Core-Shell Nano-Antenna Configurations for Array Formation with More Stability Having Conventional and Non-Conventional Directivity and Propagation Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials, Design and Analysis
2.1. Planewave Excitation
2.2. Model of Active Spherical Coated Nanoparticles
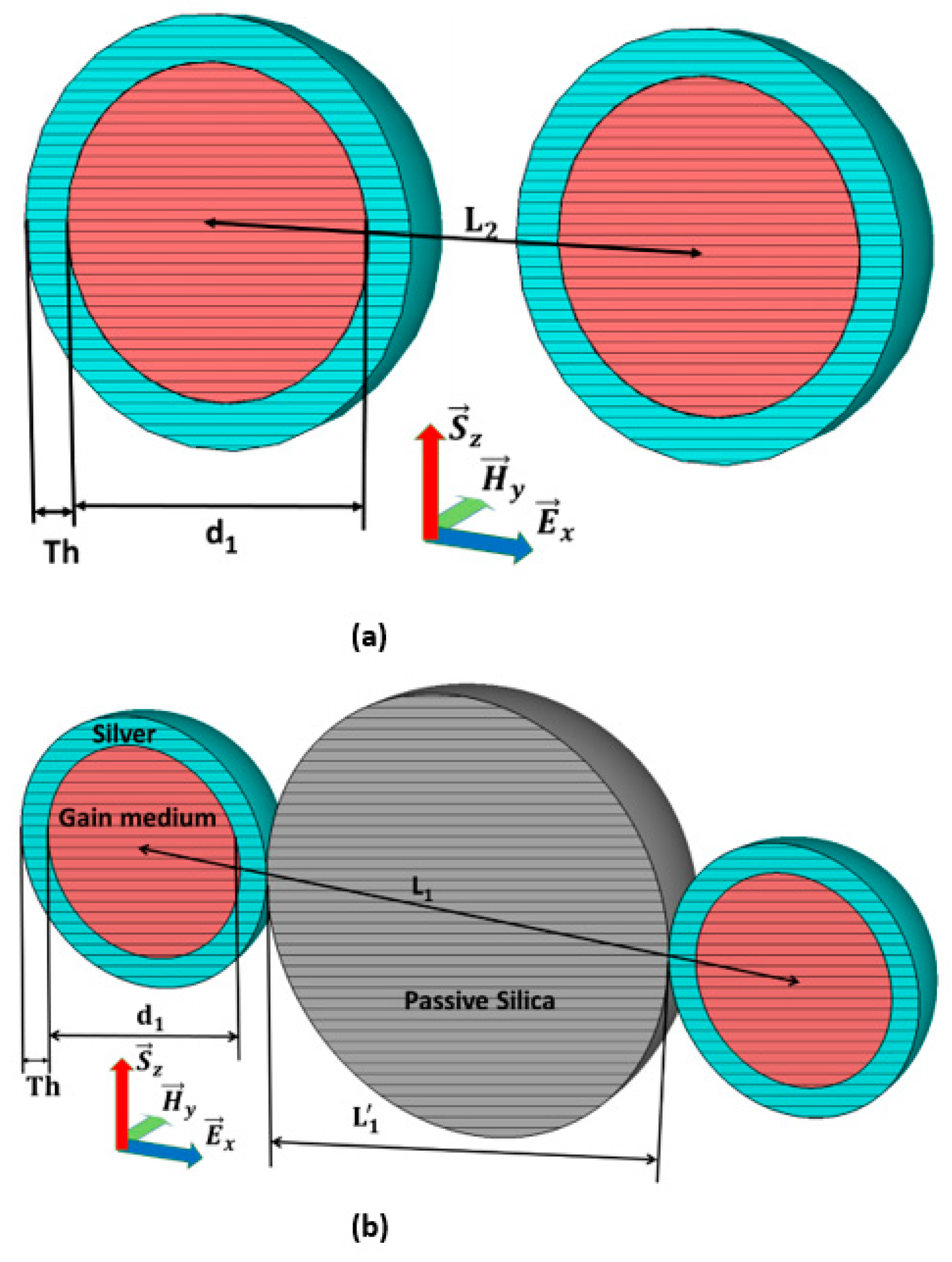
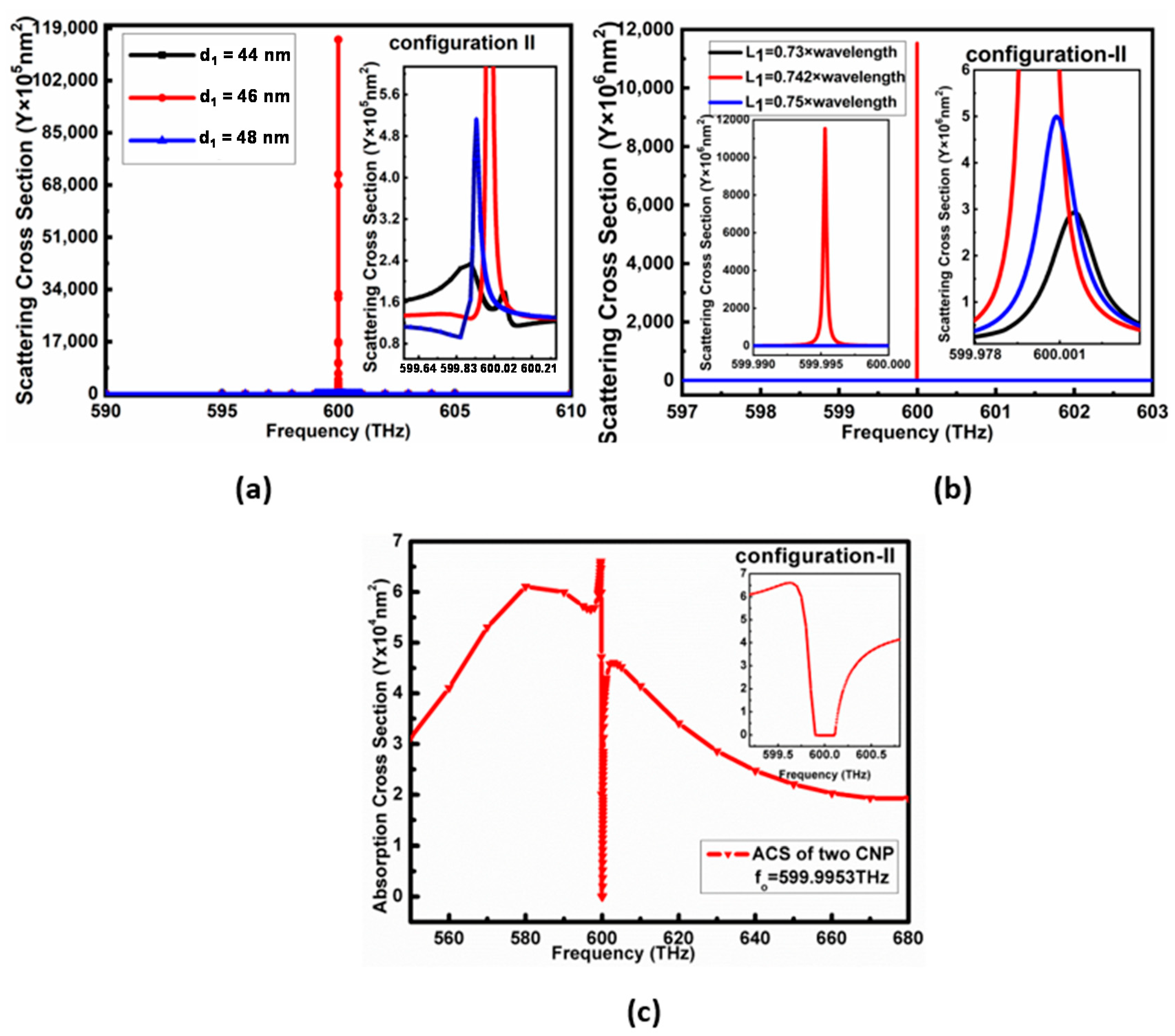
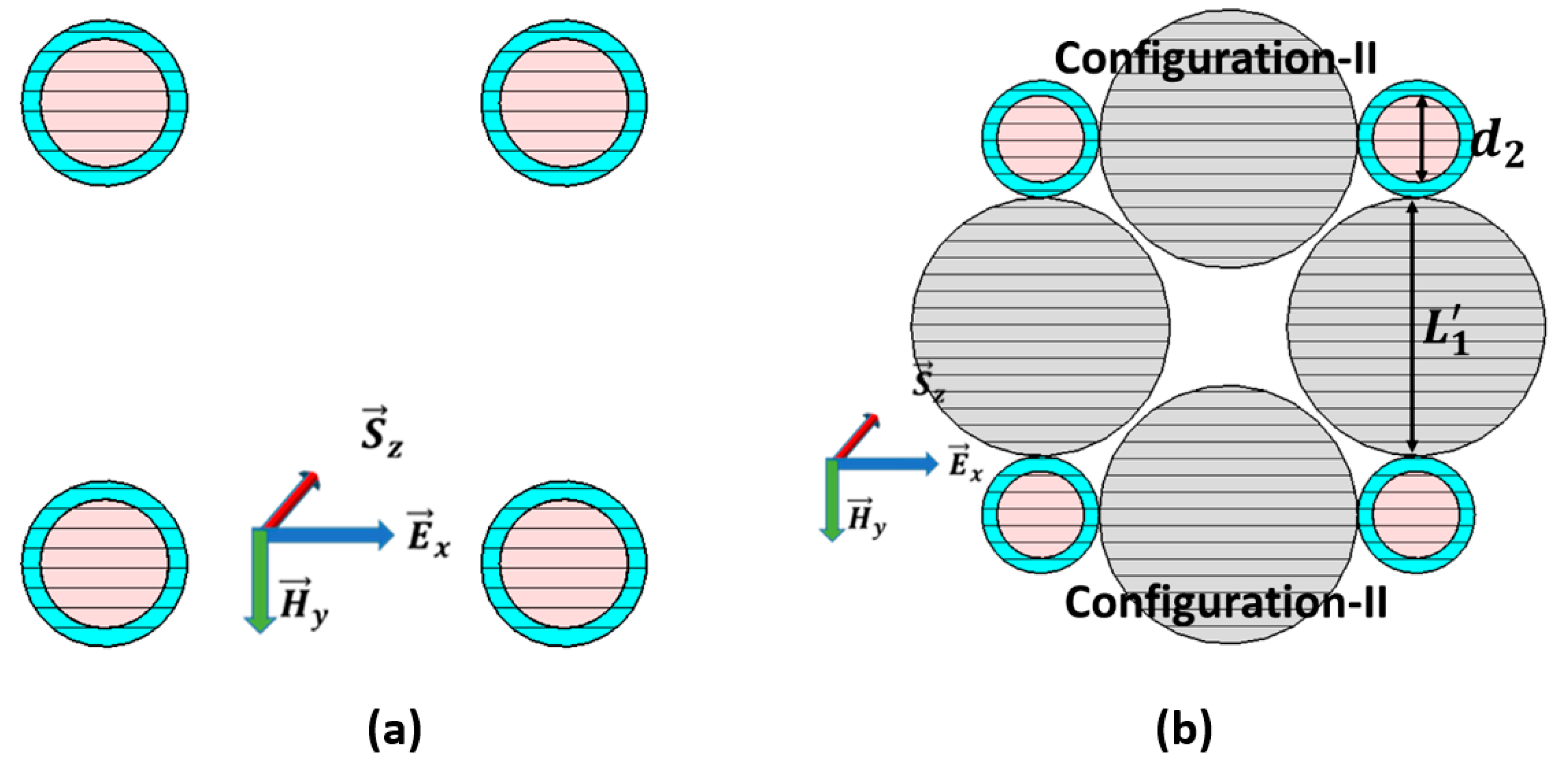
2.3. The Configuration-I from the Basic Model of the Double CNPs
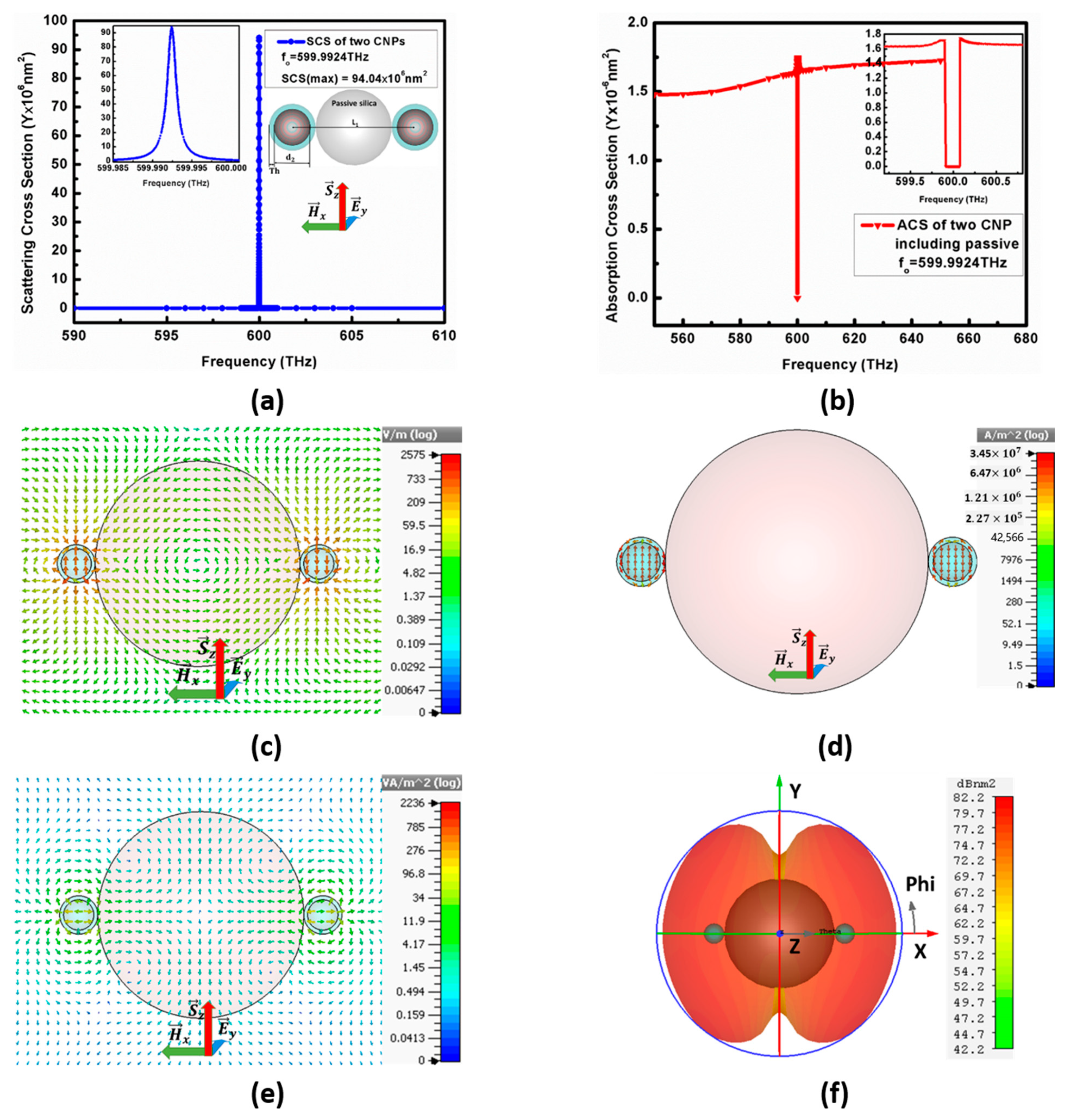
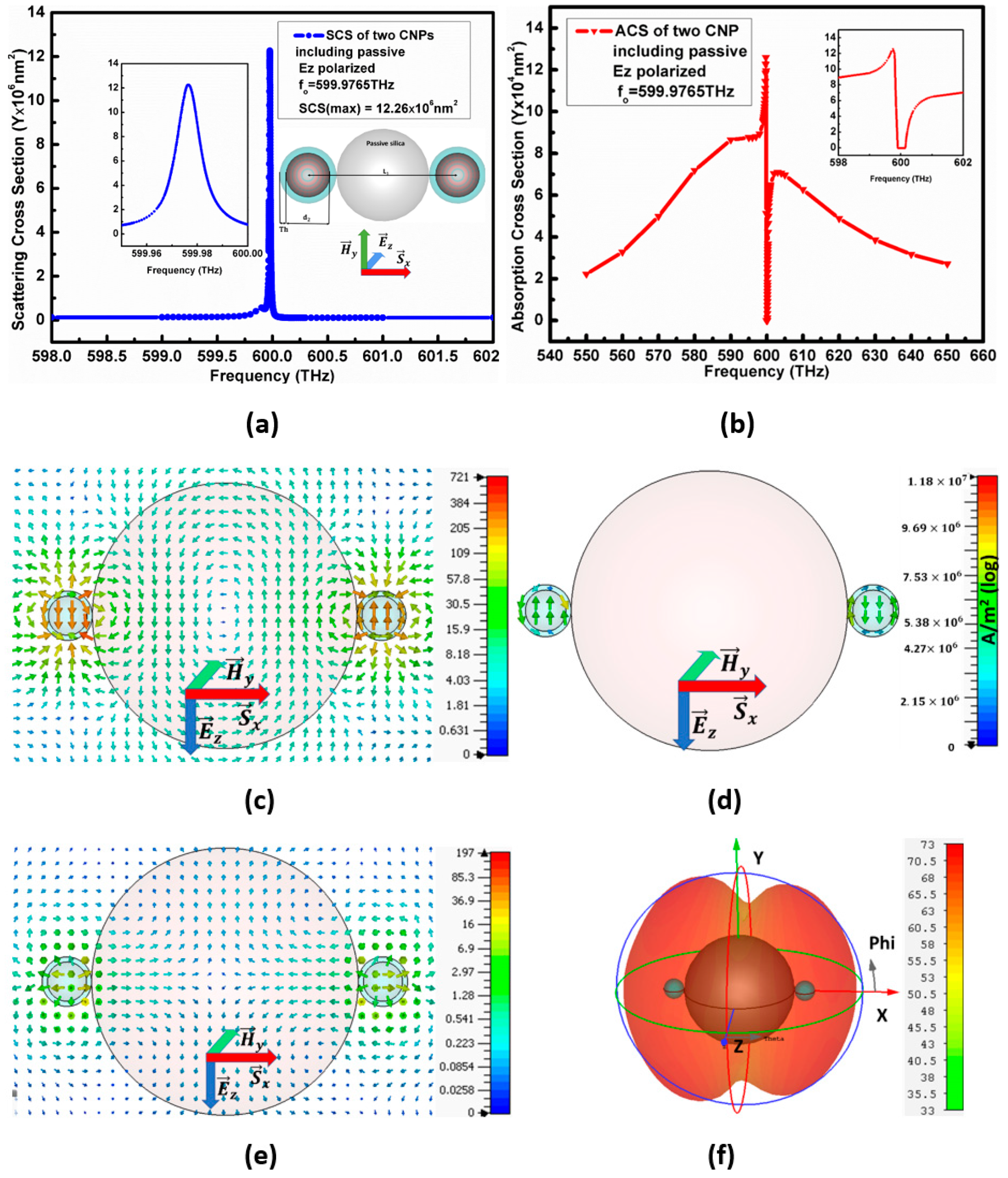
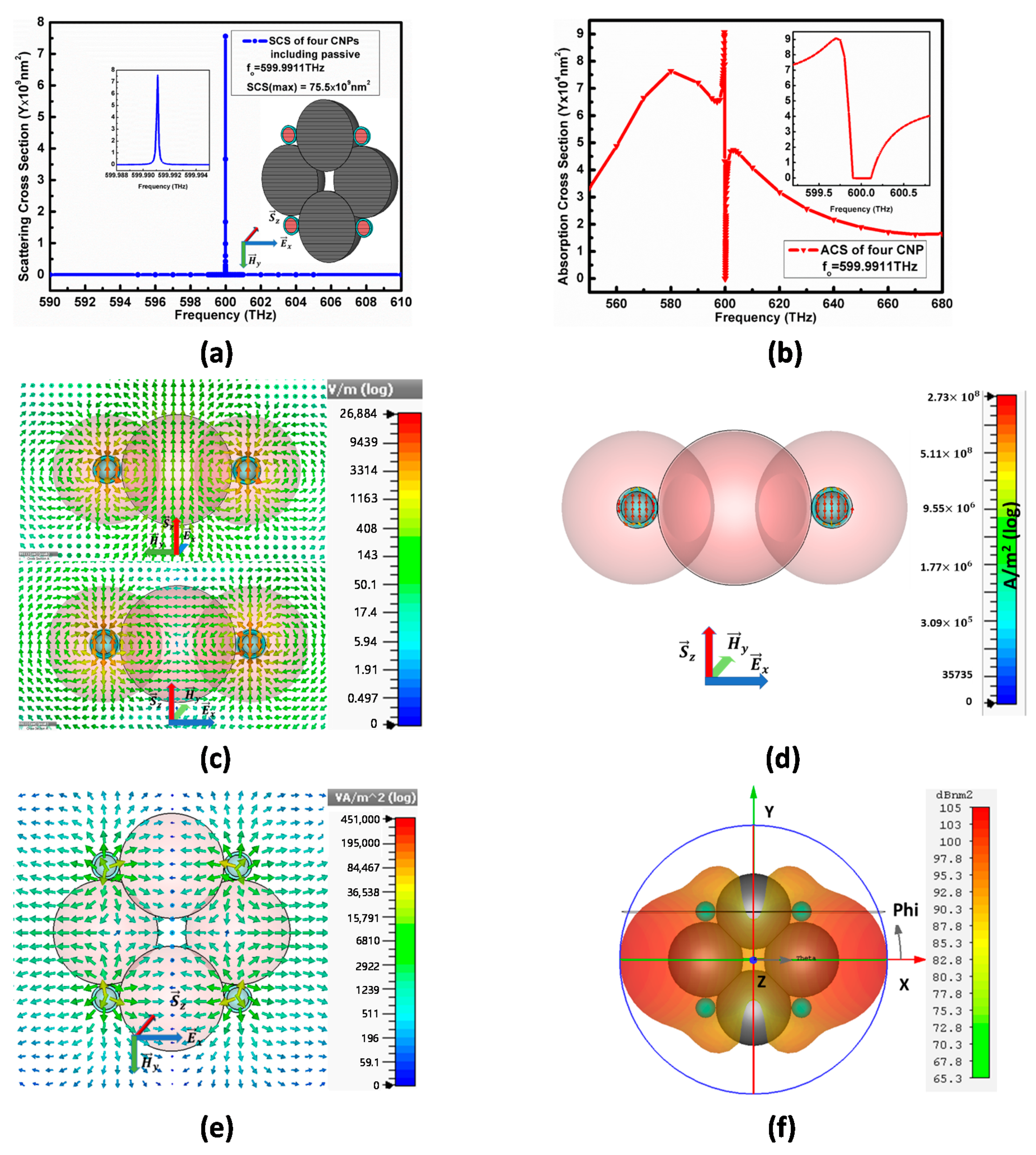
2.4. The Configuration-II from Double CNPs and Passive Nano-Spheres
3. Analysis of 2-CNP Array Unit Configurations
3.1. Polarization Plane Wave Incident
3.2. Polarized Configuration II
3.3. Polarized Plane-Wave Excitation Propagating along the x-Axis
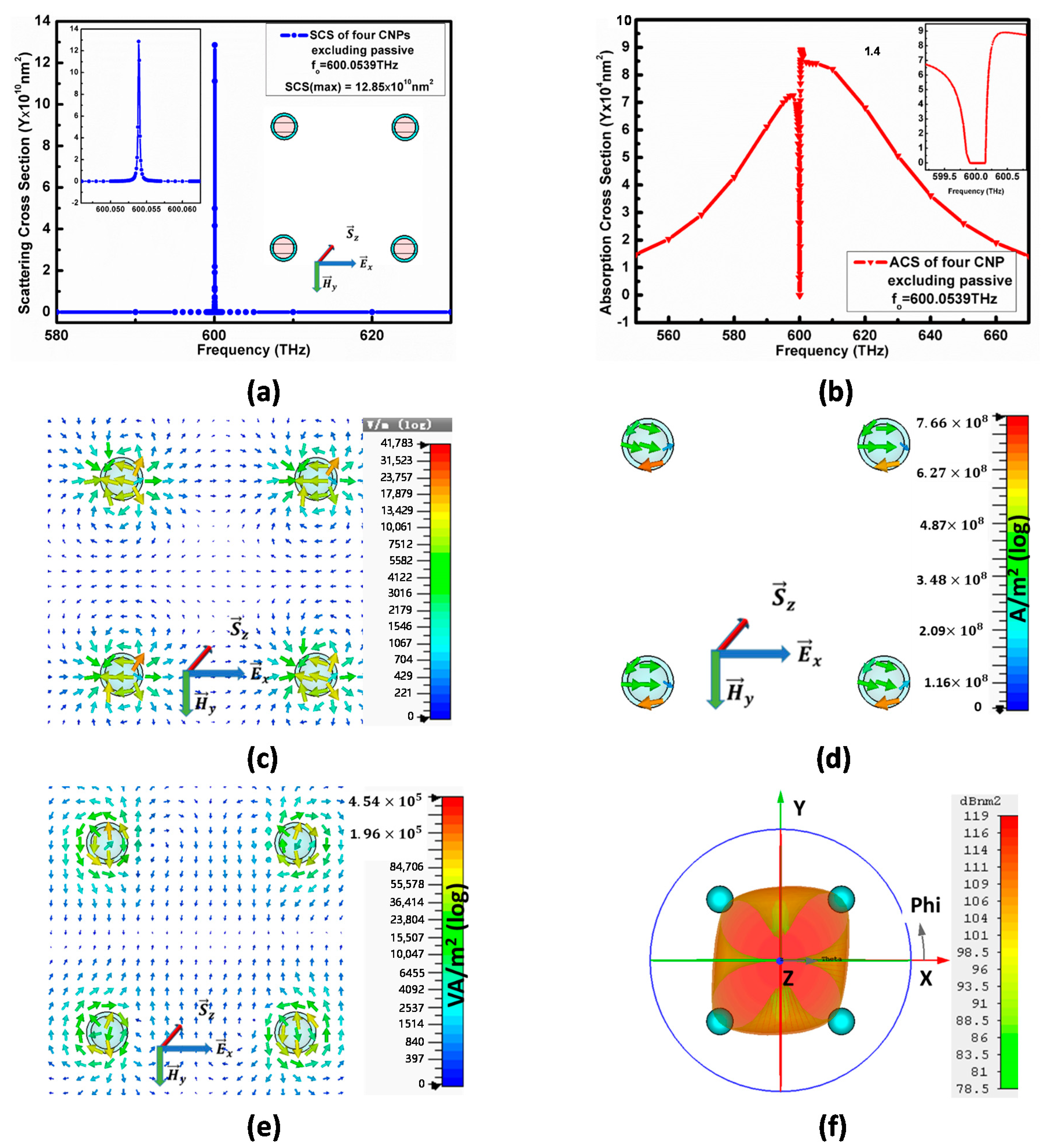
4. Comparison of Possible 4-CNP Array Models
4.1. Excitation of Model-I by Polarized Plane-Wave
4.2. Analysis of Array Model II Excited by Polarized Plane-Wave
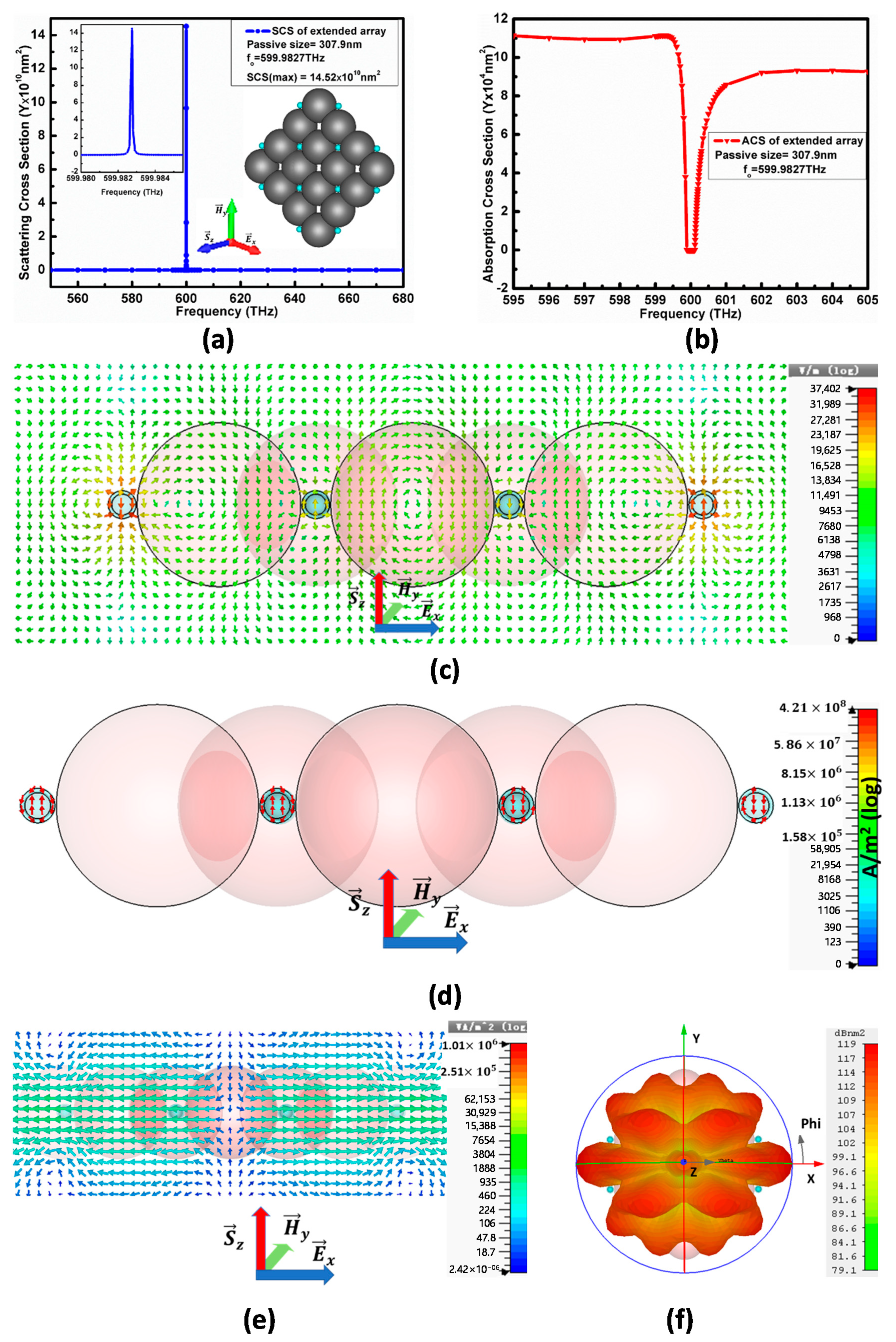
5. Extended Array of Model-II to 12 A-CNPs
Variation in Scattering Direction and Directivity at Nearby Frequencies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stockman, M.I. Nanoplasmonics: Past, present, and glimpse into future. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 22029–22106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaratne, M.; Agrawal, G.P. Light Propagation in Gain Media: Optical Amplifiers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Noble Metals on the Nanoscale: Optical and Photothermal Properties and Some Applications in Imaging, Sensing, Biology, and Medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catchpole, K.R.; Polman, A. Plasmonic solar cells. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 21793–21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Neshev, D.N.; Kivshar, Y.S. Broadband Unidirectional Scattering by Magneto-Electric Core-Shell Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5489–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Susha, A.; Caruso, F. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Core-Shell and Hollow Spheres and Ordered Assemblies Thereof. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hori, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Nogami, M. Self-assembled 3-dimensional arrays of Au@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles for enhanced optical nonlinearities. Surf. Sci. 2005, 579, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chim, W.-K. Highly Ordered Arrays of Metal/Semiconductor Core-Shell Nanoparticles with Tunable Nanostructures and Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.U.; Geng, J.; Ziolkowski, R.W.; Hang, T.; Hayat, Q.; Liang, X.; Rehman, S.U.; Jin, R. Photoluminescence Revealed Higher Order Plasmonic Resonance Modes and Their Unexpected Frequency Blue Shifts in Silver-Coated Silica Nanoparticle Antennas. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockman, M.I. The spaser as a nanoscale quantum generator and ultrafast amplifier. J. Opt. 2010, 12, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alù, A.; Engheta, N. Polarizabilities and effective parameters for collections of spherical nanoparticles formed by pairs of concentric double-negative, single-negative, and/or double-positive metamaterial layers. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 094310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alù, A.; Engheta, N. Polarizabilities and effective parameters for collection of spherical nano-particles containing concentric double-negative or single-negative shells. In Proceedings of the 2004 URSI International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory, Pisa, Italy, 23–27 May 2004; pp. 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Premaratne, M.; Gunapala, S.D.; Agrawal, G.P.; Stockman, M.I. Quasi-static analysis of controllable optical cross-sections of a layered nanoparticle with a sandwiched gain layer. J. Opt. 2014, 16, 075003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ziolkowski, R.W.; Jin, R.; Liang, X. Numerical Study of the Near-Field and Far-Field Properties of Active Open Cylindrical Coated Nanoparticle Antennas. IEEE Photonics J. 2011, 3, 1093–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanagić, S.; Ziolkowski, R.W. Active coated nano-particle excited by an arbitrarily located electric Hertzian dipole—Resonance and transparency effects. J. Opt. 2010, 12, 024014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.A.; Ziolkowski, R.W. CNP optical metamaterials. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 6692–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.A.; Ziolkowski, R.W. The design and simulated performance of a coated nano-particle laser. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 2622–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Salandrino, A.; Engheta, N. Shaping light beams in the nanometer scale: A Yagi-Uda nanoantenna in the optical domain. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 245403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirin, N.A.; Ali, T.A.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Perforated semishells: Far-field directional control and optical frequency magnetic response. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2701–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Crozier, K.B. Optical antennas integrated with concentric ring gratings: Electric field enhancement and directional radiation. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Gan, L.; Li, Z.-Y. Efficient surface plasmon amplification from gain-assisted gold nanorods. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, Q.; Geng, J.; Liang, X.; Jin, R.; He, C. Manipulation of Polarization Rotation through Spherical Active Coated Nanoparticle Antenna at Optical Wavelength. In Proceedings of the 2019 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Fall (PIERS-Fall), Xiamen, China, 17–20 December 2019; pp. 1015–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, Q.; Geng, J.; Liang, X.; Jin, R.; Hayat, K.; He, C. Subwavelength plasmonic nanoantenna as a Plasmonic Induced Polarization Rotator (PI-PR). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, B.-Z. A novel wideband antenna with reconfigurable broadside and endfire patterns. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanagic, S.; Ziolkowski, R.W. Cylindrical and Spherical Active Coated Nanoparticles as Nanoantennas: Active Nanoparticles as Nanoantennas. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2017, 59, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanagic, S.; Ziolkowski, R.W. Active coated nanoparticles: Impact of plasmonic material choice. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 103, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Array of Two A-CNPs Excluding Dielectric f0 = 600.0195 THz | Array of Two A-CNPs Including Dielectric f0 = 599.9953 THz | Array of Two A-CNPs Including Dielectric ( Polarized) f0 = 599.9924 THz | Array of Two A-CNPs Including Dielectric ( Polarized) f0 = 599.9765 THz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCS (Max) | ||||
| RCS (Far Field) | ||||
| E field (Near field) | ||||
| Power Flow | ||||
| Rotation of electric field |
| Parameters | Array of Two A-CNPs Excluding Dielectric ( Polarized) f0 = 600.0195 THz | Array of Four A-CNPs Excluding Dielectric ( Polarized) f0 = 600.0539 THz | Array of Two A-CNPs Including Dielectric ( Polarized) f0 = 599.9953 THz | Array of Four A-CNPs Including Dielectric ( Polarized) f0 = 599.9911 THz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCS (Max) | ||||
| RCS(Far Field) | ||||
| E field (Near field) | ||||
| Power Flow | ||||
| Rotation of electric field |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayat, Q.; Geng, J.; Liang, X.; Jin, R.; Ur Rehman, S.; He, C.; Wu, H.; Nawaz, H. Core-Shell Nano-Antenna Configurations for Array Formation with More Stability Having Conventional and Non-Conventional Directivity and Propagation Behavior. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010099
Hayat Q, Geng J, Liang X, Jin R, Ur Rehman S, He C, Wu H, Nawaz H. Core-Shell Nano-Antenna Configurations for Array Formation with More Stability Having Conventional and Non-Conventional Directivity and Propagation Behavior. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010099
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayat, Qaisar, Junping Geng, Xianling Liang, Ronghong Jin, Sami Ur Rehman, Chong He, Haobo Wu, and Hamza Nawaz. 2021. "Core-Shell Nano-Antenna Configurations for Array Formation with More Stability Having Conventional and Non-Conventional Directivity and Propagation Behavior" Nanomaterials 11, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010099
APA StyleHayat, Q., Geng, J., Liang, X., Jin, R., Ur Rehman, S., He, C., Wu, H., & Nawaz, H. (2021). Core-Shell Nano-Antenna Configurations for Array Formation with More Stability Having Conventional and Non-Conventional Directivity and Propagation Behavior. Nanomaterials, 11(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010099






