MRI Relaxivity Changes of the Magnetic Nanoparticles Induced by Different Amino Acid Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
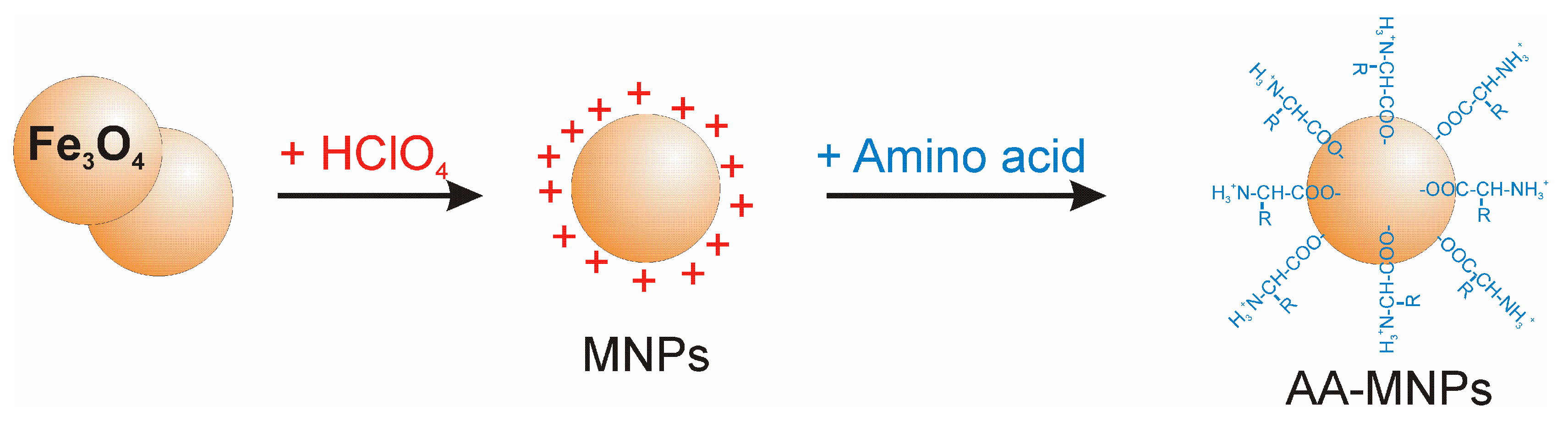
2.2. NP preparation
2.3. Characterisation
2.4. MRI
- T1 mapping—Rapid Acquisition with Refocused Echoes (RARE) pulse sequence, with repetition time TR = 5500, 3000, 1500, 800, 400 and 200 ms, and echo time TE = 7 ms.
- T2 mapping—Multi-Slice Multi-Echo (MSME) pulse sequence, with repetition time TR = 2000 ms, starting echo time TE = 8 ms, spacing = 8 ms, and 25 images.
- T2* mapping—Multi Gradient Echo (MGE) pulse sequence, with repetition time TR = 800 ms, starting echo time TE = 2.09 ms, spacing = 2.23 ms (uncoated MNPs), 5 ms (coated Gly-, Lys-, Trp-MNPs), and 10 images.
- MNPs: Magnetic fluid with acidic pH containing IONPs stabilised by HClO4, without AA coating.
- Lys-MNPs: Magnetic NPs coated with Lys.
- Gly-MNPs: Magnetic NPs coated with Gly.
- Trp-MNPs: Magnetic NPs coated with Trp.
3. Results and Discussion
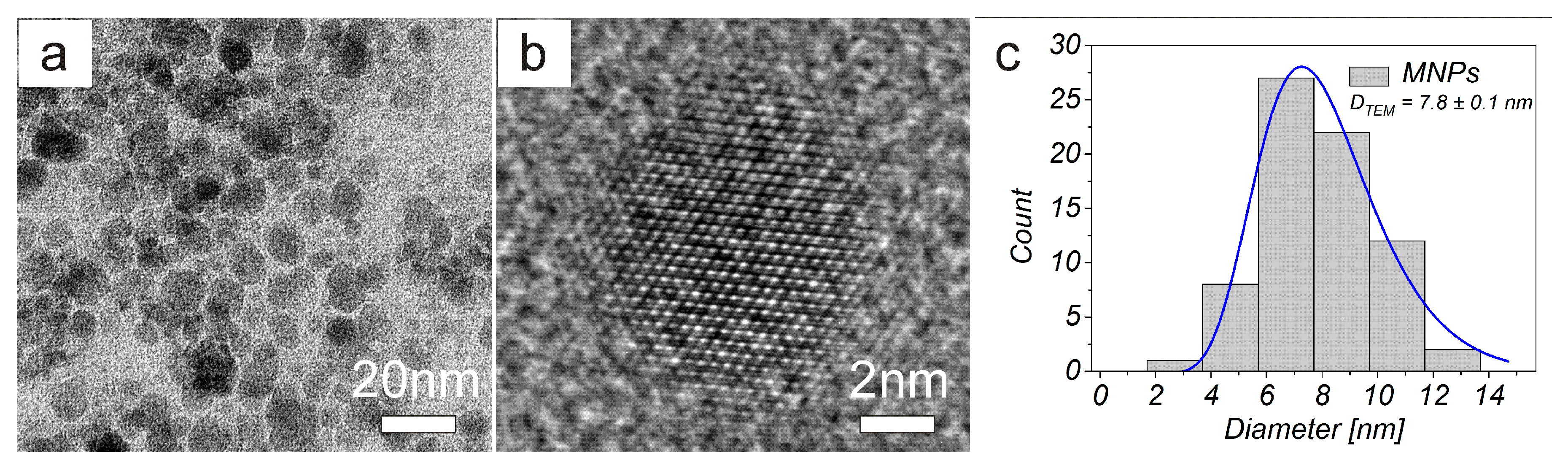
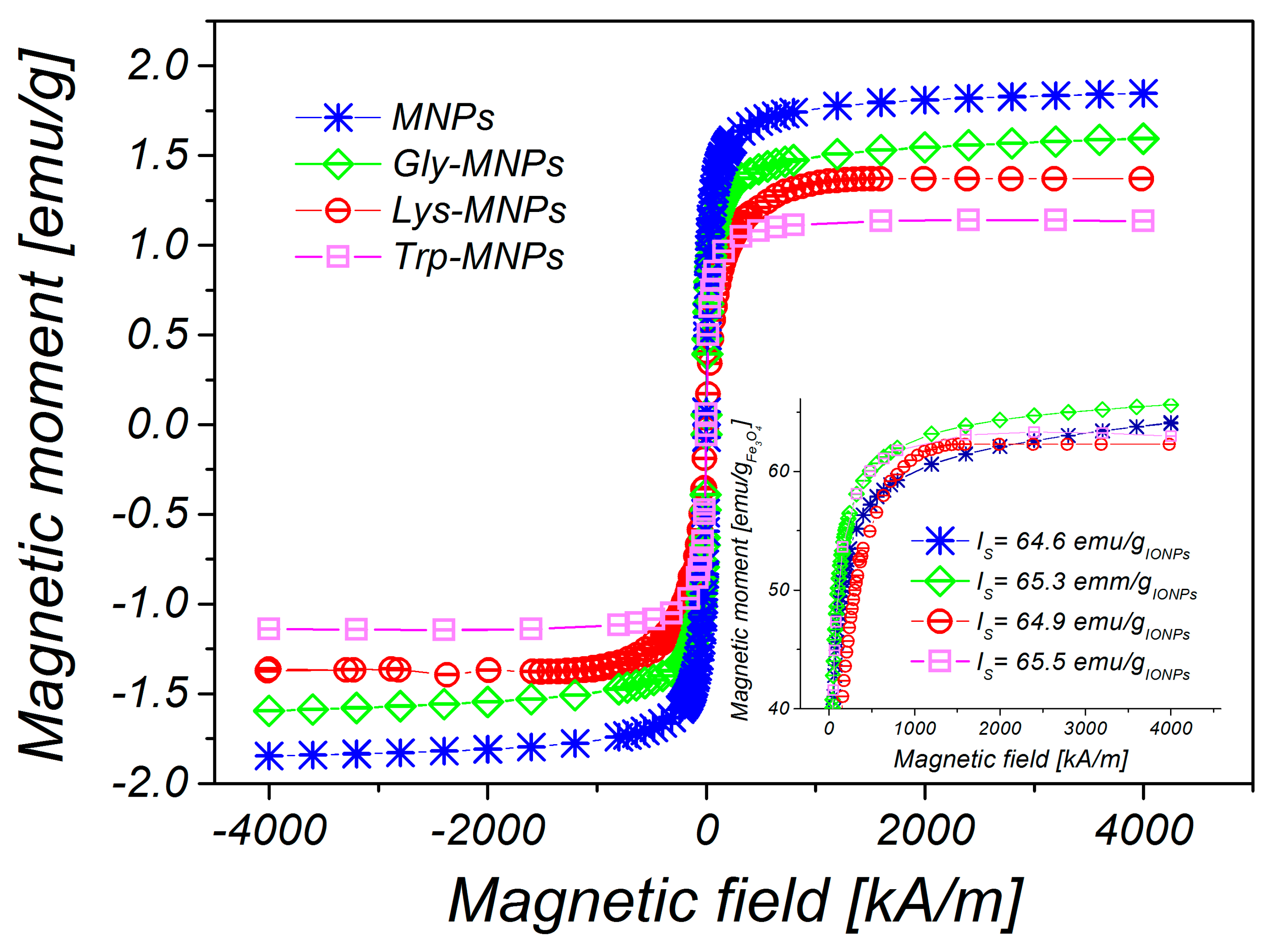
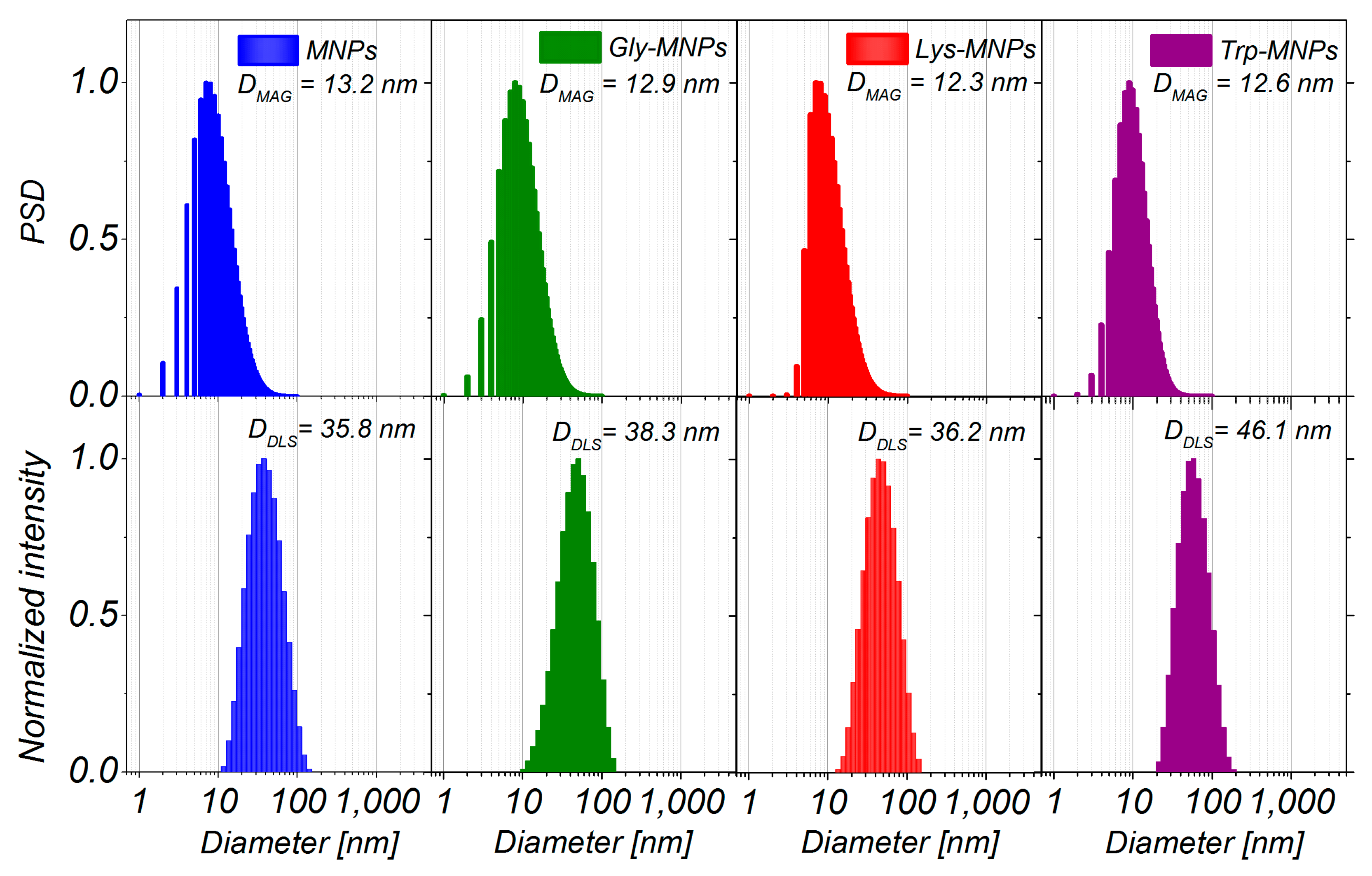
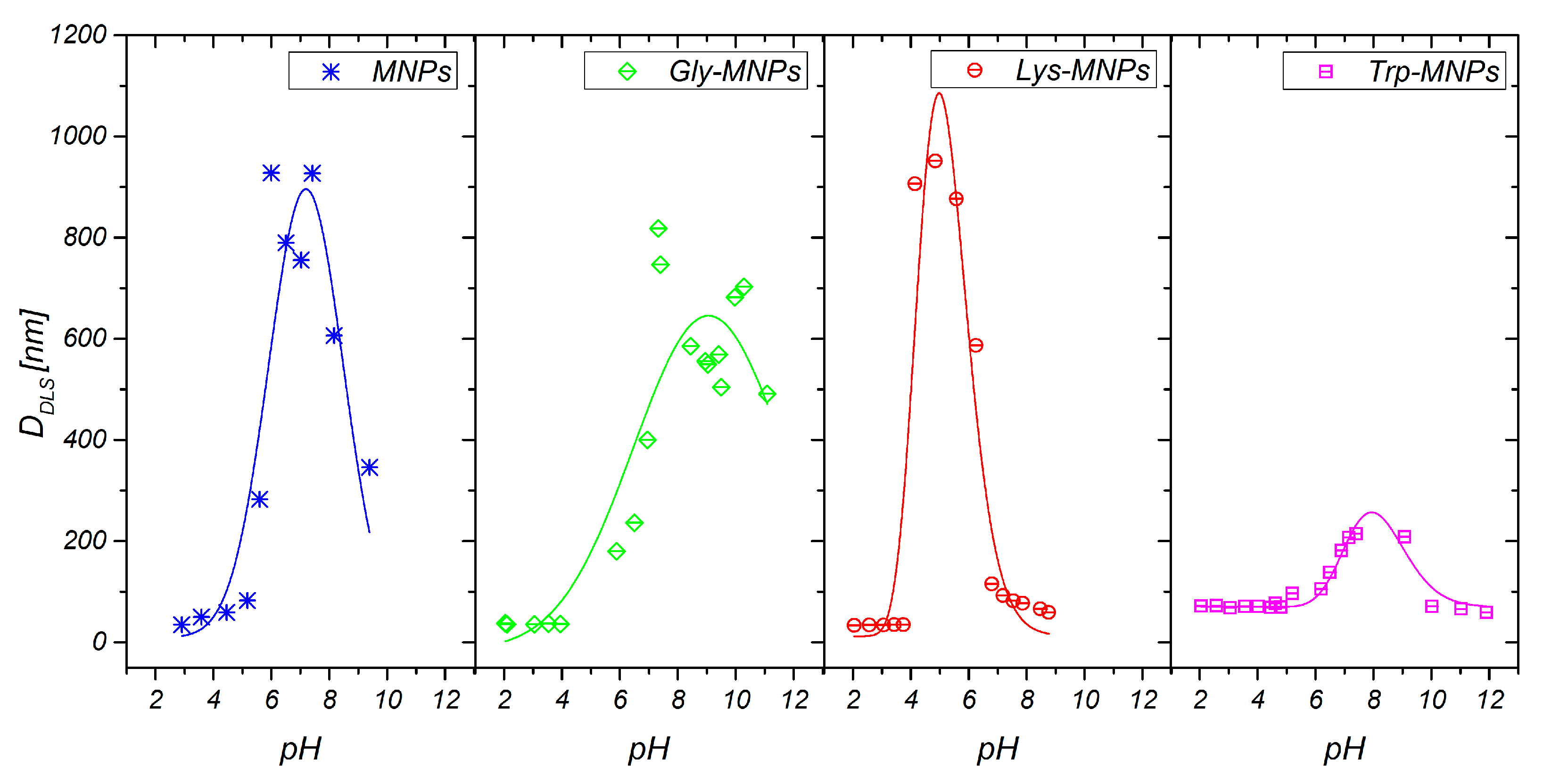
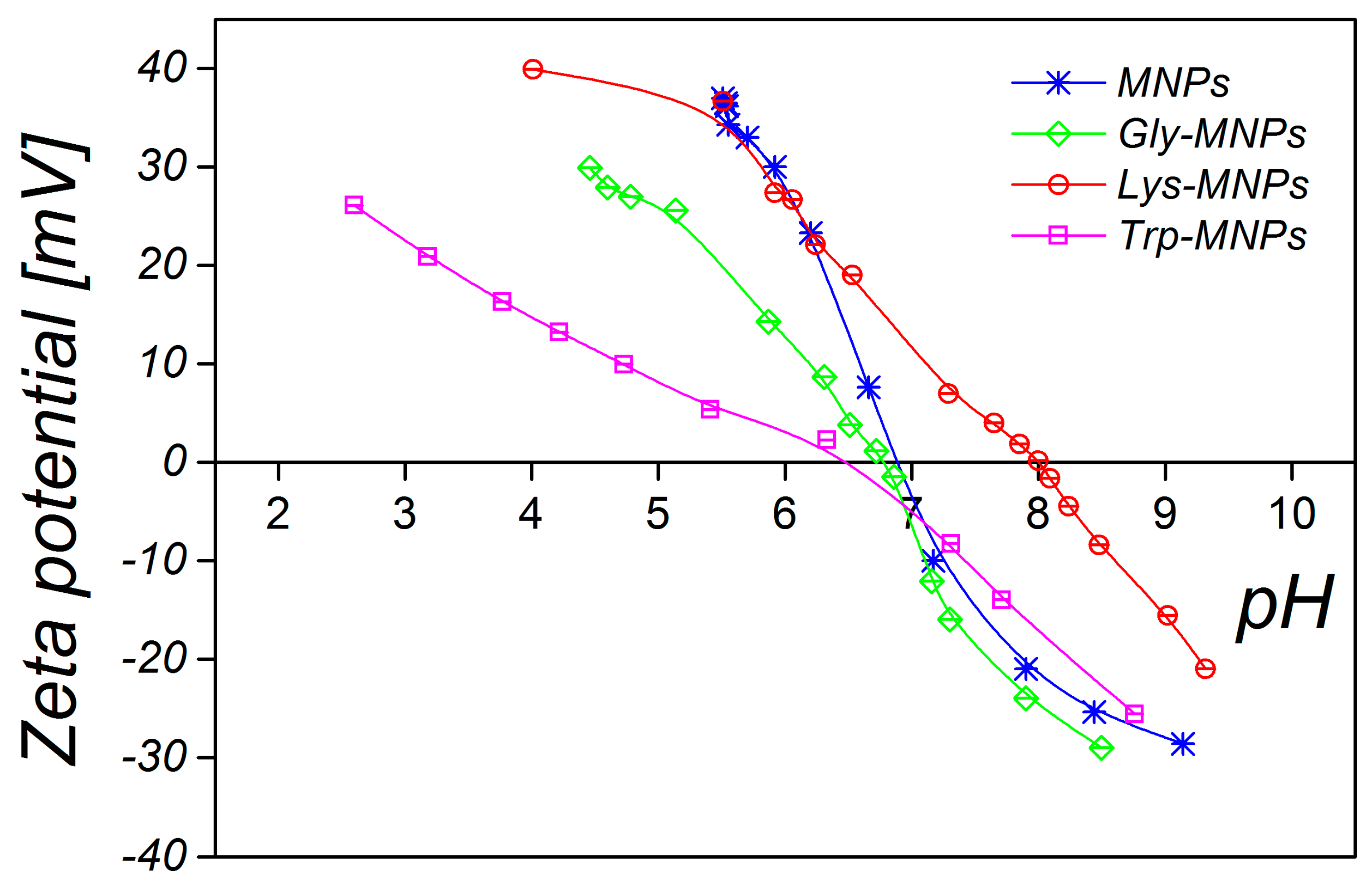
3.1. Physical Characterisation
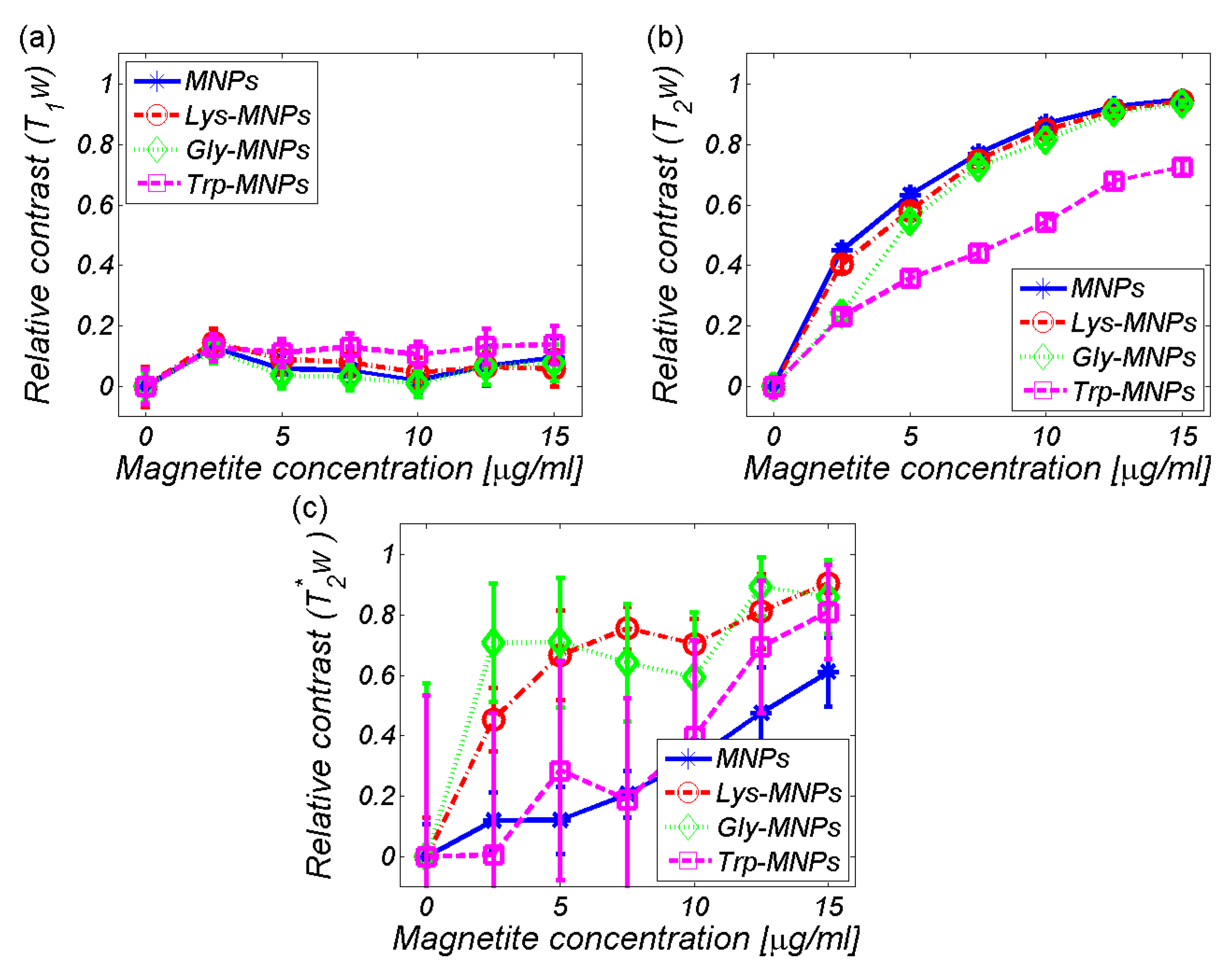
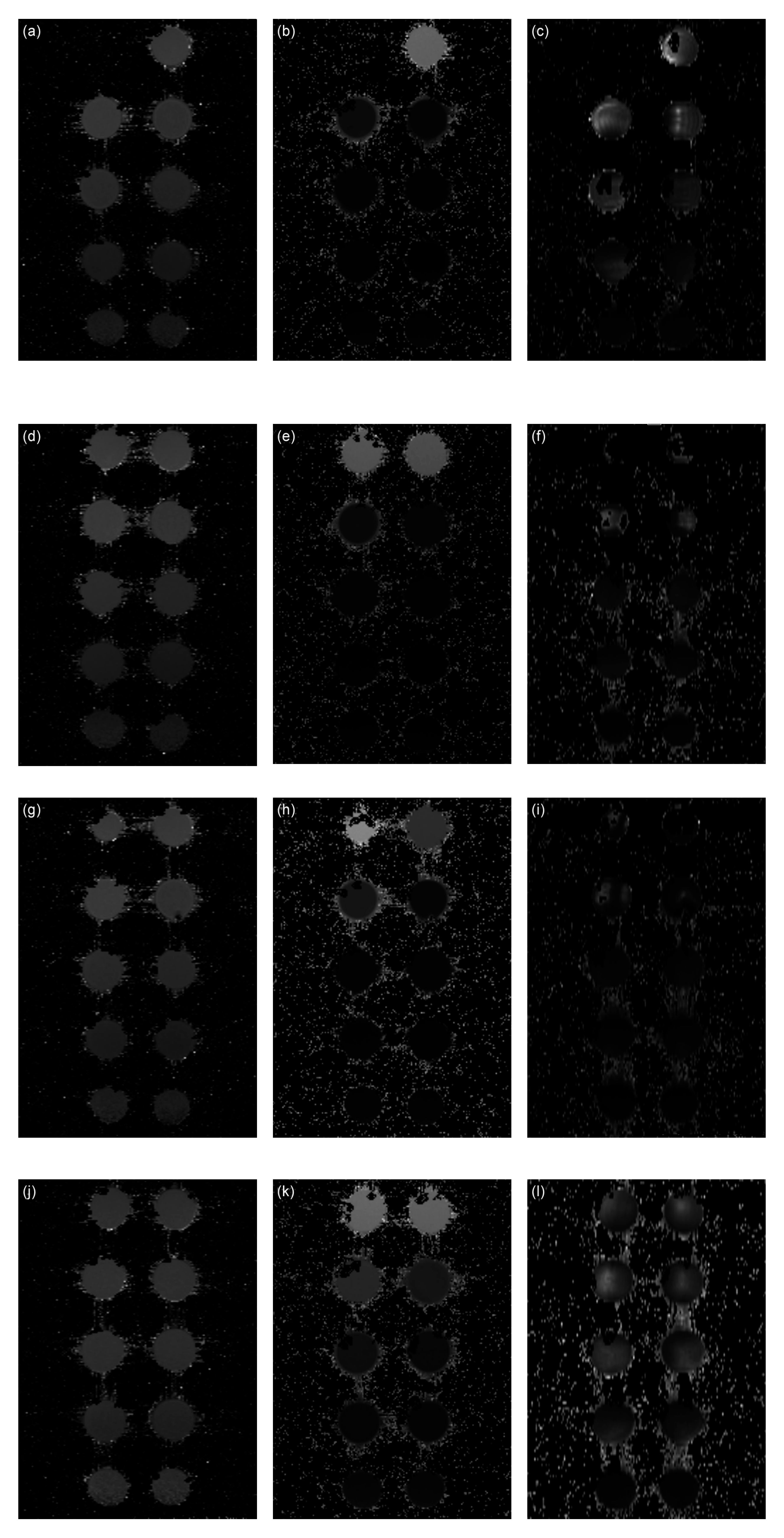
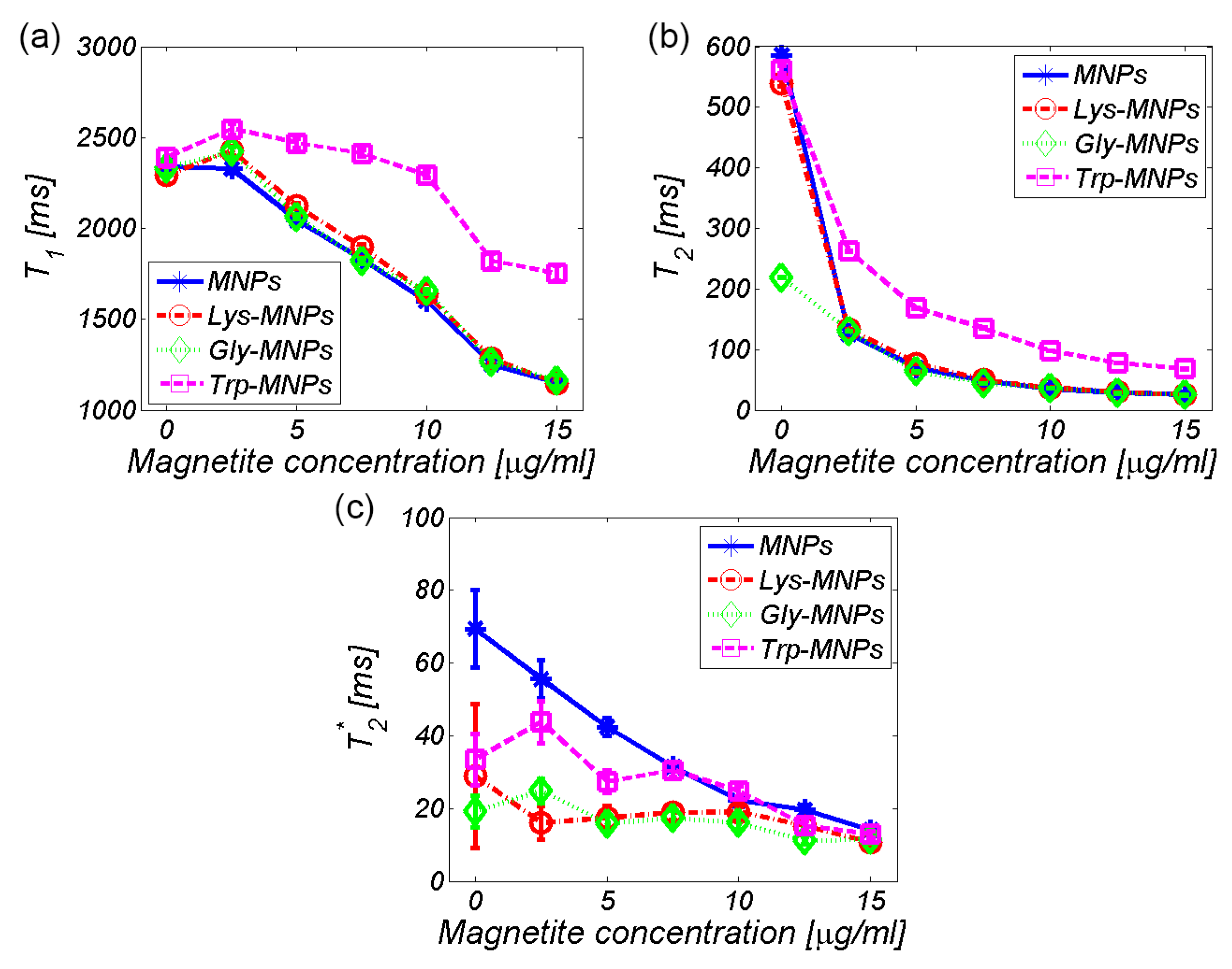
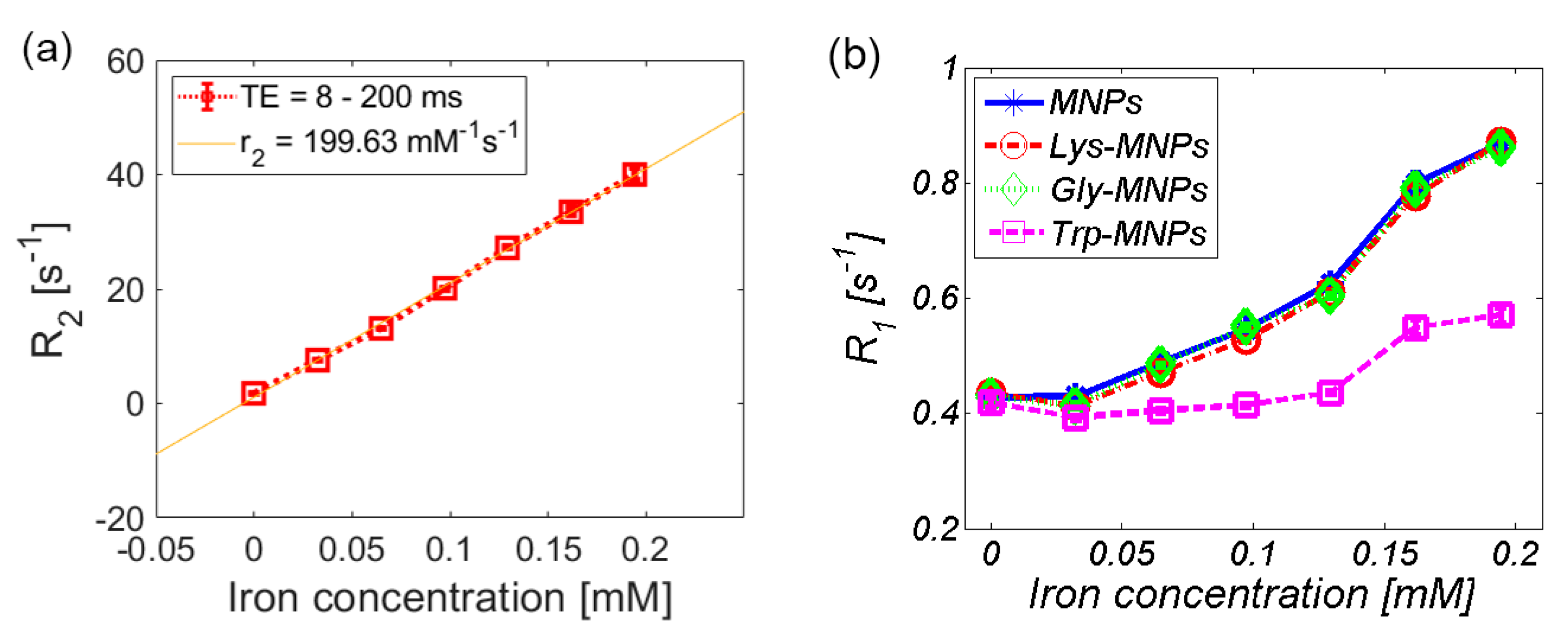
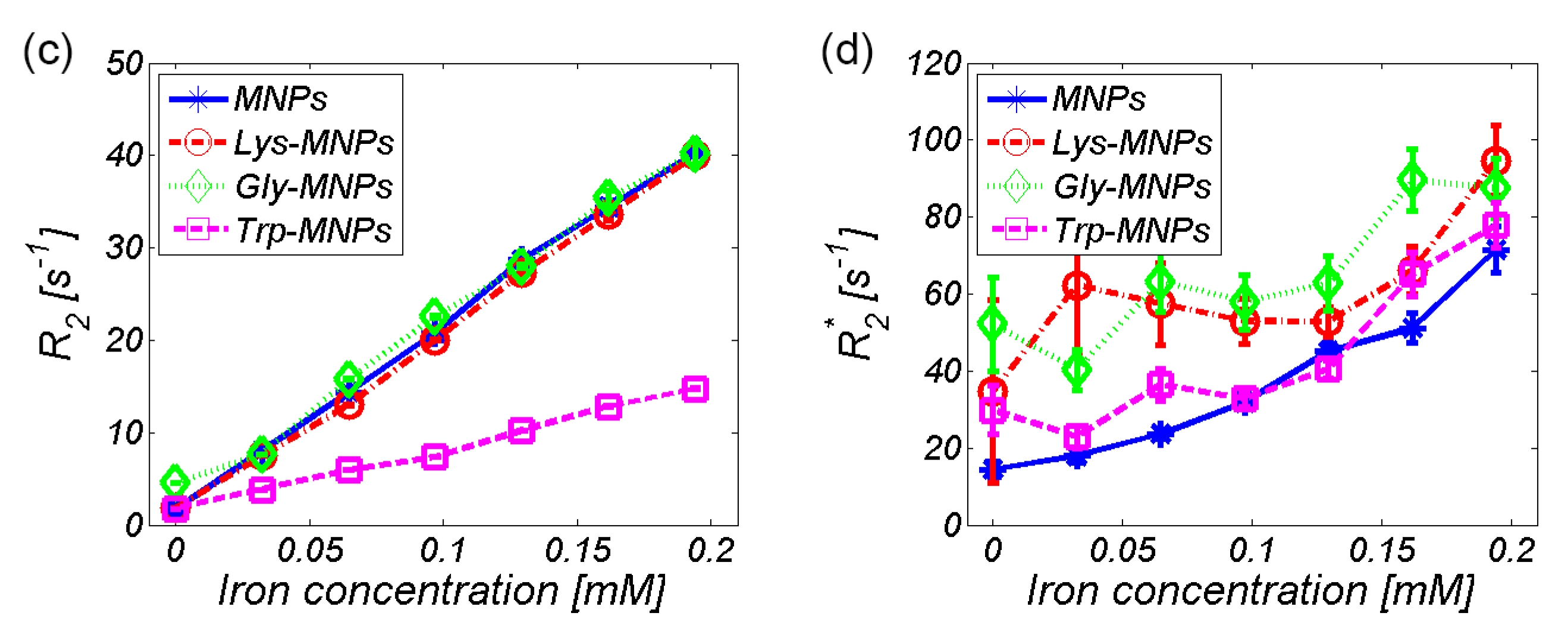
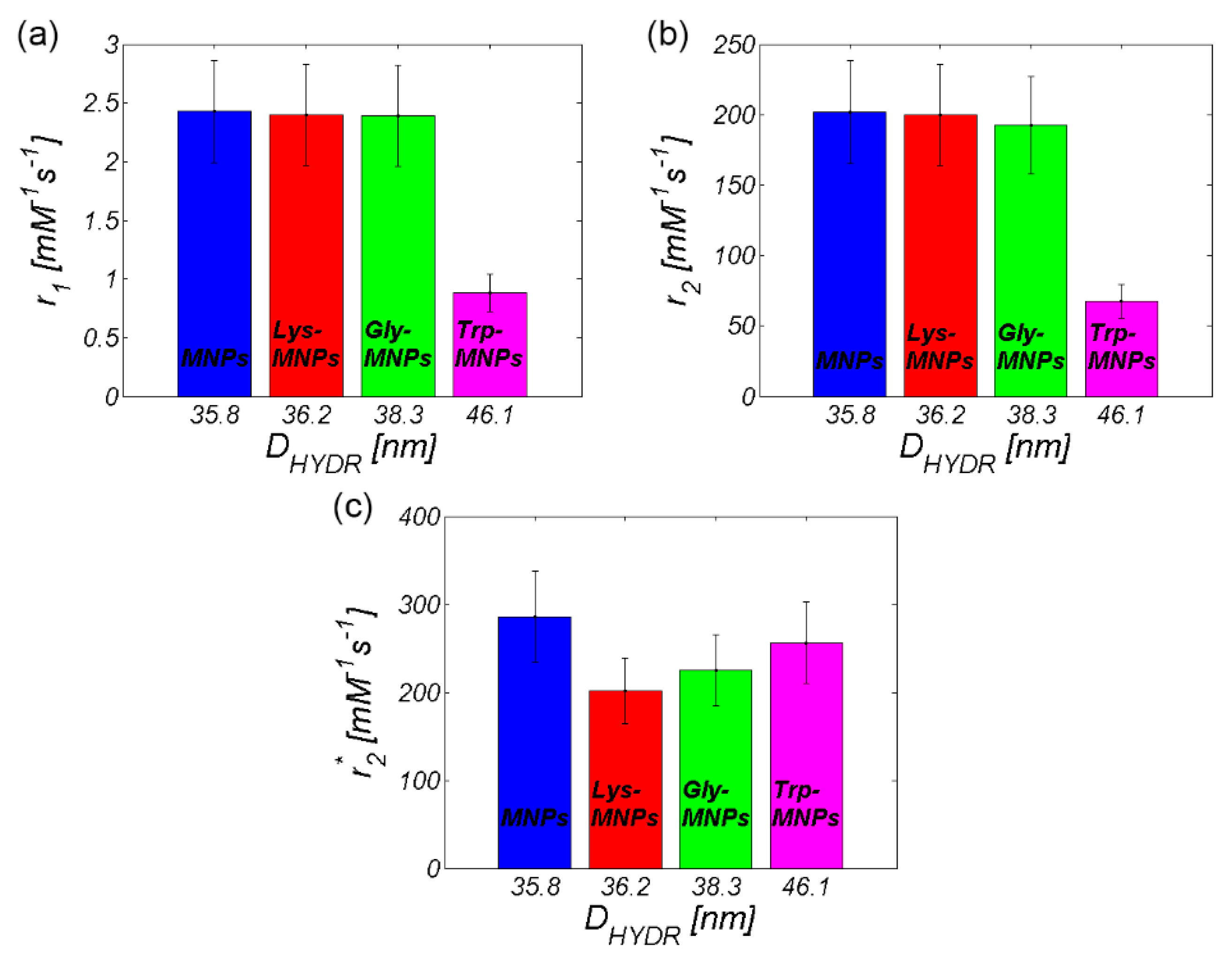
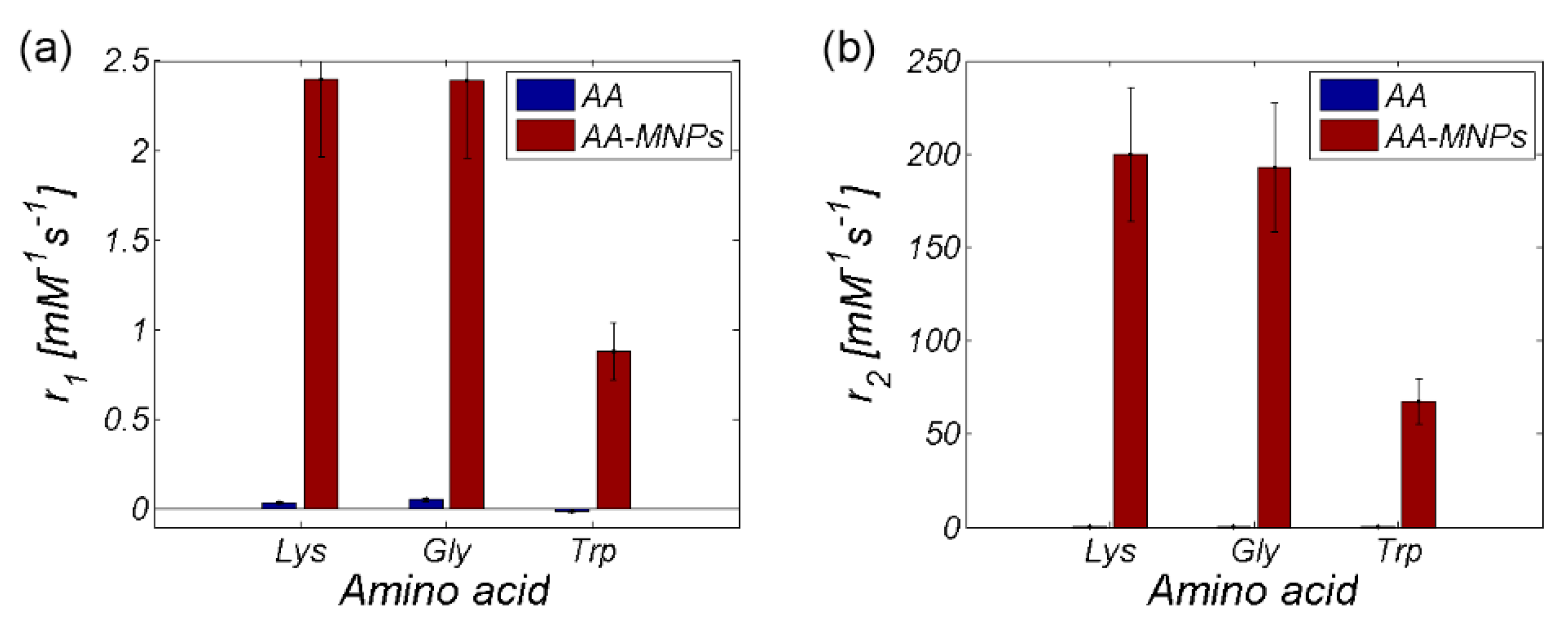
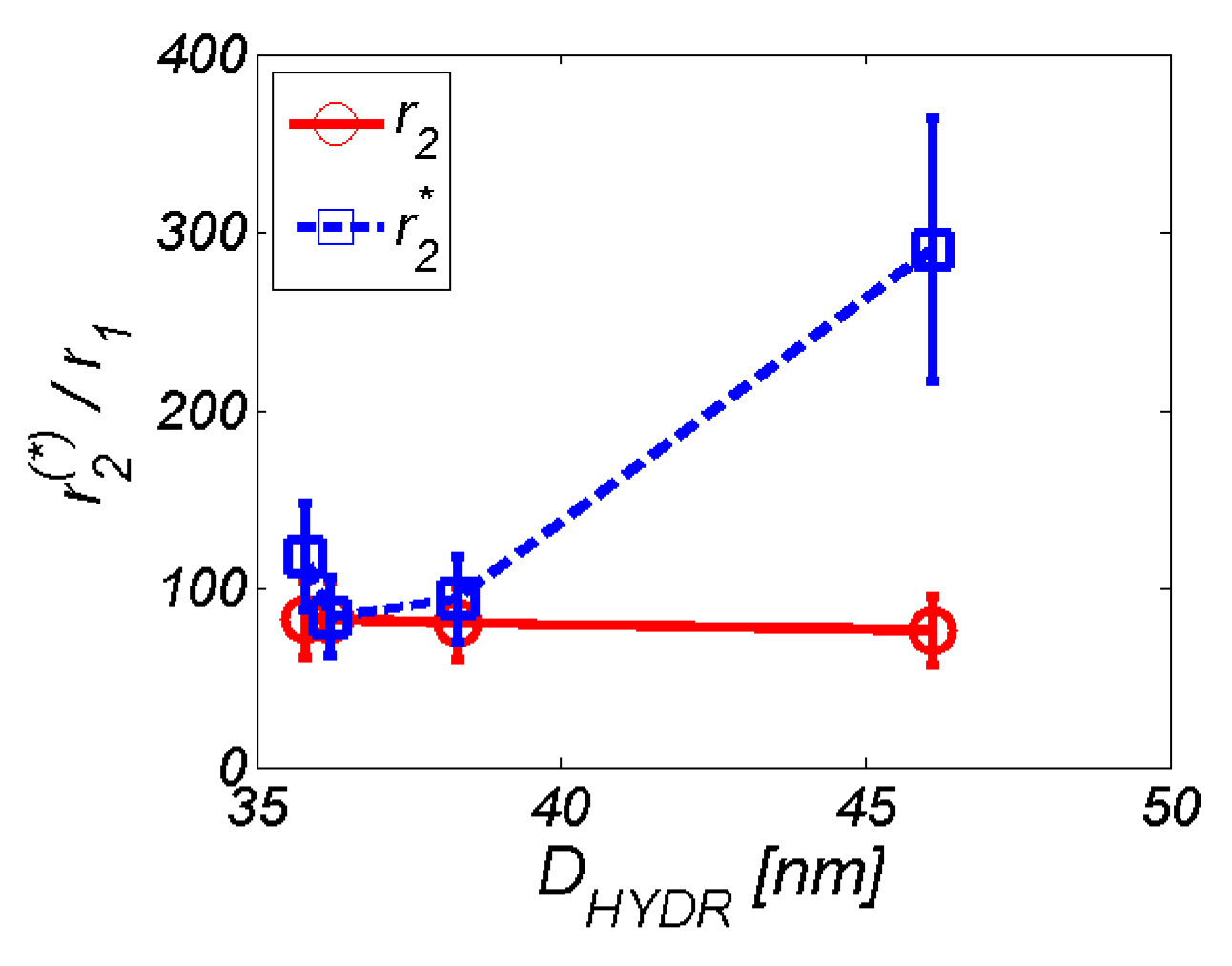
3.2. MRI analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colombo, M.; Carregal-Romero, S.; Casula, M.F.; Gutiérrez, L.; Morales, M.P.; Böhm, I.B.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Prosperi, D.; Parak, W.J. Biological applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4306–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varanda, L.C.; Júnior, M.J.; Júnior, W.B. Magnetic and Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine: Challenges and Trends in Synthesis and Surface Engineering for Diagnostic and Therapy Applications. In Biomedical Engineering; Laskovski, A.N., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.H.; Zhang, M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bao, G.; Mitragotri, S.; Tong, S. Multifunctional Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Molecular Imaging. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 15, 253–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Yang, H.; Qiao, J.; Pu, F.; Jiang, J.; Hubbard, K.; Hekmatyar, K.; Langley, J.; Salarian, M.; Long, R.C.; et al. Protein MRI contrast agent with unprecedented metal selectivity and sensitivity for liver cancer imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6607–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, A.K.; Lockhart, D.C.; Bernstorff, W.; von Spanjaard, R.A.; Joo, H.G.; Eberlein, T.J.; Goedegebuure, P.S. Soluble MUC1 secreted by human epithelial cancer cells mediates immune suppression by blocking T-cell activation. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zuo, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W. Potential biomarkers relating pathological proteins, neuroinflammatory factors and free radicals in PD patients with cognitive impairment: A cross-sectional study. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strbak, O.; Kubovcikova, M.; Baciak, L.; Khmara, I.; Gogola, D.; Koneracka, M.; Zavisova, V.; Antal, I.; Masarova, M.; Krafcik, A.; et al. Effect of BSA protein on the contrast properties of magnetite nanoparticles during MRI. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filss, C.P.; Cicone, F.; Shah, N.J.; Galldiks, N.; Langen, K.-J. Amino acid PET and MR perfusion imaging in brain tumours. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galldiks, N.; Law, I.; Pope, W.B.; Arbizu, J.; Langen, K.-J. The use of amino acid PET and conventional MRI for monitoring of brain tumor therapy. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 13, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barick, K.C.; Singh, S.; Bahadur, D.; Lawande, M.A.; Patkar, D.P.; Hassan, P.A. Carboxyl decorated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for MRI diagnosis and localized hyperthermia. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 418, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barick, K.C.; Hassan, P.A. Glycine passivated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for thermal therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 369, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-R.; Wang, S.-Q.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhao, B.-X. A novel water treatment magnetic nanomaterial for removal of anionic and cationic dyes under severe condition. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-R.; Shen, S.-L.; Wang, S.-Q.; Huang, J.; Su, P.; Wang, Q.-R.; Zhao, B.-X. A dual function magnetic nanomaterial modified with lysine for removal of organic dyes from water solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 239, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Meng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Su, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Miao, J. The effect of two novel amino acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles on survival in vascular endothelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and macrophages. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viota, J.L.; Arroyo, F.J.; Delgado, A.V.; Horno, J. Electrokinetic characterization of magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with amino acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Choi, E.S.; Baek, M.J.; Lee, G.H. Colloidal stability of amino acid coated magnetite nanoparticles in physiological fluid. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, G.; Patron, L.; Culita, D.C.; Neagoe, C.; Lepadatu, C.I.; Balint, I.; Bessais, L.; Cizmas, C.B. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of aminoacids. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2006, 8, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, S. Study of the Adsorption of L-Phenylalanine, L-Tryptophan, and L-Tyrosine from Aqueous Samples by Fe3O4 Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles with Ionic Liquid. Biquarterly Iran. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 3, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Uddin, M.S.; Hidajat, K. Adsorption of chiral aromatic amino acids onto carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin bonded Fe3O4/SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosova, A.; Bednarikova, Z.; Koneracka, M.; Antal, I.; Zavisova, V.; Kubovcikova, M.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, S.S.-S.; Gazova, Z. Destroying activity of glycine coated magnetic nanoparticles on lysozyme, α-lactalbumin, insulin and α-crystallin amyloid fibrils. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 471, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosova, A.; Bednarikova, Z.; Koneracka, M.; Antal, I.; Marek, J.; Kubovcikova, M.; Zavisova, V.; Jurikova, A.; Gazova, Z. Amino Acid Functionalized Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Inhibit Lysozyme Amyloid Fibrillization. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 7501–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R. Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 1981, 17, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, I.; Koneracka, M.; Kubovcikova, M.; Zavisova, V.; Khmara, I.; Lucanska, D.; Jelenska, L.; Vidlickova, I.; Zatovicova, M.; Pastorekova, S.; et al. d,l-lysine functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles for detection of cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek, K.; Hornowski, T.; Antal, I.; Timko, M.; Józefczak, A. Magneto-ultrasonic heating with nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 474, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubovčíková, M.; Antal, I.; Kováč, J.; Závišová, V.; Koneracká, M.; Kopčanský, P. Preparation and complex characterization of magnetic nanoparticles in magnetic fluid. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 126, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavisova, V.; Koneracka, M.; Kovac, J.; Kubovcikova, M.; Antal, I.; Kopcansky, P.; Bednarikova, M.; Muckova, M. The cytotoxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different modifications evaluated in vitro. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmara, I.; Strbak, O.; Zavisova, V.; Koneracka, M.; Kubovcikova, M.; Antal, I.; Kavecansky, V.; Lucanska, D.; Dobrota, D.; Kopcansky, P. Chitosan-stabilized iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 474, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.; Mellon, M. Thiocyanate Method for Iron: A Spectrophotometric Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1941, 13, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noval, V.E.; Carriazo, J.G. Fe3O4-TiO2 and Fe3O4-SiO2 Core-shell Powders Synthesized from Industrially Processed Magnetite (Fe3O4) Microparticles. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pušnik, K.; Peterlin, M.; Cigić, I.K.; Marolt, G.; Kogej, K.; Mertelj, A.; Gyergyek, S.; Makovec, D. Adsorption of Amino Acids, Aspartic Acid, and Lysine onto Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 14372–14381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezwan, K.; Meier, L.P.; Rezwan, M.; Vörös, J.; Textor, M.; Gauckler, L.J. Bovine Serum Albumin Adsorption onto Colloidal Al2O3 Particles: A New model based on zeta potential and UV-VIS measuerements. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10055–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, Z.R.; Kievit, F.M.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for medical MR imaging. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelrich, J.; Sanchez-Martin, M.J.; Busquets, M.A. Nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging: From simple to dual contrast agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer, M.; Bauer, H.; Mintorovitch, J.; Requardt, M.; Weinmann, H.-J. Comparison of Magnetic Properties of MRI Contrast Media Solutions at Different Magnetic Field Strengths. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
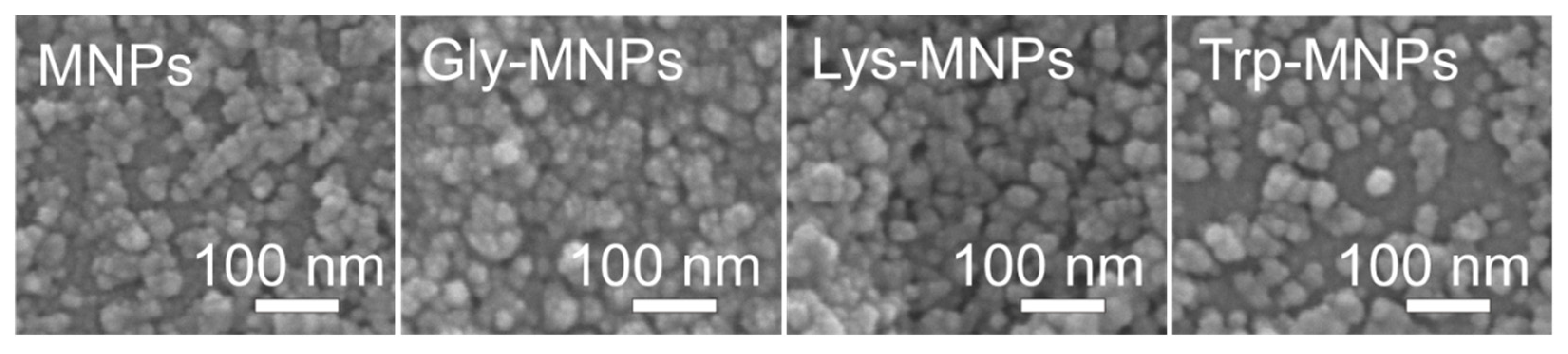

| Name | Structure | Three Letter Code | Molecular Weight | Isoelectric Point (IEP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gly (Nonpolar, aliphatic R-group) | 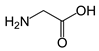 | Gly | 75 | 5.97 |
| Lys (Positively charged R-group) | 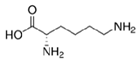 | Lys | 146 | 9.74 |
| Trp (Aromatic R-group) | 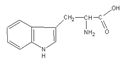 | Trp | 204 | 5.89 |
| Samples | DMAG (nm) | DTEM(nm) | DDLS(nm) | Layer Thickness (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Isoelectric Point pH | Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNPs | 13.2 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 35.8 ± 0.3 | − | 30.2±1.7 (pH = 3.6) | 6.9 | 1.76 |
| Gly-MNPs | 12.9 ± 0.1 | 8.6 ± 0.1 | 38.3 ± 0.3 | 1.25 | 39.4±1.3 (pH = 3.9) | 6.6 | 1.50 |
| Lys-MNPs | 12.3 ± 0.4 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 36.2 ± 0.4 | 1.40 | 34.6±2.3 (pH = 4.1) | 8.0 | 1.37 |
| Trp-MNPs | 12.6 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 46.1 ± 0.4 | 5.15 | 36.7±1.3 (pH = 4.6) | 6.4 | 1.15 |
| Relaxivity-Diameter | MNPs | Lys | Lys-MNPs | Gly | Gly-MNPs | Trp | Trp-MNPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1 (mM−1s−1) | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 0.036 ± 0.007 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 0.055 ± 0.01 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | −0.009 ± 0.011 | 0.9 ± 0.2 |
| r2 (mM−1s−1) | 201.9 ± 36.3 | 0.06 ± 0.011 | 199.6 ± 35.9 | 0.137 ± 0.025 | 192.6 ± 34.7 | 0.025 ± 0.003 | 67.6 ± 12.2 |
| r2*(mM−1s−1) | 285.8 ± 51.4 | NA | 201.8 ± 37.5 | NA | 225.1 ± 40.5 | NA | 256.3 ± 46.2 |
| DDLS (nm) | 35.8 ± 0,3 | NA | 36.2 ± 0.4 | NA | 38.3 ± 0.3 | NA | 46.1 ± 0.4 |
| r1 [mM−1s−1] | r2 [mM−1s−1] | Field Strength [T] | Temperature [°C] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resovist [34] | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 176 ± 9 | 4.7 | 37 |
| Feridex [34] | 2.3 ± 0.1 | 105 ± 5 | 4.7 | 37 |
| MNPs | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 201.9 ± 36.3 | 7 | 22 |
| Lys-MNPs | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 199.6 ± 35.9 | 7 | 22 |
| Gly-MNPs | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 192.6 ± 34.7 | 7 | 22 |
| Trp-MNPs | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 67.6 ± 12.2 | 7 | 22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antal, I.; Strbak, O.; Khmara, I.; Koneracka, M.; Kubovcikova, M.; Zavisova, V.; Kmetova, M.; Baranovicova, E.; Dobrota, D. MRI Relaxivity Changes of the Magnetic Nanoparticles Induced by Different Amino Acid Coatings. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020394
Antal I, Strbak O, Khmara I, Koneracka M, Kubovcikova M, Zavisova V, Kmetova M, Baranovicova E, Dobrota D. MRI Relaxivity Changes of the Magnetic Nanoparticles Induced by Different Amino Acid Coatings. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020394
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntal, Iryna, Oliver Strbak, Iryna Khmara, Martina Koneracka, Martina Kubovcikova, Vlasta Zavisova, Martina Kmetova, Eva Baranovicova, and Dusan Dobrota. 2020. "MRI Relaxivity Changes of the Magnetic Nanoparticles Induced by Different Amino Acid Coatings" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020394
APA StyleAntal, I., Strbak, O., Khmara, I., Koneracka, M., Kubovcikova, M., Zavisova, V., Kmetova, M., Baranovicova, E., & Dobrota, D. (2020). MRI Relaxivity Changes of the Magnetic Nanoparticles Induced by Different Amino Acid Coatings. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020394






