Magnetic Heating of Nanoparticles Applied in the Synthesis of a Magnetically Recyclable Hydrogenation Nanocatalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
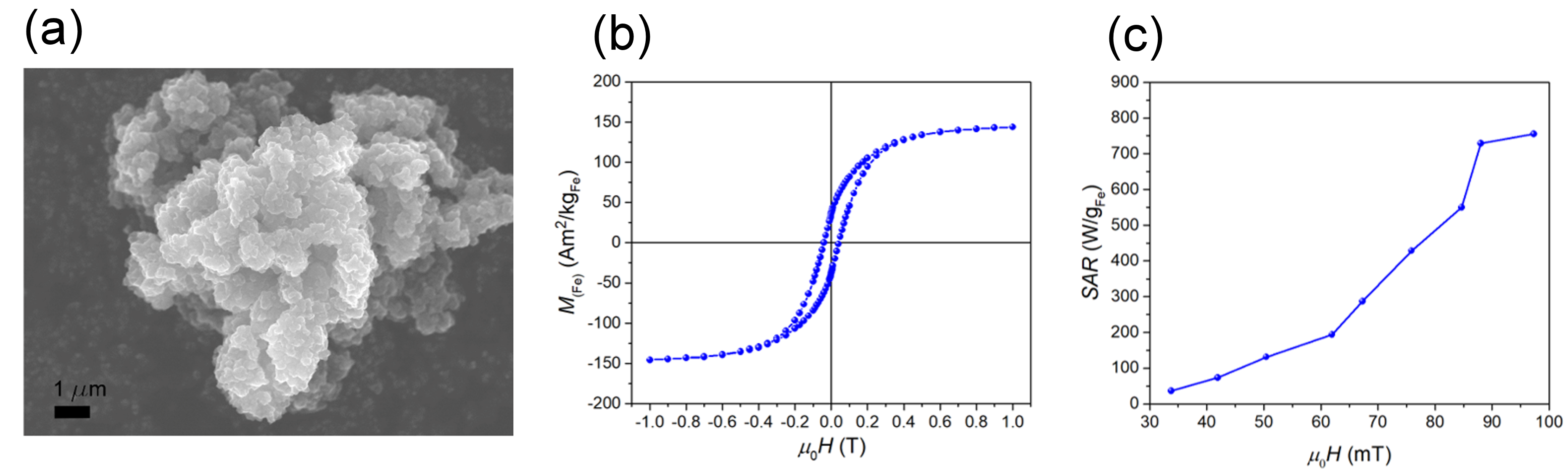
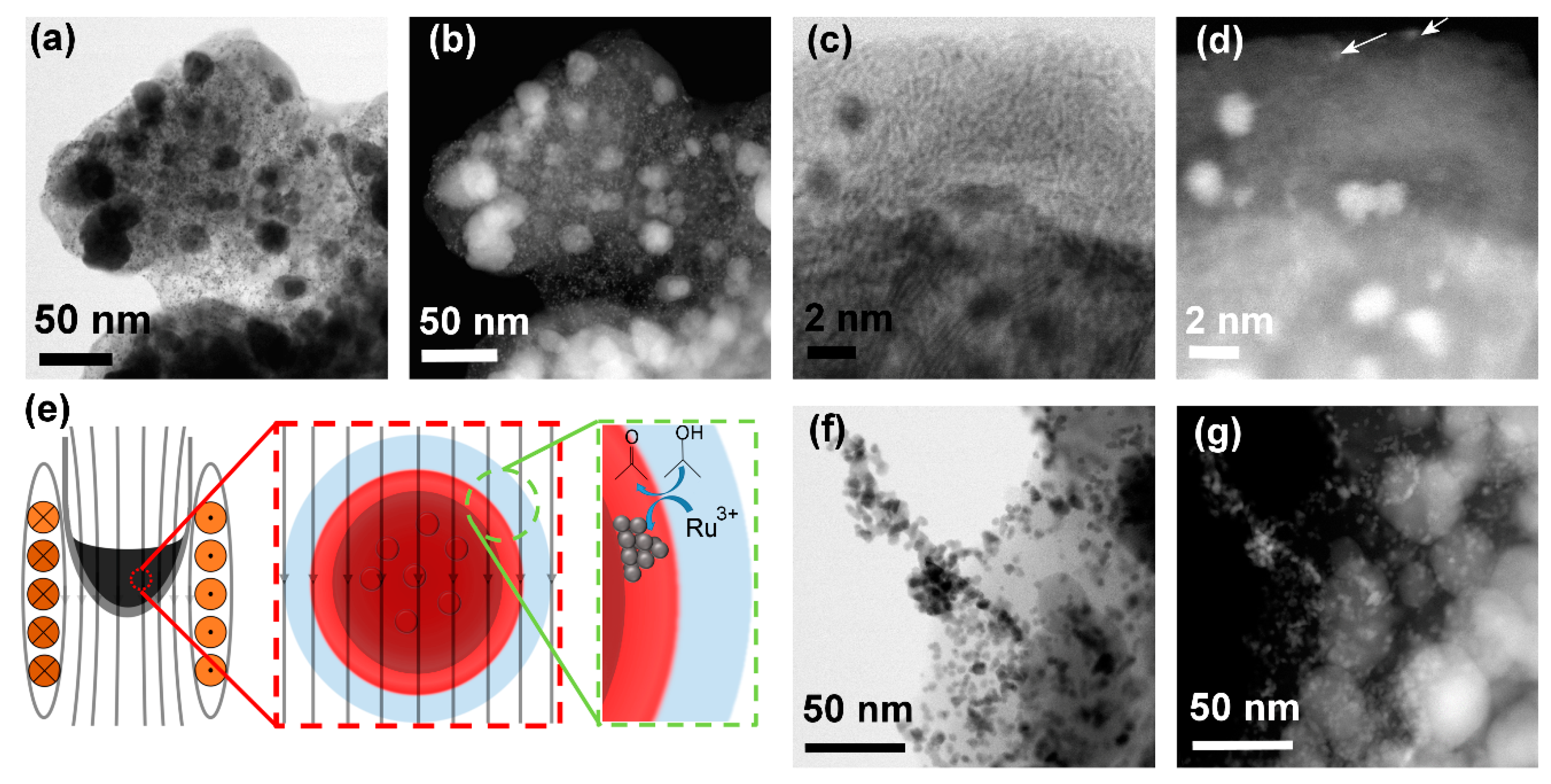
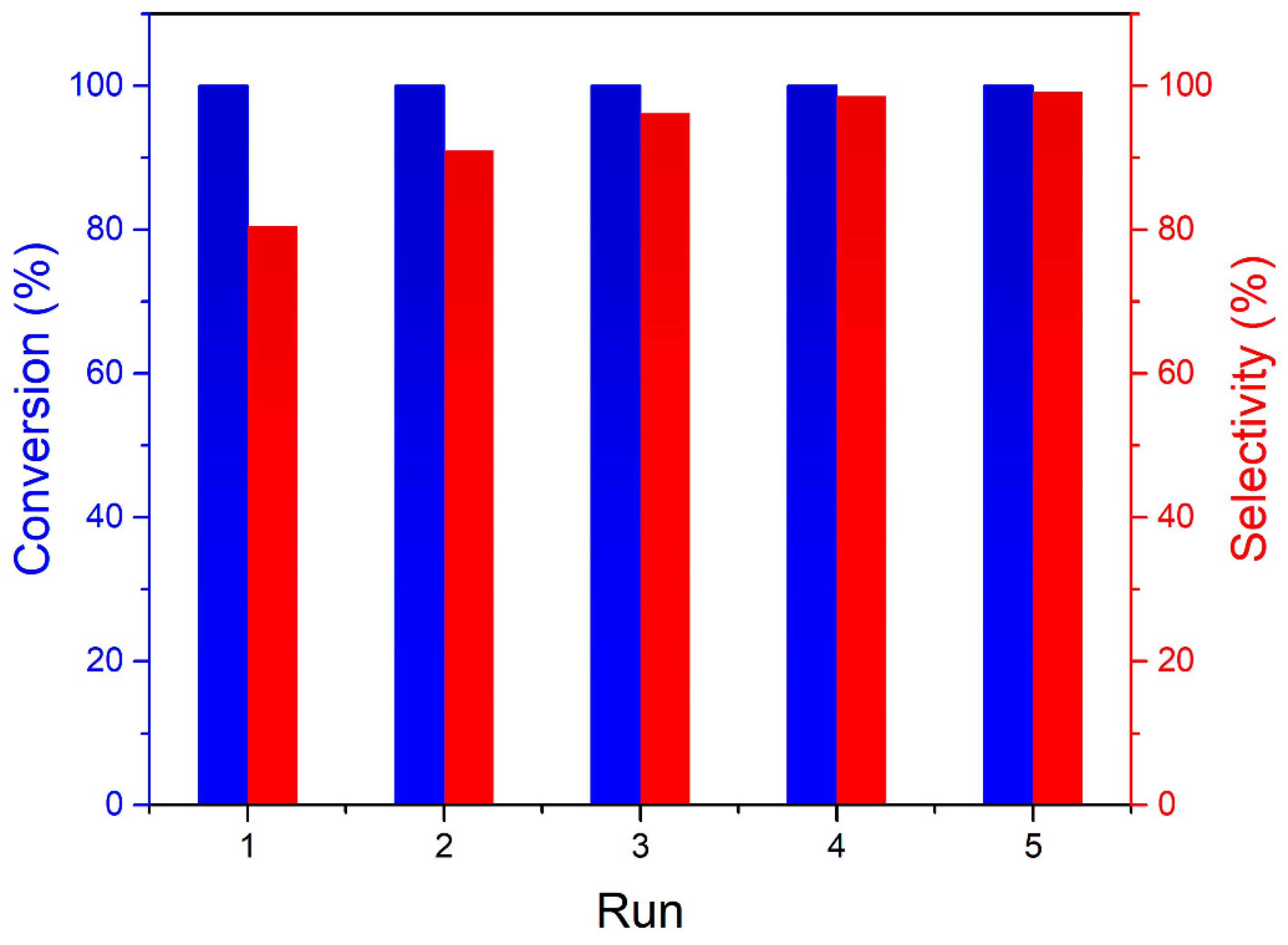
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- She, Z.W.; Kibsgaard, J.; Dickens, C.F.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K.; Jaramillo, T.F. Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: Insights into materials design. Science 2017, 355, eaad4998. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, M.; Gneveckow, U.; Thiesen, B.; Taymoorian, K.; Cho, C.H.; Waldöfner, N.; Scholz, R.; Jordan, A.; Loening, S.A.; Wust, P. Thermotherapy of prostate cancer using magnetic nanoparticles: Feasibility, imaging, and three-dimensional temperature distribution. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollert, E.; Veverka, P.; Veverka, M.; Kaman, O.; Zaveta, K.; Vasseur, S.; Epherre, R.; Goglio, G.; Duguet, E. Search of new core materials for magnetic fluid hyperthermia: Preliminary chemical and physical issues. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2009, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, S.; Friese, C.; Lammel, C.; Mazac, K.; Kirschning, A. Inductive heating for organic synthesis by using functionalized magnetic nanoparticles inside microreactors. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8950–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, J.; Ceylan, S.; Kupracz, L.; Coutable, L.; Kirschning, A. Heating under high-frequency inductive conditions: Application to the continuous synthesis of the neurolepticum Olanzapine (Zyprexa). Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9813–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, S.R.; Hartwig, J.; Kupracz, L.; Kodanek, T.; Wegner, J.; Kirschning, A. Oxidations of allylic and benzylic alcohols under inductively-heated flow conditions with gold-doped superparamagnetic nanostructured particles as catalyst and oxygen as oxidant. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 3530–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meffre, A.; Mehdaoui, B.; Connord, V.; Carrey, J.; Fazzini, P.F.; Lachaize, S.; Respaud, M.; Chaudret, B. Complex nano-objects displaying both magnetic and catalytic properties: A proof of concept for magnetically induced heterogeneous catalysis. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3241–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordet, A.; Lacroix, L.M.; Fazzini, P.F.; Carrey, J.; Soulantica, K.; Chaudret, B. Magnetically induced continuous CO2 hydrogenation using composite iron carbide nanoparticles of exceptionally high heating power. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15894–15898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tuci, G.; Duong-Viet, C.; Liu, Y.; Rossin, A.; Luconi, L.; Nhut, J.-M.; Nguyen-Dinh, L.; Pham-Huu, C.; Giambastiani, G. Induction heating: An enabling technology for the heat management in catalytic processes. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7921–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niether, C.; Faure, S.; Bordet, A.; Deseure, J.; Chatenet, M.; Carrey, J.; Chaudret, B.; Rouet, A. Improved water electrolysis using magnetic heating of FeC-Ni core-shell nanoparticles. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sadiq, M.M.; Suzuki, K.; Falcaro, P.; Hill, A.J.; Hill, M.R. Magnetic induction framework synthesis: A general route to the controlled growth of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 6186–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melag, L.; Sadiq, M.M.; Smith, S.J.D.; Konstas, K.; Suzuki, K.; Hill, M.R. Efficient delivery of oxygen: Via magnetic framework composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 3790–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, M.; Gallezot, P.; Pinel, C. Conversion of biomass into chemicals over metal catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1827–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chiang, K.; Burke, N. Porous Carbon-supported catalysts for energy and environmental applications: A short review. Catal. Today 2011, 178, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, N.; Thangavel, S.; Venugopal, G. A short review on preparation of graphene from waste and bioprecursors. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, N.; Li, X. Biomass-derived renewable carbon materials for electrochemical energy storage. Mater. Res. Lett. 2017, 5, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyergyek, S.; Kocjan, A.; Bjelić, A.; Grilc, M.; Likozar, B.; Makovec, D. Magnetically separable Ru-based nano-catalyst for the hydrogenation/hydro-deoxygenation of lignin-derived platform chemicals. Mater. Res. Lett. 2018, 6, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelić, A.; Grilc, M.; Gyergyek, S.; Kocjan, A.; Makovec, D.; Likozar, B. Catalytic hydrogenation, hydrodeoxygenation, and hydrocracking processes of a lignin monomer model compound eugenol over magnetic Ru/C–Fe2O3 and mechanistic reaction microkinetics. Catalysts 2018, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečemer, M.; Kump, P.; Ščančar, J.; Jaćimović, R.; Simčič, J.; Pelicon, P.; Budnar, M.; Jeran, Z.; Pongrac, P.; Regvar, M.; et al. Application of X-ray fluorescence analytical techniques in phytoremediation and plant biology studies. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2008, 63, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Raman spectroscopy of amorphous, nanostructured, diamond-like carbon, and nanodiamond. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A. 2004, 362, 2477–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cançado, L.G.; Pimenta, M.A.; Neves, B.R.A.; Dantas, M.S.S.; Jorio, A. Influence of the atomic structure on the raman spectra of graphite edges. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Dhamelincourt, P.; Laureyns, J.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Raman microprobe studies on carbon materials. Carbon 1994, 32, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawhari, T.; Roid, A.; Casado, J. Raman spectroscopic characterization of some commercially available carbon black materials. Carbon 1995, 33, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippel, B.; Jander, H.; Heintzenberg, J. NIR FT Raman spectroscopic study of flame soot. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 4707–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet-Ladeira, P.; Puech, P.; Toulouse, C.; Cazayous, M.; Ratel-Ramond, N.; Weisbecker, P.; Vignoles, G.L.; Monthioux, M. A Raman study to obtain crystallite size of carbon materials: A better alternative to the Tuinstra-Koenig law. Carbon 2014, 80, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarterman, P.; Sun, C.; Garcia-Barriocanal, J.; DC, M.; Lv, Y.; Manipatruni, S.; Nikonov, D.E.; Young, I.A.; Voyles, P.M.; Wang, J.P. Demonstration of Ru as the 4th ferromagnetic element at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Rodríguez-Padrón, D.; Len, C. Recent advances in catalytic hydrogenation of furfural. Catalysts 2019, 9, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, A.; Leahy, J.J.; Curtin, T. The influence of metal selection on catalyst activity for the liquid phase hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Catal. Today 2017, 279, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, C.; Bonincontro, D.; Zhang, Y.; Grazia, L.; Renom-Carrasco, M.; Thieuleux, C.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Dimitratos, N.; Cavani, F.; Albonetti, S. Tandem hydrogenation/hydrogenolysis of furfural to 2-methylfuran over a Fe/Mg/O catalyst: Structure–activity relationship. Catalysts 2019, 9, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Dimitratos, N.; Su, D.; Villa, A. Valorisation of biomass derived furfural and levulinic acid by highly efficient Pd@ND catalyst. Energy Technol. 2019, 7, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gyergyek, S.; Lisjak, D.; Beković, M.; Grilc, M.; Likozar, B.; Nečemer, M.; Makovec, D. Magnetic Heating of Nanoparticles Applied in the Synthesis of a Magnetically Recyclable Hydrogenation Nanocatalyst. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061142
Gyergyek S, Lisjak D, Beković M, Grilc M, Likozar B, Nečemer M, Makovec D. Magnetic Heating of Nanoparticles Applied in the Synthesis of a Magnetically Recyclable Hydrogenation Nanocatalyst. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061142
Chicago/Turabian StyleGyergyek, Sašo, Darja Lisjak, Miloš Beković, Miha Grilc, Blaž Likozar, Marijan Nečemer, and Darko Makovec. 2020. "Magnetic Heating of Nanoparticles Applied in the Synthesis of a Magnetically Recyclable Hydrogenation Nanocatalyst" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061142
APA StyleGyergyek, S., Lisjak, D., Beković, M., Grilc, M., Likozar, B., Nečemer, M., & Makovec, D. (2020). Magnetic Heating of Nanoparticles Applied in the Synthesis of a Magnetically Recyclable Hydrogenation Nanocatalyst. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061142








