Effect of Temperature and Branched Crosslinkers on Supported Graphene Oxide Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of GO and Fabrication of Supported GO Membranes
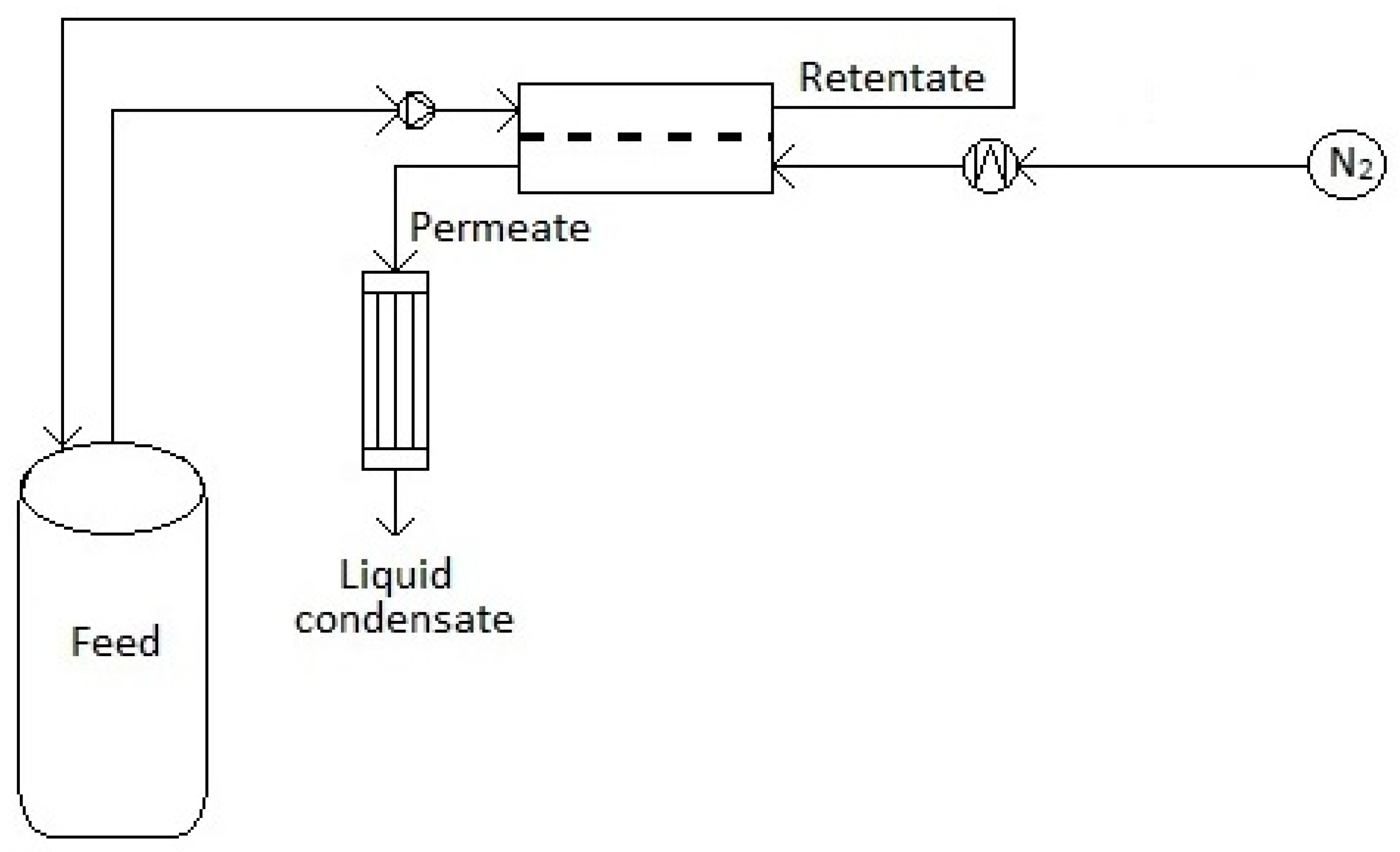
2.3. Cross-Flow Pervaporation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
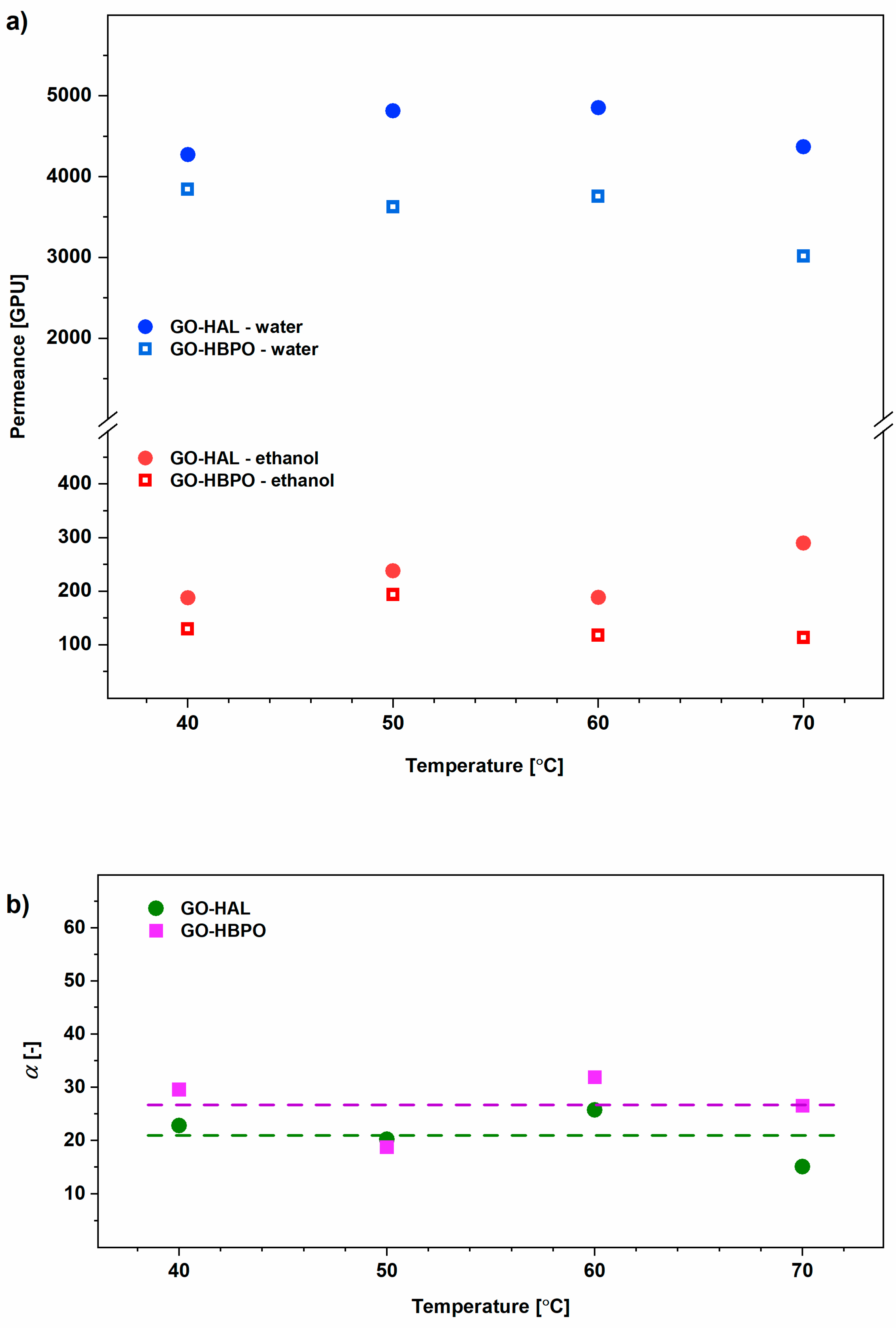
3.1. Pure Component Feed
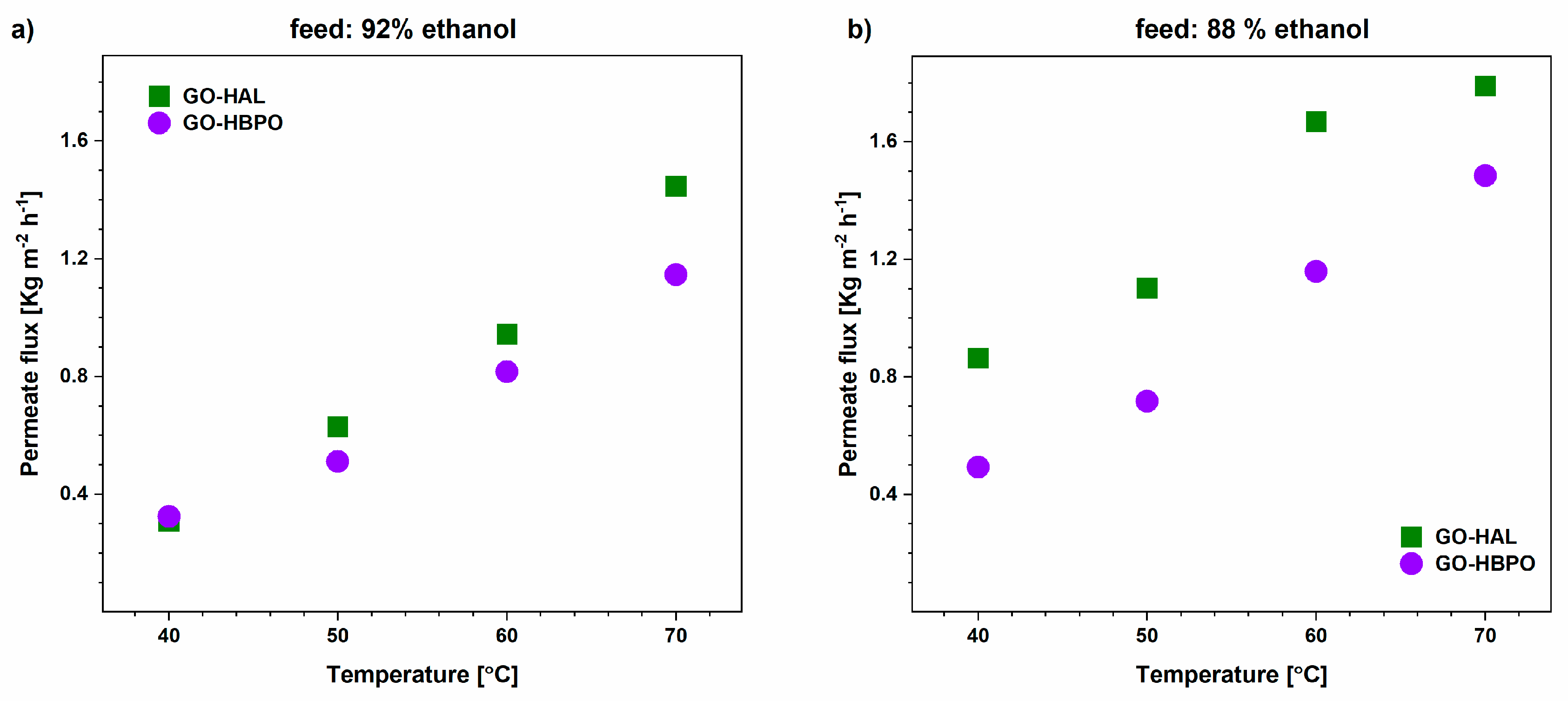
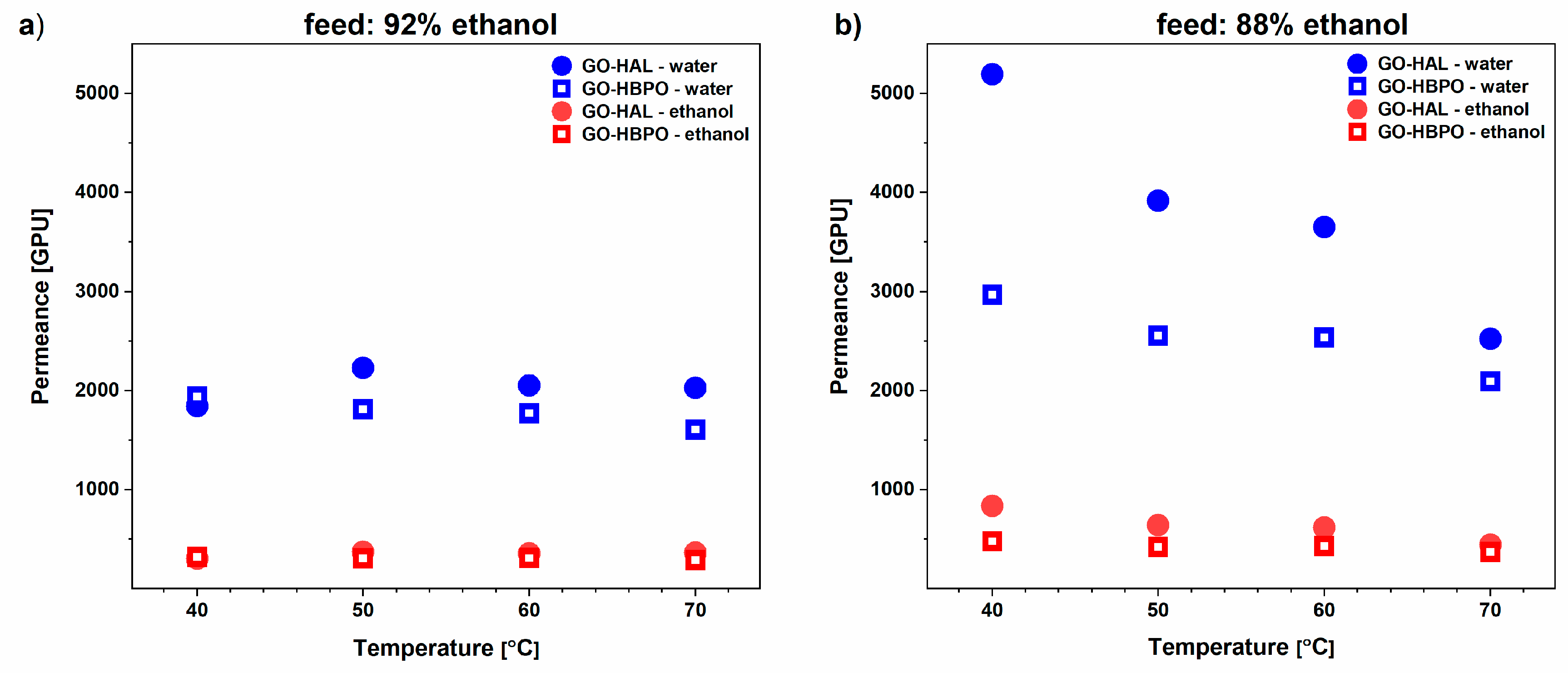
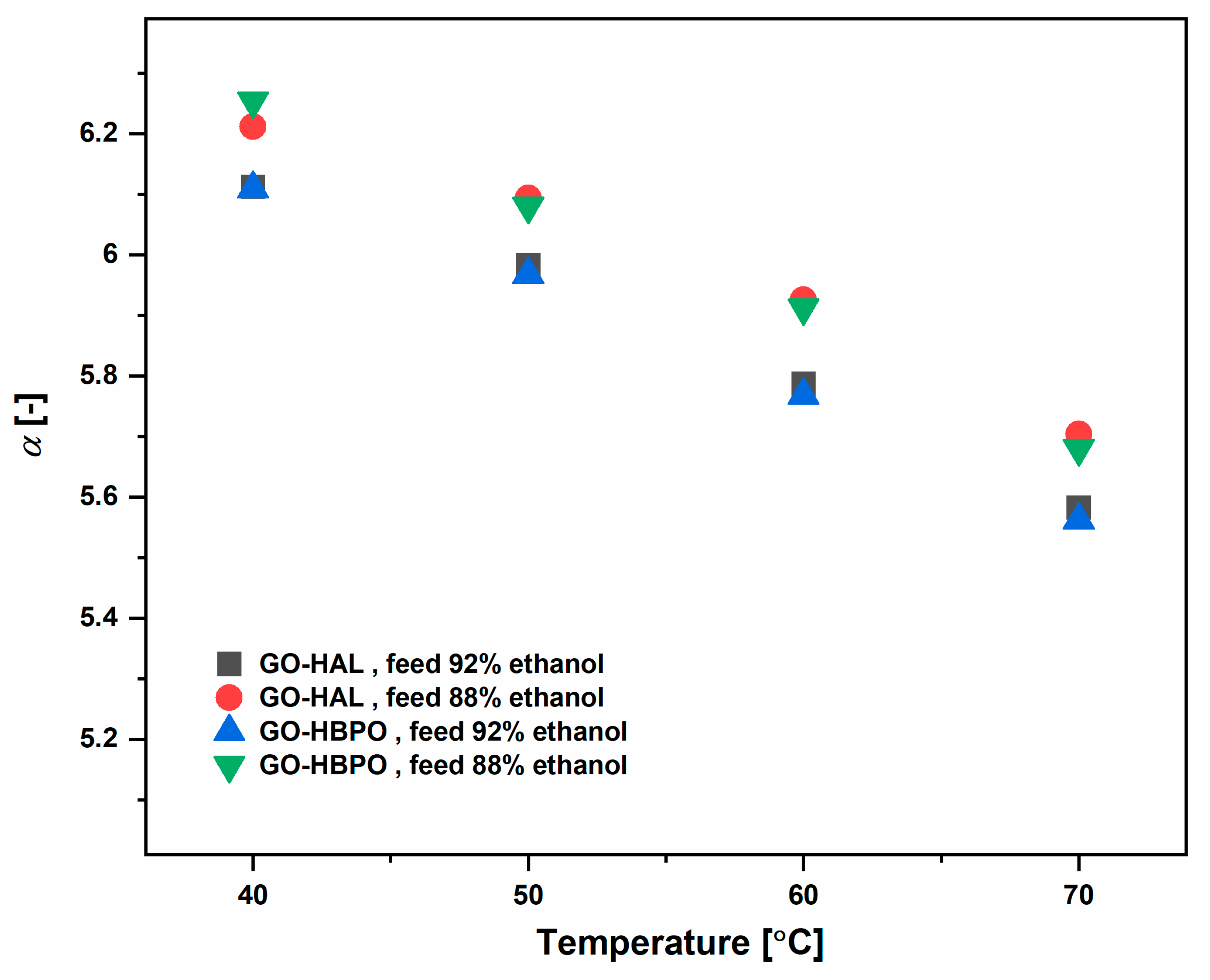
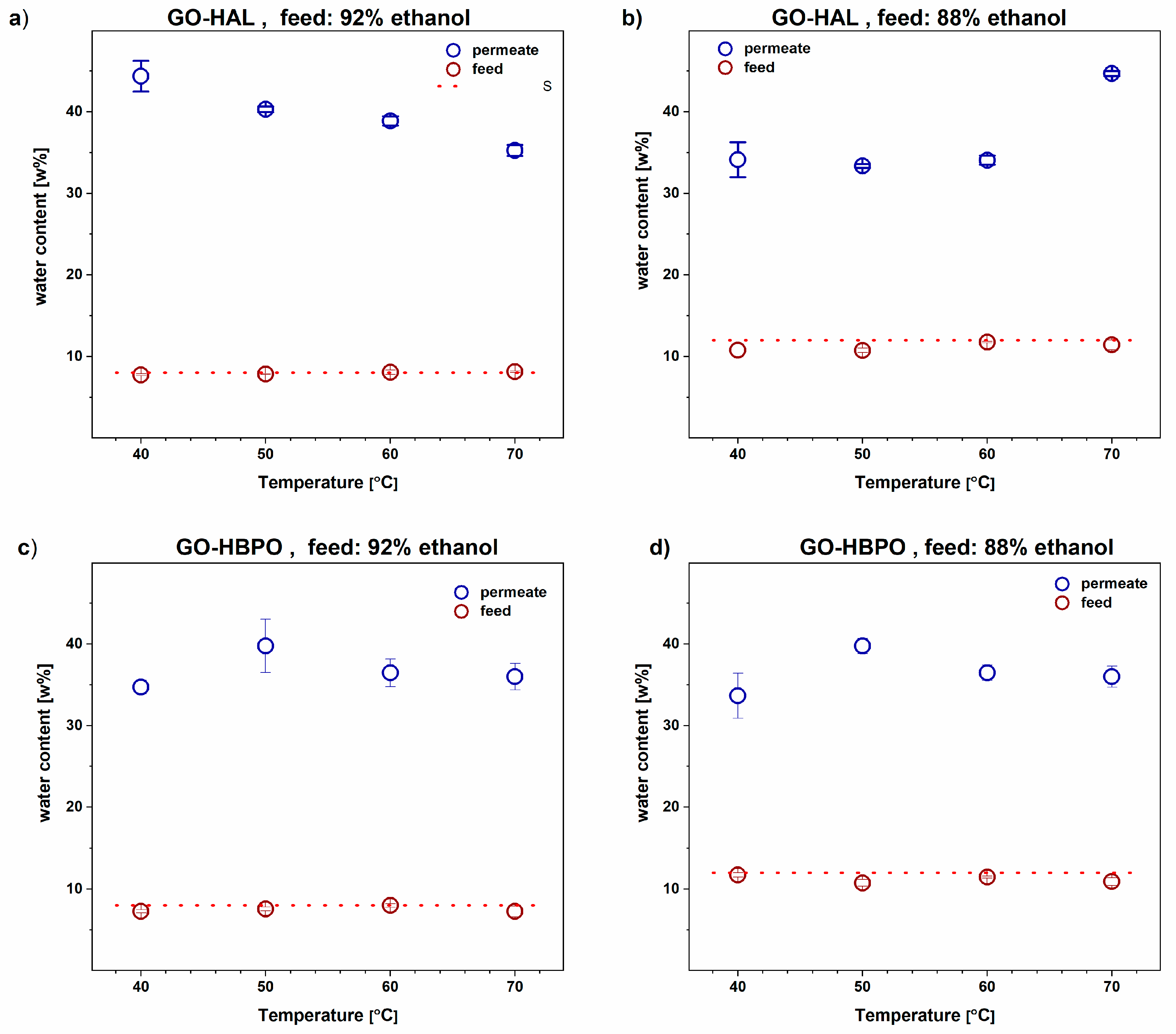
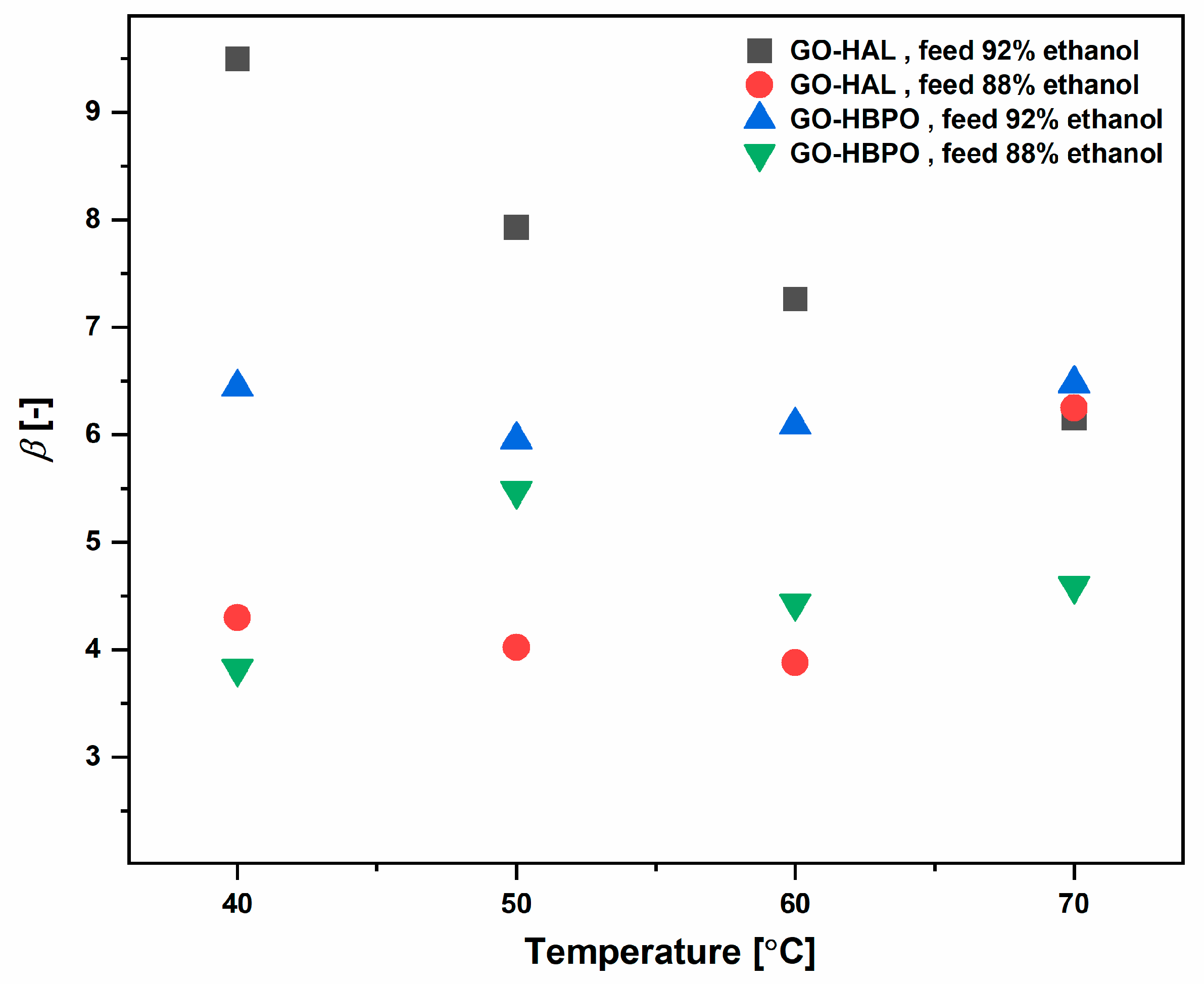
3.2. Ethanol–Water Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, D.P.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. A Mini Review on Renewable Sources for Biofuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.-K.; Hwang, K.-R.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.R.; Lee, J.-S. Recent Developments and Key Barriers to Advanced Biofuels: A Short Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.C.; Mi, L.; Pontrelli, S.; Luo, S. Fuelling the Future: Microbial Engineering for the Production of Sustainable Biofuels. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fivga, A.; Speranza, L.G.; Branco, C.M.; Ouadi, M.; Hornung, A. A Review on the Current State of the Art for the Production of Advanced Liquid Biofuels. AIMS Energy 2019, 7, 46–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Uma Maheswari, R.; Sikder, J.; Chakraborty, S.; da Silva, S.S.; dos Santos, J.C. Membranes as a Tool to Support Biorefineries: Applications in Enzymatic Hydrolysis, Fermentation and Dehydration for Bioethanol Production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, N.; Prasad, R. Anhydrous Ethanol: A Renewable Source of Energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1830–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabed, H.; Sahu, J.N.; Suely, A.; Boyce, A.N.; Faruq, G. Bioethanol Production from Renewable Sources: Current Perspectives and Technological Progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 475–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeyens, J.; Kang, Q.; Appels, L.; Dewil, R.; Lv, Y.; Tan, T. Challenges and Opportunities in Improving the Production of Bio-Ethanol. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 47, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, L.M. A Review of Pervaporation for Product Recovery from Biomass Fermentation Processes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 603–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.J.; Craig, J.C. Ethanol Production in a Continuous Fermentation/Membrane Pervaporation System. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 44, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ruckenstein, E. Pervaporation of Ethanol-Water Mixtures through Polydimethylsiloxane-Polystyrene Interpenetrating Polymer Network Supported Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 114, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Liang, L. Pervaporation of Ethanol-Water Mixtures through Polyvinyl Alcohol-Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Polymer Network Membranes Unsupported and Supported on Polyethersulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes: A Comparison. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 110, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenten, I.G.; Dharmawijaya, P.T.; Aryanti, P.T.P.; Mukti, R.R.; Khoiruddin. LTA Zeolite Membranes: Current Progress and Challenges in Pervaporation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29520–29539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.N.; Song, M.Y.; Chen, H.L. Preparation of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Sodium Alginate Hollow-Fiber Composite Membranes and Pervaporation Dehydration Characterization of Aqueous Alcohol Mixtures. Desalination 2006, 193, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guan, H.; lee Tan, W.; Qiao, X.-Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Pervaporation Study of Aqueous Ethanol Solution through Zeolite-Incorporated Multilayer Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Membranes: Effect of Zeolites. J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 276, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, L.M. Review: Membrane Materials for the Removal of Water from Industrial Solvents by Pervaporation and Vapor Permeation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, J.S.; Verbridge, S.S.; Alden, J.S.; van der Zande, A.M.; Parpia, J.M.; Craighead, H.G.; McEuen, P.L. Impermeable Atomic Membranes from Graphene Sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Wu, H.A.; Jayaram, P.N.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Unimpeded Permeation of Water Through Helium-Leak–Tight Graphene-Based Membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhvalov, D.W.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Son, Y.-W. Origin of Anomalous Water Permeation through Graphene Oxide Membrane. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3930–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobinski, L.; Lesiak, B.; Malolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Mierzwa, B.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Bieloshapka, I. Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Studied by the XRD, TEM and Electron Spectroscopy Methods. J. Electron. Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 2014, 195, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Some, S.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Yoo, H.; Lee, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, H. High-Quality Reduced Graphene Oxide by a Dual-Function Chemical Reduction and Healing Process. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimiev, A.M.; Alemany, L.B.; Tour, J.M. Graphene Oxide. Origin of Acidity, Its Instability in Water, and a New Dynamic Structural Model. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Zhou, S.; Hu, Y.; Acik, M.; Chabal, Y.J.; Berger, C.; de Heer, W.; Bongiorno, A.; Riedo, E. Room-Temperature Metastability of Multilayer Graphene Oxide Films. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Choi, M.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, Y.J. Facilitated Water Transport through Graphene Oxide Membranes Functionalized with Aquaporin-Mimicking Peptides. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Liang, F.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Jin, W. Incorporating Graphene Oxide into Alginate Polymer with a Cationic Intermediate to Strengthen Membrane Dehydration Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13903–13913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, C. High-Flux Graphene Oxide Nanofiltration Membrane Intercalated by Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8147–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Eftekhari, E.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Li, Q. Graphene Oxide Membranes with Tunable Permeability Due to Embedded Carbon Dots. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13089–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wang, Y. Covalently Crosslinked Graphene Oxide Membranes by Esterification Reactions for Ions Separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4405–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-S.; Tsou, C.-H.; De Guzman, M.; An, Q.-F.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Cross-Linking with Diamine Monomers to Prepare Composite Graphene Oxide-Framework Membranes with Varying d-Spacing. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chung, T.-S. Nanometric Graphene Oxide Framework Membranes with Enhanced Heavy Metal Removal via Nanofiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10235–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Rai, R.K.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Aldehyde Functionalized Graphene Oxide Frameworks as Robust Membrane Materials for Pervaporative Alcohol Dehydration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 161, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa, V.; Etmimi, H.; Mallon, P.E.; Tao, H.Z.; Magnacca, G.; Yue, Y.Z. Carbon-Based Building Blocks for Alcohol Dehydration Membranes with Disorder-Enhanced Water Permeability. Carbon 2017, 118, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Mi, B. Enabling Graphene Oxide Nanosheets as Water Separation Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Mi, B. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Graphene Oxide Membranes via Electrostatic Interaction. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 469, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Pu, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yang, H. An Effective Methanol-Blocking Membrane Modified with Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 117, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ma, S.; Yang, H.; Fan, S.; Lang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. A Graphene Oxide Membrane with Self-Regulated Nanochannels for the Exceptionally Stable Bio-Oil Dehydration. AIChE J. 2020, 66, e16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeynali, R.; Ghasemzadeh, K.; Sarand, A.B.; Kheiri, F.; Basile, A. Performance Evaluation of Graphene Oxide (GO) Nanocomposite Membrane for Hydrogen Separation: Effect of Dip Coating Sol Concentration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Liu, G.; Lou, Y.; Dong, Z.; Shen, J.; Jin, W. A Graphene Oxide Membrane with Highly Selective Molecular Separation of Aqueous Organic Solution. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6929–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Kravets, V.G.; Wong, S.L.; Waters, J.; Geim, A.K.; Nair, R.R. Impermeable Barrier Films and Protective Coatings Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.F.M.; Lin, Y.S. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide Membranes on Polyester Substrate by Spray Coating for Gas Separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 190, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, A.; Calzavarini, L.; Strunck, A.B.; Magnacca, G.; Boffa, V. Comparison of Chemical Cross-Linkers with Branched and Linear Molecular Structures for Stabilization of Graphene Oxide Membranes and Their Performance in Ethanol Dehydration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 18788–18797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Widjojo, N.; Shi, G.M.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C. Development of Flat-Sheet Membranes for C1–C4 Alcohols Dehydration via Pervaporation from Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone (SPPSU). J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hömmerich, U.; Rautenbach, R. Design and Optimization of Combined Pervaporation/Distillation Processes for the Production of MTBE. J. Memb. Sci. 1998, 146, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Wijmans, J.G.; Huang, Y. Permeability, Permeance and Selectivity: A Preferred Way of Reporting Pervaporation Performance Data. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 348, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, M.-B. Gas permeation: Permeability, permeance, and separation factor. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B. Pervaporation separation factor. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1509–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, M.-B. Gas Permeation Unit (GPU). In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; p. 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Cai, W.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, J. Preparation of Graphene Oxide/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Membrane and Pervaporation Performance for Ethanol Dehydration. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15457–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Taufique, M.F.N.; Devanathan, R.; Cutsforth, E.C.; Lee, J.; Liu, W.; Fifield, L.S.; Gotthold, D.W. Highly Selective Supported Graphene Oxide Membranes for Water-Ethanol Separation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, R.; Lohmann, J.; Gmehling, J. Vapor−Liquid Equilibria by UNIFAC Group Contribution. 6. Revision and Extension. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzière, S.; Launois, P.; Benito, A.M.; Maser, W.K.; Paineau, E. Unravelling the Hydration Mechanism in a Multi-Layered Graphene Oxide Paper by In-Situ X-Ray Scattering. Carbon 2018, 137, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Sundqvist, B.; Talyzin, A.V. Enormous Lattice Expansion of Hummers Graphite Oxide in Alcohols at Low Temperatures. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Buera-González, J.; de la Iglesia, O.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Malankowska, M.; Rubio, C.; Figoli, A.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Towards the Dehydration of Ethanol Using Pervaporation Cross-Linked Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 582, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Membrane | Crosslinker/GO (w/w) | Interlayer Spacing (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| GO | - | 6.55 |
| GO-HBPO | 0.2 | 7.93 |
| GO-HAL | 0.4 | 6.21 |
| GO-PEG | 10 | 12.42 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo Strunck, A.; Suri, A.; Boffa, V. Effect of Temperature and Branched Crosslinkers on Supported Graphene Oxide Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081571
Bo Strunck A, Suri A, Boffa V. Effect of Temperature and Branched Crosslinkers on Supported Graphene Oxide Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(8):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081571
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo Strunck, Azeem, Anil Suri, and Vittorio Boffa. 2020. "Effect of Temperature and Branched Crosslinkers on Supported Graphene Oxide Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration" Nanomaterials 10, no. 8: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081571
APA StyleBo Strunck, A., Suri, A., & Boffa, V. (2020). Effect of Temperature and Branched Crosslinkers on Supported Graphene Oxide Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration. Nanomaterials, 10(8), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10081571







