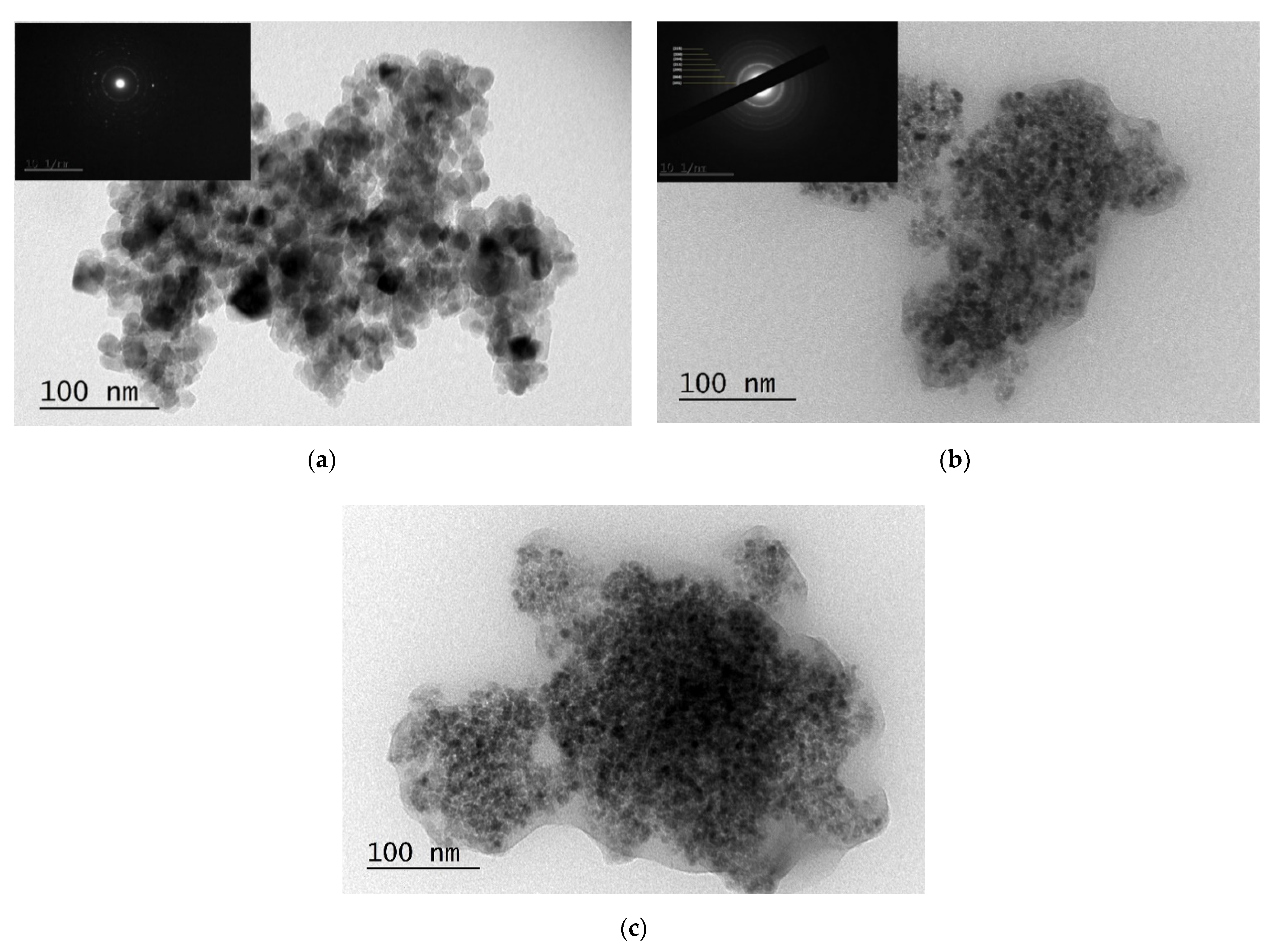
3.4. Morphological Analysis
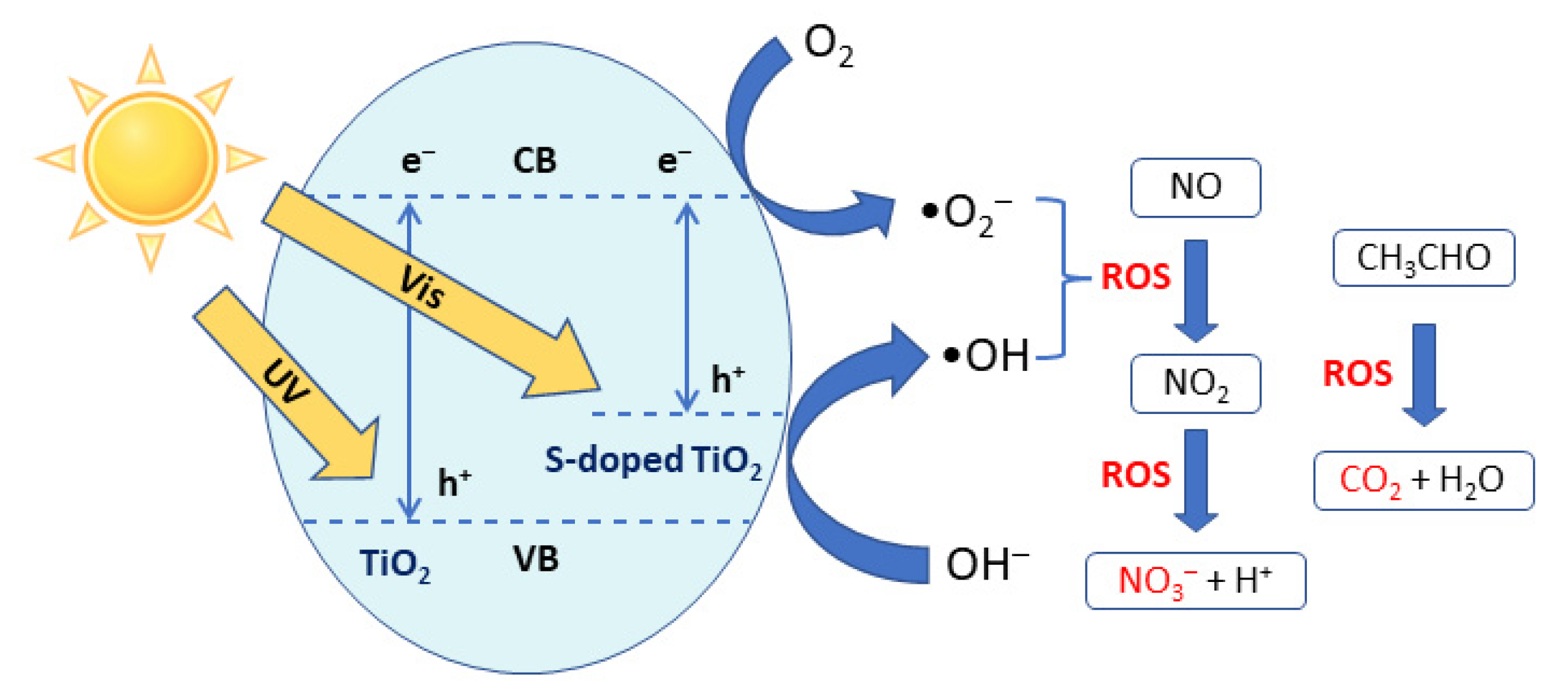
3.5. Photocatalytic Evaluation
3.5.1. Liquid Pollutant Degradation
3.5.2. Air Pollutant Degradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mamaghani, A.H.; Haghighat, F.; Lee, C.-S. Photocatalytic oxidation technology for indoor environment air purification: The state-of-the-art. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T., Jr. Photocatalysis on TiO2 Surfaces: Principles, Mechanisms, and Selected Results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, U.I.; Abdullah, A.H. Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: A review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, T.; Fujishima, A. Photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 photocatalyst and its applications for environmental purification. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2012, 13, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufique, M.F.N.; Haque, A.; Karnati, P.; Ghosh, K. ZnO–CuO Nanocomposites with Improved Photocatalytic Activity for Environmental and Energy Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 6731–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Visible-Light Active Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials with Bactericidal Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angel, R.D.; Durán-Álvarez, J.C.; Zanella, R. TiO2-Low Band Gap Semiconductor Heterostructures for Water Treatment Using Sunlight-Driven Photocatalysis. In Titanium Dioxide—Materials for a Sustainable Environment; Yang, D., Ed.; IntechOpen Ltd.: London, UK, 2018; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/60975 (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, R.; et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksibi, M.; Rossignol, S.; Tatibouet, J.M.; Trapalis, C. Synthesis and solid characterization of nitrogen and sulfur-doped TiO2 photocatalysts active under near visible light. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4204–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayegan, Z.; Lee, C.S.; Haghighat, F. TiO2 photocatalyst for removal of volatile organic compounds in gas phase—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2408–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parangi, T.; Mishra, M.K. Titania Nanoparticles as Modified Photocatalysts: A Review on Design and Development. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2019, 39, 90–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yang, M.-Q.; Fu, X.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y.-J. Defective TiO2 with oxygen vacancies: Synthesis, properties and photocatalytic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3601–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Burda, C. The Electronic Origin of the Visible-Light Absorption Properties of C-, N- and S-Doped TiO2 Nanomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5018–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Pillai, S.C.; Falaras, P.; O’Shea, K.E.; Byrne, J.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. New Insights into the Mechanism of Visible Light Photocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mittal, A.; Mari, B.; Sharma, S.; Kumari, V.; Maken, S.; Kumari, K.; Kumar, N. Non-metal modified TiO2: A step towards visible light photocatalysis. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 3186–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątkowska, A.; Janus, M.; Szymanski, K.; Mozia, S. C-,N- and S-Doped TiO2 Photocatalysts: A Review. Catalysts 2021, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umebayashi, T.; Yamaki, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Miyashita, A.; Tanaka, S.; Sumita, T.; Asai, K. Sulfur-doping of rutile-titanium dioxide by ion implantation: Photocurrent spectroscopy and first-principles band calculation studies. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 5156–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Han, L. Preparation and characterization of sulfur-doped TiO2/Ti photoelectrodes and their photoelectrocatalytic performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, X. A visible light response TiO2 photocatalyst realized by cationic S-doping and its application for phenol degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengifo-Herrera, J.A.; Pierzchala, K.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Forro, L.; Kiwi, J.; Moser, J.E.; Pulgarin, C. Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Activities of Nanoparticulate N, S-Codoped TiO2 Having Different Surface-to-Volume Ratios. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, Y.; Xing, M.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J. Improving the visible light photocatalytic activity of nano-sized titanium dioxide via the synergistic effects between sulfur doping and sulfation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115–116, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, N.; Vaimakis, T.; Petrakis, D.; Hishita, S.; Boukos, N.; Giannakopoulou, T.; Giannouri, M.; Antiohos, S.; Papageorgiou, D.; Chaniotakis, E.; et al. N and N, S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts and their activity in NOx oxidation. Catal. Today 2013, 209, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Dong, X.L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.F.; Ma, H.C. Improved Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity for TiO2 Nanomaterials by Codoping with Zinc and Sulfur. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravanzola, S.; Cesano, F.; Gaziano, F.; Scarano, D. Sulfur-Doped TiO2: Structure and Surface Properties. Catalysts 2017, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olowoyo, J.O.; Kumar, M.; Jain, S.L.; Shen, S.H.; Zhou, Z.H.; Mao, S.S.; Vorontsov, A.V.; Kumar, U. Reinforced photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to fuel by efficient S-TiO2: Significance of sulfur doping. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 17682–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, B.; Matoh, L.; Carraro, G.; Miljevic, B.; Korosec, R.C. Sulfur-, nitrogen- and platinum-doped titania thin films with high catalytic efficiency under visible-light illumination. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.Y.; Sun, H.Z.; Zhang, J.B.; Guo, Y.B.; Kuo, D.H. Cationic S-doped TiO2/SiO2 visible-light photocatalyst synthesized by co-hydrolysis method and its application for organic degradation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Akiyoshi, M.; Umebayashi, T.; Asai, K.; Mitsui, T.; Matsumura, M. Preparation of S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 265, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, A.U.; Mastoi, N.R.; Aslam, M.; Kim, J. Photocatalytic systems as an advanced environmental remediation: Recent developments, limitations and new avenues for applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4143–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, A.S.; Carvalho, A.P. Photocatalytic Degradation of Pharmaceuticals Carbamazepine, Diclofenac, and Sulfamethoxazole by Semiconductor and Carbon Materials: A Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovačić, M.; Perović, K.; Papac, J.; Tomić, A.; Matoh, L.; Žener, B.; Brodar, T.; Capan, I.; Surca, A.K.; Kušić, H.; et al. One-Pot Synthesis of Sulfur-Doped TiO2/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite (S-TiO2/rGO) with Improved Photocatalytic Activity for the Removal of Diclofenac from Water. Materials 2020, 13, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.Z.; Clark, L.A.; Yang, Q.; Anderson, M.A. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of titania-based binary metal oxides: TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/ZrO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannouri, M.; Kalampaliki, T.; Todorova, N.; Giannakopoulou, T.; Boukos, N.; Petrakis, D.; Vaimakis, T.; Trapalis, C. One-Step Synthesis of TiO2/Perlite Composites by Flame Spray Pyrolysis and Their Photocatalytic Behavior. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 729460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, D.; Serrano-Garcia, R.; Govan, J.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Synthesis Characterization and Photocatalytic Studies of Cobalt Ferrite-Silica-Titania Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sulym, I.; Goncharuk, O.; Sternik, D.; Skwarek, E.; Derylo-Marczewska, A.; Janusz, W.; Gun’ko, V.M. Silica-Supported Titania-Zirconia Nanocomposites: Structural and Morphological Characteristics in Different Media. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regalado-Raya, R.; Romero-Romero, R.; Aviles-Garcia, O.; Espino-Valencia, J. Synthesis and Characterization of TiO2/SiO2 Monoliths as Photocatalysts on Methanol Oxidation. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 8478240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.G.; Wang, G.W.; Sun, G.; Xu, F.; Li, H.M.; Li, S.; Fu, S. Facile synthesis of SiO2@TiO2 hybrid NPs with improved photocatalytic performance. Micro Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, D.; Blosi, M.; Delpivo, C.; Ortelli, S.; Costa, A.L. Silica-coating as protective shell for the risk management of nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 429, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortelli, S.; Poland, C.A.; Baldi, G.; Costa, A.L. Silica matrix encapsulation as a strategy to control ROS production while preserving photoreactivity in nano-TiO2. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortelli, S.; Costa, A.L. Nanoencapsulation techniques as a “safer by (molecular) design” tool. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 13, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengalli, R.; Ortelli, S.; Blosi, M.; Costa, A.; Mantecca, P.; Fiandra, L. In Vitro Toxicity of TiO2:SiO2 Nanocomposites with Different Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortelli, S.; Costa, A.L.; Matteucci, P.; Miller, M.R.; Blosi, M.; Gardini, D.; Tofail, S.A.M.; Tran, L.; Tonelli, D.; Poland, C.A. Silica modification of titania nanoparticles enhances photocatalytic production of reactive oxygen species without increasing toxicity potential in vitro. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40369–40377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simeone, F.C.; Blosi, M.; Ortelli, S.; Costa, A.L. Assessing occupational risk in designs of production processes of nano-materials. Nanoimpact 2019, 14, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Escalante, K.E. SiO2@TiO2 Composite Synthesis and Its Hydrophobic Applications: A Review. Catalysts 2020, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akpan, U.G.; Hameed, B.H. Parameters affecting the photocatalytic degradation of dyes using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbod, M.; Khademalrasool, M. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by a combined sol-gel ball milling method and investigation of nanoparticle size effect on their photocatalytic activities. Powder Technol. 2011, 214, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livage, J.; Sanchez, C. Sol-gel chemistry. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1992, 145, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10678:2010. Fine Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics—Determination of Photocatalytic Activity of Surfaces in an Aqueous Medium by degrAdation of Methylene Blue; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 22197-1:2007. Fine Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics—Test Method for Air-Purification Performance of Semiconducting Photocatalytic Materials—Part 1: Removal of Nitric Oxide; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 22197-2:2011. Fine Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics—Test Method for Air-Purification Performance of Semiconducting Photocatalytic Materials—Part 2: Removal of Acetaldehyde; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, A.; Hill, C.; Robertson, P.K.J. Overview of the current ISO tests for photocatalytic materials. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2012, 237, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeissa, E.S. Synthesis and characterization of sulfur-titanium dioxide nanocomposites for photocatalytic oxidation of cyanide using visible light irradiation. Chin. J. Cat. 2015, 36, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Chan, K.-Y. Synthesis of titania–silica mixed oxide mesoporous materials, characterization and photocatalytic properties. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 284, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randeniya, L.K.; Murphy, A.B.; Plumb, I.C. A study of S-doped TiO2 for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation from water. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umebayashi, T.; Yamaki, T.; Itoh, H.; Asai, K. Band gap narrowing of titanium dioxide by sulfur doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, S.; Ribeiro, C. Rapid and morphology controlled synthesis of anionic S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts for the visible-light-driven photodegradation of organic pollutants. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36516–36527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Ma, J.; Li, K.; Li, J. Hydrothermal synthesis of S-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic ability for degradation of methyl orange. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.A.; Ribeiro, C. A comparative run for visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of anionic and cationic S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: A case study of possible sulfur doping through chemical protocol. J. Mol. Cat. A Chem. 2016, 421, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballari, M.M.; Hunger, M.; Husken, G.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Modelling and experimental study of the NOx photocatalytic degradation employing concrete pavement with titanium dioxide. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | dXRD [a] | SSAcalc [b] | SSAexp [c] | VP[d] | Pore Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (nm) | (m2 gr−1) | (m2 gr−1) | (cm3 g−1) | (nm) | |
| TiO2 | 20 | 78 | 60 | 0.198 | 7.85 |
| TiO2/SiO2 | 7.6 | 206 | 195 | 0.315 | 4.67 |
| S(4)-TiO2/SiO2 | 6.7 | 233 | 195 | 0.277 | 3.67 |
| Sample | Eg1 | Eg2 |
|---|---|---|
| (eV) | (eV) | |
| TiO2 | 3.11 | - |
| TiO2/SiO2 | 3.17 | - |
| S(2)-TiO2/SiO2 | 3.08 | 2.33 |
| S(4)-TiO2/SiO2 | 3.07 | 2.29 |
| S(6)-TiO2/SiO2 | 3.04 | 2.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalampaliki, T.; Makri, S.P.; Papadaki, E.; Grigoropoulos, A.; Zoikis Karathanasis, A.; Deligkiozi, I. Visible-Light Active Sulfur-Doped Titania Nanoparticles Immobilized on a Silica Matrix: Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Degradation of Pollutants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102543
Kalampaliki T, Makri SP, Papadaki E, Grigoropoulos A, Zoikis Karathanasis A, Deligkiozi I. Visible-Light Active Sulfur-Doped Titania Nanoparticles Immobilized on a Silica Matrix: Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Degradation of Pollutants. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102543
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalampaliki, Theodora, Sofia P. Makri, Evanthia Papadaki, Alexios Grigoropoulos, Alexandros Zoikis Karathanasis, and Ioanna Deligkiozi. 2021. "Visible-Light Active Sulfur-Doped Titania Nanoparticles Immobilized on a Silica Matrix: Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Degradation of Pollutants" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102543
APA StyleKalampaliki, T., Makri, S. P., Papadaki, E., Grigoropoulos, A., Zoikis Karathanasis, A., & Deligkiozi, I. (2021). Visible-Light Active Sulfur-Doped Titania Nanoparticles Immobilized on a Silica Matrix: Synthesis, Characterization and Photocatalytic Degradation of Pollutants. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2543. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102543







