Preparation and Applications of Organo-Silica Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids
Abstract
1. Introduction
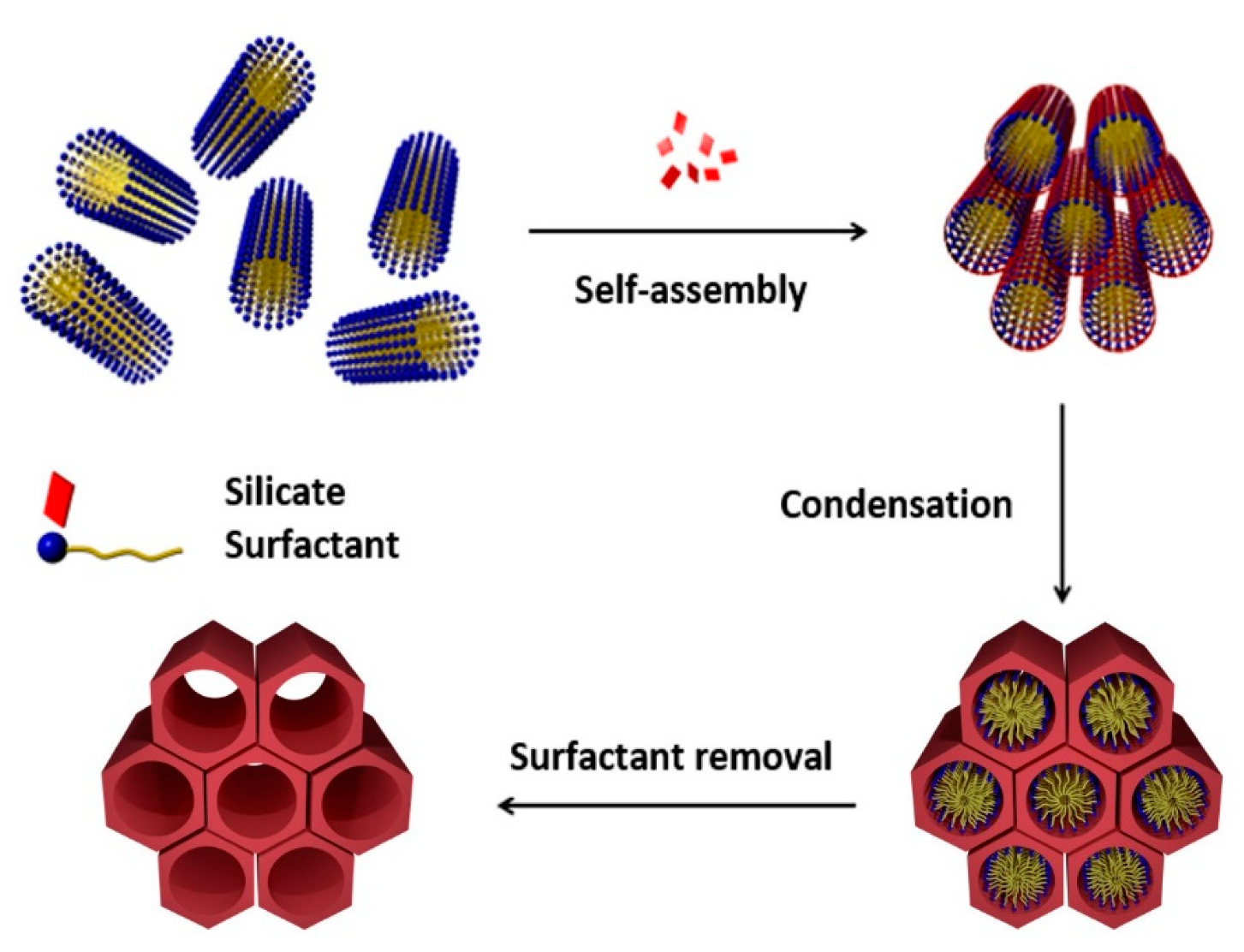
2. Mesoporous Silicas in Drug Delivery
3. Multiple Drug Delivery Systems Based on MSNs
3.1. DDSs with Drugs Grafted inside the MSNs
3.2. MSNs Containing a Drug inside the Pores and a Second Drug outside as Stopper
3.3. DDS Containing a Drug inside the Pores Using CD as Valve
3.4. DDSs Loaded with One Drug and Coated with a Polymer
4. Nano-systems Based on MSNs for the Delivery of Combination of Drugs and Nucleic Acids
4.1. DDSs with RNA Attached Covalently onto the Surface of the MSNs
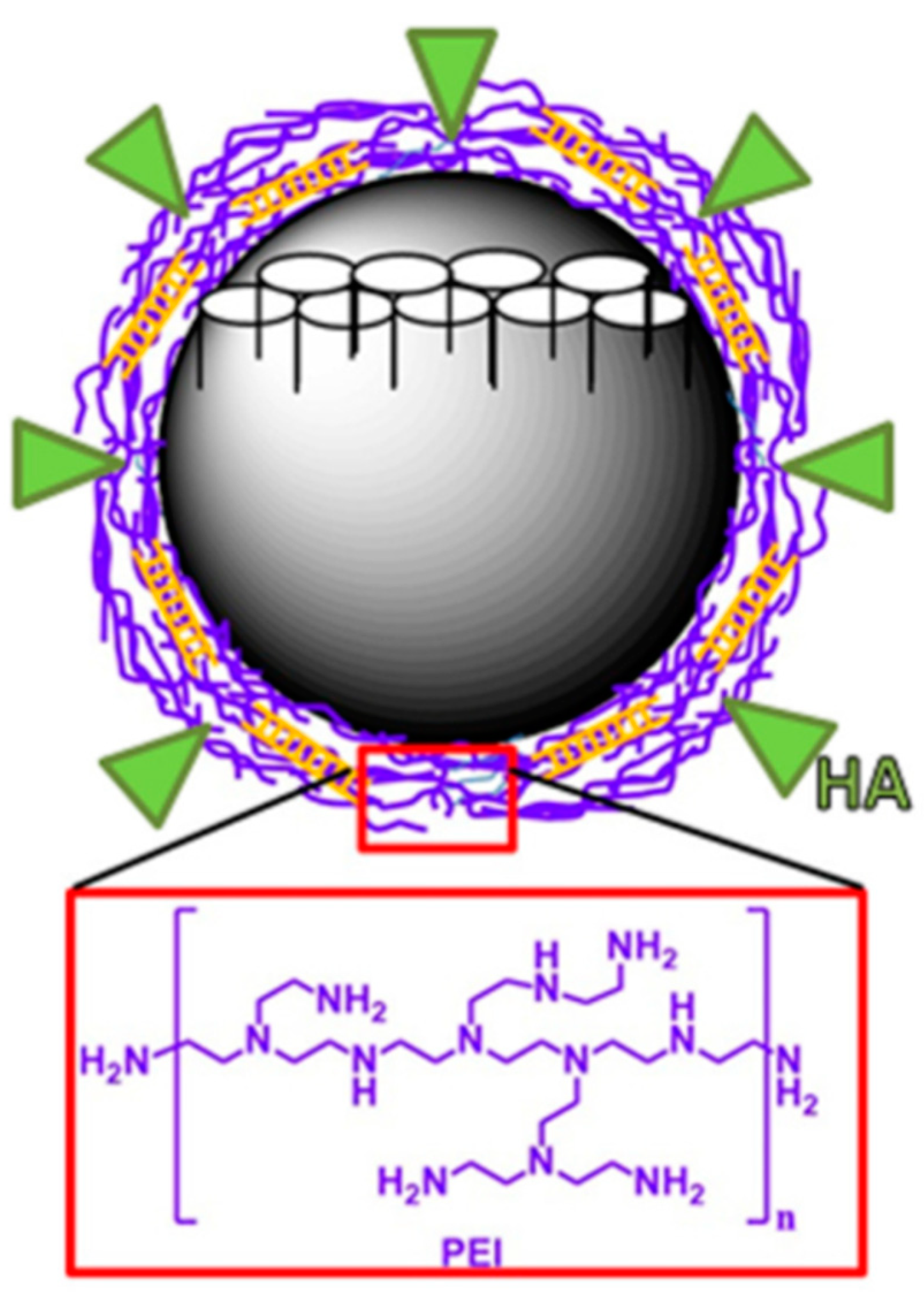
4.2. MSNs Coated by a Polycation
4.2.1. Polymer Attached to the NP by Electrostatic Interactions
4.2.2. Polycation Attached Covalently to the NP
4.2.3. Polycation Attached with a Cleavable Linker
4.3. MSN Coated by Polycation with Targeting
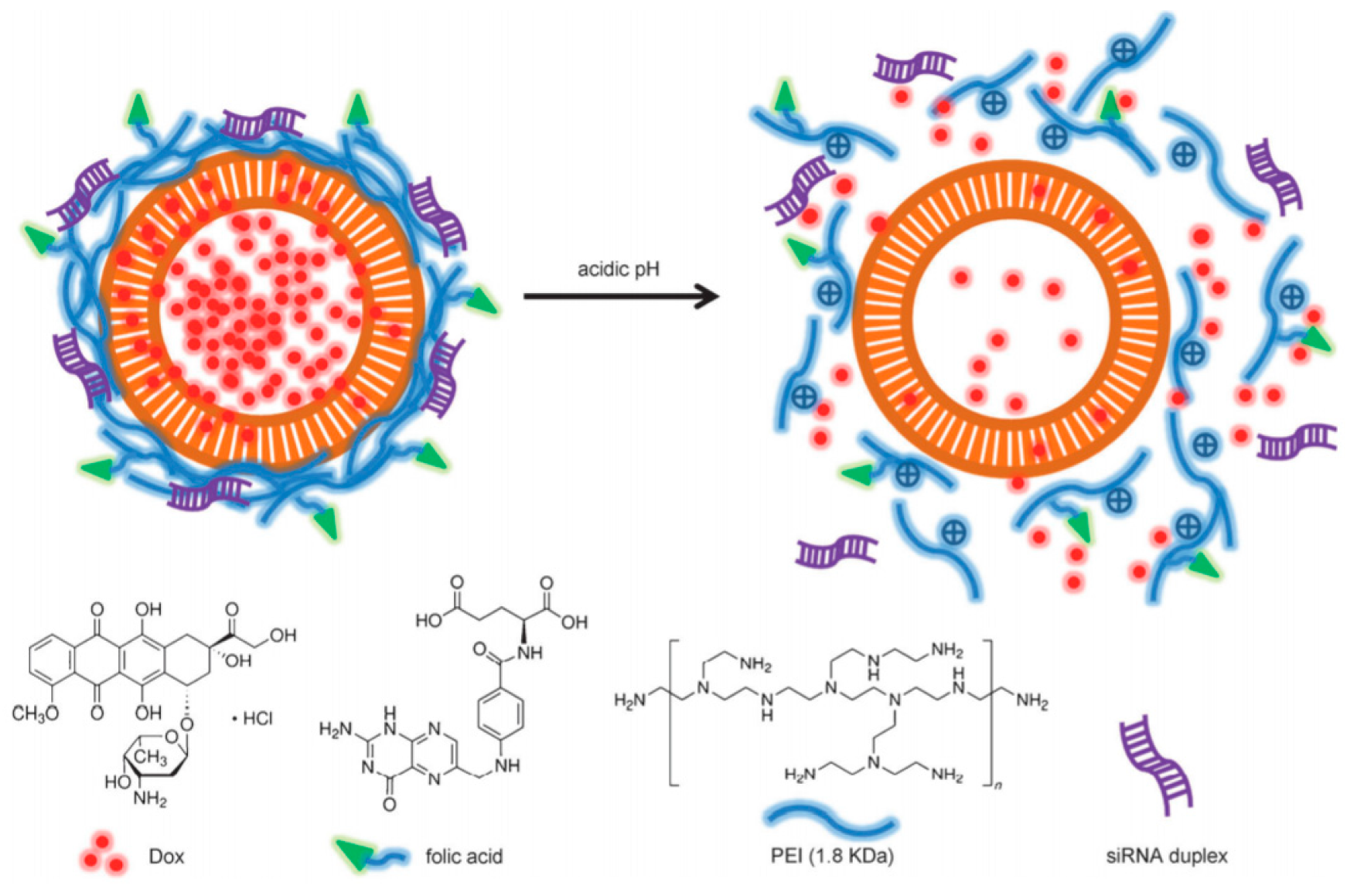
4.3.1. DDSs Decorated with Folic Acid
4.3.2. DDS Decorated with Hyaluronic Acid and Lactobionic Acid
4.3.3. DDS Decorated with Peptides
4.4. SiRNA inside the Pores
5. Biological and Medical Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Creixell, M.; Peppas, N.A. Co-delivery of siRNA and therapeutic agents using nanocarriers to overcome cancer resistance. Nano Today 2012, 7, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswathy, M.; Gong, S. Recent developments in the co-delivery of siRNA and small molecule anticancer drugs for cancer treatment. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, J.A.; Shim, M.S.; Heo, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.J. “Combo” nanomedicine: Co-delivery of multi-modal therapeutics for efficient, targeted, and safe cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 98, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, S.; Patel, M.M. Threatening cancer with nanoparticle aided combination oncotherapy. J. Controll. Releas. Off. J. Control. Releas. Soc. 2019, 301, 76–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampucci, S.; Carpi, S.; Digiacomo, M.; Polini, B.; Fogli, S.; Burgalassi, S.; Macchia, M.; Nieri, P.; Manera, C.; Monti, D. Diclofenac-Derived Hybrids for Treatment of Actinic Keratosis and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Molecules 2019, 24, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Nie, G.; Nan, K. Co-delivery strategies based on multifunctional nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturrioz-Rodriguez, N.; Correa-Duarte, M.A.; Fanarraga, M.L. Controlled drug delivery systems for cancer based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3389–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles in Cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine--recent advances. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, S.; Goel, S.; Shen, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Qin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Recent Advancements in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles towards Therapeutic Applications for Cancer. Acta Biomater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. Inorganic Nanoparticle-Based Drug Codelivery Nanosystems To Overcome the Multidrug Resistance of Cancer Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2495–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi-Bojd, M.Y.; Ansari, L.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Codelivery of anticancer drugs and siRNA by mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, R.R.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Advances in mesoporous silica-based nanocarriers for co-delivery and combination therapy against cancer. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Paris, J.L.; Vallet-Regi, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids in Oncology: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, F.; Cornelius, M.; Morell, J.; Froba, M. Silica-based mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Angew. Chem. 2006, 45, 3216–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert-Garzaran, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Influence of the surface functionalization on the fate and performance of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Kim, S.-G.; Iskandar, F.; Okuyama, K. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi Vavsari, V.; Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Badiei, A. The role of SBA-15 in drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91686–91707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewyn, B.G.; Slowing, I.I.; Giri, S.; Chen, H.T.; Lin, V.S. Synthesis and functionalization of a mesoporous silica nanoparticle based on the sol-gel process and applications in controlled release. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinàs, M.C.; Sánchez-García, D. Nanoparticulas de sílice y aplicaciones en biomedicina. Afinidad LXXI 2014, 565, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Edo, G.; Balmori, A.; Pontón, I.; Martí del Rio, A.; Sánchez-García, D. Functionalized Ordered Mesoporous Silicas (MCM-41): Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis. Catalysts 2018, 8, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Wu, C.W.; Lin, V.S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous Materials for Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Yang, Y.-W. Molecular and supramolecular switches on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3474–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles: Physical Chemistry, Biosafety, Delivery Strategies, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Glackin, C.A.; Horwitz, M.A.; Zink, J.I. Nanomachines and Other Caps on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Advances in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted stimuli-responsive drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zea, C.; Alcántara, J.; Barranco-García, R.; Morcillo, M.; De la Fuente, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Smart Corrosion Protection. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, T.-Q.; Fu, C.-Y. Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Decorated with Cyclodextrin for Inhibiting the Corrosion of Mg Alloys. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 4542–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai-Yamashita, C.; Fuji, M. Hollow silica nanoparticles: A tiny pore with big dreams. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 804–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.C.H.; Ng, D.K.P.; Fong, W.-P.; Lo, P.-C. Encapsulating pH-responsive doxorubicin-phthalocyanine conjugates in mesoporous silica nanoparticles for combined photodynamic therapy and controlled chemotherapy. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 16505–16515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Ng, D.K.P.; Fong, W.-P.; Lo, P.-C. Glutathione- and light-controlled generation of singlet oxygen for triggering drug release in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, L.H.; Hu, J.J.; Luo, G.F.; Chen, W.H.; Rong, L.; Zhang, X.Z. One-pot construction of functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the tumor-acidity-activated synergistic chemotherapy of glioblastoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7995–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinàs, M.C.; Martínez-Edo, G.; Cascante, A.; Porcar, I.; Borros, S.; Sánchez-García, D. Preparation of a mesoporous silica-based nano-vehicle for dual DOX/CPT pH-triggered delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Edo, G.; Fornaguera, C.; Borros, S.; Sanchez-Garcia, D. Glycyrrhetinic Acid-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of DOX/CPT-PEG for Targeting HepG2 Cells. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, F.; Guo, M.; Wang, A.; Zhao, J.; Qi, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, G. Responsive delivery of drug cocktail via mesoporous silica nanolamps. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 434, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; You, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. A pH-sensitive nanocarrier for co-delivery of doxorubicin and camptothecin to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy and overcome multidrug resistance in vitro. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 77097–77105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heleg-Shabtai, V.; Aizen, R.; Sharon, E.; Sohn, Y.S.; Trifonov, A.; Enkin, N.; Freage, L.; Nechushtai, R.; Willner, I. Gossypol-Capped Mitoxantrone-Loaded Mesoporous SiO2 NPs for the Cooperative Controlled Release of Two Anti-Cancer Drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14414–14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Guo, N.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Y. Active targeting co-delivery system based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antitumor therapy in ovarian cancer stem-like cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birault, A.; Giret, S.; Théron, C.; Gallud, A.; Da Silva, A.; Durand, D.; Nguyen, C.; Bettache, N.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Bartlett, J.R.; et al. Sequential delivery of synergistic drugs by silica nanocarriers for enhanced tumour treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théron, C.; Birault, A.; Bernhardt, M.; Ali, L.M.A.; Nguyen, C.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Bartlett, J.R.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Carcel, C. New precursors for the preparation of pH-sensitive, targeting, and loaded non-porous bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sha, H.; Ke, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Du, X. Combination drug release of smart cyclodextrin-gated mesoporous silica nanovehicles. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7203–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Hira, S.K.; Paladhi, A.; Singh, R.; Gupta, U.; Srivastava, D.N.; Singh, R.A.; Manna, P.P. Studies on interaction potency model based on drug synergy and therapeutic potential of triple stimuli-responsive delivery of doxorubicin and 5-fluoro-2-deoxyuridine against lymphoma using disulfide-bridged cysteine over mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Song, W.; Yin, J.; Zeng, X.; Han, S.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Tao, J.; Liu, C.-J.; He, X.-H.; Zhang, X.-Z. iRGD Modified Chemo-immunotherapeutic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Immunotherapy against Glioblastoma. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, J.; Su, H.; Mu, G.; Sun, J.-H.; Tan, C.-P.; Liang, X.-J.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W. Co-Delivery of Cisplatin Prodrug and Chlorin e6 by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Chemo-Photodynamic Combination Therapy to Combat Drug Resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13332–13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, K.K.; Mishra, D.K.; Rosling, A.; Rosenholm, J.M. Therapeutic potential of polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; He, J.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, J. Chitosan capped pH-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted chemo-photo combination therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
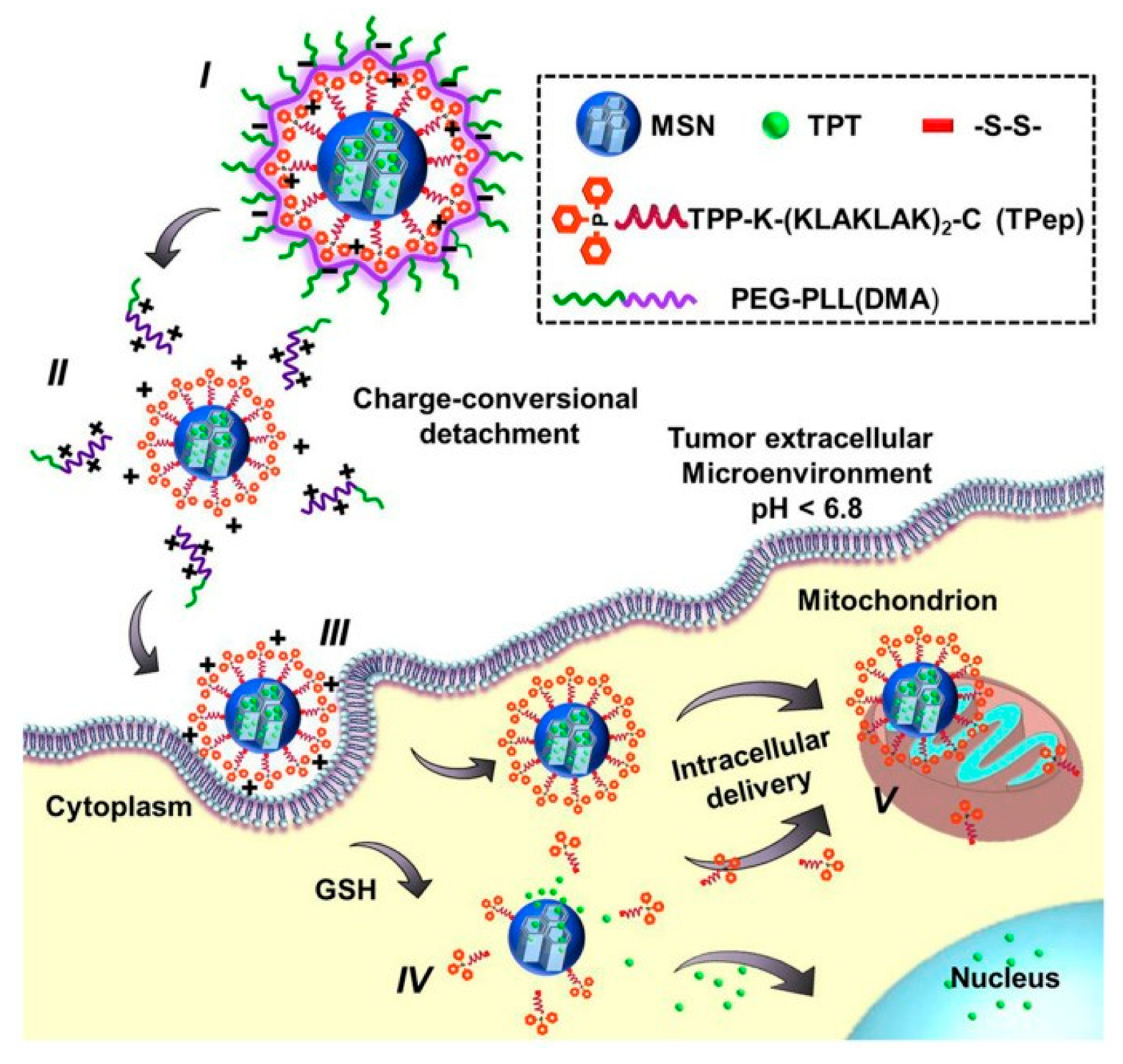
- Luo, G.F.; Chen, W.H.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Q.; Zhuo, R.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Multifunctional enveloped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for subcellular co-delivery of drug and therapeutic peptide. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
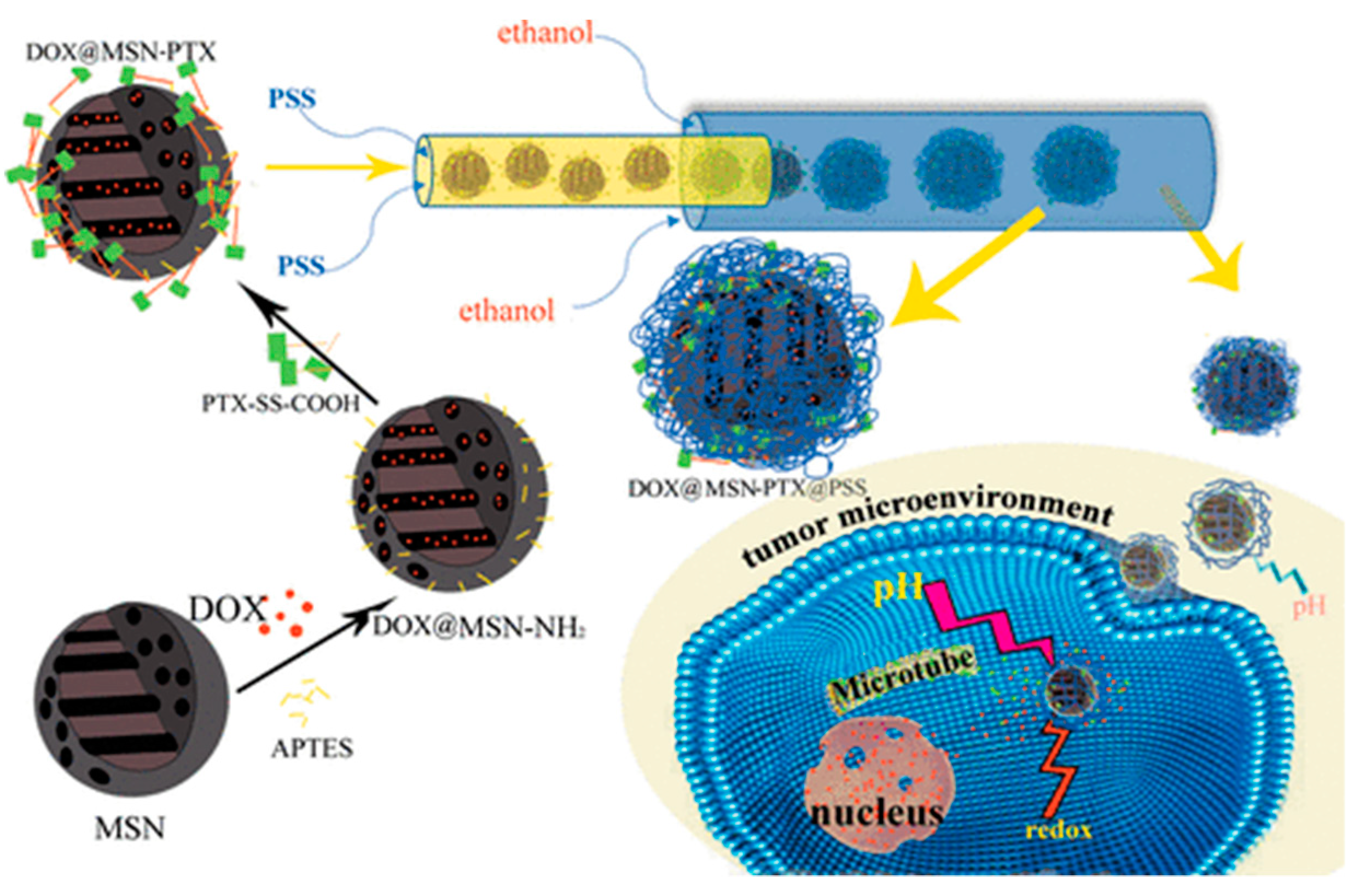
- Yan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H. Fabrication of a pH/redox-triggered mesoporous silica-based nanoparticle with microfluidics for anticancer drugs doxorubicin and paclitaxel codelivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiparti, K.; Sau, S.; Kashaw, S.K.; Iyer, A.K. siRNA Delivery Strategies: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Developments. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamegawa, R.; Naito, M.; Miyata, K. Functionalization of silica nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 5219–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taratula, O.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Chen, A.M.; Minko, T. Innovative strategy for treatment of lung cancer: Targeted nanotechnology-based inhalation co-delivery of anticancer drugs and siRNA. J. Drug Targets 2011, 19, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
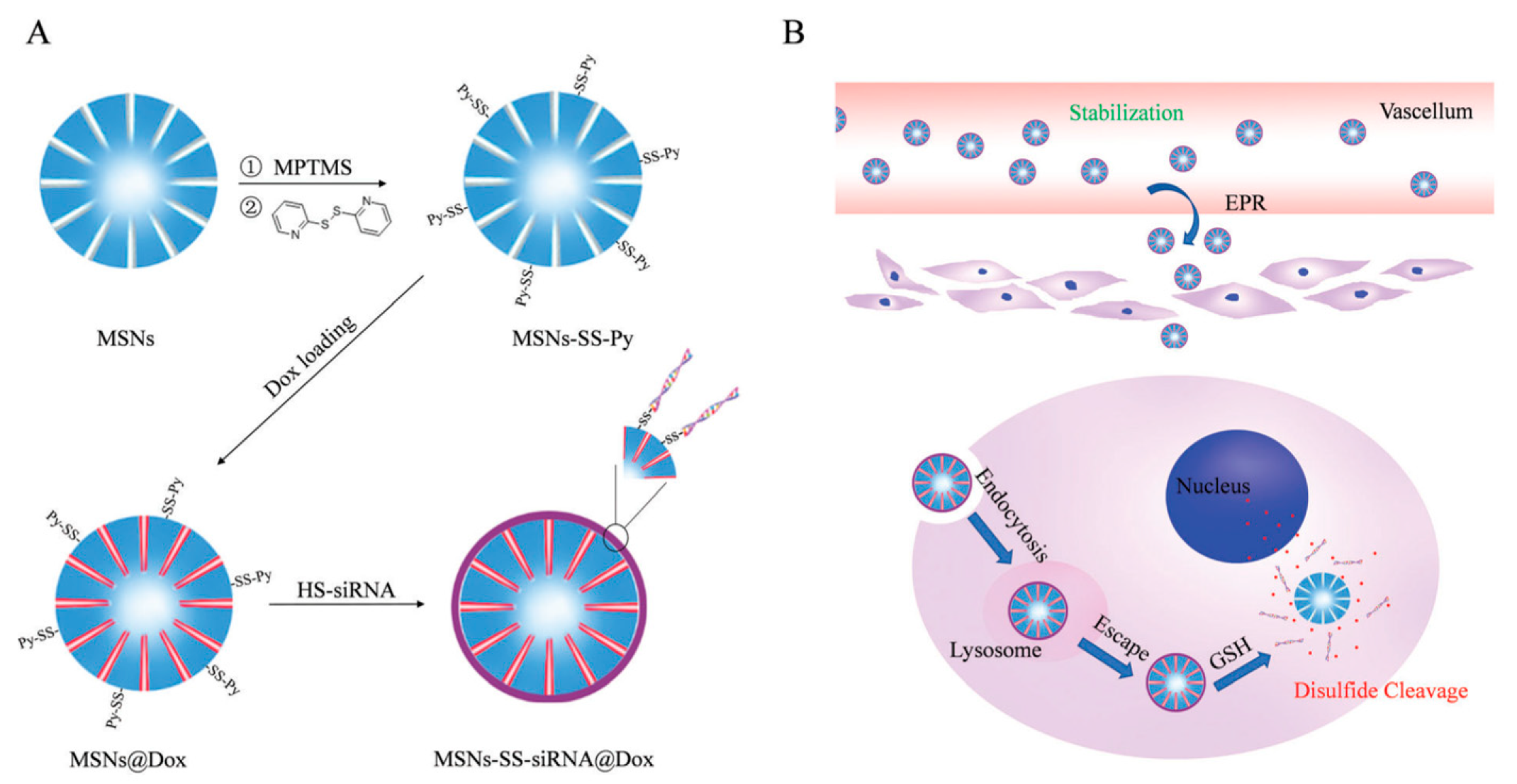
- Zhao, S.; Xu, M.; Cao, C.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J. A redox-responsive strategy using mesoporous silica nanoparticles for co-delivery of siRNA and doxorubicin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6908–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Liong, M.; Xia, T.; Li, Z.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Engineered Design of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles to Deliver Doxorubicin and P-Glycoprotein siRNA to Overcome Drug Resistance in a Cancer Cell Line. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4539–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Mai, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Codelivery of an Optimal Drug/siRNA Combination Using Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles To Overcome Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Meng, L.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Yang, B.; Sun, H. Codelivery of doxorubicin and MDR1-siRNAby mesoporous silica nanoparticles-polymerpolyethylenimine to improve oral squamous carcinoma treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Morry, J.; Gu, S.; Castro, D.J.; Goodyear, S.M.; Sangvanich, T.; Reda, M.M.; Lee, R.; Mihelic, S.A.; Beckman, B.L.; et al. Cationic Polymer Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Targeted SiRNA Delivery to HER2+ Breast Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2646–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilnawaz, F.; Sahoo, S.K. Augmented Anticancer Efficacy by si-RNA Complexed Drug-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Lung Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Xue, M.; Xia, T.; Ji, Z.; Tarn, D.Y.; Zink, J.I.; Nel, A.E. Use of Size and a Copolymer Design Feature To Improve the Biodistribution and the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect of Doxorubicin-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in a Murine Xenograft Tumor Model. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4131–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: Pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xue, J.; Gao, S.; Lu, A.; Yang, D.; Jiang, H.; He, Y.; Shi, K. Cleavable PEGylation: A strategy for overcoming the “PEG dilemma” in efficient drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Long, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, M.; Cui, T.; Wen, X.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Che, L. Smart pH-sensitive nanoassemblies with cleavable PEGylation for tumor targeted drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Salcedo, S.; Vallet-Regi, M.; Shanin, S.A.; Glackin, C.A.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous core-shell silica nanoparticles with anti-fouling properties for ovarian cancer therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.M.; Zhang, M.; Wei, D.; Stueber, D.; Taratula, O.; Minko, T.; He, H. Co-delivery of Doxorubicin and Bcl-2 siRNA by Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Enhances the Efficacy of Chemotherapy in Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cells. Small 2009, 5, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
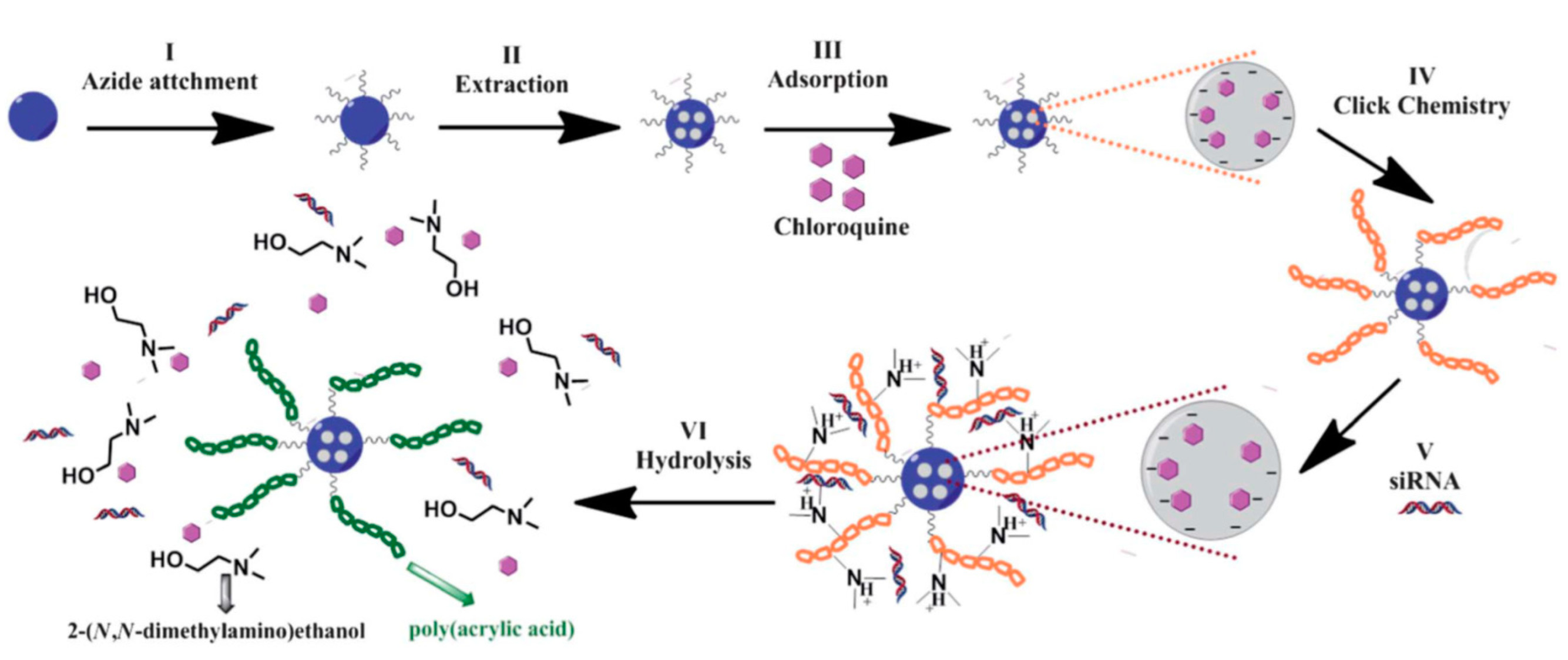
- Bhattarai, S.R.; Muthuswamy, E.; Wani, A.; Brichacek, M.; Castaneda, A.L.; Brock, S.L.; Oupicky, D. Enhanced gene and siRNA delivery by polycation-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with chloroquine. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 2556–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
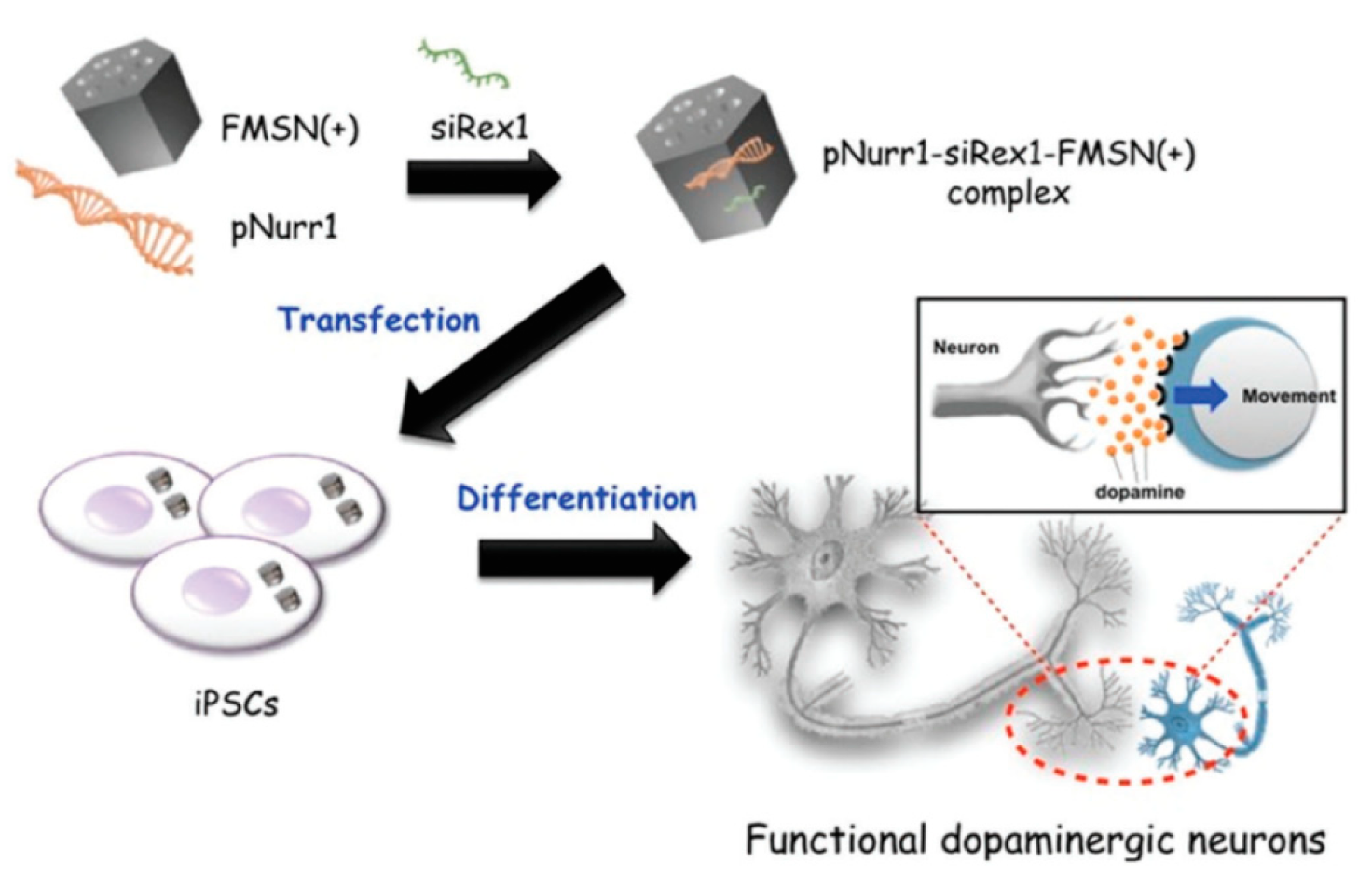
- Chang, J.-H.; Tsai, P.-H.; Chen, W.; Chiou, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y. Dual delivery of siRNA and plasmid DNA using mesoporous silica nanoparticles to differentiate induced pluripotent stem cells into dopaminergic neurons. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3012–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, S.B.; Phuoc, N.T.; Yu, M.; Jia, Z.; Monteiro, M.J.; Qiao, S.; Yu, C. Functionalized large pore mesoporous silica nanoparticles for gene delivery featuring controlled release and co-delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Survivin shRNA-Expressing Plasmid Via Microenvironment-Responsive Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2829–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, T.; Traeger, A.; Schubert, U.S. The great escape: How cationic polyplexes overcome the endosomal barrier. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6904–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
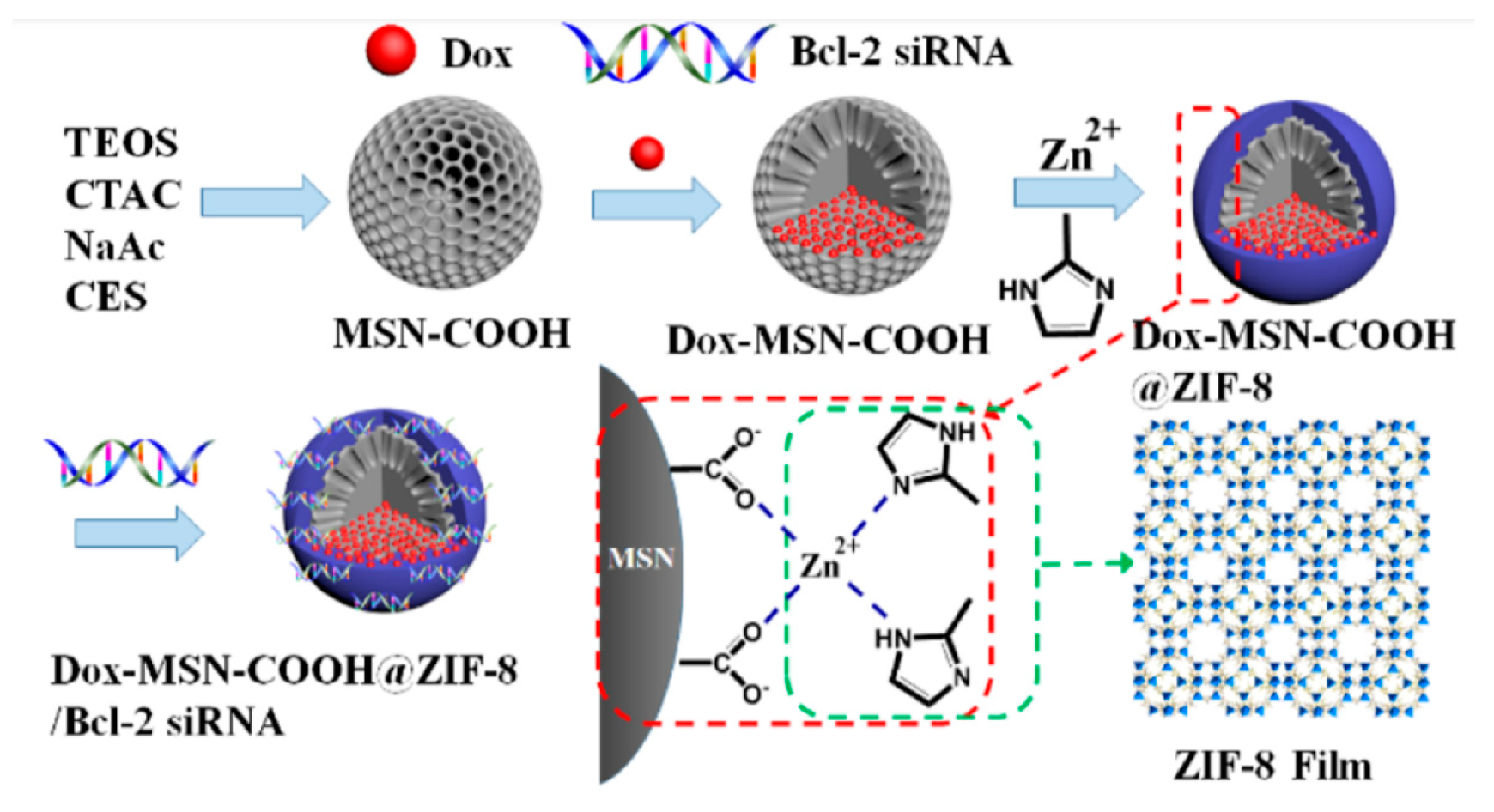
- Pan, Q.-S.; Chen, T.-T.; Nie, C.-P.; Yi, J.-T.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.-L.; Chu, X. In Situ Synthesis of Ultrathin ZIF-8 Film-Coated MSNs for Codelivering Bcl 2 siRNA and Doxorubicin to Enhance Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in Drug-Resistant Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33070–33077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Meng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Cai, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Large Pore-Sized Hollow Mesoporous Organosilica for Redox-Responsive Gene Delivery and Synergistic Cancer Chemotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xue, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Xiazeng, Z.; Cai, K.-Y.; Luo, Z. Hierarchical integration of degradable mesoporous silica nanoreservoirs and supramolecular dendrimer complex as a general-purpose tumor-targeted biomimetic nanoplatform for gene/small-molecule anticancer drug co-delivery. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16102–16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Teh, C.; Zhang, Q.; Borah, P.; Choong, C.; Korzh, V.; Zhao, Y. Redox-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Physiologically Sensitive Codelivery Vehicle for siRNA and Doxorubicin. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
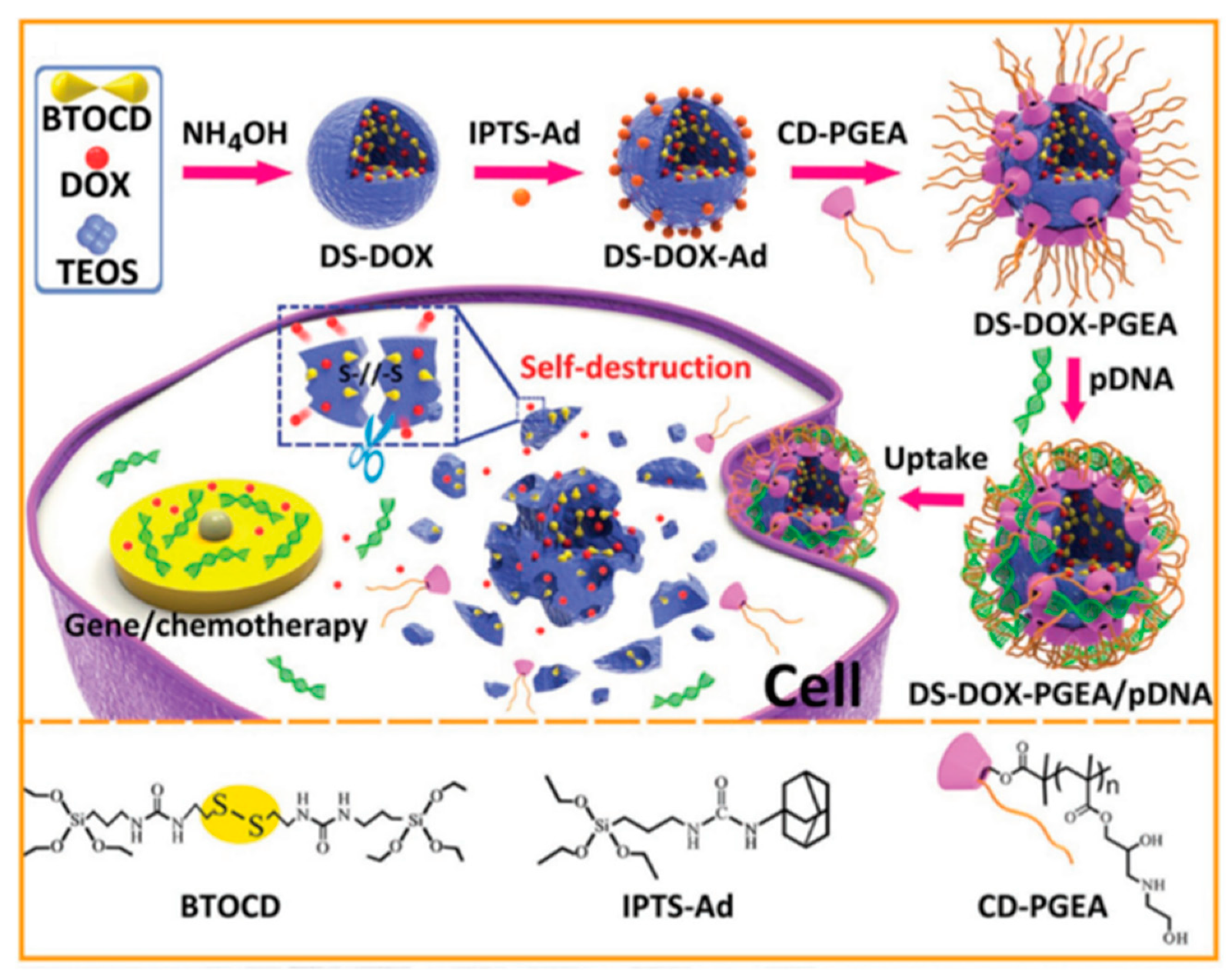
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F.-J. Redox-Responsive and Drug-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles with Unique Self-Destruction Features for Efficient Gene/Drug Codelivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
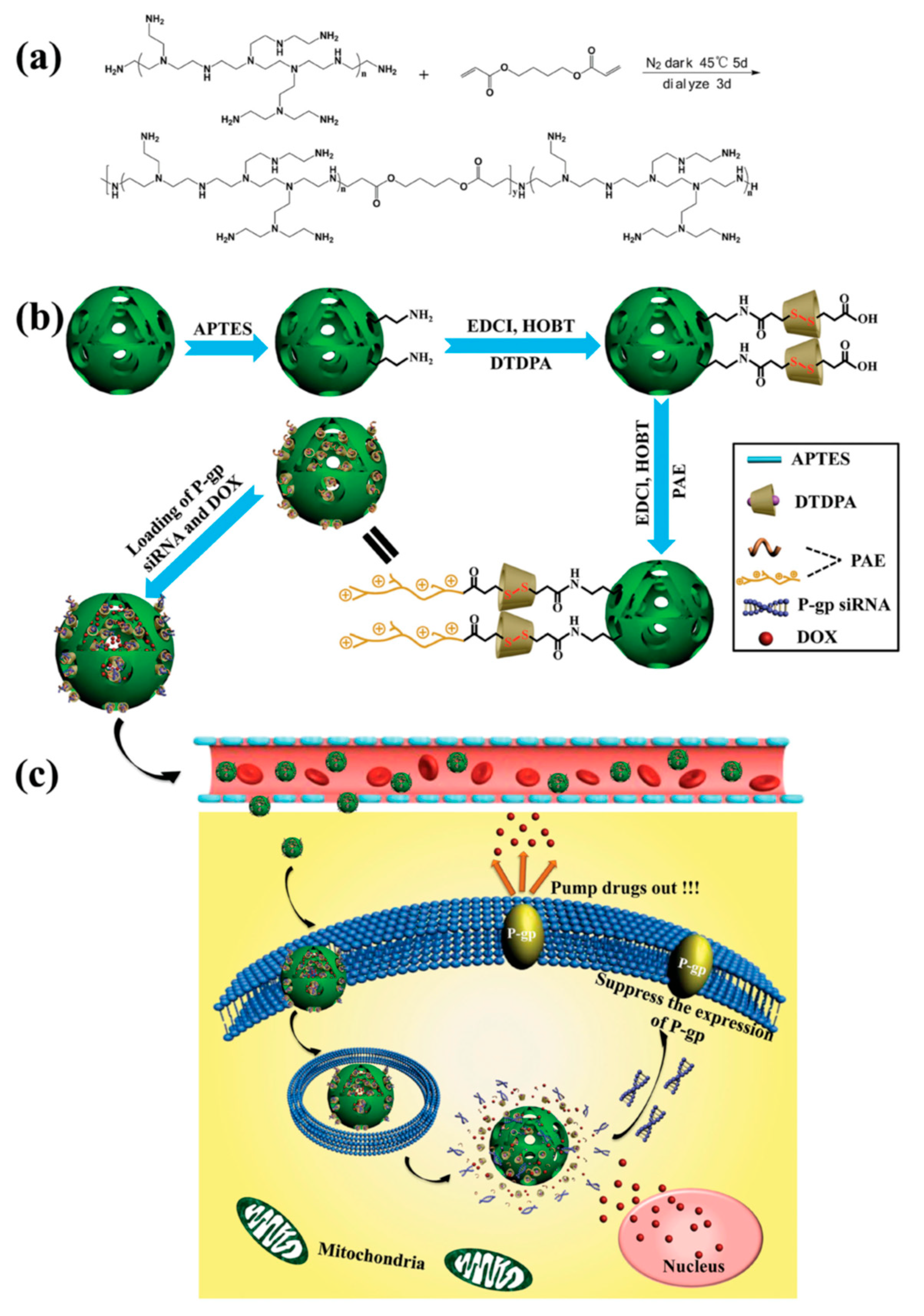
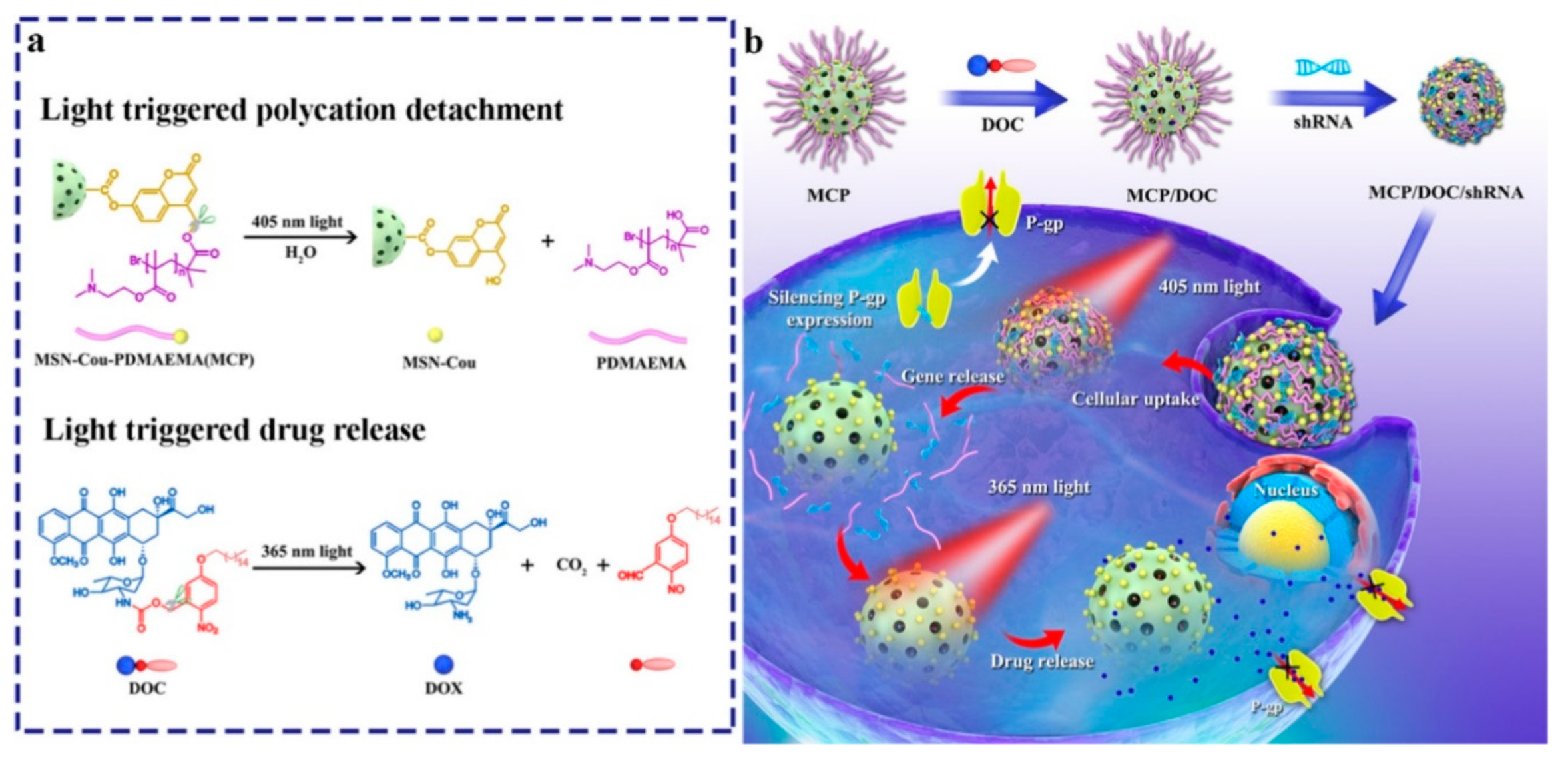
- Wu, M.; Lin, X.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, A.-x.; Zhao, B.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Photoresponsive Nanovehicle for Two Independent Wavelength Light-Triggered Sequential Release of P-gp shRNA and Doxorubicin To Optimize and Enhance Synergistic Therapy of Multidrug-Resistant Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19416–19427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Durand, J.-O. Targeted Treatment of Cancer with Nanotherapeutics Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ChemPlusChem 2015, 80, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ng, K.W.; Zhao, Y. Integrated Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Target Drug/siRNA Co-Delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15593–15603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shen, X.; Geng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Y. Folate-Functionalized Magnetic-Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug/Gene Codelivery To Potentiate the Antitumor Efficacy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13748–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, A.; Shao, J. Dual-Targeting Multifuntional Mesoporous Silica Nanocarrier for Codelivery of siRNA and Ursolic Acid to Folate Receptor Overexpressing Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6904–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Nie, W.; Wang, W.; Qin, M.; Mo, X.; Wang, H.; He, C. Dual-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Mediated Codelivery of Doxorubicin and Bcl-2 SiRNA for Targeted Treatment of Breast Cancer. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 22375–22387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, S.A.; Wang, R.; Simargi, S.I.; Contreras, A.; Parra Echavarria, L.; Qu, L.; Wen, W.; Dellinger, T.; Unternaehrer, J.; Tamanoi, F.; et al. Hyaluronic acid conjugated nanoparticle delivery of siRNA against TWIST reduces tumor burden and enhances sensitivity to cisplatin in ovarian cancer. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Bai, X.; Cao, X.; Jiao, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wen, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Nanocarrier for Co-delivery of MiR-31 and Doxorubicin To Suppress High MtEF4 Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22767–22775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
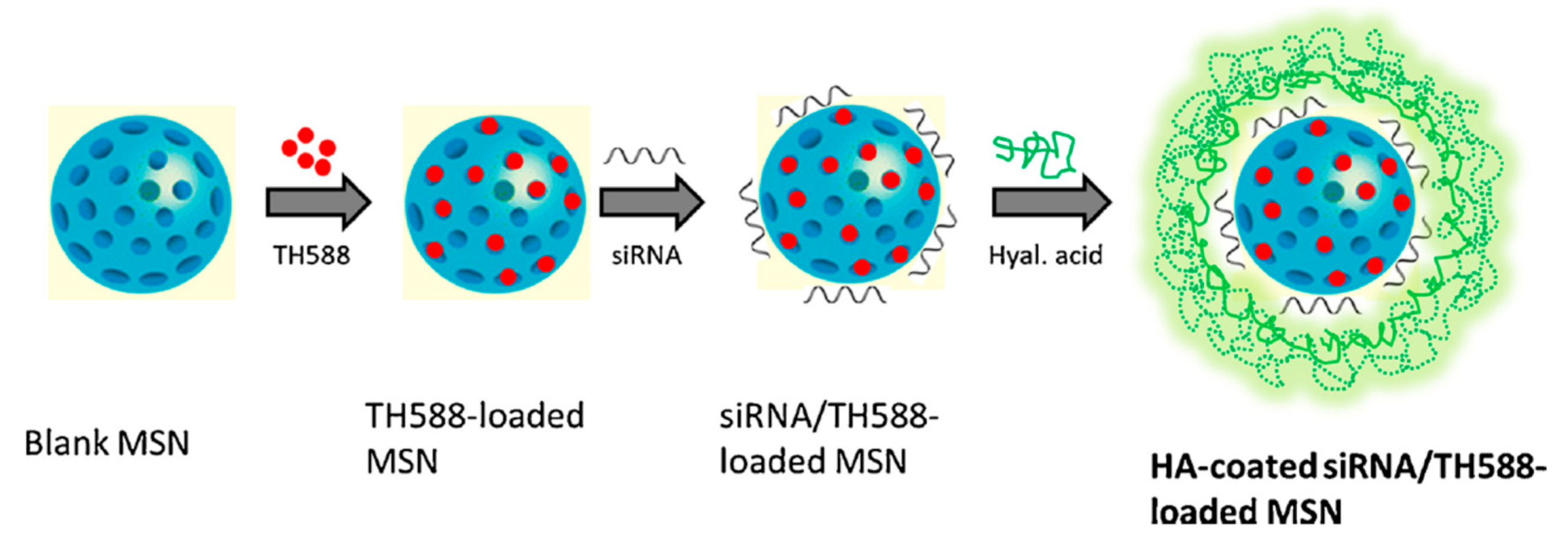
- Shi, X.-L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.-M.; Su, L.-W.; Ding, G. Delivery of MTH1 inhibitor (TH287) and MDR1 siRNA via hyaluronic acid-based mesoporous silica nanoparticles for oral cancers treatment. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 173, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Zhao, R.; Xu, A.; Shen, Z.; Chen, X.; Shao, J. Co-delivery of sorafenib and siVEGF based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for ASGPR mediated targeted HCC therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Dual-targeting and pH/redox-responsive multi-layered nanocomplexes for smart co-delivery of doxorubicin and siRNA. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-S.; Liu, T.-P.; Chien, F.-C.; Mou, C.-Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-P. Codelivery of Plasmid and Curcumin with Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Promoting Neurite Outgrowth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15322–15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liang, T.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Min, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, J. Hyaluronidase-triggered anticancer drug and siRNA delivery from cascaded targeting nanoparticles for drug-resistant breast cancer therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, G.; Su, W.-K.; Shuai, Q. Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles for Anti-tumor Drug Delivery. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Nie, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Mo, X.; He, C. Versatile nanocarrier based on functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles to codeliver osteogenic gene and drug for enhanced osteodifferentiation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Gao, N.; Liu, G.; Tao, W.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L. A Multifunctional Nanoplatform against Multidrug Resistant Cancer: Merging the Best of Targeted Chemo/Gene/Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
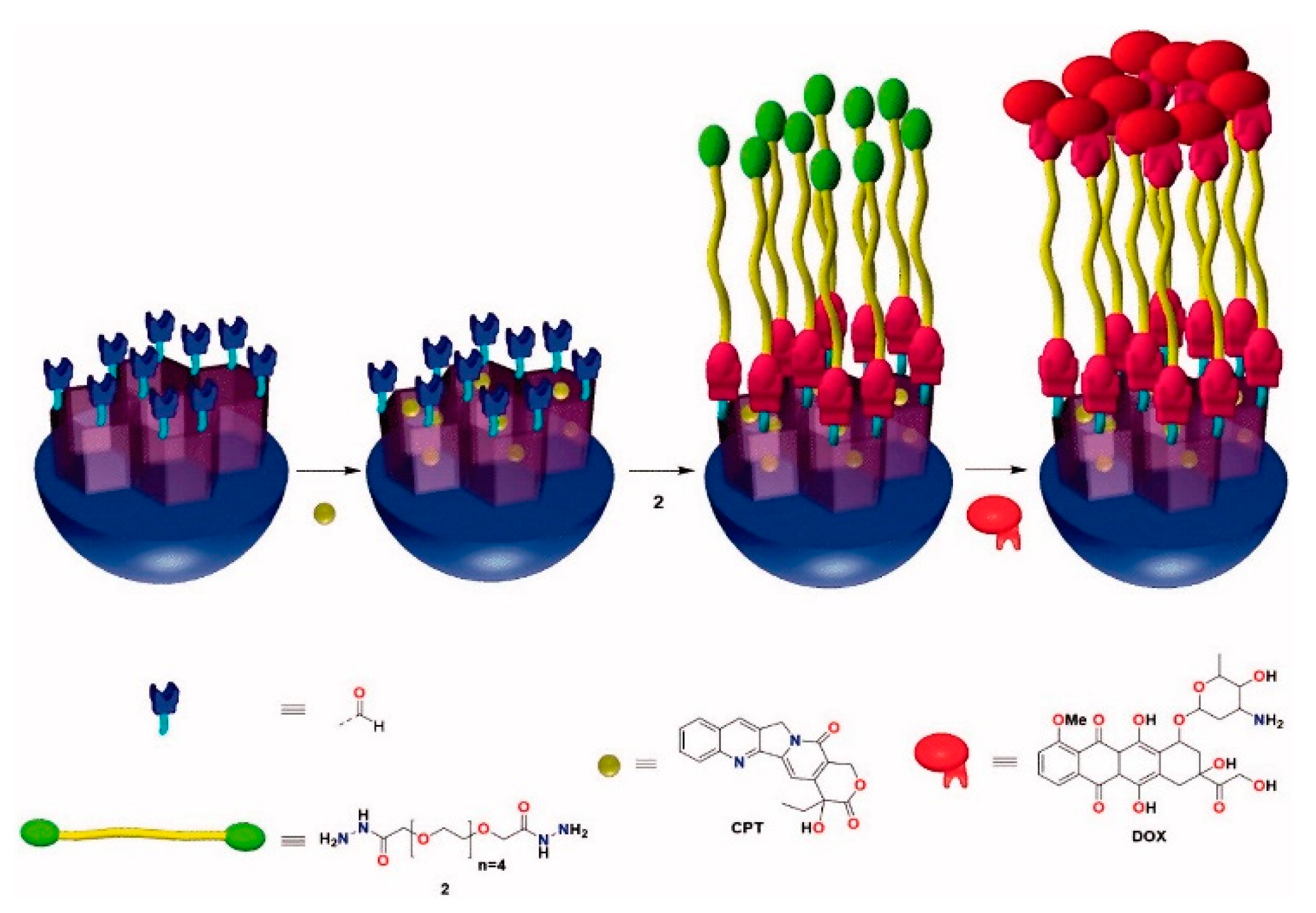


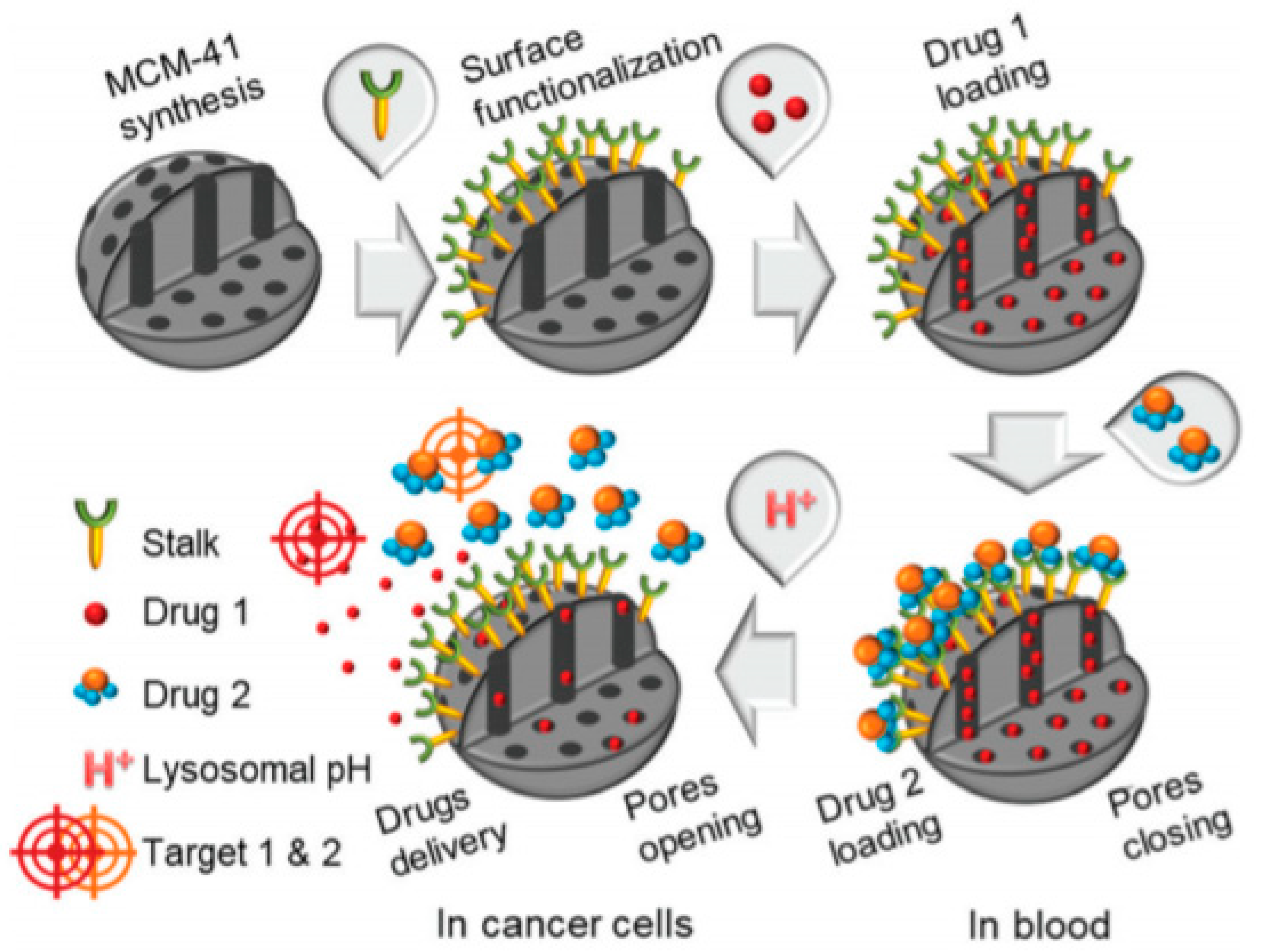

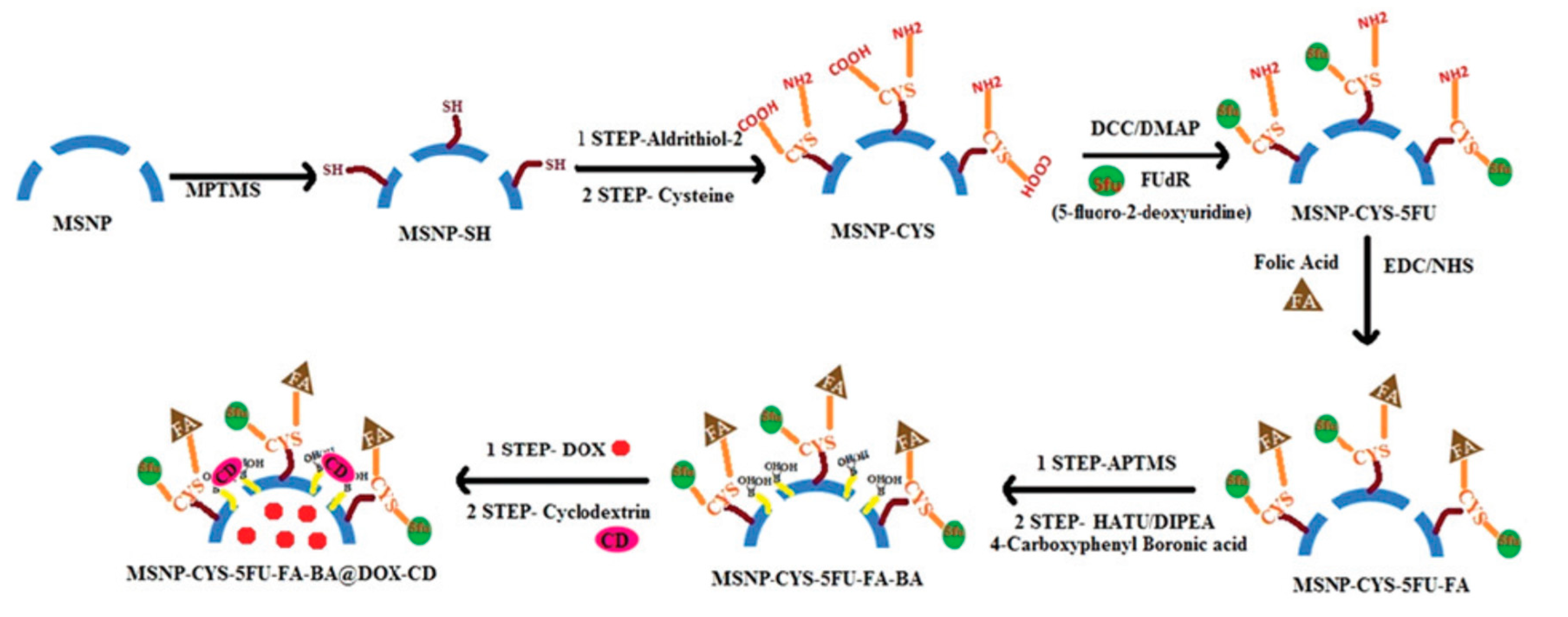
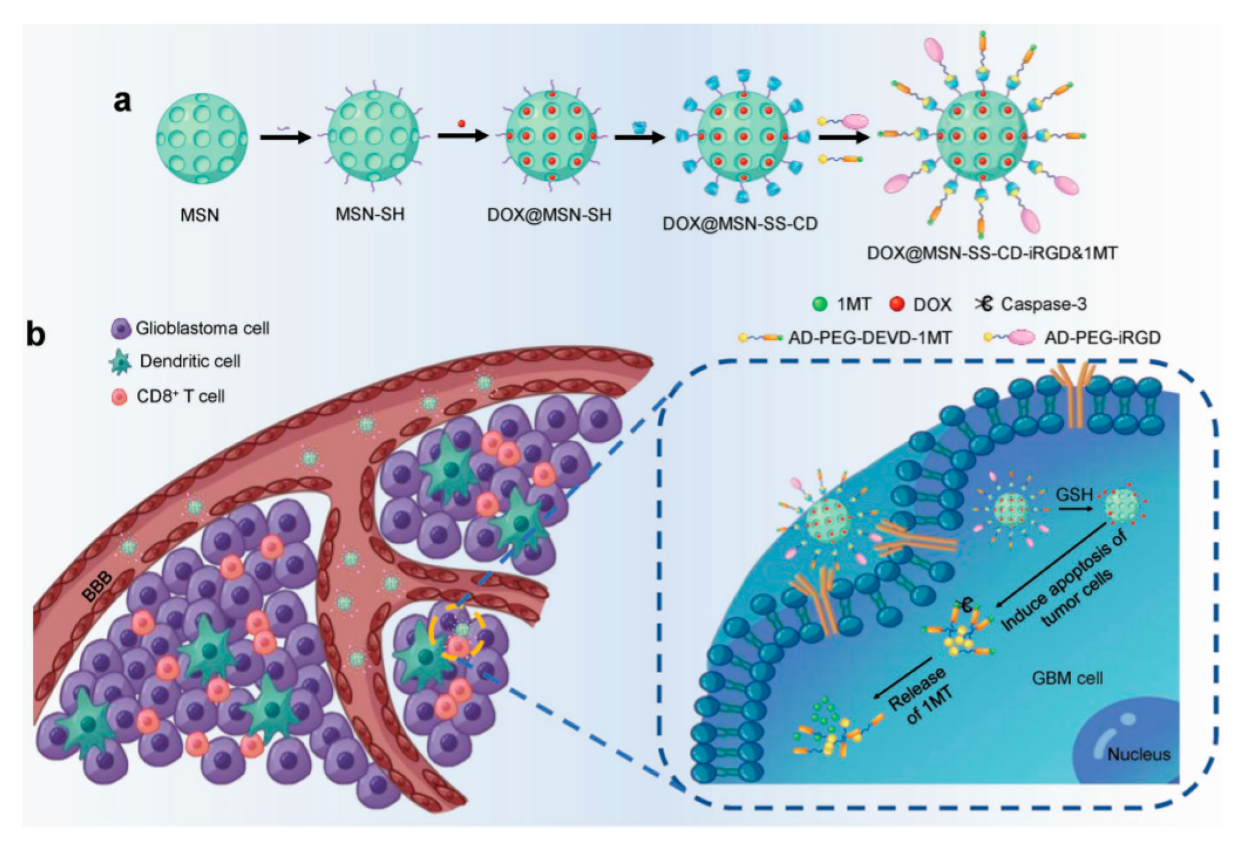
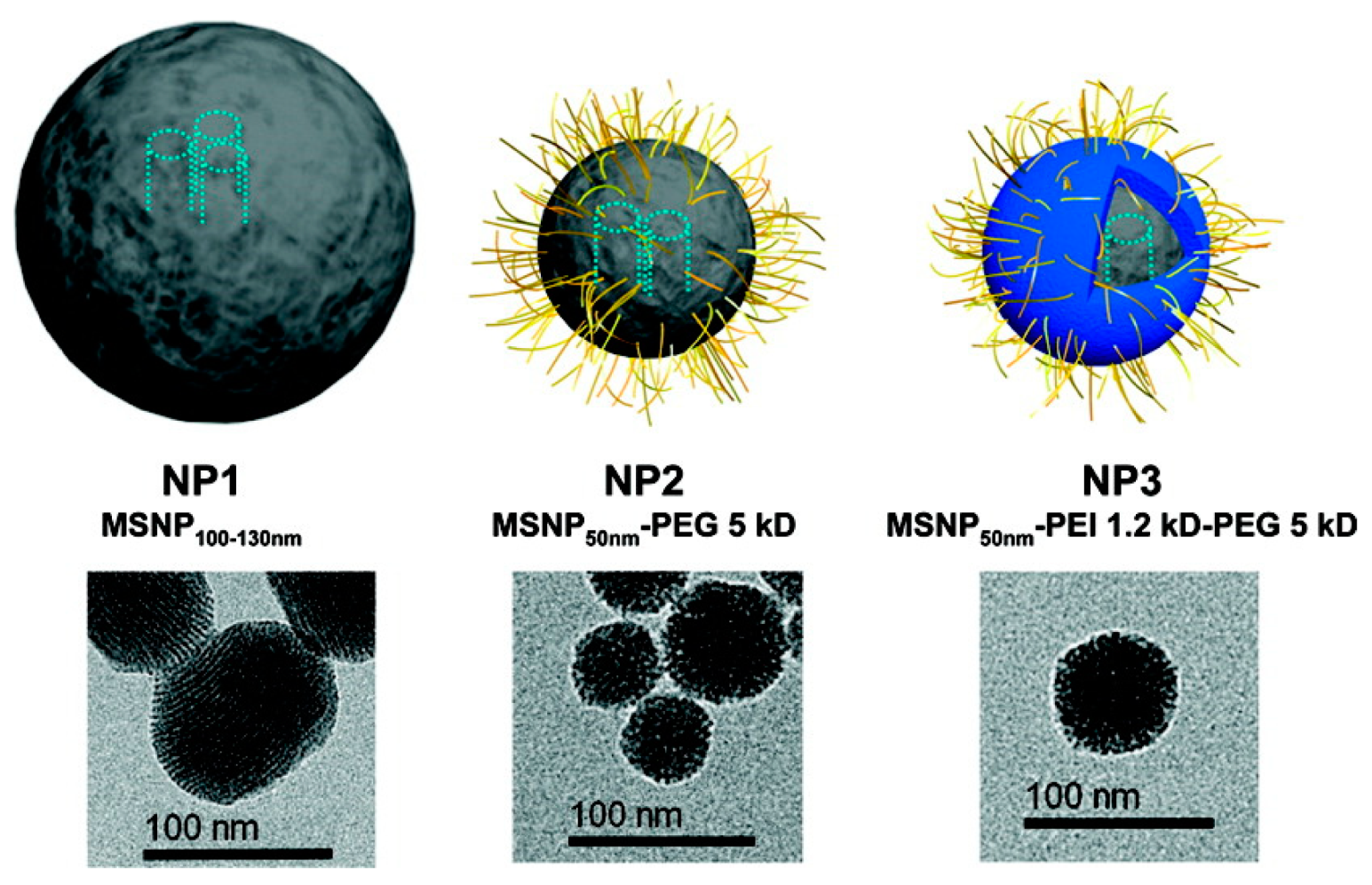
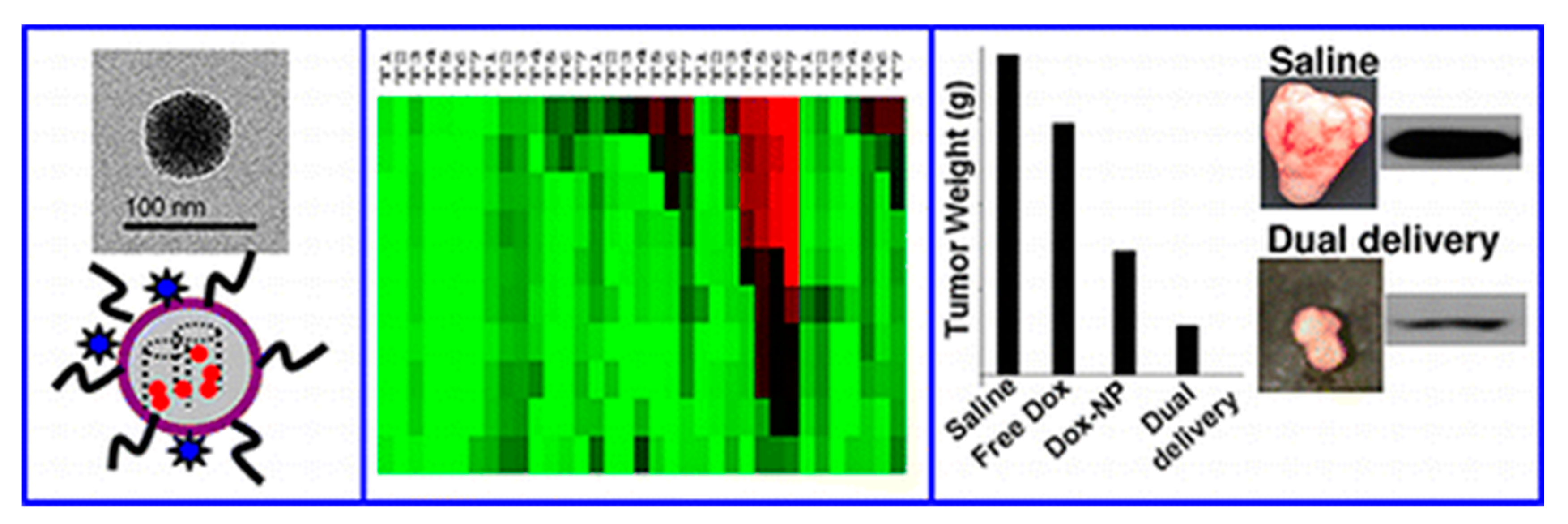
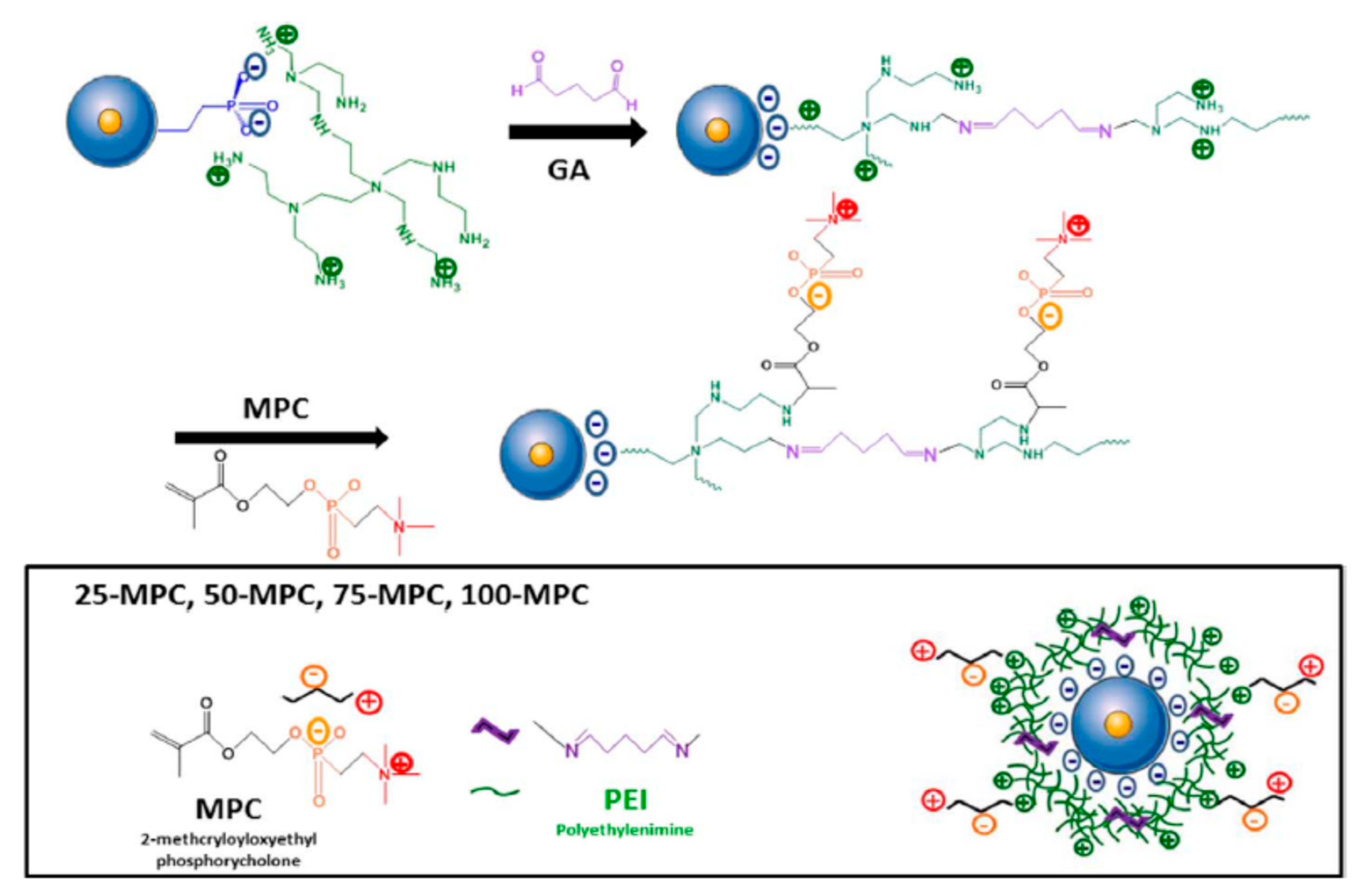
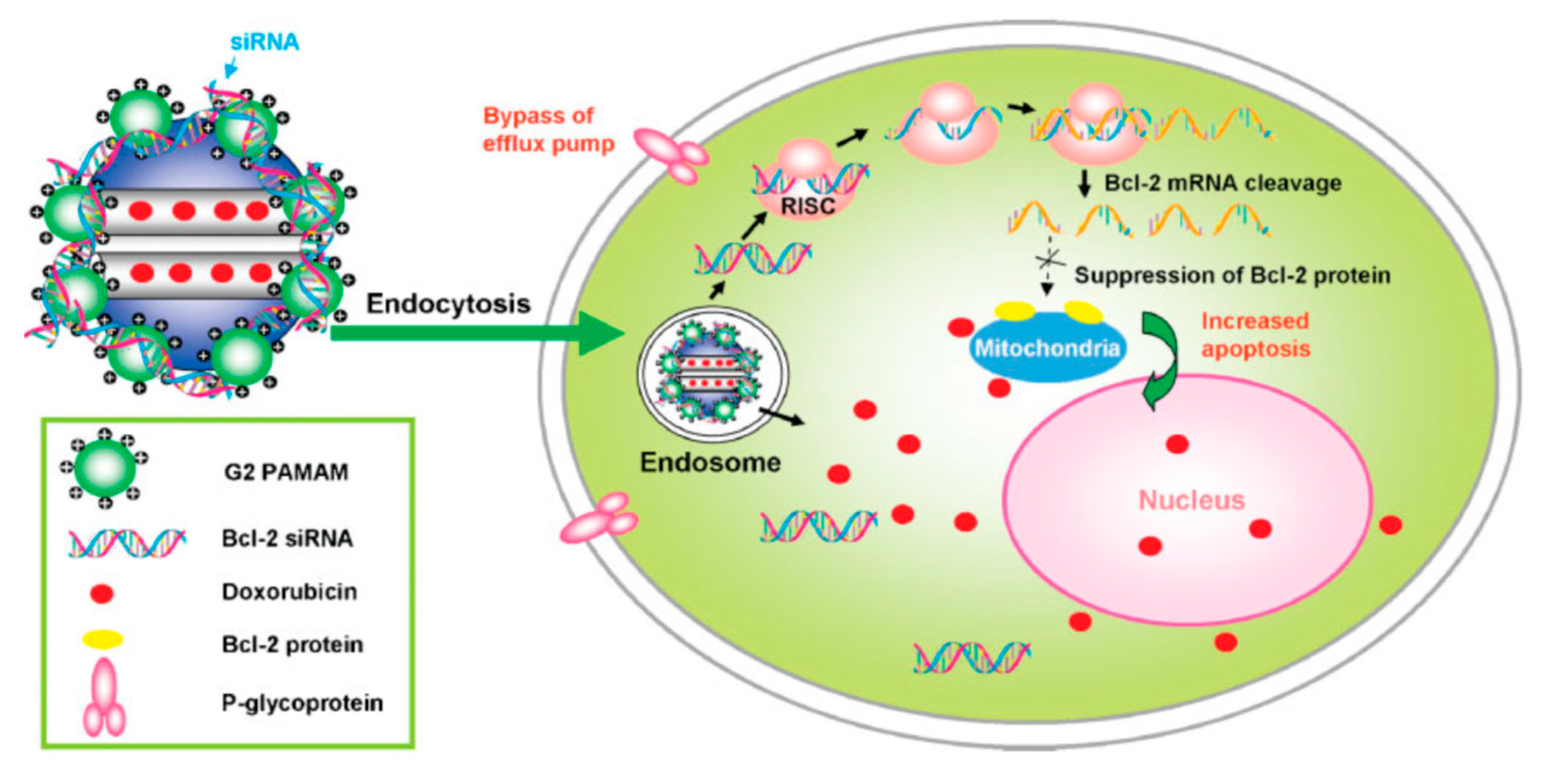



| DDS | Targeting | Cargo | Cellular Line | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
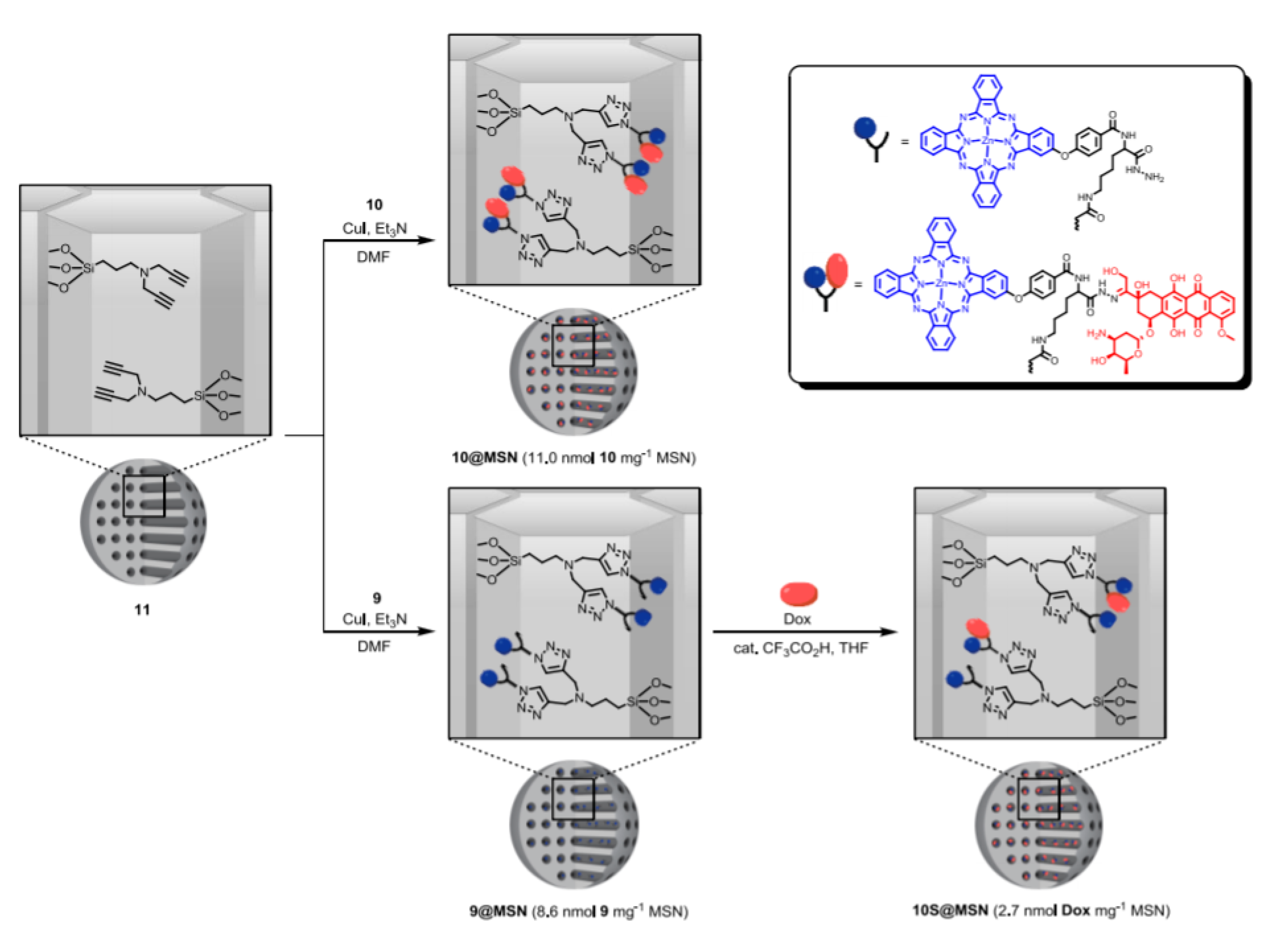
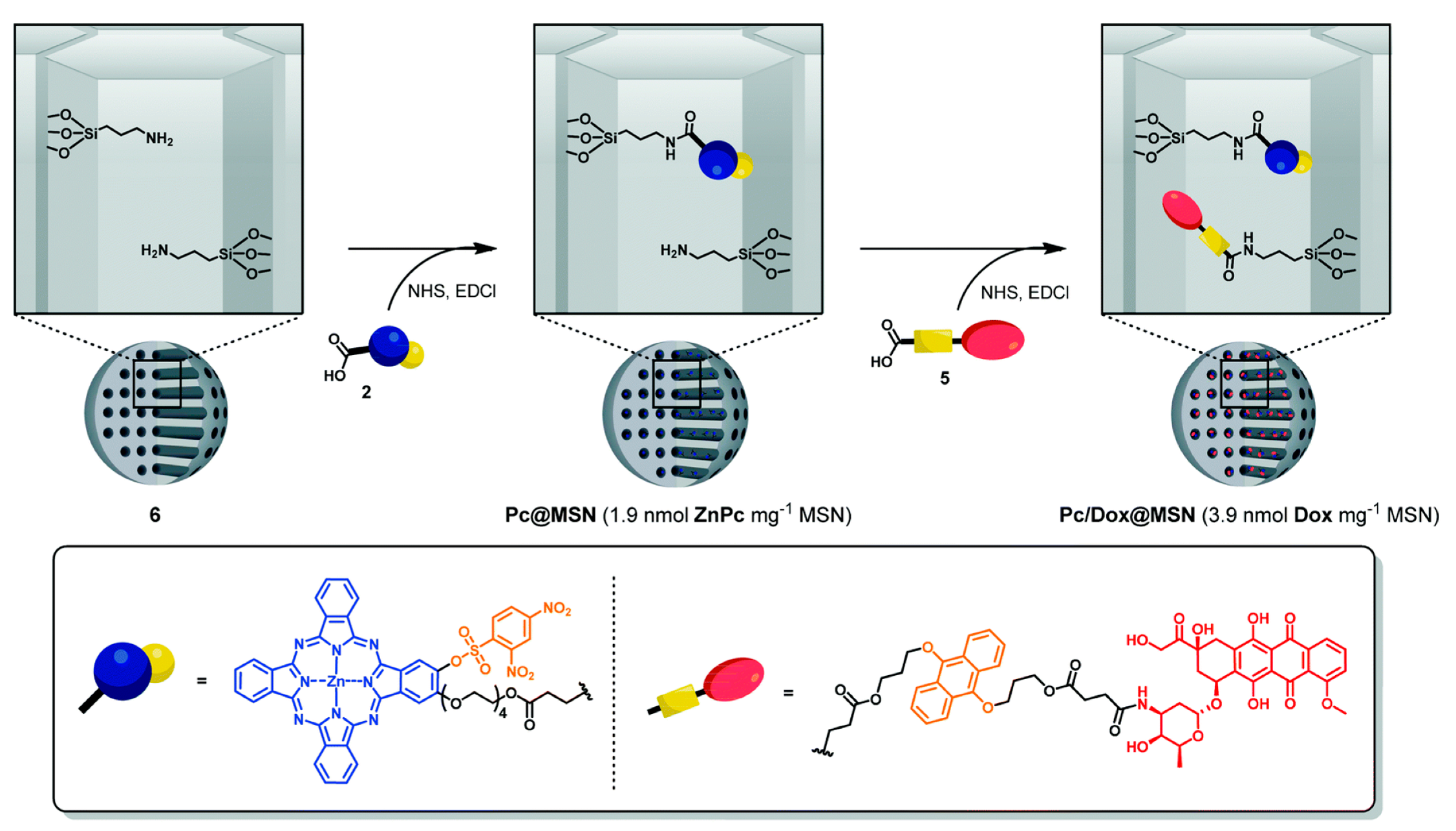
| Photoresponsive-MSN | ZnPc-Dox | HepG2 | [35,36] | |
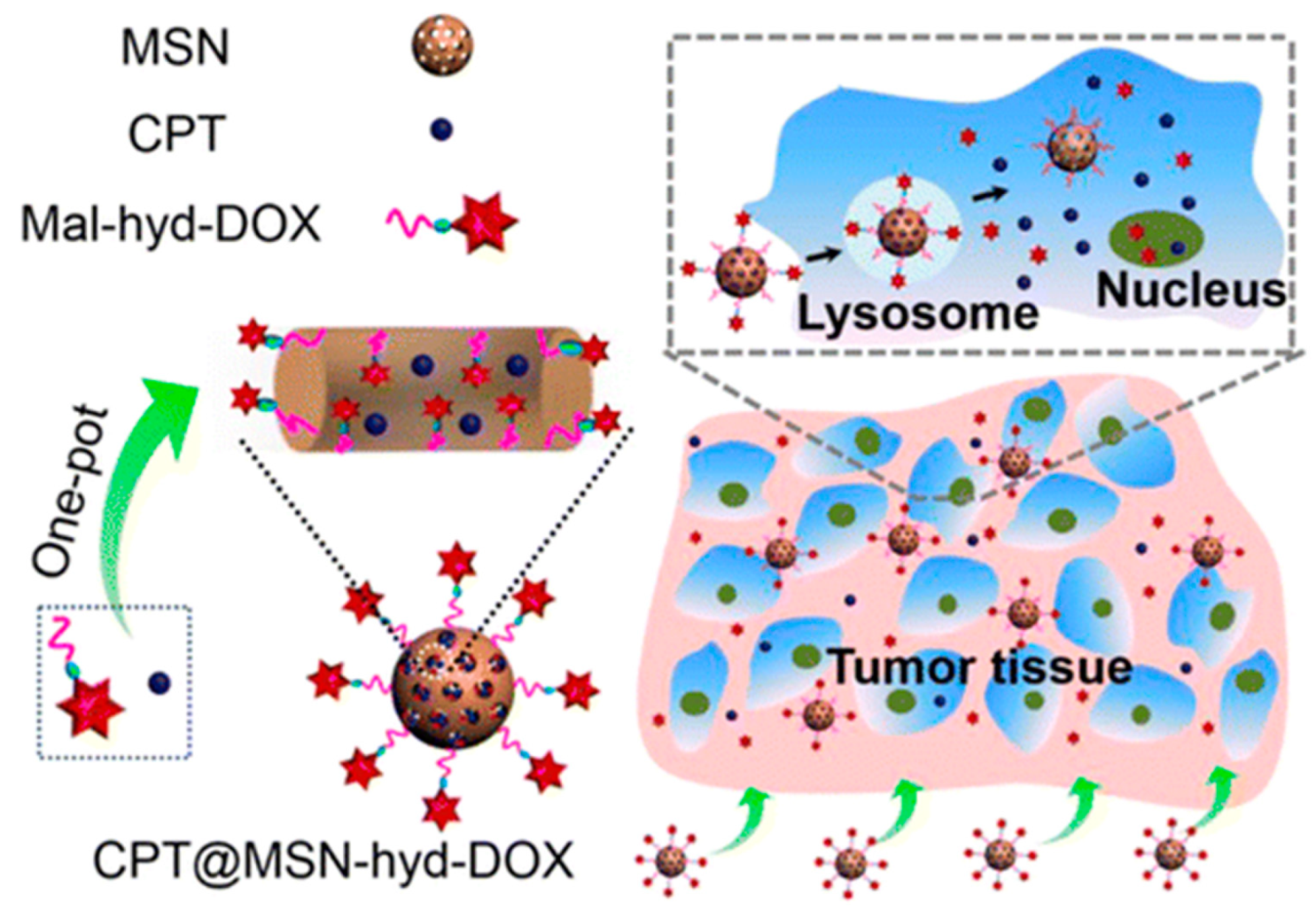
| pH-triggered MSN | Dox/CPT | HeLa and U-87 MG | [38] | |
| MSN | Dox/CPT/CdS | BxPc-3 | [40] | |
| Gossypol-capped MSN | Mitoxantrone/ gossypol | MCF-10A, MDA-MB-231 | [42] | |
| MSN | CPT/ 5-fluorouracil | MCF-7 | [44] | |
| g-CD-gated MSN | Rhodamine 6G/CPT calcein/Dox | HeLa cells, A549 cells | [46] | |
| Triple stimuli-responsive MSN | FA | Dox/ 5-Fluoro-2-Deoxyuridine | DL, DLR, MCF-7, MCF-7R, K562, K562R | [47] |
| iRGD modified MSN | iRGD | Dox | GL261, CD3+ CD4+ CD8+ T | [48] |
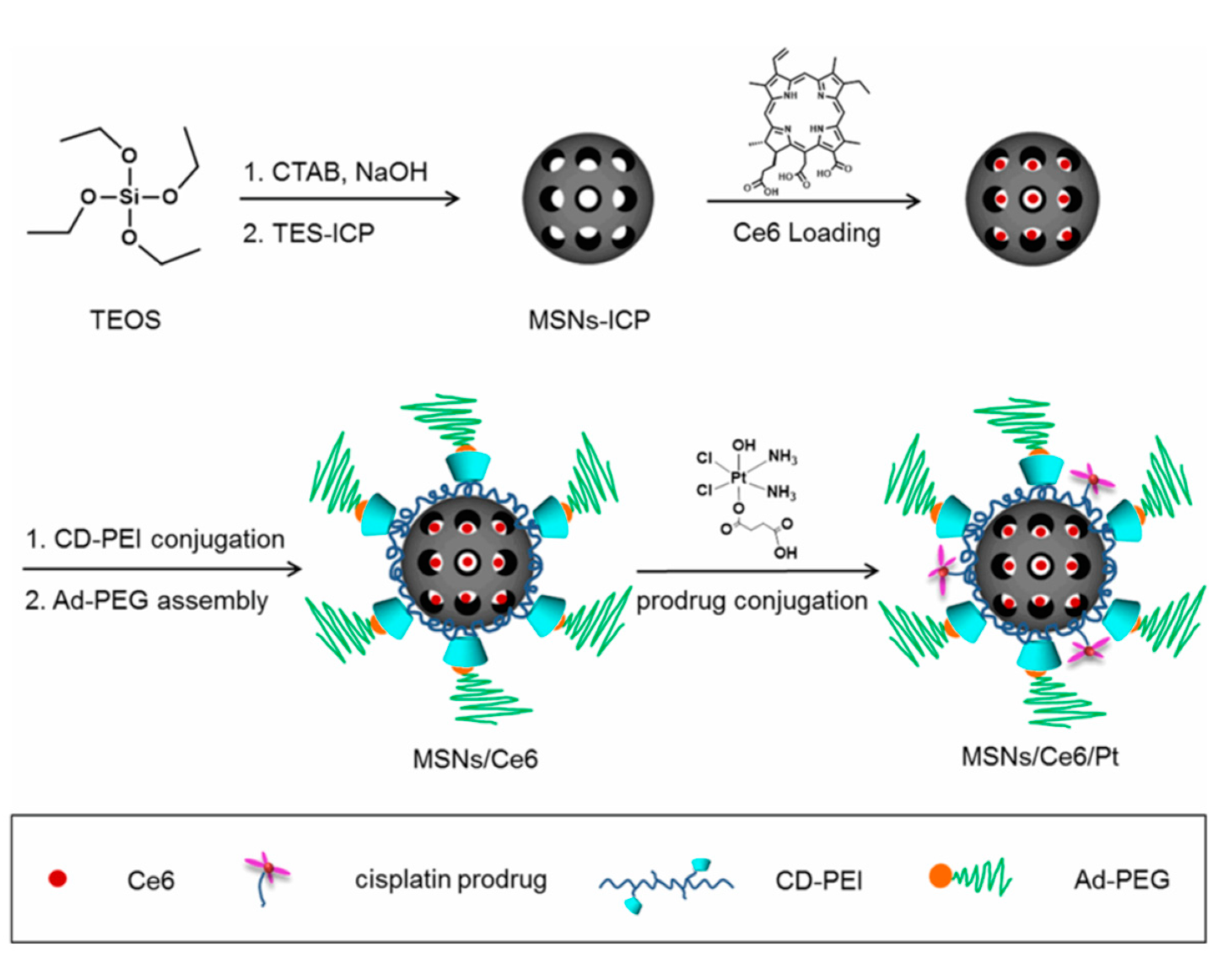
| Photoresponsive- MSN | Cisplatin Prodrug/Chlorin e6 | A549 | [49] | |
| pH/redox-triggered MSN | doxorubicin/paclitaxel | BT549, MCF-10A | [53] | |
| Pyridylthiol-terminated MSN | LHRH peptide | Doxorubicin/cisplatin/MRP1 and BCL2 mRNA | A549 | [56] |
| Redox-responsive MSN | Dox/ Bcl-2 siRNA | MCF-7, HEK 293 | [57] | |
| MSN-PEI | Doxorubicin, P-gp siRNA | KB-V1 | [58] | |
| MSN-PEI | Dox/ P-gp, MRP1, ABCG2, Bcl-2, cMyc, PXR siRNA | MCF-7 | [59] | |
| MSN-PEI | Dox/ MDR1 siRNA | KBV cells | [60] | |
| MSN MSN-PEI-PEG | Dox/ (P-g)-si-RNA | MDA-MB-231 A549 | [62] | |
| Dox | KB-31 | [63] | ||
| MSN-PEG | FA, TTA | Dox | B16-F10, HeLa, MCF-7 | [65] |
| pH-sensitive MSN | Indomethacin/ docetaxel (DTX) | B16F10, HepG | [66] | |
| Mesoporous core-shell silica nanoparticles | TWITS siRNA/ daunorubicin | Ovcar8 | [67] | |
| ICP-MSN | Dox/ Bcl-2 siRNA | A2780/AD human ovarian cancer cells | [68] | |
| Polycation-modified MSN | Chloroquine | B16F10 murine melanoma cell | [69] | |
| FMSN | pNurr1/ siRex1 | iPSCs | [70] | |
| MSN | Dox | PANC-1 | [30] | |
| FMSN | Cisplatin/siTWIST | Ovcar8-IP | [70] | |
| Modified large pore MSN Dendritic MSN | Chloroquine/siRNA | KHOS | [71,72] | |
| Dox/ Survivin shRNA | QGY-7703 | |||
| [75] | ||||
| MSN based on ZIF-8 | Dox/siRNA | MCF-7 SKOV-3 ADR | [74] | |
| Redox-sensitive HMSN | Dox/ P-gp modulator siRNA | MCF-7 ADR | [79] | |
| Redox-responsive and self-destructive MSN | Plasmid p53 | HepG2 C6 | [78] | |
| Photoresponsive-MSN | Dox/shRNA(P-gp) | MDR HepG2 ADR | [80] | |
| Light sensitive coumarin HMSN/PEI-FA | FA | Dox/siRNA(Bcl-2) | HeLa MCF-7 | [81] |
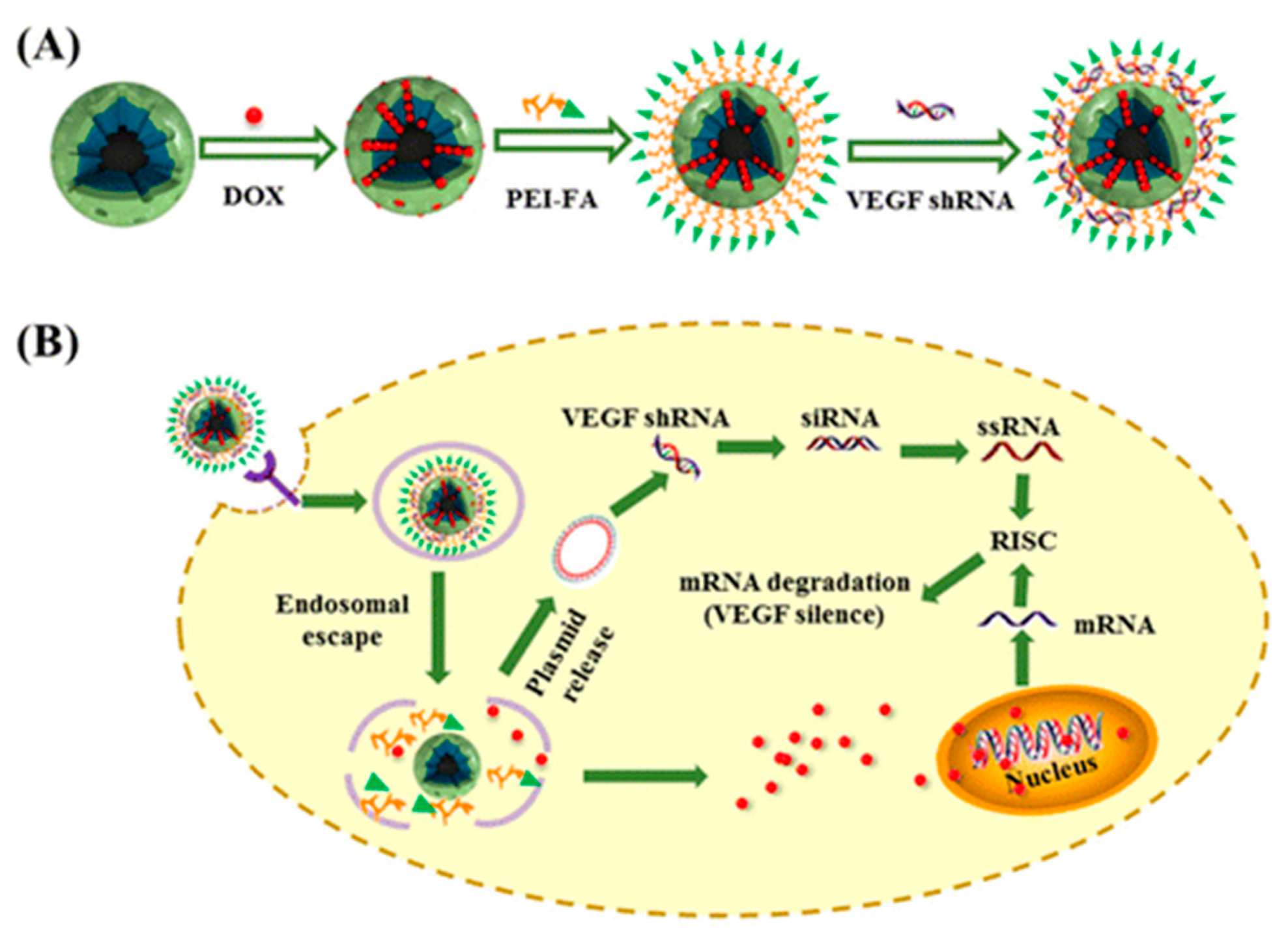
| M-MSN/PEI-FA/VEGF shRNA | Dox/shRNA(VEGF) | HeLa | [82] | |
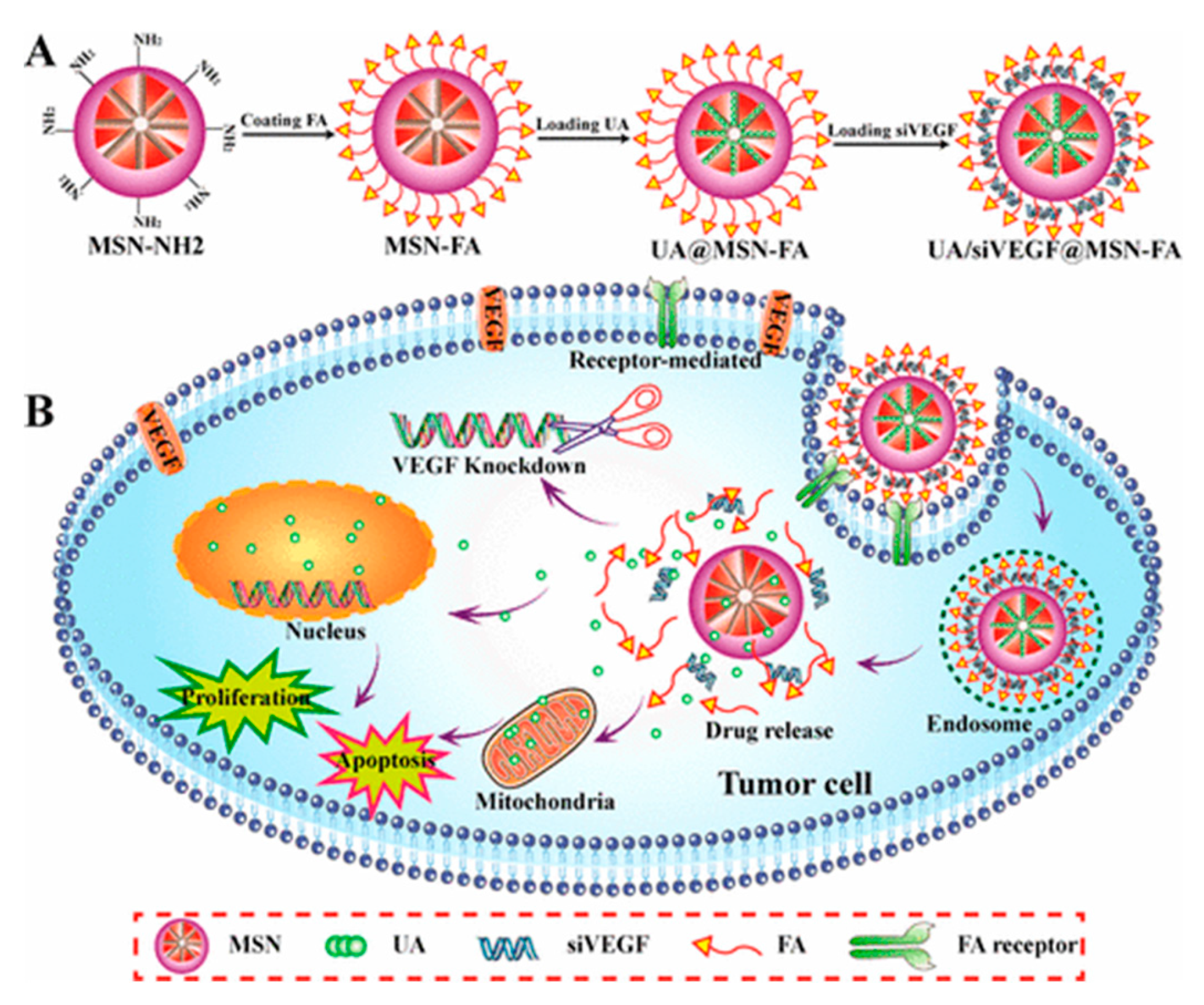
| UA/siVEGF@MSN-FA | FA | Ursolic acid/siRNA(VEGF) | HepG2 HeLa | [83] |
| Redox sensitive MSN -PPPFA | FA | Dox/Bcl-2-siRNA | MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | [84] |
| MSN-HA | HA | cisplatin/ siTWIST | Ovcar8-IP-eGFP | [85] |
| HA-siTMSN | HA | TH287/MDR1 siRNA | CAL27 | [87] |
| SO/ siVEGF@MSN-LA | HA Lactobionic acid | sorafenib/SiRNA(VEGF) | ASGPR-overexpressing Huh7 | [88] |
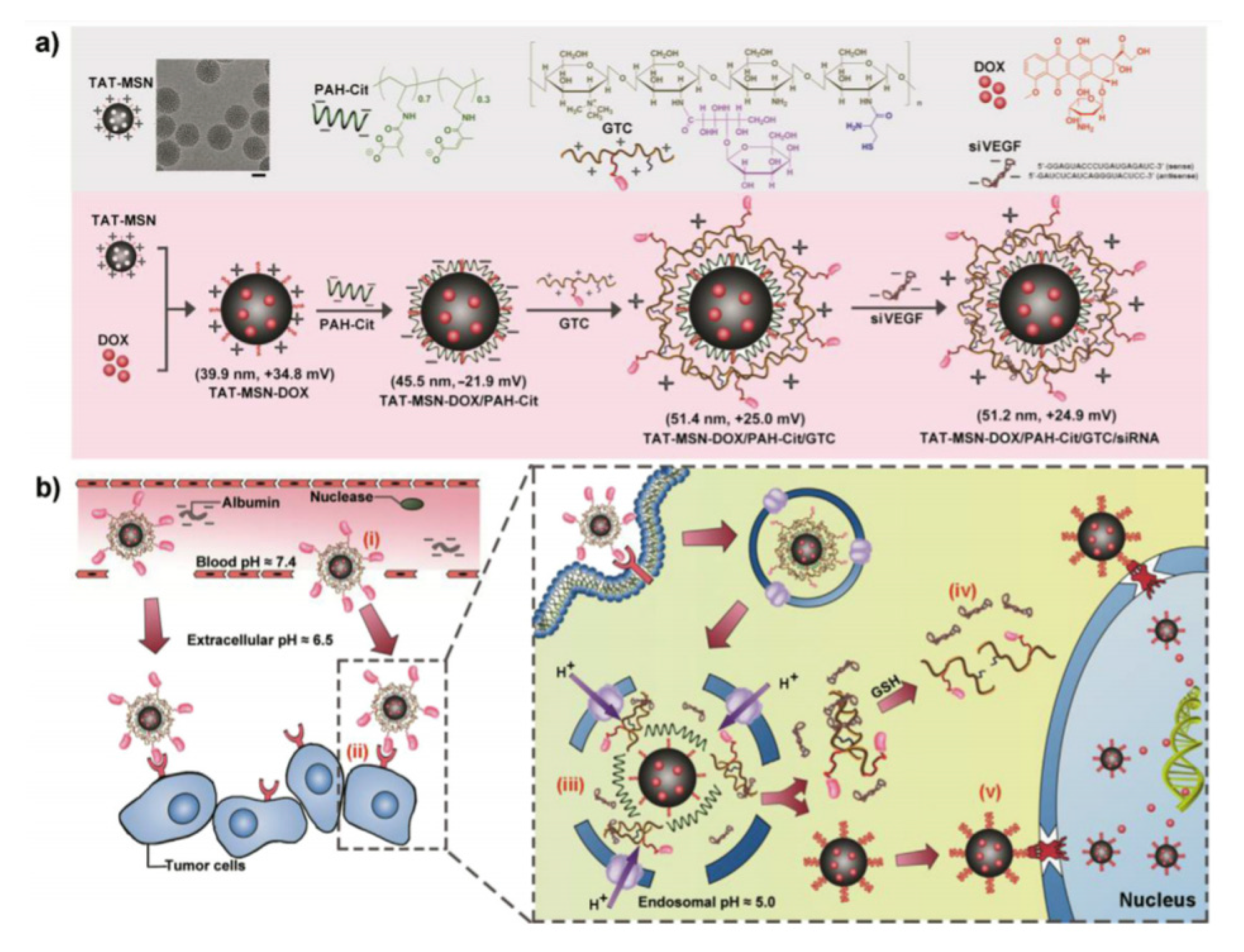
| MLNs | TAT | Dox/siRNA(VEGF) | QGY-7703 | [89] |
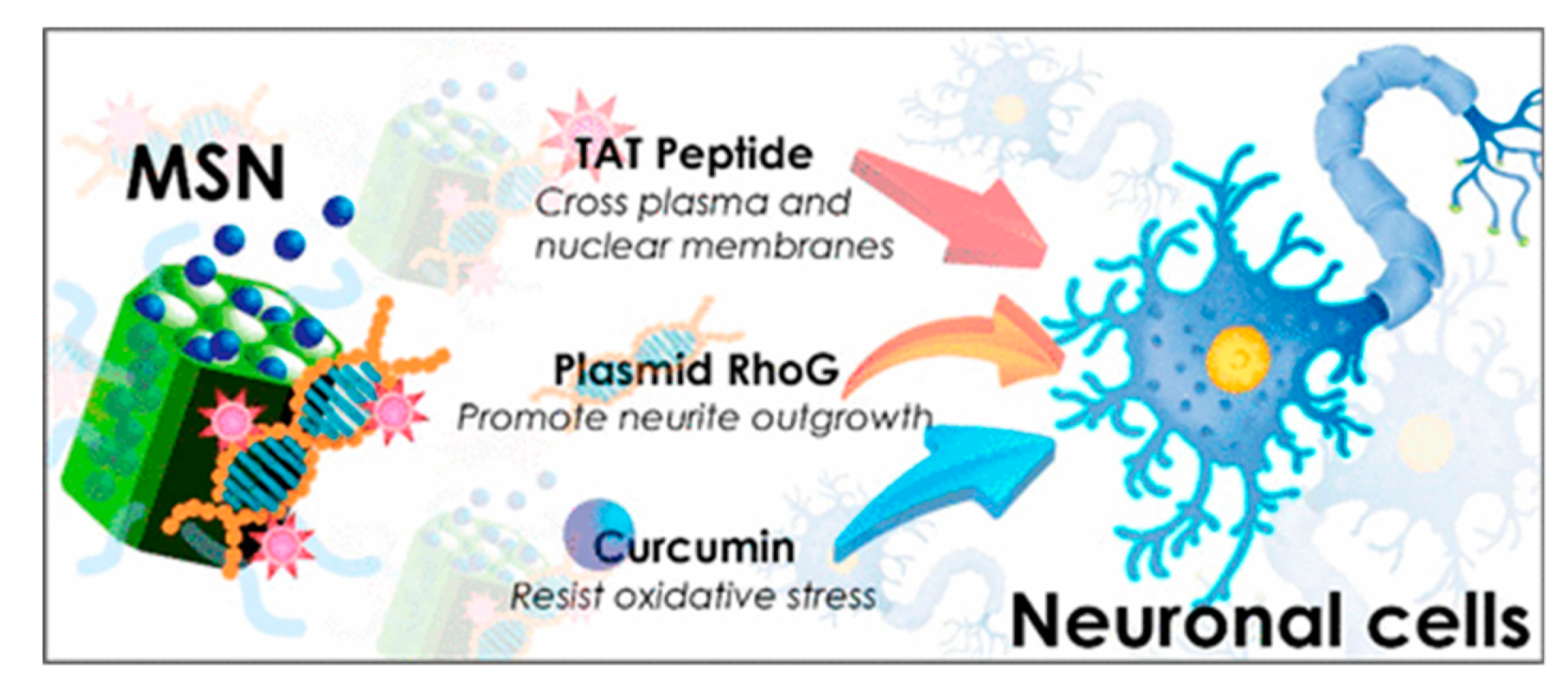
| Cur@MSN-RhoG/TAT | TAT | curcumin/ RhoG-DsRed | Neuro-2a | [90] |
| rmSiO2 | PEGA-Pvec HA | Dox/siRNA(CTGF) | MDA-MB-231 MCF-7 HeLa | [91] |
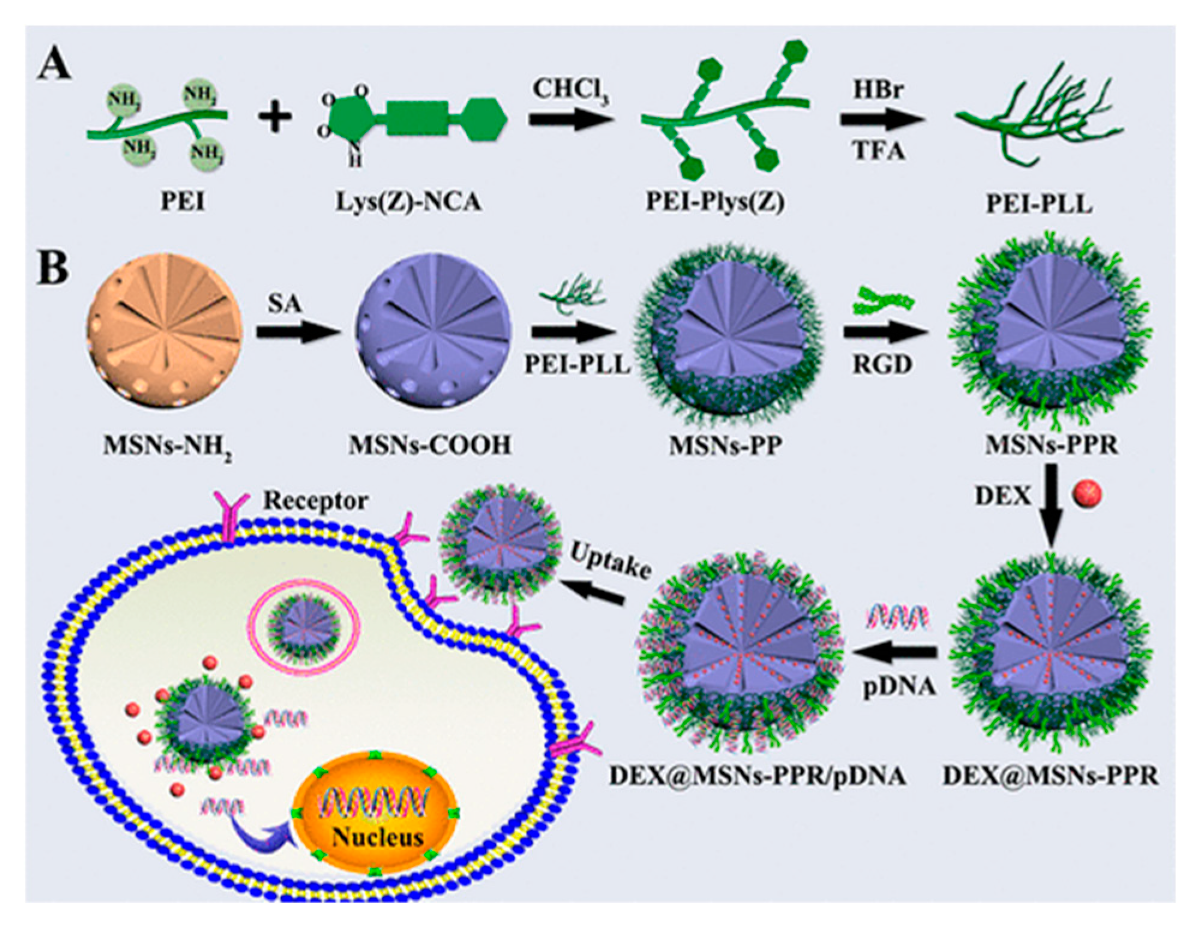
| MSN-RGD conjugated | RGD | DEX/pDNA protein-2 BMP-2 | BMSC | [93] |
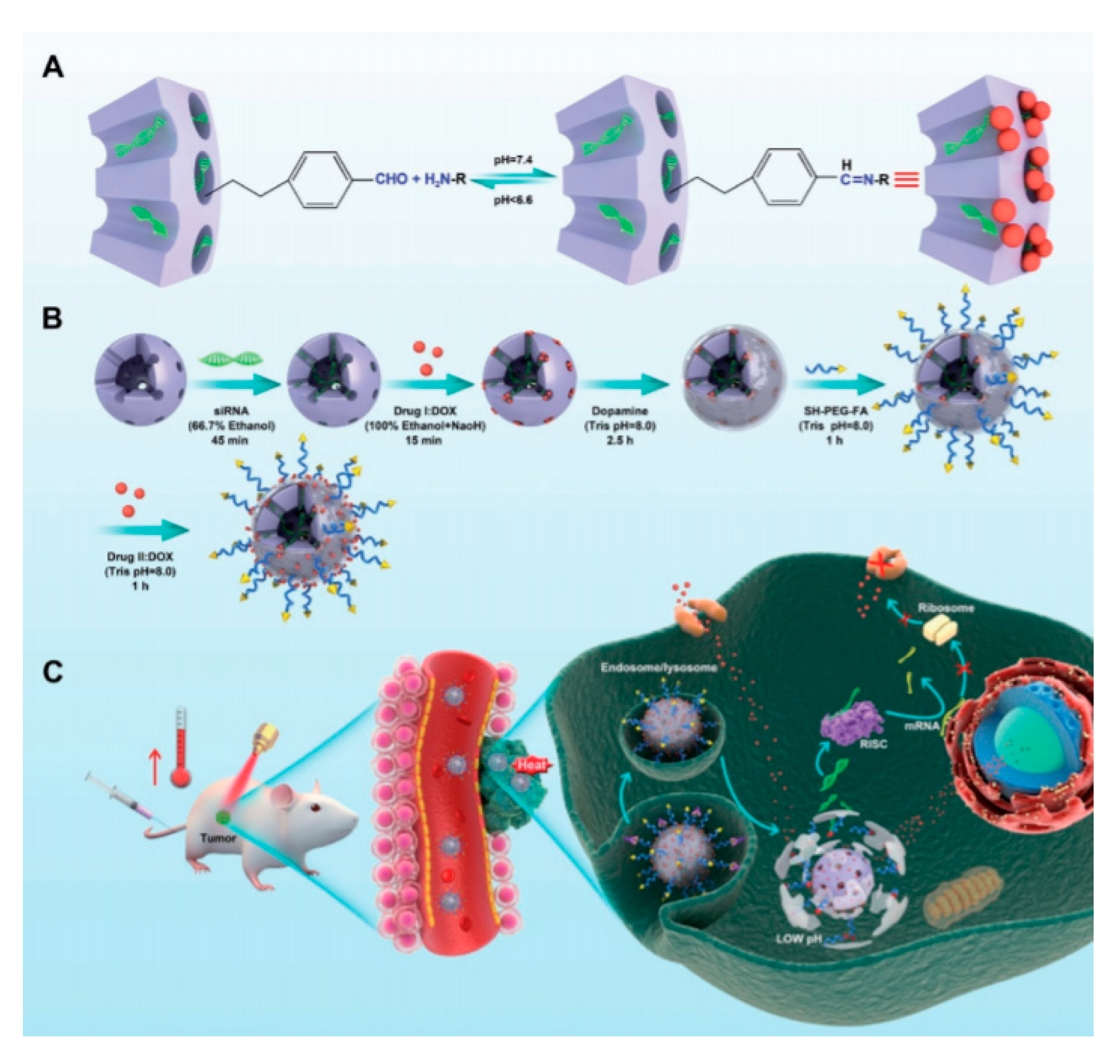
| Photoresponsive-MSN | FA | polydopamine/Dox/P-gp siRNA | MCF-7 ADR | [94] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pontón, I.; Martí del Rio, A.; Gómez Gómez, M.; Sánchez-García, D. Preparation and Applications of Organo-Silica Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122466
Pontón I, Martí del Rio A, Gómez Gómez M, Sánchez-García D. Preparation and Applications of Organo-Silica Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122466
Chicago/Turabian StylePontón, Iris, Andrea Martí del Rio, Marta Gómez Gómez, and David Sánchez-García. 2020. "Preparation and Applications of Organo-Silica Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122466
APA StylePontón, I., Martí del Rio, A., Gómez Gómez, M., & Sánchez-García, D. (2020). Preparation and Applications of Organo-Silica Hybrid Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Co-Delivery of Drugs and Nucleic Acids. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122466






