Size-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Graphene Oxide Nanosheets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of GO
2.3. Synthesis of GO with Different Lateral Sizes
2.4. Synthesis of GO–Ag NPs with Different Latteral Sizes of GO
2.5. Characterizations
2.6. Antibacterial Test
2.6.1. Time-Dependent Antibacterial Activity Assay
2.6.2. Bacterial Morphology of GO and GO–Ag NP Treatments
2.6.3. Live/Dead Cell Assay
2.6.4. Reactive Oxygen Species
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GO with Different Sizes
3.2. Characterizations of GO–Ag NPs Corresponding to Different Sizes of GO
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of GO with Different Sizes
3.4. Antibacterial Activity of GO–Ag NPs with Different GO Sizes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayukekbong, J.A.; Ntemgwa, M.; Atabe, A.N. The threat of antimicrobial resistance in developing countries: Causes and control strategies. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí, M.; Frígols, B.; Serrano-Aroca, A. Antimicrobial Characterization of Advanced Materials for Bioengineering Applications. J Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, 57710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matharu, R.K.; Ciric, L.; Edirisinghe, M. Nanocomposites: Suitable alternatives as antimicrobial agents. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 282001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.K.A.; Ahmed, D.S.; Mohammad, M.R. Studying antimicrobial activity of carbon nanotubes decorated with metal-doped ZnO hybrid materials. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, K.; Slay, B.; Knackstedt, M.; Gaharwar, A.K. Antimicrobial Activity of Metal and Metal-Oxide Based Nanoparticles. Adv. Ther. 2018, 1, 1700033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, H.E.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Sui, X.; Riaz, M.A.; Chen, Y. Antimicrobial graphene materials: The interplay of complex materials characteristics and competing mechanisms. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangadlao, J.D.; Santos, C.M.; Felipe, M.J.L.; de Leon, A.C.C.; Rodrigues, D.F.; Advincula, R.C. On the antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide (GO) Langmuir–Blodgett films. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2886–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, F.; Zhou, H.; Jeong, D.; Kwon, J.; Eom, S.; Park, T.J.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, J. Wrinkled Surface-Mediated Antibacterial Activity of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Graphite, Graphite Oxide, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Membrane and Oxidative Stress. Acs Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurantowicz, N.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S.; Kutwin, M.; Strojny, B.; Wierzbicki, M.; Szeliga, J.; Hotowy, A.; Lipińska, L.; Koziński, R.; et al. Interaction of graphene family materials with Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Sun, H.; Qu, X. Antibacterial applications of graphene-based nanomaterials: Recent achievements and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, M.; Zeng, T.H.; Wu, R.; Jiang, R.; Wei, J.; Wang, L.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Lateral Dimension-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Graphene Oxide Sheets. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12364–12372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Duan, G.; Yang, Z.; Weber, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Meng, X.; Xu, J. Particle Size-Dependent Antibacterial Activity and Murine Cell Cytotoxicity Induced by Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.F.; Perreault, F.; Elimelech, M. Elucidating the Role of Oxidative Debris in the Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.-P.; Sun, T.; Junaid, M.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.-B.; Cui, Z.-S.; Wei, D.-P.; Shi, H.-F.; Pei, D.-S. Nanotoxicity of different sizes of graphene (G) and graphene oxide (GO) in vitro and in vivo. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide Nanosheets: Why Size Matters. Acs Nano 2015, 9, 7226–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallavalle, M.; Calvaresi, M.; Bottoni, A.; Melle-Franco, M.; Zerbetto, F. Graphene Can Wreak Havoc with Cell Membranes. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4406–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Huo, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B. Antibacterial Properties of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Su, C.; Ye, S.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shao, W. Synergistic antibacterial effect of tetracycline hydrochloride loaded functionalized graphene oxide nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 505102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Tong, Z.; Deng, Z. Tailor-made Au@Ag core–shell nanoparticle 2D arrays on protein-coated graphene oxide with assembly enhanced antibacterial activity. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 205102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Ouay, B.; Stellacci, F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today 2015, 10, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vi, T.T.T.; Rajesh Kumar, S.; Rout, B.; Liu, C.-H.; Wong, C.-B.; Chang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. The Preparation of Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites: The Effect of Silver Loads on Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Antibacterial Activities. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.; Kumar, S.R.; Pang, J.S.; Liu, Y.K.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Silver-Loaded Graphene Oxide towards Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.; De-La-Pinta, I.; Quindós, G.; Fernández, M.J.; Fernández, M.D. Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticle Nanohybrids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, P. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, A.F.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Meira, S.M.M.; de Moraes, A.C.M.; Brandelli, A.; Filho, A.G.S.; Alves, O.L. Anti-adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskoro, F.; Wong, C.-B.; Kumar, S.R.; Chang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. Graphene oxide-cation interaction: Inter-layer spacing and zeta potential changes in response to various salt solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Arsalan Iqbal, M.; Qasim, M.; Park, C.H.; Yoo, H.; Hwang, J.H.; Uhm, S.J.; Song, H.; Park, C.; Do, J.T.; et al. Evaluation of Graphene Oxide Induced Cellular Toxicity and Transcriptome Analysis in Human Embryonic Kidney Cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, T.T. Morphology and dynamics of agglomerated particulates in combustion systems using light scattering techniques. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1992, 18, 13–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, P.; Quaresma, P.; Soares, C.; Neves, C.; de Almeida, M.P.; Pereira, E.; West, P. A direct comparison of experimental methods to measure dimensions of synthetic nanoparticles. Ultramicroscopy 2017, 182, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yan, C.; Texter, J. Scalable exfoliation and dispersion of two-dimensional materials – an update. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 921–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhu, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Zhu, C.; He, Z.; Li, M.; Tang, Z. Killing Dental Pathogens Using Antibacterial Graphene Oxide. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5605–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroush, A.; Ma, W.; Silvino, Y.; Rahaman, M. Surface Modification of Thin Film Composite Forward Osmosis Membrane by Silver-Decorated Graphene-Oxide Nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2015, 2, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiplak, Z.; Yildiz, N.; Çalimli, A. Investigation of Graphene/Ag Nanocomposites Synthesis Parameters for Two Different Synthesis Methods. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2014, 23, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavinkumar, T.; Varunkumar, K.; Ravikumar, V.; Manivannan, S. Anticancer activity of graphene oxide-reduced graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle composites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.S.; Hui, K.N.; Dinh, D.A.; Tsang, C.H.; Cho, Y.R.; Zhou, W.; Hong, X.; Chun, H.-H. Green synthesis of dimension-controlled silver nanoparticle–graphene oxide with in situ ultrasonication. Acta Mater. 2014, 64, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. Graphene−Metal Particle Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19841–19845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Qin, Y.; Hu, W. Fabrication of Co3O4/graphene oxide composites using supercritical fluid and their catalytic application for the decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Vargas Castrillón, S.; Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Elimelech, M. Interaction of Graphene Oxide with Bacterial Cell Membranes: Insights from Force Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.S.; Park, J.M. Studies on hexavalent chromium biosorption by chemically-treated biomass of Ecklonia sp. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, M.; Perold, W.; Dicks, L. Biosensors for the detection of Escherichia coli. Water S.A 2017, 43, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, K.; Ito, K. Structure and mechanisms of the DsbB–DsbA disulfide bond generation machine. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba) Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, L.V.; Vasilchenko, A.S.; Rakov, E.G.; Deryabin, D.G. Toxicity of Graphene Shells, Graphene Oxide, and Graphene Oxide Paper Evaluated with Escherichia coli Biotests. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 869361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camesano, T.; Logan, B. Probing Bacterial Electrosteric Interactions Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintelas, C.; Rocha, Z.; Silva, B.; Fonseca, B.; Figueiredo, H.; Tavares, T. Removal of Cd(II), Cr(VI), Fe(III) and Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by an E. coli biofilm supported on kaolin. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo, L.A.; Zapata, P.A.; Vejar, N.D.; Azócar, M.I.; Gulppi, M.A.; Zhou, X.; Thompson, G.E.; Rabagliati, F.M.; Páez, M.A. Release of silver and copper nanoparticles from polyethylene nanocomposites and their penetration into Listeria monocytogenes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 40, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.K.; Koo, H.C.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.H. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of the Silver Ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garip, S.; Bozoglu, F.; Severcan, F. Differentiation of Mesophilic and Thermophilic Bacteria with Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K.; Kim, K. Study of antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






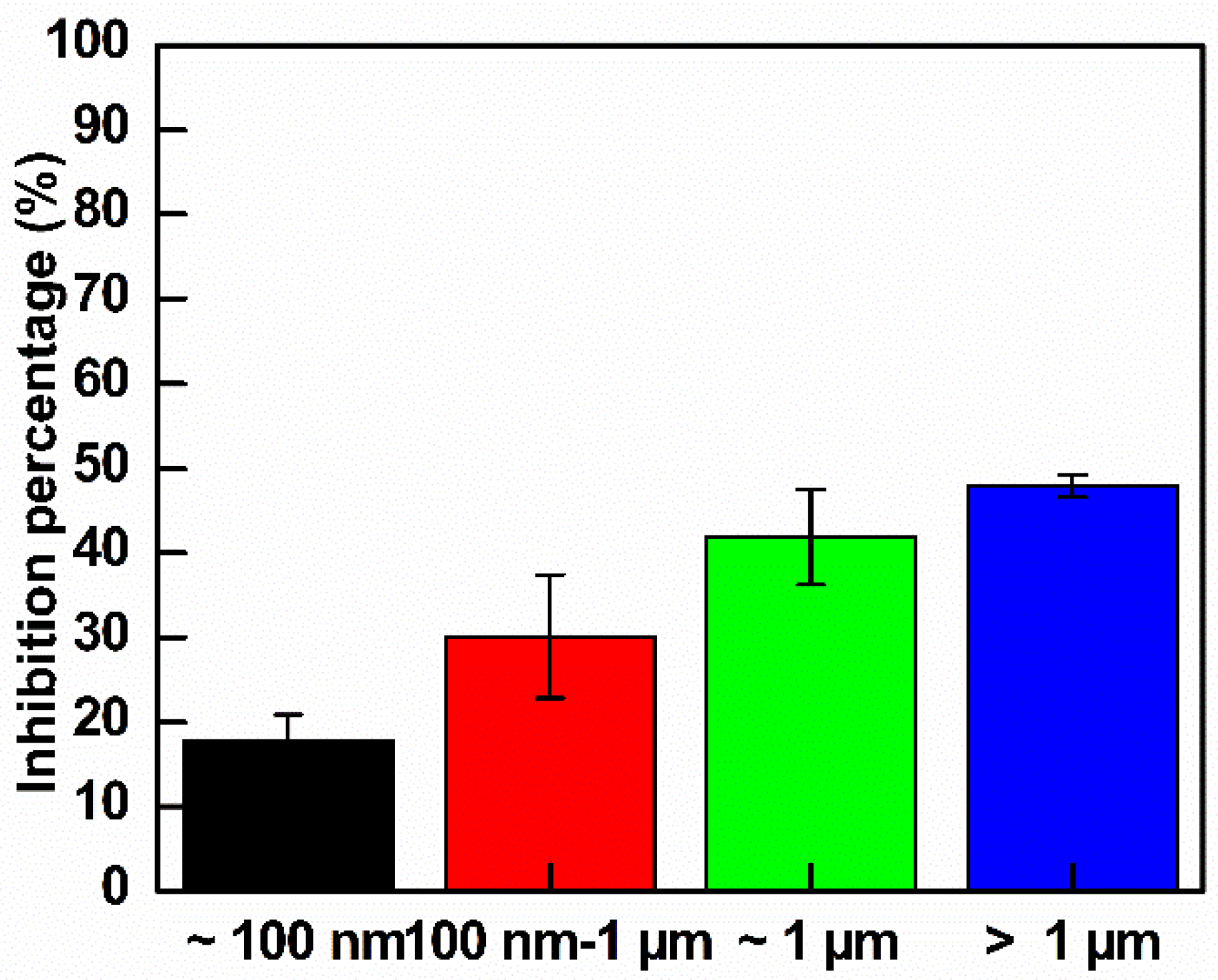

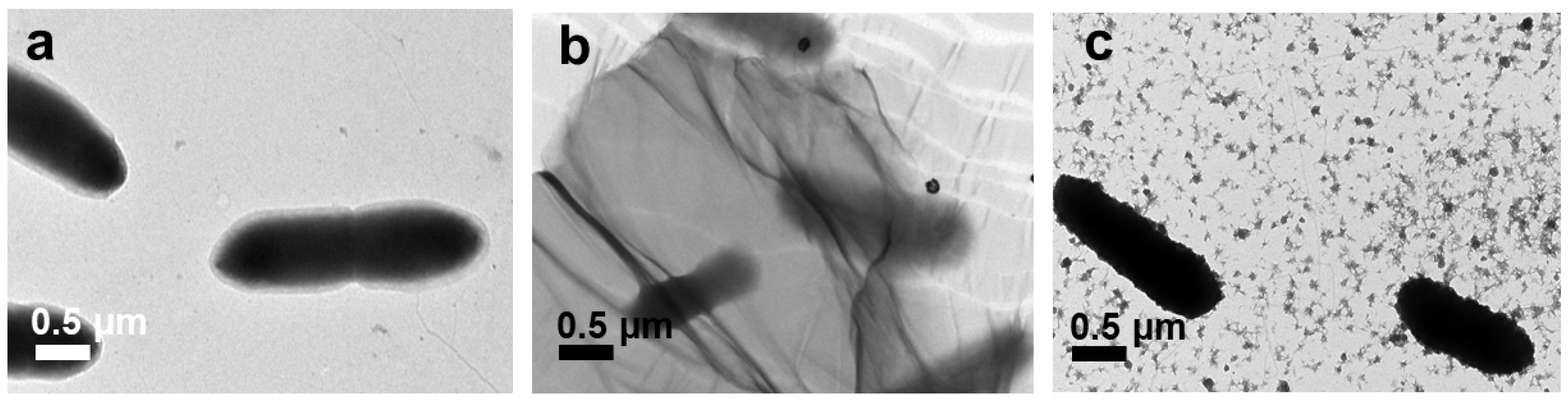
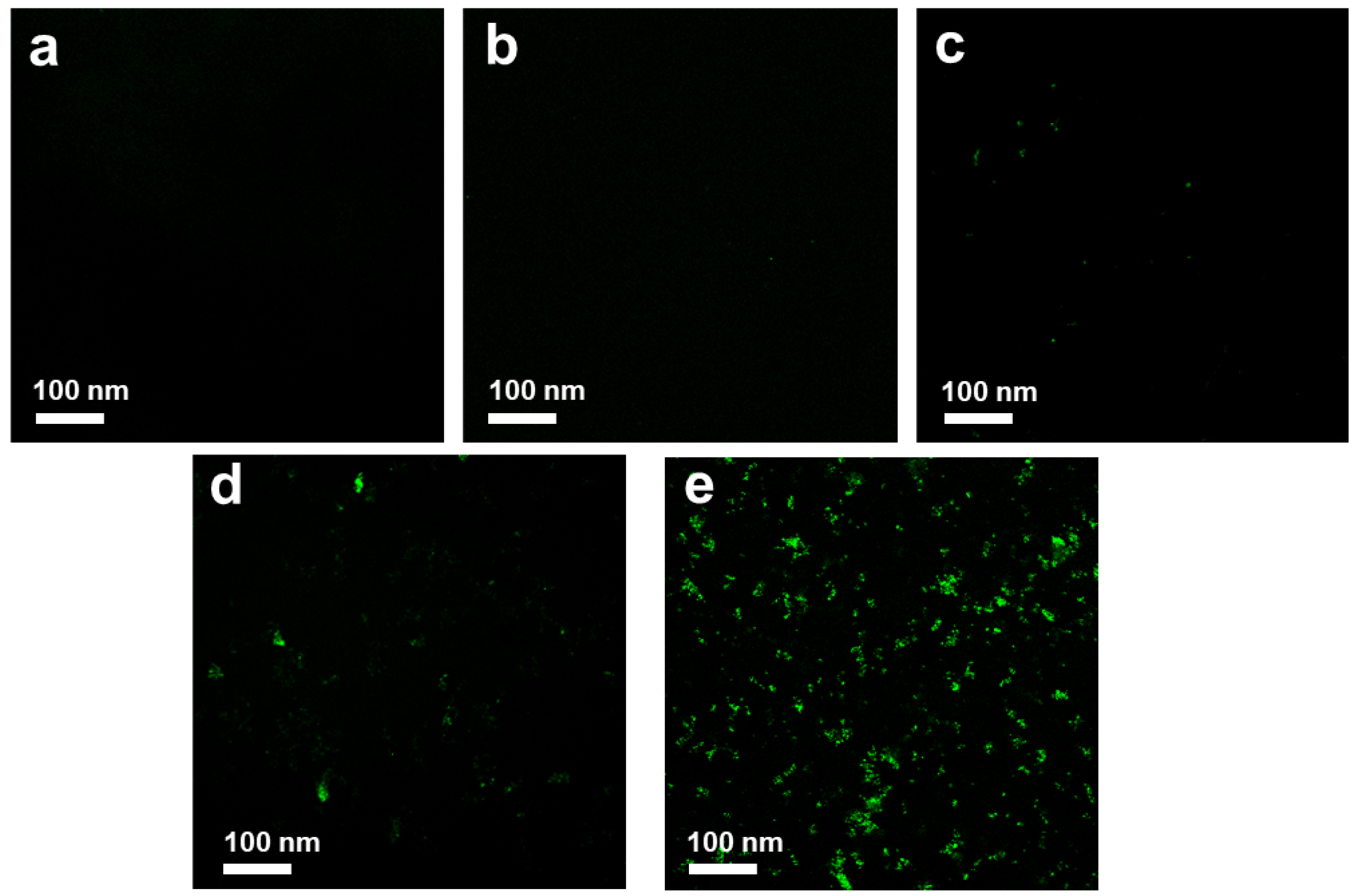
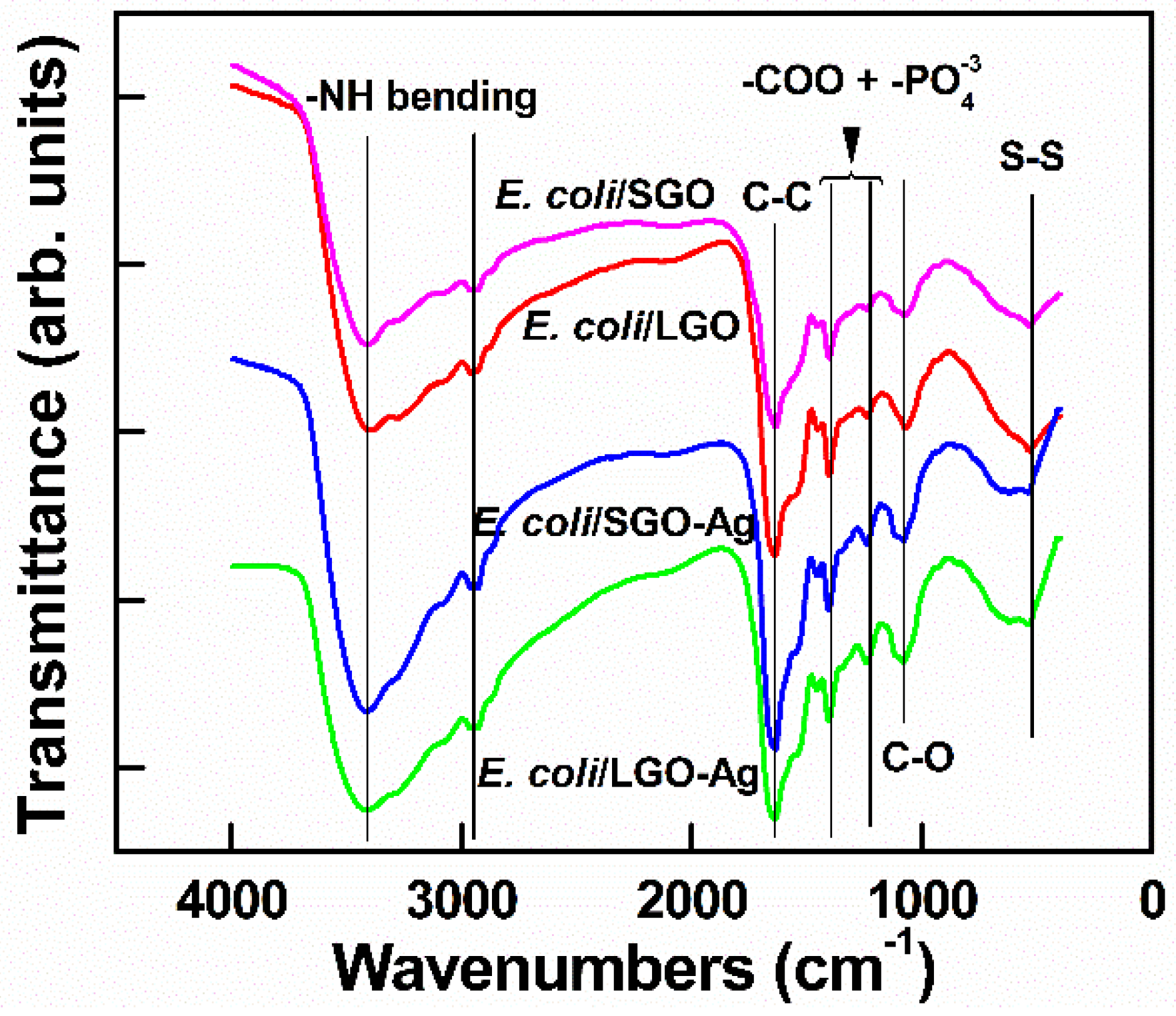



| GO | ~100 nm | 100 nm~1 µm | ~1 µm | >1 µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLS hydrodynamic size (nm) | 140.8 ± 8.8 | 320.6 ± 71.6 | 1098.7 ± 381.7 | 4605.3 ± 338.8 |
| TEM results (nm) | 69.0 ± 7.8 | 161.4 ± 44.1 | 1005.2 ± 378.9 | 4340.1 ± 1189.1 |
| ζ-potential (mV) | −35.1 ± 2.2 | −36.7 ± 10.2 | −33.1 ± 2.2 | −36.7 ± 5.3 |
| Lateral Size | Preparation | Characterization of Size | Bacteria/Cell Inactivation Results | Mechanism of Action (Finding) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0,.753, 0.127, 0.065, 0.035, 0.013, 0.01 µm2 | Preparation for 0, 10, 30, 50, 120 and 240 min |
|
|
| [14] |
| 0.65, 0.29, 0.1 and 0.01 µm2 | Preparation for 0, 1, 10 and 120 min |
|
|
| [18] |
| GQD ( <15 nm), SGO (50–200 nm) and LGO (0.5–3 µm) | Commercial products |
|
|
| [15] |
| SGO (30 nm), MGO (300 nm) and LGO (1 µm) | Synthesis using Hummer method from different size of graphites |
|
|
| [17] |
| ~100 nm, 100 nm to 1 µm, ~1 µm and >1 µm | Preparation for 0, 30, 60 and 120 min |
|
|
| This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Truong, T.T.V.; Kumar, S.R.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chen, D.W.; Liu, Y.-K.; Lue, S.J. Size-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061207
Truong TTV, Kumar SR, Huang Y-T, Chen DW, Liu Y-K, Lue SJ. Size-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061207
Chicago/Turabian StyleTruong, Thi Tuong Vi, Selvaraj Rajesh Kumar, Yu-Tzu Huang, Dave W. Chen, Yu-Kuo Liu, and Shingjiang Jessie Lue. 2020. "Size-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Graphene Oxide Nanosheets" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061207
APA StyleTruong, T. T. V., Kumar, S. R., Huang, Y.-T., Chen, D. W., Liu, Y.-K., & Lue, S. J. (2020). Size-Dependent Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061207







